Submitted:
27 December 2023
Posted:
28 December 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Marker Development
2.3. User Interface and Database Construction
3. Result
3.1. Markers
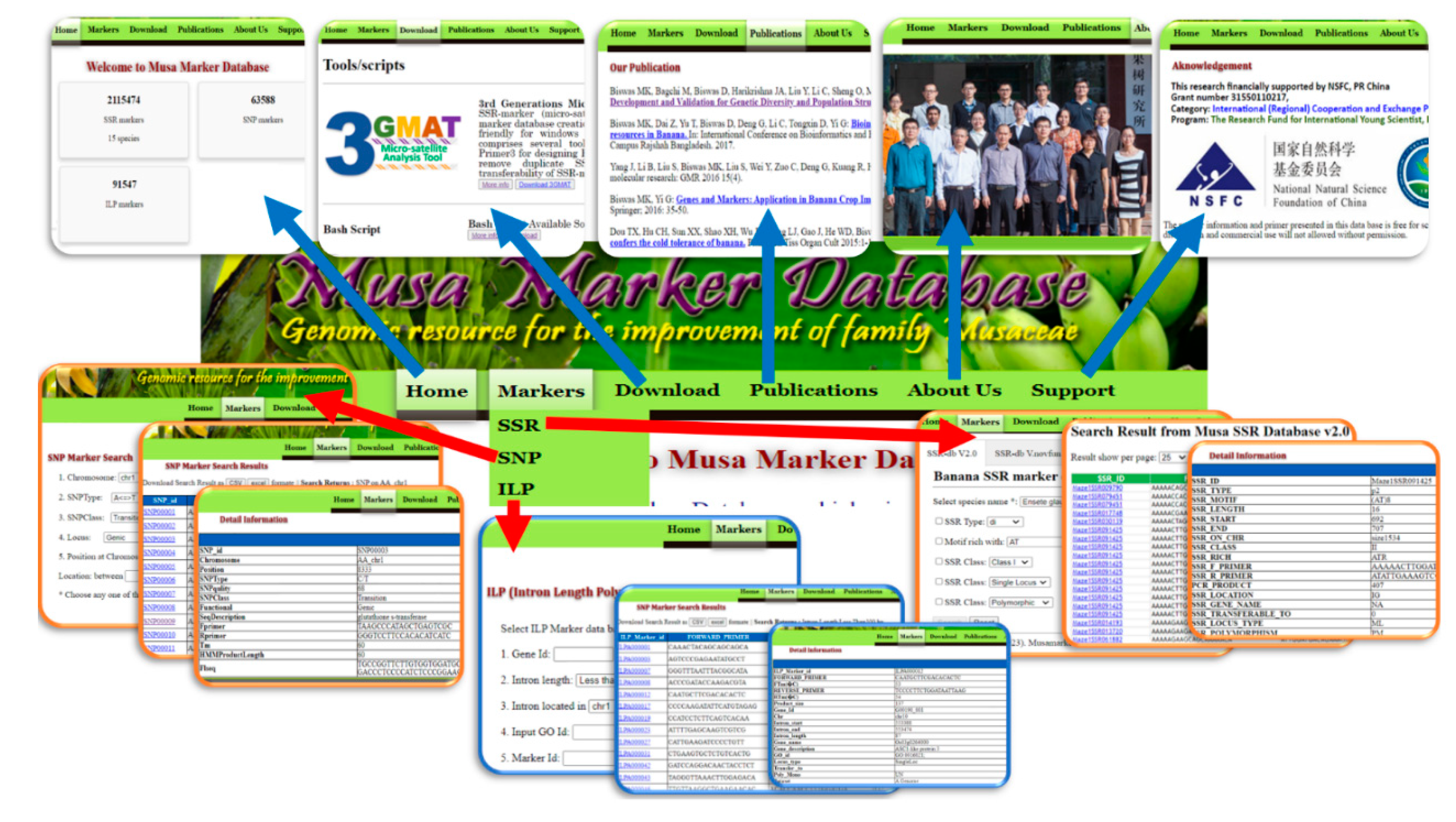
3.2. Interface and Search Criteria
3.3. Unique Feature of MMdb Compare with Others Existing Marker Database
3.4. Utility and Future Directions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biswas, M.K.; Darbar, J.N.; Borrell, J.S.; Bagchi, M.; Biswas, D.; Nuraga, G.W.; Demissew, S.; Wilkin, P.; Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. The landscape of microsatellites in the enset (Ensete ventricosum) genome and web-based marker resource development. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 15312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Xu, Q.; Deng, X. Utility of RAPD, ISSR, IRAP and REMAP markers for the genetic analysis of Citrus spp. Scientia Horticulturae 2010, 124, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Bagchi, M.; Biswas, D.; Harikrishna, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Sheng, O.; Mayer, C.; Yi, G.; Deng, G. Genome-wide novel genic microsatellite marker resource development and validation for genetic diversity and population structure analysis of banana. Genes 2020, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenda, A.; Scheffler, J.; Scheffler, B.; Palmer, M.; Lacape, J.; Yu, J.Z.; Jesudurai, C.; Jung, S.; Muthukumar, S.; Yellambalase, P. CMD: a cotton microsatellite database