Submitted:
27 December 2023
Posted:
28 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
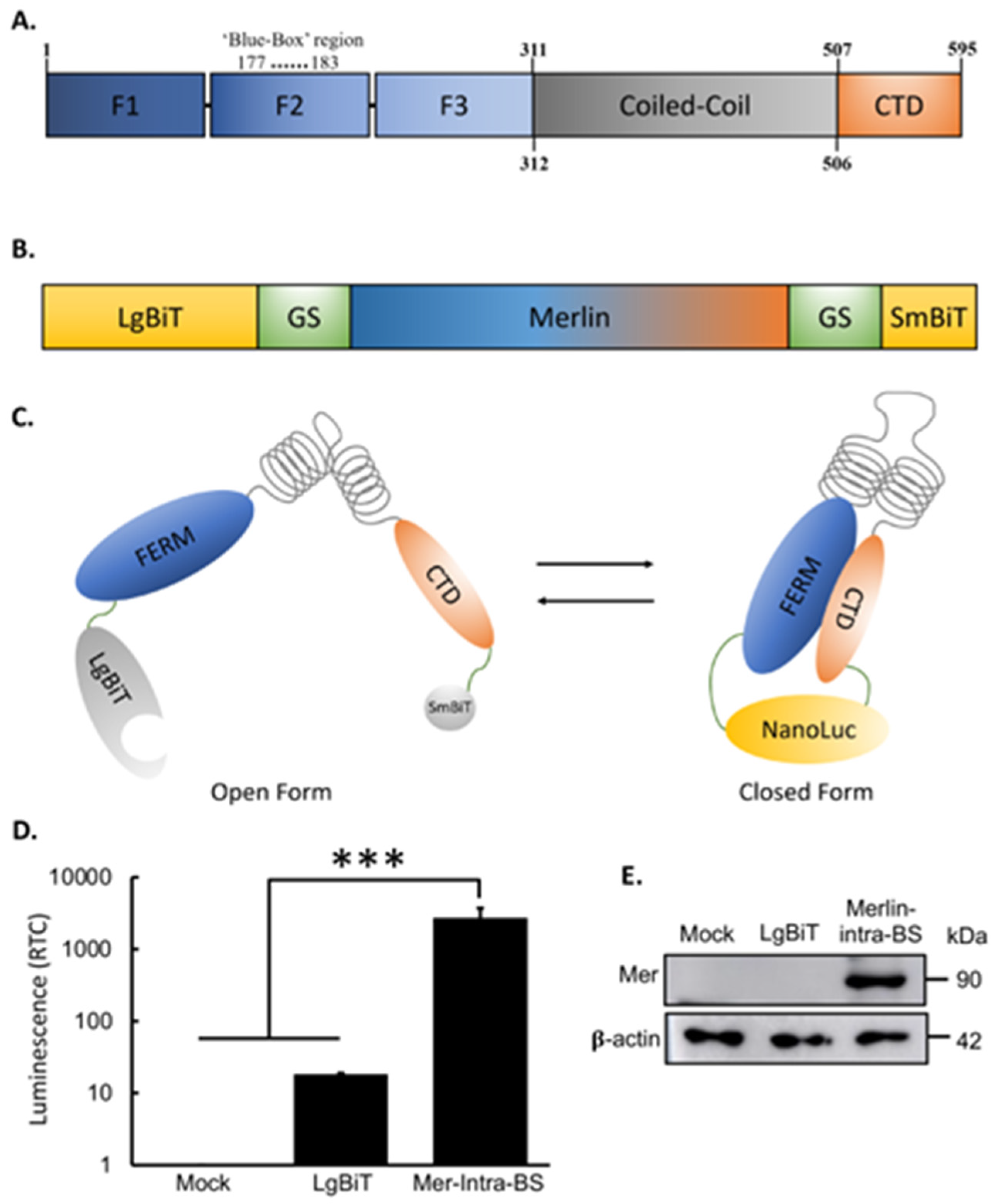
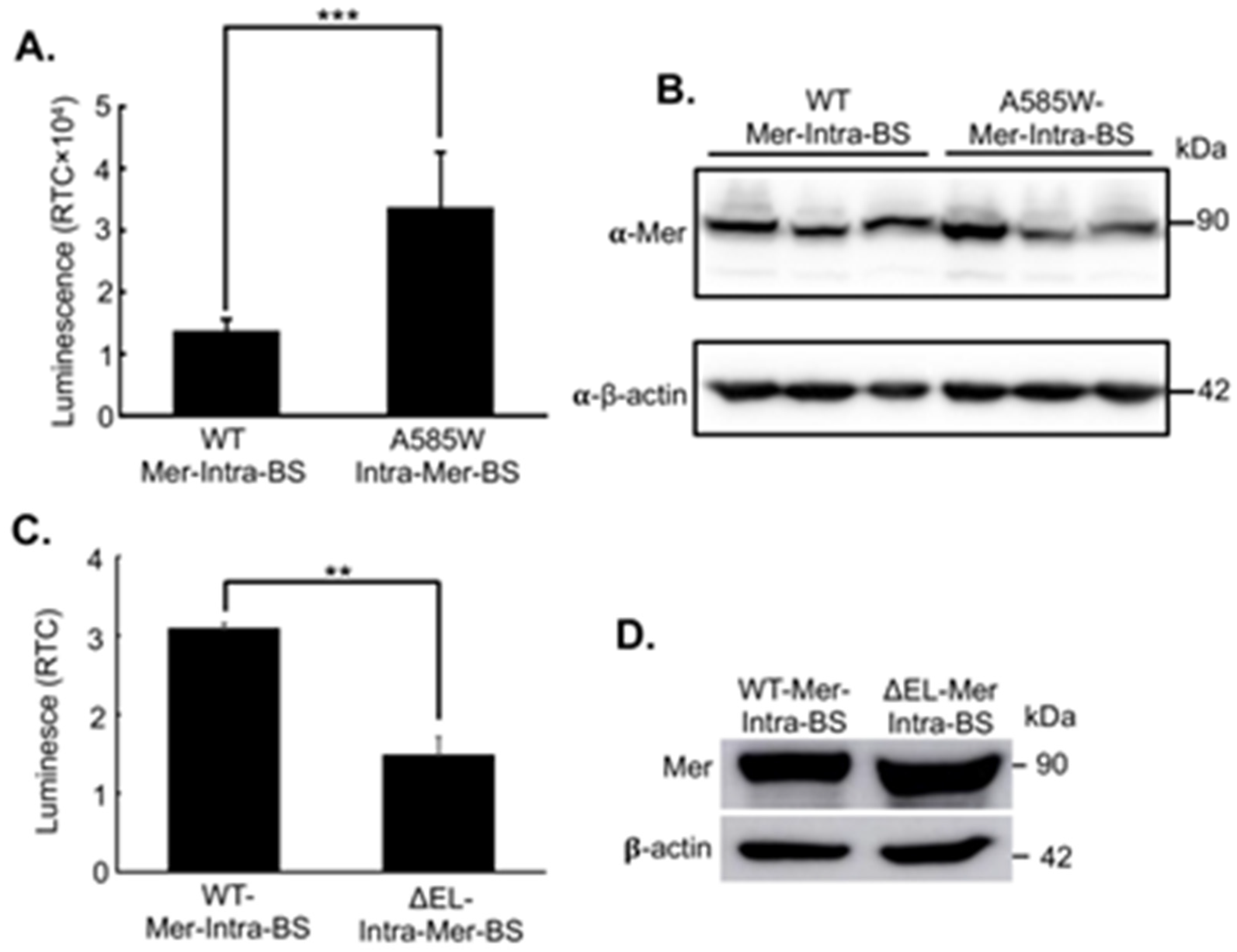
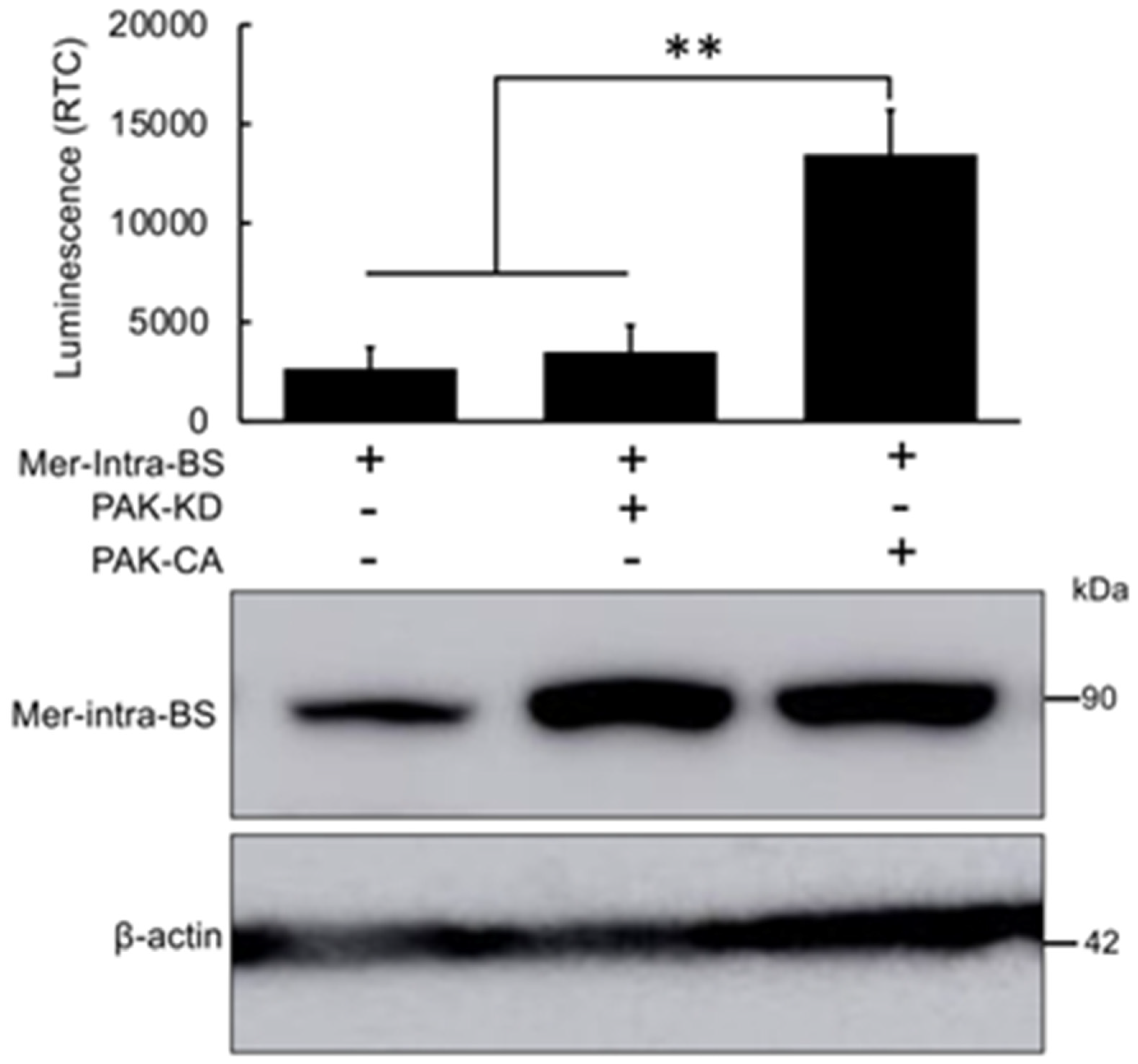
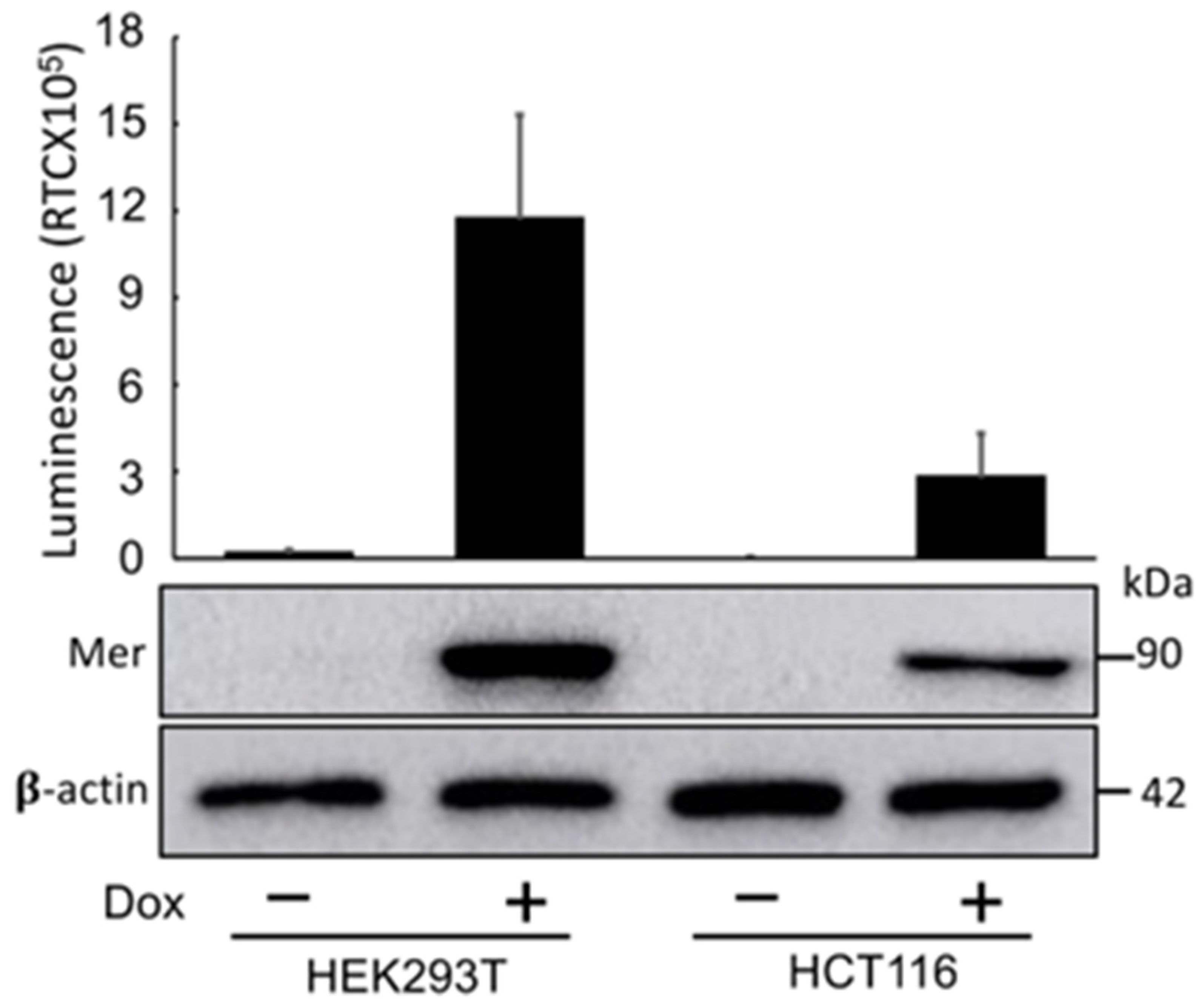
2. Results
Development and Validation of Mer-Intra-BS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biosensor Design and Construction
4.2. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Lentivirus Production and Stable Cell Line Generation
4.6. Luciferase Assays
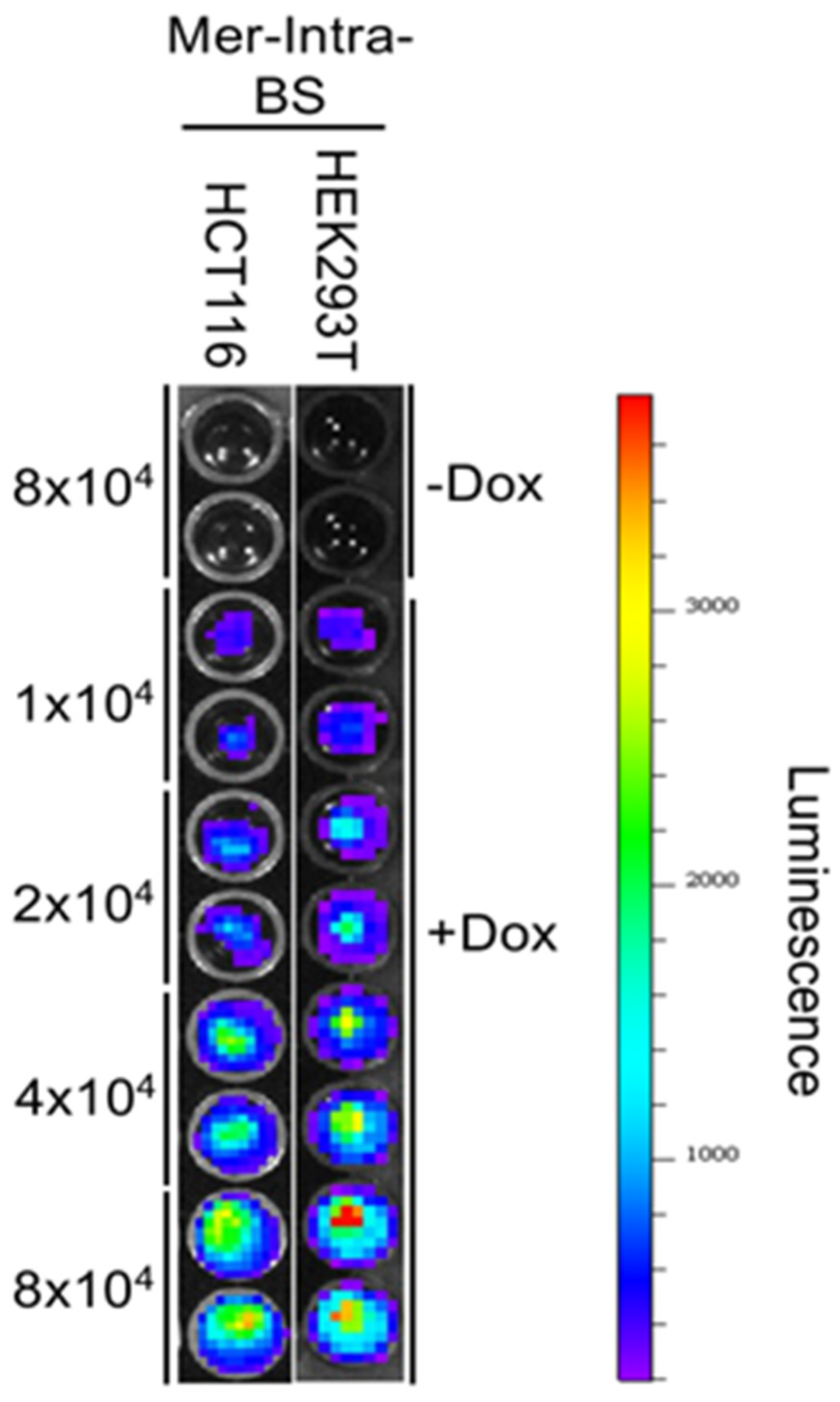
4.7. Bioluminescent imaging (BLI) analysis
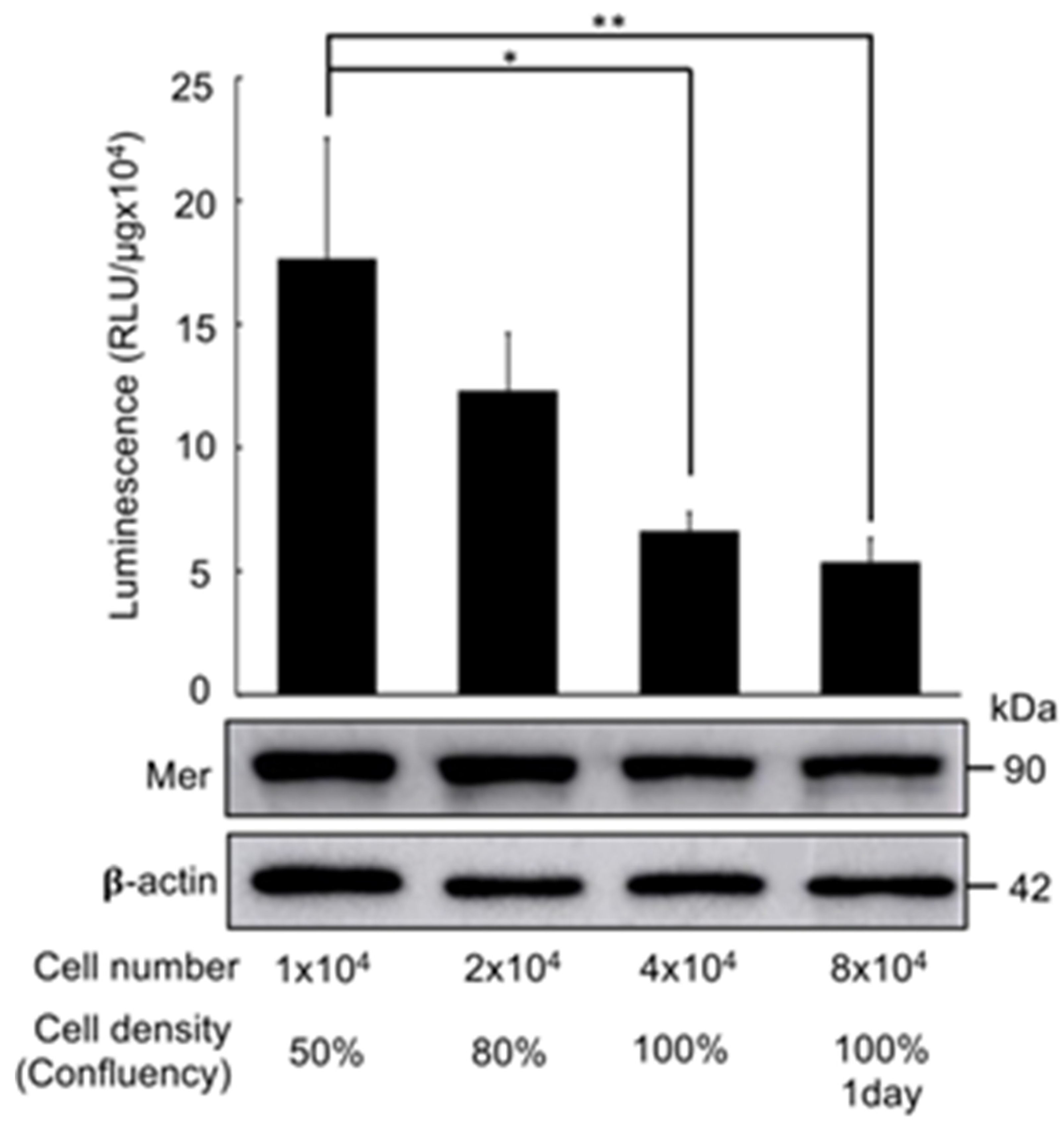
4.8. Monitoring cell density dependent activation of Mer-Intra-BS
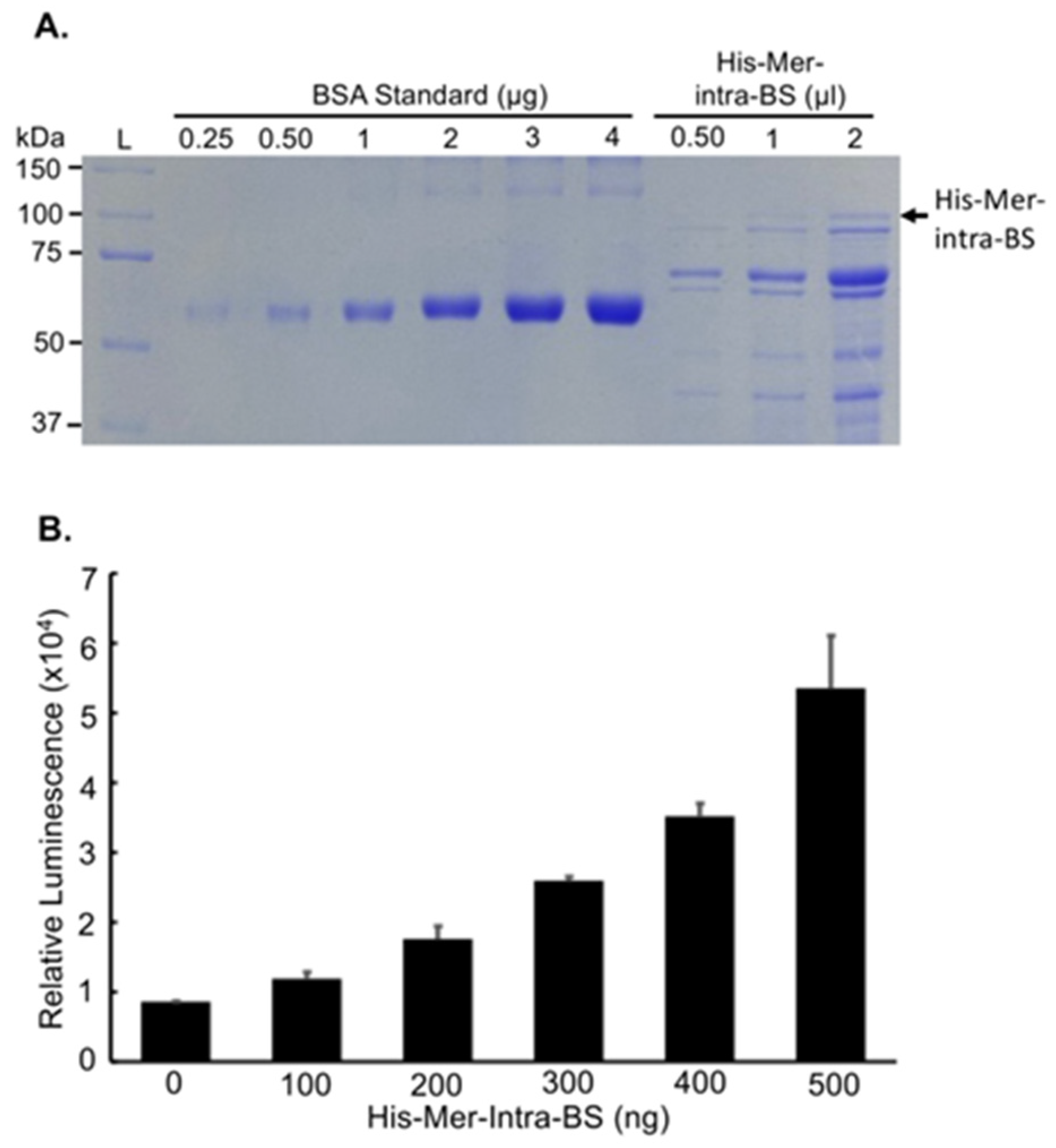
4.9. Purification of His-tagged Mer-Intra-BS
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rouleau, G. A.; Merel, P.; Lutchman, M.; Sanson, M.; Zucman, J.; Marineau, C.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Demczuk, S.; Desmaze, C.; Plougastel, B., Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2. Nature 1993, 363, (6429), 515-521. [CrossRef]
