Submitted:
26 December 2023
Posted:
26 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of experiment
2.2. Determination of basic analytical parameters in wines
2.3. Determination of individual volatile compounds by GC
2.4. Determination of individual biogenic amines by HPLC
2.5. Sensory analysis
2.6. Statistical analysis
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Determination of basic analytical parameters in wines
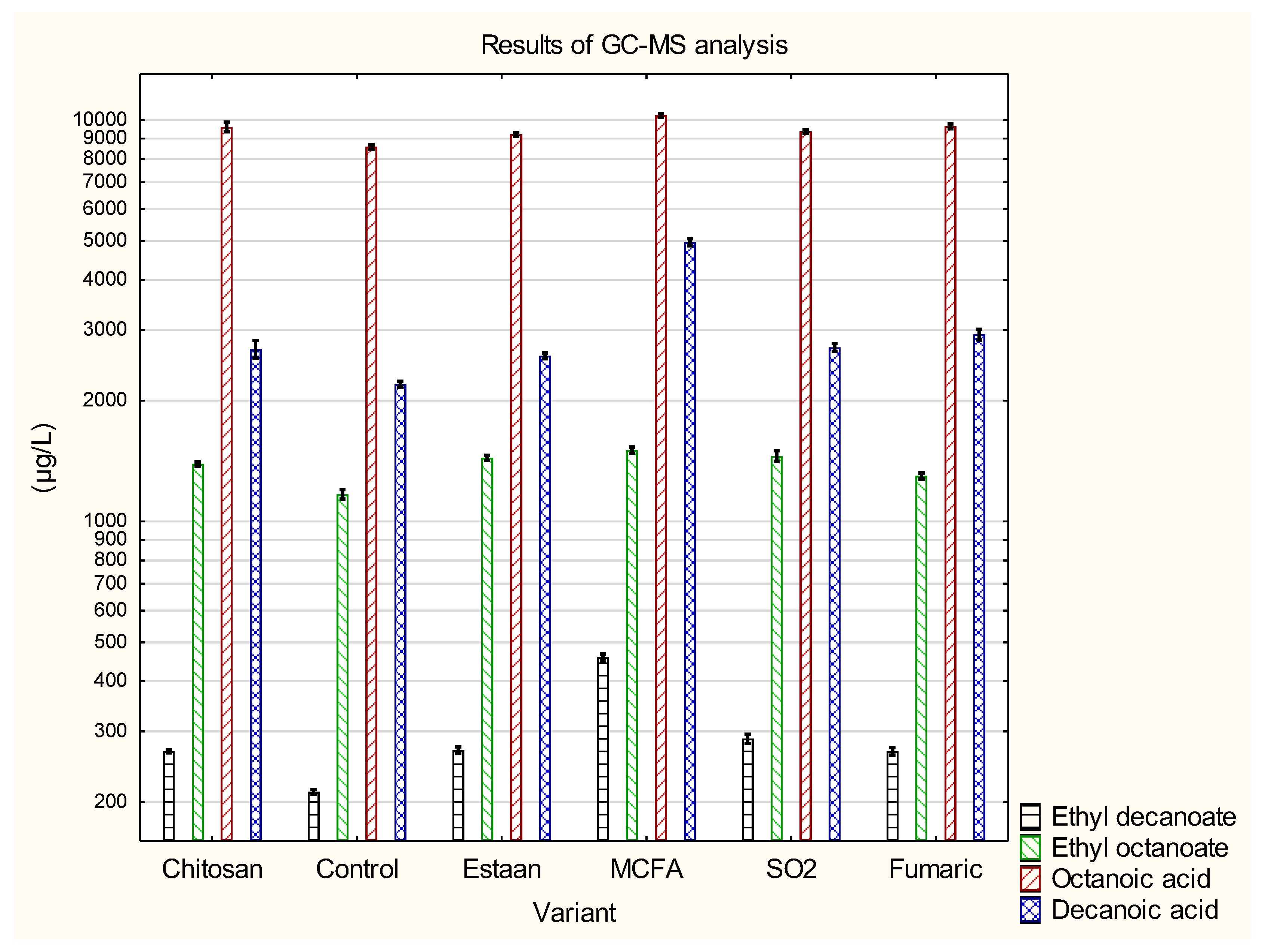
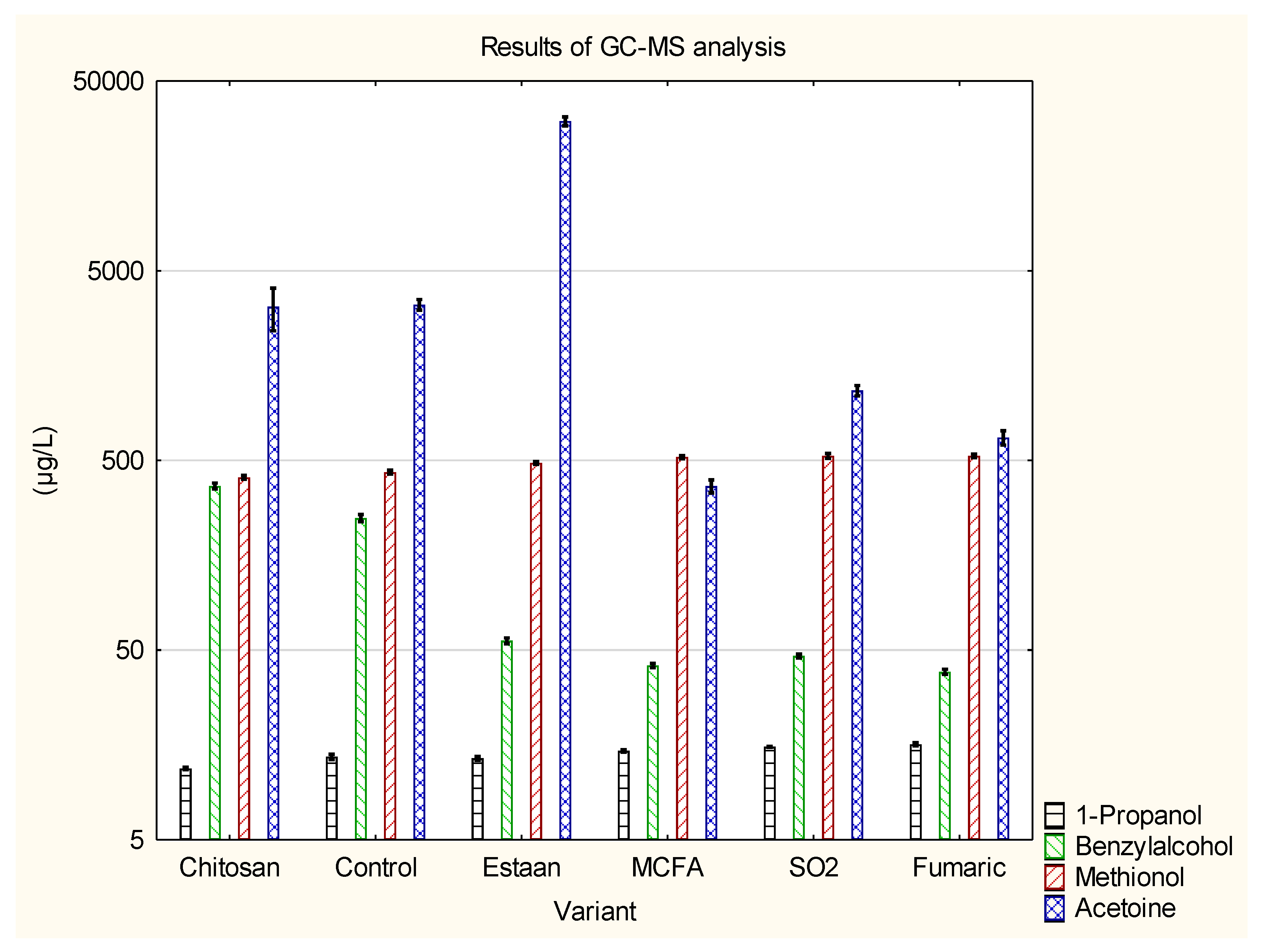
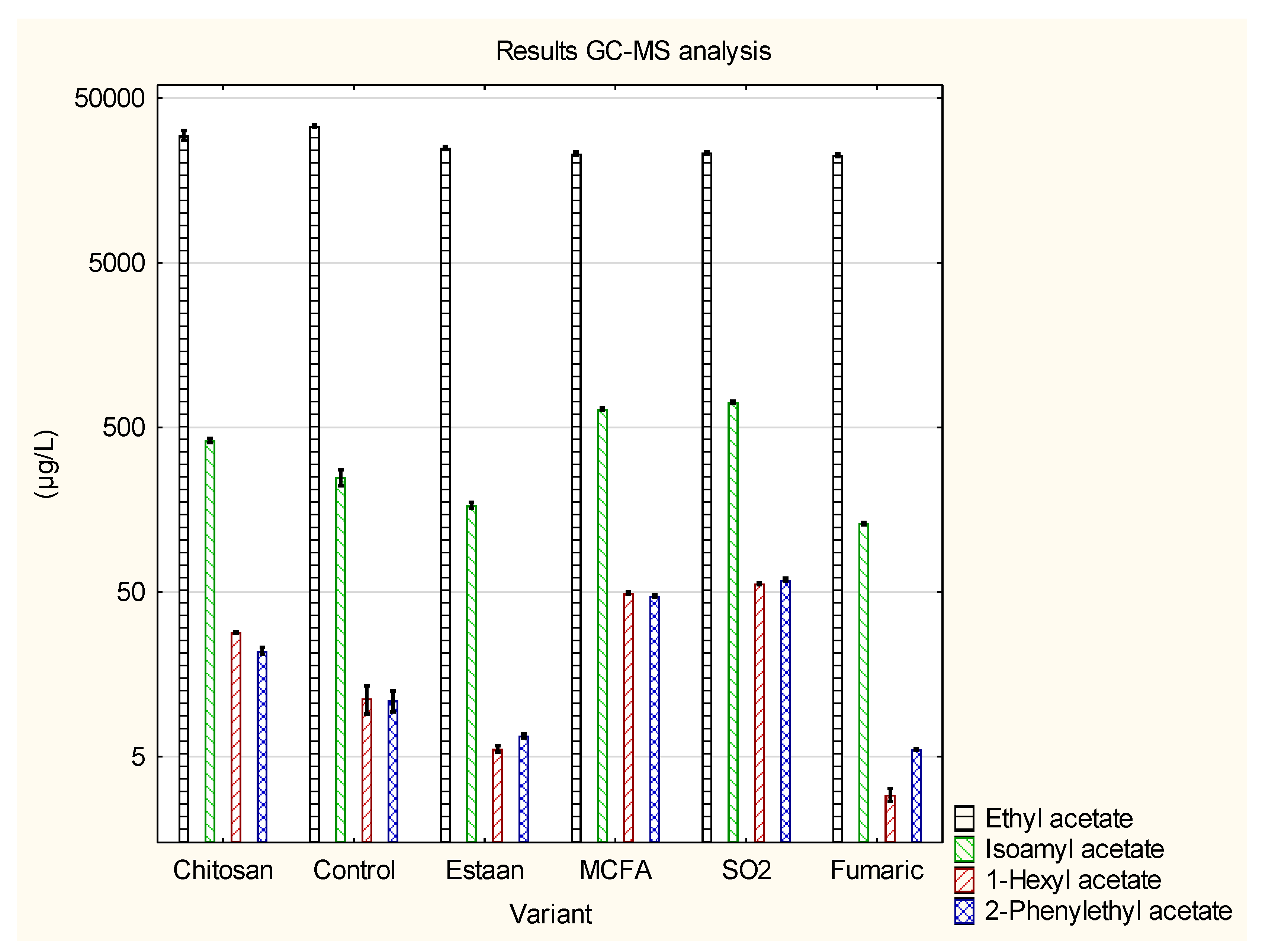
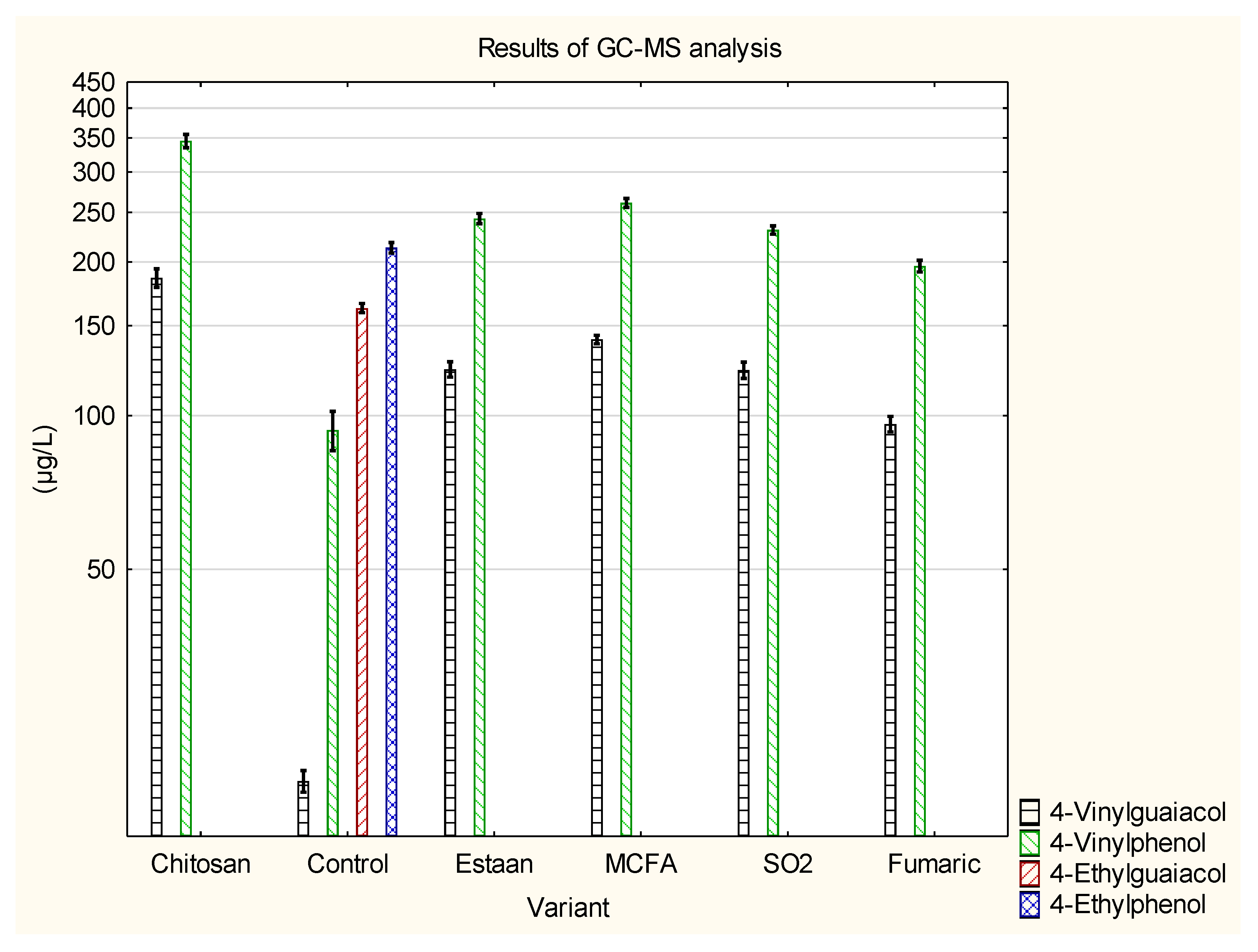
3.2. Determination of individual volatile compounds by GC-MS
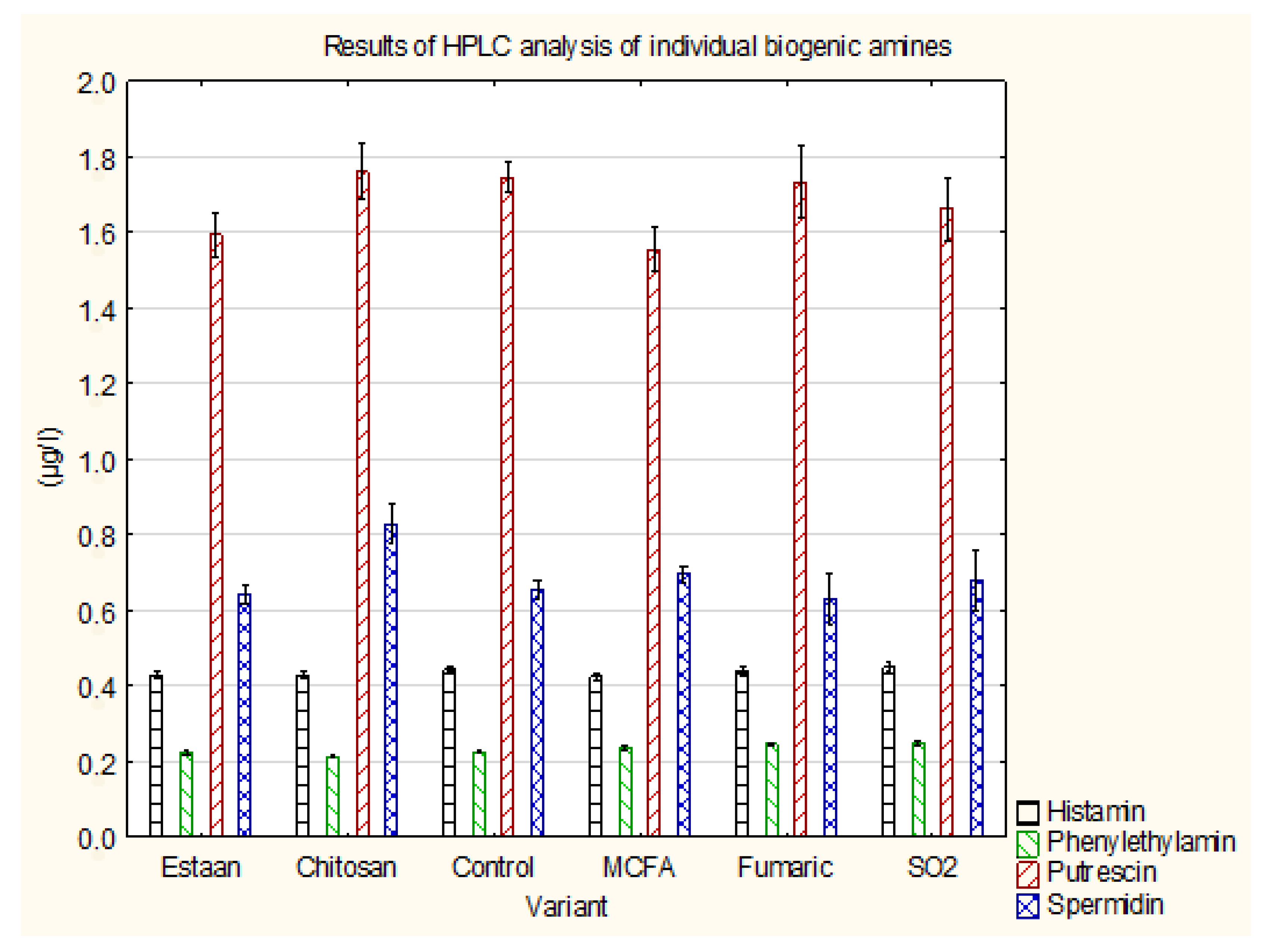
3.3. Determination of individual biogenic amines by HPLC
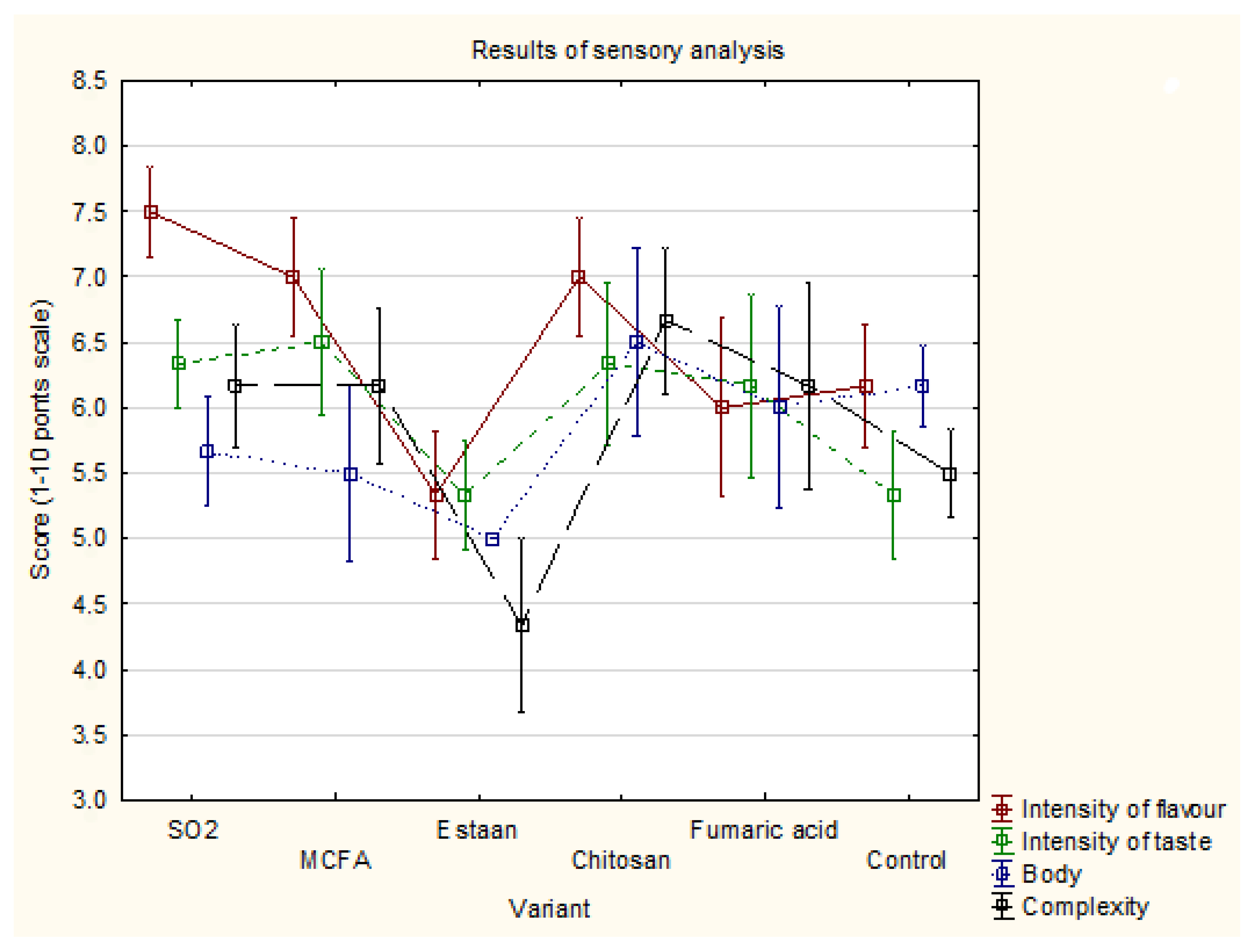
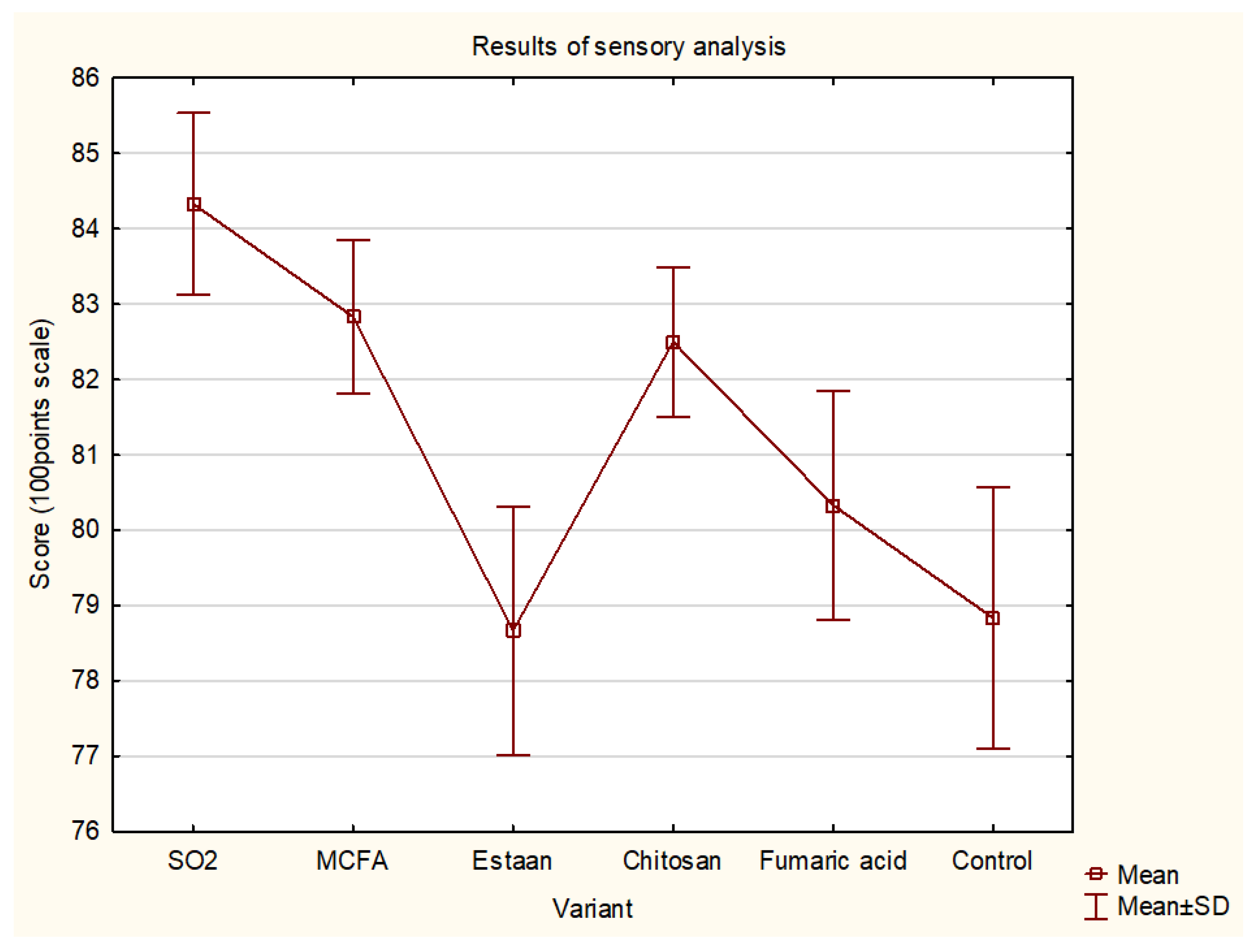
3.4. Sensory analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
| Compound (µg.L-1) |
Chitosan (Mean±SE) |
Control (Mean±SE) |
Estaan (Mean±SE) |
MCFA (Mean±SE) |
SO2 (Mean±SE) |
Fumaric a. (Mean±SE) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Propanol | 11.8±0.2 a | 13.7±0.4 b | 13.4±0.3 b | 14.7±0.2 c | 15.5±0.1 c | 15.9±0.3 d | p = 0.0000 |
| Benzylalcohol | 363±15 c | 249±11 b | 56±2 a | 41.5±1.1a | 46.6±1.1a | 38.5±1.2 a | p = 0.0000 |
| Methionol | 404±11 a | 434±10 a | 486±8 b | 521±11 c | 528±16 c | 528±12 c | p = 0.0000 |
