INTRODUCTION
Inflammation is a natural immune response to injury, infection, or irritation [
1,
2]. However, persistent inflammation can lead to organ dysfunction [
2,
3], contributing to several major diseases [
4], indicating the need for the development of effective treatment for inflammation.
Sepsis is defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by dysregulation of the host response to infection resulting in organ dysfunction and failure [
5,
6]. Upon recognizing an infection, immune cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells express pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) to initiate host defense. Pathogen and damage-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs and DAMPs, respectively) interact with toll-like receptors (TLRs) to induce inflammation and cytokine storm [
5,
6,
7]. NF-κB activation by these interactions leads to excessive cytokine production, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and nitric oxide (NOx) [
5,
6,
7]. Inflammatory cytokines induce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), damaging cells, DNA, and tissues [
8,
9]. Additionally, ROS activate signaling pathways, thereby inducing inflammatory responses and tissue damage [
10,
11]. However, hyperinflammatory responses can be treated using anti-inflammatory drugs; therefore, the discovery of novel anti-inflammatory drugs may provide an effective treatment strategy for inflammatory diseases.
In the early 1980s, idebenone was developed to treat cognitive decline and dementia [
12]. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), which has antioxidant activity, faces solubility and absorption issues [
13,
14]. Therefore, idebenone was developed to address the solubility issue of CoQ10 and enhance mitochondrial electron transport, ATP synthesis, and energy metabolism, improve ROS scavenging, and reduce oxidative stress. Although idebenone shows therapeutic promise for neuro-inflammation and other conditions [
15,
16], its effects in systemic inflammatory diseases are yet to be elucidated. Idebenone transfers electrons within the mitochondrial respiratory chain [
17] and serves as a fat-soluble antioxidant, scavenging ROS and influencing cell metabolism [
18]. Previous studies have found that CoQ10 regulates the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α [
19]. Given that idebenone is similar to CoQ10, we hypothesized that idebenone may also modulate the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Idebenone is globally utilized in clinical trials and treatments [
20] and has demonstrated therapeutic potential in various conditions, such as LHON, dementia, skin aging, and Friedrich's ataxia [
21,
22,
23].
Although idebenone has shown therapeutic effects in neuroinflammation and other diseases, its effect in systemic inflammatory diseases is yet to be elucidated. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of idebenone in murine models of cecal ligation puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced systemic inflammation and LPS-induced macrophage cell lines.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents and Antibodies
Idebenone (15475), mito-TEMPO (16621), and diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI; 81050) were purchased from Cayman Chemical Company (MI, USA). LPS (L2630) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (MO, USA) and N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; A0905) was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co. (Tokyo, Japan). The following antibodies were used for western blotting and immunohistochemical analyses: β-actin (sc-47778), SOD1 (sc-11407), SOD2 (sc-30080), Catalase (sc-50508), and α-tubulin (sc-8035) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA); iNOS (13120s), COX-2 (12282s), TNF-α (3707s), IL-1β (12242s), IκBα (4812s), p- IκBα (2859s), IKKβ (2370s), p-IKKβ (2078s), p65 (8242s), p38 (8690s), p-p38 (4511s), JNK (9252s), p-JNK (4668s), ERK (4695s), p-ERK (4370p), AKT (4691s), and p-AKT (4060s) (Cell Signaling Technology Co., MA, USA); and Lamin A (ab26300) (Abcam Ltd., Cambridge, UK). Permount was purchased from Fisher Scientific (New Jersey, USA).
Animal Experimentations
All animal handling and experimentations were in accordance with ethical guidelines and approved by the Animal Care and Use Institutional Review Committee of Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (approval number: KRIBB-AEC-22254). Eight-week-old female C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Orient (Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea) and maintained under standard conditions. For LPS induction of inflammation, idebenone-treated (10 mg/kg) or untreated mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (10 mg/kg, in a 100 μL volume of sterile saline). For Cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) induction of sepsis, CLP was surgically performed on mice according to the original protocol developed by Lee et al. [
24], with some modifications. Briefly, the mice were anesthetized using an intraperitoneal injection of avertin (500 mg/kg). A midline incision was made, and the cecum was ligated 1 cm from the apex and punctured (one hole) using a 23-G needle. Thereafter, a small fecal mass from the punctured cecum was gently squeezed out to ensure patency. The cecum was relocated, and 6-0 sutures were used to close the peritoneum and skin. Mice in the sham group underwent incision and cecal exteriorization only. At 24 h after the sham and CLP operations, the mice were either injected with 1 mL of idebenone (10 mg/kg) prepared in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) or with 1 mL of PBS only. Survival rate was assessed every 12 h over 5 days (CLP) and 12 days (LPS). Pre- and post-operatively, all mice had unlimited access to food and water.
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
Mouse tissue in lung, liver, kidney, and colon was cut into 7-µm thick sections, followed by histochemical staining using H&E. Tissue sections were deparaffinization using graded concentrations of xylene (100, 95, and 70%) for 5 min each. For nuclear staining, the sections were stained with hematoxylin solution for 5 min and washed with flowing water. Haematoxylin was removed using 1% HCl and 1% ammonia solutions, followed by immersion in an eosin solution for 2 min to stain the cytoplasm. Thereafter, the sections were dehydrated using graded concentrations of alcohol (70, 95, and 100%), followed by treatment with xylene three times (3 min each) to remove alcohol. Finally, the sections were mounted with glass coverslips and viewed using an Olympus BX43 microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Photographs were taken with an Olympus DP72 camera (Olympus).
Immunohistochemistry for iNOS
Immunohistochemical staining was performed on 4–6 μm thick sections that were fixed in 10% formalin and paraffin-embedded. Briefly, the sections were deparaffinized by washing three times with (5 min each), followed by treatment with graded concentrations of alcohol (100, 95, and 70%) for 10 min each. After rinsing twice with distilled water (dH2O) for 5 min, the sections were treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 min to block peroxidase activity. After washing twice with dH2O for 5 min each, the sections were blocked with 200 µL of blocking solution for 1 h at room temperature (25°C), followed by incubation with 200 µL of primary antibody against iNOS overnight at 4 °C. Thereafter, the samples were washed three times with wash buffer for 5 min, followed by incubation with 200 µL of secondary antibody for 30 min at RT. After washing three times with wash buffer for 5 min, the samples were treated with ABC reagent kit (Mouse IgG PK-6102, Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). Thereafter, the sections were washed three times with wash buffer and stained with 100 µL of DAB, rinse twice with dH2O for 5 min, treated twice with 95% ethanol for 10 s, and then twice in 100% ethanol. Finally, the samples were treated with xylene twice for 10 s each, mounted with coverslips, and viewed using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany), the LSM 510 META module, and 20× lenses. icroscope. Images were processed using the Start LSM Image Browser.
