1. Introduction
With the development of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, various cutaneous adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are observed. As of September 2022, 67.7% of the world population has received at least one dose of a mRNA COVID-19 vaccine with 12.58 billion doses administered globally [
1]. The mRNA COVID-19 vaccines BNT162b2 (Comirnaty®; Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Spikevax®; Moderna) became available in December 2020 [
2,
3]. In Switzerland, where our study was performed, 70% of the population had received at least one vaccination with either the mRNA-1273 (43.9%), BNT162b2 (24.7%), or JNJ-78436735 (Covid-19 Vaccine Janssen; Johnson & Johnson) (0.7%) [
4].
The application of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines can cause localized delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions (DTHRs) at the injection site (also referred to as ‘COVID arm’) as well as generalized rashes [
5,
6]. The most common ADRs reported after an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine are DTHRs at the site of injection as local reaction and disseminated reactions such as urticaria or morbilliform rashes among several others [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16].
As detailed data on the histopathological patterns of these cutaneous reactions are still sparse, the goal of this study was to characterize the histopathological aspects of the diverse ADRs after the administration of mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 vaccine and to correlate the histopathological findings with the clinical features. In comparison to previous studies, all cases could be analyzed for their histological features in addition to the clinical data. The knowledge of ADRs after mRNA COVID-19 vaccines will be of benefit for the near future when the use of mRNA vaccines is expanded for other indications such as the treatment of malignancies or prevention of other infectious diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
We conducted a retrospective study on ADRs in patients who were vaccinated either with the BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 vaccine. We included only cases in which skin biopsies of ADRs had been taken and in which clinical and histopathological findings could be analyzed. Tissue sections of 3-4 micrometer thickness - fixed in formalin (4%) and embedded in paraffin - were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), periodic-acid-Schiff (PAS) stain, and Giemsa stain. All biopsies were reevaluated by one of the authors (WK) for the presence of epidermal changes (such as acanthosis, spongiosis, hyper- or parakeratosis with or without inclusions of neutrophils, and acantholysis), interface changes (including vacuolization in the junctional zone, apoptotic keratinocytes, exocytosis of lymphocytes), pattern and composition of the dermal infiltrate (superficial and/or deep perivascular lympho-histiocytic infiltrates), subcutaneous infiltrates (septal vs. lobular, with or without vasculitis). In addition, all biopsies were evaluated for the presence of eosinophils, neutrophils, and plasma cells. Mast cells were assessed by evaluating Giemsa stains. The
histological findings were assigned to one of the following histological reaction patterns: spongiotic, superficial perivascular lympho-histiocytic without epidermal changes, psoriasiform, lichenoid, non-lichenoid interface changes, urticarial, vasculitis, panniculitis, bullous, acantholytic and dyskeratotic, pustular, folliculitis and pseudolymphomatous. To assess the clinical data, a questionnaire was sent to the treating physicians asking for the clinical morphology of the cutaneous reactions, clinical images, as well as the type of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine applied, and -if available- the latency between administration of the vaccine and onset of ADRs. We compared the clinical patterns with the histopathological patterns and categorized the reactions based on clinicopathological correlation as well as applying the criteria by McMahon et al. for V-REPP for comparison [
16] (
Table 1). The term ‘V-REPP’ had been introduced by McMahon et al. as a vaccine-related eruption of papules and plaques and defined as “
discrete edematous papules, some with central vesiculation and crusting and its histopathology including spongiotic dermatitis as robust intercellular edema with intraepidermal vesicles, papillary dermal edema, and dermal eosinophils. Interface changes may or may not be present.” [
16].
3. Results
3.1. Patients
Out of the 111 patients contacted for their written informed consent, 48 patients agreed to participate in our study. This group included a total of 24 men and 24 women. The median age was 66.3 years (ranging from 24 to 90 years). Out of 48 patients, only 2 patients (4%) stated they had experienced a Sars-CoV2-infection months before receiving the vaccine.
3.2. Vaccine types and latency
Thirty-five patients (73%) had received the mRNA-1273 vaccine and 12 (25%) received the BNT162b2 vaccine, while only 1 person (2%) had received both vaccines. Fourteen (29%) biopsies were taken after the first vaccine, 21 (44%) after the second vaccine, and 5 (10%) after the third or fourth vaccination. In 14 patients (29%), the reaction appeared after the first vaccination only. ADRs after the first dose took 10 days to develop on average, ranging from one day up to 28 days. In 21 patients (44%), the reaction occurred only after the second vaccine and manifested after 8.7 days on average (range: 1 – 21 days). Five patients (10%) developed a cutaneous reaction after the first and second doses.
3.3. Distribution of cutaneous reactions
Forty-one of 48 patients (85%) developed distant reactions on two or more body areas (distant disseminated). Three patients (6%) exhibited localized reactions which were located on the body area, other than the vaccinated arm (distant localized). The remaining 4 patients (9%) showed localized ADRs at the vaccination site.