resource for Gossypium genomics. BMC Genomics 2006, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasawa, K.; Isobe, S.; Tabata, S.; Hirakawa, H. Kazusa Marker DataBase: a database for genomics, genetics, and molecular breeding in plants. Breed Sci 2014, 64, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Seol, Y.; Lee, D.; Jeong, I.; Yoon, U.; Lee, G.; Hahn, J.; Park, D. NABIC marker database: A molecular markers information network of agricultural crops. Bioinformation 2013, 9, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarika; Arora, V.; Iquebal, M.A.; Rai, A.; Kumar, D. PIPEMicroDB: microsatellite database and primer generation tool for pigeonpea genome. Database 2013, 2013, bas054. [Google Scholar]
- Muthamilarasan, M.; Misra, G.; Prasad, M. FmMDb: a versatile database of foxtail millet markers for millets and bioenergy grasses research. PloS one 2013, 8, e71418. [Google Scholar]
- Doddamani, D.; Katta, M.A.; Khan, A.W.; Agarwal, G.; Shah, T.M.; Varshney, R.K. CicArMiSatDB: the chickpea microsatellite database. BMC Bioinformatics 2014, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jin, G.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W. PIP: a database of potential intron polymorphism markers. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2174–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.M.; Atia, M.A.M. SSRome: an integrated database and pipelines for exploring microsatellites in all organisms. