Submitted:
31 December 2023
Posted:
02 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Database Search
2.2. Title and Abstract Screening Phase
- The scope of the study includes all three of the following aspects: a) diet in the form of nutrition, prebiotics, probiotics, postbiotics, parabiotics, synbiotics/symbiotics, or compounds derived from natural sources, b) gut microbiota, and c) diabetes, including but not limited to T1DM, T2DM, GDM, prediabetes, and complications or comorbidities related to DM.
- Articles published between January 1, 2012 and December 31, 2022.
- The study language was in “English”.
2.3. Full Text Screening Phase
- The microbiota discussed in the study pertained to the naturally occurring gut flora, not to those artificially transplanted.
- Conditions such as insulin resistance, metabolic syndromes or other disorders should be associated with DM.
- The term ‘diet’ should only include nutrition, prebiotics, probiotics, postbiotics, parabiotics, synbiotics/symbiotics, or compounds derived from natural sources. We excluded all studies discussing medications, or chemical compounds not derived directly from a natural source (such as fruits, food items, etc.).
2.4. Extraction Phase
2.5. Analysis of the Data
3. Results
3.1. Top Journals in This Field
3.2. Top Organizations and Collaborations in This Field
3.3. Top Countries in This Field
3.4. Author Collaborations in This Field
3.5. Top Cited Articles in This Field
3.6. Top Study Designs in This Field
3.7. Top Experimental Subjects in This Field
3.8. Co-Occurrence of Author Keywords
3.9. Diet, DM and Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
4.1. Research Overview
4.2. Characteristics of Publications
4.3. Research Hotspots and Frontiers
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of interest
References
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract [Internet]. 2022 Jan 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];183. Available from:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34879977/.
- The Facts, Stats, and Impacts of Diabetes | CDC [Internet]. [cited 2023 Nov 9]. Available from:. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/spotlights/diabetes-facts-stats.html.
- Sapra A, Bhandari P. Diabetes. StatPearls [Internet]. 2023 May 29 [cited 2023 Jun 24]; Available from:. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551501/.
- Zorena K, Michalska M, Kurpas M, Jaskulak M, Murawska A, Rostami S. Environmental Factors and the Risk of Developing Type 1 Diabetes-Old Disease and New Data. Biology (Basel) [Internet]. 2022 Apr 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];11. Available from:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35453807/.
- Loder MK, Xavier GDS, McDonald A, Rutter GA. TCF7L2 controls insulin gene expression and insulin secretion in mature pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Soc Trans [Internet]. 2008 Jun [cited 2023 Apr 27];36(Pt 3):357–9. Available from:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18481957/.
- Zhou X, Chen C, Yin D, Zhao F, Bao Z, Zhao Y, et al. A variation in the ABCC8 gene is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and repaglinide efficacy in chinese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Intern Med. 2019;58:2341–7.
- Tabák AG, Herder C, Rathmann W, Brunner EJ, Kivimäki M. Prediabetes: a high-risk state for diabetes development. Lancet (London, England) [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2023 Jun 21];379:2279–90. Available from:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22683128/.
- Zhang L, Chu J, Hao W, Zhang J, Li H, Yang C, et al. Gut Microbiota and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Association, Mechanism, and Translational Applications. Mediators Inflamm [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Jun 24];2021. Available from:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34447287/.
- Wang J, Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature [Internet]. 2012 Oct 4 [cited 2023 Jun 21];490,55–60. Available from:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23023125/.
- Cani PD, Lecourt E, Dewulf EM, Sohet FM, Pachikian BD, Naslain D, et al. Gut microbiota fermentation of prebiotics increases satietogenic and incretin gut peptide production with consequences for appetite sensation and glucose response after a meal. Am J Clin Nutr [Internet]. 2009 Nov 1 [cited 2023 Jun 21];90,1236–43. Available from:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19776140/.
- Zhang XY, Shen DQ, Fang ZW, Jie ZY, Qiu XM, Zhang CF, et al. Human Gut Microbiota Changes Reveal the Progression of Glucose Intolerance. PLoS One. 2013;8.
- Cunningham AL, Stephens JW, Harris DA. Gut microbiota influence in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). GUT Pathog. 2021;13.
- ray A, Threlkeld RJ. Nutritional Recommendations for Individuals with Diabetes. Diabetologia [Internet]. 2019 Oct 13 [cited 2023 Jun 24];54. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279012/.
- Schwingshackl L, Morze J, Hoffmann G. Mediterranean diet and health status: Active ingredients and pharmacological mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol [Internet]. 2020 Mar 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];177,1241–57. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31243760/.
- Schwingshackl L, Missbach B, König J, Hoffmann G. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr [Internet]. 2015 Feb 10 [cited 2022 Nov 22];18,1292–9. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25145972/.
- Olfert MD, Wattick RA. Vegetarian Diets and the Risk of Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep [Internet]. 2018 Nov 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];18. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC6153574/.
- Barnard ND, Cohen J, Jenkins DJA, Turner-McGrievy G, Gloede L, Jaster B, et al. A Low-Fat Vegan Diet Improves Glycemic Control and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in a Randomized Clinical Trial in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care [Internet]. 2006 Aug 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];29,1777–83. Available from: https://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc06-0606. [CrossRef]
- Da Porto A, Cavarape A, Colussi G, Casarsa V, Catena C, Sechi LA. Polyphenols Rich Diets and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Nutr 2021, Vol 13, Page 1445 [Internet]. 2021 Apr 24 [cited 2023 Jun 24];13,1445. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/5/1445/htm.
- Azadbakht L, Fard NRP, Karimi M, Baghaei MH, Surkan PJ, Rahimi M, et al. Effects of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating plan on cardiovascular risks among type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized crossover clinical trial. Diabetes Care [Internet]. 2011 Jan [cited 2022 Nov 22];34,55–7. Available from: https://jhu.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/effects-of-the-dietary-approaches-to-stop-hypertension-dash-eatin-4.
- Porrata-Maury C, Hernández-Triana M, Ruiz-Álvarez V, Díaz-Sánchez ME, Fallucca F, Bin W, et al. Ma-Pi 2 macrobiotic diet and type 2 diabetes mellitus: pooled analysis of short-term intervention studies. Diabetes Metab Res Rev [Internet]. 2014 Mar 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];30(S1):55–66. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/dmrr.2519.
- Dowis K, Banga S. The potential health benefits of the ketogenic diet: A narrative review. Nutrients [Internet]. 2021 May 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];13,1654. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/5/1654/htm.
- Burton-Freeman B, Brzeziński M, Park E, Sandhu A, Xiao D, Edirisinghe I. A Selective Role of Dietary Anthocyanins and Flavan-3-ols in Reducing the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Recent Evidence. Nutr 2019, Vol 11, Page 841 [Internet]. 2019 Apr 13 [cited 2023 Jun 24];11,841. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/4/841/htm.
- Ma Q, Li Y, Li P, Wang M, Wang J, Tang Z, et al. Research progress in the relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and intestinal flora. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep 1;117:109138.
- Chow JM. Probiotics and prebiotics: A brief overview. J Ren Nutr [Internet]. 2002 Apr 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];12,76–86. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11953920/.
- Zepeda-Hernández A, Garcia-Amezquita LE, Requena T, García-Cayuela T. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics added to dairy products: Uses and applications to manage type 2 diabetes. Food Res Int. 2021 Apr 1;142:110208.
- Cabello-Olmo M, Araña M, Urtasun R, Encio IJ, Barajas M. Role of Postbiotics in Diabetes Mellitus: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Foods 2021, Vol 10, Page 1590 [Internet]. 2021 Jul 8 [cited 2023 Jun 24];10,1590. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/10/7/1590/htm.
- Abot A, Brochot A, Pomie N, Wemelle E, Druart C, Regnier M, et al. Camu-Camu Reduces Obesity and Improves Diabetic Profiles of Obese and Diabetic Mice: A Dose-Ranging Study. Metabolites. 2022;12.
- Adachi K, Sugiyama T, Yamaguchi Y, Tamura Y, Izawa S, Hijikata Y, et al. Gut microbiota disorders cause type 2 diabetes mellitus and homeostatic disturbances in gut-related metabolism in Japanese subjects. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2019;64,231–8.
- Adams S, Che DS, Qin GX, Rui H, Sello CT, Jiang HL. Interactions of Dietary Fibre with Nutritional Components on Gut Microbial Composition, Function and Health in Monogastrics. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19,1011–23.
- Agagunduz D, Yilmaz B, Sahin TO, Gunesliol BE, Ayten S, Russo P, et al. Dairy Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Potential Function in Dietetics: The Food-Gut-Health Axis. FOODS. 2021;10.
- Aguayo-Patron S V, de la Barca AMC. Old Fashioned vs. Ultra-Processed-Based Current Diets: Possible Implication in the Increased Susceptibility to Type 1 Diabetes and Celiac Disease in Childhood. FOODS. 2017;6.
- Ai XJ, Wu CL, Yin TT, Zhur O, Liu CL, Yan XT, et al. Antidiabetic Function of Lactobacillus fermentum MF423-Fermented Rice Bran and Its Effect on Gut Microbiota Structure in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Front Microbiol. 2021;12.
- Aliasgharzadeh A, Dehghan P, Gargari BP, Asghari-Jafarabadi M. Resistant dextrin, as a prebiotic, improves insulin resistance and inflammation in women with type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Br J Nutr. 2015;113,321–30.
- Allin KH, Nielsen T, Pedersen O. MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Gut microbiota in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Endocrinol [Internet]. 2015 Apr;172,R167–77. Available from: https://eje.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/eje/172/4/R167.xml.
- Defeudis G, Rossini M, Khazrai YM, Pipicelli AM V, Brucoli G, Veneziano M, et al. The gut microbiome as possible mediator of the beneficial effects of very low calorie ketogenic diet on type 2 diabetes and obesity: a narrative review. Eat Weight Disord Anorex Bulim Obes. 2022;27,2339–46.
- An J, Lee H, Lee S, Song Y, Kim J, Park IH, et al. Modulation of Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines in the Fat by an Aloe Gel-based Formula, QDMC, Is Correlated with Altered Gut Microbiota. IMMUNE Netw. 2021;21.
- Anhe FF, Roy D, Pilon G, Dudonne S, Matamoros S, Varin T V, et al. A polyphenol-rich cranberry extract protects from diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and intestinal inflammation in association with increased Akkermansia spp. population in the gut microbiota of mice. Gut. 2015;64,872–83.
- Arni R, Anjani G, Djamiatun K. The Effect of Fortified Dadih (Fermented Buffalo Milk) with Vitamin D-3 on Caecum Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA) Concentration and HOMA-IR of T2DM-Rats. Curr Res Nutr FOOD Sci. 2021;9,500–10.
- Aron RAC, Abid A, Vesa CM, Nechifor AC, Behl T, Ghitea TC, et al. Recognizing the Benefits of Pre-/Probiotics in Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Considering the Influence of Akkermansia muciniphila as a Key Gut Bacterium. MICROORGANISMS. 2021;9.
- Arora A, Behl T, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, Bhatia S, et al. Unravelling the involvement of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes mellitus. LIFE Sci. 2021;273.
- Asensio EM, Ortega-Azorin C, Barragan R, Alvarez-Sala A, Sorli J V, Pascual EC, et al. Association between Microbiome-Related Human Genetic Variants and Fasting Plasma Glucose in a High-Cardiovascular-Risk Mediterranean Population. MEDICINA-LITHUANIA. 2022;58.
- Axarlis K, Daskalaki MG, Michailidou S, Androulaki N, Tsoureki A, Mouchtaropoulou E, et al. Diet Supplementation with Fish-Derived Extracts Suppresses Diabetes and Modulates Intestinal Microbiome in a Murine Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Mar Drugs. 2021;19.
- Axling U, Olsson C, Xu J, Fernandez C, Larsson S, Strom K, et al. Green tea powder and Lactobacillus plantarum affect gut microbiota, lipid metabolism and inflammation in high-fat fed C57BL/6J mice. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012;9.
- Bagarolli RA, Tobar N, Oliveira AG, Araujo TG, Carvalho BM, Rocha GZ, et al. Probiotics modulate gut microbiota and improve insulin sensitivity in DIO mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2017;50:16–25.
- Bai J, Zhu Y, Dong Y. Response of gut microbiota and inflammatory status to bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) in high fat diet induced obese rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;194:717–26.
- Bai YL, Xin MG, Lin JM, Xie J, Lin RM, Peng ZS, et al. Banana starch intervention ameliorates diabetes-induced mood disorders via modulation of the gut microbiota-brain axis in diabetic rats. FOOD Agric Immunol. 2022;33,377–402.
- Bai ZY, Huang XJ, Wu GJ, Ye H, Huang WQ, Nie QX, et al. Polysaccharides from red kidney bean alleviating hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in type 2 diabetic rats via gut microbiota and lipid metabolic modulation. FOOD Chem. 2023;404.
- Balfego M, Canivell S, Hanzu FA, Sala-Vila A, Martinez-Medina M, Murillo S, et al. Effects of sardine-enriched diet on metabolic control, inflammation and gut microbiota in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot randomized trial. Lipids Health Dis. 2016;15.
- Ban QF, Cheng JJ, Sun XM, Jiang YQ, Zhao SB, Song X, et al. Effects of a synbiotic yogurt using monk fruit extract as sweetener on glucose regulation and gut microbiota in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Dairy Sci. 2020;103,2956–68.
- Bao ML, Hou KX, Xin C, Zeng DY, Cheng CL, Zhao HT, et al. Portulaca oleracea L. Extract Alleviated Type 2 Diabetes Via Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Serum Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022;66.
- Barra NG, Anhe FF, Cavallari JF, Singh AM, Chan DY, Schertzer JD. Micronutrients impact the gut microbiota and blood glucose. J Endocrinol. 2021;250,R1–21.
- Barrett HL, Callaway LK, Nitert MD. Probiotics: a potential role in the prevention of gestational diabetes? ACTA Diabetol. 2012;49:S1–13.
- Baxter NT, Lesniak NA, Sinani H, Schloss PD, Koropatkin NM. The Glucoamylase Inhibitor Acarbose Has a Diet-Dependent and Reversible Effect on the Murine Gut Microbiome. MSPHERE. 2019;4.
- Bell KJ, Saad S, Tillett BJ, McGuire HM, Bordbar S, Yap YA, et al. Metabolite-based dietary supplementation in human type 1 diabetes is associated with microbiota and immune modulation. MICROBIOME. 2022;10.
- Bezirtzoglou E, Stavropoulou E, Kantartzi K, Tsigalou C, Voidarou C, Mitropoulou G, et al. Maintaining Digestive Health in Diabetes: The Role of the Gut Microbiome and the Challenge of Functional Foods. MICROORGANISMS. 2021;9.
- Bhanja A, Nayak N, Mukherjee S, Sutar PP, Mishra M. Treating the Onset of Diabetes Using Probiotics Along with Prebiotic from Pachyrhizus erosus in High-Fat Diet Fed Drosophila melanogaster. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022;14,884–903.
- Bitner BF, Ray JD, Kener KB, Herring JA, Tueller JA, Johnson DK, et al. Common gut microbial metabolites of dietary flavonoids exert potent protective activities in beta-cells and skeletal muscle cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2018;62:95–107.
- Bjorklund G, Chirumbolo S. Role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in daily nutrition and human health. NUTRITION. 2017;33:311–21.
- Bocanegra A, Macho-Gonzalez A, Garcimartin A, Benedi J, Sanchez-Muniz FJ. Whole Alga, Algal Extracts, and Compounds as Ingredients of Functional Foods: Composition and Action Mechanism Relationships in the Prevention and Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22.
- Bolla AM, Caretto A, Laurenzi A, Scavini M, Piemonti L. Low-Carb and Ketogenic Diets in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2019;11.
- Brunkwall L, Orho-Melander M. The gut microbiome as a target for prevention and treatment of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: from current human evidence to future possibilities. Diabetologia. 2017;60,943–51.
- Cai W, Xu JX, Li G, Liu T, Guo XL, Wang HJ, et al. Ethanol extract of propolis prevents high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity in association with modulation of gut microbiota in mice. FOOD Res Int. 2020;130.
- Calabrese CM, Valentini A, Calabrese G. Gut Microbiota and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: The Effect of Mediterranean Diet. Front Nutr. 2021;7.
- Camargo A, Vals-Delgado C, Alcala-Diaz JF, Villasanta-Gonzalez A, Gomez-Delgado F, Haro C, et al. A Diet-Dependent Microbiota Profile Associated with Incident Type 2 Diabetes: From the CORDIOPREV Study. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020;64.
- Candela M, Biagi E, Soverini M, Consolandi C, Quercia S, Severgnini M, et al. Modulation of gut microbiota dysbioses in type 2 diabetic patients by macrobiotic Ma-Pi 2 diet. Br J Nutr. 2016;116,80–93.
- Cao Y, Zou SW, Xu H, Li MX, Tong Z, Xu M, et al. Hypoglycemic activity of the Baker’s yeast beta-glucan in obese/type 2 diabetic mice and the underlying mechanism. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016;60,2678–90.
- Carvalho BM, Saad MJA. Influence of Gut Microbiota on Subclinical Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013.
- Chan C, Hyslop CM, Shrivastava V, Ochoa A, Reimer RA, Huang C. Oligofructose as an adjunct in treatment of diabetes in NOD mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6.
- Chan YK, Estaki M, Gibson DL. Clinical Consequences of Diet-Induced Dysbiosis. Ann Nutr Metab. 2013;63:28–40.
- Chanmuang S, Nguyen QA, Kim HJ. Current Research on the Effects of Non-Digestible Carbohydrates on Metabolic Disease. Appl Sci. 2022;12.
- Charoensiddhi S, Chanput WP, Sae-tan S. Gut Microbiota Modulation, Anti-Diabetic and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Polyphenol Extract from Mung Bean Seed Coat (Vigna radiata L.). Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Chen C, You LJ, Huang Q, Fu X, Zhang B, Liu RH, et al. Modulation of gut microbiota by mulberry fruit polysaccharide treatment of obese diabetic db/db mice. FOOD Funct. 2018;9,3732–42.
- Chen CH, Huang XJ, Wang H, Geng F, Nie SP. Effect of beta-glucan on metabolic diseases: a review from the gut microbiota perspective. Curr Opin FOOD Sci. 2022;47.
- Chen GJ, Chen RS, Chen D, Ye H, Hu B, Zeng XX, et al. Tea Polysaccharides as Potential Therapeutic Options for Metabolic Diseases. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(International Symposium on Chemistry, Flavor, and Health Effects of Tea held at the 256th American-Chemical-Society (ACS) Meeting):5350–60.
- Chen J, Ding XQ, Wu RY, Tong B, Zhao L, Lv H, et al. Novel Sesquiterpene Glycoside from Loquat Leaf Alleviates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Improving Insulin Resistance, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota Composition. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69,14176–91.
- Chen J, Yang YY, Yu NN, Sun WX, Yang YY, Zhao M. Relationship between gut microbiome characteristics and the effect of nutritional therapy on glycemic control in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus. PLoS One. 2022;17.
- Chen K, Chen H, Faas MM, de Haan BJ, Li JH, Xiao P, et al. Specific inulin-type fructan fibers protect against autoimmune diabetes by modulating gut immunity, barrier function, and microbiota homeostasis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017;61.
- Chen K, Wei XT, Kortesniemi M, Pariyani R, Zhang YM, Yang BR. Effects of acylated and nonacylated anthocyanins extracts on gut metabolites and microbiota in diabetic Zucker rats: A metabolomic and metagenomic study. FOOD Res Int. 2022;153.
- Chen LC, Fan ZY, Wang HY, Wen DC, Zhang SY. Effect of polysaccharides from adlay seed on anti-diabetic and gut microbiota. FOOD Funct. 2019;10,4372–80.
- Chen MY, Xiao D, Liu W, Song YF, Zou BR, Li L, et al. Intake of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides reverses the disturbed gut microbiota and metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;155:890–902.
- Chen TT, Liu AB, Sun SL, Ajami NJ, Ross MC, Wang H, et al. Green Tea Polyphenols Modify the Gut Microbiome in db/db Mice as Co-Abundance Groups Correlating with the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63.
- Chen YL, Ling ZM, Wang X, Zong SM, Yang JF, Zhang Q, et al. The beneficial mechanism of chitosan and chitooligosaccharides in the intestine on different health status. J Funct Foods. 2022;97.
- Chen YZ, Gu J, Chuang WT, Du YF, Zhang L, Lu ML, et al. Slowly Digestible Carbohydrate Diet Ameliorates Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia in High-Fat Diet/Streptozocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Cheng FS, Pan D, Chang B, Jiang M, Sang LX. Probiotic mixture VSL#3: An overview of basic and clinical studies in chronic diseases. WORLD J Clin CASES. 2020;8,1361–84.
- Cheng Y, Sibusiso L, Hou LF, Jiang HJ, Chen PC, Zhang X, et al. Sargassum fusiforme fucoidan modifies the gut microbiota during alleviation of streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia in mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;131:1162–70.
- Cho GS, Konig A, Seifert S, Hanak A, Roth A, Huch M, et al. Comparative study of fecal microbiota in patients with type II diabetes after consumption of apple juice for 4 weeks. FOOD Sci Biotechnol. 2015;24,2083–94.
- Chu NTR, Chan JC, Chow E. A diet high in FODMAPs as a novel dietary strategy in diabetes? Clin Nutr. 2022;41,2103–12.
- Chu NTR, Ling JM, Jie H, Leung K, Poon E. The potential role of lactulose pharmacotherapy in the treatment and prevention of diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13.
- Ciubotaru I, Green SJ, Kukreja S, Barengolts E. Significant differences in fecal microbiota are associated with various stages of glucose tolerance in African American male veterans. Transl Res. 2015;166,401–11.
- Clark AL, Yan ZH, Chen SX, Shi V, Kulkarni DH, Diwan A, et al. High-fat diet prevents the development of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. DIABETES Obes Metab. 2021;23,2455–65.
- Connolly ML, Tzounis X, Tuohy KM, Lovegrove JA. Hypocholesterolemic and Prebiotic Effects of a Whole-Grain Oat-Based Granola Breakfast Cereal in a Cardio-Metabolic “At Risk” Population. Front Microbiol. 2016;7.
- Coppola S, Avagliano C, Calignano A, Canani RB. The Protective Role of Butyrate against Obesity and Obesity-Related Diseases. MOLECULES. 2021;26.
- Costabile A, Corona G, Sarnsamak K, Atar-Zwillenberg D, Yit C, King AJ, et al. Wholegrain fermentation affects gut microbiota composition, phenolic acid metabolism and pancreatic beta cell function in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes. Front Microbiol. 2022;13.
- Cowan TE, Palmnas MSA, Yang J, Bomhof MR, Ardell KL, Reimer RA, et al. Chronic coffee consumption in the diet-induced obese rat: impact on gut microbiota and serum metabolomics. J Nutr Biochem. 2014;25,489–95.
- Craciun CI, Neag MA, Catinean A, Mitre AO, Rusu A, Bala C, et al. The Relationships between Gut Microbiota and Diabetes Mellitus, and Treatments for Diabetes Mellitus. BIOMEDICINES. 2022;10.
- Dahl WJ, Agro NC, Eliasson AM, Mialki KL, Olivera JD, Rusch CT, et al. Health Benefits of Fiber Fermentation. J Am Coll Nutr. 2017;36,127–36.
- Daniel N, Nachbar RT, Tran TTT, Ouellette A, Varin T V, Cotillard A, et al. Gut microbiota and fermentation-derived branched chain hydroxy acids mediate health benefits of yogurt consumption in obese mice. Nat Commun. 2022;13.
- Davidson SJ, Barrett HL, Price SA, Callaway LK, Nitert MD. Probiotics for preventing gestational diabetes. COCHRANE DATABASE Syst Rev. 2021;(4).
- Davison KM, Temple NJ. Cereal fiber, fruit fiber, and type 2 diabetes: Explaining the paradox. J Diabetes Complications. 2018;32,240–5.
- De Filippis F, Pasolli E, Tett A, Tarallo S, Naccarati A, De Angelis M, et al. Distinct Genetic and Functional Traits of Human Intestinal Prevotella copri Strains Are Associated with Different Habitual Diets. Cell Host Microbe. 2019;25,444-+.
- Delzenne NM, Neyrinck AM, Cani PD. Gut microbiota and metabolic disorders: how prebiotic can work? Br J Nutr. 2013;109:S81–5.
- Deng X, Niu L, Xiao J, Guo QQ, Liang JY, Tang JY, et al. Involvement of intestinal flora and miRNA into the mechanism of coarse grains improving type 2 diabetes: an overview. J Sci Food Agric. 2022.
- Diaz-Rizzolo DA, Kostov B, Lopez-Siles M, Serra A, Colungo C, Gonzalez-de-Paz L, et al. Healthy dietary pattern and their corresponding gut microbiota profile are linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, independent of the presence of obesity. Clin Nutr. 2020;39,524–32.
