1. Introduction
Early diagnosis of lung pathologies is crucial for improving patient prognosis. Chest X-Rays are one of the most common imaging modalities used for diagnosing lung pathologies. However, diagnosing lung pathologies based on chest X-Rays can be challenging and subjective, especially for diseases with similar symptoms.
In recent years, Deep Learning (DL) has shown significant potential in enhancing the diagnosis of lung pathologies based on chest X-Rays. DL, a branch of artificial intelligence, utilizes artificial neural networks to learn complex patterns from data. DL systems for lung pathology recognition based on chest X-Rays can be classified into two main categories:
Detection Systems: these systems are designed to identify the presence of anomalies in chest X-Rays.
Classification Systems: these systems are designed to classify anomalies in chest X-Rays based on the type of lung pathology.
Common DL techniques used for lung pathology recognition based on chest X-Rays include:
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): CNNs are a class of artificial neural networks designed for image processing. They have been successfully used for recognizing various anomalies in chest X-Rays, including lung nodules, lung infiltrates, and pneumonia.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): RNNs are a class of artificial neural networks designed for processing sequence data. RNNs have been successfully used for recognizing anomalies in chest X-Rays that develop over time, such as the progression of lung cancer.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs are a class of artificial neural networks designed to generate realistic data. GANs have been successfully used for synthesizing chest X-Ray images containing anomalies, improving the training of DL systems.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of DL in analyzing chest X-Rays, achieving remarkable results in the detection and classification of lung nodules, pneumonia, and other thoracic pathologies. For example, Wang et al. developed a DL-based system for lung nodule detection with promising results [
1]. Similarly, Kermany et al. demonstrated the effectiveness of DL in classifying pneumonia from chest X-Rays [
2].
These advancements highlight the transformative potential of DL in chest X-Ray analysis. As research efforts continue to refine DL algorithms and expand their applications, this powerful technology is poised to revolutionize the detection, diagnosis, and treatment of lung diseases, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Despite the remarkable progress, several challenges remain to fully realize the potential of DL in chest X-Ray analysis. These challenges include the need for large sets of high-quality annotated image data, ensuring the generalizability of DL models to diverse patient populations, and addressing ethical and regulatory considerations associated with deploying AI in healthcare.
To address these challenges, research efforts should focus on creating comprehensive image datasets, developing robust DL models capable of effectively handling real clinical scenarios, and establishing clear guidelines for the ethical and responsible use of AI in healthcare.
The healthcare landscape is undergoing a profound transformation driven by the convergence of advanced technologies, including, as discussed, DL, but also the Internet of Things (IoT) and digital twins (DTs). These innovations offer enormous potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery in general and, particularly, in the field of monitoring lung pathologies.
IoT sensors integrated into wearable devices connected to the internet enable real-time monitoring of physiological parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and X-Ray images of various organs. These continuous data streams enable proactive healthcare interventions, allowing for early detection of potential complications and facilitating remote patient monitoring.
DTs, virtual representations of physical objects or systems, offer a holistic approach to monitoring lung pathologies. By integrating data from IoT sensors, clinical records, and other relevant sources, DTs can provide a comprehensive view of an individual’s lung health, allowing for early detection of subtle changes and personalized treatment recommendations.
To fully harness the potential of these technologies, a unified platform is essential to seamlessly integrate AI-enhanced image analysis, IoT sensor data, and DT simulations. This platform would provide clinicians with a centralized hub for real-time information, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize patient care.
In particular, lung pathology monitoring based on DL, IoT, and DTs offers numerous benefits, including:
Early and Accurate Detection of Lung Pathologies: AI-enhanced image analysis systems can support radiologists in identifying anomalies in chest X-rays, providing technological assistance for a quick and precise diagnosis;
Personalization of Diagnosis and Treatment: data collected from IoT sensors and DTs can be used to develop personalized diagnoses and treatment plans that are more effective and cost-efficient;
Improvement of Patients’ Quality of Life: remote monitoring systems enable patients to receive care from home, improving their quality of life and reducing healthcare costs.
In this study, we present a proposal for the application of DT technology in the classification of lung pathologies, using chest X-Ray images as input. The main objectives of our work, which also constitute the innovative aspect compared to the state of the art described in
Section 2, are as follows:
Implementation of a case study that includes a proof-of-concept of a Lung-DT based on a microservices architecture characterized by an artificial intelligence component.
The proposed Lung-DT architecture is designed to acquire various input signals, including chest X-Ray images (the subject of our study) and blood oxygen saturation (to be integrated later), allowing for a more comprehensive evaluation of lung conditions.
Extension of the second-level architecture previously proposed in [
3]. This extension involves the integration of DTs related to other organs to define the presence of various pathologies. The use of information from different organs enables a more comprehensive detection and classification of pathological conditions.
Accurate classification of lung pathologies into 5 categories to contribute to a more detailed and specific diagnosis.
Expansion of the neural network’s training and validation dataset by integrating two public datasets. This integration aims to enhance the predictive capacity of the model, improving its adaptability to a wider range of pathologies. Use of a third dataset completely unknown to the neural network to perform additional testing. This step is aimed at confirming the robustness of the model by evaluating its performance on novel data.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows:
Section 2 provides an overview of the state of the art regarding DT-based systems applied to lung pathologies recognition using Chest X-Ray images and DT architecture applied to the lung. The architecture and implementation of the Lung-DT, and more generally, the healthcare DT platform are described in
Section 3. The setup description of the Lung-DT is conducted in
Section 4. This section outlines the dataset made up of four lung pathologies, including the "normal" classification, the neural network model, and the obtained results.
Section 5, the comparison of the research present in the state of the art and the Lung-DT proposed in this paper has been provided. Finally,
Section 6 shows the conclusion of this study.
2. Related Work
The field of medical diagnostics is undergoing a revolution thanks to the advanced use of artificial intelligence techniques applied to the analysis of chest X-Ray images. This chapter aims to examine the latest methodologies proposed in the scientific literature for the diagnosis of lung diseases through the use of artificial neural networks and machine learning algorithms.
In recent years, especially during and after the COVID-19 pandemic, numerous DL methods have been proposed based on the detection of lung diseases with X-Ray images. Some of these studies [
4,
5,
6] adopt a simpler approach, directly classifying chest X-Ray images into a set of categories corresponding to each lung disease, without preprocessing and feature extraction. These approaches are generally simpler and computationally efficient. Other studies [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15], on the other hand, use more complex approaches typically consisting of two phases: feature extraction and classification. In the feature extraction phase, DL algorithms extract relevant features from chest X-Ray images, and in the classification phase, these features are used to classify images into different categories of lung diseases. Compared to the first approach, these methods are computationally more complex and slower. Finally, there are works [
16,
17] that combine both approaches to conduct more comprehensive studies and compare the performance of various systems in terms of accuracy.
In [
4], a self-supervised deep neural network is proposed, using chest X-Rays as an efficient and widely available method for classifying respiratory diseases. The self-supervised deep neural network, pretrained on an unlabeled dataset, utilizes contrastive learning to transfer learned representations to subsequent classification tasks. The results demonstrate that this approach achieves competitive performance without requiring large amounts of labeled training data. This study adopts a straightforward approach without a separate feature extraction phase. Similarly, in [
5], the authors present a hybrid architecture that combines contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) with a deep convolutional network for the classification of lung images into different pathology classes. Through the use of chest X-Ray images, the authors claim that this method outperforms traditional approaches by 20% in terms of accuracy, demonstrating its effectiveness in early diagnosis and categorization of lung diseases. In [
6], the authors propose a classification algorithm based on the SqueezeNet neural network to distinguish between chest X-Rays of individuals with or without lung diseases. Using a dataset of chest X-Ray images, the model is tested with an accuracy of 94%, demonstrating its ability to discriminate between "Normal" and "Pneumonia" images.
In [
7], a hybrid approach with modular neural networks is represented, where the authors propose an approach that uses modular artificial neural networks integrated with fuzzy logic for the diagnosis of lung diseases. This method focuses on the analysis of digitized chest X-Ray images, using descriptors such as the gray-scale histogram and gray-level co-occurrence matrix. The use of a multi-objective genetic algorithm to reduce features enables the creation of an optimized neuro-fuzzy classifier, demonstrating high accuracy in classifying pathologies in the analyzed X-Rays. In [
8], the authors define a classification of pneumonia using pretrained convolutional neural network models. This Ensemble Learning method combines features extracted from three well-known CNN models (DenseNet169, MobileNetV2, and Vision Transformer) to achieve exceptional results with an accuracy of 93.91% and an F1-score of 93.88% on the test phase.