| Ethyl acetate | 28 974±2273 b | 33 896±671 c | 24 921±521 a | 23 012±581 a | 23 298±439 a | 22 506±441 a | p = 0.0000 |
| Isoamyl acetate | 415±15 c | 249±28 b | 168±7 a | 646±12 d | 710±13 e | 130±2 a | p = 0.0000 |
| 1-Hexyl acetate | 28.2±0.4 c | 11.3±2.2 b | 5.6±0.2 a | 49.4±0.7 d | 56.1±0.8 e | 2.9±0.3 a | p = 0.0000 |
| 2-Phenylethyl acetate |
21.5±1.2 c | 10.9±1.6 b | 6.7±0.2 a | 47.2±0.8 d | 59.3±1.3 e | 5.5±0.1 a | p = 0.0000 |
| Ethyl octanoate | 1 390±19 c | 1 168±32 a | 1 441±21 c,d | 1 505±27 d | 1 458±45 c,d | 1 300±22 b | p = 0.0000 |
| Ethyl decanoate | 268±3 b | 212±3 a | 269±5 b | 459±9 d | 288±8 c | 268±6 b | p = 0.0000 |
| Octanoic acid | 9 522±298 b,c | 8 579±110 a | 9 215±98 b | 10 277±116 d | 9 374±101 b,c | 9 659±130 c | p = 0.0000 |
| Decanoic acid | 2637±151 b | 2197±38 a | 2 588±42 b | 4 965±97 d | 2716±61 b,c | 2 924±88 c | p = 0.0000 |
| 4-Vinylguaiacol | 183±9 e | 19.2±0.9 a | 123±4 c | 141±3 d | 123±5 c | 96.3±3.4 b | p = 0.0000 |
| 4-Vinylphenol | 340±11 e | 93.7±8.3 a | 243±6 c,d | 261±5 d | 231±4 c | 196±5 b | p = 0.0000 |
| 4-Ethylguaiacol | 0±0 a | 162±3 b | 0±0 a | 0±0 a | 0±0 a | 0±0 a | p = 0.0000 |
| 4-Ethylphenol | 0±0 a | 213±5 b | 0±0 a | 0±0 a | 0±0 a | 0±0 a | p = 0.0000 |
| Acetoine | 3680±842 c | 3315±211 b,c | 30735±1699 d | 366±29 a | 1169±74 a,b | 659±57 a | p = 0.0000 |
| Compound (µg.L-1) |
Estaan (Mean±SE) |
Chitosan (Mean±SE) |
Control (Mean±SE) |
MCFA (Mean±SE) |
SO2 (Mean±SE) |
