Submitted:
25 December 2023
Posted:
26 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
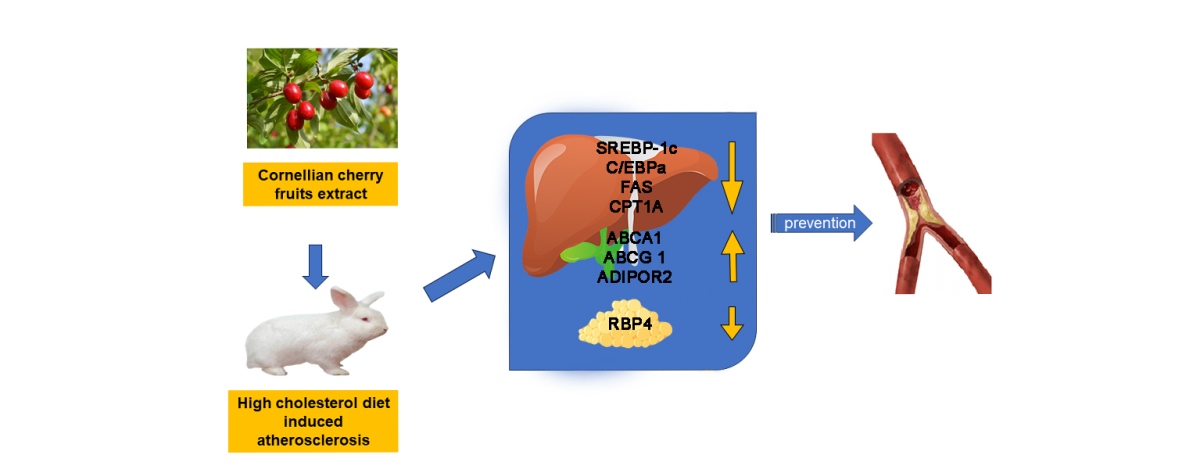
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
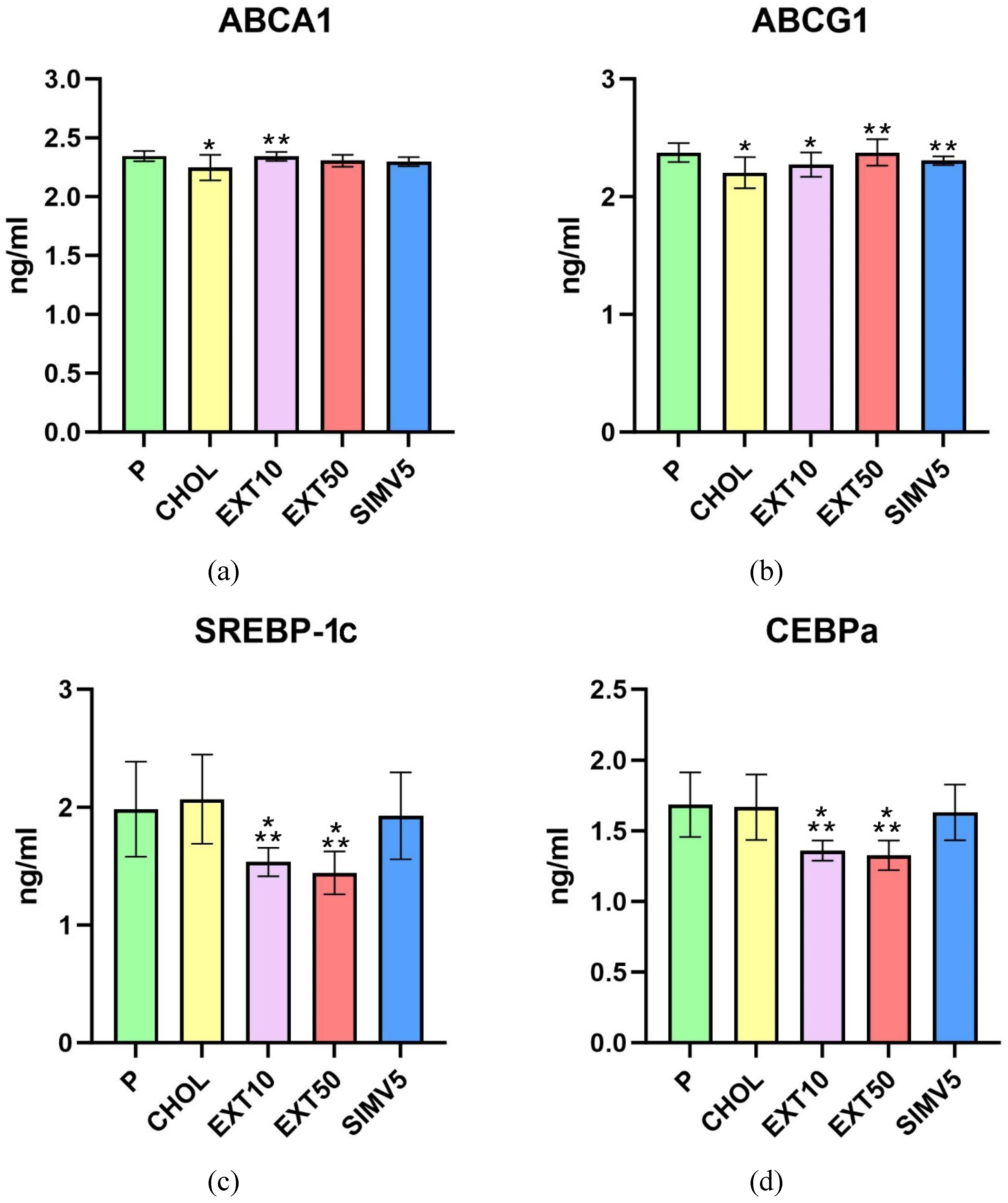
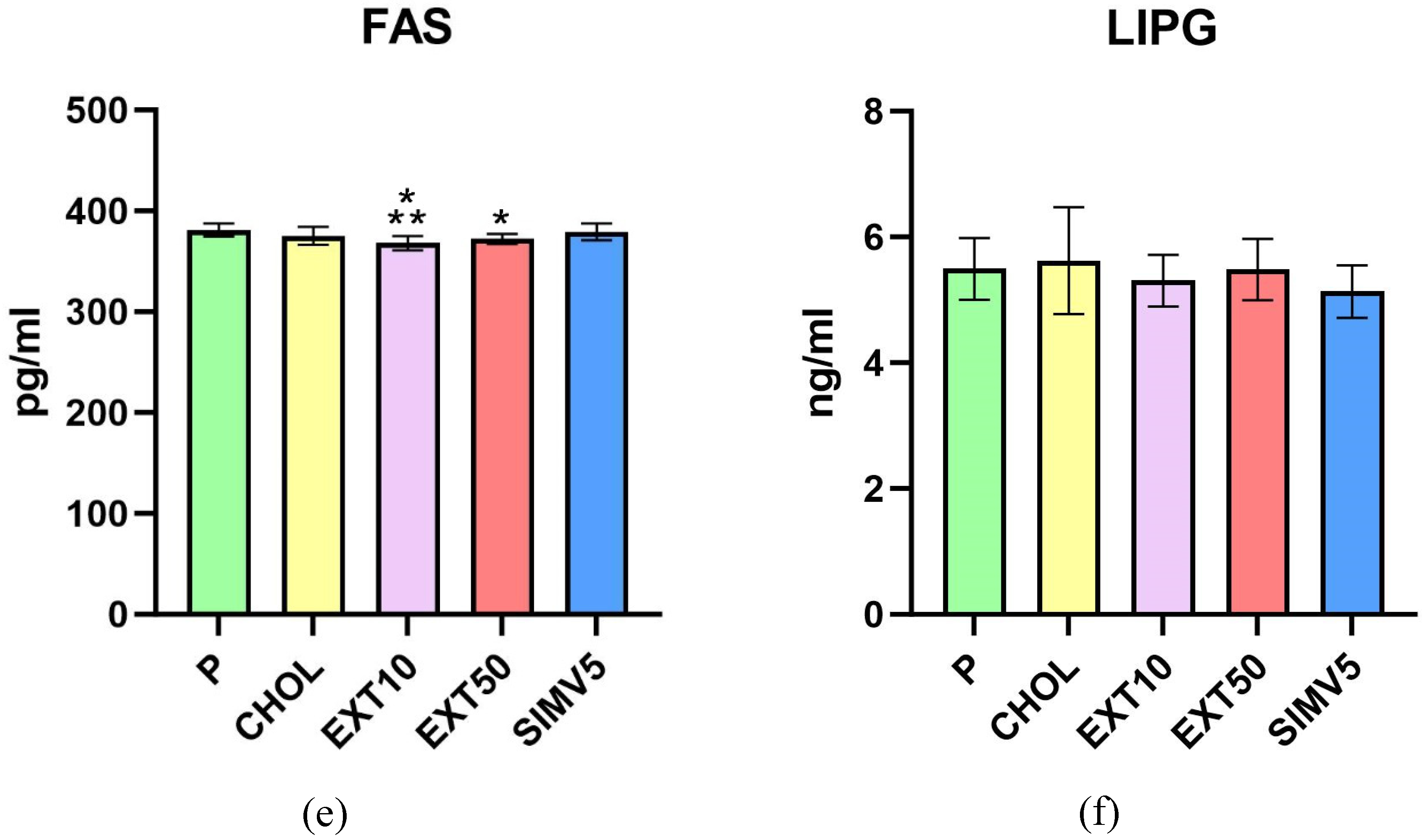
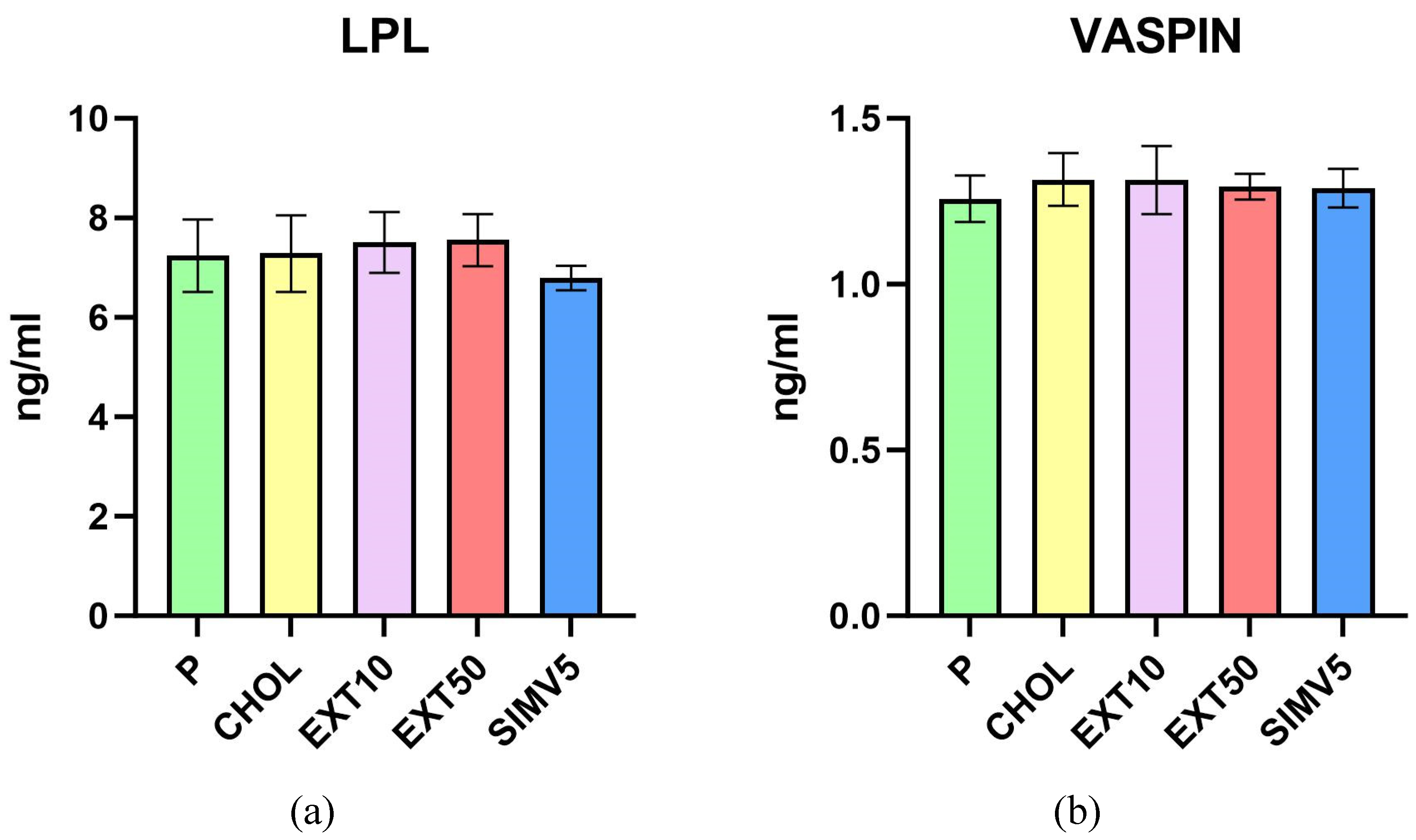
2.1. Quantification of ABCA1, ABCG1, C/EBPα, FAS, LIPG, LPL, SREBP-1c and Vaspin by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.2. Assessment of AdipoR2, CPT1A, and RBP4 Expression by Western Blot
2.3. Determination of Common Carotid Arteries and Aortas Resistive Index by Ultrasonography
2.4. Histopathological Evaluation of the Common Carotid Arteries
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Model
4.2. Plant Materials and Preparation of the Extract