In [
9], the authors address the increase in lung diseases by proposing a multiclass classification of 10 different lung pathologies using a refined CNN model. With the use of various pretrained networks, the proposed model, named LungNet22, achieves an accuracy of 98.89% through parameter optimization and the construction of a model derived from VGG16. Similarly, the study in [
10] proposes a DL model to classify chest X-Ray images into 14 different lung pathology conditions. Using transfer learning on pretrained neural networks such as DenseNet and ResNet, the model shows better accuracy than a competing network, highlighting the importance of data preprocessing to improve model performance.
In [
11], the authors address the theme of the COVID-19 pandemic and its early identification using chest X-Ray images. Through a model that combines a pretrained VGG19 network with three blocks of a convolutional neural network, the proposed approach achieves an accuracy of 96.48%, providing a reliable means to accelerate diagnosis and improve treatment efficiency. Similarly, in [
12], an Ensemble model called PulDi-COVID is proposed for the diagnosis of nine lung diseases, including COVID-19. Using various pretrained neural networks and combining them through an Ensemble strategy, the approach offers remarkable results, with an accuracy of 99.70%, precision of 98.68%, and recall of 98.67%, highlighting its effectiveness in multipathological diagnosis. In [
13], an analysis of post-COVID lung diseases is carried out using a combination of an architecture to capture global features with Inception modules and a Transformer network to analyze local features. The use of an asymmetric loss function for multiclass classification demonstrates the superiority of the proposed model over other well-known architectures. The work in [
14] focuses on globally relevant lung diseases such as pneumonia, COVID-19, tuberculosis, and pneumothorax. The proposed approach uses eight pretrained convolutional neural networks to automatically classify chest X-Ray images. The best model, Densenet-201, achieves an accuracy of 97.2%, surpassing other state-of-the-art methods and demonstrating the potential for automation in the rapid diagnosis of lung diseases.
An approach for the detection of lung diseases through chest X-Ray images, using an optimized Deep Convolutional Spiking Neural Network (DCSNN) with the Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm (AOA) and the Kaggle NIH dataset, is proposed in [
15]. The method includes a preprocessing phase of images, including an anisotropic diffusion filter and an enhancement scheme. The DCSNN, enhanced by AOA, achieves a sensitivity of 31.87%, specificity of 26.88%, and recall of 28.14%, surpassing other methods in the literature, such as LDC-SVM-SMO and LDC-XGBoost-PSO.
In [
16], the authors propose a neural network model called Lung-GANs for the classification of lung diseases from chest X-Ray images. This approach uses a multi-level structure of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to learn interpretable representations of lung disease images from unlabeled data. The model eliminates the need for large labeled datasets, making it advantageous for new and complex lung diseases. During experiments, Lung-GANs outperforms existing unsupervised models, achieving exceptional accuracy in the range of 94%–99.5% on six extensive datasets of lung diseases. The strength of Lung-GANs lies in its ability to generalize without requiring a high amount of labeled data. The model is applicable to various classifications of lung diseases, such as TB vs. healthy, pneumonia vs. normal, COVID-19 vs. pneumonia, COVID-19 vs. non-COVID, demonstrating superiority in terms of accuracy (up to 99.5%) and sensitivity compared to existing methods.
In [
17], the challenge of automatic segmentation of the lungs in chest X-Ray images is addressed. Through the use of a convolutional neural network with concatenation blocks and transpose layers, the proposed model achieves promising results with an accuracy of 97%, an IoU of 93%, and a Dice coefficient of 96%.
In summary, current scientific studies in the literature show significant progress in the field of lung disease diagnosis through the use of sophisticated artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques. The implementation of these proposals offers new perspectives to improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnosis, promoting rapid identification and timely treatment of lung diseases. In general, the discussed progress has been driven by the development of:
More powerful DL architectures: new DL architectures, such as DenseNet, ResNet, Transformers, and Inception, have been developed to effectively capture complex features from X-Ray images.
Large X-Ray datasets: the availability of large X-Ray datasets, such as the NIH ChestX-ray14 dataset, has allowed the training of more accurate DL models.
Collective learning: collective learning techniques, combining multiple DL models to improve performance, have been used to achieve the best results in lung disease detection.
The detection of lung diseases through DL techniques based on X-Ray images has numerous potential applications, including:
Fast and accurate diagnosis: DL models can be implemented on mobile devices or in hospitals to provide a rapid and accurate diagnosis of lung diseases.
Early detection of lung cancer: DL models can be used to identify early signs of lung cancer, leading to early treatment and better outcomes for patients.
Risk classification: DL models can be used to classify patients based on their risk of developing lung diseases, providing useful information for therapeutic decision-making.
In the current research landscape, studies focus exclusively on the application of DL techniques to chest images to optimize the classification of lung pathologies.
Regarding DT-based applications in the pulmonary field, scientific literature has seen a little development in recent years. Some studies [
18,
19,
20,
21] propose DT-based systems to create virtual representations of the lungs, which have been used to improve the diagnosis of diseases such as pneumonia and COVID-19.
For example, in [
18], a digital-twin-based smart healthcare system integrated with medical devices is proposed to collect information regarding the current health condition, configuration, and maintenance history of the device/machine/system. The system also analyzes medical images using a DL model to detect COVID-19 infection. The system is based on the cascade recurrent convolution neural network (RCNN) architecture, achieving a mean average precision rate of 94%. In [
19], a new system for telemedical simulation in remote lung cancer implementation is presented, combining DL, DTs, mixed reality, and medical IoT. The system aims to improve accuracy and immersion during remote surgical implementation. The system is based on a robust auxiliary classifier generative adversarial network (rAC-GAN) for patient-specific data analysis and prediction. The rAC-GAN model is trained on data from 90 lung cancer patients with pulmonary embolism (PE) and 1372 lung cancer control groups. The system achieved area under the curve (AUC) values of 92% and 93%, showing significant performance improvement in processing clinical data. The work conducted by the authors in [
20] proposes a new Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) framework using DT models and DL to improve image quality and anti-noise performance. The proposed EIT framework incorporates DT models to generate a virtual dataset of EIT measurements and lung information. The framework also includes a DL-based image reconstruction network (IR-Net) to leverage labeled data and reconstruct conductivity distributions within the lungs during respiration. The IR-Net achieves superior image quality and anti-noise performance compared to traditional EIT algorithms. Finally, in [
21], an intelligent Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) platform for automatic pneumonia diagnosis in chest X-Ray images is proposed. The platform utilizes DT technology to create a virtual representation of the lung based on real-time X-Ray data. The article introduces an Enhanced Vision Transformer Model (EVTM) for analyzing chest X-Ray images, which uses vision transformer technology to convert images into sequences for improved feature extraction. The model is trained on a dataset of chest X-Ray images and outperforms baseline models with higher precision, recall, accuracy, and F-score values.
However, none of these studies focuses on developing a multilevel platform capable of acquiring, processing, storing, and sharing information useful for the prevention or diagnosis of pathologies related to abnormal values from multiple organs.
This work, introduces an architecture based on DTs, incorporating multiple levels of abstraction. These levels encompass organ-based DTs and pathology-based DTs, with the integration of artificial intelligence models. In fact, the goal is not only to integrate the classification results obtained from neural network models related to lung images but to create a broader structure composed of DTs related to various organs, as in the case of the study on the heart in [
3]. This architecture aims to accumulate multi-organ information to support doctors in the diagnosis and prevention of diseases (such as acute coronary syndrome), considering the interactions between different sub-pathologies related to each organ. The main challenges that the proposed architecture in our study aims to address are the following:
Continuous and personalized patient monitoring: utilize DTs to optimize the real-time collection and processing of data from various medical devices, including wearable sensors, clinical records, and other applications. This data can be used to create a digital model of the patient, predict the risk of diseases, identify anomalies, and optimize therapies.
Unified patient management platform: use a platform that allows monitoring different organs and pathologies, through the creation of Organ DTs that, working collaboratively, provide the medical world with a tool for a comprehensive view of the patient’s health and optimize treatment planning.