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, D244–D252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Hua, X.; Tang, H.; Yang, L.; Ming, R.; Zhang, J. PGD: pineapple genomics database. Horticulture Research 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, M.K.; Natarajan, S.; Biswas, D.; Howlader, J.; Park, J.-.; Nou, I.-. Lily Database: A Comprehensive Genomic Resource for the Liliaceae Family. Horticulturae 2024, 23, DOI. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dossa, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Liao, B.; Zhang, X. PMDBase: a database for studying microsatellite DNA and marker development in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45, D1046–D1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droc, G.; Lariviere, D.; Guignon, V.; Yahiaoui, N.; This, D.; Garsmeur, O.; Dereeper, A.; Hamelin, C.; Argout, X.; Dufayard, J. The banana genome hub. Database 2013, 2013, bat035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.; Kapoor, N.; Fatma, S.; Jaiswal, S.; Iquebal, M.A.; Rai, A.; Kumar, D. BanSatDB, a whole-genome-based database of putative and experimentally validated microsatellite markers of three Musa species. The Crop Journal 2018, 6, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Sheng, O.; Mayer, C.; Yi, G. Genome-wide computational analysis of Musa microsatellites: classification, cross-taxon transferability, functional annotation, association with transposons & miRNAs, and genetic marker potential. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0131312. [Google Scholar]
