Submitted:
26 December 2023
Posted:
27 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Data processing: QSM
2.3. Data processing: OEF using multi-echo complex QQ (mcQQ)
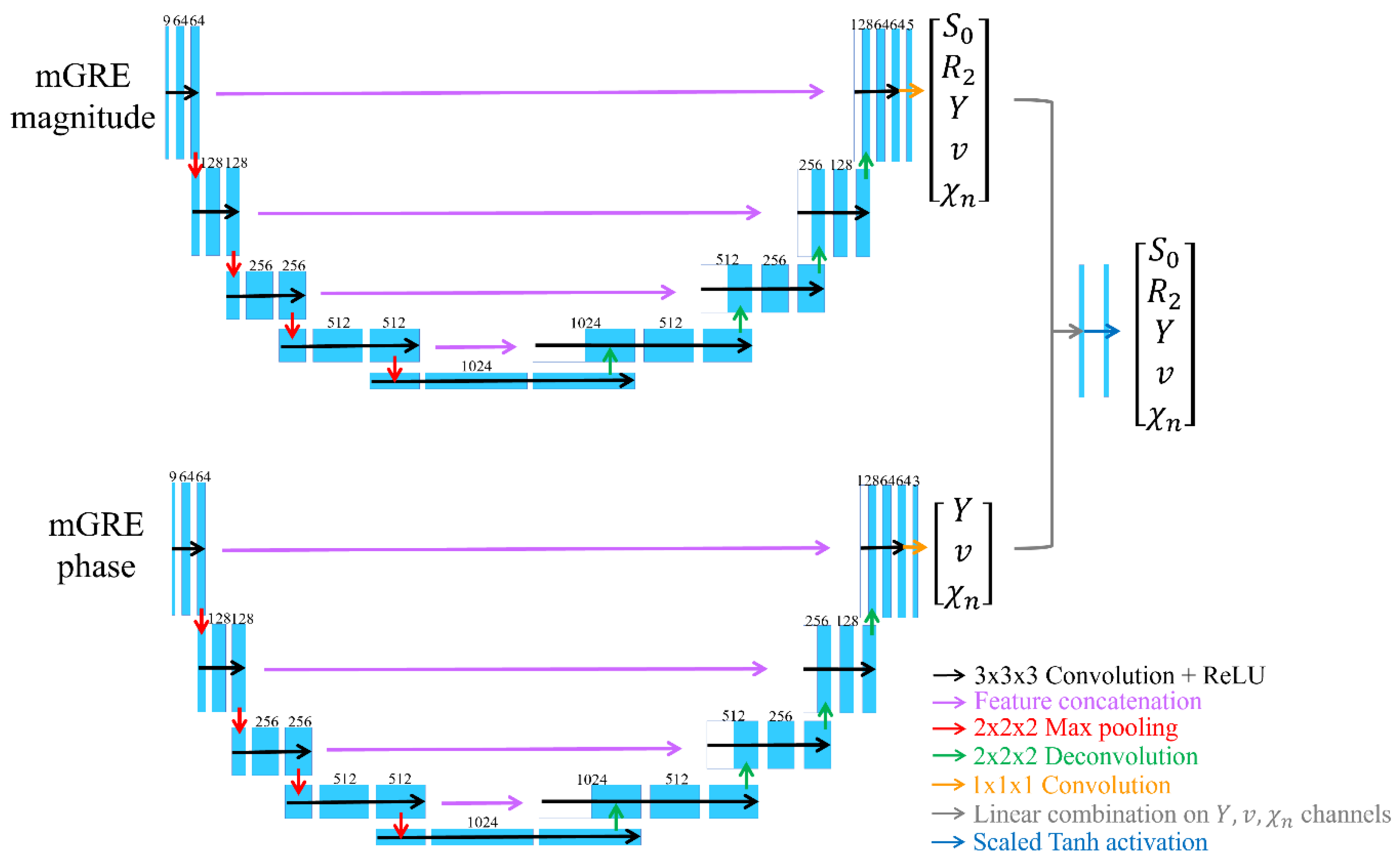
2.4. Deep neural network for mcQQ (mcQQ-NET)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
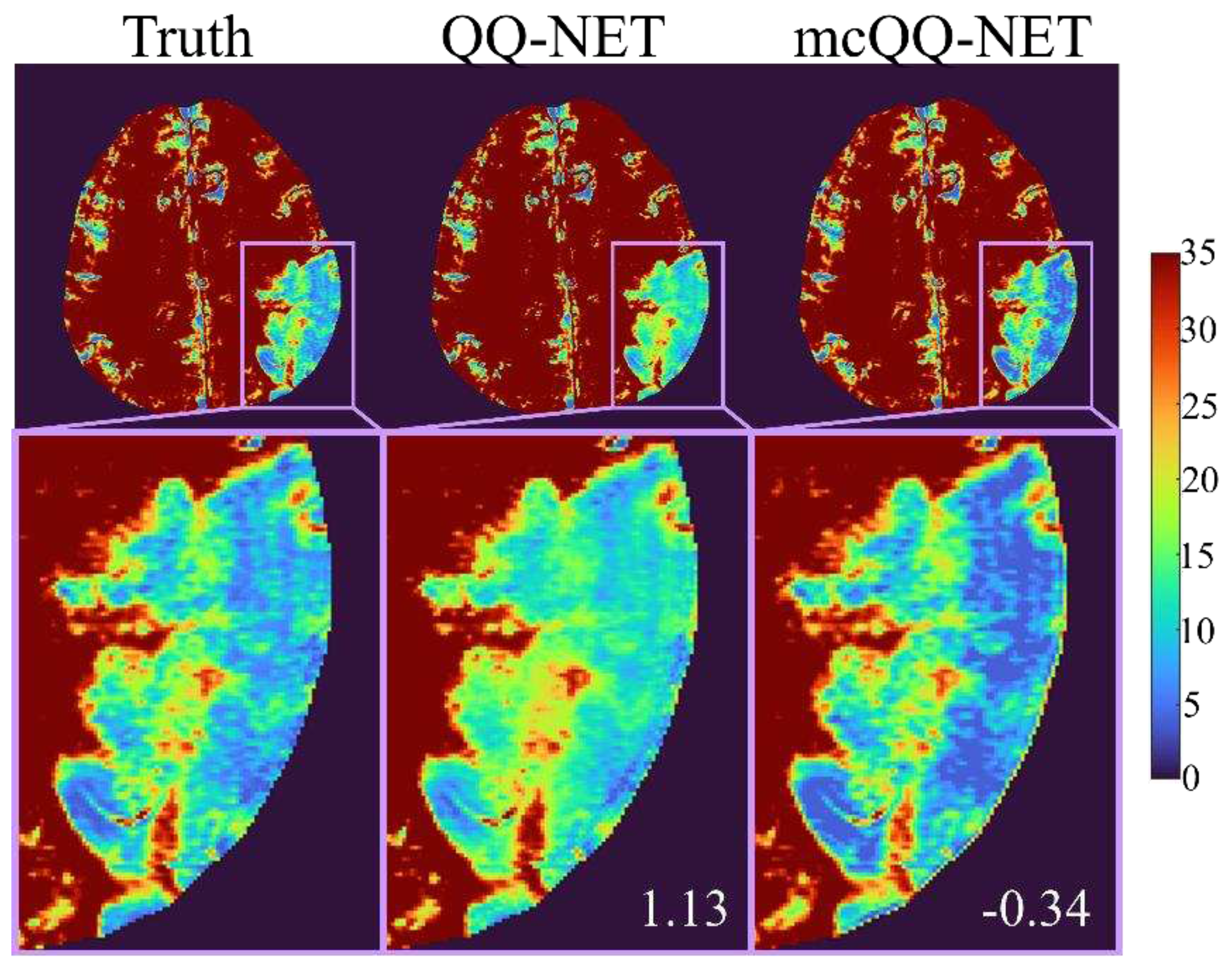
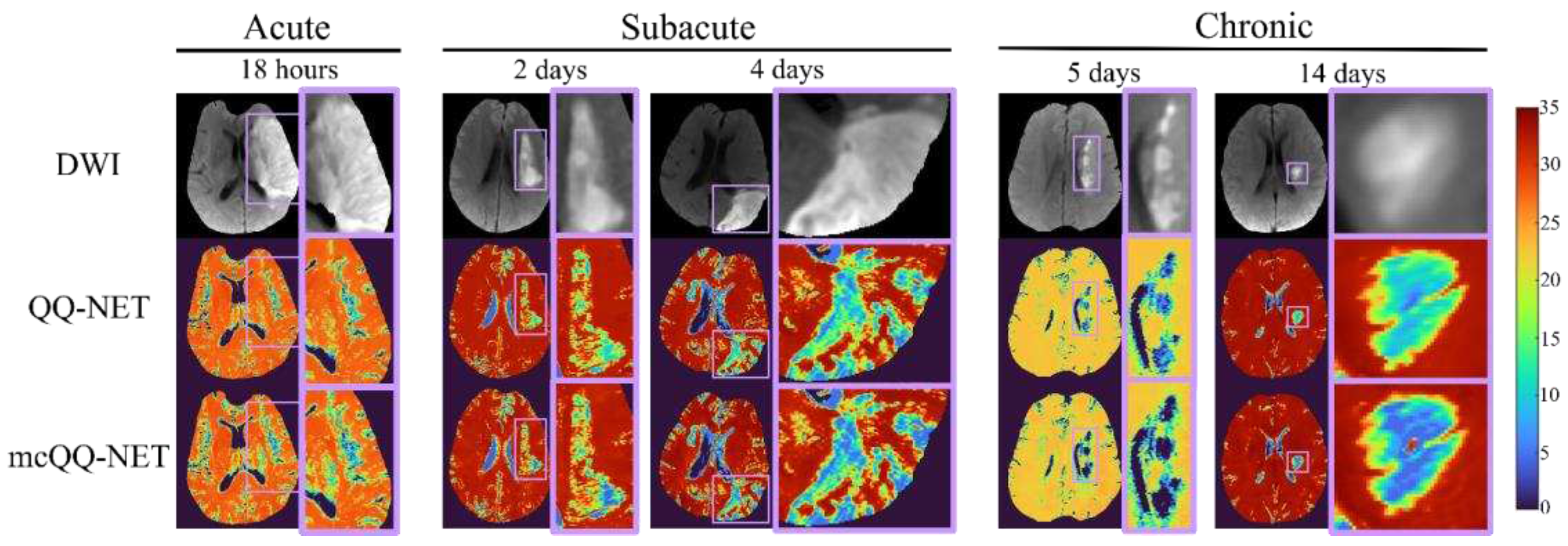
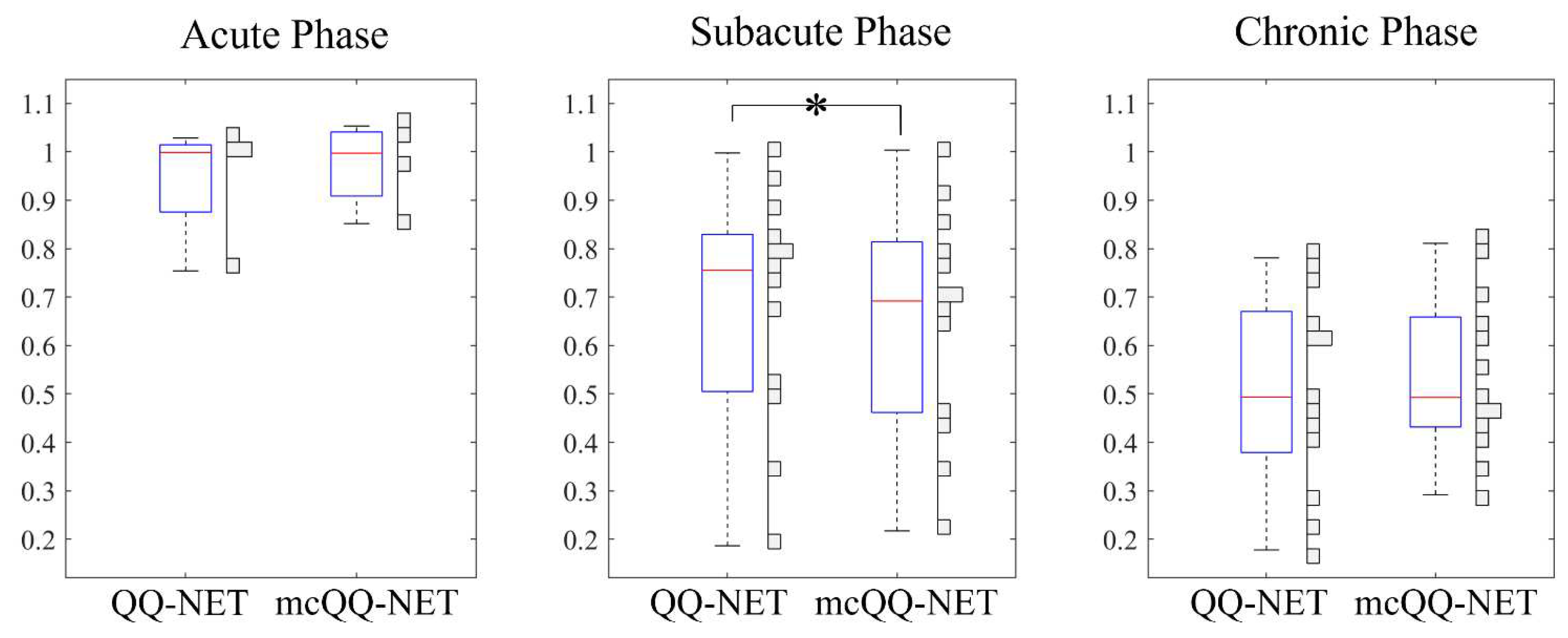
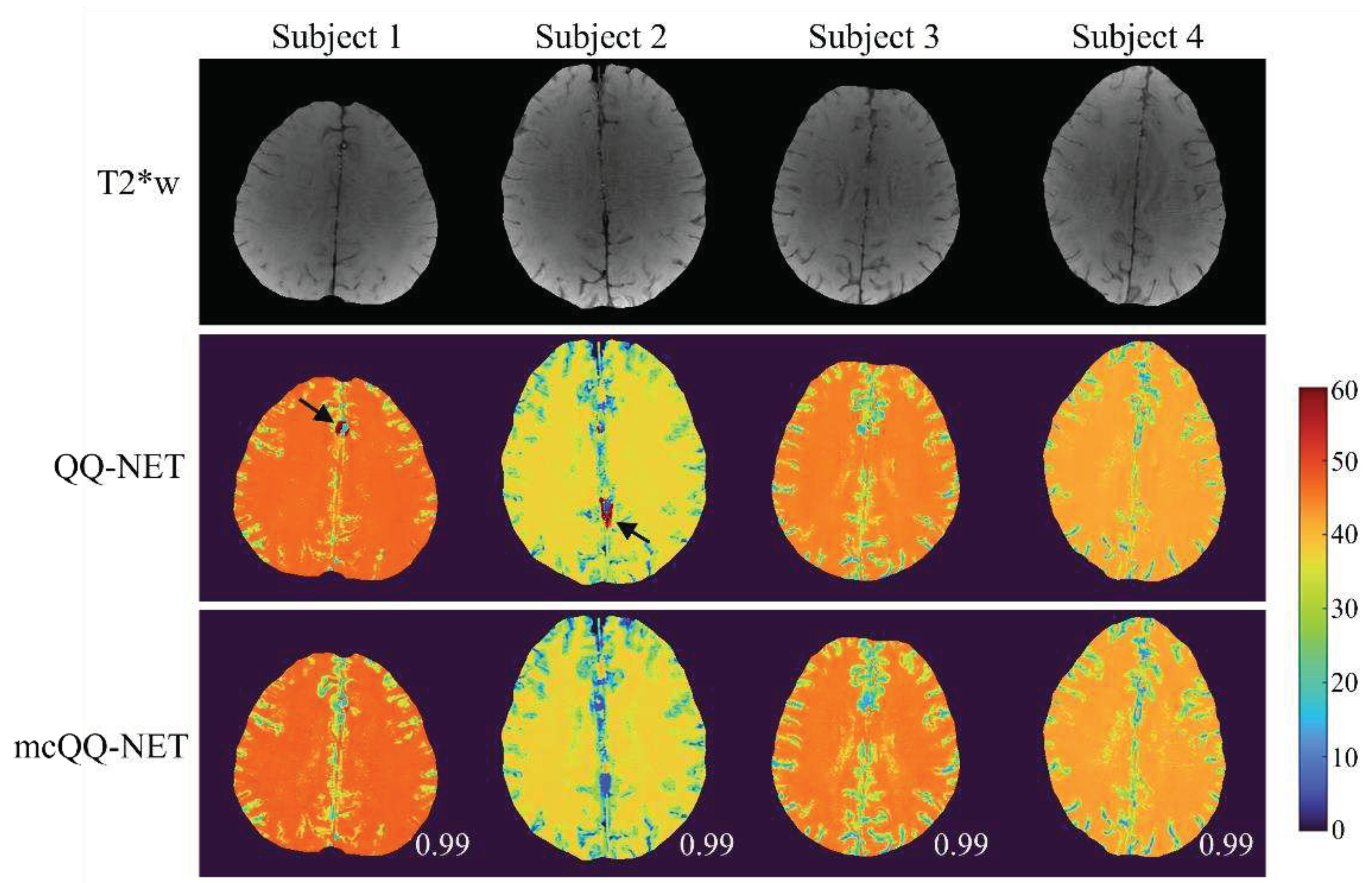
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Videen, T.O.; Yundt, K.D.; Fritsch, S.M.; Carpenter, D.A.; Grubb, R.L.; Powers, W.J. Variability of cerebral blood volume and oxygen extraction: Stages of cerebral haemodynamic impairment revisited. Brain A J. Neurol. 2002, 125, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Chazen, J.L.; Hartman, M.; Delgado, D.; Anumula, N.; Shao, H.; Mazumdar, M.; Segal, A.Z.; Kamel, H.; Leifer, D.; et al. Cerebrovascular reserve and stroke risk in patients with carotid stenosis or occlusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 2012, 43, 2884–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Baradaran, H.; Schweitzer, A.D.; Kamel, H.; Pandya, A.; Delgado, D.; Wright, D.; Hurtado-Rua, S.; Wang, Y.; Sanelli, P.C. Oxygen Extraction Fraction and Stroke Risk in Patients with Carotid Stenosis or Occlusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Buchan, R.J.; Yokoyama, E.; Kondoh, Y.; Sato, M.; Terashi, H.; Satoh, Y.; Watahiki, Y.; Senova, M.; Hirata, Y.; et al. Misery perfusion with preserved vascular reactivity in Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1997, 826, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghammer, P.; Vafaee, M.; Ostergaard, K.; Rodell, A.; Bailey, C.; Cumming, P. Effect of memantine on CBF and CMRO2 in patients with early Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand 2008, 117, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Kondo, S.; Hirai, S.; Sun, X.; Yamagishi, T.; Okamoto, K. Cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in progressive dementia associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 1993, 120, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D.J.; Leenders, K.L.; Head, G.; Marshall, J.; Legg, N.J.; Jones, T. Studies on regional cerebral oxygen utilisation and cognitive function in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1984, 47, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, H.L.; Stickland, R.C.; Patitucci, E.; Germuska, M.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Foster, C.; Bhome-Dhaliwal, S.; Lancaster, T.M.; Saxena, N.; Khot, S.; et al. Reduced brain oxygen metabolism in patients with multiple sclerosis: Evidence from dual-calibrated functional MRI. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulte, D.P.; Kelly, M.; Germuska, M.; Xie, J.; Chappell, M.A.; Okell, T.W.; Bright, M.G.; Jezzard, P. Quantitative measurement of cerebral physiology using respiratory-calibrated MRI. NeuroImage 2012, 60, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, C.J.; Hoge, R.D. Magnetic