Optimization in the fusion and sharing of clinical information: consult, through a single frontend, the entirety of patient medical information and create a shared virtual environment where doctors can collaborate on patient care, share data, discuss clinical cases, and plan surgeries.
Tool to improve procedures and reduce healthcare costs: use DTs in medical scenarios to simulate medical procedures in a safe virtual environment before performing them on a real patient, receive feedback to improve organizational efficiency. These simulations can be a valuable tool to assess the critical points of the entire medical supply chain and optimize the use of medical resources, such as medical devices and staff, to reduce healthcare costs.
3. Lung-DT
Building on the architecture of the Heart Digital Twin (HDT) [
3], the authors aim to extend the concept to create a Digital Twin of the lung. Similar to the approach adopted for the HDT, the creation of a Lung-DT involves various functional components in both the digital and real-world domains. This extension enriches the platform, requiring the implementation of scalable, dynamic, and resilient systems, along with a modular approach.
3.1. Lung-DT Architecture
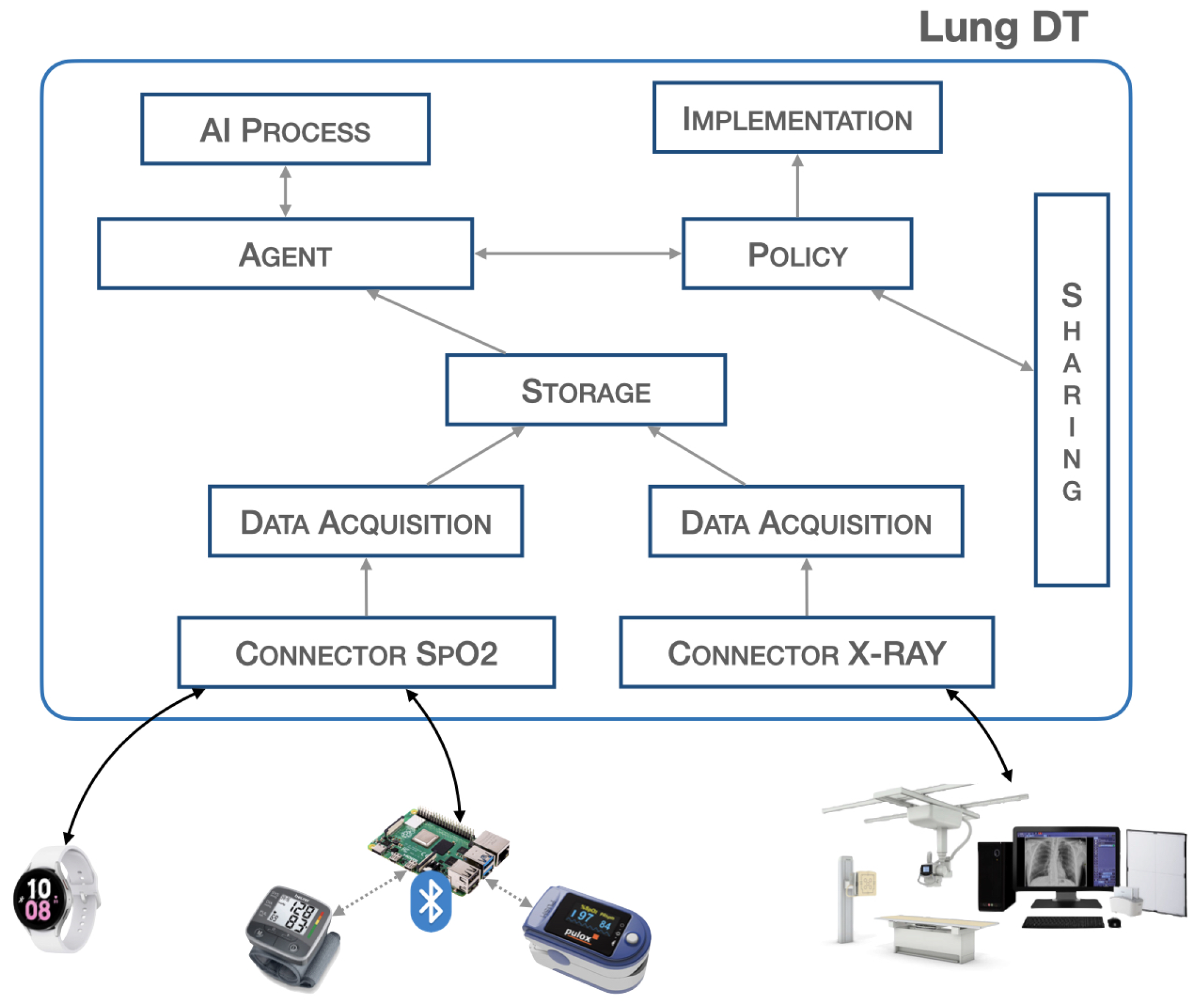
The lung architecture characterizes the DT based on the specific context. In scenarios of lung pathologies, input data can be diverse, including numerical data and images such as X-Ray images. Unlike the Heart DT, the Lung-DT must be able to acquire images. Therefore, in addition to the two connectors, there are two distinct acquisition blocks to process raw data from the real world.
The two present connectors are dedicated to acquiring the SpO2 value from a smartwatch and data from lung X-Rays. In addition to the connectors, the data acquisition block related to the X-Ray connector performs resize and categorization operations on the images before storing them in the storage block. Subsequently, the storage block is responsible for storing pre-processed data for future use.
The agent block initiates different decision-making processes based on the data input into the storage and programmatically triggers data analysis. Depending on the nature of the analysis, the agent will activate the AI process block, responsible for processing images or saturation data.
The AI process block can download various models from the AI services block, the reference model for making inferences based on the required analysis. In the following chapters, the methodology and results of the inference process when the Lung-DT needs to process lung images will be detailed.
Finally, once the agent block obtains the processing result, it will assess the necessary actions, such as sharing information with other DTs or implementing actions in the real world through the implementation block. Similar to the heart case, the policy block holds all policies and thresholds to prevent actions harmful to the organ itself.
As shown in
Figure 1, the implementation provided in this study on the Lung-DT involves two distinct connectors, both designed to interface directly with the physical world for data acquisition. The first connector is used to acquire SpO2 values from wearable medical devices, such as a smartwatch, while the second is dedicated to acquiring X-Ray images from the real world.