- Trofatter, J. A.; MacCollin, M. M.; Rutter, J. L.; Murrell, J. R.; Duyao, M. P.; Parry, D. M.; Eldridge, R.; Kley, N.; Menon, A. G.; Pulaski, K.; et al., A novel moesin-, ezrin-, radixin-like gene is a candidate for the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor. Cell 1993, 75, (4), 826. [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. G., Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): a clinical and molecular review. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2009, 4, 16. [CrossRef]
- Asthagiri, A. R.; Parry, D. M.; Butman, J. A.; Kim, H. J.; Tsilou, E. T.; Zhuang, Z.; Lonser, R. R., Neurofibromatosis type 2. Lancet 2009, 373, (9679), 1974-86. [CrossRef]
- Blakeley, J. O.; Plotkin, S. R., Therapeutic advances for the tumors associated with neurofibromatosis type 1, type 2, and schwannomatosis. Neuro Oncol 2016, 18, (5), 624-38. [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Slopis, J.; Hong, D. S.; Ketonen, L. M.; Hamilton, J.; McCutcheon, I. E.; Kurzrock, R., Treatment of patients with advanced neurofibromatosis type 2 with novel molecularly targeted therapies: from bench to bedside. J Clin Oncol 2012, 30, (5), e64-8. [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S. R.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A. O.; Barker, F. G., 2nd; Halpin, C.; Padera, T. P.; Tyrrell, A.; Sorensen, A. G.; Jain, R. K.; di Tomaso, E., Hearing improvement after bevacizumab in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2. N Engl J Med 2009, 361, (4), 358-67. [CrossRef]
- Gusella, J. F.; Ramesh, V.; MacCollin, M.; Jacoby, L. B., Merlin: the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999, 1423, (2), M29-36. [CrossRef]
- McClatchey, A. I.; Giovannini, M., Membrane organization and tumorigenesis--the NF2 tumor suppressor, Merlin. Genes & development 2005, 19, (19), 2265-2277.