- Ding QZ, Zhang BW, Zheng W, Chen XJ, Zhang J, Yan RY, et al. Liupao tea extract alleviates diabetes mellitus and modulates gut microbiota in rats induced by streptozotocin and high-fat, high-sugar diet. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118.
- Ding Z, Zhao Y, Liu JH, Ge WH, Xu X, Wang SM, et al. Dietary Succinoglycan Riclin Improves Glycemia Control in Mice with Type 2 Diabetes. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70,1819–29.
- Dingeo G, Brito A, Samouda H, Iddir M, La Frano MR, Bohn T. Phytochemicals as modifiers of gut microbial communities. FOOD Funct. 2020;11,8444–71.
- Dolpady J, Sorini C, Di Pietro C, Cosorich I, Ferrarese R, Saita D, et al. Oral Probiotic VSL#3 Prevents Autoimmune Diabetes by Modulating Microbiota and Promoting Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-Enriched Tolerogenic Intestinal Environment. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016.
- Dong J, Liang QX, Niu Y, Jiang SJ, Zhou L, Wang JM, et al. Effects of Nigella sativa seed polysaccharides on type 2 diabetic mice and gut microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;159:725–38.
- Drozdz K, Nabrdalik K, Hajzler W, Kwiendacz H, Gumprecht J, Lip GYH. Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD), Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease: Associations with Fructose Metabolism and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Du Y, Li DX, Lu DY, Zhang R, Zheng XX, Xu BJ, et al. Morus alba L. water extract changes gut microbiota and fecal metabolome in mice induced by high-fat and high-sucrose diet plus low-dose streptozotocin. Phyther Res. 2022;36,1241–57.
- Dupuit M, Chavanelle V, Chassaing B, Perriere F, Etienne M, Plissonneau C, et al. The TOTUM-63 Supplement and High-Intensity Interval Training Combination Limits Weight Gain, Improves Glycemic Control, and Influences the Composition of Gut Mucosa-Associated Bacteria in Rats on a High Fat Diet. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Eid HM, Wright ML, Kumar NVA, Qawasmeh A, Hassan STS, Mocan A, et al. Significance of Microbiota in Obesity and Metabolic Diseases and the Modulatory Potential by Medicinal Plant and Food Ingredients. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8.
- Emani R, Asghar MN, Toivonen R, Lauren L, Soderstrom M, Toivola DM, et al. Casein hydrolysate diet controls intestinal T cell activation, free radical production and microbial colonisation in NOD mice. Diabetologia. 2013;56,1781–91.
- Erejuwa OO, Sulaiman SA, Ab Wahab MS. Oligosaccharides Might Contribute to the Antidiabetic Effect of Honey: A Review of the Literature. MOLECULES. 2012;17,248–66.
- Ericson U, Brunkwall L, Hellstrand S, Nilsson PM, Orho-Melander M. A Health-Conscious Food Pattern Is Associated with Prediabetes and Gut Microbiota in the Malmo Offspring Study. J Nutr. 2020;150,861–72.
- Everard A, Matamoros S, Geurts L, Delzenne NM, Cani PD. Saccharomyces boulardii Administration Changes Gut Microbiota and Reduces Hepatic Steatosis, Low-Grade Inflammation, and Fat Mass in Obese and Type 2 Diabetic db/db Mice. MBio. 2014;5.
- Fallucca F, Porrata C, Fallucca S, Pianesi M. Influence of diet on gut microbiota, inflammation and type 2 diabetes mellitus. First experience with macrobiotic Ma-Pi 2 diet. DIABETES-METABOLISM Res Rev. 2014;30:48–54.
- Fan L, Yu DX, Zhu XZ, Huang X, Murff HJ, Azcarate-Peril MA, et al. Magnesium and imidazole propionate. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021;41:436–8.
- Fangmann D, Theismann EM, Turk K, Schulte DM, Relling I, Hartmann K, et al. Targeted Microbiome Intervention by Microencapsulated Delayed-Release Niacin Beneficially Affects Insulin Sensitivity in Humans. Diabetes Care. 2018;41,398–405.
- Feng YW, Zhu J, Wang QY, Cao H, He F, Guan Y, et al. White common bean extract remodels the gut microbiota and ameliorates type 2 diabetes and its complications: A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13.
- Fraga CG, Croft KD, Kennedy DO, Tomas-Barberan FA. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. FOOD Funct. 2019;10,514–28.
- Frediansyah A, Romadhoni F, Suryani, Nurhayati R, Wibowo AT. Fermentation of Jamaican Cherries Juice Using Lactobacillus plantarum Elevates Antioxidant Potential and Inhibitory Activity against Type II Diabetes-Related Enzymes. MOLECULES. 2021;26.
- Friedman, M. Mushroom Polysaccharides: Chemistry and Antiobesity, Antidiabetes, Anticancer, and Antibiotic Properties in Cells, Rodents, and Humans. FOODS. 2016;5.
- Fu JX, Xu KL, Ni XM, Li XQ, Zhu XF, Xu WH. Habitual Dietary Fiber Intake, Fecal Microbiota, and Hemoglobin A1c Level in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Fu YX, Yin RY, Liu ZY, Niu Y, Guo EH, Cheng RH, et al. Hypoglycemic Effect of Prolamin from Cooked Foxtail Millet (Setaria italic) on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Ganesan K, Chung SK, Vanamala J, Xu BJ. Causal Relationship between Diet-Induced Gut Microbiota Changes and Diabetes: A Novel Strategy to Transplant Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in Preventing Diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19.
- Gao H, Wen JJ, Hu JL, Nie QX, Chen HH, Xiong T, et al. Fermented Momordica charantia L. juice modulates hyperglycemia, lipid profile, and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic rats. FOOD Res Int. 2019;121:367–78.
- Gao XX, Liu D, Gao LY, Ouyang YZ, Wen YX, Ai C, et al. Health benefits of Grifola frondosa polysaccharide on intestinal microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. FOOD Sci Hum WELLNESS. 2022;11,68–73.
- Garcia-Mazcorro JF, Lage NN, Mertens-Talcott S, Talcott S, Chew B, Dowd SE, et al. Effect of dark sweet cherry powder consumption on the gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and biomarkers of gut health in obese db/db mice. PeerJ. 2018;6.
- Garcia-Montero C, Fraile-Martinez O, Gomez-Lahoz AM, Pekarek L, Castellanos AJ, Noguerales-Fraguas F, et al. Nutritional Components in Western Diet Versus Mediterranean Diet at the Gut Microbiota-Immune System Interplay. Implications for Health and Disease. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Garonzi C, Forsander G, Maffeis C. Impact of Fat Intake on Blood Glucose Control and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Gavin PG, Hamilton-Williams EE. The gut microbiota in type 1 diabetes: friend or foe? Curr Opin Endocrinol DIABETES Obes. 2019;26,207–12.
- Geurts L, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Knauf C, Cani PD. Gut microbiota controls adipose tissue expansion, gut barrier and glucose metabolism: novel insights into molecular targets and interventions using prebiotics. Benef Microbes. 2014;5,3–17.
- Ghalwash AA, Baalash AA, Gaafar NK, Wasfy RE, Noeman S. The interplay between oat beta glucan, gut microbiota and gut-liver axis in treatment of obesity associated non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and Type II diabetes mellitus. INDIAN J Biochem Biophys. 2022;59,14-22 WE-Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E.
- Ghorbani Y, Schwenger KJP, Allard JP. Manipulation of intestinal microbiome as potential treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Eur J Nutr. 2021;60,2361–79.
- Gill PA, Inniss S, Kumagai T, Rahman FZ, Smith AM. The Role of Diet and Gut Microbiota in Regulating Gastrointestinal and Inflammatory Disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13.
- Glaysher MA, Mohanaruban A, Prechtl CG, Goldstone AP, Miras AD, Lord J, et al. A randomised controlled trial of a duodenal-jejunal bypass sleeve device (EndoBarrier) compared with standard medical therapy for the management of obese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open. 2017;7.
- Goldsmith F, Guice J, Page R, Welsh DA, Taylor CM, Blanchard EE, et al. Obese ZDF rats fermented resistant starch with effects on gut microbiota but no reduction in abdominal fat. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017;61.
- Gomes AC, Bueno AA, de Souza RGM, Mota JF. Gut microbiota, probiotics and diabetes. Nutr J. 2014;13.
- Gomes JMG, Costa JA, Alfenas RC. Could the beneficial effects of dietary calcium on obesity and diabetes control be mediated by changes in intestinal microbiota and integrity? Br J Nutr. 2015;114,1756–65.
- Goralska K, Dzikowiec M. Role of Microbiota in Maintaining the Homeostasis in the Human Body. Postep Mikrobiol. 2018;57,5-11 WE-Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EX.
- Gorowska-Kowolik K, Chobot A. The role of gut micorbiome in obesity and diabetes. WORLD J Pediatr. 2019;15,332–40.
- Gou WL, Ling CW, He Y, Jiang ZL, Fu YQ, Xu FZ, et al. Interpretable Machine Learning Framework Reveals Robust Gut Microbiome Features Associated With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021;44,358–66.
- Gowd V, Karim N, Shishir MRI, Xie LH, Chen W. Dietary polyphenols to combat the metabolic diseases via altering gut microbiota. TRENDS FOOD Sci Technol. 2019;93:81–93.
- Gowd V, Xie LH, Zheng XD, Chen W. Dietary fibers as emerging nutritional factors against diabetes: focus on the involvement of gut microbiota. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019;39,524–40.
- Grigorescu I, Dumitrascu DL. Implication of Gut Microbiota in Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. ACTA Endocrinol. 2016;12,206–14.
- Gruneck L, Kullawong N, Kespechara K, Popluechai S. Gut microbiota of obese and diabetic Thai subjects and interplay with dietary habits and blood profiles. PeerJ. 2020;8.
- Gu YX, Chen HR, Li X, Li D, Sun Y, Yang L, et al. Lactobacillus paracasei IMC 502 ameliorates type 2 diabetes by mediating gut microbiota-SCFA-hormone/inflammation pathway in mice. J Sci Food Agric. 2022.
- Gudi R, Perez N, Johnson BM, Sofi MH, Brown R, Quan S, et al. Complex dietary polysaccharide modulates gut immune function and microbiota, and promotes protection from autoimmune diabetes. Immunology. 2019;157,70–85.
- Guilbaud A, Howsam M, Niquet-Leridon C, Delguste F, Fremont M, Lestavel S, et al. The Effect of Lactobacillus fermentum ME-3 Treatment on Glycation and Diabetes Complications. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020;64.
- Gulnaz A, Nadeem J, Han JH, Lew LC, Son JD, Park YH, et al. Lactobacillus Sps in Reducing the Risk of Diabetes in High-Fat Diet-Induced Diabetic Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiome and Inhibiting Key Digestive Enzymes Associated with Diabetes. BIOLOGY-BASEL. 2021;10.
- Guo WL, Deng JC, Pan YY, Xu JX, Hong JL, Shi FF, et al. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides and their relationships with the modulation of intestinal microflora in diabetic mice induced by high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;153:1231–40.
- Guo YJ, Huang ZH, Sang D, Gao Q, Li QJ. The Role of Nutrition in the Prevention and Intervention of Type 2 Diabetes. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8.
- Guo ZN, Pan JJ, Zhu HY, Chen ZY. Metabolites of Gut Microbiota and Possible Implication in Development of Diabetes Mellitus. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70,5945–60.
- Halkjaer SI, Nilas L, Carlsen EM, Cortes D, Halldorsson TI, Olsen SF, et al. Effects of probiotics (Vivomixx (R)) in obese pregnant women and their newborn: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2016;17.
- Hameed A, Galli M, Adamska-Patruno E, Kretowski A, Ciborowski M. Select Polyphenol-Rich Berry Consumption to Defer or Deter Diabetes and Diabetes-Related Complications. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Hamilton-Williams EE, Lorca GL, Norris JM, Dunne JL. A Triple Threat? The Role of Diet, Nutrition, and the Microbiota in T1D Pathogenesis. Front Nutr. 2021;8.
- Hampe CS, Roth CL. Probiotic strains and mechanistic insights for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocrine. 2017;58,207–27.
- Han H, Li YY, Fang J, Liu G, Yin J, Li TJ, et al. Gut Microbiota and Type 1 Diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19.
- Han LH, Li TG, Du M, Chang R, Zhan BY, Mao XY. Beneficial Effects of Potentilla discolor Bunge Water Extract on Inflammatory Cytokines Release and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Nutrients. 2019;11.
- Han S, Luo Y, Hu ZM, Qin DD, Luo FJ. Targeting gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Potential roles of dietary flavonoids. FOOD Biosci. 2022;45.
- Hanninen ALM, Toivonen RK. On the role of gut bacteria and infant diet in the development of autoimmunity for type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2015;58,2195–6.
- Hansen CHF, Krych L, Buschard K, Metzdorff SB, Nellemann C, Hansen LH, et al. A Maternal Gluten-Free Diet Reduces Inflammation and Diabetes Incidence in the Offspring of NOD Mice. Diabetes. 2014;63,2821–32.
- Hansen CHF, Larsen CS, Petersson HO, Zachariassen LF, Vegge A, Lauridsen C, et al. Targeting gut microbiota and barrier function with prebiotics to alleviate autoimmune manifestations in NOD mice. Diabetologia. 2019;62,1689–700.
- Hao JY, Zhang YL, Wu T, Liu R, Sui WJ, Zhu JG, et al. The antidiabetic effects of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BL21 through regulating gut microbiota structure in type 2 diabetic mice. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,9947–58.
- Harbison JE, Thomson RL, Wentworth JM, Louise J, Roth-Schulze A, Battersby RJ, et al. Associations between diet, the gut microbiome and short chain fatty acids in youth with islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2021;22,425–33.
- Haro C, Montes-Borrego M, Rangel-Zuniga OA, Alcala-Diaz JF, Gomez-Delgado F, Perez-Martinez P, et al. Two Healthy Diets Modulate Gut Microbial Community Improving Insulin Sensitivity in a Human Obese Population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101,232–41.
- Hartstra A V, Bouter KEC, Backhed F, Nieuwdorp M. Insights Into the Role of the Microbiome in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38,159–65.
- Hasain Z, Mokhtar NM, Kamaruddin NA, Ismail NAM, Razalli NH, Gnanou J V, et al. Gut Microbiota and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Host-Gut Microbiota Interactions and Their Therapeutic Potential. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10.
- Hashimoto Y, Hamaguchi M, Fukui M. Microbe-associated metabolites as targets for incident type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2021;12,476–8.
- Hashimoto Y, Hamaguchi M, Kaji A, Sakai R, Osaka T, Inoue R, et al. Intake of sucrose affects gut dysbiosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2020;11,1623–34.
- Haupt-Jorgensen M, Holm LJ, Josefsen K, Buschard K. Possible Prevention of Diabetes with a Gluten-Free Diet. Nutrients. 2018;10.
- He MQ, Shi BY. Gut microbiota as a potential target of metabolic syndrome: the role of probiotics and prebiotics. CELL Biosci. 2017;7.
- He XQ, Li WZ, Chen YY, Lei L, Li FH, Zhao JC, et al. Dietary fiber of Tartary buckwheat bran modified by steam explosion alleviates hyperglycemia and modulates gut microbiota in db/db mice. FOOD Res Int. 2022;157.
- Heianza Y, Sun DJY, Li X, DiDonato JA, Bray GA, Sacks FM, et al. Gut microbiota metabolites, amino acid metabolites and improvements in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism: the POUNDS Lost trial. Gut. 2019;68,263–70.
- Henneke L, Schlicht K, Andreani NA, Hollstein T, Demetrowitsch T, Knappe C, et al. A dietary carbohydrate - gut Parasutterella - human fatty acid biosynthesis metabolic axis in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Gut Microbes. 2022;14.
- Henschel AM, Cabrera SM, Kaldunski ML, Jia S, Geoffrey R, Roethle MF, et al. Modulation of the diet and gastrointestinal microbiota normalizes systemic inflammation and beta-cell chemokine expression associated with autoimmune diabetes susceptibility. PLoS One. 2018;13.
- Hereu M, Ramos-Romero S, Busquets C, Atienza L, Amezqueta S, Miralles-Perez B, et al. Effects of combined D-fagomine and omega-3 PUFAs on gut microbiota subpopulations and diabetes risk factors in rats fed a high-fat diet. Sci Rep. 2019;9.
- Hernandez-Alonso P, Canueto D, Giardin S, Salas-Salvado J, Canellas N, Correig X, et al. Effect of pistachio consumption on the modulation of urinary gut microbiota-related metabolites in prediabetic subjects. J Nutr Biochem. 2017;45:48–53.
- Hernandez MAG, Canfora EE, Jocken JWE, Blaak EE. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate in Body Weight Control and Insulin Sensitivity. Nutrients. 2019;11.
- Hijova, E. Synbiotic Supplements in the Prevention of Obesity and Obesity-Related Diseases. Metabolites. 2022;12.
- Hills RD, Pontefract BA, Mishcon HR, Black CA, Sutton SC, Theberge CR. Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease. Nutrients. 2019;11.
- Ho J, Reimer RA, Doulla M, Huang C. Effect of prebiotic intake on gut microbiota, intestinal permeability and glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2016;17.
- Homayouni-Rad A, Soroush AR, Khalili L, Norouzi-Panahi L, Kasaie Z, Ejtahed HS. Diabetes Management by Probiotics: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2016;86(5–6):215–27.
- Hosomi K, Saito M, Park J, Murakami H, Shibata N, Ando M, et al. Oral administration of Blautia wexlerae ameliorates obesity and type 2 diabetes via metabolic remodeling of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun. 2022;13.
- Houghton D, Hardy T, Stewart C, Errington L, Day CP, Trenell MI, et al. Systematic review assessing the effectiveness of dietary intervention on gut microbiota in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2018;61,1700–11.
- Hsieh FC, Lee CL, Chai CY, Chen WT, Lu YC, Wu CS. Oral administration of Lactobacillus reuteri GMNL-263 improves insulin resistance and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in high fructose-fed rats. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2013;10.
- Hu CY, Wong FS, Wen L. Type 1 diabetes and gut microbiota: Friend or foe? Pharmacol Res. 2015;98:9–15.
- Hu JL, Nie SP, Xie MY. Antidiabetic Mechanism of Dietary Polysaccharides Based on Their Gastrointestinal Functions. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66,4781–6.
- Hu TG, Wen P, Liu J, Long XS, Liao ST, Wu H, et al. Combination of mulberry leaf and oat bran possessed greater hypoglycemic effect on diabetic mice than mulberry leaf or oat bran alone. J Funct Foods. 2019;61.
- Hu TG, Wen P, Shen WZ, Liu F, Li Q, Li EN, et al. Effect of 1-Deoxynojirirnycin Isolated from Mulberry Leaves on Glucose Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in a Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mouse Model. J Nat Prod. 2019;82,2189–200.
- Huang F, Nilholm C, Roth B, Linninge C, Hoglund P, Nyman M, et al. Anthropometric and metabolic improvements in human type 2 diabetes after introduction of an Okinawan-based Nordic diet are not associated with changes in microbial diversity or SCFA concentrations. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2018;69,729–40.
- Huang GN, Xu J, Cai DP, Chen SY, Nagy T, Guo TL. Exacerbation of Type 1 Diabetes in Perinatally Genistein Exposed Female Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) Mouse Is Associated With Alterations of Gut Microbiota and Immune Homeostasis. Toxicol Sci. 2018;165,291–301.
- Huang GN, Xu J, Lefever DE, Glenn TC, Nagy T, Guo TL. Genistein prevention of hyperglycemia and improvement of glucose tolerance in adult non-obese diabetic mice are associated with alterations of gut microbiome and immune homeostasis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017;332:138–48.
- Huang HR, Chen JJ, Chen Y, Xie JH, Xue PY, Ao TX, et al. Metabonomics combined with 16S rRNA sequencing to elucidate the hypoglycemic effect of dietary fiber from tea residues. FOOD Res Int. 2022;155.
- Huang HR, Chen JJ, Hu XB, Chen Y, Xie JH, Ao TX, et al. Elucidation of the interaction effect between dietary fiber and bound polyphenol components on the anti-hyperglycemic activity of tea residue dietary fiber. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,2710–28.
- Huang JZ, Guan BB, Lin LJ, Wang YP. Improvement of intestinal barrier function, gut microbiota, and metabolic endotoxemia in type 2 diabetes rats by curcumin. Bioengineered. 2021;12,11947–58.
- Huang YC, Wu BH, Chu YL, Chang WC, Wu MC. Effects of Tempeh Fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum and Rhizopus oligosporus on Streptozotocin-Induced Type II Diabetes Mellitus in Rats. Nutrients. 2018;10.
- Huang ZR, Zhao LY, Zhu FR, Liu Y, Xiao JY, Chen ZC, et al. Anti-Diabetic Effects of Ethanol Extract from Sanghuangporous vaninii in High-Fat/Sucrose Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota. FOODS. 2022;11.
- Huda MN, Kim M, Bennett BJ. Modulating the Microbiota as a Therapeutic Intervention for Type 2 Diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12.
- Hui SC, Liu Y, Chen MT, Wang XL, Lang HD, Zhou M, et al. Capsaicin Improves Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity Through Modulation of the Gut Microbiota-Bile Acid-FXR Axis in Type 2 Diabetic db/db Mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63.
- Hussein HM, Elyamany MF, Rashed LA, Sallam NA. Vitamin D mitigates diabetes-associated metabolic and cognitive dysfunction by modulating gut microbiota and colonic cannabinoid receptor 1. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022;170.
- Ibrahim I, Bashir M, Singh P, Al Khodor S, Abdullahi H. The Impact of Nutritional Supplementation During Pregnancy on the Incidence of Gestational Diabetes and Glycaemia Control. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Ibrahim M, Anishetty S. A meta-metabolome network of carbohydrate metabolism: Interactions between gut microbiota and host. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;428,278–84.
- Inchingolo AD, Malcangi G, Inchingolo AM, Piras F, Settanni V, Garofoli G, et al. Benefits and Implications of Resveratrol Supplementation on Microbiota Modulations: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23.
- Ionita-Mindrican CB, Ziani K, Mititelu M, Oprea E, Neacsu SM, Morosan E, et al. Therapeutic Benefits and Dietary Restrictions of Fiber Intake: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Ismael S, Silvestre MP, Vasques M, Araujo JR, Morais J, Duarte MI, et al. A Pilot Study on the Metabolic Impact of Mediterranean Diet in Type 2 Diabetes: Is Gut Microbiota the Key? Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Ismail HM, Evans-Molina C. Does the Gut Microbiome Play a Role in Obesity in Type 1 Diabetes? Unanswered Questions and Review of the Literature. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12.
- Isolauri E, Rautava S, Collado MC, Salminen S. Role of probiotics in reducing the risk of gestational diabetes. DIABETES Obes Metab. 2015;17,713–9.
- Israelian N, Danska JS. Sex Effects at the Ramparts: Nutrient- and Microbe-Mediated Regulation of the Immune-Metabolic Interface. In: MauvaisJarvis F, editor. SEX AND GENDER FACTORS AFFECTING METABOLIC HOMEOSTASIS, DIABETES AND OBESITY. Univ Toronto, Dept Immunol, Toronto, ON, Canada; 2017. p. 113–40.
- Jabbehdari S, Sallam AB. Gut microbiome and diabetic retinopathy. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2022;32,2494–7.
- Jaja-Chimedza A, Zhang L, Wolff K, Graf BL, Kuhn P, Moskal K, et al. A dietary isothiocyanate-enriched moringa (Moringa oleifera) seed extract improves glucose tolerance in a high-fat-diet mouse model and modulates the gut microbiome. J Funct Foods. 2018;47:376–85.
- Jana UK, Kango N, Pletschke B. Hemicellulose-Derived Oligosaccharides: Emerging Prebiotics in Disease Alleviation. Front Nutr. 2021;8.
- Jardon KM, Canfora EE, Goossens GH, Blaak EE. Dietary macronutrients and the gut microbiome: a precision nutrition approach to improve cardiometabolic health. Gut. 2022;71,1214–26.
- Jayasimhan A, Marino E. Dietary SCFAs, IL-22, and GFAP: The Three Musketeers in the Gut-Neuro-Immune Network in Type 1 Diabetes. Front Immunol. 2019;10.
- Jean-Marie E, Bereau D, Robinson JC. Benefits of Polyphenols and Methylxanthines from Cocoa Beans on Dietary Metabolic Disorders. FOODS. 2021;10.
- Jeong DY, Daily JW, Lee GH, Ryu MS, Yang HJ, Jeong SY, et al. Short-Term Fermented Soybeans with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Potentiated Insulin Secretion Capacity and Improved Gut Microbiome Diversity and Intestinal Integrity To Alleviate Asian Type 2 Diabetic Symptoms. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68,13168–78.