Cells and Cell Culture
The murine macrophage cell lines Raw 264.7 and J774A.1 were obtained from the Korean Cell Line Bank (Seoul, Korea). RAW 264.7 cells were, was cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (SH30243.01, Hyclone, UT, USA) supplemented with 10% calf serum (26170-043, GibcoTM, MA, USA) and 1% antibiotics (LS 203-01, WELGENE Inc., Gyeongsan, Korea). The J774A.1 cell line was cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (SH30243.01, Hyclone, UT, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (SH30919.03, Hyclone, UT, USA), 1% antibiotics (LS 203-01, WELGENE Inc., Gyeongsan, Korea), and 25 mM HEPES (15630-080, GibcoTM, MA, USA) at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. The cells were treated with LPS at 1 μg/ml.
Western Blot Analysis
Total cell lysates and Tissue were lysed on ice using radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer and 1X protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich) for 30 min. The protein contents of cell and tissue lysates were quantified using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay kit (23209, Thermo Scientific, IL, USA). Thereafter, proteins (10–50 μg) were separated on a 6–15% gel via sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane using a Trans-Blot® TurboTM Transfer pack (Bio-Rad, CA, USA). The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk/TBST for 1 h and incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C. After three washes, membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies for 40 min at RT. After washing for 2 h, the protein bands were visualized using Clarity Western ECL Substrate (1705061; Bio-Rad, CA, USA).
Determination of the Concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and PGE2
The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the culture medium were determined using the Duoset ELISA system (DY410, DY406 and DY401, R&D Systems, MN, USA). PGE2 concentration was determined using PGE2 ELISA kit (514010, Cayman Chemicals, MI, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a SpectraMax ABS Plus microplate reader (Molecular Devices, CA, USA).
Immunofluorescence Assay
RAW 264.7 cells were grown on 12-mm cover glasses in 12-well culture plates containing DMEM, followed by pretreatment with idebenone (20 μM) for 2 h and treatment with LPS (1 μg/mL). After 1 h, the cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min, and permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 in PBS for 20 min. Thereafter, the cells were blocked with 3% BSA for 1 h, followed by incubation with the appropriate primary antibody overnight at 4°C. After washing, the cells were incubated with an Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated secondary antibody (A-21442, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for 30 min. After washing twice with PBS, the cells were mounted with Vectashield mounting medium containing DAPI (H-1500, Vector Laboratories, CA, USA), and images were acquired using a fluorescence microscope (Olympus, BX53, NY, USA).
Measurement of ROS Production
ROS production by Raw 264.7 cells was detected using a DCFDA/H2DCFDA-Cellular ROS Assay kit (ab113851, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were seeded in six– well plates (35 mm plates) at a density of 1 × 106 cells/well, followed by treatment with LPS (1 μg/mL), idebenone (5, 10, 20, and 40 μM), N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) (5 mM), mito-TEMPO (50 μM), and Diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI) (10 μM). The cells were harvested using trypsin and washed with cold PBS. Finally, the cells were stained with 20 μM of 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFDA) for 20 min and analyzed using a NovoCyte Flow Cytometer (150014, Agilent Technologies Inc., CA, USA).
Lipid Peroxidation Assay
The malondialdehyde (MDA) content of the cell lysates was assessed using a lipid peroxidation assay kit (ab83366, Abcam, CA, UK), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Statistical Analysis
Quantitative data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Significant differences between groups were determined using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. Statistical significance was set at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and #p < 0.001.
DISCUSSION
Idebenone, a synthetic derivative of CoQ10, has received considerable attention owing to its potential use in various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders. However, recent findings suggest that idebenone exerts anti-inflammatory effect [
15,
25]. Therefore, we conducted in vitro and in vivo experiments to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of idebenone.
CoQ10 treatment has been shown to reduce joint inflammation and inflammatory cytokine levels and improve histopathological outcomes in arthritis models [
26]. Similarly, idebenone treatment showed protective effects in an acute lung injury model by suppressing both inflammation and oxidative stress [
27]. Additionally, idebenone treatment reduced proinflammatory cytokine levels and ER stress in the colon in a murine model of chronic colitis. Consistent with previous findings [
28], idebenone treatment improved tissue conditions and decreased the levels of inflammatory cytokines and NOx in mice models of CLP-induced sepsis and LPS-induced inflammation in the present study. Collectively, these findings indicate that idebenone has therapeutic efficacy in inflammatory models.
The anti-inflammatory effects of idebenone appear to be associated with its multifaceted mechanisms of action. For instance, idebenone exerts antioxidant effects to relieve oxidative stress. This is a characteristic of inflammatory reactions. Similarly, idebenone exerted significant ROS scavenging activity in the present study, which was comparable to those of several ROS inhibitors. The antioxidants SOD and catalase are responsible for the direct removal of active superoxide radicals to protect against lipid peroxidation [
29,
30]. Consistent with previous findings [
31,
32], idebenone treatment restored LPS-induced increase in the activity of antioxidant enzymes to normal in the present study.