Fumaric a. (Mean±SE) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histamin | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.43±0.01 a | 0.44±0.01 a | 0.42±0.01 a | 0.45±0.01 a | 0.44±0.01 a | p = 0.5263 |
| Phenylethylamin | 0.22±0.01 a,b | 0.22±0.01 a | 0.23±0.00 a,b | 0.24±0.01 b,c | 0.25±0.01 c | 0.25±0.00 c | p = 0.0002 |
| Putrescin | 1.59±0.06 a,b | 1.76±0.07 b | 1.75±0.04 a,b | 1.56±0.06 a | 1.66±0.08 a,b | 1.73±0.10 a,b | p = 0.2200 |
| Spermidin | 0.64±0.03 a | 0.83±0.05 b | 0.66±0.02 a | 0.70±0.02 a,b | 0.68±0.08 a | 0.63±0.07 a | p = 0.1061 |
| Category | SO2 (Mean±SE) |
MCFA (Mean±SE) |
Estaan (Mean±SE) |
Chitosan (Mean±SE) |
Fumaric a. (Mean±SE) |
Control (Mean±SE) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score (100 points) | 84.3±1.2 c | 82.8±1.0 b,c | 78.7±1.6 a | 82.5±1.0 a,b,c | 80.3±1.5 a.b | 78.8±1.7 a | 0.034 |
|
Intensity of flavour |
7.5±0.3 c | 7.0±0.4 b,c | 5.3±0.5 a | 7.0±0.4 b,c | 6.0±0.7 a,c | 6.2±0.5 a,b,c | 0.042 |
| Intensity of taste | 6.3±0.3 a | 6.5±0.6 a | 5.3±0.4 a | 6.3±0.6 a | 6.2±0.7 a | 5.3±0.5 a | 0.453 |
| Body | 5.7±0.4 a | 5.5±0.7 a | 5.0±0.0 a | 6.5±0.7 a | 6.0±0.8 a | 6.2±0.3 a | 0.487 |
| Complexity | 6.2±0.5 b | 6.2±0.6 b | 4.3±0.7 a | 6.7±0.6 b | 6.2±0.8 b | 5.5±0.3 a,b | 0.116 |
References