- McClatchey, A. I., Merlin and ERM proteins: unappreciated roles in cancer development? Nat Rev Cancer 2003, 3, (11), 877-83. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R. A., Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011, 144, (5), 646-74. [CrossRef]
- Zirn, B.; Arning, L.; Bartels, I.; Shoukier, M.; Hoffjan, S.; Neubauer, B.; Hahn, A., Ring chromosome 22 and neurofibromatosis type II: proof of two-hit model for the loss of the NF2 gene in the development of meningioma. Clin Genet 2012, 81, (1), 82-7. [CrossRef]
- Knudson, A. G., Jr., Mutation and cancer: statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1971, 68, (4), 820-3. [CrossRef]
- Petrilli, A. M.; Fernández-Valle, C., Role of Merlin/NF2 inactivation in tumor biology. Oncogene 2016, 35, (5), 537-48. [CrossRef]
- Brastianos, P. K.; Horowitz, P. M.; Santagata, S.; Jones, R. T.; McKenna, A.; Getz, G.; Ligon, K. L.; Palescandolo, E.; Van Hummelen, P.; Ducar, M. D.; Raza, A.; Sunkavalli, A.; Macconaill, L. E.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A. O.; Louis, D. N.; Hahn, W. C.; Dunn, I. F.; Beroukhim, R., Genomic sequencing of meningiomas identifies oncogenic SMO and AKT1 mutations. Nat Genet 2013, 45, (3), 285-9. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Karas, P. J.; Hadley, C. C.; Bayley, V. J.; Khan, A. B.; Jalali, A.; Sweeney, A. D.; Klisch, T. J.; Patel, A. J., The Role of Merlin/NF2 Loss in Meningioma Biology. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, (11). [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, D. H.; Giordano, M. J.; Fishback, A. S.; Guha, A., Loss of merlin expression in sporadic meningiomas, ependymomas and schwannomas. Neurology 1997, 49, (1), 267-70. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, A. B.; Mitsunaga, S. I.; Cheng, J. Q.; Klein, W. M.; Jhanwar, S. C.; Seizinger, B.; Kley, N.; Klein-Szanto, A. J.; Testa, J. R., High frequency of inactivating mutations in the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene (NF2) in primary malignant mesotheliomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995, 92, (24), 10854-8. [CrossRef]
- Sekido, Y.; Sato, T., NF2 alteration in mesothelioma. Front Toxicol 2023, 5, 1161995. [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Sekido, Y., NF2/Merlin Inactivation and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Mesothelioma. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, (4). [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, A. B.; Hara, T.; Ramesh, V.; Gao, J.; Klein-Szanto, A. J.; Morin, F.; Menon, A. G.; Trofatter, J. A.; Gusella, J. F.; Seizinger, B. R.; et al., Mutations in transcript isoforms of the neurofibromatosis 2 gene in multiple human tumour types. Nat Genet 1994, 6, (2), 185-92. [CrossRef]
- Morrow, K. A.; Das, S.; Metge, B. J.; Ye, K.; Mulekar, M. S.; Tucker, J. A.; Samant, R. S.; Shevde, L. A., Loss of tumor suppressor Merlin in advanced breast cancer is due to post-translational regulation. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, (46), 40376-85. [CrossRef]
- Cačev, T.; Aralica, G.; Lončar, B.; Kapitanović, S., Loss of NF2/Merlin expression in advanced sporadic colorectal cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2014, 37, (1), 69-77.