The ability of Idebenone to scavenge ROS and reduce oxidative stress may influence the activation of the NF-κB pathway. During ROS scavenging, idebenone can potentially inhibit upstream events that trigger NF-κB activation, thus preventing the subsequent transcription of proinflammatory genes. Thus, the inhibition of ROS production may suppress the phosphorylation of the NF-κB signaling pathway [
33]. This ROS-modulating property of idebenone aligns with the observed suppression of proinflammatory cytokines, suggesting a potential link between ROS and NF-κB inhibition. Additionally, the ability of idebenone to preserve mitochondrial function may indirectly affect inflammation. Healthy mitochondria potentially function in cellular homeostasis, immune regulation, and inflammatory pathways [
34]. In the present study, both
in vivo and
in vitro experiments confirmed that idebenone inhibited the expression of inflammatory cytokines and NOx induced by inflammatory diseases. Several in vitro studies have explored the effects of idebenone on inflammatory pathways. Given that the NF-κB pathway regulates the expression of various anti-inflammatory cytokines, we examined the effect of idebenone on the NF-κB pathway in this study. Idebenone inhibits NF-κB activation, which suppresses the production of interleukin and TNF-α [
35]. Similarly, idebenone treatment inhibited NF-κB phosphorylation and the expression of inflammatory cytokines in the present study. Collectively, these findings suggest the anti-inflammatory potential of idebenone at the molecular level.
Collectively, this study confirmed that idebenone has therapeutic effects in mice models of CLP-induced sepsis and LPS-induced inflammation, including increased survival rate, tissue damage recovery, and reduced expression of inflammatory genes. Additionally, in vitro experiments showed that idebenone treatment ameliorated inflammatory response in macrophages by suppressing LPS-induced expression of inflammatory genes, inhibiting activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, and suppressing ROS production. Overall, these results suggest a novel role for idebenone as an anti-inflammatory agent in inflammatory diseases. However, an extensive understanding of the mechanisms and clinical implications of idebenone is necessary to facilitate clinical application in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Therefore, comprehensive clinical trials are required to validate these findings in humans.
Author Contributions
Yumin Choi, Young-Lai Cho contributed equally to this work. Conceptualization, Y.C., Y-L.C. and S-J.L.; Methodology, Y.C, Y-L.C., M.K.P., S.J.P., M.J.K. and I-A. L.; Validation, M.K.P., Y-J.P, S.W.C, H.D.L, and S-J.L. Fortmat Analysis, Y.C., ; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, Y.C.; Writing – Review & Editing, S-J.L.; Visualization, Y.C.; Supervision, S-J.L.; Project Administration, S-J.L.; Funding Acquisition, S-J.L.