- Davis, C.; Wibowo, D.; Eschenbruch, R.; Lee, T.; Fleet, G. Practical Implications Of Malolactic Fermentation - A Review. American Journal Of Enology And Viticulture 1985, 36, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.; Dicks, L. Control Of Malolactic Fermentation In Wine. A Review. South African J Enol Viticult 2004, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonvaud-Funel, A. Lactic Acid Bacteria In The Quality Improvement And Depreciation Of Wine. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek International Journal Of General And Molecular Microbiology 1999, 76, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanvuuren, H.; Dicks, L. Leuconostoc Oenos - A Review. American Journal Of Enology And Viticulture 1993, 44, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, A.; Bañuelos, M.; López, C.; Song, C.; Vejarano, R.; Loira, I.; Palomero, F.; Lepe, J. Use Of Fumaric Acid To Control Ph And Inhibit Malolactic Fermentation In Wines. Food Additives And Contaminants Part A-Chemistry Analysis Control Exposure & Risk Assessment 2020, 37, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.; Edwards, C. Inhibition Of Malolactic Fermentation By Saccharomyces During Alcoholic Fermentation Under Low- And High-Nitrogen Conditions:: A Study In Synthetic Media. Australian Journal Of Grape And Wine Research 2006, 12, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, A.; Loira, I.; Vejarano, R.; González, C.; Callejo, M.; Suárez-Lepe, J. Emerging Preservation Technologies In Grapes For Winemaking. Trends In Food Science & Technology 2017, 67, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raúl, F.