3.4. Cutaneous reactions – spectrum of clinical manifestations
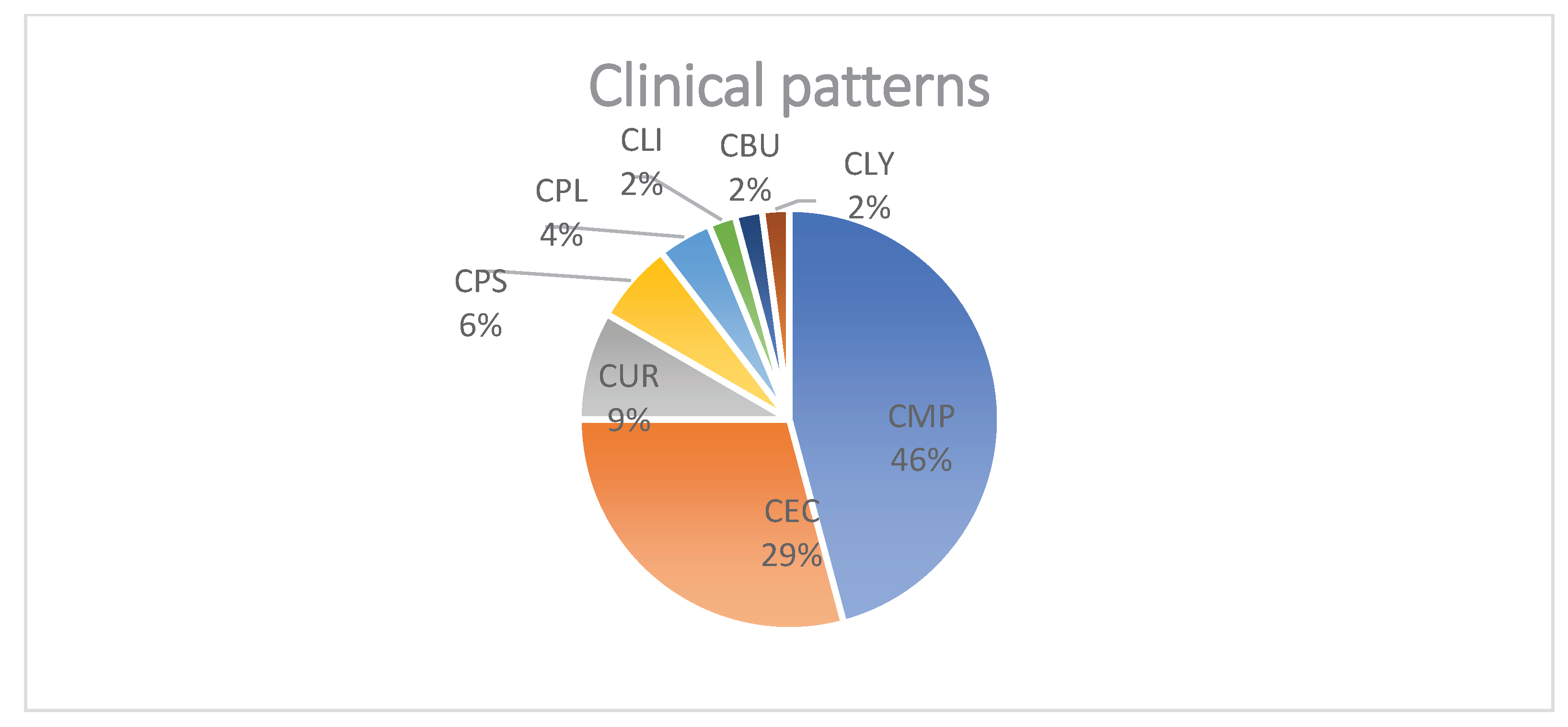
Clinically, skin lesions were reported as maculo-papular exanthema (n=22, 46%), spongiotic dermatitis (n=14, 29%,), urticarial (n=4, 9%), psoriasis-like (n=3, 6%) and plaque-like (n=2, 4%) reactions as well as lichenoid (2%), bullous (2%) and pseudolymphomatous (2%) patterns in one patient each (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). Fourteen out of 48 patients (29%) clinically showed spongiotic dermatitis after mRNA-1273 (n=9), and BNT162b2 (n=4). Three patients experienced a reaction after the first vaccine only, 5 only after the second, 2 after the first and second doses, 2 only after the third vaccine, and 2 patients after all three doses. One patient received mRNA-1273 for their first vaccine dose and then switched to BNT162b2 for the second and third doses but experienced a clinically spongiotic reaction after all three doses. Eight patients clinically presenting with maculo-papular exanthema developed the reaction after the first vaccine only, 11 after the second vaccine only, 2 after the third vaccination only, and 1 patient after both the first and second vaccination. All these ADRs were skin diseases of new onset.
3.5. Cutaneous reactions – spectrum of histopathological features
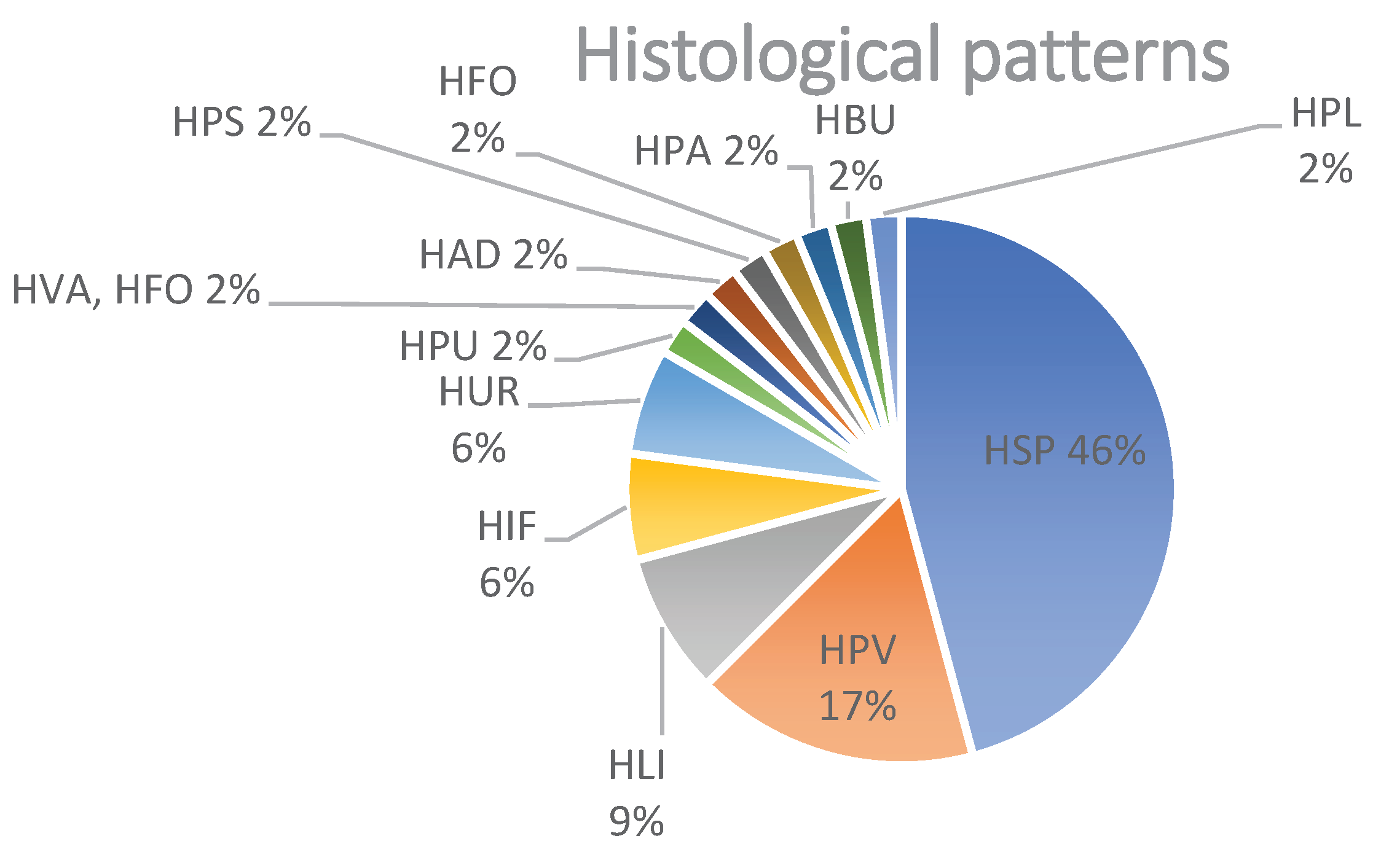
The most common histopathological patterns were spongiotic (n=22; 46%) followed by superficial perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (in the absence of epidermal changes) (n=8; 17%), and lichenoid pattern (n=4; 9%). Less common histological patterns were comprised of an urticarial pattern (n=3; 6%), interface changes (n=3; 6%), and additional patterns represented each by one biopsy (n=1, 2%): psoriasiform, pustular, bullous, vasculitis, panniculitis), pseudolymphomatous, folliculitis and acantholytic and dyskeratotic changes (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). Neutrophils were present in 14 biopsies (29%), and plasma cells in 4 biopsies (8%). Mast cells assessed in Giemsa stains were identified in the HSP and HPV patterns, but we did not see any increased number of mast cells. Eosinophils were found in a total of 32 biopsies (66%) including spongiotic pattern (16 of 20 patients; 80%), superficial perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (5 of 8 patients; 63%), urticarial pattern (3 of 3 patients; 100%), lichenoid pattern (2 of 4 patients; 50%), interface changes (2 of 3 patients; 66%) patterns, and in one patient each with folliculitis, bullous, acantholytic and dyskeratotic changes, and a combination of vasculitis and folliculitis. Based on the number of eosinophils found in one high power field (HPF), we divided the biopsies with eosinophils into three groups (E1-E3): E1, in which 1 eosinophil per HPF was detected, was the biggest group with 14 biopsies (44%); E2 (n=12; 37%) when 2-5 eosinophils per HPF were detected; E3 (n=6; 19%) for > 5 eosinophils per HPF.