Figure 1.
Idebenone prevents inflammation-induced mortality and inflammatory responses and restores tissue damage in vivo. Idebenone decreased the mortality rate of mice with CLP-induced sepsis and LPS-induced inflammation. (A) Mice were subjected to CLP or sham operation, and then intraperitoneally injected with idebenone (10 mg/kg). Mortality in the CLP + phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; sham operation, white) and CLP + idebenone (black) groups was monitored daily for five days after surgery. (B) C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (20 mg/kg), followed by treatment with idebenone (10 mg/kg). Mortality in the LPS only (white box) and LPS + idebenone (black box) groups was monitored daily for 12 days after injection (n = 10/group). Idebenone protects against inflammation-induced tissue damaged in mice with CLP-induced sepsis and LPS-induced inflammation. (C) iNOS expression in the lung, liver, kidney, and colon tissues of mice in the sham and CLP + idebenone groups was examined using immunohistochemical analysis. (D) H&E staining was performed to examine histological changes in the lung, liver, kidney, and colon tissues of mice in sham and LPS + idebenone groups. All tissues were collected in each group at 24 h after CLP surgery and LPS injection, with or without idebenone administration.
Figure 1.
Idebenone prevents inflammation-induced mortality and inflammatory responses and restores tissue damage in vivo. Idebenone decreased the mortality rate of mice with CLP-induced sepsis and LPS-induced inflammation. (A) Mice were subjected to CLP or sham operation, and then intraperitoneally injected with idebenone (10 mg/kg). Mortality in the CLP + phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; sham operation, white) and CLP + idebenone (black) groups was monitored daily for five days after surgery. (B) C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (20 mg/kg), followed by treatment with idebenone (10 mg/kg). Mortality in the LPS only (white box) and LPS + idebenone (black box) groups was monitored daily for 12 days after injection (n = 10/group). Idebenone protects against inflammation-induced tissue damaged in mice with CLP-induced sepsis and LPS-induced inflammation. (C) iNOS expression in the lung, liver, kidney, and colon tissues of mice in the sham and CLP + idebenone groups was examined using immunohistochemical analysis. (D) H&E staining was performed to examine histological changes in the lung, liver, kidney, and colon tissues of mice in sham and LPS + idebenone groups. All tissues were collected in each group at 24 h after CLP surgery and LPS injection, with or without idebenone administration.
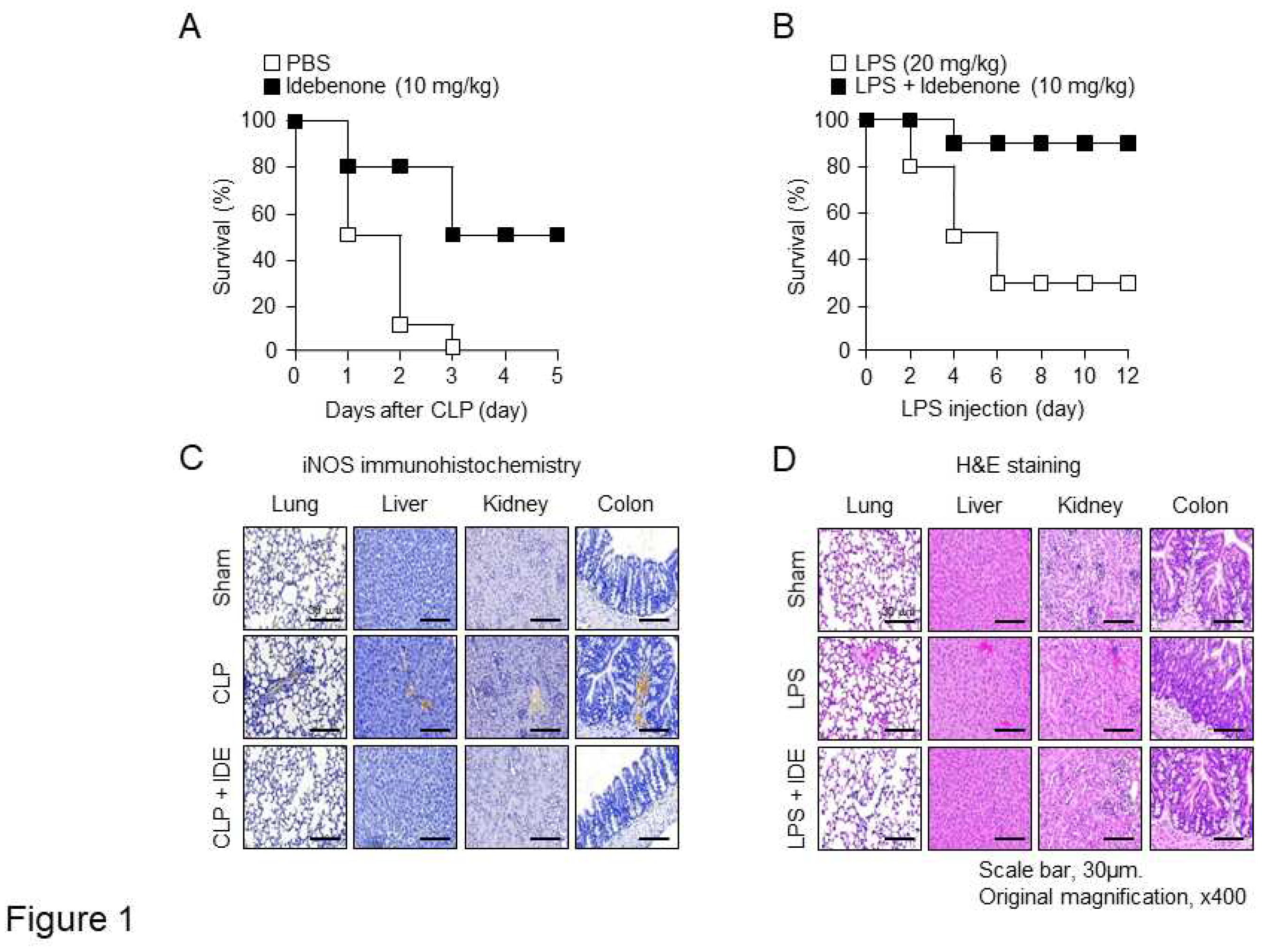
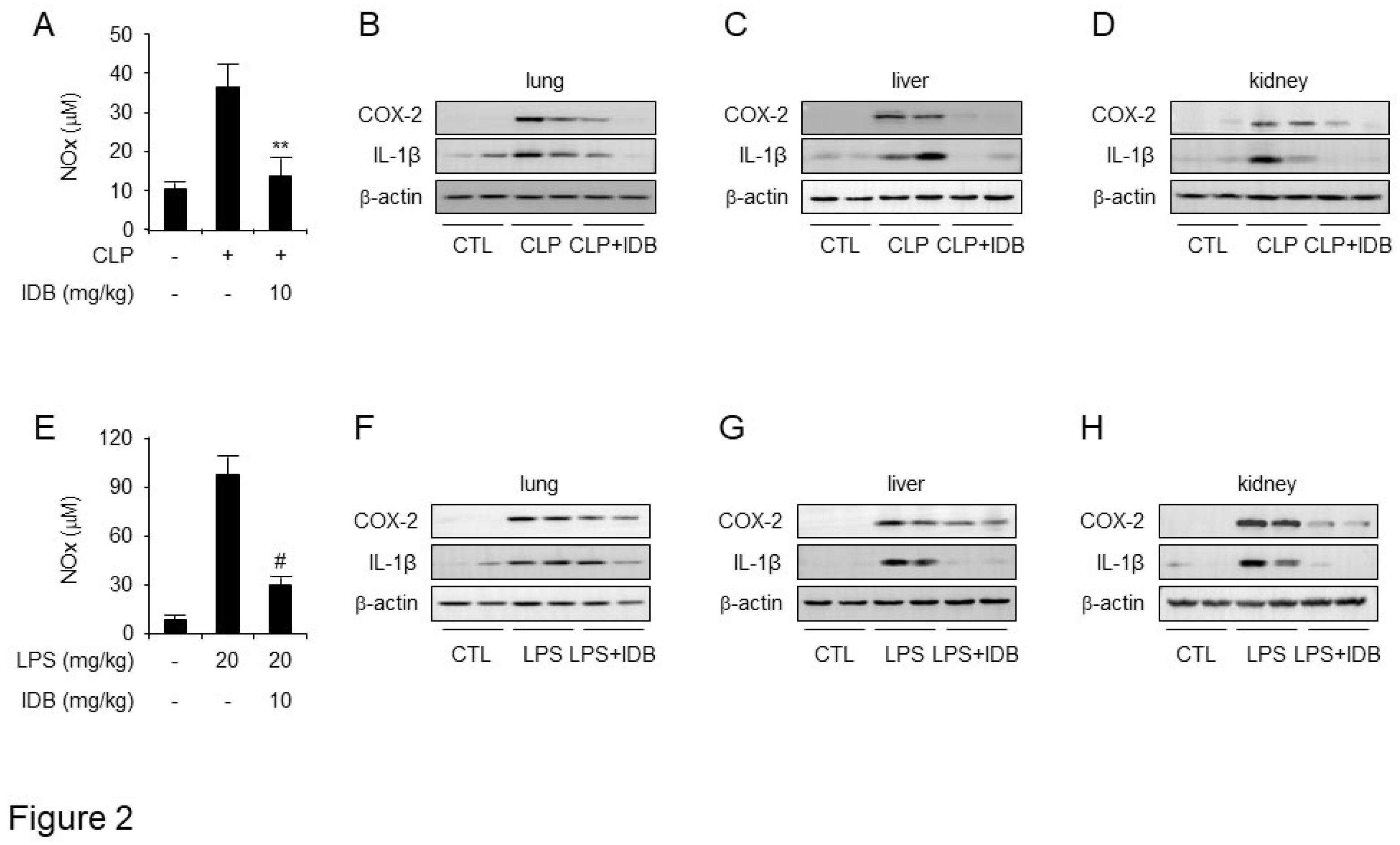
Figure 2.