4.3. Quantification of ABCA1, ABCG1, C/EBPα, FAS, LIPG, LPL, SREBP-1c, and Vaspin by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- ABCA1 - Rabbit ATP Binding Cassette Transporter A1 ELISA Kit, ELK9787, ELK Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Denver, CO, USA
- ABCG1 - Rabbit ATP Binding Cassette Transporter G1 ELISA Kit, QY-E30356, QAYEE Bio-Technology Co., Ltd.; Shanghai, China
- C/EBPα - Rabbit CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein Alpha ELISA Kit, ELK9791, ELK Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Denver, CO, USA
- FAS - Rabbit Fatty Acid Synthase ELISA Kit, ELK9790, ELK Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Denver, CO, USA
- LIPG - Rabbit Endothelial Lipase ELISA Kit, ELK9795, ELK Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Denver, CO, USA
- SREBP-1c - Rabbit Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 1c, ELISA Kit, ELK9798, ELK Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Denver, CO, USA
- LPL - Rabbit Lipoprotein Lipase ELISA Kit, ELK9789, ELK Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Denver, CO, USA
- VASPIN - Rabbit Visceral Adipose Specific Serine Protease Inhibitor ELISA Kit, QY-E30362, QAYEE Bio-Technology Co., Ltd.; Shanghai, China
4.4. Assessment of AdipoR2, CPT1A, and RBP4 Expression by Western Blot
- anti-AdipoR2 (ADIPOR2 Antibody, ARP60819_P050, Aviva Systems Biology, Corp., San Diego, CA, USA)
- anti-CPT1A (CPT1A Antibody, ARP44796_P050, Aviva Systems Biology, Corp., San Diego, CA, USA)
- anti-RBP4 (RBP4 Antibody, ARP41578_P050, Aviva Systems Biology, Corp., San Diego, CA, USA)
4.5. Determination of Common Carotid Arteries and Aortas Resistive Index by Ultrasonography
4.6. Histopathological Evaluation of the Common Carotid Arteries
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, W. How Western Diet And Lifestyle Drive The Pandemic Of Obesity And Civilization Diseases. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2019, 12, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszak, M.; Szulińska, M.; Bogdański, P. You Are What You Eat-The Relationship between Diet, Microbiota, and Metabolic Disorders-A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutrition Hub. Available online: https://www.nutrition-hub.com/post/nutrition-trends-report-2023 (accessed on 12-11-2023).