3.6. Correlation of histological patterns with clinical presentations
The correlation of histological spongiotic changes with the clinical features revealed that only 11 of 22 (50%) patients also clinically showed spongiotic dermatitis. Remarkably, the other 10 patients (45%) exhibited clinically a macular-papular exanthema, and 1 patient clinically showed plaques (5%). Vice versa, the patients with clinically spongiotic dermatitis (n=14) displayed spongiotic changes (n=11; 79%), dermal superficial perivascular lympho-histiocytic infiltrates (n=1; 7%), psoriasiform (n=1; 7%), and vacuolar pattern of interface changes (n=1; 7%) in their biopsies. The second most common histological group was characterized by superficial perivascular lympho-histiocytes without epidermal changes (n=8; 17% of all patients). Seven of these 8 patients (87%) clinically manifested with a maculo-papular exanthema and 1 patient (13%) with clinically spongiotic dermatitis. The 22 patients (46% of all patients) with clinical presentation of a maculo-papular exanthema showed histologically spongiotic changes (n=10; 45.5%), while a superficial perivascular lympho-histiocytic infiltrate was found in 7 patients (32%). Other histological patterns were for 1 patient each interface changes (4.5%), pustular (4.5%), lichenoid (4.5%), acantholytic and dyskeratotic (4.5%), and folliculitis (4.5%). Out of those, 19 (86%) received mRNA-1273 and 3 (14%) were vaccinated with BNT162b2. Applying the criteria for V-REPP by McMahon et al., V-REPP was found in 23 patients (48%). The robust form accounted for 20/23 biopsies (87%) whereas the moderate (n=0) and mild forms (n=3/23; 13%) of V-REPP were rarely observed. Of these patients with V-REPP, 20 (87%) were vaccinated with mRNA-1273 whereas the remaining 3 patients (13%) were vaccinated with BNT162b2. Eight patients (35%) experienced this reaction after the first vaccine only, 8 (35%) after the second vaccine only, and 4 (17%) after the third vaccine only. The cutaneous reaction appeared between 1 and 9 days in 12 patients (52%), between 10 and 14 days in 5 patients (22%), and between 21 and 28 days in 6 patients (26%).
3.7. New-onset cutaneous reaction vs. aggravation of preexisting skin disease
Eleven patients (23%) experienced an aggravation of preexisting skin disease, including 4 of the patients with clinical spongiotic dermatitis, 1 of our V-REPP patients, 1 patient with a psoriasiform reaction, 1 with a lichenoid pattern, all 3 of the patients with urticaria and 1 patient with bullous pemphigoid. Thirty-seven patients (77%) experienced a new-onset skin reaction after an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
3.8. Duration of cutaneous reactions
Information about the duration of the ADRs could be obtained from 45 patients (94%). In most patients (24/45; 53%) ADRs regressed within 28 days or less (range 1-28 days), whereas ADRs lasted more than 28 days in 21 patients (21/45; 47%).