3.2. Lung-DT Workflow
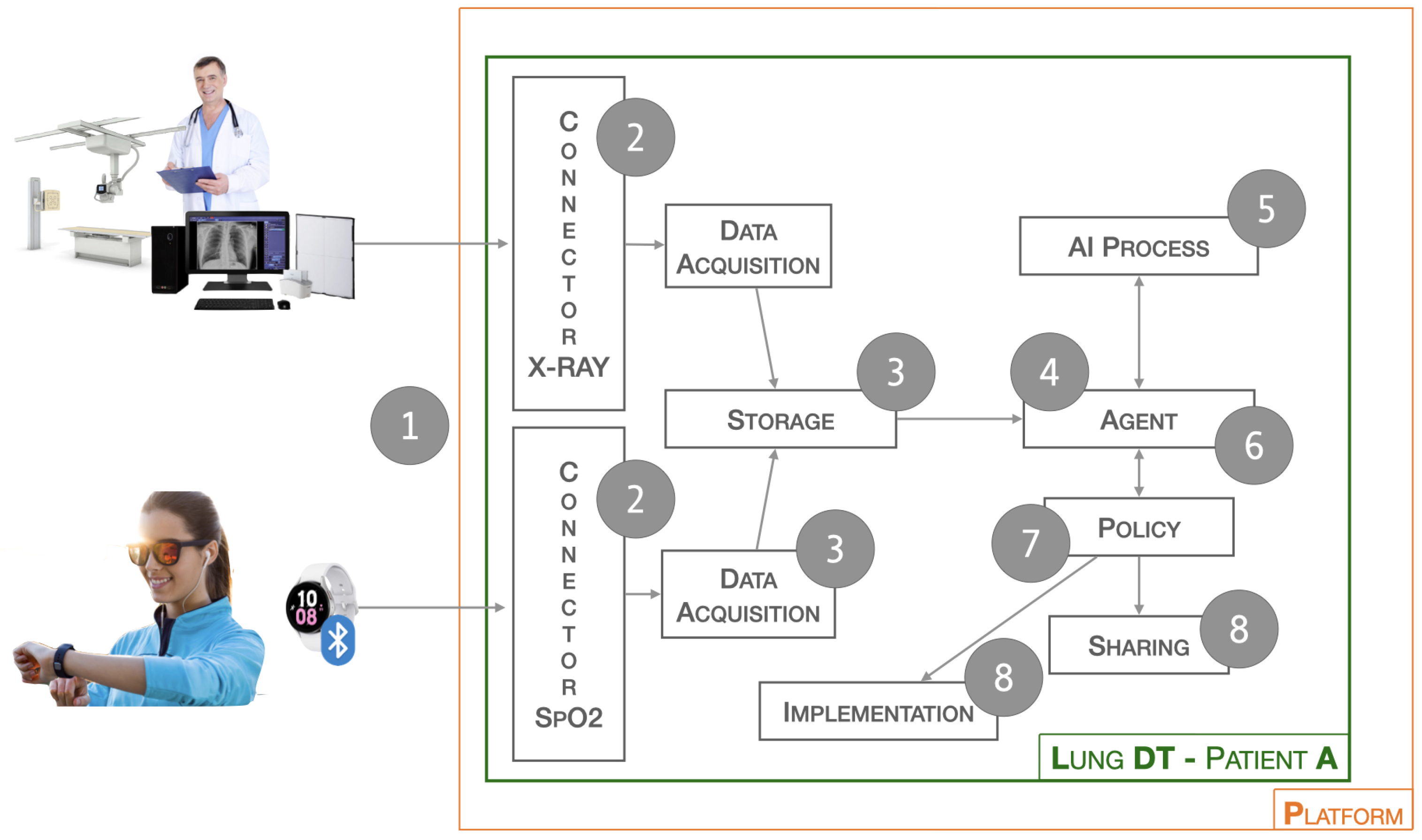
Below is the workflow related to the Lung-DT. Data from the real world is acquired through a single endpoint to which IoT devices and various systems can connect. The platform exposes various services, as shown in
Figure 2, with two connectors (1) dedicated to data acquisition. For saturation data, they are sent via REST API or MQTT, while for X-Ray images, there is an FTP repository where files can be uploaded. It is essential to emphasize that medical personnel uploading the clinical report will only have access to the Lung-DT repository specific to the individual patient.
The next phase (2) involves reading the data and performing cleaning and normalization operations. In this process, operations such as the removal of non-useful metadata, uniformity of format, and file type are carried out. The Storage block (3) is responsible for storing the raw and cleaned data for future use.
The Agent block (4), through cyclical checks or external interactions, initiates the validation and inference process for previously acquired data. In particular, if a new image has been received, it will contact the AI Process block (5) to start the validation process. In the case of an X-Ray image, the AI Process block will contact the AI Long Instance X-Ray block to check for the presence of a new updated model, which will be used for inference.
Once completed, the result is returned to the Agent block (6) to assess future actions. Specifically, based on the thresholds set in the Policy block (7), certain actions will or will not be taken. These actions may include physical world actions through the Implementation block or sharing with other DTs through the Sharing block (8).
Although the Implementation block (8) is not currently utilized in the context of this study, it is nevertheless crucial to include it for two main reasons. Firstly, this structure adheres to the model proposed in [
3] for HDT. Secondly, considering a broader context, such as the architecture we propose, it could be leveraged in the future to control actuators or notification subsystems. The idea is to establish a modular and dynamic architecture capable of adapting to various application scenarios and, above all, facilitating the seamless integration of new functionalities without compromising the integrity of the entire system.
3.3. Healthcare DT platform
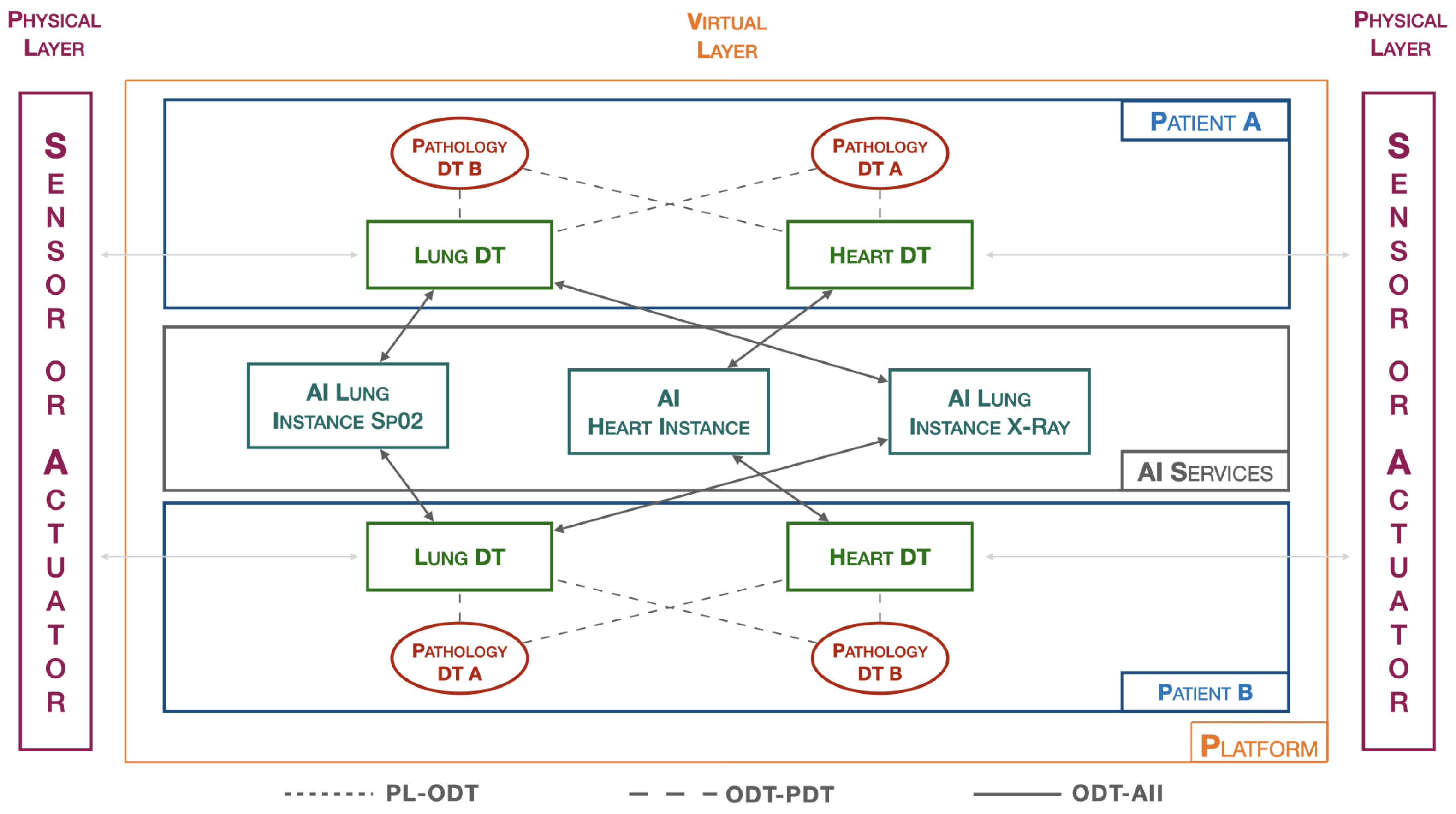
The platform introduced by the authors [
3] has been characterized for a specific application related to the lung, as illustrated in
Figure 3. In the patient-dedicated section, there are DTs related to both the heart and the lung, while two generic DTs for pathologies are exemplified. The AI Services section includes three instances, one focused on the cardiac context (AI Heart Instance), while the other two are dedicated to the pulmonary domain. Specifically, there is the AI Lung SpO2 Instance, related to blood saturation data, and the AI Lung X-Ray Instance, which handles the processing of lung images. All instances are independent of each other, allowing updates and changes without affecting the behavior of the entire platform. This flexibility enables adapting the platform to specific needs, facilitating the seamless integration of new elements to enhance the overall capabilities of the system. The modular structure of the platform provides the opportunity to customize and expand functionalities based on the evolving requirements of the application.