resonance imaging of resting OEF and CMRO2 using a generalized calibration model for hypercapnia and hyperoxia. NeuroImage 2012, 60, 1212–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoge, R.D. Calibrated FMRI. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, R.G.; Harris, A.D.; Stone, A.J.; Murphy, K. Measurement of OEF and absolute CMRO 2: MRI-based methods using interleaved and combined hypercapnia and hyperoxia. NeuroImage 2013, 83, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolar, D.S.; Rosen, B.R.; Sorensen, A.; Adalsteinsson, E. QUantitative Imaging of eXtraction of oxygen and TIssue consumption (QUIXOTIC) using venular-targeted velocity-selective spin labeling. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wong, E.C. Venous oxygenation mapping using velocity-selective excitation and arterial nulling. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1458–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Ge, Y. Quantitative evaluation of oxygenation in venous vessels using T2-Relaxation-Under-Spin-Tagging MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Deng, S.; Franklin, C.G.; O'Boyle, M.; Zhang, W.; Heyl, B.L.; Pan, L.; Jerabek, P.A.; Fox, P.T.; Lu, H. Validation of T2-based oxygen extraction fraction measurement with 15O positron emission tomography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yablonskiy, D.A. Quantitative BOLD: Mapping of human cerebral deoxygenated blood volume and oxygen extraction fraction: Default state. Magn Reson Med. 2007, 57, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhu, M.; Yablonskiy, D.A. Validation of oxygen extraction fraction measurement by qBOLD technique. Magn Reson Med. 2008, 60, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, X.; Yablonskiy, D.A. Separation of cellular and BOLD contributions to T2* signal relaxation. Magn Reson Med. 2016, 75, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yablonskiy, D.A.; Haacke, E.M. Theory of NMR signal behavior in magnetically inhomogeneous tissues: The static dephasing regime.