- Salgotra, R.K.; Chauhan, B.S. Genetic diversity, conservation, and utilization of plant genetic resources. Genes 2023, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dida, G. Molecular Markers in Breeding of Crops: Recent Progress and Advancements. J.Microbiol.Biotechnol 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savadi, S.; Muralidhara, B.M.; Venkataravanappa, V.; Adiga, J.D. Genome-wide survey and characterization of microsatellites in cashew and design of a web-based microsatellite database: CMDB. Frontiers in Plant Science 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Xu, Q.; Mayer, C.; Deng, X. Genome wide characterization of short tandem repeat markers in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). PloS one 2014, 9, e104182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, V.; Gaikwad, P.N.; Sidhu, G.S.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, N.; Jindal, T.; Chhuneja, P.; Rattanpal, H.S. Comprehensive genome-wide identification and transferability of chromosome-specific highly variable microsatellite markers from citrus species. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, T.; Rui, F. Development of EST-SSR markers derived from transcriptome of Saccharina japonica and their application in genetic diversity analysis. J Appl Phycol 2018, 30, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; An, Y.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, S.; Wei, C. Genome-wide identification of simple sequence repeats and development of polymorphic SSR markers for genetic studies in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Mol Breed 2018, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Bohra, A.; Singh, V.K.; Thudi, M.; Saxena, R.K. Toward the sequence-based breeding in legumes in the post-genome sequencing era. Theor Appl Genet 2019, 132, 797–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Tantwai, K.; Nema, S.; Tripathi, N.; Tiwari, S. Cross Transferability of SSR Markers from Finger Millet, Pearl Millet and Rice to Indian Little Millet and their Genetic Diversity Analysis.
- Liu, J.; Luo, W.; Qin, N.; Ding, P.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Mu, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. A 55 K SNP array-based genetic map and its utilization in QTL mapping for productive tiller number in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 2018, 131, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, B.; Mavi, G.S.; Gill, M.S.; Saini, D.K. Utilization of KASP technology for wheat improvement. Cereal Research Communications 2020, 48, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; George, A.W.; Reverter, A.; Li, Y. Genomic prediction of breeding values using a subset of SNPs identified by three machine learning methods. Frontiers in genetics 2018, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, W. Genome-wide investigation of intron length polymorphisms and their potential as molecular markers in rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Research 