4. Testbed setup of Lung-DT
In this section, we will outline the steps that led to the creation of the neural network model integrated into Lung-DT, capable of classifying Chest X-Ray images into 5 classes of lung diseases. Specifically, we will describe the two public datasets used in this study, the pre-processing phase of the images before being input into the network, the convolutional neural network model used with its respective stages (training, validation, and testing), and finally, the results obtained during the training and testing phases of the neural network.
4.1. Datasets
In this section, we will illustrate the dataset used to train and test the neural network, described in sub
Section 4.2, for classifying 5 different classes of lung pathologies, including the "Normal" class. Specifically, to have 5 different pathology classes and a significant number of lung images (from different individuals with different genders and ages) for training and validating the network, two open datasets on Kaggle were used: the "
" [
22] and the "
" [
23]. A third public dataset "
" [
24], also available on Kaggle, was used for testing (prediction) of the trained network.
The first dataset [
22] contains chest X-Ray images in various formats (PNG and JPEG) and includes 4 classes of lung diseases (Pneumonia, Covid, Tuberculosis, and Lung Opacity) and one "Normal" class. The number of images in each class is as follows: 1,583 for the "Normal" class, 4,273 for "Pneumonia," 6,011 for "Lung Opacity," 4,192 for "Covid," and 703 for "Tuberculosis."
The second dataset [
23] is similar to the first, containing chest X-Ray images in JPEG format. This dataset was created by integrating other publicly available datasets, excluding the first one mentioned. It presents 4 classes of lung diseases (Bacterial and Viral Pneumonia, Corona Virus Disease, Tuberculosis) and a "Normal" class. To ensure a significant amount of data, a data augmentation factor of 6 was applied, resulting in just over 10,000 images distributed as follows: 2,013 for the "Normal" class, 2,009 for "Bacterial Pneumonia," 2,008 for "Viral Pneumonia," 2,031 for "Corona Virus Disease," and 2,075 for "Tuberculosis."
The third dataset [
24] includes four main classes: "Covid," "Normal," "Pneumonia," and "Lung_Cancer." The images in the dataset have various formats, including PNG and JPEG. Specifically, the dataset consists of 106 images for the "Covid" class, 132 images for the "Normal" class, 103 images for "Pneumonia," and 49 images for "Lung_Cancer."
After analyzing all the found public datasets, the first two were chosen to create a unified dataset for training and validating the YOLOv8 neural network. In particular, for each class, the images were combined, ensuring there were no duplicates, and the format of all images was standardized to PNG.
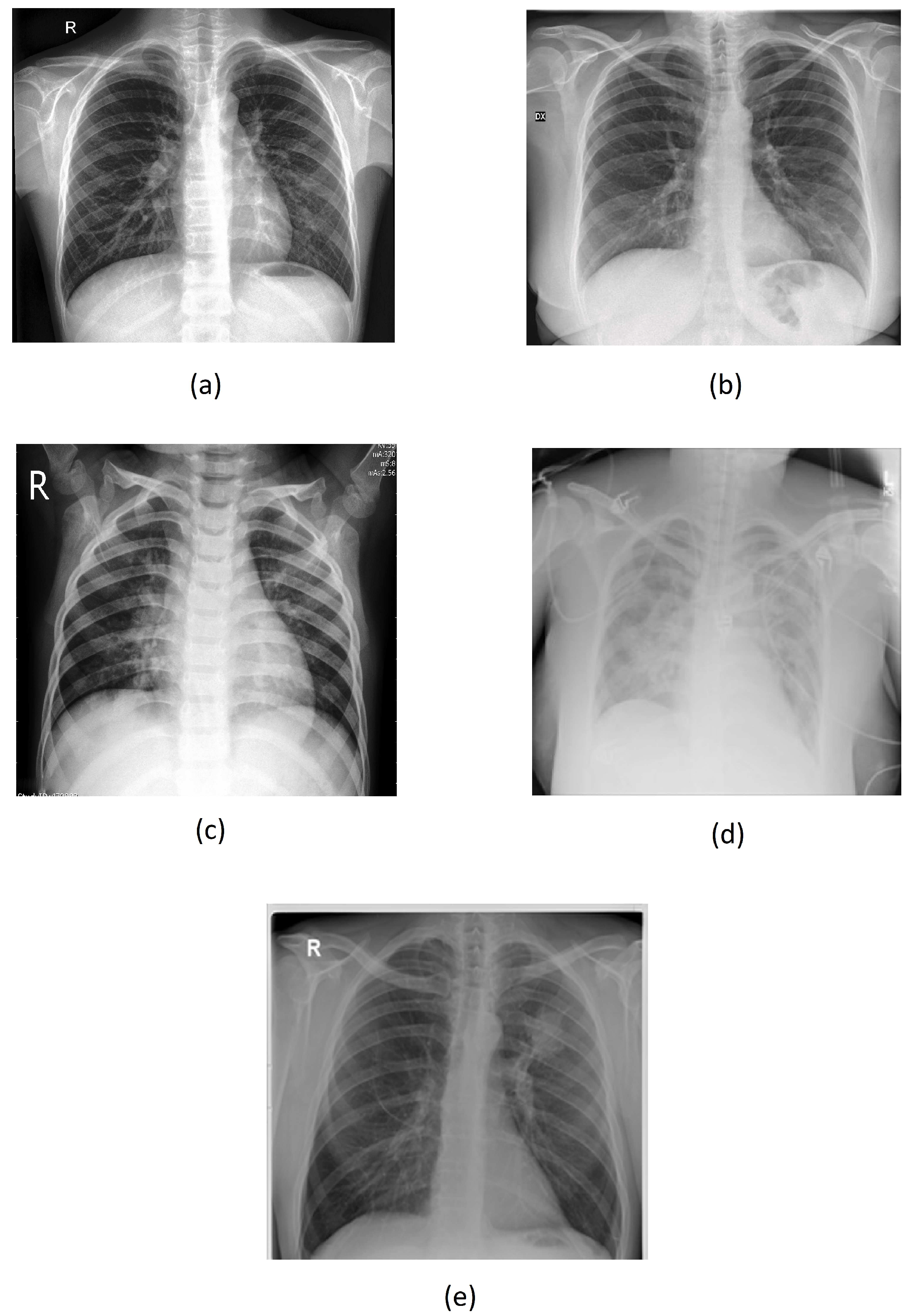
Figure 4a–e below illustrate corresponding to the “Normal,” "Covid," "Lung Opacity," "Pneumonia," and "Tuberculosis" class.
The unified dataset contains a total of 23,442 images and was subsequently randomly divided into Training Set and Validation Set according to the following proportions: 70% and 30%. Therefore, the number of elements within each class for the Training Set is as follows:
"Normal": 1,481 images;
"Covid": 3,997 images;
"Pneumonia": 5,348 images;
"Lung Opacity": 4,207 images;
"Tuberculosis": 1,330 images.
While the number of elements within each class for the Validation Set is as follows:
"Normal": 635 images;
"Covid": 1,697 images;
"Pneumonia": 2,291 images;
"Lung Opacity": 1,803 images;
"Tuberculosis": 653 images.
The dataset [
24], as mentioned earlier, was utilized during the testing (prediction) phase of the network. Specifically, only three pathology classes were considered, aligning with the classes used in the training and validation phases: "Normal," "Covid," and ’Pneumonia."