Idebenone inhibits CLP- and LPS-induced inflammatory responses. Idebenone inhibits NO metabolites (NO), COX-2, and IL-1β levels in murine models of CLP- and LPS-induced inflammatory models. The secretion of NO metabolites after CLP (A) and LPS (E) were determined using NO assay. Protein expression of COX-2 and IL-1β in the (B) lung, (C) liver, and (D) kidney tissues of mice in the sham, CLP, and CLP + idebenone groups was analyzed using western blotting. Protein expression of COX-2 and IL-1β in the (F) lung, (G) liver, and (H) kidney tissues of mice in the sham, LPS only, and LPS + idebenone groups was analyzed using western blotting. All tissues were randomly collected from two mice per group at 24 h after CLP and LPS; β-actin was used as a loading control; Statistical analyses were performed using paired two-tailed Student’s t-test. **p < 0.01, #p < 0.001.
Figure 2.
Idebenone inhibits CLP- and LPS-induced inflammatory responses. Idebenone inhibits NO metabolites (NO), COX-2, and IL-1β levels in murine models of CLP- and LPS-induced inflammatory models. The secretion of NO metabolites after CLP (A) and LPS (E) were determined using NO assay. Protein expression of COX-2 and IL-1β in the (B) lung, (C) liver, and (D) kidney tissues of mice in the sham, CLP, and CLP + idebenone groups was analyzed using western blotting. Protein expression of COX-2 and IL-1β in the (F) lung, (G) liver, and (H) kidney tissues of mice in the sham, LPS only, and LPS + idebenone groups was analyzed using western blotting. All tissues were randomly collected from two mice per group at 24 h after CLP and LPS; β-actin was used as a loading control; Statistical analyses were performed using paired two-tailed Student’s t-test. **p < 0.01, #p < 0.001.
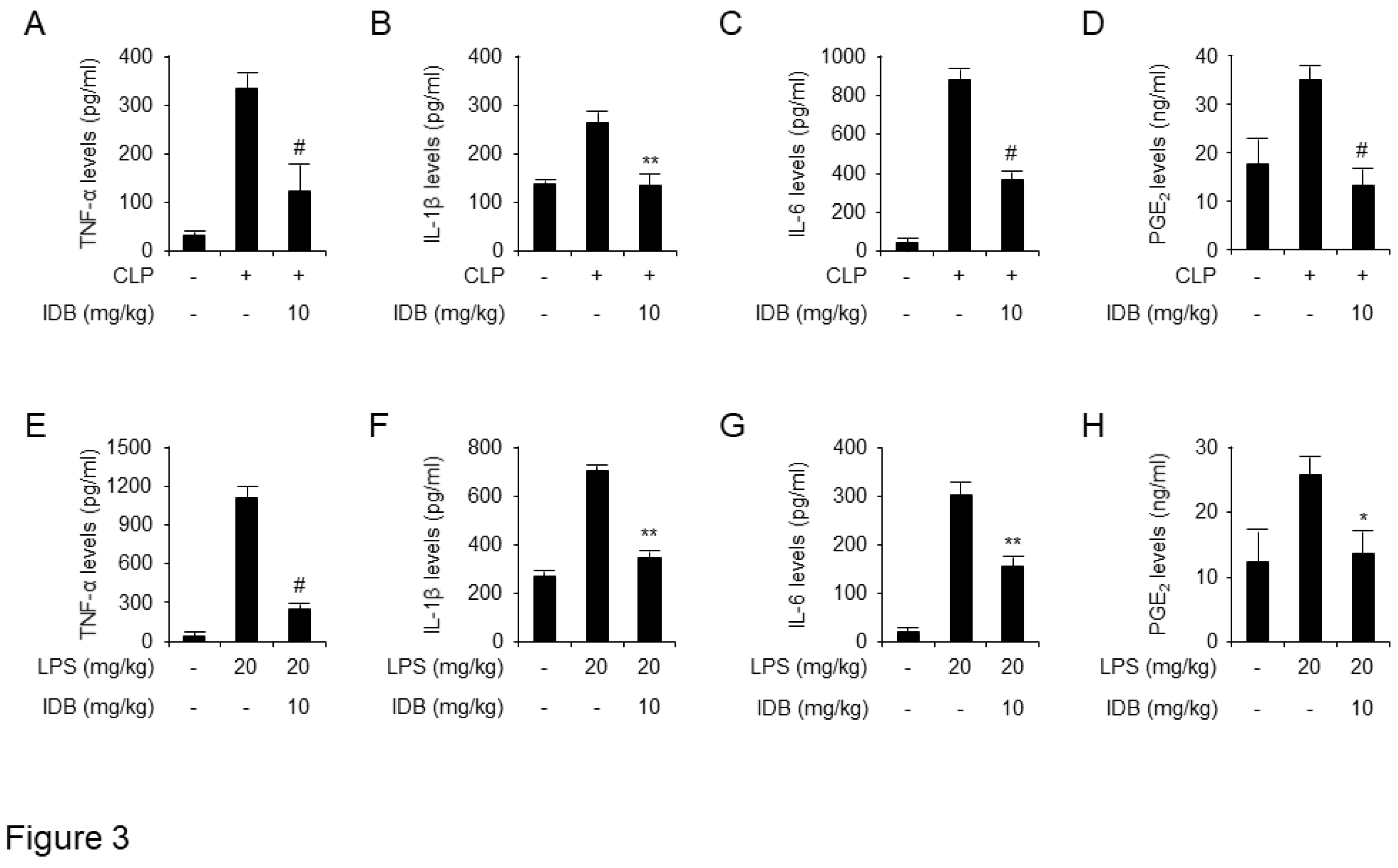
Figure 3.
Idebenone inhibits the inflammatory response in mouse models of CLP- and LPS-induced inflammation. Idebenone inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and PGE2 production in CLP- and LPS-induced inflammatory disease models. Serum levels of (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-1β, (C) IL-6 and (D) PGE2 following treatment with or without idebenone after CLP were determined using ELISA assay. Serum levels of (E) TNF-α, (F) IL-1β, (G) IL-6, and (H) PGE2 following treatment with or without idebenone after LPS injection were determined using ELISA assay. n = 3/group; Graph represents mean of three independent mouse serums levels of indicated mediator and cytokines. Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, #p < 0.001.
Figure 3.