4. Discussion
The results of our study highlight the broad spectrum of clinical and histopathological presentations of ADRs in patients receiving mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. In the generalized form of ADRs, maculo-papular exanthema and spongiotic dermatitis were the most common clinical manifestations accounting for 75% of all generalized cutaneous reactions. The incidence of urticarial reaction in our study seems to be slightly lower than in other studies [
6,
11,
17]. Most patients (3 of 4; 75%) with a clinically urticarial rash had preexisting urticaria triggered by the vaccination.
Histologically, the spongiotic pattern and the superficial perivascular lympho-histiocytic pattern were the most common ones, accounting for more than half of the biopsies. In contrast, interface changes with a vacuolar or lichenoid pattern were less common.
Interestingly, the spongiotic pattern was the histological correlate of most cases presenting clinically with maculo-papular exanthema and fewer showed dermal superficial perivascular lympho-histiocytic changes as the major histological finding.
In the study by Magro et al. as well as in our study only half of the cases with histologically spongiotic features were also clinically described as a spongiotic reaction [
10,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. Conversely, not all cases presenting clinically with spongiotic dermatitis showed also histologically spongiotic changes. These results demonstrate that clinical presentation and histologic features may diverge in individual cases. Dermatologists and dermatopathologists should be aware of this potential discrepancy.
A large series with 58 biopsies of ADRs to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines was analyzed by McMahon et al. [
16]. These biopsies, however, represented only 7% of all ADRs recorded in their registry. Spongiotic changes were the most common histopathological reaction which clinically correlated with papules, plaques, or pityriasis rosea-like eruptions. For this constellation, the acronym ''V-REPP'' was proposed by McMahon et al. with three different grades (robust, moderate, and mild). Almost half of our patients showed clinical features compatible with V-REPP which thereby represented the most common ADR in our series applying the criteria by McMahon et al. Within this group, the robust form accounted for almost 90% of the biopsies, whereas the moderate and mild forms were rarely observed. V-REPP, however, is clinically and histologically heterogeneous. The histological hallmark of V-REPP is spongiosis, associated with interface changes in various degrees, ranging from significant spongiosis with intraepidermal vesicle formation and minimal or no interface changes (robust V-REPP), to pityriasiform spongiosis (moderate V-REPP) or minimal spongiosis with more prominent interface changes (mild V-REPP). Interestingly the spongiotic pattern was not associated with interface changes in our cohort. Most patients in our cohort with histologically spongiotic changes might be classified as V-REPP applying the criteria by McMahon et al. We classified patients with clinical features of spongiotic dermatitis and histological spongiotic changes, however, synoptically as spongiotic dermatitis, and not as a robust form of V-REPP. This difference may explain the higher rate of spongiotic dermatitis in our cohort. A similarly high rate of clinical spongiotic reaction was also observed by Kroumpouzos et al. [
17]. Since the vast majority of our patients with clinically and/or histologically spongiotic changes had received the mRNA-1273 vaccine, these findings may indicate that mRNA-1273 more commonly induces spongiotic dermatitis than other vaccines.
Histological analysis demonstrated that eosinophils were a consistent feature of all reaction patterns and were found in two third of the biopsies. Eosinophils were present in the majority of the HSP reaction pattern and over half of the HPV reaction pattern similar to other studies [
10,
18]. There was an admixture of mast cells in all reactions, but their number was not increased. However, it cannot be excluded that the mast cells involved in vaccine-related reactions require different staining techniques to be highlighted [
19]. Plasma cells were only found in a small subset of biopsies.
The localized form of ADRs is characterized by erythema and swelling at the injection site ('COVID arm'). This delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction (DHSR) is histologically characterized by subtle and only very focal epidermal changes with spongiosis and exocytosis of a few lymphocytes, and sleeve-like perivascular infiltrates with features of erythema annulare centrifugum [
5,
7,
20]. In our 4 patients with COVID arm, we noticed similar findings.
In more than 70% of patients in our cohort, the ADRs were a new-onset skin disease and showed a self-limiting course. A subset of ADRs after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination, however, represented an aggravation of a previously existing inflammatory skin disorder such as atopic dermatitis. It reflects the result of immune activation which is not specific to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines as aggravation or relapse of preexisting skin diseases after vaccination, in general, can be observed [
17,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Further studies need to be conducted to determine if patients with preexisting skin diseases or atopy do have a higher probability of developing ADRs after mRNA vaccines [
17,
24].
In the literature, heterogenous data on the occurrence of ADRs after the first or subsequent doses was reported [
6,
16,
17,
26,
27]. The ADRs in our study most frequently occurred after the second dose, which contrasts with the 2.3% and 26.9% of ADRs after the second dose in previous studies [
11,
17]. The differences may be related to the predominance of the mRNA-1273 vaccine given to the patients in our series.
Whereas 'COVID arm' usually resolves within 1 or 2 weeks, generalized ADRs lasted in our cohort in many patients for more than 28 days and in some patients even longer than 6 months. This duration is longer than the data reported by other groups which observed regression of ADRs in most patients within 14 days [
5,
6,
28,
29]. In V-REPP, however, longer duration times of up to 49 days and rarely up to 90 days were reported.
Our cohort differs in two epidemiologic aspects from other studies. In our cohort, the gender distribution is equal, whereas other studies reported a higher number of ADRs in women [
6,
9,
17,
23,
26,
28]. Second, the vast majority of our patients (75%) had received the mRNA-1273 vaccine, as in Switzerland far more people in general were vaccinated with mRNA-1273 [
4]. McMahon et al. stated that they received more reports on cutaneous reactions after the mRNA-1273 vaccine than after the BNT162b2 vaccine as well [
6].
Pathogenetically, V-REPP seems to be initiated by Th1-cells, whereas Th2-cells trigger the development of spongiotic dermatitis [
10]. The mode of action may differ between various vaccines, but increased interferon-gamma produced by vaccine-induced receptor binding domain-specific CD8
+ and CD4
+ T cells seems to play a crucial role in the mediation of vaccine-related ADRs [
10,
30].