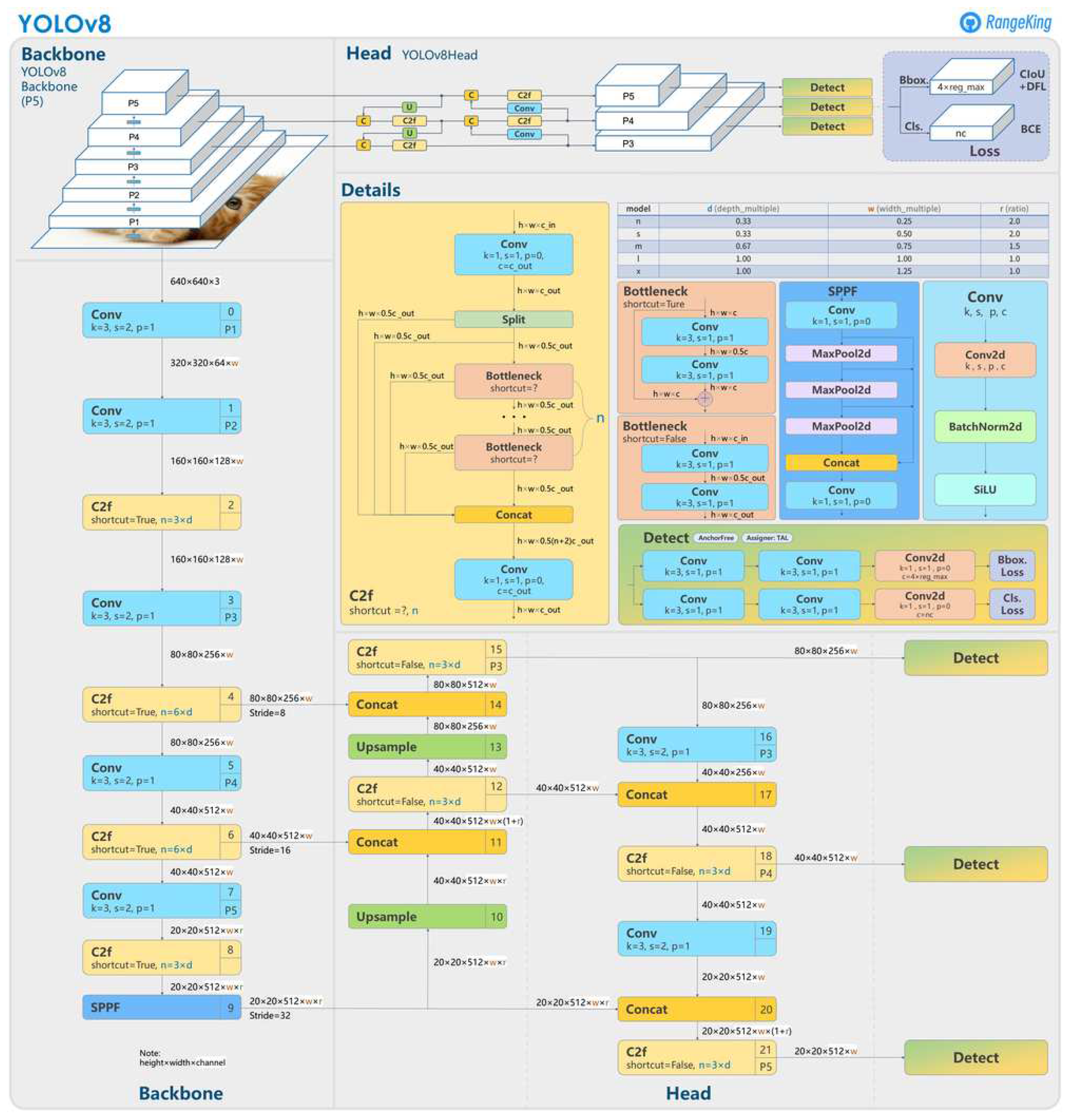
4.2. Convolutional Neural Network: YOLOv8
YOLOv8 [
25] is the latest model in the YOLO (You Only Look Once) series, designed for object detection, image classification, and instance segmentation. Developed by Ultralytics, also known for the YOLOv5 model, YOLOv8 introduces numerous architectural changes and improvements in the developer experience compared to YOLOv5.
The YOLO series of models gained prominence in the computer vision community due to its remarkable accuracy and compact model size. YOLO was initially implemented in C in versions 1-4, using a custom DL framework called Darknet. YOLOv8 emerged as part of the YOLOv5 development process when Glenn Jocher of Ultralytics began contributing to the YOLOv3 repository in PyTorch.
YOLOv8 is characterized by several features that make it appealing for computer vision projects:
High Accuracy: YOLOv8 has demonstrated high accuracy measured through COCO and Roboflow 100 metrics.
Developer Convenience: the model offers many features for developer convenience, including an easy-to-use command-line interface (CLI) and a well-structured Python package.
Large Community: YOLO has a large community, and the YOLOv8 community is growing. This means there are many online resources and experts in computer vision who can provide support and guidance.
YOLOv8 achieves strong accuracy on COCO. For instance, the YOLOv8m model, the medium-sized model, achieves a mAP of 50.2% when measured on COCO. When evaluated against Roboflow 100, a dataset specifically designed to assess model performance across various specific task domains, YOLOv8 has substantially outperformed YOLOv5. Further details on this are provided in our performance analysis later in the article.
Moreover, the developer-friendly features in YOLOv8 are significant. Unlike other models where tasks are distributed across many different Python files that need to be run, YOLOv8 comes with a CLI that makes model training more intuitive. This is in addition to a Python package that provides a smoother coding experience compared to previous models.
Despite the absence of an official paper, some features of the YOLOv8 architecture have been analyzed by Ultralytics. Some key updates include:
Anchor-Free Detection: YOLOv8 adopts an anchor-free model, predicting the object’s center directly rather than the offset from a known anchored box.
New Convolutions: changes have been made to the model’s structure, including replacing 6x6 convolutions with 3x3 convolutions and modifications to the main building blocks.
Mosaic Augmentation Closure: YOLOv8 uses mosaic augmentation during online training but disables this technique in the last ten epochs to improve performance.
The architecture of the YOLOv8 network is defined in
Figure 5.
4.3. Results
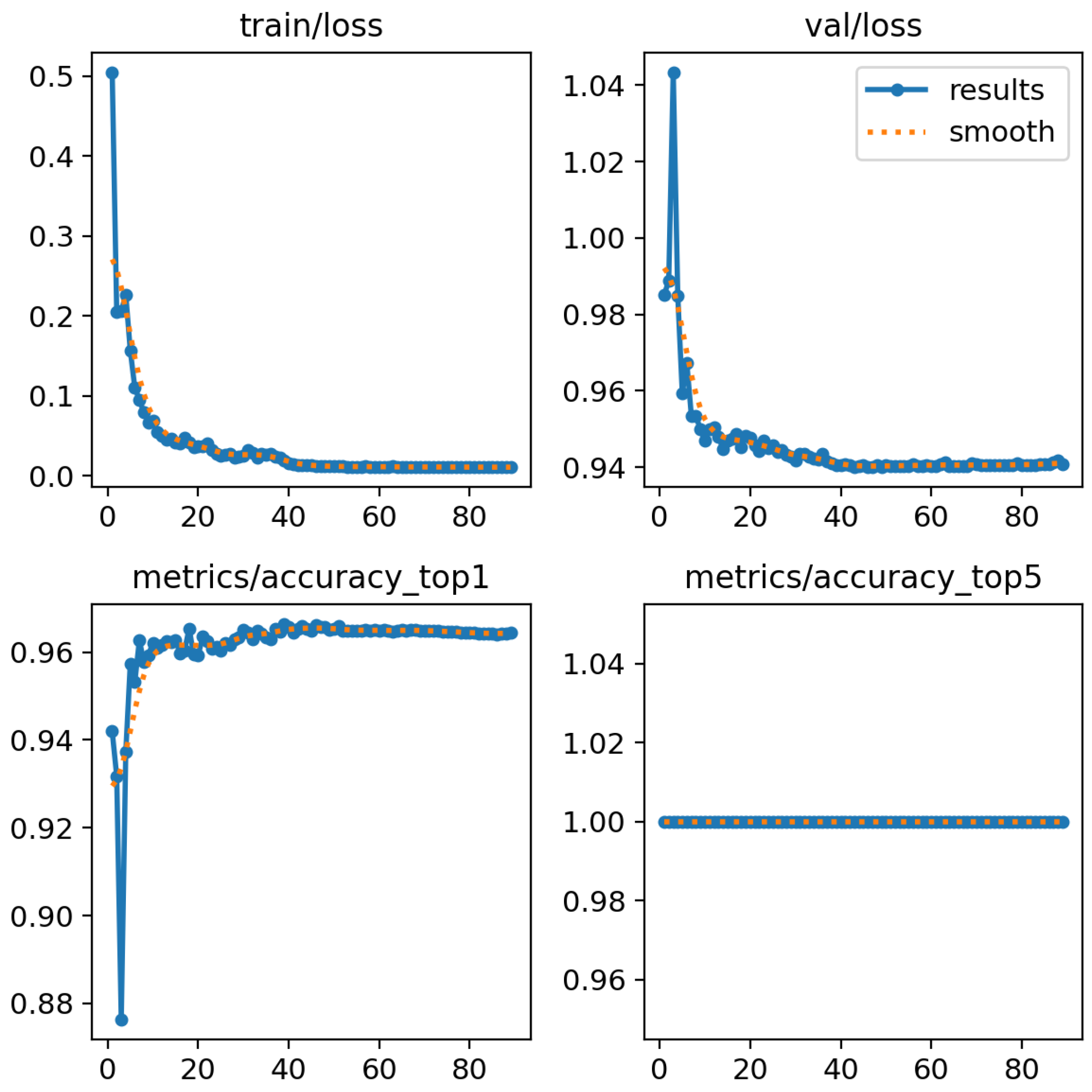
In order to obtain a neural network model capable of classifying pulmonary pathologies into 5 classes, the YOLOv8 neural network, as described above, was trained with fine-tuning, setting the initial weights corresponding to those used by the author on the model trained on COCO. Subsequently, 100 training epochs were conducted, resulting in an average accuracy of 96.6%.