- Jia LL, Li DY, Feng NH, Shamoon M, Sun ZH, Ding L, et al. Anti-diabetic Effects of Clostridium butyricum CGMCC0313.1 through Promoting the Growth of Gut Butyrate-producing Bacteria in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7.
- Jia RB, Li ZR, Wu J, Ou ZR, Sun BG, Lin LZ, et al. Antidiabetic effects and underlying mechanisms of anti-digestive dietary polysaccharides fromSargassum fusiformein rats. FOOD Funct. 2020;11,7023–36.
- Jiang HR, Cai MM, Shen BY, Wang Q, Zhang TC, Zhou X. Synbiotics and Gut Microbiota: New Perspectives in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. FOODS. 2022;11.
- Jiang ZL, Sun TY, He Y, Gou WL, Zuo LSY, Fu YQ, et al. Dietary fruit and vegetable intake, gut microbiota, and type 2 diabetes: results from two large human cohort studies. BMC Med. 2020;18.
- Jovandaric MZ, Milenkovic SJ, Babovic IR, Babic S, Dotlic J. The Effect of Glucose Metabolism and Breastfeeding on the Intestinal Microbiota of Newborns of Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. MEDICINA-LITHUANIA. 2022;58.
- Ju CG, Zhu L, Wang W, Gao H, Xu YB, Jia TZ. Cornus officinalis prior and post-processing: Regulatory effects on intestinal flora of diabetic nephropathy rats. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13.
- Ju MZ, Liu YQ, Li MY, Cheng MJ, Zhang Y, Deng GZ, et al. Baicalin improves intestinal microecology and abnormal metabolism induced by high-fat diet. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;857.
- Jung MJ, Lee J, Shin NR, Kim MS, Hyun DW, Yun JH, et al. Chronic Repression of mTOR Complex 2 Induces Changes in the Gut Microbiota of Diet-induced Obese Mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6.
- Kahalehili HM, Newman NK, Pennington JM, Kolluri SK, Kerkvliet NI, Shulzhenko N, et al. Dietary Indole-3-Carbinol Activates AhR in the Gut, Alters Th17-Microbe Interactions, and Exacerbates Insulitis in NOD Mice. Front Immunol. 2021;11.
- Kanbay M, Onal EM, Afsar B, Dagel T, Yerlikaya A, Covic A, et al. The crosstalk of gut microbiota and chronic kidney disease: role of inflammation, proteinuria, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018;50,1453–66.
- Kao PC, Han QJ, Liu SY, Li XJ, Inman KS, Chia N. Letter to the Editor: The Surge of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in China - an International Alert: Physical Exercise and Low-Caloric Diet May Reduce the Risks of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Dementia. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016;46,114-118 WE-Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI.
- Karamzin AM, Ropot A V, Sergeyev O V, Sechenov EOK. Akkermansia muciniphila and host interaction within the intestinal tract. Anaerobe. 2021;72.
- Karusheva Y, Koessler T, Strassburger K, Markgraf D, Mastrototaro L, Jelenik T, et al. Short-term dietary reduction of branched-chain amino acids reduces meal-induced insulin secretion and modifies microbiome composition in type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled crossover trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019;110,1098–107.
- Kasprzak-Drozd K, Oniszczuk T, Stasiak M, Oniszczuk A. Beneficial Effects of Phenolic Compounds on Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22.
- Kassaian N, Feizi A, Rostami S, Aminorroaya A, Yaran M, Amini M. The effects of 6 mo of supplementation with probiotics and synbiotics on gut microbiota in the adults with prediabetes: A double blind randomized clinical trial. NUTRITION. 2020;79–80.
- Kaur AP, Bhardwaj S, Dhanjal DS, Nepovimova E, Cruz-Martins N, Kuca K, et al. Plant Prebiotics and Their Role in the Amelioration of Diseases. Biomolecules. 2021;11.
- Kellow NJ, Coughlan MT, Savige GS, Reid CM. Effect of dietary prebiotic supplementation on advanced glycation, insulin resistance and inflammatory biomarkers in adults with pre-diabetes: a study protocol for a double-blind placebo-controlled randomised crossover clinical trial. BMC Endocr Disord. 2014;14.
- Khairudin MAS, Jalil AMM, Hussin N. Effects of Polyphenols in Tea (Camellia sinensis sp.) on the Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Human Trials and Animal Studies. Gastroenterol INSIGHTS. 2021;12,202–16.
- Khat-udomkiri N, Toejing P, Sirilun S, Chaiyasut C, Lailerd N. Antihyperglycemic effect of rice husk derived xylooligosaccharides in high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rat model. FOOD Sci Nutr. 2020;8,428–44.
- Kim MS, Hwang SS, Park EJ, Bae JW. Strict vegetarian diet improves the risk factors associated with metabolic diseases by modulating gut microbiota and reducing intestinal inflammation. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2013;5,765–75.
- Kolb H, Kempf K, Martin S. Health Effects of Coffee: Mechanism Unraveled? Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Kondo Y, Hashimoto Y, Hamaguchi M, Ando S, Kaji A, Sakai R, et al. Unique Habitual Food Intakes in the Gut Microbiota Cluster Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Kong FH, Kang SM, Zhang J, Zhao HW, Peng YQ, Yang M, et al. Whey protein and xylitol complex alleviate type 2 diabetes in C57BL/6 mice by regulating the intestinal microbiota. FOOD Res Int. 2022;157.
- Kong HC, Yu LX, Gu ZB, Li CM, Ban XF, Cheng L, et al. Novel Short-Clustered Maltodextrin as a Dietary Starch Substitute Attenuates Metabolic Dysregulation and Restructures Gut Microbiota in db/db Mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68,12400–12.
- Koudoufio M, Desjardins Y, Feldman F, Spahis S, Delvin E, Levy E. Insight into Polyphenol and Gut Microbiota Crosstalk: Are Their Metabolites the Key to Understand Protective Effects against Metabolic Disorders? ANTIOXIDANTS. 2020;9.
- Kumar M, Pal N, Sharma P, Kumawat M, Sarma DK, Nabi B, et al. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Interaction with the Gut Microbiome in the Prevention and Amelioration of Type-2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Lakshmanan AP, Kohil A, El Assadi F, Al Zaidan S, Al Abduljabbar S, Bangarusamy DK, et al. Akkermansia, a Possible Microbial Marker for Poor Glycemic Control in Qataris Children Consuming Arabic Diet-A Pilot Study on Pediatric T1DM in Qatar. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Lau E, Carvalho D, Pina-Vaz C, Barbosa JA, Freitas P. Beyond gut microbiota: understanding obesity and type 2 diabetes. Horm J Endocrinol Metab. 2015;14,358–69.
- Lau E, Neves JS, Ferreira-Magalhaes M, Carvalho D, Freitas P. Probiotic Ingestion, Obesity, and Metabolic-Related Disorders: Results from NHANES, 1999-2014. Nutrients. 2019;11.
- Le Roy CI, Kurilshikov A, Leeming ER, Visconti A, Bowyer RCE, Menni C, et al. Yoghurt consumption is associated with changes in the composition of the human gut microbiome and metabolome. BMC Microbiol. 2022;22.
- Lee HC, Yu SC, Lo YC, Lin IH, Tung TH, Huang SY. A high linoleic acid diet exacerbates metabolic responses and gut microbiota dysbiosis in obese rats with diabetes mellitus. FOOD Funct. 2019;10,786–98.
- Lee SY, Yuk HG, Ko SG, Cho SG, Moon GS. Gut Microbiome Prolongs an Inhibitory Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on High-Fat-Diet-Induced Mouse Obesity. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Li CN, Wang X, Sun SJ, Liu SN, Huan Y, Li RC, et al. Effects of a ready-to-eat cereal formula powder on glucose metabolism, inflammation, and gut microbiota in diabetic db/db mice. FOOD Sci Nutr. 2020;8,4523–33.
- Li XX, Zhang XX, Zhang R, Ni ZJ, Elam E, Thakur K, et al. Gut modulation based anti-diabetic effects of carboxymethylated wheat bran dietary fiber in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice and their potential mechanisms. FOOD Chem Toxicol. 2021;152.
- Li ZR, Jia RB, Luo DH, Lin LZ, Zheng QW, Zhao MM. The positive effects and underlying mechanisms of Undaria pinnatifida polysaccharides on type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats. FOOD Funct. 2021;12,11898–912.
- Liang L, Liu GM, Yu GY, Zhang FM, Linhardt RJ, Li QH. Urinary metabolomics analysis reveals the anti-diabetic effect of stachyose in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;229.
- Lin GP, Liu XY, Yan X, Liu D, Yang CF, Liu B, et al. Role of Green Macroalgae Enteromorpha Prolifera Polyphenols in the Modulation of Gene Expression and Intestinal Microflora Profiles in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20.
- Lin R, He X, Chen HF, He Q, Yao ZT, Li YF, et al. Oil tea improves glucose and lipid levels and alters gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. Nutr Res. 2018;57:67–77.
- Liu CG, Shao W, Gao M, Liu JY, Guo QY, Jin J, et al. Changes in intestinal flora in patients with type 2 diabetes on a low-fat diet during 6 months of follow-up. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20.
- Liu GM, Bei J, Liang L, Yu GY, Li L, Li QH. Stachyose Improves Inflammation through Modulating Gut Microbiota of High-Fat Diet/Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018;62.
- Liu GM, Liang L, Yu GY, Li QH. Pumpkin polysaccharide modifies the gut microbiota during alleviation of type 2 diabetes in rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:711–7.
- Liu H, Zhang Z, Li JP, Liu W, Warda M, Cui B, et al. Oligosaccharides derived from Lycium barbarum ameliorate glycolipid metabolism and modulate the gut microbiota community and the faecal metabolites in a type 2 diabetes mouse model: metabolomic bioinformatic analysis. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,5416–29.
- Liu HC, Zhang M, Ma QY, Tian BM, Nie CX, Chen ZF, et al. Health beneficial effects of resistant starch on diabetes and obesity via regulation of gut microbiota: a review. FOOD Funct. 2020;11,5749–67.
- Liu J, Lv YJ, Pan JX, Jiang YL, Zhu YJ, Zhang SK. Effects of tea polyphenols and EGCG on glucose metabolism and intestinal flora in diabetic mice fed a cornstarch-based functional diet. FOOD Sci Technol. 2022;42.
- Liu NN, Chen MY, Song JN, Zhao YY, Gong P, Chen XF. Effects of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharides on Gut Microbiota Composition in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. MOLECULES. 2022;27.
- Liu S, Qin PP, Wang J. High-Fat Diet Alters the Intestinal Microbiota in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Mice. MICROORGANISMS. 2019;7.
- Liu SQ, Yin XQ, Hou C, Liu XR, Ma HJ, Zhang XX, et al. As a Staple Food Substitute, Oat and Buckwheat Compound Has Health-Promoting Effects for Diabetic Rats. Front Nutr. 2021;8.
- Liu YY, Wang CR, Li JS, Li TT, Zhang Y, Liang YX, et al. Phellinus linteus polysaccharide extract improves insulin resistance by regulating gut microbiota composition. FASEB J. 2020;34,1065–78.
- Luo W, Zhou JL, Yang X, Wu RY, Liu H, Shao HG, et al. A Chinese medical nutrition therapy diet accompanied by intermittent energy restriction alleviates type 2 diabetes by enhancing pancreatic islet function and regulating gut microbiota composition. FOOD Res Int. 2022;161.
- Lupien-Meilleur J, Andrich DE, Quinn S, Micaelli-Baret C, St-Amand R, Roy D, et al. Interplay Between Gut Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Peptides: Potential Outcomes on the Regulation of Glucose Control. Can J DIABETES. 2020;44,359–67.
- Ma QY, Zhai RH, Xie XQ, Chen T, Zhang ZQ, Liu HC, et al. Hypoglycemic Effects of Lycium barbarum Polysaccharide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice via Modulating Gut Microbiota. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Macchione IG, Lopetuso LR, Ianiro G, Napoli M, Gibiino G, Rizzatti G, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila: key player in metabolic and gastrointestinal disorders. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23,8075–83.
- Machate DJ, Figueiredo PS, Marcelino G, Guimaraes RDA, Hiane PA, Bogo D, et al. Fatty Acid Diets: Regulation of Gut Microbiota Composition and Obesity and Its Related Metabolic Dysbiosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21.
- Macho-Gonzalez A, Garcimartin A, Redondo N, Cofrades S, Bastida S, Nova E, et al. Carob fruit extract-enriched meat, as preventive and curative treatments, improves gut microbiota and colonic barrier integrity in a late-stage T2DM model. FOOD Res Int. 2021;141.
- Mahizir D, Briffa JF, Wood JL, Anevska K, Hill-Yardin EL, Jefferies AJ, et al. Exercise improves metabolic function and alters the microbiome in rats with gestational diabetes. FASEB J. 2020;34,1728–44.
- Maioli TU, Borras-Nogues E, Torres L, Barbosa SC, Martins VD, Langella P, et al. Possible Benefits of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii for Obesity-Associated Gut Disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12.
- Malekipoor R, Johnson SK, Bhattarai RR. Lupin Kernel Fibre: Nutritional Composition, Processing Methods, Physicochemical Properties, Consumer Acceptability and Health Effects of Its Enriched Products. Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Man AWC, Zhou YW, Xia N, Li HG. Involvement of Gut Microbiota, Microbial Metabolites and Interaction with Polyphenol in Host Immunometabolism. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Mandalari G, Barreca D, Gervasi T, Roussell MA, Klein B, Feeney MJ, et al. Pistachio Nuts (Pistacia vera L.): Production, Nutrients, Bioactives and Novel Health Effects. PLANTS-BASEL. 2022;11.
- Marietta E, Horwath I, Balakrishnan B, Taneja V. Role of the intestinal microbiome in autoimmune diseases and its use in treatments. Cell Immunol. 2019;339:50–8.
- Marietta E V, Gomez AM, Yeoman C, Tilahun AY, Clark CR, Luckey DH, et al. Low Incidence of Spontaneous Type 1 Diabetes in NonObese Diabetic Mice Raised on Gluten-Free Diets Is Associated with Changes in the Intestinal Microbiome. PLoS One. 2013;8.
- Marino E, Richards JL, McLeod KH, Stanley D, Yap YA, Knight J, et al. Gut microbial metabolites limit the frequency of autoimmune T cells and protect against type 1 diabetes. Nat Immunol. 2017;18,552–62.
- Marlatt KL, White UA, Beyl RA, Peterson CM, Martin CK, Marco ML, et al. Role of resistant starch on diabetes risk factors in people with prediabetes: Design, conduct, and baseline results of the STARCH trial. Contemp Clin Trials. 2018;65:99–108.
- Marques AM, Linhares BS, Novaes RMD, Freitas MB, Sarandy MM, Goncalves R V. Effects of the amount and type of carbohydrates used in type 2 diabetes diets in animal models: A systematic review. PLoS One. 2020;15.
- Marques AM, Sarandy MM, Novaes RMD, Goncalves R V, Freitas MB. Preclinical relevance of probiotics in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Int J Exp Pathol. 2020;101(3–4):68–79.
- Marques TM, Patterson E, Wall R, Sullivan OO, Fitzgerald GF, Cotter PD, et al. Influence of GABA and GABA-producing Lactobacillus brevis DPC 6108 on the development of diabetes in a streptozotocin rat model. Benef Microbes. 2016;7,409–20.
- Martel J, Ojcius DM, Chang CJ, Lin CS, Lu CC, Ko YF, et al. Anti-obesogenic and antidiabetic effects of plants and mushrooms. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13,149–60.
- Martens PJ, Centelles-Lodeiro J, Ellis D, Cook DP, Sassi G, Verlinden L, et al. High Serum Vitamin D Concentrations, Induced via Diet, Trigger Immune and Intestinal Microbiota Alterations Leading to Type 1 Diabetes Protection in NOD Mice. Front Immunol. 2022;13.
- Martin, C. A role for plant science in underpinning the objective of global nutritional security? Ann Bot. 2018;122,541–53.
- Martin-Pelaez S, Fito M, Castaner O. Mediterranean Diet Effects on Type 2 Diabetes Prevention, Disease Progression, and Related Mechanisms. A Review. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Martina A, Felis GE, Corradi M, Maffeis C, Torriani S, Venema K. Effects of functional pasta ingredients on different gut microbiota as revealed by TIM-2 in vitro model of the proximal colon. Benef Microbes. 2019;10,301–13.
- Martinez-Lopez YE, Esquivel-Hernandez DA, Sanchez-Castaneda JP, Neri-Rosario D, Guardado-Mendoza R, Resendis-Antonio O. Type 2 diabetes, gut microbiome, and systems biology: A novel perspective for a new era. Gut Microbes. 2022;14.
- Mateos R, Perez-Correa JR, Dominguez H. Bioactive Properties of Marine Phenolics. Mar Drugs. 2020;18.
- Medina-Vera I, Sanchez-Tapia M, Noriega-Lopez L, Granados-Portillo O, Guevara-Cruz M, Flores-Lopez A, et al. A dietary intervention with functional foods reduces metabolic endotoxaemia and attenuates biochemical abnormalities by modifying faecal microbiota in people with type 2 diabetes. DIABETES Metab. 2019;45,122–31.
- Megur A, Daliri EBM, Baltriukiene D, Burokas A. Prebiotics as a Tool for the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity and Diabetes: Classification and Ability to Modulate the Gut Microbiota. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23.
- Mejia-Leon ME, de la Barca AMC. Diet, Microbiota and Immune System in Type 1 Diabetes Development and Evolution. Nutrients. 2015;7,9171–84.
- Mejia-Leon ME, Lopez-Dominguez L, Aguayo-Patron S V, Caire-Juvera G, de la Barca AMC. Dietary Changes and Gut Dysbiosis in Children With Type 1 Diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr. 2018;37,501–7.
- Meloncelli N, Wilkinson SA, de Jersey S. Searching for Utopia, the Challenge of Standardized Medical Nutrition Therapy Prescription in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Management: A Critical Review. Semin Reprod Med. 2020;38,389–97.
- Lassen PB, Attaye I, Adriouch S, Nicolaou M, Aron-Wisnewsky J, Nielsen T, et al. Protein Intake, Metabolic Status and the Gut Microbiota in Different Ethnicities: Results from Two Independent Cohorts. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Miao M, Wang Q, Wang XY, Fan C, Luan T, Yan LN, et al. The Protective Effects of Inulin-Type Fructans Against High-Fat/Sucrose Diet-Induced Gestational Diabetes Mice in Association With Gut Microbiota Regulation. Front Microbiol. 2022;13.
- Miller B, Mainali R, Nagpal R, Yadav H. A Newly Developed Synbiotic Yogurt Prevents Diabetes by Improving the Microbiome-Intestine-Pancreas Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22.
- Mirghani HO, Alatawi SAS, Alsharef KF. The Diet-Induced Gut Microbiota Diversity Improved Glycemic Control: A Meta-Analysis. PHARMACOPHORE. 2020;11,51-60 WE-Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI).
- Mishra S, Wang SH, Nagpal R, Miller B, Singh R, Taraphder S, et al. Probiotics and Prebiotics for the Amelioration of Type 1 Diabetes: Present and Future Perspectives. MICROORGANISMS. 2019;7.
- Mitchell CM, Davy BM, Ponder MA, McMillan RP, Hughes MD, Hulver MW, et al. Prebiotic Inulin Supplementation and Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity in adults at Elevated Risk for Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Mitchelson KAJ, Tran TTT, Dillon ET, Vlckova K, Harrison SM, Ntemiri A, et al. Yeast beta-Glucan Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Mice Humanized with Obese Type 2 Diabetic Gut Microbiota. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022.
- Mokkala K, Paulin N, Houttu N, Koivuniemi E, Pellonpera O, Khan S, et al. Metagenomics analysis of gut microbiota in response to diet intervention and gestational diabetes in overweight and obese women: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Gut. 2021;70,309–18.
- Moriconi E, Feraco A, Marzolla V, Infante M, Lombardo M, Fabbri A, et al. Neuroendocrine and Metabolic Effects of Low-Calorie and Non-Calorie Sweeteners. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11.
- Morshedi M, Saghafi-Asl M, Hosseinifard ES. The potential therapeutic effects of the gut microbiome manipulation by synbiotic containing-Lactobacillus plantarum on neuropsychological performance of diabetic rats. J Transl Med. 2020;18.
- Moszak M, Szulinska M, Bogdanski P. You Are What You Eat-The Relationship between Diet, Microbiota, and Metabolic Disorders-A Review. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Mullins AP, Arjmandi BH. Health Benefits of Plant-Based Nutrition: Focus on Beans in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Munoz-Almagro N, Montilla A, Villamiel M. Role of pectin in the current trends towards low-glycaemic food consumption. FOOD Res Int. 2021;140.
- Munoz-Hernandez L, Marquez-Lopez Z, Mehta R, Aguilar-Salinas CA. Intermittent Fasting as Part of the Management for T2DM: from Animal Models to Human Clinical Studies. Curr Diab Rep. 2020;20.
- Murakami S, Goto Y, Ito K, Hayasaka S, Kurihara S, Soga T, et al. The Consumption of Bicarbonate-Rich Mineral Water Improves Glycemic Control. EVIDENCE-BASED Complement Altern Med. 2015;2015.
- Mustad VA, Huynh DTT, Lopez-Pedrosa JM, Campoy C, Rueda R. The Role of Dietary Carbohydrates in Gestational Diabetes. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Nagase N, Ikeda Y, Tsuji A, Kitagishi Y, Matsuda S. Efficacy of probiotics on the modulation of gut microbiota in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. World J Diabetes. 2022;13,150–60.
- Nakamura YK, Omaye ST. Metabolic diseases and pro- and prebiotics: Mechanistic insights. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012;9.
- Nam Y, Yoon S, Baek J, Kim JH, Park M, Hwang K, et al. Heat-Killed Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LRCC5314 Mitigates the Effects of Stress- Related Type 2 Diabetes in Mice via Gut Microbiome Modulation. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;32,324–32.
- Nayor M, Shah STH, Murthy V, Shah R V. Molecular Aspects of Lifestyle and Environmental Effects in Patients With Diabetes JACC Focus Seminar. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;78,481–95.
- Neri-Numa IA, Cazarin CBB, Ruiz A, Paulino BN, Molina G, Pastore GM. Targeting flavonoids on modulation of metabolic syndrome. J Funct Foods. 2020;73.
- Neyrinck AM, Possemiers S, Verstraete W, De Backer F, Cani PD, Delzenne NM. Dietary modulation of clostridial cluster XIVa gut bacteria (Roseburia spp.) by chitin-glucan fiber improves host metabolic alterations induced by high-fat diet in mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2012;23,51–9.
- Ni YH, Zheng AQ, Hu YT, Rong NK, Zhang QP, Long WM, et al. Compound dietary fiber and high-grade protein diet improves glycemic control and ameliorates diabetes and its comorbidities through remodeling the gut microbiota in mice. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Nie CX, He T, Zhang WJ, Zhang GL, Ma X. Branched Chain Amino Acids: Beyond Nutrition Metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19.
- Nie QX, Chen HH, Hu JL, Fan ST, Nie SP. Dietary compounds and traditional Chinese medicine ameliorate type 2 diabetes by modulating gut microbiota. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(3rd International Symposium on Phytochemicals in Medicine and Food (ISPMF)):848–63.
- Nie QX, Hu JL, Chen HH, Geng F, Nie SP. Arabinoxylan ameliorates type 2 diabetes by regulating the gut microbiota and metabolites. FOOD Chem. 2022;371.
- Nie QX, Hu JL, Gao H, Fan LL, Chen HH, Nie SP. Polysaccharide from Plantago asiatica L. attenuates hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and affects colon microbiota in type 2 diabetic rats. FOOD Hydrocoll. 2019;86(19th Gums and Stabilisers for the Food Industry Conference):34–42.
- Nie QX, Hu JL, Gao H, Li MZ, Sun YG, Chen HH, et al. Bioactive Dietary Fibers Selectively Promote Gut Microbiota to Exert Antidiabetic Effects. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69,7000–15.
- Nielsen DS, Krych L, Buschard K, Hansen CHF, Hansen AK. Beyond genetics. Influence of dietary factors and gut microbiota on type 1 diabetes. FEBS Lett. 2014;588,4234–43.
- Nikbakht E, Khalesi S, Singh I, Williams LT, West NP, Colson N. Effect of probiotics and synbiotics on blood glucose: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57,95–106.
- Nishida A, Ando Y, Kimura I, Miyamoto J. Involvement of Gut Microbial Metabolites Derived from Diet on Host Energy Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23.
- Nishitsuji K, Watanabe S, Xiao JZ, Nagatomo R, Ogawa H, Tsunematsu T, et al. Effect of coffee or coffee components on gut microbiome and short-chain fatty acids in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome. Sci Rep. 2018;8.
- Niu MM, Zhao YQ, Xiang L, Jia YX, Yuan JF, Dai X, et al. 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis of gut microbiome in a mini-pig diabetes model. Anim Model Exp Med. 2022;5,81–8.