- Luo, Z. L.; Cheng, S. Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H. L.; Zhang, C. Z.; Chen, H. Y.; Qiu, B. J.; Tang, L.; Hu, C. L.; Wang, H. Y.; Li, Z., A splicing variant of Merlin promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 8457. [CrossRef]
- Benhamouche, S.; Curto, M.; Saotome, I.; Gladden, A. B.; Liu, C. H.; Giovannini, M.; McClatchey, A. I., Nf2/Merlin controls progenitor homeostasis and tumorigenesis in the liver. Genes & development 2010, 24, (16), 1718-1730.
- Horiguchi, A.; Zheng, R.; Shen, R.; Nanus, D. M., Inactivation of the NF2 tumor suppressor protein merlin in DU145 prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2008, 68, (9), 975-84. [CrossRef]
- Thurneysen, C.; Opitz, I.; Kurtz, S.; Weder, W.; Stahel, R. A.; Felley-Bosco, E., Functional inactivation of NF2/merlin in human mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, (2), 140-7. [CrossRef]
- Chishti, A. H.; Kim, A. C.; Marfatia, S. M.; Lutchman, M.; Hanspal, M.; Jindal, H.; Liu, S. C.; Low, P. S.; Rouleau, G. A.; Mohandas, N.; Chasis, J. A.; Conboy, J. G.; Gascard, P.; Takakuwa, Y.; Huang, S. C.; Benz, E. J., Jr.; Bretscher, A.; Fehon, R. G.; Gusella, J. F.; Ramesh, V.; Solomon, F.; Marchesi, V. T.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S.; Hoover, K. B.; et al., The FERM domain: a unique module involved in the linkage of cytoplasmic proteins to the membrane. Trends Biochem Sci 1998, 23, (8), 281-2. [CrossRef]
- Michie, K. A.; Bermeister, A.; Robertson, N. O.; Goodchild, S. C.; Curmi, P. M. G., Two Sides of the Coin: Ezrin/Radixin/Moesin and Merlin Control Membrane Structure and Contact Inhibition. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, (8). [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.; Giancotti, F. G., Molecular insights into NF2/Merlin tumor suppressor function. FEBS letters 2014, 588, (16), 2743-2752. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Seto, A.; Maita, N.; Hamada, K.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S.; Hakoshima, T., Structural basis for neurofibromatosis type 2. Crystal structure of the merlin FERM domain. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, (12), 10332-6. [CrossRef]
- Bretscher, A.; Edwards, K.; Fehon, R. G., ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002, 3, (8), 586-99. [CrossRef]
- Kissil, J. L.; Johnson, K. C.; Eckman, M. S.; Jacks, T., Merlin phosphorylation by p21-activated kinase 2 and effects of phosphorylation on merlin localization. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, (12), 10394-9. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G. H.; Beeser, A.; Chernoff, J.; Testa, J. R., p21-activated kinase links Rac/Cdc42 signaling to merlin. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, (2), 883-6. [CrossRef]
- Alfthan, K.; Heiska, L.; Grönholm, M.; Renkema, G. H.; Carpén, O., Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates merlin at serine 518 independently of p21-activated kinase and promotes merlin-ezrin heterodimerization. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, (18), 18559-66. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, F.; Chan, S. W.; Lin, Z.; Wei, Z.; Yang, Z.; Guo, F.; Lim, C. J.; Xing, W.; Shen, Y.; Hong, W.; Long, J.; Zhang, M., Angiomotin binding-induced activation of Merlin/NF2 in the Hippo pathway. Cell Res 2015, 25, (7), 801-17. [CrossRef]
- Hamaratoglu, F.; Willecke, M.; Kango-Singh, M.; Nolo, R.; Hyun, E.; Tao, C.; Jafar-Nejad, H.; Halder, G., The tumour-suppressor genes NF2/Merlin and Expanded act through Hippo signalling to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis. Nature cell biology 2006, 8, (1), 27-36. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, J.; Klusza, S.; Deng, W. M.; Pan, D., Kibra functions as a tumor suppressor protein that regulates Hippo signaling in conjunction with Merlin and Expanded. Dev Cell 2010, 18, (2), 288-99. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Bai, H.; David, K. K.; Dong, J.; Zheng, Y.; Cai, J.; Giovannini, M.; Liu, P.; Anders, R. A.; Pan, D., The Merlin/NF2 tumor suppressor functions through the YAP oncoprotein to regulate tissue homeostasis in mammals. Developmental cell 2010, 19, (1), 27-38. [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, N.; Pan, D., Spatial organization of Hippo signaling at the plasma membrane mediated by the tumor suppressor Merlin/NF2. Cell 2013, 154, (6), 1342-55. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Guan, K. L., Hippo Signaling in Embryogenesis and Development. Trends Biochem Sci 2021, 46, (1), 51-63. [CrossRef]
- Sarmasti Emami, S.; Zhang, D.; Yang, X., Interaction of the Hippo Pathway and Phosphatases in Tumorigenesis. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, (9). [CrossRef]
- Azad, T., Ghahremani M., Yang, X., The role of YAP and TAZ in angiogenesis and vascular mimicry. Cells 2019, 8, 407. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X., Chapter 8: Targeting the Hippo pathway to improve response to chemotherapy. Tarteting Cell Survival Pathways to Enhance Response to Chemotherapy. Elsevier Publishing Company: 2019; Vol. 3.