- Yablonskiy, D.A.; Sukstanskii, A.L.; He, X. BOLD-based Techniques for Quantifying Brain Hemodynamic and Metabolic Properties – Theoretical Models and Experimental Approaches. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 963–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Langham, M.C.; Wehrli, F.W. MRI Estimation of Global Brain Oxygen Consumption Rate. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrli, F.W.; Fan, A.P.; Rodgers, Z.B.; Englund, E.K.; Langham, M.C. Susceptibility-based time-resolved whole-organ and regional tissue oximetry. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrli, F.W.; Rodgers, Z.B.; Jain, V.; Langham, M.C.; Li, C.; Licht, D.J.; Magland, J. Time-resolved MRI oximetry for quantifying CMRO(2) and vascular reactivity. Acad. Radiol. 2014, 21, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, A.P.; Benner, T.; Bolar, D.S.; Rosen, B.R.; Adalsteinsson, E. Phase-based regional oxygen metabolism (PROM) using MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2012, 67, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, A.P.; Bilgic, B.; Gagnon, L.; Witzel, T.; Bhat, H.; Rosen, B.R.; Adalsteinsson, E. Quantitative oxygenation venography from MRI phase. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, K.; Liu, T.; Murakami, T.; Goodwin, J.; Uwano, I.; Yamashita, F.; Higuchi, S.; Wang, Y.; Ogasawara, K.; Ogawa, A.; et al. Oxygen extraction fraction measurement using quantitative susceptibility mapping: Comparison with positron emission tomography. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cho, J.; Zhou, D.; Nguyen, T.D.; Spincemaille, P.; Gupta, A.; Wang, Y. Quantitative susceptibility mapping-based cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen mapping with minimum local variance. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, T.; Gupta, A.; Spincemaille, P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Wang, Y. Quantitative mapping of cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM). Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, D.; Nguyen, T.D.; Spincemaille, P.; Gupta, A.; Wang, Y. Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) mapping with hyperventilation challenge using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM). Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, H.; Cho, J.; Mazerolle, E.L.; Wang, Y.; Pike, G.B. Cerebral OEF quantification: A comparison study between quantitative susceptibility mapping and dual-gas calibrated BOLD imaging. 2020, 83, 68–82. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mazerolle, E.L.; Cho, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Pike, G.B. Quantification of brain oxygen extraction fraction using QSM and a hyperoxic challenge. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 3271–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rochefort, L.; Liu, T.; Kressler, B.; Liu, J.; Spincemaille, P.; Lebon, V.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Quantitative susceptibility map reconstruction from MR phase data using bayesian regularization: Validation and application to brain imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2010, 63, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): Decoding MRI data for a tissue magnetic biomarker. Magn Reson Med. 2015, 73, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Dimov, A.; Cho, J.; Rochefort, L.d.; Seo, J.K.; Wang, Y. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) Algorithms: Mathematical Rationale and Computational Implementations. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2531–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Ma, Y.; Spincemaille, P.; Pike, G.B.; Wang, Y. Cerebral oxygen extraction fraction: Comparison of dual-gas challenge calibrated BOLD with CBF and challenge-free gradient echo QSM+qBOLD. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Spincemaille, P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Gupta, A.; Wang, Y. Temporal clustering, tissue composition, and total variation for mapping oxygen extraction fraction using QSM and quantitative BOLD. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Zhang, S.; Kee, Y.; Spincemaille, P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Hubertus, S.; Gupta, A.; Wang, Y. Cluster analysis of time evolution (CAT) for quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) and quantitative blood oxygen level-dependent magnitude (qBOLD)-based oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Lee, J.; An, H.; Goyal, M.S.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y. Cerebral oxygen extraction fraction (OEF): Comparison of challenge-free gradient echo QSM+qBOLD (QQ) with 15O PET in healthy adults. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 0271678X20973951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Kee, Y.; Spincemaille, P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Zhang, J.; Gupta, A.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) mapping by combining quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) and quantitative blood oxygenation level-dependent imaging (qBOLD). Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubertus, S.; Thomas, S.; Cho, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Schad, L.R. Using an artificial neural network for fast mapping of the oxygen extraction fraction with combined QSM and quantitative BOLD. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 2199–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubertus, S.; Thomas, S.; Cho, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Schad, L.R. Comparison of gradient echo and gradient echo sampling of spin echo sequence for the quantification of the oxygen extraction fraction from a combined quantitative susceptibility mapping and quantitative BOLD (QSM+qBOLD) approach. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cho, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Spincemaille, P.; Gupta, A.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y. Initial Experience of Challenge-Free MRI-Based Oxygen Extraction Fraction Mapping of Ischemic Stroke at Various Stages: Comparison With Perfusion and Diffusion Mapping. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Cho, J.; Shen, N.; Li, S.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yan, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. The Spatiotemporal Evolution of MRI-Derived Oxygen Extraction Fraction and Perfusion in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Huang, W.; Sweeney, E.M.; Luo, X.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Zhang, S.; Gillen, K.M.; Spincemaille, P.; Gupta, A.; et al. Brain oxygen extraction fraction mapping in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 271678x211048031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Zhang, S.; Cho, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W. Application of Cluster Analysis of Time Evolution for Magnetic Resonance Imaging -Derived Oxygen Extraction Fraction Mapping: A Promising Strategy for the Genetic Profile Prediction and Grading of Glioma. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Grinsven, E.E.; de Leeuw, J.; Siero, J.C.W.; Verhoeff, J.J.C.; van Zandvoort, M.J.E.; Cho, J.; Philippens, M.E.P.; Bhogal, A.A. Evaluating Physiological MRI Parameters in Patients with Brain Metastases Undergoing Stereotactic Radiosurgery—A Preliminary Analysis and Case Report. Cancers 2023, 15, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, G.C.; Cho, J.; Dyke, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Tokov, M.; Nguyen, T.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Amoashiy, M.; de Leon, M.; et al. Brain oxygen extraction and neural tissue susceptibility are associated with cognitive impairment in older individuals. J Neuroimaging 2022, 32, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Cho, J.; Chen, T.; Gillen, K.M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y. Oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) assesses cerebral oxygen metabolism of deep gray matter in patients with pre-eclampsia. Eur Radiol 2022, 32, 6058–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Lu, J.; Li, Y.; Cho, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal patterns of brain iron-oxygen metabolism in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur. Radiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Zhang, J.; Spincemaille, P.; Zhang, H.; Hubertus, S.; Wen, Y.; Jafari, R.; Zhang, S.; Nguyen, T.D.; Dimov, A.V.; et al. QQ-NET - using deep learning to solve quantitative susceptibility mapping and quantitative blood oxygen level dependent magnitude (QSM+qBOLD or QQ) based oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) mapping. Magn Reson Med 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Spincemaille, P.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. MEDI+0: Morphology enabled dipole inversion with automatic uniform cerebrospinal fluid zero reference for quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn Reson Med. 2018, 79, 2795–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; de Rochefort, L.; Ledoux, J.; Khalidov, I.; Chen, W.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Wisnieff, C.; Spincemaille, P.; Prince, M.R.; et al. Morphology enabled dipole inversion for quantitative susceptibility mapping using structural consistency between the magnitude image and the susceptibility map. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudbjartsson, H.; Patz, S. The Rician distribution of noisy MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wisnieff, C.; Lou, M.; Chen, W.; Spincemaille, P.; Wang, Y. Nonlinear formulation of the magnetic field to source relationship for robust quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Khalidov, I.; de Rochefort, L.; Spincemaille, P.; Liu, J.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Wang, Y. A novel background field removal method for MRI using projection onto dipole fields (PDF). NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kressler, B.; de Rochefort, L.; Liu, T.; Spincemaille, P.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y. Nonlinear regularization for per voxel estimation of magnetic susceptibility distributions from MRI field maps. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2010, 29, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S. A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med. Image Anal. 2001, 5, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.; Lin, W. Cerebral venous and arterial blood volumes can be estimated separately in humans using magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 2002, 48, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, F.; Nakazawa, K.; Tazaki, Y.; Ishii, K.; Hino, H.; Igarashi, H.; Kanda, T. Regional cerebral blood volume and hematocrit measured in normal human volunteers by single-photon emission computed tomography. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1985, 5, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savicki, J.P.; Lang, G.; Ikeda-Saito, M. Magnetic susceptibility of oxy- and carbonmonoxyhemoglobins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5417–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice; Churchill Livingstone: 2005.