In conclusion, we found a wide spectrum of cutaneous ADRs in our patients. Although the histological pattern correlated in many patients with the clinical manifestation, discrepant findings could be observed, especially regarding spongiotic changes. The majority of ADRs were self-limited, however, a few ADRs were lasting for more than one month. The vast majority of ADRs were new-onset reactions while the remaining ADRs represented an aggravation of preexisting skin disease. The knowledge of the spectrum of cutaneous ADRs after vaccination with mRNA vaccines will be helpful for dermatologists and other specialties in counseling patients regarding these vaccinations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.K. and U.S.; methodology, W.K. and U.S.; Investigation, U.S.; resources, W.K., K.P., J.G., I.H. and S.C.; data curation, U.S.; writing – original draft preparation, U.S. and W.K.; writing – review and editing, U.S., J.G., K.P, I.H., S.C., W.K; visualization, U.S.; supervision, W.K.; project administration, W.K. and U.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the ethical committee (IRB) of Kanton Zurich, Switzerland (KEK 2021-01926).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to patient confidentiality.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge and thank the following colleagues for providing the patient’s information necessary for conduction this study: Marc Albisser MD, Marc Baumgartner MD, Petra Becker-Wegerich MD, Mirjam Beveler MD, Marcel Blickenstorfer MD, Jeannine Both MD, Simon Brechbühler MD, Michael Buslau MD, Patrizia Carrozza MD, Salomé Courvoisier MD, Tanja Gut MD, Mario Graf MD, Daniela Haiges MD, Matilde Iorizzo MD, Nathalie Irla MD, Theodor Karamdilov MD, Beat Keller MD, Jens Kimmritz MD, Fabiola Kind MD, Anna Isabella Kirsch MD, Kerstin Klötgen MD, Andreas Kühne MD, Kerstin Langer MD, Heidi Meier MD, Francesco Pelloni MD, Tobias Plaza MD, Gerald Rehor MD, Dominic Reinhardt MD, Zoi Spanou MD, Sabine Vida MD, Matthias Wigger MD, Myriam Wyss Fopp MD.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccinations. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- FDA Approves First COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-covid-19-vaccine (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- FDA takes additional Action in Fight against COVID-19 by Issuing emergency use authorization for Second COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-takes-additional-action-fight-against-covid-19-issuing-emergency-use-authorization-second-covid (accessed on 19 April 2021).
- Covid-19 Schweiz: Informationen zur aktuellen Lage. Available online: https://www.covid19.admin.ch/de/vaccination/persons (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Kempf, W.; Kettelhack, N.; Kind, F.; Courvoisier, S.; Galambos, J.; Pfaltz, K. 'COVID arm' - histological features of a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to Moderna mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV2 vaccine. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, D. E.; Amerson, E.; Rosenbach, M.; Lipoff, J. B.; Moustafa, D.; Tyagi, A.; Desai, S. R.; French, L. E.; Lim, H. W.; Thiers, B. H.; et al. Cutaneous reactions reported after Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination: A registry-based study of 414 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol 2021, 85, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, K. G.; Freeman, E. E.; Saff, R. R.; Robinson, L. B.; Wolfson, A. R.; Foreman, R. K.; Hashimoto, D.; Banerji, A.; Li, L.; Anvari, S.; et al. Delayed Large Local Reactions to mRNA-1273 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. N Engl J Med 2021, 384, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinato, F.; Maurelli, M.; Gisondi, P.; Girolomoni, G. Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. J Clin Med 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Català, A.; Muñoz-Santos, C.; Galván-Casas, C.; Roncero Riesco, M.; Revilla Nebreda, D.; Solá-Truyols, A.; Giavedoni, P.; Llamas-Velasco, M.; González-Cruz, C.; Cubiró, X.; et al. Cutaneous reactions after SARS-COV-2 vaccination: A cross-sectional Spanish nationwide study of 405 cases. Br J Dermatol 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niebel, D.; Novak, N.; Wilhelmi, J.; Ziob, J.; Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Bieber, T.; Wenzel, J.; Braegelmann, C. Cutaneous Adverse Reactions to COVID-19 Vaccines: Insights from an Immuno-Dermatological Perspective. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, L. B.; Fu, X.; Hashimoto, D.; Wickner, P.; Shenoy, E. S.; Landman, A. B.; Blumenthal, K. G. Incidence of Cutaneous Reactions After Messenger RNA COVID-19 Vaccines. JAMA Dermatol 2021, 157, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Fathy, R.; McMahon, D. E.; Freeman, E. E. COVID-19 Vaccines and the Skin: The Landscape of Cutaneous Vaccine Reactions Worldwide. Dermatol Clin 2021, 39, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tihy, M.; Menzinger, S.; André, R.; Laffitte, E.; Toutous-Trellu, L.; Kaya, G. Clinicopathological features of cutaneous reactions after mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021, 35, 2456–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avallone, G.; Quaglino, P.; Cavallo, F.; Roccuzzo, G.; Ribero, S.; Zalaudek, I.; Conforti, C. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-related cutaneous manifestations: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol 2022, 61, 1187–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, V.; Seidenberg, R.; Caplan, A.; Brinster, N. K.; Meehan, S. A.; Kim, R. H. Clinical and histopathological spectrum of delayed adverse cutaneous reactions following COVID-19 vaccination. J Cutan Pathol 2022, 49, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, D. E.; Kovarik, C. L.; Damsky, W.; Rosenbach, M.; Lipoff, J. B.; Tyagi, A.; Chamberlin, G.; Fathy, R.; Nazarian, R. M.; Desai, S. R.; et al. Clinical and pathologic correlation of cutaneous COVID-19 vaccine reactions including V-REPP: A registry-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2022, 86, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroumpouzos, G.; Paroikaki, M. E.; Yumeen, S.; Bhargava, S.; Mylonakis, E. Cutaneous Complications of mRNA and AZD1222 COVID-19 Vaccines: A Worldwide Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, C.; Crowson, A. N.; Franks, L.; Schaffer, P. R.; Whelan, P.; Nuovo, G. The histologic and molecular correlates of COVID-19 vaccine-induced changes in the skin. Clin Dermatol 2021, 39, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askenase, P. W. Rare Skin Reactions after mRNA Vaccination, Similar to Jones-Mote Basophil Responses. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 1720–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, M. S.; Galan, A.; Watsky, K. L.; Little, A. J. Delayed Localized Hypersensitivity Reactions to the Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine: A Case Series. JAMA Dermatol 2021, 157, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aram, K.; Patil, A.; Goldust, M.; Rajabi, F. COVID-19 and exacerbation of dermatological diseases: A review of the available literature. Dermatol Ther 2021, 34, e15113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambichler, T.; Boms, S.; Susok, L.; Dickel, H.; Finis, C.; Abu Rached, N.; Barras, M.; Stücker, M.; Kasakovski, D. Cutaneous findings following COVID-19 vaccination: review of world literature and own experience. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2022, 36, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niebel, D.; Wenzel, J.; Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Ziob, J.; Wilhelmi, J.; Braegelmann, C. Single-Center Clinico-Pathological Case Study of 19 Patients with Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Following COVID-19 Vaccines. Dermatopathology (Basel) 2021, 8, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alelq, N. A.; Kubieniec, M. E.; French, L. E.; Prinz, J. C. Influence of Covid-19 vaccination on immune-mediated skin diseases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesqué, D.; Lopez-Trujillo, E.; Marcantonio, O.; Giménez-Arnau, A. M.; Pujol, R. M. New-onset and exacerbations of psoriasis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccines: two sides of the same coin? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2022, 36, e80–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez Guerrero, A.; Domínguez Estirado, A.; Crespo Quirós, J.; Rojas-Pérez-Ezquerra, P. Delayed cutaneous reactions after the administration of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantisani, C.; Chello, C.; Grieco, T.; Ambrosio, L.; Kiss, N.; Tammaro, A.; Tosti, G.; Paolino, G.; Pellacani, G. Cutaneous Reactions to COVID-19 Vaccines in a Monocentric Study: A Case Series. J Clin Med 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulee, A.; Salem, S.; Yahia, R.; Yang, K.; Garcia, D.; Holmes, A.; Furukawa, B. Cutaneous reactions due to Pfizer's BNT162b2 mRNA and Moderna's mRNA-1273 vaccines. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2022, 36, e332–e334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, S.; Amini, Z.; Goodarzi, A. A comparative review on mucocutaneous reactions caused by Covid-19 infection versus Covid-19 vaccination. Exp Dermatol 2022, 31, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Derhovanessian, E.; Vogler, I.; Kranz, L. M.; Vormehr, M.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K.; Quandt, J.; Maurus, D.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and T. Nature 2020, 586, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Distribution (%) of clinical patterns after vaccination with either mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2. Abbreviations: maculo-papular exanthema (CMP), spongiotic dermatitis (syn. eczema) (CEC), urticarial (CUR), psoriasis-like (CPS), plaque-like (CPL), lichenoid (CLI), bullous (CBU) and pseudolymphomatous (CLY).
Figure 1.
Distribution (%) of clinical patterns after vaccination with either mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2. Abbreviations: maculo-papular exanthema (CMP), spongiotic dermatitis (syn. eczema) (CEC), urticarial (CUR), psoriasis-like (CPS), plaque-like (CPL), lichenoid (CLI), bullous (CBU) and pseudolymphomatous (CLY).
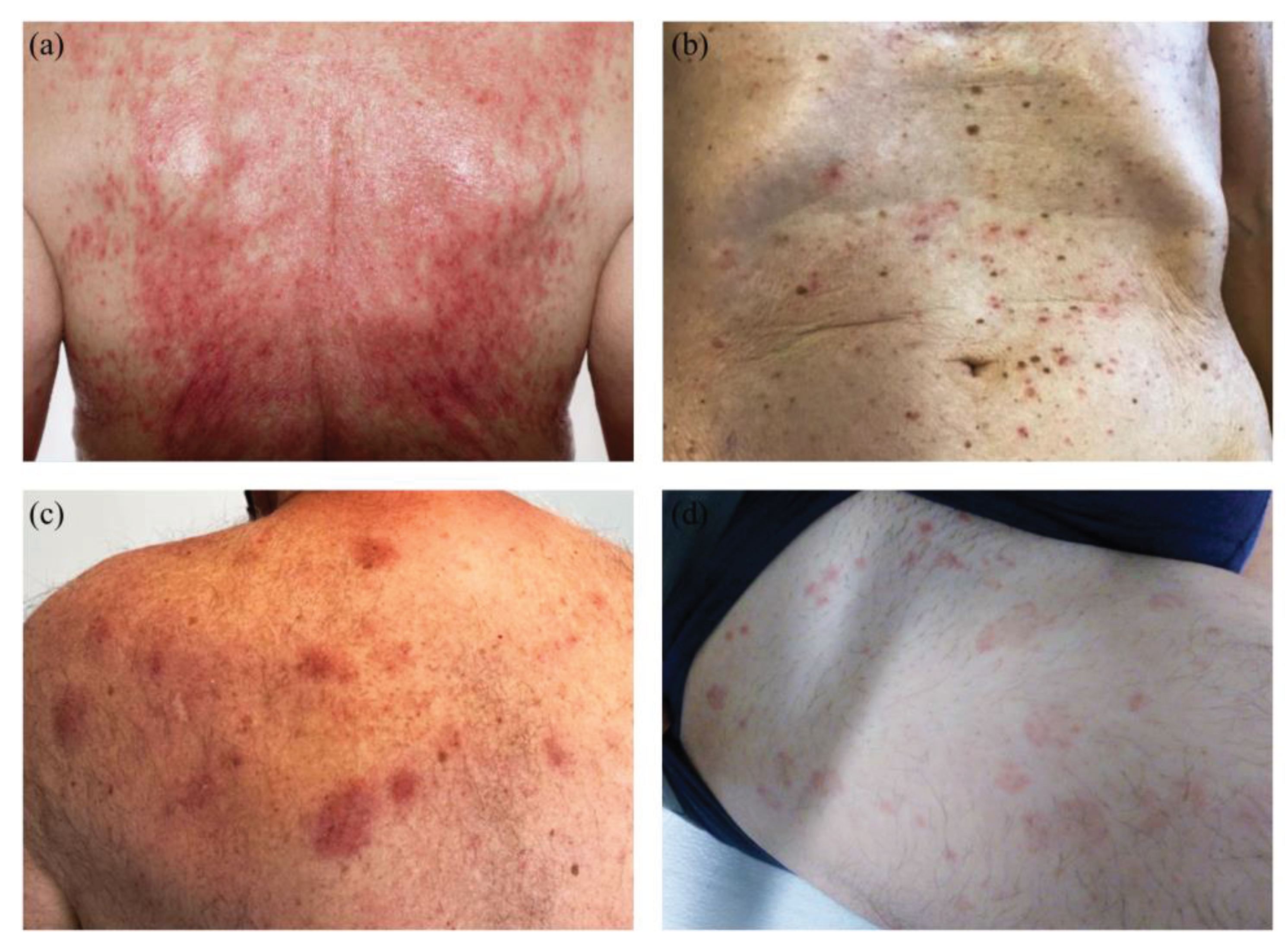
Figure 2.