- Wu, L.; Yang, X., Targeting the Hippo pathway for breast cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, (11), E422. [CrossRef]
- Sher, I.; Hanemann, C. O.; Karplus, P. A.; Bretscher, A., The tumor suppressor merlin controls growth in its open state, and phosphorylation converts it to a less-active more-closed state. Dev Cell 2012, 22, (4), 703-5. [CrossRef]
- Primi, M. C.; Rangarajan, E. S.; Patil, D. N.; Izard, T., Conformational flexibility determines the Nf2/merlin tumor suppressor functions. Matrix Biol Plus 2021, 12, 100074. [CrossRef]
- Hong, A. W.; Meng, Z.; Plouffe, S. W.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Guan, K. L., Critical roles of phosphoinositides and NF2 in Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev 2020, 34, (7-8), 511-525. [CrossRef]
- LaJeunesse, D. R.; McCartney, B. M.; Fehon, R. G., Structural analysis of Drosophila merlin reveals functional domains important for growth control and subcellular localization. J Cell Biol 1998, 141, (7), 1589-99. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K. C.; Kissil, J. L.; Fry, J. L.; Jacks, T., Cellular transformation by a FERM domain mutant of the Nf2 tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene 2002, 21, (39), 5990-7. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R. S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, P.; Ye, K.; Chinnaiyan, A.; Halder, G.; Lai, Z. C.; Guan, K. L., Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes & Development 2007, 21, (21), 2747-2761. [CrossRef]
- Dupont, S.; Morsut, L.; Aragona, M.; Enzo, E.; Giulitti, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Zanconato, F.; Le Digabel, J.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S.; Elvassore, N.; Piccolo, S., Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature 2011, 474, (7350), 179-183. [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Guan, K. L., The Hippo Pathway: Biology and Pathophysiology. Annu Rev Biochem 2019, 88, 577-604. [CrossRef]
- Azad, T. N., K; Janse van Rensburg, HJ; Maritan, SM; Wu, L; Hao, Y; Montminy, T; Yu, J; Khanal, K; Mulligan, LM; Yang, X, A gain-of-functional screen identifies the Hippo pathway as a central mediator of receptor tyrosine kinases during tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2020, 39, 334-355. [CrossRef]
- Nouri, K. A., T; Lightbody, E; Khanal, P; Nicol, CJ; Yang, X, A kinome-wide screen using a NanoLuc LATS luminescent biosensor identifies ALK as a novel regulator of the Hippo pathway in tumorigenesis and immune evasion. FASEB Journal 2019, 33, 12487-12499.
- Nouri, K.; Azad, T.; Ling, M.; van Rensburg, H. J. J.; Pipchuk, A.; Shen, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X., Identification of celastrol as a novel YAP-TEAD inhibitor for cancer therapy by high throughput screening with ultrasensitive YAP/TAZ-TEAD biosensors. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, (10), 1596. [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.; Janse van Rensburg, H. J.; Lightbody, E. D.; Neveu, B.; Champagne, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Kay, V. R.; Hao, Y.; Shen, H.; Yeung, B.; Croy, B. A.; Guan, K. L.; Pouliot, F.; Zhang, J.; Nicol, C. J. B.; Yang, X., A LATS biosensor functional screen identifies VEGFR as a novel regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat.Commun. 2018, 9, 1061.
- Wu, L., Ge, A., Hao, Y., Yang, X, Development of a New HiBiT Biosensor Monitoring Stability of YAP/TAZ Proteins in Cells. Chemosensors 2023, 11, (9), 492. [CrossRef]
- Pipchuk, A.; Yang, X., Using Biosensors to Study Protein-Protein Interaction in the Hippo Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 660137. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A. S.; Schwinn, M. K.; Hall, M. P.; Zimmerman, K.; Otto, P.; Lubben, T. H.; Butler, B. L.; Binkowski, B. F.; Machleidt, T.; Kirkland, T. A.; Wood, M. G.; Eggers, C. T.; Encell, L. P.; Wood, K. V., NanoLuc complementation reporter optimized for accurate measurement of protein interactions in cells. ACS Chemical Biology 2016, 11, (2), 400-408. [CrossRef]
- Hall, M. P.; Unch, J.; Binkowski, B. F.; Valley, M. P.; Butler, B. L.; Wood, M. G.; Otto, P.; Zimmerman, K.; Vidugiris, G.; Machleidt, T.; Robers, M. B.; Benink, H. A.; Eggers, C. T.; Slater, M. R.; Meisenheimer, P. L.; Klaubert, D. H.; Fan, F.; Encell, L. P.; Wood, K. V., Engineered luciferase reporter from a deep sea shrimp utilizing a novel imidazopyrazinone substrate. ACS chemical biology 2012, 7, (11), 1848-1857. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, R.; Reczek, D.; Bretscher, A., Hierarchy of merlin and ezrin N- and C-terminal domain interactions in homo- and heterotypic associations and their relationship to binding of scaffolding proteins EBP50 and E3KARP. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, (10), 7621-9. [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chun, A.; Cheung, K.; Rashidi, B.; Yang, X., Tumor suppressor LATS1 is a negative regulator of oncogene YAP. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 2008, 283, (9), 5496-5509. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