- Spees, W.M.; Yablonskiy, D.A.; Oswood, M.C.; Ackerman, J.J. Water proton MR properties of human blood at 1.5 Tesla: Magnetic susceptibility, T(1), T(2), T*(2), and non-Lorentzian signal behavior. Magn Reson Med 2001, 45, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse Annotation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2016, Cham; 2016; pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, Cham, 2015; 2015//; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Chintala, S.; Chanan, G.; Yang, E.; DeVito, Z.; Lin, Z.; Desmaison, A.; Antiga, L.; Lerer, A. Automatic differentiation in PyTorch. Conf. Proc. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Birenbaum, D.; Bancroft, L.W.; Felsberg, G.J. Imaging in acute stroke. West J Emerg Med 2011, 12, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- X., U.; DA., Y. 70. X., U.; DA., Y. Enhancing image contrast in human brain by voxel spread function method. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Meeting of ISMRM Milan, Italy, Abstract 3197.
- Cusack, R.; Papadakis, N. New robust 3-D phase unwrapping algorithms: Application to magnetic field mapping and undistorting echoplanar images. Neuroimage 2002, 16, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, A.P.; Khalil, A.A.; Fiebach, J.B.; Zaharchuk, G.; Villringer, A.; Villringer, K.; Gauthier, C.J. Elevated brain oxygen extraction fraction measured by MRI susceptibility relates to perfusion status in acute ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 271678X19827944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Spincemaille, P.; Liu, Z.; Dimov, A.; Deh, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Gillen, K.M.; Wilman, A.H.; et al. Clinical quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): Biometal imaging and its emerging roles in patient care. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2017, 46, 951–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, A.D.; Liu, T.; Gupta, A.; Zheng, K.; Seedial, S.; Shtilbans, A.; Shahbazi, M.; Lange, D.; Wang, Y.; Tsiouris, A.J. Quantitative susceptibility mapping of the motor cortex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateral sclerosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015, 204, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, A.V.; Liu, Z.; Spincemaille, P.; Prince, M.R.; Du, J.; Wang, Y. Bone quantitative susceptibility mapping using a chemical species-specific R2* signal model with ultrashort and conventional echo data. Magn Reson Med. 2018, 79, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, A.V.; Liu, T.; Spincemaille, P.; Ecanow, J.S.; Tan, H.; Edelman, R.R.; Wang, Y. Joint estimation of chemical shift and quantitative susceptibility mapping (chemical QSM). Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 2100–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Spincemaille, P.; Nguyen, T.; Cho, J.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Anderson, J.; Wu, G.; Yang, B.; Fung, M.; Li, K.; et al. Multiecho complex total field inversion method (mcTFI) for improved signal modeling in quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 86, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatazawa, J.; Shimosegawa E Fau - Toyoshima, H.; Toyoshima H Fau - Ardekani, B.A.; Ardekani Ba Fau - Suzuki, A.; Suzuki A Fau - Okudera, T.; Okudera T Fau - Miura, Y.; Miura, Y. Cerebral blood volume in acute brain infarction: A combined study with dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI and 99mTc-HMPAO-SPECT.
- Baron, J.C. Mapping the Ischaemic Penumbra with PET: Implications for Acute Stroke Treatment. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1999, 9, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonova, P.; Burda, J.; Danielisova, V.; Nemethova, M.; Gottlieb, M. Development of a pattern in biochemical parameters in the core and penumbra during infarct evolution after transient MCAO in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirnagl, U.; Iadecola, C.; Moskowitz, M.A. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: An integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintun, M.A.; Raichle, M.E.; Martin, W.R.; Herscovitch, P. Brain oxygen utilization measured with O-15 radiotracers and positron emission tomography. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 1984, 25, 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Raichle, M.E.; MacLeod, A.M.; Snyder, A.Z.; Powers, W.J.; Gusnard, D.A.; Shulman, G.L. A default mode of brain function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001, 98, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; He, G.; Qing, H.; Zhou, W.; Dobie, F.; Cai, F.; Staufenbiel, M.; Huang, L.E.; Song, W. Hypoxia facilitates Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis by up-regulating BACE1 gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 18727–18732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Williams, G.B.; Cardenas-Blanco, A.; Arnold, R.J.; Lupson, V.; Nestor, P.J. In vivo quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) in Alzheimer's disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, B.D.; Stys, P.K. Virtual hypoxia and chronic necrosis of demyelinated axons in multiple sclerosis. Lancet. Neurol. 2009, 8, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