Clinical Manifestation of COVID-vaccine associated adverse reaction (ADR): (a): maculo-papulous confluent and erosive pattern on the back. (b): maculo-papulous Exanthema located at the frontal torso. (c): erythematous plaques on left upper back. (d): wheals located on the thigh, frontal and lateral.
Figure 2.
Clinical Manifestation of COVID-vaccine associated adverse reaction (ADR): (a): maculo-papulous confluent and erosive pattern on the back. (b): maculo-papulous Exanthema located at the frontal torso. (c): erythematous plaques on left upper back. (d): wheals located on the thigh, frontal and lateral.
Figure 3.
Distribution (%) of histological patterns after vaccination with either mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2. Abbreviations: spongiotic (HSP), superficial perivascular lympho-histiocytic without epidermal changes (HPV), psoriasiform (HPS), lichenoid (HLI), non-lichenoid interface changes (HIF), urticarial (HUR), vasculitis (HVA), panniculitis (HPA), bullous (HBU), acantholytic and dyskeratotic (HAD), pustular (HPU), folliculitis (HFO) and pseudolymphomatous (HPL).
Figure 3.
Distribution (%) of histological patterns after vaccination with either mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2. Abbreviations: spongiotic (HSP), superficial perivascular lympho-histiocytic without epidermal changes (HPV), psoriasiform (HPS), lichenoid (HLI), non-lichenoid interface changes (HIF), urticarial (HUR), vasculitis (HVA), panniculitis (HPA), bullous (HBU), acantholytic and dyskeratotic (HAD), pustular (HPU), folliculitis (HFO) and pseudolymphomatous (HPL).
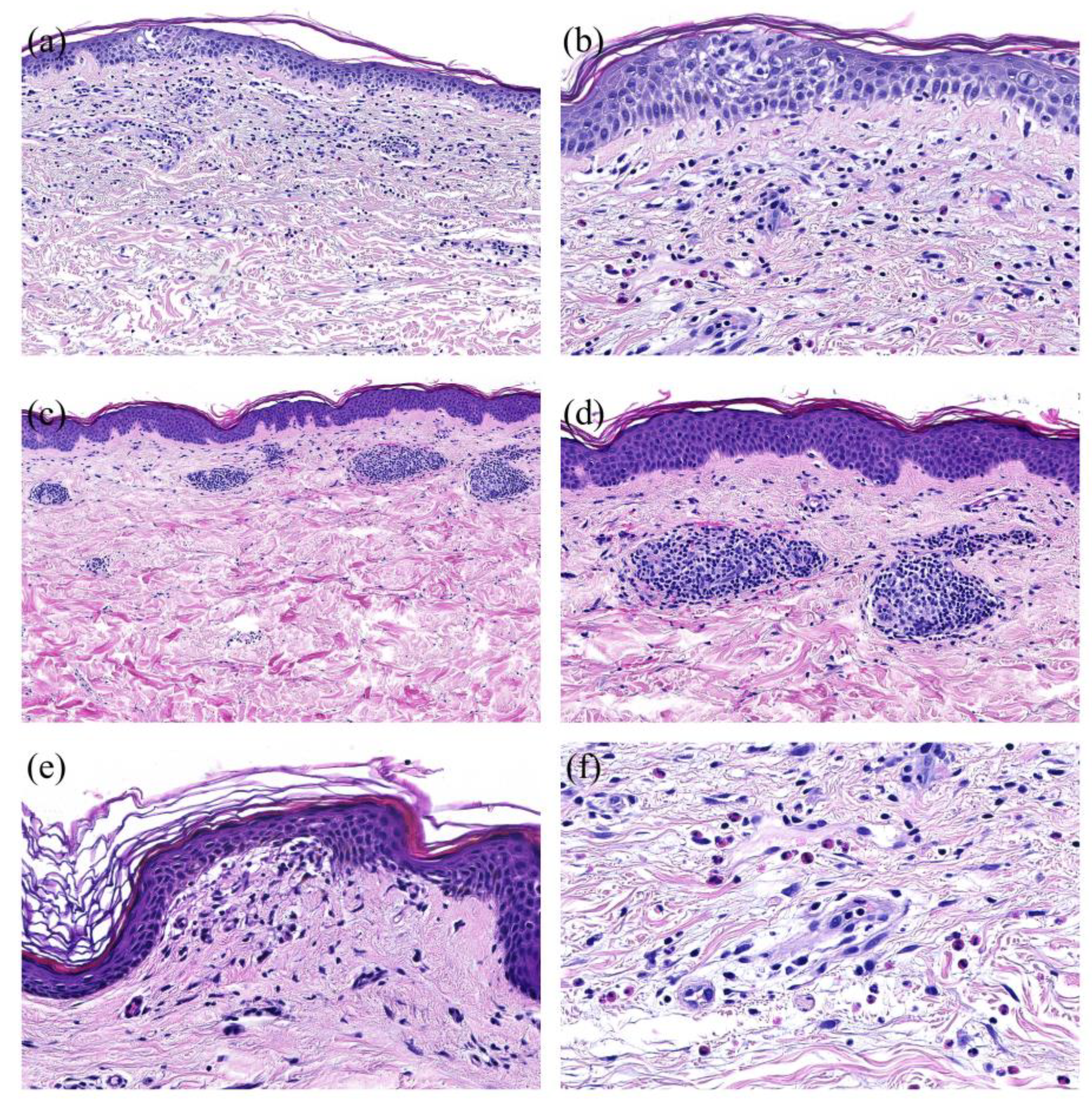
Figure 4.