As depicted in
Figure 6, the x-axis represents the number of epochs, while the y-axis indicates the loss and accuracy values on the training and validation datasets during the training phase of the network model.
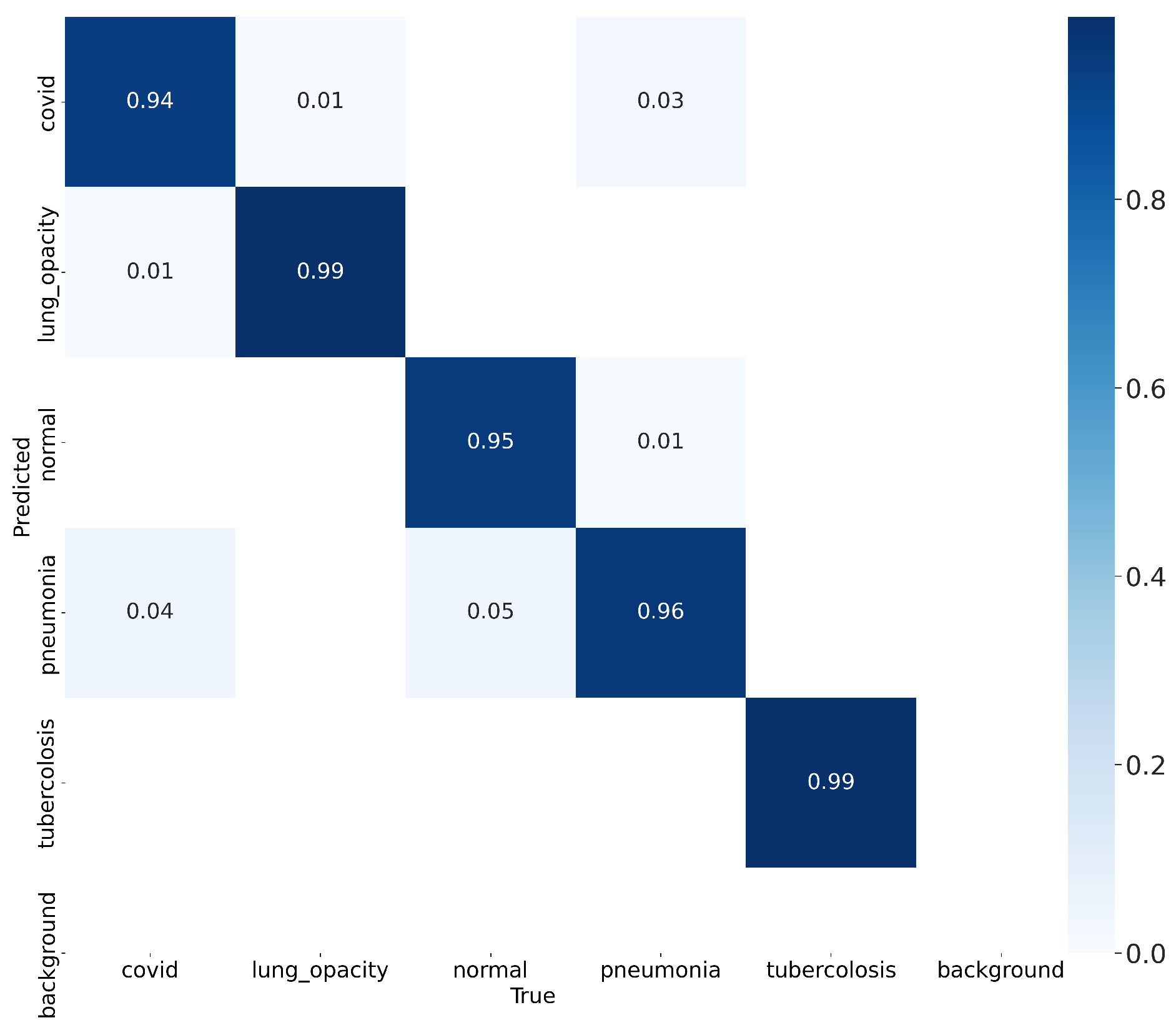
At the end of the network training, the testing phase is carried out using the testing set to evaluate the network’s performance. In the
Figure 7 shows the confusion matrix to assess the accuracy of the classification of the network model during the testing phase.
To obtain a more accurate assessment of the performance of the trained and tested model using the dataset described in
Section 4.1, a third dataset [
24] (completely unknown to the network, not belonging to either the training set or the validation set) was used for the testing (prediction) phase to carefully examine the classification of each image. The detailed results are documented in
Table 1.
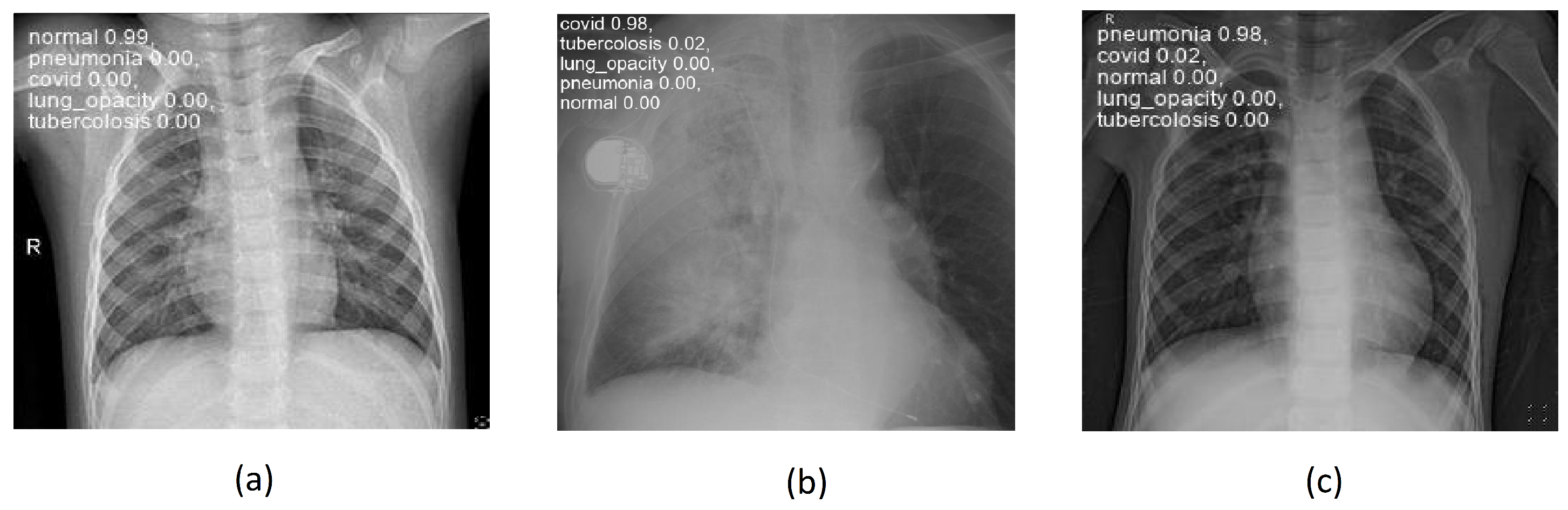
For the other two classes, "Lung Opacity" and "Tuberculosis," it was not possible to perform an inference phase as these classes were not present in the "" dataset.
Figure 8 shows some examples of lung images, each corresponding to its respective pathology, with the classification percentage result for all classes. As can be observed, the model performs very well even on images it has never seen before, achieving accuracies ranging from 97-99%.