Idebenone inhibits the inflammatory response in mouse models of CLP- and LPS-induced inflammation. Idebenone inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and PGE2 production in CLP- and LPS-induced inflammatory disease models. Serum levels of (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-1β, (C) IL-6 and (D) PGE2 following treatment with or without idebenone after CLP were determined using ELISA assay. Serum levels of (E) TNF-α, (F) IL-1β, (G) IL-6, and (H) PGE2 following treatment with or without idebenone after LPS injection were determined using ELISA assay. n = 3/group; Graph represents mean of three independent mouse serums levels of indicated mediator and cytokines. Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, #p < 0.001.
Figure 4.
Idebenone inhibits LPS-induced expression of pro-inflammatory mediators in RAW 264.7 cells. Idebenone inhibited LPS-induced increase in the levels NO metabolites, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and PGE2 in RAW 264.7 cells. (A) NO metabolite secretion was assessed using Griess reagent. (B) Western blotting was used to analyze the protein expression of inflammatory enzymes (iNOS, COX-2) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α) in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells in the presence or absence of idebenone (1, 5, 10, 20 μM). Cells were pretreated with idebenone (1, 5, 10, 20 μM) for 2 h before LPS treatment (1 μg/mL). After 18 h, the cells were harvested for western blotting, with β-actin as the loading control. The expression of (C) TNF-α, (D) IL-1β, (E) IL-6, and (F) PGE2 in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells in the presence or absence of idebenone was determined using ELISA assay. Graphs depict the mean of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using paired two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05, #p < 0.001.
Figure 4.
Idebenone inhibits LPS-induced expression of pro-inflammatory mediators in RAW 264.7 cells. Idebenone inhibited LPS-induced increase in the levels NO metabolites, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and PGE2 in RAW 264.7 cells. (A) NO metabolite secretion was assessed using Griess reagent. (B) Western blotting was used to analyze the protein expression of inflammatory enzymes (iNOS, COX-2) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α) in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells in the presence or absence of idebenone (1, 5, 10, 20 μM). Cells were pretreated with idebenone (1, 5, 10, 20 μM) for 2 h before LPS treatment (1 μg/mL). After 18 h, the cells were harvested for western blotting, with β-actin as the loading control. The expression of (C) TNF-α, (D) IL-1β, (E) IL-6, and (F) PGE2 in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells in the presence or absence of idebenone was determined using ELISA assay. Graphs depict the mean of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using paired two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05, #p < 0.001.
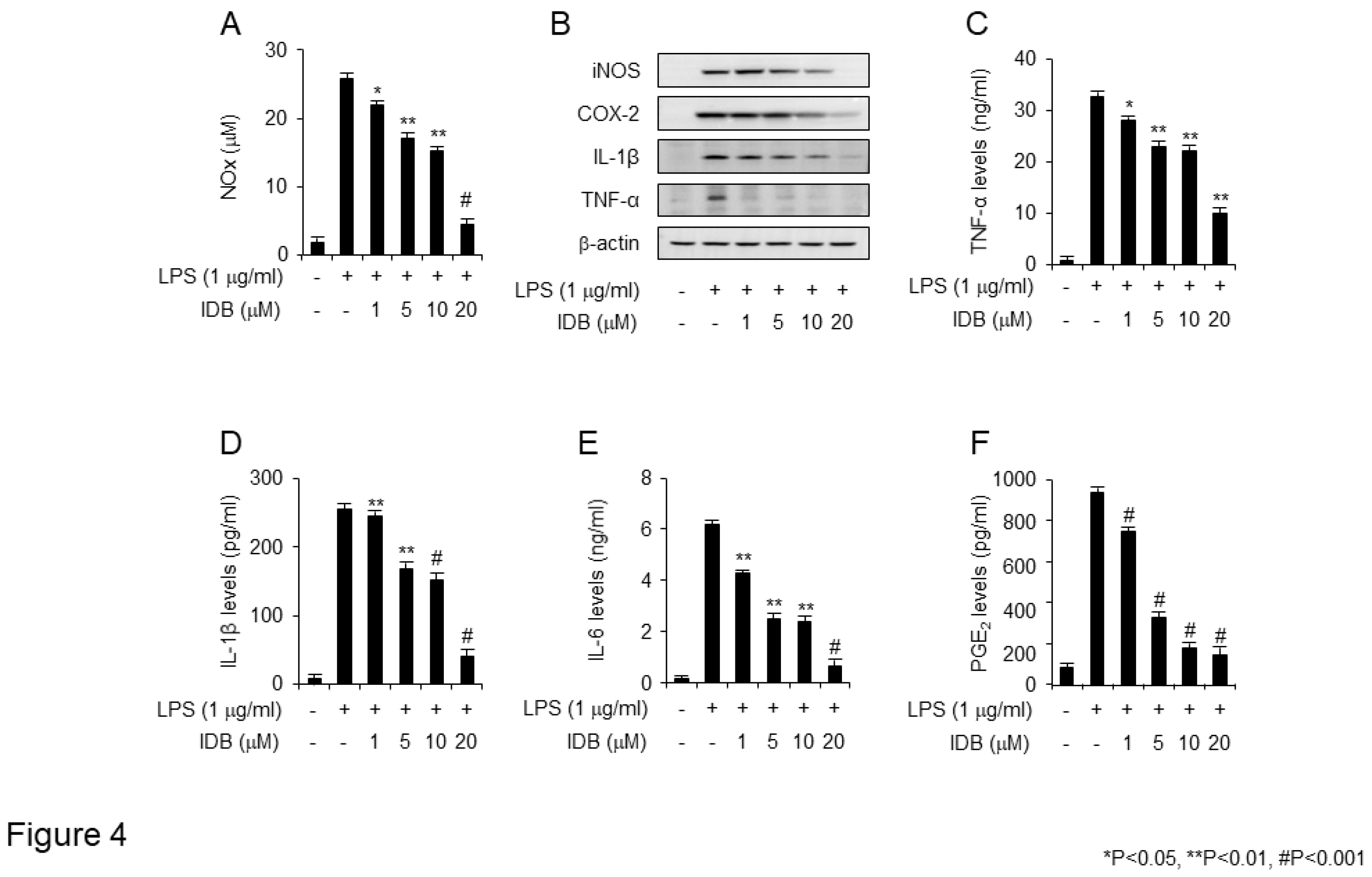
Figure 5.