- Niwa Y, Ishikawa K, Ishigami M, Honda T, Achiwa K, Izumoto T, et al. Effect of hyperglycemia on hepatocellular carcinoma development in diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;463,344–50.
- Nova P, Pimenta-Martins A, Silva JL, Silva AM, Gomes AM, Freitas AC. Health benefits and bioavailability of marine resources components that contribute to health - what’s new? Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60,3680–92.
- Nuli R, Cai JX, Kadeer A, Zhang YY, Mohemaiti P. Integrative Analysis Toward Different Glucose Tolerance-Related Gut Microbiota and Diet. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10.
- Nunes S, Viana SD, Preguica I, Alves A, Fernandes R, Teodoro JS, et al. Blueberry Counteracts Prediabetes in a Hypercaloric Diet-Induced Rat Model and Rescues Hepatic Mitochondrial Bioenergetics. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Nunes S, Vieira P, Gomes P, Viana SD, Reis F. Blueberry as an Attractive Functional Fruit to Prevent (Pre)Diabetes Progression. ANTIOXIDANTS. 2021;10.
- Nunez-Sanchez MA, Herisson FM, Cluzel GL, Caplice NM. Metabolic syndrome and synbiotic targeting of the gut microbiome. Curr Opin FOOD Sci. 2021;41:60–9.
- Nuno K, Villarruel-Lopez A, Puebla-Perez AM, Romero-Velarde E, Puebla-Mora AG, Ascencio F. Effects of the marine microalgae Isochrysis galbana and Nannochloropsis oculata in diabetic rats. J Funct Foods. 2013;5,106–15.
- Petschow B, Dore J, Hibberd P, Dinan T, Reid G, Blaser M, et al. Probiotics, prebiotics, and the host microbiome: the science of translation. Vol. 1306, ANNALS REPORTS. Transcend Biomed Commun LLC, Youngsville, NC USA; 2013. 1–17 p.
- Nyavor Y, Brands CR, May G, Kuther S, Nicholson J, Tiger K, et al. High-fat diet-induced alterations to gut microbiota and gut-derived lipoteichoic acid contributes to the development of enteric neuropathy. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;32.
- Oellgaard J, Winther SA, Hansen TS, Rossing P, von Scholten BJ. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) as a New Potential Therapeutic Target for Insulin Resistance and Cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23,3699–712.
- Oh MR, Jang HY, Lee SY, Jung SJ, Chae SW, Lee SO, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum HAC01 Supplementation Improves Glycemic Control in Prediabetic Subjects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Ohlsson, B. An Okinawan-based Nordic diet improves glucose and lipid metabolism in health and type 2 diabetes, in alignment with changes in the endocrine profile, whereas zonulin levels are elevated. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17,2883–93.
- Ojo O, Feng QQ, Ojo OO, Wang XH. The Role of Dietary Fibre in Modulating Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Ojo O, Ojo OO, Zand N, Wang XH. The Effect of Dietary Fibre on Gut Microbiota, Lipid Profile, and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Ojo O, Wang XH, Ojo OO, Adegboye ARA. The Effects of Almonds on Gut Microbiota, Glycometabolism, and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Olvera-Rosales LB, Cruz-Guerrero AE, Ramirez-Moreno E, Quintero-Lira A, Contreras-Lopez E, Jaimez-Ordaz J, et al. Impact of the Gut Microbiota Balance on the Health-Disease Relationship: The Importance of Consuming Probiotics and Prebiotics. FOODS. 2021;10.
- Park JM, Shin Y, Kim SH, Jin M, Choi JJ. Dietary Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Alters the Gut Microbiota of Obese Diabeticdb/dbMice:LactobacillusIs a Putative Target. J Med Food. 2020;23,1033–42.
- Park S, Zhang T, Qiu JY, Wu X, Lee JY, Lee BY. Acid Hydrolyzed Silk Peptide Consumption Improves Anti-Diabetic Symptoms by Potentiating Insulin Secretion and Preventing Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in Non-Obese Type 2 Diabetic Animals. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Pengrattanachot N, Thongnak L, Lungkaphin A. The impact of prebiotic fructooligosaccharides on gut dysbiosis and inflammation in obesity and diabetes related kidney disease. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,5925–45.
- Perraudeau F, McMurdie P, Bullard J, Cheng AN, Cutcliffe C, Deo A, et al. Improvements to postprandial glucose control in subjects with type 2 diabetes: a multicenter, double blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial of a novel probiotic formulation. BMJ OPEN DIABETES Res CARE. 2020;8.
- Petersen C, Bharat D, Wankhade UD, Kim JS, Cutler BR, Denetso C, et al. Dietary Blueberry Ameliorates Vascular Complications in Diabetic Mice Possibly through NOX4 and Modulates Composition and Functional Diversity of Gut Microbes. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022;66.
- Petersen C, Wankhade UD, Bharat D, Wong K, Mueller JE, Chintapalli S V, et al. Dietary supplementation with strawberry induces marked changes in the composition and functional potential of the gut microbiome in diabetic mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2019;66:63–9.
- Petroni ML, Brodosi L, Marchignoli F, Sasdelli AS, Caraceni P, Marchesini G, et al. Nutrition in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Present Knowledge and Remaining Challenges. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Pino JL, Mujica V, Arredondo M. Effect of dietary supplementation with oat beta-glucan for 3 months in subjects with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. J Funct Foods. 2021;77.
- Pircalabioru GG, Corcionivoschi N, Gundogdu O, Chifiriuc MC, Marutescu LG, Ispas B, et al. Dysbiosis in the Development of Type I Diabetes and Associated Complications: From Mechanisms to Targeted Gut Microbes Manipulation Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22.
- Pitocco D, Di Leo M, Tartaglione L, De Leva F, Petruzziello C, Saviano A, et al. The role of gut microbiota in mediating obesity and diabetes mellitus. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24,1548–62.
- Plovier H, Everard A, Druart C, Depommier C, Van Hul M, Geurts L, et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat Med. 2017;23,107–13.
- Ponzo V, Fedele D, Goitre I, Leone F, Lezo A, Monzeglio C, et al. Diet-Gut Microbiota Interactions and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM). Nutrients. 2019;11.
- Ponzo V, Ferrocino I, Zarovska A, Amenta MB, Leone F, Monzeglio C, et al. The microbiota composition of the offspring of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). PLoS One. 2019;14.
- Portincasa P, Bonfrate L, Vacca M, De Angelis M, Farella I, Lanza ELS, et al. Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids: Implications in Glucose Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23.
- Prapa I, Yanni AE, Nikolaou A, Kostomitsopoulos N, Kalogeropoulos N, Bezirtzoglou E, et al. Dietary Pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) Beneficially Alters Fatty Acid Profiles in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rat. Appl Sci. 2022;12.
- Prodam F, Chiocchetti A, Dianzani U. Diet as a strategy for type 1 diabetes prevention. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018;15,1–4.
- Qi QB, Li J, Yu B, Moon JY, Chai JC, Merino J, et al. Host and gut microbial tryptophan metabolism and type 2 diabetes: an integrative analysis of host genetics, diet, gut microbiome and circulating metabolites in cohort studies. Gut. 2022;71,1095–105.
- Qi WW, Liu JC, Yu TT, Huang SC, Song RT, Qiao ZY. Ae1/Sbe1 maize-derived high amylose improves gut barrier function and ameliorates type II diabetes in high-fat diet-fed mice by increasing Akkermansia. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Raimundo AF, Ferreira S, Tomas-Barberan FA, Santos CN, Menezes R. Urolithins: Diet-Derived Bioavailable Metabolites to Tackle Diabetes. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Ramos-Romero S, Hereu M, Atienza L, Casas J, Jauregui O, Amezqueta S, et al. Mechanistically different effects of fat and sugar on insulin resistance, hypertension, and gut microbiota in rats. Am J Physiol Metab. 2018;314,E552–63.
- Ramos-Romero S, Hereu M, Atienza L, Casas J, Taltavull N, Romeu M, et al. Functional Effects of the Buckwheat Iminosugar D-Fagomine on Rats with Diet-Induced Prediabetes. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018;62.
- Raposo MFD, de Morais A, de Morais R. Emergent Sources of Prebiotics: Seaweeds and Microalgae. Mar Drugs. 2016;14.
- Ratiner K, Shapiro H, Goldenberg K, Elinav E. Time-limited diets and the gut microbiota in cardiometabolic disease. J Diabetes. 2022;14,377–93.
- Razmifard F, Barzeghari A, Farrin N, Safaiyan A, Ghaem-maghami SJ, Mobasseri M, et al. Changes in Akkermansia muciniphila and its relationship with dietary habits in type 2 diabetic obese patients. Prog Nutr. 2019;21:130–7.
- Regnier M, Rastelli M, Morissette A, Suriano F, Le Roy T, Pilon G, et al. Rhubarb Supplementation Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity and Diabetes in Association with Increased Akkermansia muciniphila in Mice. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Regnier M, Van Hul M, Knauf C, Cani PD. Gut microbiome, endocrine control of gut barrier function and metabolic diseases. J Endocrinol. 2021;248,R67–82.
- Rehman AU, Siddiqui NZ, Farooqui NA, Alam G, Gul A, Ahmad B, et al. Morchella esculenta mushroom polysaccharide attenuates diabetes and modulates intestinal permeability and gut microbiota in a type 2 diabetic mice model. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Reimer RA, Wharton S, Green TJ, Manjoo P, Ramay HR, Lyon MR, et al. Effect of a functional fibre supplement on glycemic control when added to a year-long medically supervised weight management program in adults with type 2 diabetes. Eur J Nutr. 2021;60,1237–51.
- Rein M, Ben-Yacov O, Godneva A, Shilo S, Zmora N, Kolobkov D, et al. Effects of personalized diets by prediction of glycemic responses on glycemic control and metabolic health in newly diagnosed T2DM: a randomized dietary intervention pilot trial. BMC Med. 2022;20.
- Reitmeier S, Kiessling S, Clavel T, List M, Almeida EL, Ghosh TS, et al. Arrhythmic Gut Microbiome Signatures Predict Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Host Microbe. 2020;28,258-+.
- Ren GX, Fan X, Teng C, Li YJ, Everaert N, Blecker C. The Beneficial Effect of Coarse Cereals on Chronic Diseases through Regulating Gut Microbiota. FOODS. 2021;10.
- Ren MX, Zhang HY, Qi JD, Hu AN, Jiang Q, Hou YY, et al. An Almond-Based Low Carbohydrate Diet Improves Depression and Glycometabolism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes through Modulating Gut Microbiota and GLP-1: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Ren X, Wang LX, Chen ZL, Zhang M, Hou DZ, Xue Y, et al. Foxtail millet supplementation improves glucose metabolism and gut microbiota in rats with high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetes. FOOD Sci Hum WELLNESS. 2022;11,119–28.
- Ren XX, Sun Y, Guo QF, Liu HD, Jiang H, He XS, et al. Ameliorating Effect of the Total Flavonoids of Morus nigra L. on Prediabetic Mice Based on Regulation of Inflammation and Insulin Sensitization. J Agric Food Chem. 2022.
- Rendon-Huerta JA, Juarez-Flores B, Pinos-Rodriguez JM, Aguirre-Rivera JR, Delgado-Portales RE. Effects of Different Sources of Fructans on Body Weight, Blood Metabolites and Fecal Bacteria in Normal and Obese non-diabetic and Diabetic Rats. PLANT FOODS Hum Nutr. 2012;67,64–70.
- Rinninella E, Cintoni M, Raoul P, Ianiro G, Laterza L, Lopetuso LR, et al. Gut Microbiota during Dietary Restrictions: New Insights in Non-Communicable Diseases. MICROORGANISMS. 2020;8.
- Robertson MD. Prebiotics and type 2 diabetes: targeting the gut microbiota for improved glycaemic control? Pract DIABETES. 2020;37,133–7.
- Rodrigues RR, Gurung M, Li ZP, Garcia-Jaramillo M, Greer R, Gaulke C, et al. Transkingdom interactions between Lactobacilli and hepatic mitochondria attenuate western diet-induced diabetes. Nat Commun. 2021;12.
- Rodriguez-Pasten A, Perez-Hernandez N, Anorve-Morga J, Jimenez-Alvarado R, Carino-Cortes R, Sosa-Lozada T, et al. The Activity of Prebiotics and Probiotics in Hepatogastrointestinal Disorders and Diseases Associated with Metabolic Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23.
- Rong BH, Wu Q, Saeed M, Sun C. Gut microbiotada positive contributor in the process of intermittent fasting-mediated obesity control. Anim Nutr. 2021;7,1283–95.
- Rosca AE, Iesanu MI, Zahiu CDM, Voiculescu SE, Paslaru AC, Zagrean AM. Capsaicin and Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease. MOLECULES. 2020;25.
- Roshanravan N, Mahdavi R, Alizadeh E, Ghavami A, Saadat YR, Alamdari NM, et al. The effects of sodium butyrate and inulin supplementation on angiotensin signaling pathway via promotion of Akkermansia muciniphila abundance in type 2 diabetes; A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2017;9,183–90.
- Rustanti N, Murdiati A, Juffrie M, Rahayu ES. Effect of Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Dad-13 on Metabolic Profiles and Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetic Women: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. MICROORGANISMS. 2022;10.
- Salamone D, Rivellese AA, Vetrani C. The relationship between gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the possible role of dietary fibre. ACTA Diabetol. 2021;58,1131–8.
- Salles BIM, Cioffi D, Ferreira SRG. Probiotics supplementation and insulin resistance: a systematic review. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2020;12.
- Sanchez-Tapia M, Tovar AR, Torres N. Diet as Regulator of Gut Microbiota and its Role in Health and Disease. Arch Med Res. 2019;50,259–68.
- Sane F, Scuotto A, Pierrat V, Kacet N, Hober D, Romond MB. Diabetes progression and alterations in gut bacterial translocation: prevention by diet supplementation with human milk in NOD mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2018;62:108–22.
- Sangwan V, Tomar SK, Ali B, Singh RRB, Singh AK. Hypoglycaemic effect of galactooligosaccharides in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Dairy Res. 2015;82,70–7.
- Santos-Marcos JA, Perez-Jimenez F, Camargo A. The role of diet and intestinal microbiota in the development of metabolic syndrome. J Nutr Biochem. 2019;70:1–27.
- Sargin P, Roethle MF, Jia S, Pant T, Ciecko AE, Atkinson SN, et al. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v supplementation modulates beta-cell ER stress and antioxidative defense pathways and prevents type 1 diabetes in gluten-free BioBreeding rats. Gut Microbes. 2022;14.
- Sato J, Kanazawa A, Azuma K, Ikeda F, Goto H, Komiya K, et al. Probiotic reduces bacterial translocation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomised controlled study. Sci Rep. 2017;7.
- Scazzocchio B, Minghetti L, D’Archivio M. Interaction between Gut Microbiota and Curcumin: A New Key of Understanding for the Health Effects of Curcumin. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Schmidt NS, Lorentz A. Dietary restrictions modulate the gut microbiota: Implications for health and disease. Nutr Res. 2021;89:10–22.
- Scott FW, Pound LD, Patrick C, Eberhard CE, Crookshank JA. Where genes meet environment-integrating the role of gut luminal contents, immunity and pancreas in type 1 diabetes. Transl Res. 2017;179:183–98.
- Selber-Hnatiw S, Sultana T, Tse W, Abdollahi N, Abdullah S, Al Rahbani J, et al. Metabolic networks of the human gut microbiota. MICROBIOLOGY-SGM. 2020;166,96–119.
- Serena G, Camhi S, Sturgeon C, Yan S, Fasano A. The Role of Gluten in Celiac Disease and Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2015;7,7143–62.
- Serino M, Luche E, Gres S, Baylac A, Berge M, Cenac C, et al. Metabolic adaptation to a high-fat diet is associated with a change in the gut microbiota. Gut. 2012;61,543–53.
- Shah BR, Li B, Al Sabbah H, Xu W, Mraz J. Effects of prebiotic dietary fibers and probiotics on human health: With special focus on recent advancement in their encapsulated formulations. TRENDS FOOD Sci Technol. 2020;102:178–92.
- Shan K, Qu HY, Zhou KR, Wang LF, Zhu CM, Chen HQ, et al. Distinct Gut Microbiota Induced by Different Fat-to-Sugar-Ratio High-Energy Diets Share Similar Pro-obesity Genetic and Metabolite Profiles in Prediabetic Mice. MSYSTEMS. 2019;4.
- Shannon E, Conlon M, Hayes M. Seaweed Components as Potential Modulators of the Gut Microbiota. Mar Drugs. 2021;19.
- Shao TY, Yu QH, Zhu TS, Liu AH, Gao XM, Long XH, et al. Inulin from Jerusalem artichoke tubers alleviates hyperglycaemia in high-fat-diet-induced diabetes mice through the intestinal microflora improvement. Br J Nutr. 2020;123,308–18.
- Sharma BR, Jaiswal S, Ravindra P V. Modulation of gut microbiota by bioactive compounds for prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;152.
- Shen HK, Zhao ZT, Zhao ZJ, Chen YY, Zhang LH. Native and Engineered Probiotics: Promising Agents against Related Systemic and Intestinal Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23.
- Shen JH, Zhang L, Wang YQ, Chen ZQ, Ma J, Fang XY, et al. Beneficial Actions of Essential Fatty Acids in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Sheng Y, Zheng SJ, Ma TS, Zhang CH, Ou XQ, He XY, et al. Mulberry leaf alleviates streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by attenuating NEFA signaling and modulating intestinal microflora. Sci Rep. 2017;7.
- Sheng Y, Zheng SJ, Zhang CH, Zhao CH, He XY, Xu WT, et al. Mulberry leaf tea alleviates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PKC signaling and modulating intestinal flora. J Funct Foods. 2018;46:118–27.
- Shibayama J, Goto M, Kuda T, Fukunaga M, Takahashi H, Kimura B. Effect of rice bran fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus plantarum on gut microbiome of mice fed high-sucrose diet. Benef Microbes. 2019;10,811–21.
- Shilo S, Godneva A, Rachmiel M, Korem T, Kolobkov D, Karady T, et al. Prediction of Personal Glycemic Responses to Food for Individuals With Type 1 Diabetes Through Integration of Clinical and Microbial Data. Diabetes Care. 2022;45,502–11.
- Shimozato A, Sasaki M, Ogasawara N, Funaki Y, Ebi M, Goto C, et al. Transglucosidase improves the bowel movements in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A preliminary randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. UNITED Eur Gastroenterol J. 2017;5,898–907.
- Siddiqui NZ, Rehman AU, Yousuf W, Khan AI, Farooqui NA, Zang SZ, et al. Effect of crude polysaccharide from seaweed, Dictyopteris divaricata (CDDP) on gut microbiota restoration and anti-diabetic activity in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced T1DM mice. GUT Pathog. 2022;14.
- Singer-Englar T, Barlow G, Mathur R. Obesity, diabetes, and the gut microbiome: an updated review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;13,3–15.
- Singh RK, Chang HW, Yan D, Lee KM, Ucmak D, Wong K, et al. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J Transl Med. 2017;15.
- Singh S, Sharma RK, Malhotra S, Pothuraju R, Shandilya UK. Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCDC17 ameliorates type-2 diabetes by improving gut function, oxidative stress and inflammation in high-fat-diet fed and streptozotocin-treated rats. Benef Microbes. 2017;8,243–55.
- Singh V, Park YJ, Lee G, Unno T, Shin JH. Dietary regulations for microbiota dysbiosis among post-menopausal women with type 2 diabetes. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022.
- Singhvi N, Gupta V, Gaur M, Sharma V, Puri A, Singh Y, et al. Interplay of Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Wellness. INDIAN J Microbiol. 2020;60,26–36.
- Sircana A, Framarin L, Leone N, Berrutti M, Castellino F, Parente R, et al. Altered Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes: Just a Coincidence? Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18.
- Snelson M, de Pasquale C, Ekinci EI, Coughlan MT. Gut microbiome, prebiotics, intestinal permeability and diabetes complications. BEST Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;35.
- Sofi MH, Gudi R, Karumuthil-Melethil S, Perez N, Johnson BM, Vasu C. pH of Drinking Water Influences the Composition of Gut Microbiome and Type 1 Diabetes Incidence. Diabetes. 2014;63,632–44.
- Sohail MU, Shabbir MZ, Steiner JM, Ahmad S, Kamran Z, Anwar H, et al. Molecular analysis of the gut microbiome of diabetic rats supplemented with prebiotic, probiotic, and synbiotic foods. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2017;37,419–25.
- Song JX, Ren H, Gao YF, Lee CY, Li SF, Zhang F, et al. Dietary Capsaicin Improves Glucose Homeostasis and Alters the Gut Microbiota in Obese Diabetic ob/ob Mice. Front Physiol. 2017;8.
- Song XQ, Dong HH, Zang ZZ, Wu WT, Zhu WF, Zhang H, et al. Kudzu Resistant Starch: An Effective Regulator of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021.
- Song Y, Wu MS, Tao G, Lu MW, Lin J, Huang JQ. Feruloylated oligosaccharides and ferulic acid alter gut microbiome to alleviate diabetic syndrome. FOOD Res Int. 2020;137.
- Souza A, Gabardo S, Coelho RDS. Galactooligosaccharides: Physiological benefits, production strategies, and industrial application. J Biotechnol. 2022;359:116–29.
- Soverini M, Turroni S, Biagi E, Quercia S, Brigidi P, Candela M, et al. Variation of Carbohydrate-Active Enzyme Patterns in the Gut Microbiota of Italian Healthy Subjects and Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Front Microbiol. 2017;8.
- Stefanaki C, Michos A, Mastorakos G, Mantzou A, Landis G, Zosi P, et al. Probiotics in Adolescent Prediabetes: A Pilot RCT on Glycemic Control and Intestinal Bacteriome. J Clin Med. 2019;8.
- Stenman LK, Waget A, Garret C, Briand F, Burcelin R, Sulpice T, et al. Probiotic B420 and prebiotic polydextrose improve efficacy of antidiabetic drugs in mice. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015;7.
- Su HM, Xie LH, Xu Y, Ke HH, Bao T, Li YT, et al. Pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside Derived from Wild Raspberry Exerts Antihyperglycemic Effect by Inducing Autophagy and Modulating Gut Microbiota. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68,13025–37.
- Su LL, Hong ZF, Zhou T, Jian YY, Xu M, Zhang XP, et al. Health improvements of type 2 diabetic patients through diet and diet plus fecal microbiota transplantation. Sci Rep. 2022;12.
- Su XH, Yu WX, Liu AR, Wang CX, Li XZ, Gao JJ, et al. San-Huang-Yi-Shen Capsule Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy in Rats Through Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Overall Metabolism. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12.
- Sun CY, Zheng ZL, Chen CW, Lu BW, Liu D. Targeting Gut Microbiota With Natural Polysaccharides: Effective Interventions Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Diseases. Front Microbiol. 2022;13.
- Sun MB, Li D, Hua M, Miao XY, Su Y, Chi YP, et al. Black bean husk and black rice anthocyanin extracts modulated gut microbiota and serum metabolites for improvement in type 2 diabetic rats. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,7377–91.
- Sun Q, Wedick NM, Pan A, Townsend MK, Cassidy A, Franke AA, et al. Gut Microbiota Metabolites of Dietary Lignans and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Investigation in Two Cohorts of U. S. Women. Diabetes Care. 2014;37,1287–95.
- Sun Q, Zhang Y, Li ZW, Yan H, Li JP, Wan XY. Mechanism analysis of improved glucose homeostasis and cholesterol metabolism in high-fat-induced obese mice treated with La-SJLH001 via transcriptomics and culturomics. FOOD Funct. 2019;10,3556–66.
- Sun SY, Lei OK, Nie JL, Shi QD, Xu YM, Kong ZW. Effects of Low-Carbohydrate Diet and Exercise Training on Gut Microbiota. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Sun Y, Huang YC, Ye FH, Liu WW, Jin XH, Lin KX, et al. Effects of probiotics on glycemic control and intestinal dominant flora in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99.
- Sun YM, Qu W, Liao JB, Chen L, Cao YJ, Li HL. Jiangtangjing ameliorates type 2 diabetes through effects on the gut microbiota and cAMP/PKA pathway. Tradit Med Res. 2022;7.
- Sun ZK, Sun XJ, Li J, Li ZY, Hu QW, Li LL, et al. Using probiotics for type 2 diabetes mellitus intervention: Advances, questions, and potential. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60,670–83.
- Swallah MS, Fan HL, Wang SN, Yu HS, Piao CH. Prebiotic Impacts of Soybean Residue (Okara) on Eubiosis/Dysbiosis Condition of the Gut and the Possible Effects on Liver and Kidney Functions. MOLECULES. 2021;26.
- Taherian M, Samadi PM, Rastegar H, Faramarzi MA, Rostami-Nejad M, Yazdi MH, et al. An Overview on Probiotics as an Alternative Strategy for Prevention and Treatment of Human Diseases. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019;18:31–50.