-G.; Miquel, P.; Laura, M.; Enric, N.; Claudio, H.; Imma, A. Microbiological, Physical, And Chemical Procedures To Elaborate High-Quality So2-Free Wines. In Grapes And Wines; Intechopen: Rijeka, 2017; P. Ch. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Krentz, S.; Darius, S.; Power, J.; Lagarde, G. Inhibition Of Spoilage Lactic Acid Bacteria By Lysozyme During Wine Alcoholic Fermentation. Australian Journal Of Grape And Wine Research 2002, 8, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerm, E.; Engelbrecht, L.; Du Toit, M. Malolactic Fermentation: The Abc's Of MLF. South African Journal Of Enology And Viticulture 2010, 31, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancín-Azpilicueta, C.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; Moler, J.; Nieto-Rojo, R.; Urmeneta, H. Effects Of Reduced Levels Of Sulfite In Wine Production Using Mixtures With Lysozyme And Dimethyl Dicarbonate On Levels Of Volatile And Biogenic Amines. Food Additives And Contaminants Part A-Chemistry Analysis Control Exposure & Risk Assessment 2016, 33, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnici, F.; Natali, N.; Riponi, C. Efficacy Of Chitosan In Inhibiting The Oxidation Of (+)-Catechin In White Wine Model Solutions. Journal Of Agricultural And Food Chemistry 2014, 62, 