Introduction
Doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (doxy-PEP) has been shown to reduce the incidence of bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men who have sex with men (MSM) and transgender women [
1,
2]. However, the increased consumption of doxycycline could select for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in bacterial commensals, pathobionts and STIs [
3,
4,
5]. Two recent doxy-PEP trials found that the receipt of doxycycline had no effect on doxycycline resistance in
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) [
1,
2]. In contrast, a similar study by Harrison et al. from 1979, came to the opposite conclusion [
6]. One possible explanation for these contrasting findings is the different methods these studies used to assess AMR. The two studies that found no effect on resistance used a dichotomized marker of resistance, whereas the study with an effect used minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) distribution as the outcome measure [
1,
2,
6]. These results are compatible with previous studies that found that testing the MICs of individual colonies is a more sensitive method to ascertain the effects of antimicrobials on resistance than testing the proportion of colonies with resistance [
6,
7]. The proportion method dichotomizes all MICs into susceptible or resistant, which results in a loss of information and reduces the probability of detecting various types of shifts in MIC values [
7,
8]. For example, if the proportion method used by Luetkemeyer et al. is applied to the Harrison et al. results, then the use of tetracycline is no longer associated with tetracycline resistance [
9].
The Harrison et al. study was conducted over 40 years ago with minocycline rather than doxycycline, and in sailors visiting sex workers in the Philippines [
6]. This has led to questions about its relevance to contemporary MSM populations [
9]. This provided the motivation for this study, where we assess if MIC distribution is a more sensitive method than proportion resistant in ascertaining the effect of an antimicrobial on AMR. We assessed this in the ResistAZM trial [
10], a randomized controlled trial comparing the effect on the resistome of monotherapy with ceftriaxone versus dual therapy with ceftriaxone and azithromycin for the treatment of NG in MSM. Surprisingly, the study found that dual therapy did not lead to an increase in streptococcal phenotypic macrolide resistance compared with monotherapy. The proportion resistant methodology was used to determine phenotypic resistance. We cultured commensal streptococci on selective plates with and without azithromycin (2µg/mL). The proportions of streptococci that were macrolide resistant between the two treatment arms at both visits were calculated by dividing the number of colonies on the plates containing azithromycin by the number of colonies on the plates without azithromycin. The receipt of azithromycin was not associated with an increase in the proportion of streptococci with azithromycin 14 days later. In the current study, we assessed the effect of ceftriaxone/azithromycin on streptococcal azithromycin MIC distributions.
Methods
The ResistAZM study methodology is described in detail elsewhere [
10]. Briefly, this was an open-label, single-center, RCT comparing the effect on the resistome of ceftriaxone 1g intramuscular injection (IMI) plus azithromycin 2g orally versus ceftriaxone 1g IMI alone for the treatment of NG. Twenty MSM with genital, anorectal, or pharyngeal NG infection were randomized into the ceftriaxone/azithromycin arm and 22 to the ceftriaxone arm. An oral rinse specimen was taken prior to and 14 days after treatment and an aliquot of the oral rinse specimens was stored in skim milk with 30% glycerol at -80°C. Oral commensal streptococci were cultured with and without azithromycin (2 μg/mL), according to Laumen et al. [
11].
In the current study, we assessed if there was a change in individual colony MICs between the day 0 and 14 samples from the azithromycin/ceftriaxone arm. We did this by assessing azithromycin MICs of three randomly selected colonies of streptococci per sample. More specifically, an aliquot of the original oral rinse specimens was diluted to 1:1000 in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and 100µl was spread plated onto Columbia CNA agar plates with 5% sheep blood (Beckton-Dickinson, Belgium). After 24 to 48 hours incubation, three colonies with a streptococcal morphology were randomly selected, species identities was confirmed by MALDI-TOF MS, and MICs were ascertained via Etests (BioMérieux, France) on Mueller Hinton agar with 5% horse blood and 20 mg/l ß-NAD (BioMérieux, France). We describe continuous variables with means and interquartile ranges (IQR), and compare the day 0 and 14 MIC distributions of the confirmed streptococcal colonies using the Wilcoxon Rank sum test in Stata/MP V.16.