2005, 12, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Min, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Genome-wide development and utilization of novel intron-length polymorphic (ILP) markers in Medicago sativa. Mol Breed 2017, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
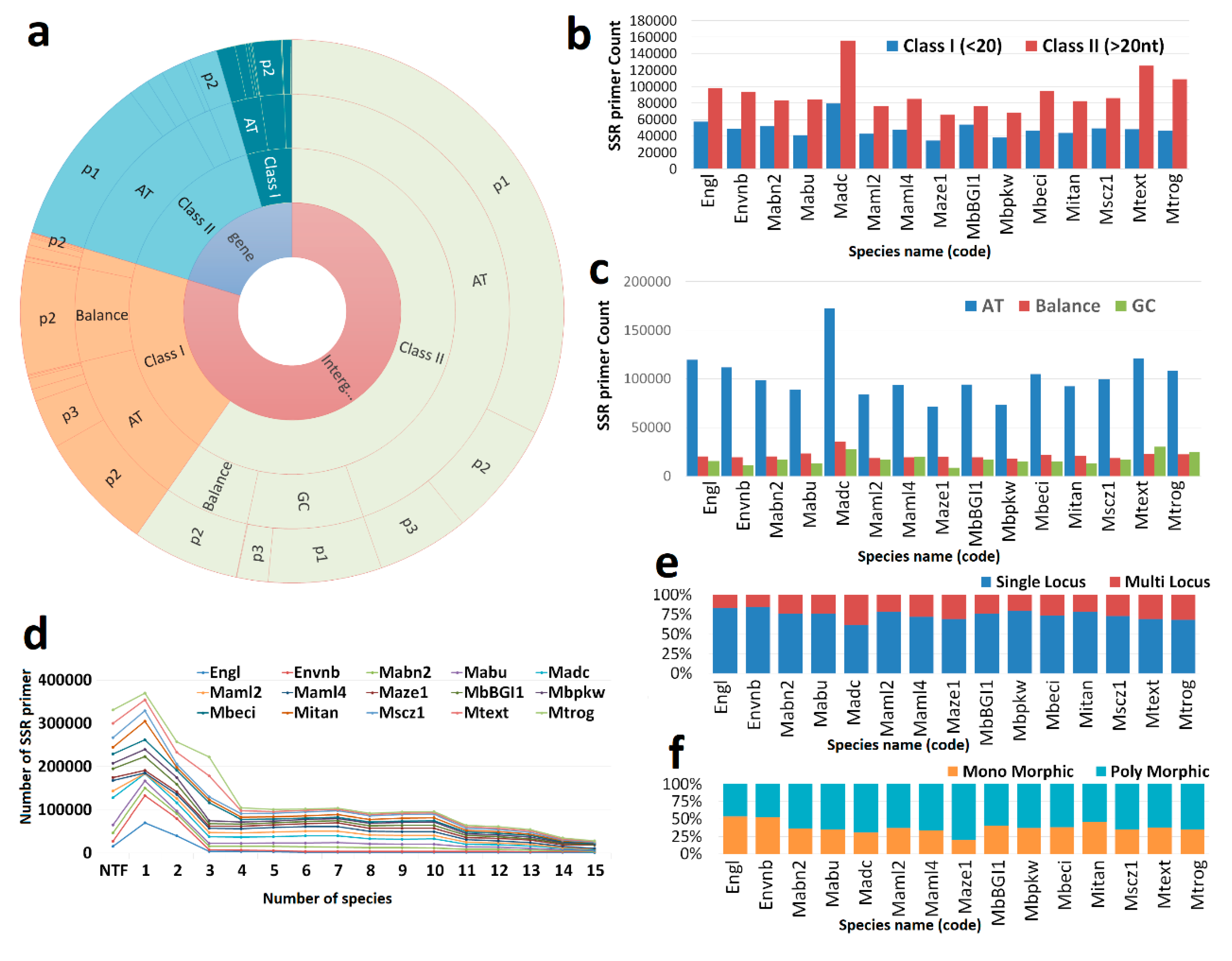
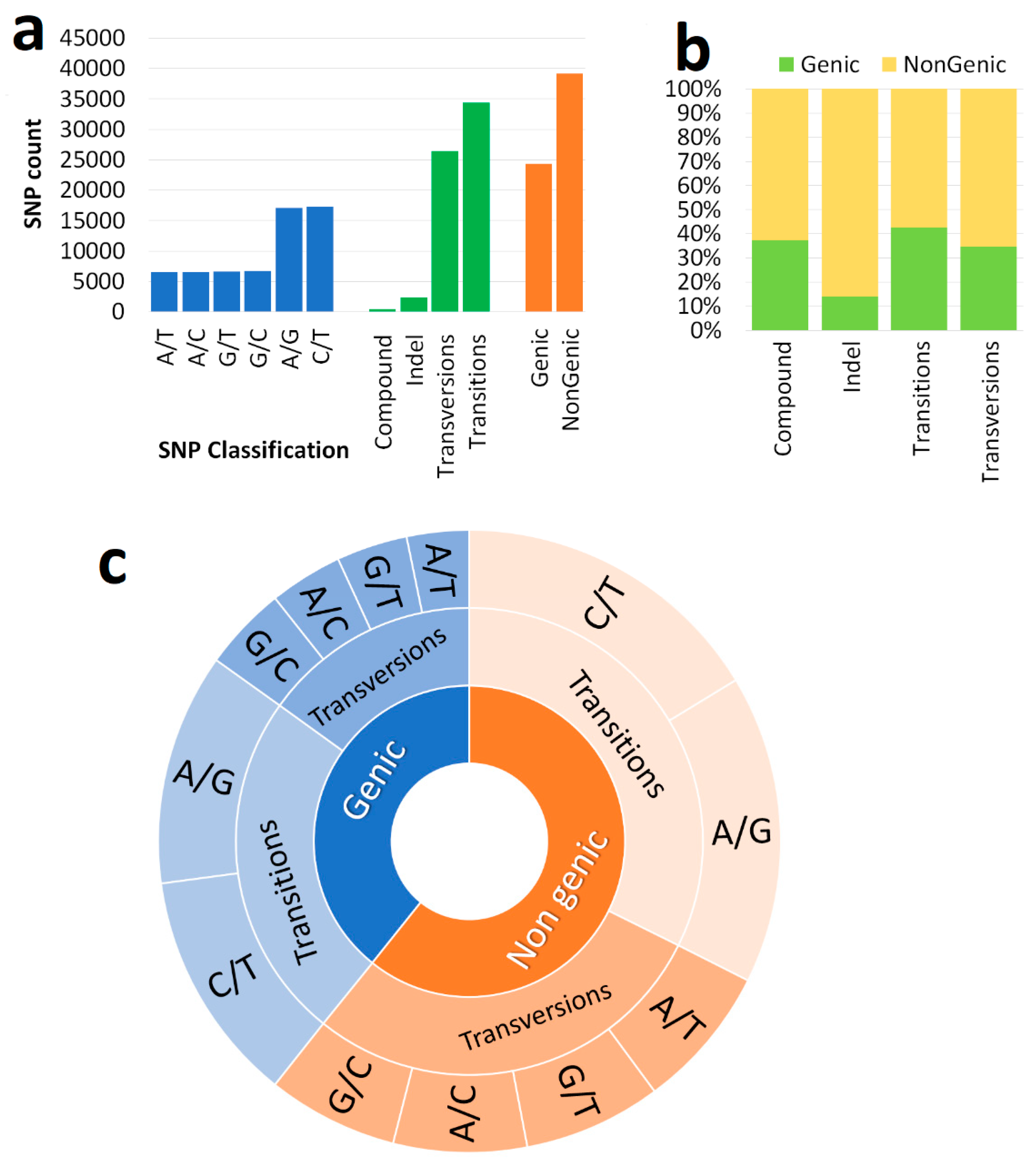
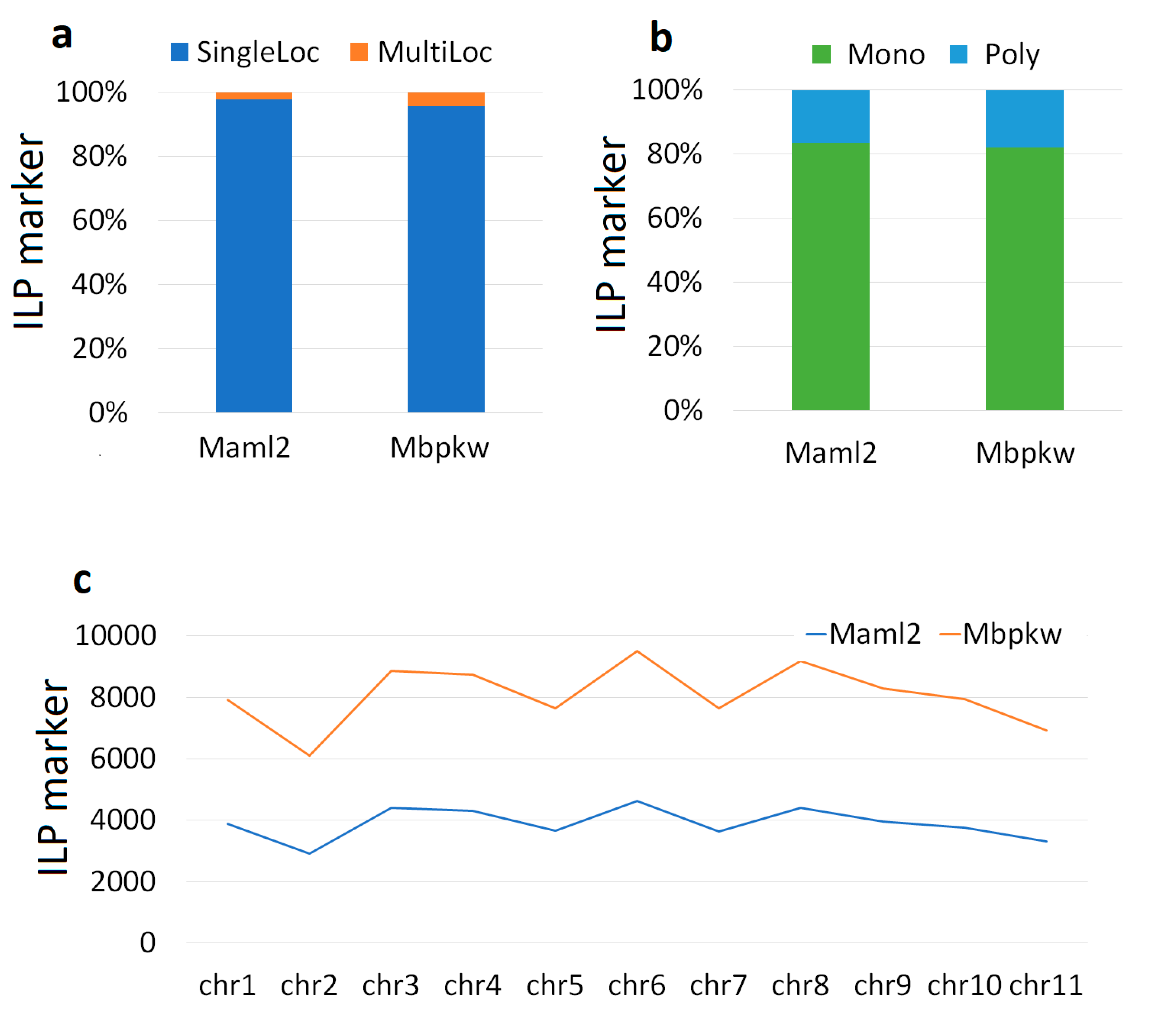
| List of the genome | Genome code | Total Number of SSR |
Primer design (count) |
% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Musa acuminata banksii | Mabn2 | 183911 | 135187 | 74 |
| Musa acuminata Dwarf_Cavendish | Madc | 267698 | 235211 | 88 |
| Musa acuminata burmannica | Mabu | 141919 | 125946 | 89 |
| Musa acuminata malaccensis V2 | Maml2 | 147255 | 118834 | 81 |
| Musa acuminata malaccensis V4 | Maml4 | 185328 | 132721 | 72 |
| Musa acuminata zebrina | Maze1 | 111705 | 100182 | 90 |
| Musa balbisiana BGI11 | MbBGI1 | 320858 | 130377 | 41 |
| Musa balbisiana pkw | Mbpkw | 131403 | 106302 | 81 |
| Musa beccarii | Mbeci | 181767 | 141466 | 78 |
| Musa itinerans | Mitan | 151683 | 126107 | 83 |
| Musa schizocarpa | Mscz1 | 178889 | 135556 | 76 |
| Musa textilis | Mtext | 215660 | 173840 | 81 |
| Musa troglodytarum | Mtrog | 197524 | 155701 | 79 |
| Ensete glaucum | Engl | 181817 | 155508 | 86 |
| Ensete ventricosum Bedadeti | Envnb | 163773 | 142536 | 87 |
| Total | 2761190 | 2115474 | 77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