9868–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, R.; Ng, T.; Wong, J.; Chan, W. Chitosan: An Update On Potential Biomedical And Pharmaceutical Applications. Marine Drugs 2015, 13, 5156–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillandier, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Jentzer, J.; Gautier, S.; Sieczkowski, N.; Granes, D.; Brandam, C. Effect Of A Fungal Chitosan Preparation On Brettanomyces Bruxellensis, A Wine Contaminant. Journal Of Applied Microbiology 2015, 118, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Rivas, L.; Escudero-Abarca, B.; Aguilar-Uscanga, M.; Hayward-Jones, P.; Mendoza, P.; Ramírez, M. Selective Antimicrobial Action Of Chitosan Against Spoilage Yeasts In Mixed Culture Fermentations. Journal Of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology 2004, 31, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Baños, S.; Romanazzi, G.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.; Bautistabanos, S.; Jimenezaparicio, A. Chitosan In The Preservation Of Agricultural Commodities Preface. Chitosan In The Preservation Of Agricultural Commodities 2016, Xv–Xvii. [Google Scholar]
- Mandon P, P.E. Chitosan Market By Source (Shrimp, Squid, Crab, Krill, And Others) And Application (Water Treatment, Biomedical & Pharmaceutical, Cosmetics, Food & Beverage, And Others): Global Opportunity Analysis And Industry Forecast, 2020–2027.. Available Online: (Accessed On .