The
Table 1 shows the average accuracy values and the standard deviation obtained during the inference phase for each individual image, considering all images for each pathology class.
5. Discussion
In this section we will discuss and compare the state of the art of research on the topic and the Lung-DT proposed in this paper.
The
Table 2 shows a comparison between our study and the state of the art in the literature regarding the use of DL techniques for the classification of X-Ray images for the detection of specific pulmonary pathologies.
In particular, the table compares the technology used, classes and performance in terms of accuracy.
Considering the references reported in
Table 2, two fundamental innovations characterize our work. The first relates to the improvement of the classification process, while the second focuses on the application of the DT paradigm.
Regarding classification, the dataset for model training was created by merging two distinct public datasets. This strategic choice aims to ensure a level of completeness and robustness in managing data diversity. To confirm this, high performances were obtained using a large testing dataset totally unrelated to the training dataset, a very important aspect introduced in this work. Furthermore, our study stands out for considering five classes in the classification process. The results obtained indicate that the accuracy is above the average found in the literature, suggesting the effectiveness of the model in the classification task compared to traditional approaches.
Regarding the use of the DT paradigm, an Lung-DT characterized by pulmonary X-Ray images was implemented. The incorporation of an Lung-DT within the platform allows for extending the monitoring of patients’ health through collaboration between DTs of different organs.
6. Conclusion
The present study represents a significant contribution in the field of lung disease classification through the innovative use of DT technology. The results obtained highlight the effectiveness of our proposal, which distinguishes itself in several key aspects compared to the state of the art.
Our work focuses on the implementation of a practical case study, providing a proof-of-concept for a Pulmonary DT. This implementation is characterized by a microservices architecture, integrating an artificial intelligence component that operates on heterogeneous input signals. Specifically, our Pulmonary DT architecture receives data from chest X-Ray images and blood oxygen saturation, allowing for a more comprehensive and detailed evaluation.
The novelty of our proposal also arises from the extension of the second-level architecture previously presented [
3], incorporating DTs related to other organs, such as the lung in addition to the heart. This multi-level approach enables the identification and classification of a wide range of pathologies, leveraging information from various body systems.
In the context of training the neural network model based on YOLOv8, the integration of two open datasets has proven its effectiveness, achieving an average accuracy of 96% in the classification of lung pathologies into 5 classes. Furthermore, testing on a third completely unknown dataset confirmed the high robustness of our model, with an average precision of 98%.
It is relevant to note that the performance achieved in our study often surpasses those found in existing literature, suggesting a significant advancement in the application of DTs to the classification of lung pathologies. The proposed multi-level architecture, which incorporates models related to other organs such as the heart, offers an innovative approach to the diagnosis and classification of pathologies related to multi-organ issues. This work substantially contributes to the progress of computational medicine and technology-assisted diagnostics using DT technology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; methodology, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; software, R.A. and C.R.; validation, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; formal analysis, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; investigation, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; resources, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; data curation, R.A. and C.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; writing—review and editing, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; visualization, R.A., F.B., A.L., and C.R.; supervision, F.B. and A.L.; project administration, A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the two researchers involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI |
Artificial Intelligence |
| CNN |
Convolutional Neural Network |
| DL |
Deep Learning |
| DT |
Digital Twin |
| FTP |
File Tranfer Protocol |
| GAN |
Generative Adversarial Network |
| HDT |
Heart Digital Twin |
| IoT |
Internet of Things |
| MQTT |
Message-Queuing Telemetry Transport |
| RNN |
Recurrent Neural Network |
| YOLO |
You Only Look Once |
References
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Lu, L.; Lu, Z.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M. ChestX-Ray8: Hospital-Scale Chest X-Ray Database and Benchmarks on Weakly-Supervised Classification and Localization of Common Thorax Diseases. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; Dong, J.; Prasadha, M.K.; Pei, J.; Ting, M.Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Hewett, S.; Dong, J.; Ziyar, I.; Shi, A.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, L.; Hou, R.; Shi, W.; Fu, X.; Duan, Y.; Huu, V.A.; Wen, C.; Zhang, E.D.; Zhang, C.L.; Li, O.; Wang, X.; Singer, M.A.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Tafreshi, A.; Lewis, M.A.; Xia, H.; Zhang, K. Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avanzato, R.; Beritelli, F.; Lombardo, A.; Ricci, C. Heart DT: Monitoring and Preventing Cardiac Pathologies Using AI and IoT Sensors. Future Internet 2023, 15, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazda, M.; Plavka, J.; Gazda, J.; Drotar, P. Self-supervised deep convolutional neural network for chest X-ray classification. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 151972–151982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, F.; Mughaid, A.; AlZu’bi, S.; El-Salhi, S.M.; Abuhaija, B.; Abualigah, L.; Gandomi, A.H. Hybrid clahe-cnn deep neural networks for classifying lung diseases from x-ray acquisitions. Electronics 2022, 11, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanzato, R.; Beritelli, F. Thorax Disease Classification based on the Convolutional Network SqueezeNet. 12th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications, 2023.
- Varela-Santos, S.; Melin, P. A new modular neural network approach with fuzzy response integration for lung disease classification based on multiple objective feature optimization in chest X-ray images. Expert Systems with Applications 2021, 168, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, A.; Díaz Redondo, R.P.; Dahou, A.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Kayed, M. Pneumonia detection on chest X-ray images using ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamrat, F.J.M.; Azam, S.; Karim, A.; Islam, R.; Tasnim, Z.; Ghosh, P.; De Boer, F. LungNet22: a fine-tuned model for multiclass classification and prediction of lung disease using X-ray images. Journal of Personalized Medicine 2022, 12, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Bu, S. Transfer-learning-based approach for the diagnosis of lung diseases from chest X-ray images. Entropy 2022, 24, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshmrani, G.M.M.; Ni, Q.; Jiang, R.; Pervaiz, H.; Elshennawy, N.M. A deep learning architecture for multi-class lung diseases classification using chest X-ray (CXR) images. Alexandria Engineering Journal 2023, 64, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, Y.H.; Patnaik, K.S. PulDi-COVID: Chronic obstructive pulmonary (lung) diseases with COVID-19 classification using ensemble deep convolutional neural network from chest X-ray images to minimize severity and mortality rates. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 81, 104445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezina, A.; Burget, R. Detection of post-COVID-19-related pulmonary diseases in X-ray images using Vision Transformer-based neural network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2024, 87, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaddi, S.H.; Sharma, L.D. Automated multi-class classification of lung diseases from CXR-images using pre-trained convolutional neural networks. Expert Systems with Applications 2023, 211, 118650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Karthick, R.; Meenalochini, P.; Kalaichelvi, T. Deep Convolutional Spiking Neural Network optimized with Arithmetic optimization algorithm for lung disease detection using chest X-ray images. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 79, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Menon, N.; Ravi, V.; Vishvanathan, S. Lung-GANs: unsupervised representation learning for lung disease classification using chest CT and X-ray images. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, A.; Anand, V.; Gupta, S.; Asiri, Y.; Elmagzoub, M.; Reshan, M.S.A.; Shaikh, A. A Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Segmentation of Lung Diseases Using Chest X-ray Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, M.; Jeon, G. Integrating digital twins and deep learning for medical image analysis in the era of COVID-19. Virtual Reality & Intelligent Hardware 2022, 4, 292–305. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, C.; Chang, V.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Guizani, M. Digital-Twin-Enabled IoMT System for Surgical Simulation Using rAC-GAN. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9, 20918–20931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, W.; Soleimani, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M. Electrical Impedance Tomography Guided by Digital Twins and Deep Learning for Lung Monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, X. An Enhanced Vision Transformer Model in Digital Twins Powered Internet of Medical Things for Pneumonia Diagnosis. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaggle, Multiclass Chest X-Ray Disease Dataset. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/saifurrahmanshatil/multiclass-chest-xray-disease-dataset (10 December 2023).
- Kaggle, Lungs Disease Dataset (4 types). Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/omkarmanohardalvi/lungs-disease-dataset-4-types (10 December 2023).
- Kaggle, Multi Classe Chest X-Ray DATASET(VERSION 2). Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sourov509/multi-classe-chest-x-ray-datasetversion-2 (10 December 2023).
- YOLOv8, Roboflow,. Available online: https://blog.roboflow.com/whats-new-in-yolov8/ (15 December 2023).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).