- Tai NW, Wong FS, Wen L. The role of gut microbiota in the development of type 1, type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2015;16,55–65.
- Takewaki F, Nakajima H, Takewaki D, Hashimoto Y, Majima S, Okada H, et al. Habitual Dietary Intake Affects the Altered Pattern of Gut Microbiome by Acarbose in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Tamura A, Murabayashi M, Nishiya Y, Mizushiri S, Hamaura K, Ito R, et al. Interrelations between Gut Microbiota Composition, Nutrient Intake and Diabetes Status in an Adult Japanese Population. J Clin Med. 2022;11.
- Tan JK, McKenzie C, Marino E, Macia L, Mackay CR. Metabolite-Sensing G Protein-Coupled Receptors-Facilitators of Diet-Related Immune Regulation. In: Littman DR, Yokoyama WM, editors. ANNUAL REVIEW OF IMMUNOLOGY, VOL 35. Monash Univ, Monash Biomed Discovery Inst, Infect & Immun Program, Clayton, Vic 3800, Australia; 2017. p. 371–402.
- Tan YQ, Tam CC, Rolston M, Alves P, Chen L, Meng S, et al. Quercetin Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Restores Gut Microbiome in Mice on High-Fat Diets. ANTIOXIDANTS. 2021;10.
- Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Neculae E, Costea CF, Ciocoiu M, Hurjui LL, et al. Role of Gut Microbiota on Onset and Progression of Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM). Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Tang TP, Li Q, Huang ZW, Wu YJ, Yan BW, Zhao JX, et al. Evaluation of Shandong pancake with sourdough fermentation on the alleviation of type 2 diabetes symptoms in mice. J Funct Foods. 2022;90.
- Tang WHW, Wang ZN, Li XMS, Fan YY, Li DS, Wu YP, et al. Increased Trimethylamine N-Oxide Portends High Mortality Risk Independent of Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin Chem. 2017;63,297–306.
- Tang ZH, Luo T, Huang P, Luo M, Zhu JH, Wang X, et al. Nuciferine administration in C57BL/6J mice with gestational diabetes mellitus induced by a high-fat diet: the improvement of glycolipid disorders and intestinal dysbacteriosis. FOOD Funct. 2021;12,1174–89.
- Tawfick MM, Xie HL, Zhao C, Shao P, Farag MA. Inulin fructans in diet: Role in gut homeostasis, immunity, health outcomes and potential therapeutics. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;208:948–61.
- Taylor BL, Woodfall GE, Sheedy KE, O’Riley ML, Rainbow KA, Bramwell EL, et al. Effect of Probiotics on Metabolic Outcomes in Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2017;9.
- Taylor HB, Vasu C. Impact of Prebiotic beta-glucan Treatment at Juvenile Age on the Gut Microbiota Composition and the Eventual Type 1 Diabetes Onset in Non-obese Diabetic Mice. Front Nutr. 2021;8.
- Tettamanzi F, Bagnardi V, Louca P, Nogal A, Monti GS, Mambrini SP, et al. A High Protein Diet Is More Effective in Improving Insulin Resistance and Glycemic Variability Compared to a Mediterranean Diet-A Cross-Over Controlled Inpatient Dietary Study. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Therdtatha P, Shinoda A, Nakayama J. Crisis of the Asian gut: associations among diet, microbiota, and metabolic diseases. Biosci MICROBIOTA FOOD Heal. 2022;41,83–93.
- Thushara RM, Gangadaran S, Solati Z, Moghadasian MH. Cardiovascular benefits of probiotics: a review of experimental and clinical studies. FOOD Funct. 2016;7,632–42.
- Tian JL, Si X, Shu C, Wang YH, Tan H, Zang ZH, et al. Synergistic Effects of Combined Anthocyanin and Metformin Treatment for Hyperglycemia In Vitro and In Vivo. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70,1182–95.
- Tian JX, Li M, Lian FM, Tong XL. The hundred most-cited publications in microbiota of diabetes research A bibliometric analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96.
- Tian PJ, Li BL, He CX, Song W, Hou AJ, Tian SC, et al. Antidiabetic (type 2) effects of Lactobacillus G15 and Q14 in rats through regulation of intestinal permeability and microbiota. FOOD Funct. 2016;7,3789–97.
- Tian SH, Li XF, Wang YF, Lu YJ. The protective effect of sulforaphane on type II diabetes induced by high-fat diet and low-dosage streptozotocin. FOOD Sci Nutr. 2021;9,747–56.
- Toivonen RK, Emani R, Munukka E, Rintala A, Laiho A, Pietila S, et al. Fermentable fibres condition colon microbiota and promote diabetogenesis in NOD mice. Diabetologia. 2014;57,2183–92.
- Tomas-Barberan F, Osorio C. Advances in Health-Promoting Food Ingredients. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67,9121–3.
- Tonucci L, Dos Santos KMO, Ferreira C, Ribeiro SMR, De Oliveira LL, Martino HSD. Gut microbiota and probiotics: Focus on diabetes mellitus. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017;57,2296–309.
- Tonucci LB, dos Santos KMO, de Oliveira LL, Ribeiro SMR, Martino HSD. Clinical application of probiotics in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Nutr. 2017;36,85–92.
- Tosh SM, Bordenave N. Emerging science on benefits of whole grain oat and barley and their soluble dietary fibers for heart health, glycemic response, and gut microbiota. Nutr Rev. 2020;78(International Symposium on Whole Grains, Dietary Fiber and Public Health):13–20.
- Tosti V, Bertozzi B, Fontana L. Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms. JOURNALS Gerontol Ser A-BIOLOGICAL Sci Med Sci. 2018;73,318–26.
- Trautwein EA, Peters HPF, Mela DJ, Edwards C, Herrema H, Fu JY, et al. Is gut microbiota a relevant and competitive dietary target for cardio-metabolic health? Proceedings of an expert workshop. TRENDS FOOD Sci Technol. 2018;81:146–54.
- Traversi D, Rabbone I, Scaioli G, Vallini C, Carletto G, Racca I, et al. Risk factors for type 1 diabetes, including environmental, behavioural and gut microbial factors: a case-control study. Sci Rep. 2020;10.
- Tremaroli V, Backhed F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature. 2012;489,242–9.
- Tung YT, Zeng JL, Ho ST, Xu JW, Lin IH, Wu JH. Djulis Hull Improves Insulin Resistance and Modulates the Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Induced Hyperglycaemia. ANTIOXIDANTS. 2022;11.
- Tungland B, Tungland B. Intestinal Dysbiosis in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Related Metabolic Diseases: Therapeutic Strategies Utilizing Dietary Modification, Pro- and Prebiotics, and Fecal Microbial Transplant (FMT) Therapy. HUMAN MICROBIOTA IN HEALTH AND DISEASE: PATHOGENESIS TO THERAPY. 2018. 463–515 p.
- Tuomainen M, Lindstrom J, Lehtonen M, Auriola S, Pihlajamaki J, Peltonen M, et al. Associations of serum indolepropionic acid, a gut microbiota metabolite, with type 2 diabetes and low-grade inflammation in high-risk individuals. Nutr Diabetes. 2018;8.
- Turner A, Veysey M, Keely S, Scarlett CJ, Lucock M, Beckett EL. Intense Sweeteners, Taste Receptors and the Gut Microbiome: A Metabolic Health Perspective. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17.
- Uma K V, Sutheeswaran G, Martin J V, Gujadhur M, Moudgil K. An educational review on Probiotics. Curr ISSUES Pharm Med Sci. 2021;34,114–7.
- Umirah F, Neoh CF, Ramasamy K, Lim SM. Differential gut microbiota composition between type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and healthy controls: A systematic review. DIABETES Res Clin Pract. 2021;173.
- Unger AL, Jetton TL, Kraft J. Dietary fat quality impacts metabolic impairments of type 2 diabetes risk differently in male and female CD-1 (R) mice. Br J Nutr. 2022;128,1013–28.
- Upadhyaya S, Banerjee G. Type 2 diabetes and gut microbiome: at the intersection of known and unknown. Gut Microbes. 2015;6,85–92.
- Ussar S, Griffin NW, Bezy O, Fujisaka S, Vienberg S, Softic S, et al. Interactions between Gut Microbiota, Host Genetics and Diet Modulate the Predisposition to Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. CELL Metab. 2015;22,516–30.
- Vaarala, O. Is the origin of type 1 diabetes in the gut? Immunol Cell Biol. 2012;90,271–6.
- Valenlia KB, Morshedi M, Saghafi-Asl M, Shahabi P, Abbasi MM. Beneficial impacts of Lactobacillus plantarum and inulin on hypothalamic levels of insulin, leptin, and oxidative markers in diabetic rats. J Funct Foods. 2018;46:529–37.
- Vallianou NG, Stratigou T, Tsagarakis S. Microbiome and diabetes: Where are we now? DIABETES Res Clin Pract. 2018;146:111–8.
- Vamanu, E. Complementary Functional Strategy for Modulation of Human Gut Microbiota. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24,4144–9.
- Van Hul M, Geurts L, Plovier H, Druart C, Everard A, Stahlman M, et al. Reduced obesity, diabetes, and steatosis upon cinnamon and grape pomace are associated with changes in gut microbiota and markers of gut barrier. Am J Physiol Metab. 2018;314,E334–52.
- Varsha KK, Maheshwari AP, Nampoothiri KM. Accomplishment of probiotics in human health pertaining to immunoregulation and disease control. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021;44:26–37.
- Vasishta S, Ganesh K, Umakanth S, Joshi MB. Ethnic disparities attributed to the manifestation in and response to type 2 diabetes: insights from metabolomics. METABOLOMICS. 2022;18.
- Verdu EF, Danska JS. Common ground: shared risk factors for type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. Nat Immunol. 2018;19,685–95.
- Verduci E, Mameli C, Amatruda M, Petitti A, Vizzuso S, El Assadi F, et al. Early Nutrition and Risk of Type 1 Diabetes: The Role of Gut Microbiota. Front Nutr. 2020;7.
- Verhoog S, Taneri PE, Diaz ZMR, Marques-Vidal P, Troup JP, Bally L, et al. Dietary Factors and Modulation of Bacteria Strains of Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2019;11.
- Villa-Rodriguez JA, Ifie I, Gonzalez-Aguilar GA, Roopchand DE. The Gastrointestinal Tract as Prime Site for Cardiometabolic Protection by Dietary Polyphenols. Adv Nutr. 2019;10,999–1011.
- Virtanen SM. Dietary factors in the development of type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016;17:49–55.
- Visser JTJ, Bos NA, Harthoorn LF, Stellaard F, Beijer-Liefers S, Rozing J, et al. Potential mechanisms explaining why hydrolyzed casein-based diets outclass single amino acid-based diets in the prevention of autoimmune diabetes in diabetes-prone BB rats. DIABETES-METABOLISM Res Rev. 2012;28,505–13.
- Vitaglione P, Mennella I, Ferracane R, Goldsmith F, Guice J, Page R, et al. Gut fermentation induced by a resistant starch rich whole grain diet explains serum concentration of dihydroferulic acid and hippuric acid in a model of ZDF rats. J Funct Foods. 2019;53:286–91.
- Vu V, Muthuramalingam K, Singh V, Choi C, Kim YM, Unno T, et al. Schizophyllum commune-derived beta-glucan improves intestinal health demonstrating protective effects against constipation and common metabolic disorders. Appl Biol Chem. 2022;65.
- Wagenaar CA, van de Put M, Bisschops M, Walrabenstein W, de Jonge CS, Herrema H, et al. The Effect of Dietary Interventions on Chronic Inflammatory Diseases in Relation to the Microbiome: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Walker WA, Iyengar RS. Breast milk, microbiota, and intestinal immune homeostasis. Pediatr Res. 2015;77,220–8.
- Wan JY, Ma JM. Efficacy of dietary supplements targeting gut microbiota in the prevention and treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus. Front Microbiol. 2022;13.
- Wan XZ, Li TT, Zhong RT, Chen HB, Xia X, Gao LY, et al. Anti-diabetic activity of PUFAs-rich extracts of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Spirulina platensis in rats. FOOD Chem Toxicol. 2019;128(1st International Conference on Natural Toxicology and Pharmacology (ICNTP)):233–9.
- Wang CQ, Hu MH, Yi YH, Wen XN, Lv CH, Shi M, et al. Multiomic analysis of dark tea extract on glycolipid metabolic disorders in db/db mice. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Wang DD, Hu FB. Precision nutrition for prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. LANCET DIABETES Endocrinol. 2018;6,416–26.
- Wang DD, Qi QB, Wang Z, Usyk M, Sotres-Alvarez D, Mattei J, et al. The Gut Microbiome Modifies the Association Between a Mediterranean Diet and Diabetes in USA Hispanic/Latino Population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107,E924–34.
- Wang F, Zhang CF, Zeng Q. Gut microbiota and immunopathogenesis of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2. Front Biosci. 2016;21:900-906 WE-Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI.
- Wang F, Zhu HJ, Hu MY, Wang J, Xia H, Yang X, et al. Perilla Oil Supplementation Improves Hypertriglyceridemia and Gut Dysbiosis in Diabetic KKAy Mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018;62.
- Wang G, Li XF, Zhao JX, Zhang H, Chen W. Lactobacillus casei CCFM419 attenuates type 2 diabetes via a gut microbiota dependent mechanism. FOOD Funct. 2017;8,3155–64.
- Wang G, Si Q, Yang SR, Jiao T, Zhu HY, Tian PJ, et al. Lactic acid bacteria reduce diabetes symptoms in mice by alleviating gut microbiota dysbiosis and inflammation in different manners. FOOD Funct. 2020;11,5898–914.
- Wang GQ, Liu J, Xia YJ, Ai LZ. Probiotics-based interventions for diabetes mellitus: A review. FOOD Biosci. 2021;43.
- Wang GQ, Song JJ, Huang YCA, Li XQ, Wang HW, Zhang Y, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum SHY130 isolated from yak yogurt attenuates hyperglycemia in C57BL/6J mice by regulating the enteroinsular axis. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,675–87.
- Wang H, Chen ZJ, Wang M, Long MX, Ren TY, Chen C, et al. The Effect of Polyphenol Extract from Rosa Roxburghii Fruit on Plasma Metabolome and Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. FOODS. 2022;11.
- Wang H, Zhang HY, Gao ZZ, Zhang QQ, Gu CJ. The mechanism of berberine alleviating metabolic disorder based on gut microbiome. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12.
- Wang HJ, Gou WL, Su C, Du WW, Zhang JG, Miao ZL, et al. Association of gut microbiota with glycaemic traits and incident type 2 diabetes, and modulation by habitual diet: a population-based longitudinal cohort study in Chinese adults (June, 2022, 10.1007/s00125-022-05687-5). Diabetologia. 2022;65,1572.
- Wang HY, Guo LX, Hu WH, Peng ZT, Wang C, Chen ZC, et al. Polysaccharide from tuberous roots of Ophiopogon japonicus regulates gut microbiota and its metabolites during alleviation of high-fat diet-induced type-2 diabetes in mice. J Funct Foods. 2019;63.
- Wang JH, Shin NR, Lim SK, Im U, Song EJ, Nam YD, et al. Diet Control More Intensively Disturbs Gut Microbiota Than Genetic Background in Wild Type and ob/ob Mice. Front Microbiol. 2019;10.
- Wang JK, He YT, Yu DQ, Jin L, Gong XB, Zhang BS. Perilla oil regulates intestinal microbiota and alleviates insulin resistance through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in type-2 diabetic KKAy mice. FOOD Chem Toxicol. 2020;135.
- Wang JP, Xie ZL, Chen PP, Wang YH, Li BQ, Dai F. Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance. OPEN LIFE Sci. 2022;17,202–7.
- Wang KL, Wang YX, Chen S, Gu JL, Ni YY. Insoluble and Soluble Dietary Fibers from Kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) Modify Gut Microbiota to Alleviate High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced TYPE 2 Diabetes in Rats. Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Wang NN, Ma YN, Liu ZQ, Liu L, Yang KM, Wei YG, et al. Hydroxytyrosol prevents PM2.5-induced adiposity and insulin resistance by restraining oxidative stress related NF-kappa B pathway and modulation of gut microbiota in a murine model. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;141:393–407.
- Wang RY, Zhang ZF, Aihemaitijiang S, Ye C, Halimulati M, Huang XJ, et al. Oat beta Glucan Ameliorates Renal Function and Gut Microbiota in Diabetic Rats. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Wang XL, Yang ZM, Xu X, Jiang H, Cai C, Yu GL. Odd-numbered agaro-oligosaccharides alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus and related colonic microbiota dysbiosis in mice. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;240(International Conference on Polysaccharides for Nutraceuticals and Biomaterials (ICPNB)).
- Wang XW, Wang YQ, Han MZ, Liang JJ, Zhang MN, Bai X, et al. Evaluating the changes in phytochemical composition, hypoglycemic effect, and influence on mice intestinal microbiota of fermented apple juice. FOOD Res Int. 2022;155.
- Wang XX, Zhang LP, Qin L, Wang YF, Chen FS, Qu CF, et al. Physicochemical Properties of the Soluble Dietary Fiber from Laminaria japonica and Its Role in the Regulation of Type 2 Diabetes Mice. Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Wang Y, Liu HY, Zheng MY, Yang YH, Ren HZ, Kong Y, et al. Berberine Slows the Progression of Prediabetes to Diabetes in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats by Enhancing Intestinal Secretion of Glucagon-Like Peptide-2 and Improving the Gut Microbiota. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12.
- Wang YL, Ning YJ, Yuan C, Cui B, Liu GM, Zhang Z. The protective mechanism of a debranched corn starch/konjac glucomannan composite against dyslipidemia and gut microbiota in high-fat-diet induced type 2 diabetes. FOOD Funct. 2021;12,9273–85.
- Wang YM, Dilidaxi D, Wu YC, Sailike J, Sun X, Nabi XH. Composite probiotics alleviate type 2 diabetes by regulating intestinal microbiota and inducing GLP-1 secretion in db/db mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;125.
- Ward RE, Benninghoff AD, Hintze KJ. Food matrix and the microbiome: considerations for preclinical chronic disease studies. Nutr Res. 2020;78:1–10.
- Warma S, Lee Y, Brietzke E, McIntyre RS. Microbiome abnormalities as a possible link between diabetes mellitus and mood disorders: Pathophysiology and implications for treatment. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022;137.
- Watanabe A, Kadota Y, Kamio R, Tochio T, Endo A, Shimomura Y, et al. 1-Kestose supplementation mitigates the progressive deterioration of glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes OLETF rats. Sci Rep. 2020;10.
- Watanabe M, Sianoya A, Mishima R, Therdtatha P, Rodriguez A, Ramos DC, et al. Gut microbiome status of urban and rural Filipino adults in relation to diet and metabolic disorders. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2021;368.
- Wei M, Gu EY, Luo J, Zhang ZH, Xu D, Tao XY, et al. Enterococcus hirae WEHI01 isolated from a healthy Chinese infant ameliorates the symptoms of type 2 diabetes by elevating the abundance of Lactobacillales in rats. J Dairy Sci. 2020;103,2969–81.
- Wei SY, Han RM, Zhao JY, Wang S, Huang MQ, Wang YN, et al. Intermittent administration of a fasting-mimicking diet intervenes in diabetes progression, restores beta cells and reconstructs gut microbiota in mice. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2018;15.
- Wei SY, Zhao JY, Wang S, Huang MQ, Wang YN, Chen Y. Intermittent administration of a leucine-deprived diet is able to intervene in type 2 diabetes in db/db mice. HELIYON. 2018;4.
- Wei T, Jia Y, Xue W, Ma M, Wu WH. Nutritional Effects of the Enteral Nutritional Formula on Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Level in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice. DIABETES Metab Syndr OBESITY-TARGETS Ther. 2021;14:1855–69.
- Wei YG, Yang HX, Zhu CH, Deng JJ, Fan DD. Hypoglycemic Effect of Ginsenoside Rg5 Mediated Partly by Modulating Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Diabetic db/db Mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68,5107–17.
- Weickert MO, Pfeiffer AFH. Impact of Dietary Fiber Consumption on Insulin Resistance and the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes. J Nutr. 2018;148,7–12.
- Wen L, Duffy A. Factors Influencing the Gut Microbiota, Inflammation, and Type 2 Diabetes. J Nutr. 2017;147,1468S-1475S.
- Wilson AS, Koller KR, Ramaboli MC, Nesengani LT, Ocvirk S, Chen CX, et al. Diet and the Human Gut Microbiome: An International Review. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65,723–40.
- Wilson R, Willis J, Gearry RB, Hughes A, Lawley B, Skidmore P, et al. SunGold Kiwifruit Supplementation of Individuals with Prediabetes Alters Gut Microbiota and Improves Vitamin C Status, Anthropometric and Clinical Markers. Nutrients. 2018;10.
- Winiarska-Mieczan A, Tomaszewska E, Donaldson J, Jachimowicz K. The Role of Nutritional Factors in the Modulation of the Composition of the Gut Microbiota in People with Autoimmune Diabetes. Nutrients. 2022;14.
- Wlodarczyk M, Slizewska K. Efficiency of Resistant Starch and Dextrins as Prebiotics: A Review of the Existing Evidence and Clinical Trials. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Wolf KJ, Daft JG, Tanner SM, Hartmann R, Khafipour E, Lorenz RG. Consumption of Acidic Water Alters the Gut Microbiome and Decreases the Risk of Diabetes in NOD Mice. J Histochem Cytochem. 2014;62,237–50.
- Woting A, Blaut M. The Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolic Disease. Nutrients. 2016;8.
- Wu CF, Pan LL, Niu WY, Fang X, Liang WJ, Li JH, et al. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Low Methoxyl Pectin Attenuates Type 1 Diabetes in Non-obese Diabetic Mice. Front Immunol. 2019;10.
- Wu CX, Liu J, Li YX, Wang NN, Yan QJ, Jiang ZQ. Manno-oligosaccharides from cassia seed gum ameliorate inflammation and improve glucose metabolism in diabetic rats. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,6674–87.
- Wu GJ, Liu AB, Xu Y, Wang Y, Zhao LP, Hara Y, et al. The Effects of Green Tea on Diabetes and Gut Microbiome in db/db Mice: Studies with Tea Extracts vs. Tea Powder. Nutrients. 2021;13.
- Wu H, Tremaroli V, Backhed F. Linking Microbiota to Human Diseases: A Systems Biology Perspective. TRENDS Endocrinol Metab. 2015;26,758–70.
- Wu L, Tang BS, Lai PF, Weng MJ, Zheng HG, Chen JC, et al. Analysis of the effect of okra extract on the diversity of intestinal flora in diabetic rats based on 16S rRNA sequence. FOOD Sci Technol. 2022;42.
- Wu N, Mo H, Mu Q, Liu P, Liu GL, Yu WD. The Gut Mycobiome Characterization of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Association With Dietary Intervention. Front Microbiol. 2022;13.
- Wu N, Zhou JW, Mo H, Mu Q, Su HT, Li M, et al. The Gut Microbial Signature of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and the Association With Diet Intervention. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;11.
- Wu QF, Wu SY, Cheng Y, Zhang ZS, Mao GX, Li SJ, et al. Sargassum fusiforme fucoidan modifies gut microbiota and intestinal metabolites during alleviation of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic mice. FOOD Funct. 2021;12,3572–85.
- Wu RY, Zhou LN, Chen Y, Ding XQ, Liu Y, Tong B, et al. Sesquiterpene glycoside isolated from loquat leaf targets gut microbiota to prevent type 2 diabetes mellitus in db/db mice. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,1519–34.
- Wu SY, Zuo JH, Cheng Y, Zhang Y, Zhang ZS, Wu MJ, et al. Ethanol extract of Sargarsum fusiforme alleviates HFD/STZ-induced hyperglycemia in association with modulation of gut microbiota and intestinal metabolites in type 2 diabetic mice. FOOD Res Int. 2021;147.
- Wu T, Zhang YL, Li W, Zhao YJ, Long HR, Muhindo EM, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus LRa05 Ameliorate Hyperglycemia through a Regulating Glucagon-Mediated Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69,8797–806.
- Wu TR, Lin CS, Chang CJ, Lin TL, Martel J, Ko YF, et al. Gut commensal Parabacteroides goldsteinii plays a predominant role in the anti-obesity effects of polysaccharides isolated from Hirsutella sinensis. Gut. 2019;68,248–62.
- Wu Y, Zong MH, Wu H, He D, Li L, Zhang X, et al. Dietary Advanced Glycation End-Products Affects the Progression of Early Diabetes by Intervening in Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022;66.
- Xi Y, Xu PF. Diabetes and gut microbiota. World J Diabetes. 2021;12,1693–703.
- Xia H, Shi XL, Zhou BJ, Sui J, Yang C, Liu HC, et al. Milled flaxseed-added diets ameliorated hepatic inflammation by reducing gene expression of TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway and altered gut microbiota in STZ-induced type 1 diabetic mice. FOOD Sci Hum WELLNESS. 2022;11,32–40.