- Vaara, M. Agents That Increase The Permeability Of The Outer-Membrane. Microbiological Reviews 1992, 56, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonvaudfunel, A.; Desaad, A. Purification And Properties Of A Malolactic Enzyme From A Strain Of Leuconostoc-Mesenteroides Isolated From Grapes. Applied And Environmental Microbiology 1982, 43, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 20. D. R. Cofran, B.J.M. The Effect Of Fumaric Acid On Malo-Lactic Fermentation. Agricultural And Food Sciences 1970, 21, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchelistcheff, A.; Peterson, R.; Vangelde. M. Control Of Malo-Lactic Fermentation In Wine. American Journal Of Enology And Viticulture 1971, 22, 1-+. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilone, G.; Rankine, B.; Pilone, D. Inhibiting Malo-Lactic Fermentation In Australian Dry Red Wines By Adding Fumaric Acid. American Journal Of Enology And Viticulture 1974, 25, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.; Williams, J.; Moore, C. Effects Of Fumarates On Inflammatory Human Astrocyte Responses And Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Annals Of Clinical And Translational Neurology 2017, 4, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortereal, M.; Leao, C. Transport Of Malic-Acid And Other Dicarboxylic-Acids In The Yeast Hansenula-Anomala. Applied And Environmental Microbiology 1990, 56, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saayman, M.; Van Vuuren, H.; Van Zyl, W.; Viljoen-Bloom, M. Differential Uptake Of Fumarate By Candida utilis And Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Applied Microbiology And Biotechnology 2000, 54, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, H.; Costello, P.; Remize, F.; Guzzo, J.; Guilloux-Benatier, M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae - Oenococcus oeni Interactions In Wine:: Current Knowledge And Perspectives. International Journal Of Food Microbiology 2004, 93, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.; Beelman, R.; Bartley, C.; Mcconnell, A. Production Of Decanoic Acid And Other Volatile Compounds And The Growth Of Yeast And Malolactic Bacteria During Vinification. American Journal Of Enology And Viticulture 1990, 41, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R, C.; Mt, V.; A, B.; M, C. Inhibitory Effect Of Sulfur Dioxide And Other Stress Compounds In Wine On The Atpase Activity Of Oenococcus oeni. Microbiol Lett. 2, 2. [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, A.; Moreno-Arribas, M.; Martín-Alvarez, P.; Bartolomé, B. Comparative Study Of The Inhibitory Effects Of Wine Polyphenols On The Growth Of Enological Lactic Acid Bacteria. International Journal Of Food Microbiology 2011, 145, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivala, M.; Villecco, M.; Fanzone, M.; Jofre, V.; Rodríguez-Vaquero, M.; Aredes, P. Characterization, Antibacterial And Biological Activities Of Phenolic Fraction Of Argentinean Red Wines. The Open Conference Proceedings Journal 2014, 5, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivala, M.; Villecco, M.; Fanzone, M.; Jofré, V.; Aredes-Fernández, P. Characterization Of The Phenolic Fraction From Argentine Wine And Its Effect On Viability And Polysaccharide Production Of Pediococcus pentosaceus. Biotechnology Letters 2015, 37, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, A.; Bertrand, A.; Lonvaud-Funel, A.; De Revel, G. Vanillin Production From Simple Phenols By Wine-Associated Lactic Acid Bacteria. Letters In Applied Microbiology 2007, 44, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.; Couto, J.; Hogg, T. Influence Of Phenolic Acids On Growth And Inactivation Of Oenococcus oeni And Lactobacillus hilgardii. Journal Of Applied Microbiology 2003, 94, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.; Campos, F.; De Freitas, V.; Hogg, T.; Couto, J. Effect Of Phenolic Aldehydes And Flavonoids On Growth And Inactivation Of Oenococcus oeni And Lactobacillus hilgardii. Food Microbiology 2008, 25, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ruiz, A.; Bartolomé, B.; Cueva, C.; Martín-Alvarez, P.; Moreno-Arribas, M. Inactivation Of Oenological Lactic Acid Bacteria (Lactobacillus hilgardii And Pediococcus pentosaceus) By Wine Phenolic Compounds. Journal Of Applied Microbiology 2009, 107, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landete, J.; Rodríguez, H.; De Las Rivas, B.; Muñoz, R. High-Added-Value Antioxidants Obtained From The Degradation Of Wine Phenolics By Lactobacillus plantarum. Journal Of Food Protection 2007, 70, 2670–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguant, C.; Bordons, A.; Arola, L.; Rozès, N. Influence Of Phenolic Compounds On The Physiology Of Oenococcus oeni From Wine. Journal Of Applied Microbiology 2000, 88, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stead, D. The Effect Of Hydroxycinnamic Acids On The Growth Of Wine-Spoilage Lactic-Acid Bacteria. Journal Of Applied Bacteriology 1993, 75, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, S.; Pfeiffer, P.; Zuber, U.; König, H. Influence Of Epigallocatechin Gallate And Phenolic Compounds From Green Tea On The Growth Of Oenococcus oeni. Journal Of Applied Microbiology 2008, 104, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, N.; Lonvaudfunel, A.; Glories, Y. Effect Of Phenolic Acids And Anthocyanins On Growth, Viability And Malolactic Activity Of A Lactic Acid Bacterium. Food Microbiology 1997, 14, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartowsky, E. Bacterial Spoilage Of Wine And Approaches To Minimize It. Letters In Applied Microbiology 2009, 48, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, A.; Bartolomé, B.; Martínez-Rodríguez, A.; Pueyo, E.; Martín-Alvarez, P.; Moreno-Arribas, M. Potential Of Phenolic Compounds For Controlling Lactic Acid Bacteria Growth In Wine. Food Control 2008, 19, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.; Hanlon, G.; Denyer, S.; Lambert, R. Membrane Damage To Bacteria Caused By Single And Combined Biocides. Journal Of Applied Microbiology 2003, 94, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, H.; Curiel, J.; Landete, J.; De Las Rivas, B.; De Felipe, F.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Mancheño, J.; Muñoz, R. Food Phenolics And Lactic Acid Bacteria. International Journal Of Food Microbiology 2009, 132, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anli, R.E.; Bayram, M. Biogenic Amines In Wines. 2009, 25, 86-102. [CrossRef]