Idebenone inhibits LPS-induced activation of NF-κB in macrophages. (A) The phosphorylation levels of IκBα and (B) IKKβ in RAW 264.7 cell was examined using western blotting analysis. The cells were pre-incubated with or without idebenone (20 μM) for 2 h and subsequently treated with 1 μg/mL of LPS for the indicated times. (C) Western blot analysis for p65 expression in the cytosol and nuclear fraction of RAW 264.7 cells treated with or without idebenone (20 μM), followed by stimulation with 1 μg/mL of LPS for 30 min; Lamin A and tubulin were used as nuclear and cytosolic fraction loading controls. (D) Nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 subunit in RAW 264.7 cells pretreated with or without 20 μM of idebenone for 2 h, followed by stimulation with 1 μg/mL of LPS for 30 min, was detected using immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar = 50 μm. (E) The phosphorylation levels of AKT, ERK, JNK, and p38 in macrophages was examined using western blotting analysis. Macrophages were pre-incubated with or without idebenone (20 μM) for 2 h and subsequently stimulateed with 1 μg/mL of LPS for the indicated times; β-actin was used as a loading control.
Figure 5.
Idebenone inhibits LPS-induced activation of NF-κB in macrophages. (A) The phosphorylation levels of IκBα and (B) IKKβ in RAW 264.7 cell was examined using western blotting analysis. The cells were pre-incubated with or without idebenone (20 μM) for 2 h and subsequently treated with 1 μg/mL of LPS for the indicated times. (C) Western blot analysis for p65 expression in the cytosol and nuclear fraction of RAW 264.7 cells treated with or without idebenone (20 μM), followed by stimulation with 1 μg/mL of LPS for 30 min; Lamin A and tubulin were used as nuclear and cytosolic fraction loading controls. (D) Nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 subunit in RAW 264.7 cells pretreated with or without 20 μM of idebenone for 2 h, followed by stimulation with 1 μg/mL of LPS for 30 min, was detected using immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar = 50 μm. (E) The phosphorylation levels of AKT, ERK, JNK, and p38 in macrophages was examined using western blotting analysis. Macrophages were pre-incubated with or without idebenone (20 μM) for 2 h and subsequently stimulateed with 1 μg/mL of LPS for the indicated times; β-actin was used as a loading control.
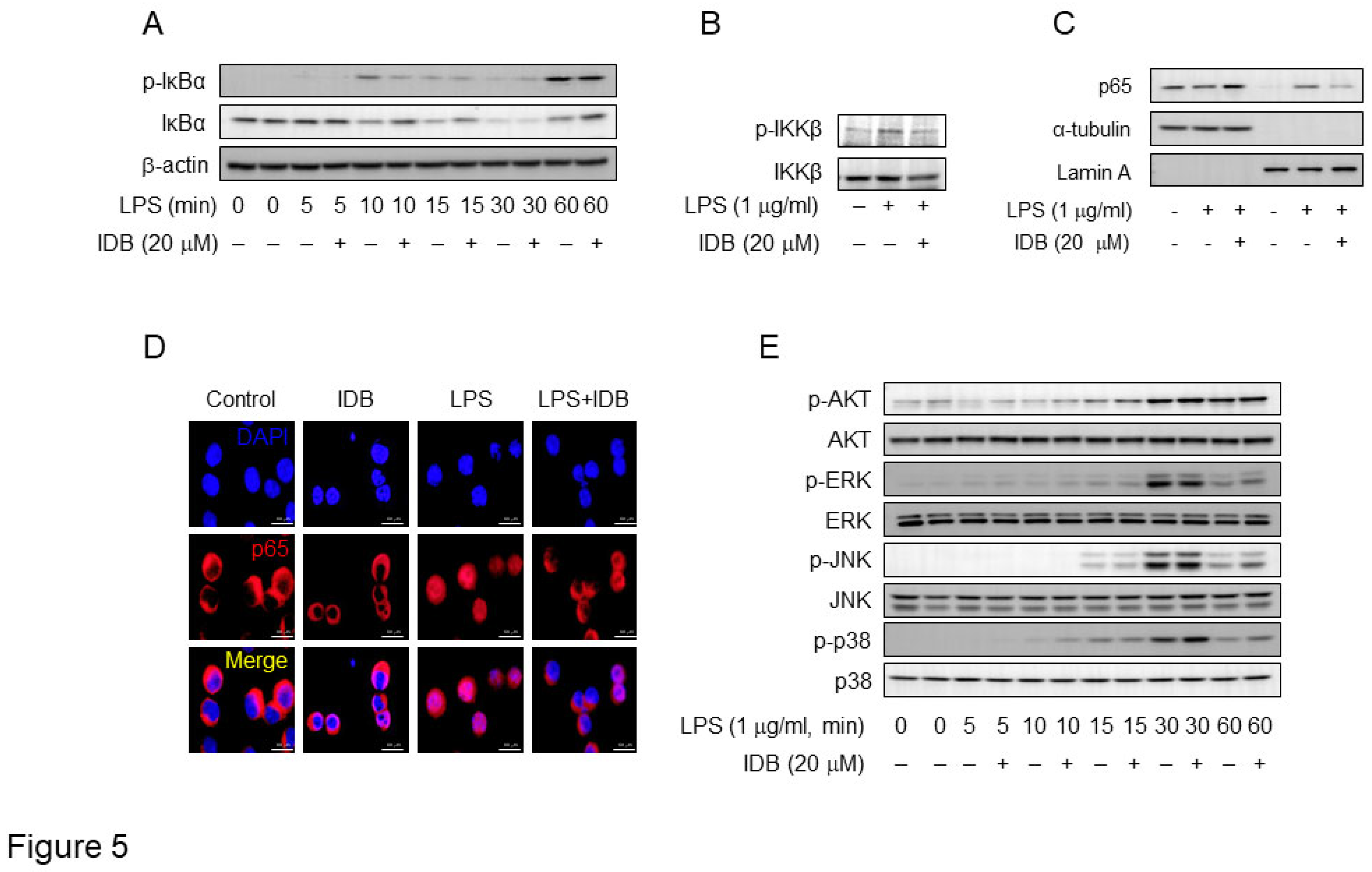
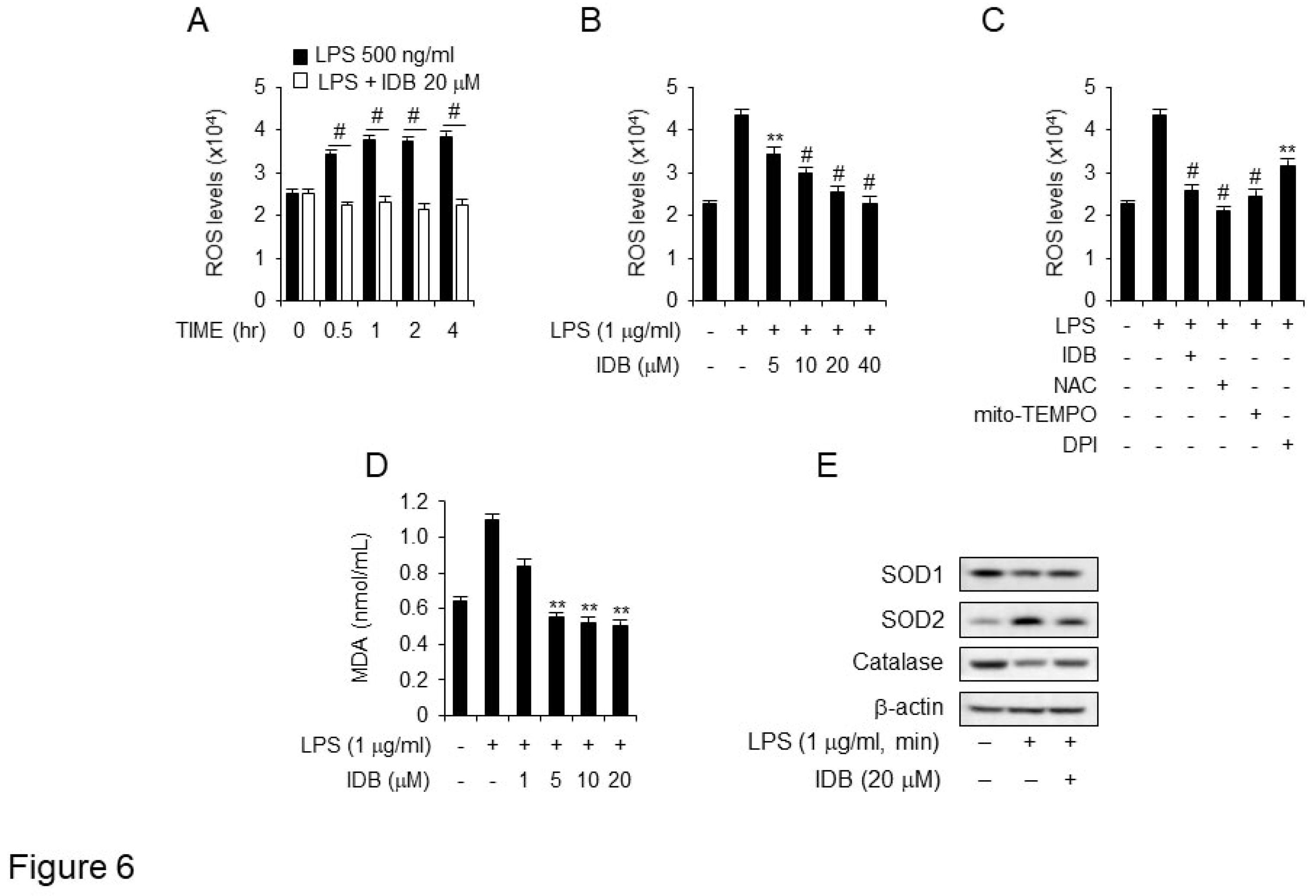
Figure 6.