- Xia T, Liu CS, Hu YN, Luo ZY, Chen FL, Yuan LX, et al. Coix seed polysaccharides alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus via gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids activation of IGF1/PI3K/ AKT signaling. FOOD Res Int. 2021;150.
- Xia T, Zhang ZJ, Zhao YX, Kang CY, Zhang XL, Tian YL, et al. The anti-diabetic activity of polyphenols-rich vinegar extract in mice via regulating gut microbiota and liver inflammation. FOOD Chem. 2022;393.
- Xiang L, Wu QB, Osada H, Yoshida M, Pan WS, Qi JH. Peanut skin extract ameliorates the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice by alleviating inflammation and maintaining gut microbiota homeostasis. AGING-US. 2020;12,13991-14018 WE-Science Citation Index Expanded.
- Xiao HH, Lu L, Poon CCW, Chan CO, Wang LJ, Zhu YX, et al. The lignan-rich fraction from Sambucus Williamsii Hance ameliorates dyslipidemia and insulin resistance and modulates gut microbiota composition in ovariectomized rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137.
- Xiao L, Van’t Land B, van de Worp W, Stahl B, Folkerts G, Garssen J. Early-Life Nutritional Factors and Mucosal Immunity in the Development of Autoimmune Diabetes. Front Immunol. 2017;8.
- Xiao R, Wang R, Li SS, Kang XH, Ren YM, Sun EN, et al. Preliminary Evaluation of Potential Properties of Three Probiotics and Their Combination with Prebiotics on GLP-1 Secretion and Type 2 Diabetes Alleviation. J Food Qual. 2022;2022.
- Xie DD, Zhao XT, Chen MW. Prevention and treatment strategies for type 2 diabetes based on regulating intestinal flora. Biosci Trends. 2021;15,313–20.
- Xie J, Song W, Liang XC, Zhang Q, Shi Y, Liu W, et al. Protective effect of quercetin on streptozotocin-induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy rats through modulating gut microbiota and reactive oxygen species level. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127.
- Xie YQ, Xiao M, Ni YL, Jiang SF, Feng GZ, Sang SG, et al. Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. Extract Prevents Diabetes in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018.
- Xiong WY, Chen J, He JQ, Xiao MF, He XY, Liu B, et al. Anti-Diabetic Potential of Chlorella Pyrenoidosa-Based Mixture and its Regulation of Gut Microbiota. PLANT FOODS Hum Nutr. 2022;77,292–8.
- Xu BC, Fu J, Qiao YX, Cao JP, Deehan EC, Li Z, et al. Higher intake of microbiota-accessible carbohydrates and improved cardiometabolic risk factors: a meta-analysis and umbrella review of dietary management in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;113,1515–30.
- Xu JJ, Sun W, Li H, Gao ZX, Hu GA, Wu JR, et al. Xanthan gum oligosaccharides ameliorate glucose metabolism and related gut microbiota dysbiosis in type 2 diabetic mice. FOOD Biosci. 2022;50.
- Xu N, Zhou YJ, Lu XY, Chang YN. Auricularia auricula-judae (Bull.) polysaccharides improve type 2 diabetes in HFD/STZ-induced mice by regulating the AKT/AMPK signaling pathways and the gut microbiota. J Food Sci. 2021;86,5479–94.
- Xu SY, Wang YP, Wang JJ, Geng WT. Kombucha Reduces Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes of Mice by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites. FOODS. 2022;11.
- Xu T, Wu XY, Liu J, Sun JY, Wang XB, Fan G, et al. The regulatory roles of dietary fibers on host health via gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022;62:36–42.
- Xu Z, Dai XX, Zhang QY, Su SL, Yan H, Zhu Y, et al. Protective effects and mechanisms of Rehmannia glutinosa leaves total glycoside on early kidney injury in db/db mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;125.
- Xue ML, Liang H, Ji XQ, Liu Y, Ge YL, Hou L, et al. Fucoidan prevent murine autoimmune diabetes via suppression TLR4-signaling pathways, regulation DC/Treg induced immune tolerance and improving gut microecology. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019;16.
- Xue ML, Liu Y, Xu HW, Zhou ZT, Ma Y, Sun T, et al. Propolis modulates the gut microbiota and improves the intestinal mucosal barrier function in diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118.
- Yamaguchi Y, Adachi K, Sugiyama T, Shimozato A, Ebi M, Ogasawara N, et al. Association of Intestinal Microbiota with Metabolic Markers and Dietary Habits in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Digestion. 2016;94,66–72.
- Yan D, Fan PC, Sun WL, Ding QZ, Zheng W, Xiao WD, et al. Anemarrhena asphodeloides modulates gut microbiota and restores pancreatic function in diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133.
- Yan FF, Li N, Shi JL, Li HZ, Yue YX, Jiao WS, et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus alleviates type 2 diabetes by regulating hepatic glucose, lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. FOOD Funct. 2019;10,5804–15.
- Yan FF, Li N, Yue YX, Wang CF, Zhao L, Evivie SE, et al. Screening for Potential Novel Probiotics With Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV-Inhibiting Activity for Type 2 Diabetes Attenuation in vitro and in vivo. Front Microbiol. 2020;10.
- Yan J, Li JJ, Xue QY, Xie SQ, Jiang JJ, Li P, et al. Bacillus sp. DU-106 ameliorates type 2 diabetes by modulating gut microbiota in high-fat-fed and streptozotocin-induced mice. J Appl Microbiol. 2022;133,3126–38.
- Yan MR, Welch R, Rush EC, Xiang XS, Wang X. A Sustainable Wholesome Foodstuff; Health Effects and Potential Dietotherapy Applications of Yacon. Nutrients. 2019;11.
- Yan X, Yang CF, Lin GP, Chen YQ, Miao S, Liu B, et al. Antidiabetic Potential of Green Seaweed Enteromorpha prolifera Flavonoids Regulating Insulin Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. J Food Sci. 2019;84,165–73.
- Yan ZH, Wu H, Yao HL, Pan WJ, Su MM, Chen TB, et al. Rotundic Acid Protects against Metabolic Disturbance and Improves Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes Rats. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Yang BG, Hur KY, Lee MS. Alterations in Gut Microbiota and Immunity by Dietary Fat. YONSEI Med J. 2017;58,1083–91.
- Yang CF, Lai SS, Chen YH, Liu D, Liu B, Ai C, et al. Anti-diabetic effect of oligosaccharides from seaweed Sargassum confusum via JNK-IRS1/PI3K signalling pathways and regulation of gut microbiota. FOOD Chem Toxicol. 2019;131(4th International Conference on Natural Products Utilization (ICNPU)-From Plants to Pharmacy Shelf).
- Yang F, Zhu WJ, Edirisuriya P, Ai Q, Nie K, Ji XM, et al. Characterization of metabolites and biomarkers for the probiotic effects of Clostridium cochlearium on high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice. Eur J Nutr. 2022;61,2217–29.
- Yang HJ, Kim MJ, Kwon DY, Kim DS, Zhang T, Ha C, et al. Combination of Aronia, Red Ginseng, Shiitake Mushroom and Nattokinase Potentiated Insulin Secretion and Reduced Insulin Resistance with Improving Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in Insulin Deficient Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Nutrients. 2018;10.
- Yang HJ, Zhang T, Wu XG, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Yang ES, et al. Aqueous Blackcurrant Extract Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion and Modulates the Gut Microbiome in Non-Obese Type 2 Diabetic Rats. ANTIOXIDANTS. 2021;10.
- Yang JL, Dong HB, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Zhang WN, Lu YM, et al. Cordyceps cicadae polysaccharides ameliorated renal interstitial fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy rats by repressing inflammation andmodulating gut microbiota dysbiosis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;163:442–56.
- Yang R, Jia Q, Mehmood S, Ma SF, Liu XF. Genistein ameliorates inflammation and insulin resistance through mediation of gut microbiota composition in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur J Nutr. 2021;60,2155–68.
- Yang TT, Zhou WT, Xu WQ, Ran LW, Yan YM, Lu L, et al. Modulation of gut microbiota and hypoglycemic/hypolipidemic activity of flavonoids from the fruits of Lycium barbarum on high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,11169–84.
- Yao Y, Yan LJ, Chen H, Wu N, Wang WB, Wang DS. Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides alleviate type 2 diabetic symptoms by modulating gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids. PHYTOMEDICINE. 2020;77.
- Yarar-Fisher C, Li J, McLain A, Gower B, Oster R, Morrow C. Utilizing a low-carbohydrate/high-protein diet to improve metabolic health in individuals with spinal cord injury (DISH): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2019;20.
- Yerlikaya A, Dagel T, King C, Kuwabara M, Lanaspa MA, Andres-Hernando A, et al. Dietary and commercialized fructose: Sweet or sour? Int Urol Nephrol. 2017;49,1611–20.
- Yin RY, Xue Y, Hu JR, Hu XS, Shen Q. The effects of diet and streptozotocin on metabolism and gut microbiota in a type 2 diabetes mellitus mouse model. FOOD Agric Immunol. 2020;31,723–39.
- Yoo JY, Kim SS. Probiotics and Prebiotics: Present Status and Future Perspectives on Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients. 2016;8.
- Youn HS, Kim JH, Lee JS, Yoon YY, Choi SJ, Lee JY, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum Reduces Low-Grade Inflammation and Glucose Levels in a Mouse Model of Chronic Stress and Diabetes. Infect Immun. 2021;89.
- Yousefi B, Eslami M, Ghasemian A, Kokhaei P, Sadeghnejhad A. Probiotics can really cure an autoimmune disease? GENE REPORTS. 2019;15.
- Yu DX, Shu XO, Rivera ES, Zhang XL, Cai QY, Calcutt MW, et al. Urinary Levels of Trimethylamine-N-Oxide and Incident Coronary Heart Disease: A Prospective Investigation Among Urban Chinese Adults. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8.
- Yu LL, Zhou XT, Duan H, Chen Y, Cui SM, Guo RM, et al. Synergistic Protective Effects of Different Dietary Supplements Against Type 2 Diabetes via Regulating Gut Microbiota. J Med Food. 2021;24,319–30.
- Yu N, Gu N, Wang YX, Zhou B, Lu DF, Li JP, et al. The Association of Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide with Coronary Atherosclerotic Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Among a Chinese North Population. DIABETES Metab Syndr OBESITY-TARGETS Ther. 2022;15:69–78.
- Yuan HB, Wang WJ, Chen DY, Zhu XP, Meng LN. Effects of a treatment with Se-rich rice flour high in resistant starch on enteric dysbiosis andchronic inflammation in diabetic ICR mice. J Sci Food Agric. 2017;97,2068–74.
- Yuan QC, Zhan BY, Chang R, Du M, Mao XY. Antidiabetic Effect of Casein Glycomacropeptide Hydrolysates on High-Fat Diet and STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice via Regulating Insulin Signaling in Skeletal Muscle and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2020;12.
- Yuan Y, Zheng YF, Zhou JH, Geng YT, Zou P, Li YQ, et al. Polyphenol-Rich Extracts from Brown Macroalgae Lessonia trabeculate Attenuate Hyperglycemia and Modulate Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67,12472–80.
- Yuan Y, Zhou JH, Zheng YF, Xu ZC, Li YQ, Zhou S, et al. Beneficial effects of polysaccharide-rich extracts from Apocynum venetum leaves on hypoglycemic and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127.
- Yue SJ, Shan B, Peng CX, Tan C, Wang QP, Gong JS. Theabrownin-targeted regulation of intestinal microorganisms to improve glucose and lipid metabolism in Goto-Kakizaki rats. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,1921–40.
- Yue SJ, Zhao D, Peng CX, Tan C, Wang QP, Gong JS. Effects of theabrownin on serum metabolites and gut microbiome in rats with a high-sugar diet. FOOD Funct. 2019;10,7063–80.
- Zaky A, Glastras SJ, Wong MYW, Pollock CA, Saad S. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Diabetes and Obesity-Related Kidney Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22.
- Zawada A, Rychter AM, Ratajczak AE, Lisiecka-Masian A, Dobrowolska A, Krela-Kazmierczak I. Does Gut-Microbiome Interaction Protect against Obesity and Obesity-Associated Metabolic Disorders? MICROORGANISMS. 2021;9.
- Zeevi D, Korem T, Zmora N, Israeli D, Rothschild D, Weinberger A, et al. Personalized Nutrition by Prediction of Glycemic Responses. Cell. 2015;163,1079–94.
- Zeng Z, Guo XX, Zhang JL, Yuan QP, Chen SW. Lactobacillus paracasei modulates the gut microbiota and improves inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats. FOOD Funct. 2021;12,6809–20.
- Zeng Z, Yuan QP, Yu R, Zhang JL, Ma HQ, Chen SW. Ameliorative Effects of Probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei NL41 on Insulin Sensitivity, Oxidative Stress, and Beta-Cell Function in a Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rat Model. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63.
- Zhai BQ, Zhang CH, Sheng Y, Zhao CH, He XY, Xu WT, et al. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effect of S-allyl-cysteine sulfoxide (alliin) in DIO mice. Sci Rep. 2018;8.
- Zhai LX, Wu JY, Lam YY, Kwan HY, Bian ZX, Wong HLX. Gut-Microbial Metabolites, Probiotics and Their Roles in Type 2 Diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22.
- Zhang AW, Jiang XJ, Ge Y, Xu QP, Li ZJ, Tang HC, et al. The Effects of GABA-Rich Adzuki Beans on Glycolipid Metabolism, as Well as Intestinal Flora, in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Zhang B, Jin Z, Zhai T, Ding Q, Yang H, Wang J, et al. Global research trends on the links between the gut microbiota and diabetes between 2001 and 2021: A bibliometrics and visualized study. Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 29;13:3664.
- Zhang CC, Jiang JC, Wang C, Li SJ, Yu LL, Tian FW, et al. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of the effects of probiotics on type 2 diabetes in adults. Clin Nutr. 2022;41,365–73.
- Zhang HH, Liu J, Lv YJ, Jiang YL, Pan JX, Zhu YJ, et al. Changes in Intestinal Microbiota of Type 2 Diabetes in Mice in Response to Dietary Supplementation With Instant Tea or Matcha. Can J DIABETES. 2020;44,44–52.
- Zhang JJ, Cao W, Zhao HA, Guo S, Wang Q, Cheng N, et al. Protective Mechanism of Fagopyrum esculentum Moench. Bee Pollen EtOH Extract Against Type II Diabetes in a High-Fat Diet/Streptozocin-Induced C57BL/6J Mice. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Zhang JL, Wang SB, Zeng Z, Qin YX, Shen Q, Li PL. Anti-diabetic effects of Bifidobacterium animalis 01 through improving hepatic insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic rat model. J Funct Foods. 2020;67.
- Zhang L, Qin QQ, Liu MN, Zhang XL, He F, Wang GQ. Akkermansia muciniphila can reduce the damage of gluco/lipotoxicity, oxidative stress and inflammation, and normalize intestine microbiota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pathog Dis. 2018;76.
- Zhang L, Wang XZ, Zhang X. Modulation of Intestinal Flora by Dietary Polysaccharides: A Novel Approach for the Treatment and Prevention of Metabolic Disorders. FOODS. 2022;11.
- Zhang L, Zhang T, Sun J, Huang Y, Liu T, Ye Z, et al. Calorie restriction ameliorates hyperglycemia, modulates the disordered gut microbiota, and mitigates metabolic endotoxemia and inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats. J Endocrinol Invest. 2022.
- Zhang LC, Wu XY, Yang RB, Chen F, Liao Y, Zhu ZF, et al. Effects of Berberine on the Gastrointestinal Microbiota. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;10.
- Zhang LP, Wang F, He HL, Jiao TT, Wu LL. Tangnaikang Alleviates Hyperglycemia and Improves Gut Microbiota in Diabetic Mice. EVIDENCE-BASED Complement Altern Med. 2021;2021.
- Zhang Q, Yu HY, Xiao XH, Hu L, Xin FJ, Yu XB. Inulin-type fructan improves diabetic phenotype and gut microbiota profiles in rats. PeerJ. 2018;6.
- Zhang SS, Zhang NN, Guo S, Liu SJ, Hou YF, Li SM, et al. Glycosides and flavonoids from the extract of Pueraria thomsonii Benth leaf alleviate type 2 diabetes in high-fat diet plus streptozotocin-induced mice by modulating the gut microbiota. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,3931–45.
- Zhang TH, Yang Y, Liang Y, Jiao X, Zhao CH. Beneficial Effect of Intestinal Fermentation of Natural Polysaccharides. Nutrients. 2018;10.
- Zhang XG, Zhang B, Li L, Li XB, Zhang JQ, Chen GY. Fermented noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) fruit juice improved oxidative stress and insulin resistance under the synergistic effect of Nrf2/ARE pathway and gut flora in db/db mice and HepG2 cells. FOOD Funct. 2022;13,8254–73.
- Zhang XL, Shao H, Zheng X. Amino acids at the intersection of nutrition and insulin sensitivity. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24,1038–43.
- Zhang XW, Dong LH, Jia XC, Liu L, Chi JW, Huang F, et al. Bound Phenolics Ensure the Antihyperglycemic Effect of Rice Bran Dietary Fiber in db/db Mice via Activating the Insulin Signaling Pathway in Skeletal Muscle and Altering Gut Microbiota. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68,4387–98.
- Zhang XW, Zhang MW, Dong LH, Jia XC, Liu L, Ma YX, et al. Phytochemical Profile, Bioactivity, and Prebiotic Potential of Bound Phenolics Released from Rice Bran Dietary Fiber during in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion and Colonic Fermentation. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67,12796–805.
- Zhang Y, Guo X, Guo JL, He QW, Li H, Song YQ, et al. Lactobacillus casei reduces susceptibility to type 2 diabetes via microbiota-mediated body chloride ion influx. Sci Rep. 2014;4.
- Zhang Y, Liu J, Mao GX, Zuo JH, Li SJ, Yang Y, et al. Sargassum fusiforme fucoidan alleviates diet-induced insulin resistance by inhibiting colon-derived ceramide biosynthesis. FOOD Funct. 2021;12,8440–53.
- Zhang YL, Wu T, Li W, Zhao YJ, Long HR, Liu R, et al. Lactobacillus casei LC89 exerts antidiabetic effects through regulating hepatic glucagon response and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. FOOD Funct. 2021;12,8288–99.
- Zhao C, Yang CF, Chen MJ, Lv XC, Liu B, Yi LZ, et al. Regulatory Efficacy of Brown Seaweed Lessonia nigrescens Extract on the Gene Expression Profile and Intestinal Microflora in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018;62.
- Zhao C, Yang CF, Wai STC, Zhang YB, Portillo MP, Paoli P, et al. Regulation of glucose metabolism by bioactive phytochemicals for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(3rd International Symposium on Phytochemicals in Medicine and Food (ISPMF)):830–47.
- Zhao M, Ren KQ, Xiong XW, Cheng M, Zhang ZD, Huang Z, et al. Protein O-GlcNAc Modification Links Dietary and Gut Microbial Cues to the Differentiation of Enteroendocrine L Cells. Cell Rep. 2020;32.
- Zhao XQ, Guo S, Lu YY, Hua Y, Zhang F, Yan H, et al. Lycium barbarum L. leaves ameliorate type 2 diabetes in rats by modulating metabolic profiles and gut microbiota composition. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121.
- Zhao YQ, Barrere-Cain RE, Yang X. Nutritional systems biology of type 2 diabetes. GENES Nutr. 2015;10.
- Zheng J, Xiao XH, Zhang Q, Yu M, Xu JP, Qi CJ, et al. The programming effects of nutrition-induced catch-up growth on gut microbiota and metabolic diseases in adult mice. Microbiologyopen. 2016;5,296–306.
- Zheng J, Zhang L, Gao Y, Wu HH, Zhang JQ. The dynamic effects of maternal high-calorie diet on glycolipid metabolism and gut microbiota from weaning to adulthood in offspring mice. Front Nutr. 2022;9.
- Zheng JL, Li H, Zhang XJ, Jiang M, Luo CQ, Lu ZM, et al. Prebiotic Mannan-Oligosaccharides Augment the Hypoglycemic Effects of Metformin in Correlation with Modulating Gut Microbiota. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66,5821–31.
- Zheng LX, Chen XQ, Cheong KL. Current trends in marine algae polysaccharides: The digestive tract, microbial catabolism, and prebiotic potential. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;151:344–54.
- Zheng YF, Zhou X, Wang CX, Zhang JL, Chang DN, Liu WJ, et al. Effect of Tanshinone IIA on Gut Microbiome in Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairment. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13.
- Zhong H, Abdullah, Deng LL, Zhao MJ, Tang J, Liu T, et al. Probiotic-fermented blueberry juice prevents obesity and hyperglycemia in high fat diet-fed mice in association with modulating the gut microbiota. FOOD Funct. 2020;11,9192–207.
- Zhong L, Peng XJ, Wu CT, Li Q, Chen YF, Wang M, et al. Polysaccharides and flavonoids from cyclocarya paliurus modulate gut microbiota and attenuate hepatic steatosis, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2022.
- Zhong MW, Li Y, Cheng YG, Liu QR, Hu SY, Zhang GY. Effect of oligofructose on resistance to postoperative high-fat diet-induced damage of metabolism in diabetic rats after sleeve gastrectomy. World J Diabetes. 2021;12,453–65.
- Zhong RT, Chen LB, Liu YY, Xie SX, Li SM, Liu B, et al. Anti-diabetic effect of aloin via JNK-IRS1/PI3K pathways and regulation of gut microbiota. FOOD Sci Hum WELLNESS. 2022;11,189–98.
- Zhou JC, Zhang XW. Akkermansia muciniphila: a promising target for the therapy of metabolic syndrome and related diseases. Chin J Nat Med. 2019;17,835-841 WE-Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI.
- Zhou JJ, Chun L, Liu JF. A Comprehensive Understanding of Dietary Effects on C. elegans Physiology. Curr Med Sci. 2019;39,679–84.
- Zhou, KQ. Strategies to promote abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila, an emerging probiotics in the gut, evidence from dietary intervention studies. J Funct Foods. 2017;33:194–201.
- Zhou LY, Xiao XH, Zhang Q, Zheng J, Li M, Yu M, et al. Improved Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in the Early Life of Female Offspring by Maternal Dietary Genistein Is Associated With Alterations in the Gut Microbiota. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9.
- Zhou WT, Chen GJ, Chen D, Ye H, Zeng XX. The antidiabetic effect and potential mechanisms of natural polysaccharides based on the regulation of gut microbiota. J Funct Foods. 2020;75.
- Zhou WT, Yang TT, Xu WQ, Huang YJ, Ran LW, Yan YM, et al. The polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium barbarum L. confer anti-diabetic effect by regulating gut microbiota and intestinal barrier. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;291.
- Zhou Z, Sun B, Yu DS, Zhu CS. Gut Microbiota: An Important Player in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12.
- Zhu D, Yan QJ, Liu J, Wu X, Jiang ZQ. Can functional oligosaccharides reduce the risk of diabetes mellitus? FASEB J. 2019;33,11655–67.
- Zhu LL, Sha LP, Li K, Wang Z, Wang T, Li YW, et al. Dietary flaxseed oil rich in omega-3 suppresses severity of type 2 diabetes mellitus via anti-inflammation and modulating gut microbiota in rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2020;19.
- Zhu TT, Goodarzi MO. Metabolites Linking the Gut Microbiome with Risk for Type 2 Diabetes. Curr Nutr Rep. 2020;9,83–93.
- Zhu Y, Bai J, Zhang Y, Xiao X, Dong Y. Effects of bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) on the gut microbiota in high fat diet and low dose streptozocin-induced rats. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2016;67,686–95.
- Zhu YY, Dong LE, Huang L, Shi ZX, Dong JL, Yao Y, et al. Effects of oat beta-glucan, oat resistant starch, and the whole oat flour on insulin resistance, inflammation, and gut microbiota in high-fat-diet-induced type 2 diabetic rats. J Funct Foods. 2020;69.
- Zhuang P, Shou QY, Wang WQ, He LL, Wang J, Chen JN, et al. Essential Fatty Acids Linoleic Acid and alpha-Linolenic Acid Sex-Dependently Regulate Glucose Homeostasis in Obesity. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018;62.
- Ziegler MC, Garbim EE, Jahnke VS, Moura JGL, Brasil CS, da Cunha PHS, et al. Impact of probiotic supplementation in a patient with type 2 diabetes on glycemic and lipid profile. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2022;49:264–9.
- Zilli AMH, Zilli EM. Review of Evidence and Perspectives of Flavonoids on Metabolic Syndrome and Neurodegenerative Disease. PROTEIN Pept Lett. 2021;28,725–34.
- Zou H, Zhang M, Zhu XT, Zhu LY, Chen S, Luo MJ, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 Improves Metabolic Disorder in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Associated With Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Front Microbiol. 2022;13.