- Jastrzebska, A.; Piasta, A.; Szlyk, E. Simultaneous Determination Of Selected Biogenic Amines In Alcoholic Beverage Samples By Isotachophoretic And Chromatographic Methods. Food Additives And Contaminants Part A-Chemistry Analysis Control Exposure & Risk Assessment 2014, 31, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihak, Z.; Prusova, B.; Kumsta, M.; Baron, M. Effect Of Must Hyperoxygenation On Sensory Expression And Chemical Composition Of The Resulting Wines. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusova, B.; Baron, M. Effect Of Controlled Micro Oxygenation On White Wine. Ciencia E Tecnica Vitivinicola 2018, 33, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumsta, M.; Helmová, T.; Stusková, K.; Baron, M.; Prusová, B.; Sochor, J. Hplc/Hilic Determination Of Biogenic Amines In Wines Produced By Different Winemaking Technologies. Acta Alimentaria 2023, 52, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugliano, M.; Moio, L. Changes In The Concentration Of Yeast-Derived Volatile Compounds Of Red Wine During Malolactic Fermentation With Four Commercial Starter Cultures Of Oenococcus oeni. Journal Of Agricultural And Food Chemistry 2005, 53, 10134–10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Chen, Z.; Jin, C. Combined Influence Of Lactic Acid Bacteria Starter And Final Ph On The Induction Of Malolactic Fermentation And Quality Of Cherry Wines. Lwt-Food Science And Technology 2018, 89, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, C.; Fritsch, S.; Schnell, S.; Grossmann, M.; Rauhut, D.; Du Toit, M. Influence Of Ph And Ethanol On Malolactic Fermentation And Volatile Aroma Compound Composition In White Wines. Lwt-Food Science And Technology 2011, 44, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Gong, H.; Liu, W.; Jin, C. Application And Validation Of Autochthonous Lactobacillus plantarum Starter Cultures For Controlled Malolactic Fermentation And Its Influence On The Aromatic Profile Of Cherry Wines. Food Microbiology 2016, 55, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, C.; Fritsch, S.; Schnell, S.; Grossmann, M.; Krieger-Weber, S.; Du Toit, M.; Rauhut, D. Impact Of Different Malolactic Fermentation Inoculation Scenarios On Riesling Wine Aroma. World Journal Of Microbiology & Biotechnology 2012, 28, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Bayón, M.; Alegría, E.; Polo, M.; Tenorio, C.; Martín-Alvarez, P.; De La Banda, M.; Ruiz-Larrea, F.; Moreno-Arribas, M. Wine Volatile And Amino Acid Composition After Malolactic Fermentation:: Effect Of Oenococcus oeni And Lactobacillus plantarum Starter Cultures. Journal Of Agricultural And Food Chemistry 2005, 53, 8729–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licek, J.; Baron, M.; Sochor, J.; Kumsta, M.; Mlcek, J. Observation Of Residues Content After Application Of A Medium-Chain Fatty Acids Mixture At The End Of Alcoholic Fermentation. Fermentation-Basel 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugliano, M.; Henschke, P.A. Yeasts And Wine Flavour. In Wine Chemistry And Biochemistry; Springer New York: New York, Ny, 2009; Pp. 313-392. [Google Scholar]
- Swiegers, J.H.; Pretorius, I.S. Yeast Modulation Of Wine Flavor. Advances In Applied Microbiology 2005, 57, 131–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licek, J.; Baron, M.; Sochor, J. Comparison Of Mcfa And Other Methods Of Terminating Alcohol Fermentation And Their Influence On The Content Of Carbonyl Compounds In Wine. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, P.; Suzzi, G. Origin And Production Of Acetoin During Wine Yeast Fermentation. Applied And Environmental Microbiology 1996, 62, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamini, R.; De Luca, G.; Di Stefano, R. Changes In Carbonyl Compounds In Chardonnay And Cabernet Sauvignon Wines As A Consequence Of Malolactic Fermentation. Vitis 2002, 41, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Martineau, B.; Acree, T.E.; Henickkling, T. Effect Of Wine Type On The Detection Threshold For Diacetyl. Food Research International 1995, 28, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, H.; Ren, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, B. Dibasic Ammonium Phosphate Application Enhances Aromatic Compound Concentration In Bog Bilberry Syrup Wine. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Lan, Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, B. Modifications Of Phenolic Compounds, Biogenic Amines, And Volatile Compounds In Cabernet Gernishct Wine Through Malolactic Fermentation By Lactobacillus plantarum And Oenococcus oeni. Fermentation-Basel 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatonnet, P.; Dubourdieu, D.; Boidron, J.; Lavigne, V. Synthesis Of Volatile Phenols By Saccharomycesn cerevisiae In Wines. Journal Of The Science Of Food And Agriculture 1993, 62, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatonnet, P.; Dubourdieu, D.; Boidron, J.; Pons, M. The Origin Of Ethylphenols In Wines. Journal Of The Science Of Food And Agriculture 1992, 60, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Han, Y. Biogenic Amines In Wine: A Review. International Journal Of Food Science And Technology 2015, 50, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.; De Nadra, M. Biogenic Amine Production By Lactobacillus. Journal Of Applied Microbiology 2001, 90, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañas, P.; Alonso, S.; Pérez, P.; Prieto, S.; Romero, E.; Herreros, M. Biogenic Amine Production By Oenococcus oeni Isolates From Malolactic Fermentation Of Tempranillo Wine. Journal Of Food Protection 2009, 72, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, S.; Mangani, S.; Granchi, L.; Vincenzini, M. Biogenic Amine Production By Oenococcus oeni. Current Microbiology 2002, 44, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variant | Term | Alcohol (% vol.) |
Titr. Acids (g.L-1) |
Res. Sugar (g.L-1) |
pH | Malic acid (g.L-1) |
Lactic acid (g.L-1) |
Acetic acid (g.L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8.3. | 11.76±0.28 | 6.13±0.17 | 0.26±0.19 | 3.34±0.02 | 0.35±0.10 | 1.18±0.11 | 0.31±0.02 |
| 18.9. | 12.16±0.02 | 6.18±0.03 | 0.32±0.32 | 2.98±0.02 | 0.79±0.18 | 1.32±0.16 | 0.25±0.02 | |
| SO2 | 8.3. | 12.01±0.06 | 6.89±0.04 | 0.00±0.00 | 3.26±0.02 | 1.97±0.14 | 0.43±0.12 | 0.25±0.02 |
| 18.9. | 12.12±0.02 | 6.61±0.1 | 1.29±0.47 | 3.14±0.01 | 2.16±0.23 | 0.09±0.06 | 0.30±0.02 | |
| Estaan | 8.3. | 12.20±0.04 | 7.18±0.11 | 0.00±0.00 | 3.24±0.01 | 2.18±0.12 | 0.26±0.09 | 0.26±0.02 |
| 18.9. | 12.19±0.04 | 5.76±0.04 | 1.69±0.60 | 3.12±0.07 | 0.61±0.21 | 0.90±0.10 | 0.34±0.02 | |
| MCFA | 8.3. | 12.08±0.03 | 7.10±0.08 | 0.00±0.00 | 3.24±0.02 | 2.23±0.08 | 0.19±0.07 | 0.29±0.02 |
| 18.9. | 12.15±0.04 | 6.60±0.12 | 1.66±0.67 | 3.16±0.02 | 1.93±0.17 | 0.06±0.06 | 0.30±0.02 | |
| Fumaric | 8.3. | 12.10±0.04 | 7.22±0.12 | 0.12±0.11 | 3.22±0.02 | 2.27±0.22 | 0.09±0.05 | 0.29±0.03 |
| 18.9. | 12.15±0.02 | 6.72±0.11 | 2.45±0.39 | 3.12±0.02 | 2.21±0.22 | 0.03±0.03 | 0.32±0.02 | |
| Chitosan | 8.3. | 12.08±0.02 | 7.12±0.13 | 0.12±0.12 | 3.23±0.02 | 2.01±0.21 | 0.33±0.11 | 0.31±0.03 |
| 18.9. | 12.13±0.04 | 6.21±0.06 | 0.00±0.00 | 3.00±0.03 | 0.17±0.07 | 1.53±0.07 | 0.31±0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