Histopathological Patterns of COVID-vaccine associated cutaneous adverse reaction (ADR): (a): Spongiotic pattern with focal spongiosis of the epidermis and perivascular predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate (H&E, magnification X20). (b): Spongiotic pattern (detail) with focal spongiosis of the epidermis and exocytosis of lymphocytes in the spongiotic areas (H&E, magnification X200). (c): Perivascular pattern with perivascular predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis in the absence of epidermal changes (H&E, magnification X20). (d): Perivascular pattern (detail) with sleeve-like perivascular predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis (H&E, magnification X200). (e): Interface pattern with vacuolization in the junctional zone (H&E, magnification X200). (f): High number of eosinophils in the infiltrate (H&E, magnification X200).
Figure 4.
Histopathological Patterns of COVID-vaccine associated cutaneous adverse reaction (ADR): (a): Spongiotic pattern with focal spongiosis of the epidermis and perivascular predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate (H&E, magnification X20). (b): Spongiotic pattern (detail) with focal spongiosis of the epidermis and exocytosis of lymphocytes in the spongiotic areas (H&E, magnification X200). (c): Perivascular pattern with perivascular predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis in the absence of epidermal changes (H&E, magnification X20). (d): Perivascular pattern (detail) with sleeve-like perivascular predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis (H&E, magnification X200). (e): Interface pattern with vacuolization in the junctional zone (H&E, magnification X200). (f): High number of eosinophils in the infiltrate (H&E, magnification X200).
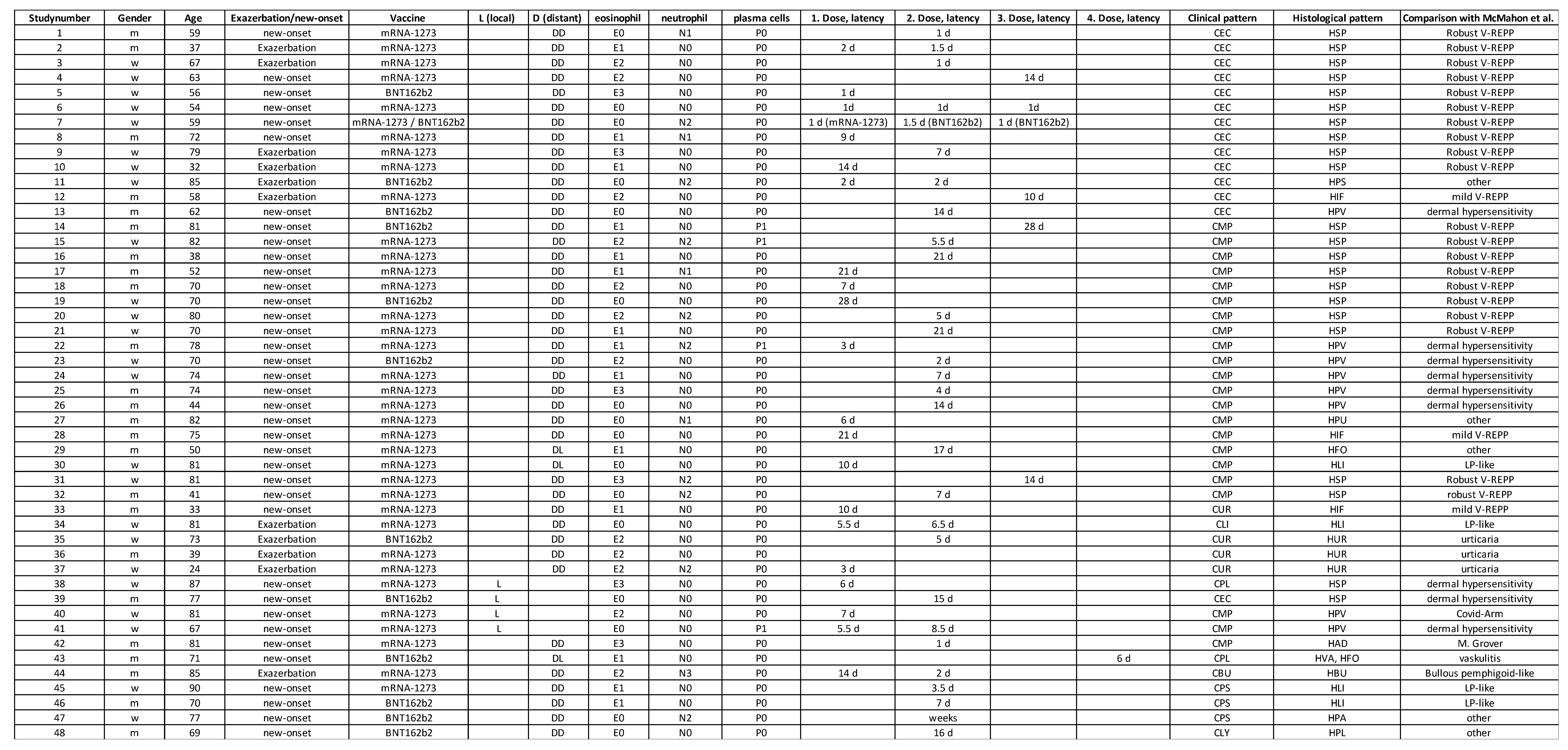
Table 1.
Overview of patient’s data including age, gender, vaccine-type, exacerbation/new-onset, latency as well as clinical and histological patterns.
Table 1.
Overview of patient’s data including age, gender, vaccine-type, exacerbation/new-onset, latency as well as clinical and histological patterns.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).