Results
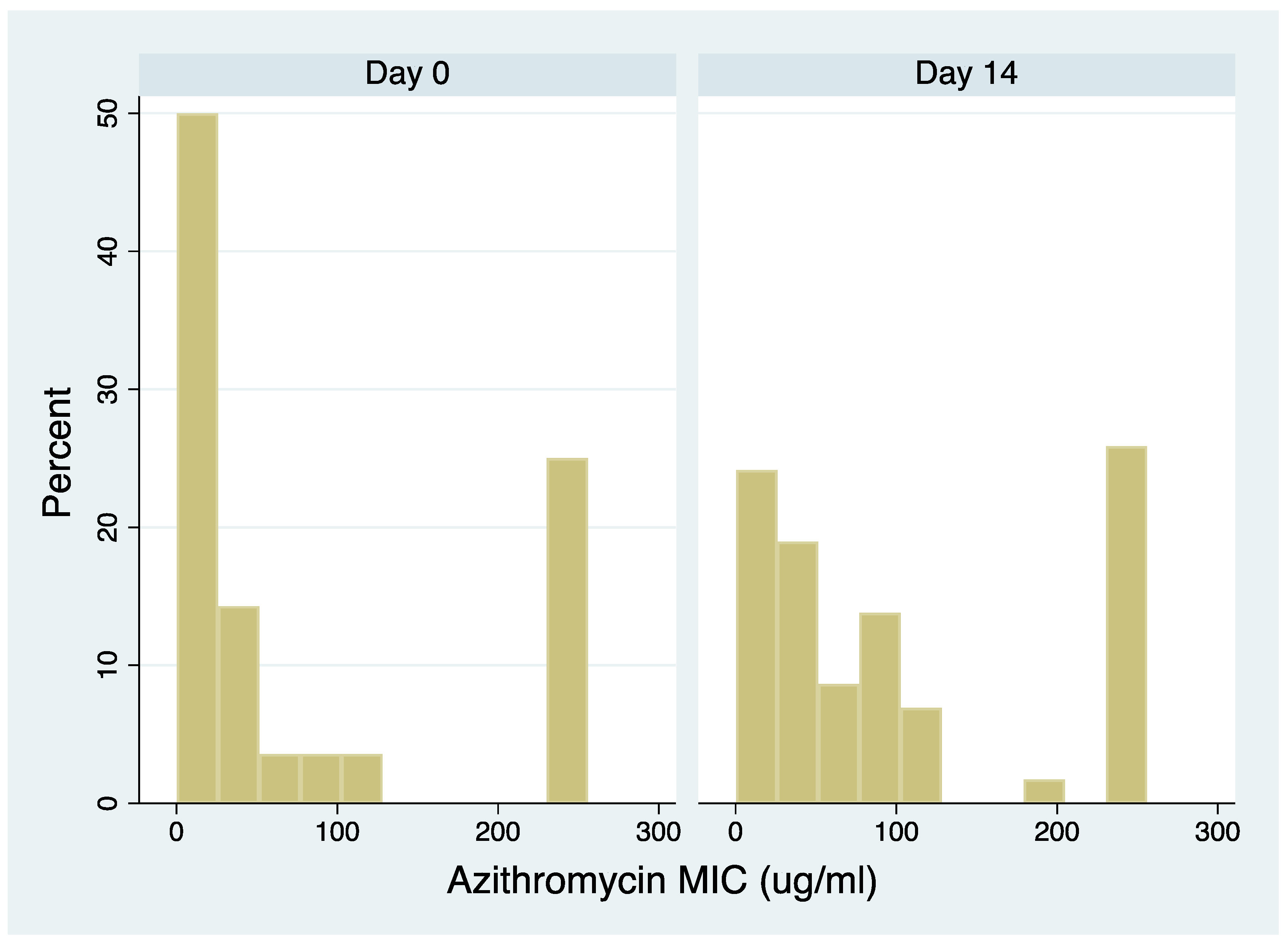
All 20 individuals who received azithromycin/ceftriaxone had samples available from both days 0 and 14 and were included in the analysis. These individuals contributed azithromycin MICs for 114 colonies of streptococci (four of the day 0 and 2 of the day 14 colonies were identified as non-streptococcal species; Table S1). The azithromycin MICs of the day 14 samples were higher than the day 0 samples (median 64 µg/ml; IQR 32-256 µg/ml and median 28 µg/ml; IQR 1-192 µg/ml [P=0.0044], respectively,
Figure 1). Similar results were obtained when restricting the analysis to the most prevalent streptococcal species (
S. mitis; Figure S1).
Discussion
By measuring individual colony MICs, we found that the receipt of ceftriaxone/azithromycin was associated with an increase in streptococcal azithromycin MICs 14 days later. This is biologically more plausible than our previous results based on assessing the proportion of resistance, which found that treatment had no effect on AMR [
12].
The major limitation of our analysis is that we did not perform the MIC- distribution and proportion-resistant-testing at the same time. Although both susceptibility assays were performed on the same frozen aliquots, it is possible that differing subpopulations of streptococci were sampled from the aliquots at the two time points. We also did not assess the genotypic and phenotypic basis of the reduced susceptibility and did not follow the participants up for longer than 14 days. A large, well-conducted previous study has, however, described the genetic drivers of macrolide resistance and established that a 3-day course of azithromycin can lead to raised azithromycin MICs in oral streptococci for over 6 months [
12].
Of note, this study used proportion resistant as the primary method to ascertain the resistogenic effect of macrolide ingestion. The study participants were, however, university students who had not ingested any antimicrobials in the prior 3 months. This is very different to our study population, where 43% reported using antimicrobials in the preceding 12 months (1). Likewise, in the two recent doxy-PEP studies, diagnosis/treatment of a bacterial STI in the preceding 12 months was required for study inclusion [
1,
2]. It is thus possible that the proportion method is sufficiently sensitive to detect resistogenicity in low- but not high-antimicrobial-consumption populations.