Idebenone suppresses ROS generation and lipid peroxidation in LPS-induced macrophage. (A) ROS production in DCFDA-stained RAW 264.7 cells was detected using flow cytometry. The cells were preincubated with or without 20 μM of idebenone for 2 h, followed by incubation with medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for indicated times. (B) The cells were preincubated with or without of idebenone (5, 10, 20, 40 μM) for 2 h, and then incubated with a medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for 2 h. (C) The cells were preincubated with 20 μM of idebenone and the ROS inhibitors NAC (5 mM), mito-TEMPO (50 μM), and DPI (10 μM) for 2 h, followed by incubation in a medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for 2 h. (D) MDA production in Raw 264.7 cells was measured using lipid peroxidation assay kit. The cells were preincubated with idebenone (1, 5, 10, 20 μM) for 2 h, followed by incubation in a medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for 12 h. (E) Raw 264.7 cells were harvested, and the levels of SOD1 [Superoxide dismutase 1 (Cu-Zn)], SOD2 [Superoxide Dismutase 2 (MnSOD)], and catalase were measured using western blotting. The cells were pretreated with 20 μM of idebenone for 2 h, followed by incubation in a medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for 12 h. Statistical analyses were performed using paired two-tailed Student’s t-test. **p < 0.01, #p < 0.001.
Figure 6.
Idebenone suppresses ROS generation and lipid peroxidation in LPS-induced macrophage. (A) ROS production in DCFDA-stained RAW 264.7 cells was detected using flow cytometry. The cells were preincubated with or without 20 μM of idebenone for 2 h, followed by incubation with medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for indicated times. (B) The cells were preincubated with or without of idebenone (5, 10, 20, 40 μM) for 2 h, and then incubated with a medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for 2 h. (C) The cells were preincubated with 20 μM of idebenone and the ROS inhibitors NAC (5 mM), mito-TEMPO (50 μM), and DPI (10 μM) for 2 h, followed by incubation in a medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for 2 h. (D) MDA production in Raw 264.7 cells was measured using lipid peroxidation assay kit. The cells were preincubated with idebenone (1, 5, 10, 20 μM) for 2 h, followed by incubation in a medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for 12 h. (E) Raw 264.7 cells were harvested, and the levels of SOD1 [Superoxide dismutase 1 (Cu-Zn)], SOD2 [Superoxide Dismutase 2 (MnSOD)], and catalase were measured using western blotting. The cells were pretreated with 20 μM of idebenone for 2 h, followed by incubation in a medium containing 1 μg/mL of LPS for 12 h. Statistical analyses were performed using paired two-tailed Student’s t-test. **p < 0.01, #p < 0.001.