- Zou J, Reddivari L, Shi ZD, Li SY, Wang YL, Bretin A, et al. Inulin Fermentable Fiber Ameliorates Type I Diabetes via IL22 and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Experimental Models. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12,983–1000.
- Zoumpopoulou G, Pot B, Tsakalidou E, Papadimitriou K. Dairy probiotics: Beyond the role of promoting gut and immune health. Int DAIRY J. 2017;67:46–60.
- owie CC, Casagrande SS, Geiss LS. Prevalence and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes. Diabetes Am [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 Apr 27]; Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK568004/.
- Mojsak P, Rey-Stolle F, Parfieniuk E, Kretowski A, Ciborowski M. The role of gut microbiota (GM) and GM-related metabolites in diabetes and obesity. A review of analytical methods used to measure GM-related metabolites in fecal samples with a focus on metabolites’ derivatization step. J Pharm Biomed Anal [Internet]. 2020 Nov 30 [cited 2023 Apr 27];191. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32971497/.
- Wang L, Yu X, Xu X, Ming J, Wang Z, Gao B, et al. The Fecal Microbiota Is Already Altered in Normoglycemic Individuals Who Go on to Have Type 2 Diabetes. Front Cell Infect Microbiol [Internet]. 2021 Feb 18 [cited 2023 Nov 9];11:1. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC7930378/.
- Dash NR, Al Bataineh MT. Metagenomic Analysis of the Gut Microbiome Reveals Enrichment of Menaquinones (Vitamin K2) Pathway in Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab J [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Nov 9];45,77. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC7850878/.
- Chester B, Babu JR, Greene MW, Geetha T. The effects of popular diets on type 2 diabetes management. Diabetes Metab Res Rev [Internet]. 2019 Nov 1 [cited 2023 Apr 27];35. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31121637/.
- Yamamoto JM, Kellett JE, Balsells M, García-Patterson A, Hadar E, Solà I, et al. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Examining the Impact of Modified Dietary Interventions on Maternal Glucose Control and Neonatal Birth Weight. Diabetes Care [Internet]. 2018 Jul 1 [cited 2023 Apr 27];41,1346–61. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29934478/.
- Sami W, Ansari T, Butt NS, Hamid MRA. Effect of diet on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 Nov 9];11,65. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC5426415/.
- Pintarič M, Langerholc T. Probiotic Mechanisms Affecting Glucose Homeostasis: A Scoping Review. Life [Internet]. 2022 Aug 1 [cited 2023 Nov 9];12. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC9409775/.
- Mahboobi S, Rahimi F, Jafarnejad S. Effects of Prebiotic and Synbiotic Supplementation on Glycaemia and Lipid Profile in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv Pharm Bull [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 Nov 9];8,565. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC6311648/.
- Zhang L, Zhang H, Xie Q, Xiong S, Jin F, Zhou F, et al. A bibliometric study of global trends in diabetes and gut flora research from 2011 to 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 21;13:2645.
- Wang L, Peng W, Zhao Z, Zhang M, Shi Z, Song Z, et al. Prevalence and Treatment of Diabetes in China, 2013-2018. JAMA [Internet]. 2021 Dec 28 [cited 2023 Apr 27];326,2498–506. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34962526/.
- Chan JCN, Zhang Y, Ning G. Diabetes in China: a societal solution for a personal challenge. lancet Diabetes Endocrinol [Internet]. 2014 Dec 1 [cited 2023 Apr 27];2,969–79. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25218728/.
- Tian J, Li M, Lian F, Tong X. The hundred most-cited publications in microbiota of diabetes research A bibliometric analysis. 2017 [cited 2023 Apr 27]; Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007338. [CrossRef]
- leming DM, Schellevis FG, Van Casteren V. The prevalence of known diabetes in eight European countries. Eur J Public Health [Internet]. 2004 Mar [cited 2023 Apr 27];14,10–4. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15080383/.
- Reed J, Bain S, Kanamarlapudi V. A Review of Current Trends with Type 2 Diabetes Epidemiology, Aetiology, Pathogenesis, Treatments and Future Perspectives. Diabetes, Metab Syndr Obes Targets Ther [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Apr 27];14:3567. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC8369920/.
- ildner G. Are rats more human than mice? Immunobiology [Internet]. 2019 Jan 1 [cited 2023 Apr 27];224,172–6. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30342883/.
- Cunningham AL, Stephens JW, Harris DA. Gut microbiota influence in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Gut Pathog [Internet]. 2021 Dec 1 [cited 2023 Jun 24];13. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC8343927/.
- Shan Z, Rehm CD, Rogers G, Ruan M, Wang DD, Hu FB, et al. Trends in Dietary Carbohydrate, Protein, and Fat Intake and Diet Quality Among US Adults, 1999-2016. JAMA [Internet]. 2019 Sep 9 [cited 2023 Dec 30];322,1178. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC6763999/.
- Merra G, Noce A, Marrone G, Cintoni M, Tarsitano MG, Capacci A, et al. Influence of Mediterranean Diet on Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients [Internet]. 2021 Jan 1 [cited 2023 Dec 30];13,1–12. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC7822000/.
- Dolpady J, Sorini C, Di Pietro C, Cosorich I, Ferrarese R, Saita D, et al. Oral Probiotic VSL#3 Prevents Autoimmune Diabetes by Modulating Microbiota and Promoting Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-Enriched Tolerogenic Intestinal Environment. J Diabetes Res [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2023 Nov 9];2016. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC4686713/.
- McRae MP. Dietary Fiber Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses. J Chiropr Med [Internet]. 2018 Mar 1 [cited 2023 Nov 9];17,44. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC5883628/.
- Dehghan P, Gargari BP, Asgharijafarabadi M. Effects of High Performance Inulin Supplementation on Glycemic Status and Lipid Profile in Women with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Heal Promot Perspect [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 Nov 9];3,55. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC3963683/.
- Chen J, Raymond K. Beta-glucans in the treatment of diabetes and associated cardiovascular risks. Vasc Health Risk Manag [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2023 Nov 9];4,1265. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC2663451/.