In populations with high levels of antimicrobial usage, the proportion of colonies with AMR may be saturated [
10]. All the individuals in the ResistAZM study had streptococci that were resistant to azithromycin (>1mg/L) at baseline [
10]. In contrast, a recent study from Niger found that only 3% of individuals harboured azithromycin resistant oral streptococci [
13]. In a saturated setting, measuring the effect of antimicrobials on individual colony MICs may be a more sensitive method to evaluate resistogenicity. It is worth noting that the consumption of antimicrobials such as macrolides in MSM on PrEP is up to 9-fold higher than thresholds associated with selection of AMR in a number of bacterial species [
14]. Studies have shown that the introduction of doxy-PEP in MSM PrEP cohorts will likely result in a small decline in cephalosporin and macrolide consumption but up to 90-fold increase in tetracycline consumption [
15]. Recent studies have noted that doxy-PEP could select for tetracycline resistance and resistance to a range of other antimicrobials in bacterial STIs and other pathobionts [
3,
4,
5]. These findings suggest that as doxy-PEP is rolled out to a broader segment of MSM, it will be important to ensure that the methods used to assess resistogenicity are sufficiently sensitive to detect meaningful changes in susceotibility. Our results build on those from previous studies suggesting that measuring individual colony MICs would be preferable to only measuring the proportion of colonies resistant [
6,
7,
10]. This is likely to be particularly true in populations heavily exposed to antimicrobials, such as MSM taking HIV PrEP.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Luetkemeyer, A.F.; Donnell, D.; Dombrowski, J.C.; Cohen, S.; Grabow, C.; Brown, C.E.; Malinski, C.; Perkins, R.; Nasser, M.; Lopez, C.; et al. Postexposure Doxycycline to Prevent Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections. New Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.M.; Charreau, I.; Chidiac, C.; Pialoux, G.; Cua, E.; Delaugerre, C.; Capitant, C.; Rojas-Castro, D.; Fonsart, J.; Bercot, B.; et al. Post-exposure prophylaxis with doxycycline to prevent sexually transmitted infections in men who have sex with men: An open-label randomised substudy of the ANRS IPERGAY trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gestels, Z.; Manoharan-Basil, S.S.; Kenyon, C. Doxycycline post exposure prophylaxis could select for cross-resistance to other antimicrobials in various pathogens: An in silico analysis. Int. J. STD AIDS 2023, 34, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C.; Gestels, Z.; Vanbaelen, T.; Britto, B.; Manoharan-Basil, S.S. Doxycycline PEP can induce doxycycline resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Galleria mellonella model of PEP. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1208014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.Y.S.; Kenyon, C.; Unemo, M. Important considerations regarding the widespread use of doxycycline chemoprophylaxis against sexually transmitted infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, dkad129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, W.O.; Hooper, R.R.; Wiesner, P.J.; Campbell, A.F.; Karney, W.W.; Reynolds, G.H.; Jones, O.G.; Holmes, K.K. A trial of minocycline given after exposure to prevent gonorrhea. New Engl. J. Med. 1979, 300, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawack, K.; Li, M.; Booth, J.G.; Love, W.; Lanzas, C.; Gröhn, Y.T. Monitoring antimicrobial resistance in the food supply chain and its implications for FDA policy initiatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5302–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, V.; Mannino, F.; Zhang, R. Consequences of dichotomization. Pharmaceutical Statistics: The Journal of Applied Statistics in the Pharmaceutical Industry 2009, 8, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaut, V.; Manoharan-Basil, S.; Kenyon, C. 45 Years of Tetracycline Post Exposure Prophylaxis for STIs and the Risk of Tetracycline Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. preprints.org 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbaelen, T.; Florence, E.; Van Dijck, C.; Tsoumanis, A.; Laumen, J.G.E.; Manoharan-Basil, S.S.; Abdellati, S.; de Block, T.; De Baetselier, I.; Van den Bossche, D.; et al. Effect on the resistome of dual- vs monotherapy for the treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Results from a randomized controlled trial (ResistAZM Trial). Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 11, ofae104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumen, J.G.E.; Abdellati, S.; Van Dijck, C.; Martiny, D.; De Baetselier, I.; Manoharan-Basil, S.S.; Van den Bossche, D.; Kenyon, C. A Novel Method to Assess Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Commensal Oropharyngeal Neisseria—A Pilot Study. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Lammens, C.; Coenen, S.; Van Herck, K.; Goossens, H. Effect of azithromycin and clarithromycin therapy on pharyngeal carriage of macrolide-resistant streptococci in healthy volunteers: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 2007, 369, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, T.; Worden, L.; Hinterwirth, A.; Arzika, A.M.; Maliki, R.; Abdou, A.; Zhong, L.; Chen, C.; Cook, C.; Lebas, E.; et al. Macrolide and Nonmacrolide Resistance with Mass Azithromycin Distribution. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C.; Baetselier, I.D.; Wouters, K. Screening for STIs in PrEP cohorts results in high levels of antimicrobial consumption. Int. J. STD AIDS 2020, 31, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanbaelen, T.; Tsoumanis, A.; Kenyon, C. Total Antimicrobial Consumption in Doxycycline Postexposure Prophylaxis Cohorts and the Intensity of Screening for Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, ciad553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).