- Zhu D, Yan Q, Liu J, Wu X, Jiang Z. Can functional oligosaccharides reduce the risk of diabetes mellitus? FASEB J [Internet]. 2019 Nov 1 [cited 2023 Nov 9];33,11655. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC6902710/.
- Gurung M, Li ZP, You H, Rodrigues R, Jump DB, Morgun A, et al. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBIOMEDICINE. 2020;51.
- Canfora EE, Jocken JW, Blaak EE. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat Rev Endocrinol [Internet]. 2015 Oct 19 [cited 2023 Jun 23];11,577–91. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26260141/.
- Cui J, Ramesh G, Wu M, Jensen ET, Crago O, Bertoni AG, et al. Butyrate-Producing Bacteria and Insulin Homeostasis: The Microbiome and Insulin Longitudinal Evaluation Study (MILES). Diabetes [Internet]. 2022 Nov 1 [cited 2023 Jun 23];71,2438–46. Available from. [CrossRef]
- Paul P, Kaul R, Harfouche M, Arabi M, Al-Najjar Y, Sarkar A, et al. The effect of microbiome-modulating probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics on glucose homeostasis in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of clinical trials. Pharmacol Res. 2022 Nov 1;185:106520.
- Paul P, Kaul R, Abdellatif B, Arabi M, Upadhyay R, Saliba R, et al. The Promising Role of Microbiome Therapy on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic and Narrative Review. Front Nutr. 2022 May 25;9:906243.
- Al-Najjar Y, Arabi M, Paul P, Chaari A. Can probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic supplementation modulate the gut-liver axis in type 2 diabetes? A narrative and systematic review of clinical trials. Front Nutr. 2022 Dec 1;9:1052619.
- Paul P, Kaul R, Chaari A. Renal Health Improvement in Diabetes through Microbiome Modulation of the Gut–Kidney Axis with Biotics: A Systematic and Narrative Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2022 Dec 1 [cited 2023 Jun 23];23,14838. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/23/23/14838/htm.
- Kaul R, Paul P, Harfouche M, Saliba R, Chaari A. Microbiome-modulating nutraceuticals ameliorate dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of clinical trials. Diabetes Metab Res Rev [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Nov 10];e3675. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/dmrr.3675.
- Hills RD, Pontefract BA, Mishcon HR, Black CA, Sutton SC, Theberge CR. Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease. Nutrients [Internet]. 2019 Jul 1 [cited 2023 Nov 9];11. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC6682904/.
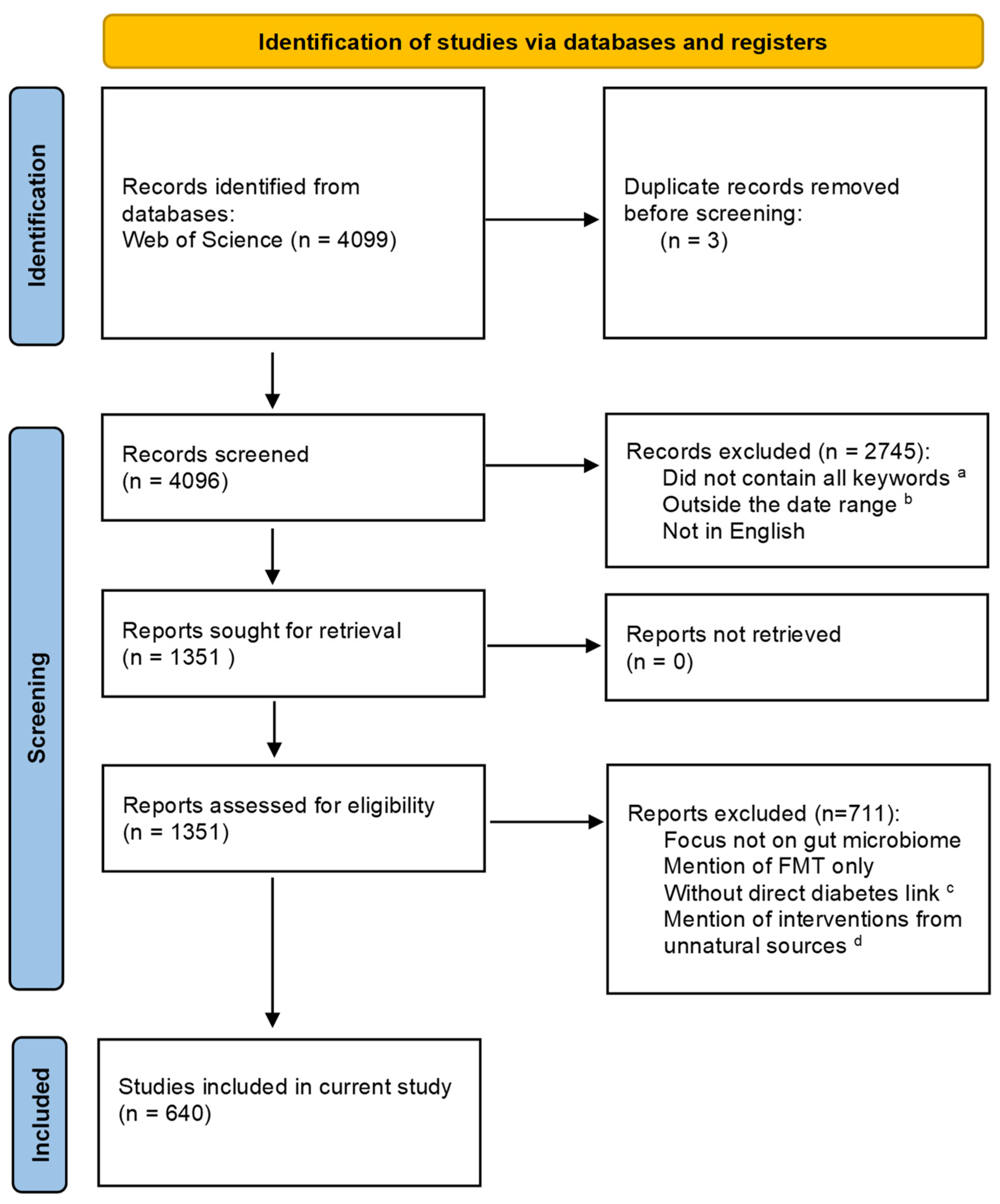
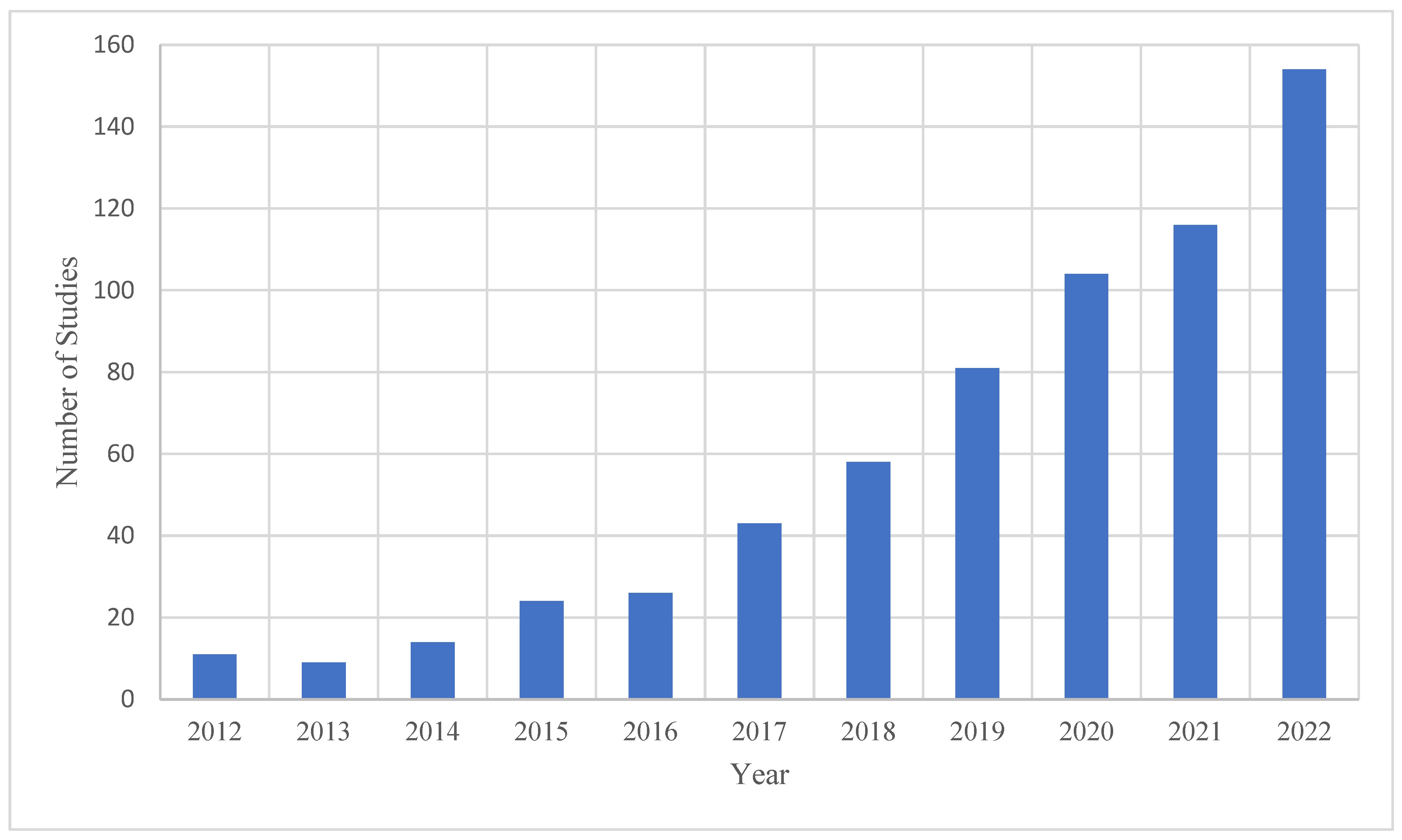
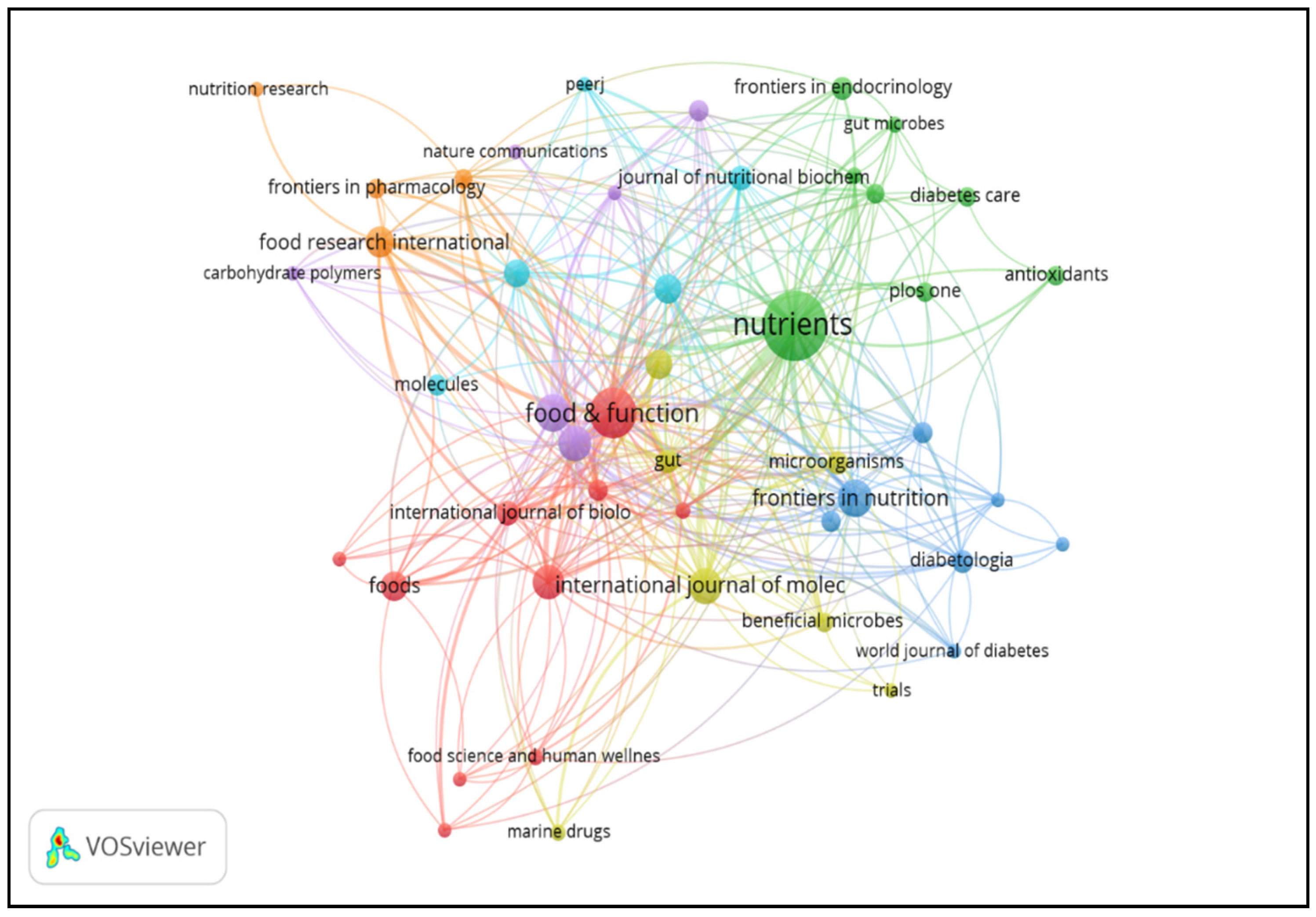
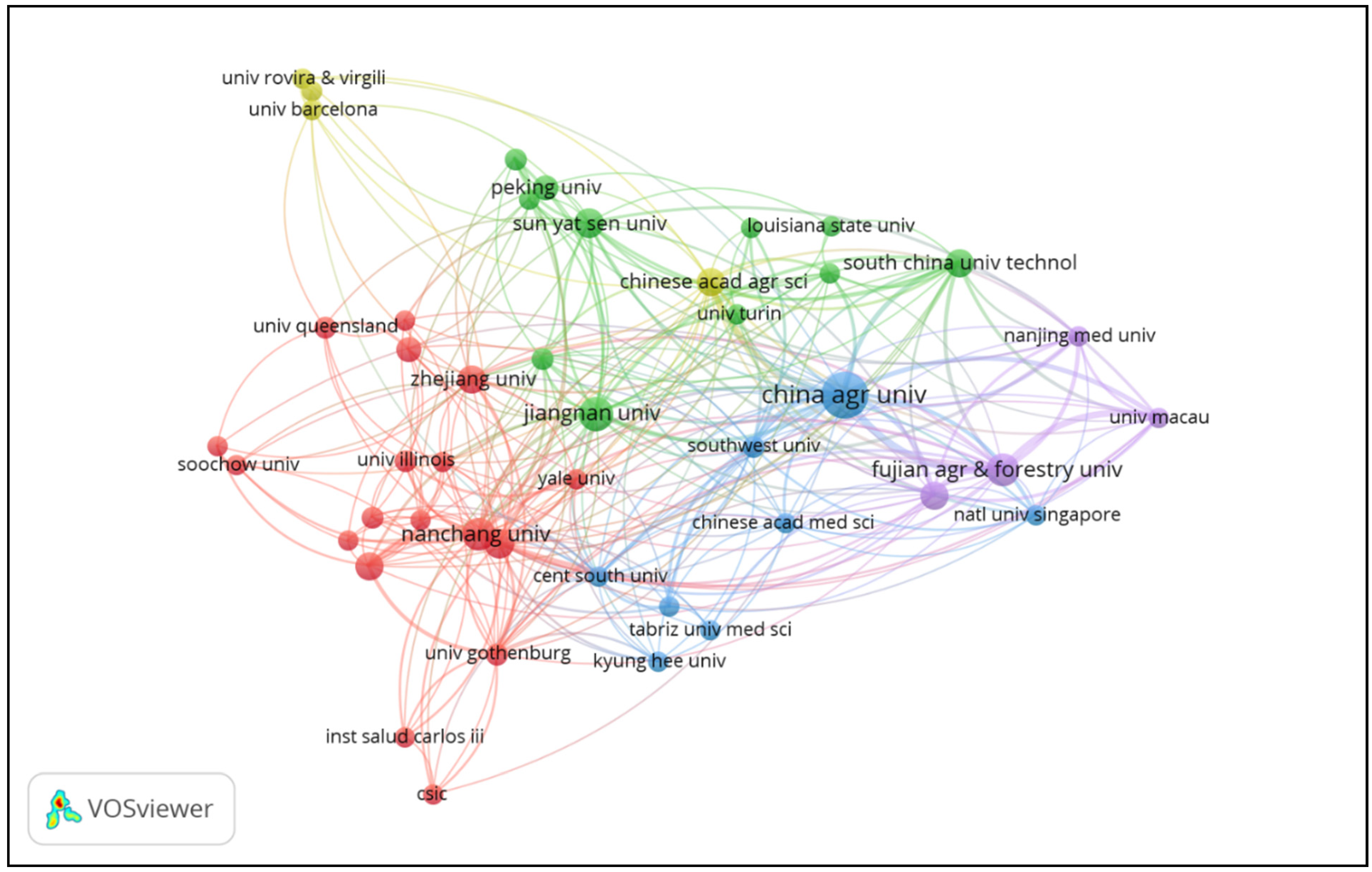
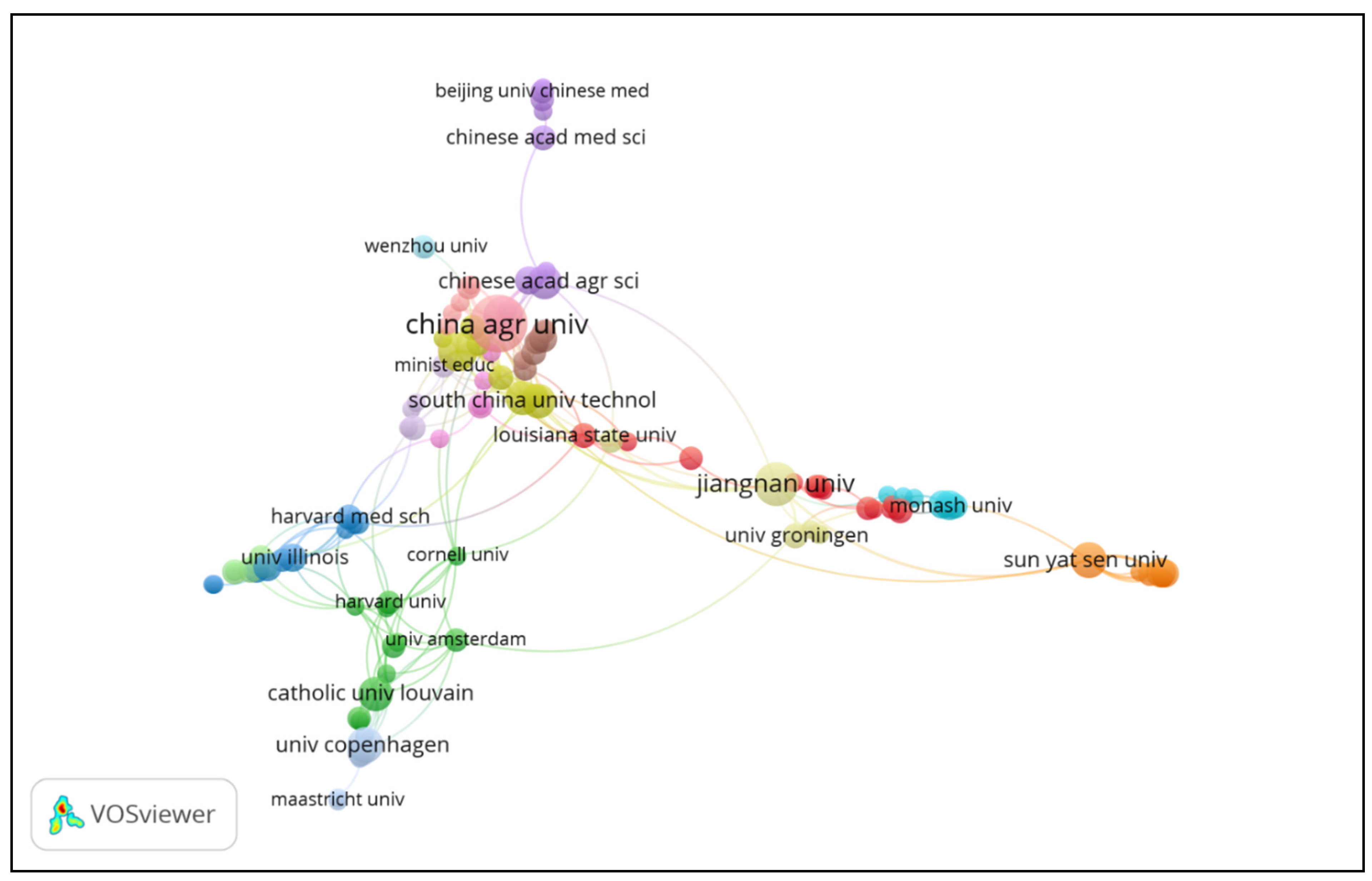
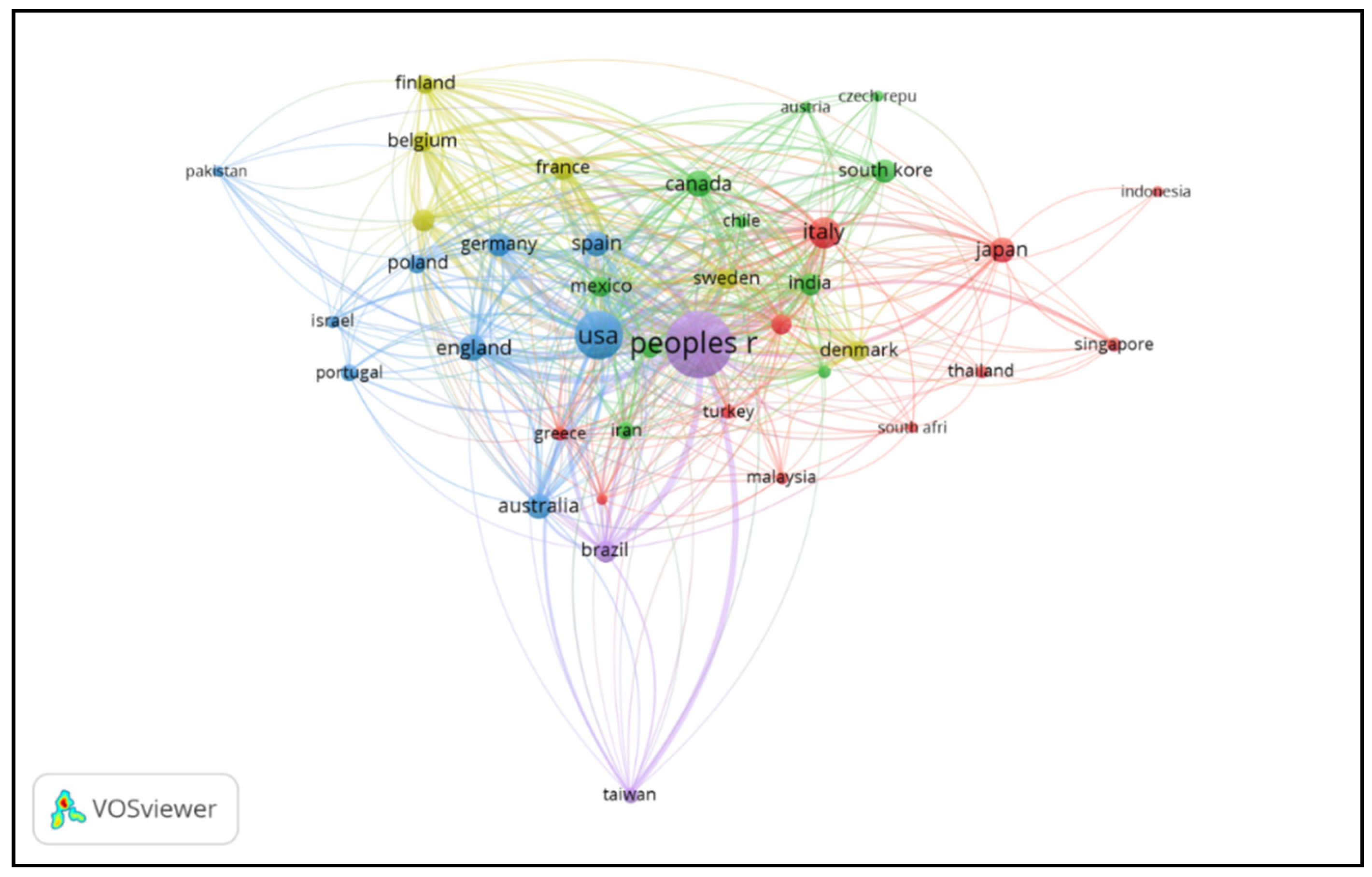
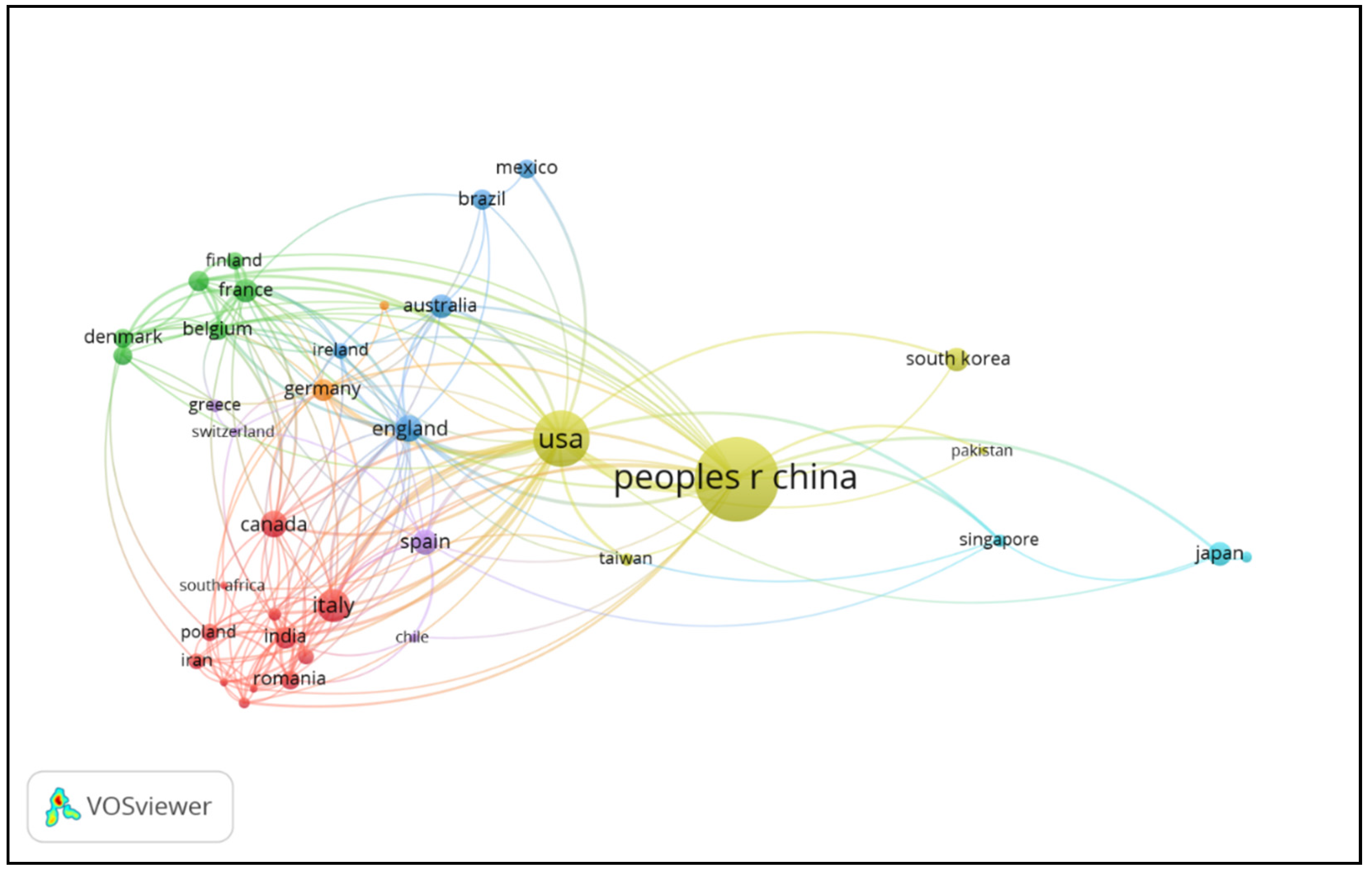
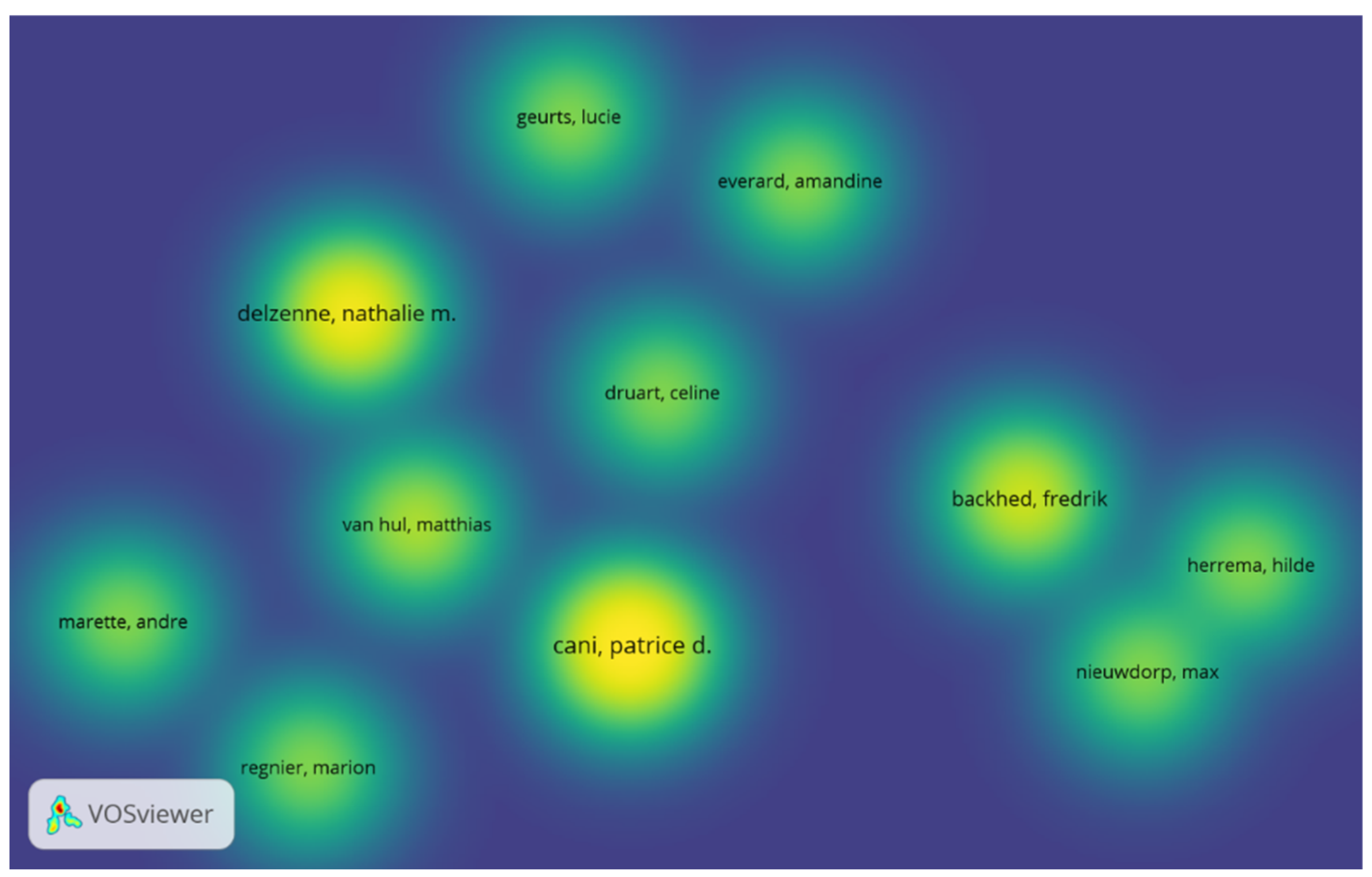
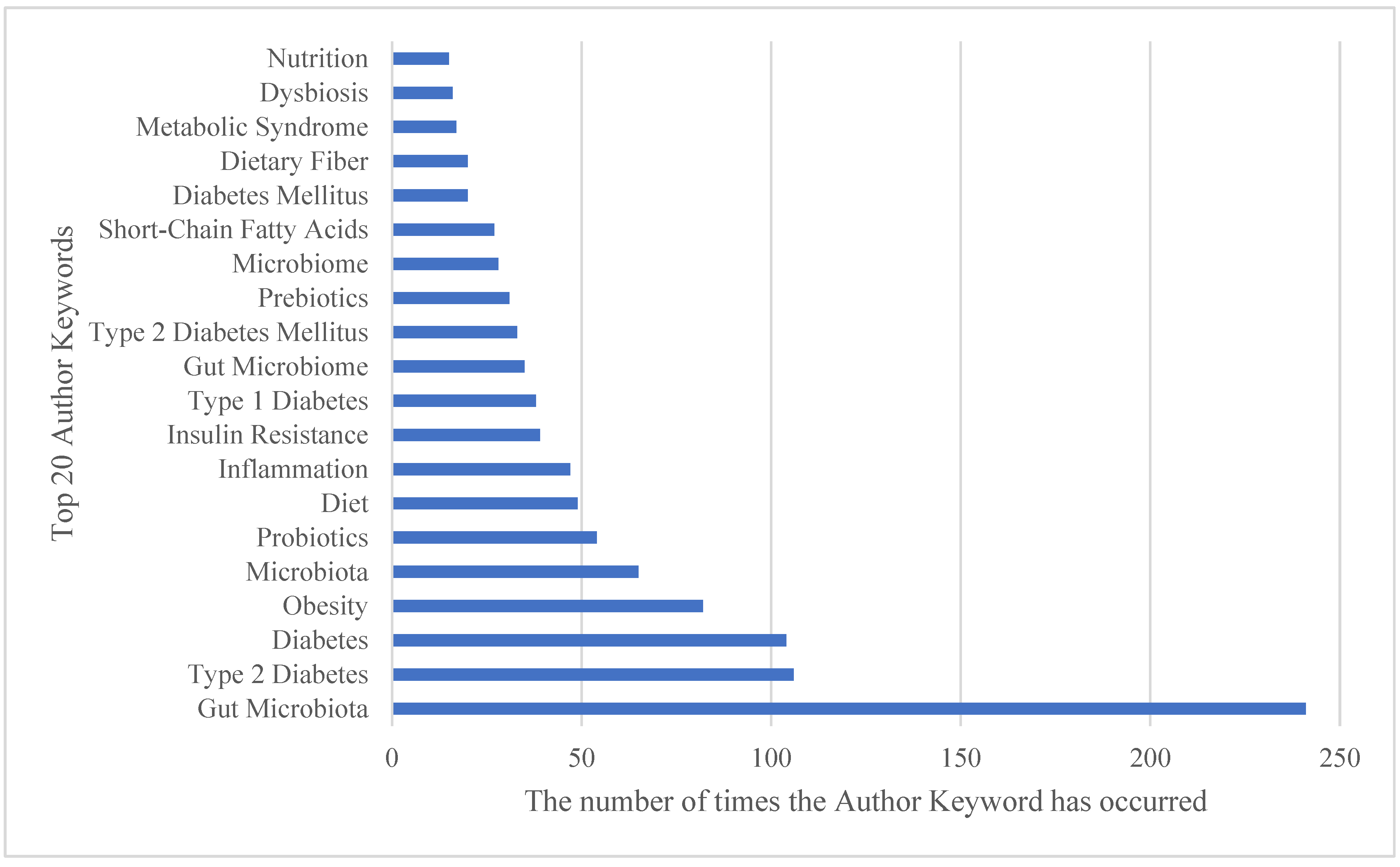
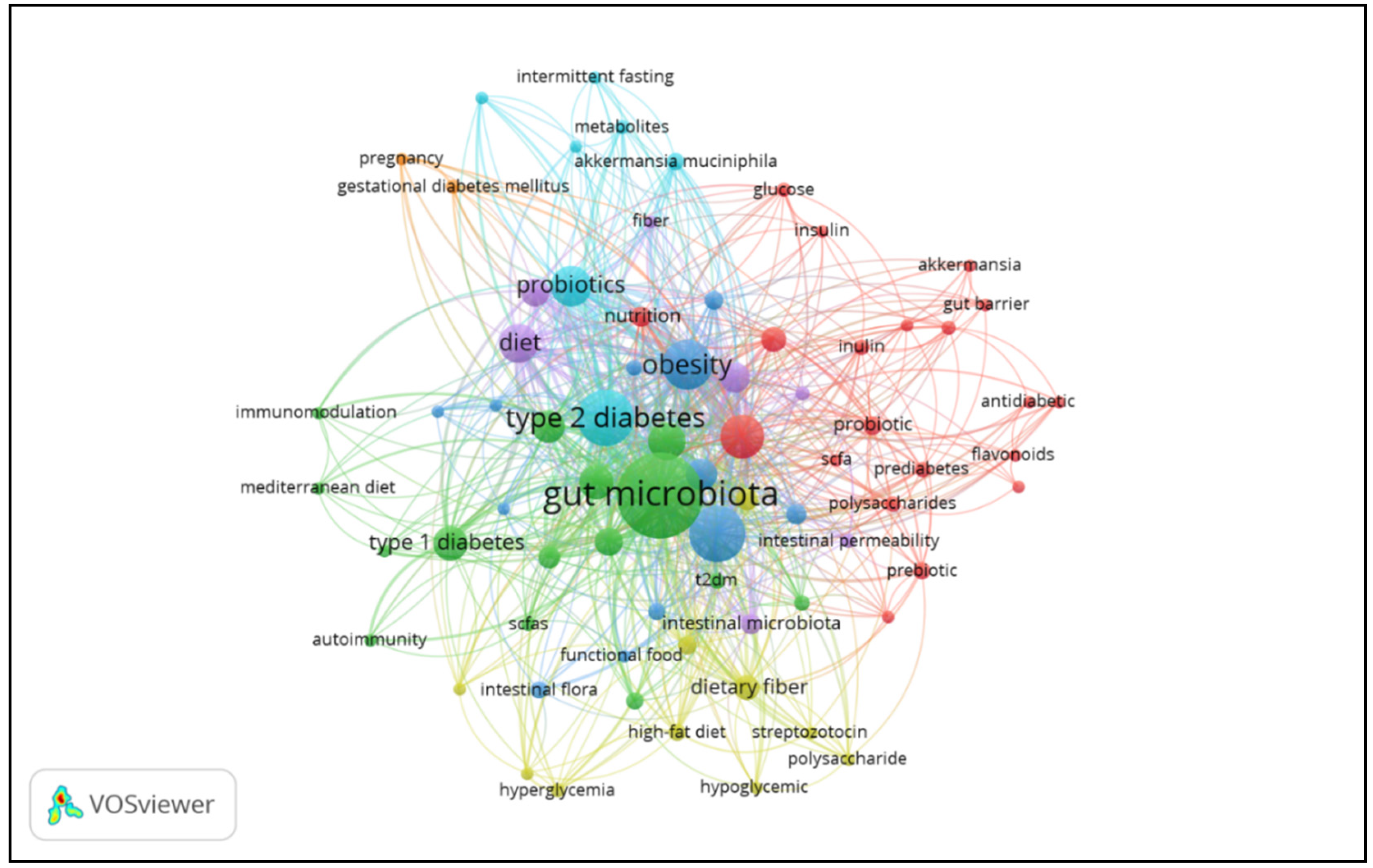
| Journals | Documents, n |
|---|---|
| Nutrients | 63 |
| Food & Function | 34 |
| Frontiers in Nutrition | 19 |
| Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry | 19 |
| International Journal of Molecular Sciences | 18 |
| Molecular Nutrition & Food Research | 17 |
| Journal of Functional Foods | 15 |
| Food Research International | 14 |
| Scientific Reports | 12 |
| FOODS | 11 |
| Frontiers in Microbiology | 11 |
| Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy | 8 |
| Frontiers in Endocrinology | 8 |
| Country | Frequency Tally |
|---|---|
| China | 188 |
| United States | 41 |
| Japan | 13 |
| South Korea | 13 |
| Iran | 7 |
| Spain | 7 |
| Australia | 6 |
| Canada | 6 |
| France | 6 |
| Poland | 6 |
| Author | Title of the Paper | Times cited | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tremaroli et al., 2012 | Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism | 2704 | (471) |
| Zeevi et al., 2015 | Personalized Nutrition by Prediction of Glycemic Responses | 1214 | (609) |
| Singh et al., 2017 | Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health | 1008 | (416) |
| Plovier et al., 2017 | A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice | 932 | (355) |
| Anhe et al., 2015 | A polyphenol-rich cranberry extract protects from diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and intestinal inflammation in association with increased Akkermansia spp. population in the gut microbiota of mice | 700 | (37) |
| Serino et al., 2012 | Metabolic adaptation to a high-fat diet is associated with a change in the gut microbiota | 416 | (401) |
| Fraga et al., 2019 | The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health | 399 | (121) |
| Hartstra et al., 2015 | Insights Into the Role of the Microbiome in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes | 378 | (168) |
| Marino et al., 2017 | Gut microbial metabolites limit the frequency of autoimmune T cells and protect against type 1 diabetes | 366 | (279) |
| Ussar et al., 2015 | Interactions between Gut Microbiota, Host Genetics and Diet Modulate the Predisposition to Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome | 348 | (480) |
| Study Design | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Randomized controlled trial | 207 |
| Literature review | 157 |
| Non-randomized experimental study | 54 |
| Case control study | 53 |
| Systematic review | 26 |
| Experiment | 25 |
| Cohort study | 19 |
| Cross-sectional study | 13 |
| Meta-analysis/Systematic review | 7 |
| Type of experimental subject | Frequency Tally |
|---|---|
| Animal | 278 |
| Human | 138 |
| Human, animal | 14 |
| In Vitro, mice | 2 |
| In Vitro, rats | 1 |
| In Vitro, human | 1 |
| Animal/Human subjects | Frequency Tally |
|---|---|
| Mice | 183 |
| Human | 138 |
| Rats | 83 |
| Mice, Humans | 7 |
| Mice, Rats | 4 |
| Mice, Rats, Humans | 3 |
| Animal, Human | 2 |
| Hamsters | 1 |
| Mice, Piglets | 1 |
| Mice, Rabbits, Humans | 1 |
| Mice, Rats, Rodents | 1 |
| Pigs (piglets & swine) | 1 |
| Rats, Human | 1 |
| Rodents | 1 |
| Rodents, Swine | 1 |
| Animals (unspecified) | 2 |
| Type of Diabetes | Frequency Tally |
|---|---|
| Type 2 Diabetes | 397 |
| Type 1 Diabetes | 69 |
| Gestational Diabetes Mellitus | 17 |
| Prediabetes | 17 |
| Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes | 15 |
| Type 2 Diabetes, Prediabetes | 7 |
| Diabetic Nephropathy | 6 |
| Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 Diabetes | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