- Sozański, T.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Szumny, A.; Magdalan, J.; Bielska, K.; Merwid-Ląd, A.; Woźniak, A.; Dzimira, S.; Piórecki, N.; Trocha, M. The protective effect of the Cornus mas fruits (cornelian cherry) on hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis through PPARα activation in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozański, T.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Rapak, A.; Szumny, D.; Trocha, M.; Merwid-Ląd, A.; Dzimira, S.; Piasecki, T.; Piórecki, N.; Magdalan, J.; Szeląg, A. Iridoid-loganic acid versus anthocyanins from the Cornus mas fruits (cornelian cherry): Common and different effects on diet-induced atherosclerosis, PPARs expression and inflammation. Atherosclerosis 2016, 254, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozański, T.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Dzimira, S.; Magdalan, J.; Szumny, D.; Matuszewska, A.; Nowak, B.; Piórecki, N.; Szeląg, A.; Trocha, M. Loganic acid and anthocyanins from cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) fruits modulate diet-induced atherosclerosis and redox status in rabbits. Adv Clin Exp Med 2018, 27, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozański, T.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Wiśniewski, J.; Fleszar, M.G.; Rapak, A.; Gomułkiewicz, A.; Dzięgiel, P.; Magdalan, J.; Nowak, B.; Szumny, D.; Matuszewska, A.; Piórecki, N.; Szeląg, A.; Trocha, M. The iridoid loganic acid and anthocyanins from the cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) fruit increase the plasma l-arginine/ADMA ratio and decrease levels of ADMA in rabbits fed a high-cholesterol diet. Phytomedicine 2019, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielewski, M.; Matuszewska, A.; Nowak, B.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Sozański, T. The Effects of Natural Iridoids and Anthocyanins on Selected Parameters of Liver and Cardiovascular System Functions. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 2735790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, B.; Matuszewska, A.; Tomanik, M.; Filipiak, J.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Piórecki, N.; Jędrzejuk, D.; Zduniak, K.; Trocha, M.; Bolanowski, M.; Szeląg, A.; Sozański, T. Cornelian cherry extract ameliorates osteoporosis associated with hypercholesterolemia in New Zealand rabbits. Adv Clin Exp Med 2020, 29, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szandruk-Bender, M.; Rutkowska, M.; Merwid-Ląd, A.; Wiatrak, B.; Szeląg, A.; Dzimira, S.; Sobieszczańska, B.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Matuszewska, A.; Nowak, B.; Piórecki, N.; Duda-Madej, A.; Walczuk, U.; Turniak, M.; Bednarz-Misa, I.; Sozański, T. Cornelian Cherry Iridoid-Polyphenolic Extract Improves Mucosal Epithelial Barrier Integrity in Rat Experimental Colitis and Exerts Antimicrobial and Antiadhesive Activities In Vitro. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 7697851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielewski, M.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Matuszewska, A.; Rapak, A.; Gomułkiewicz, A.; Dzimira, S.; Dzięgiel, P.; Nowak, B.; Trocha, M.; Magdalan, J.; Piórecki, N.; Szeląg, A.; Sozański, T. Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) Iridoid and Anthocyanin Extract Enhances PPAR-α, PPAR-γ Expression and Reduces I/M Ratio in Aorta, Increases LXR-α Expression and Alters Adipokines and Triglycerides Levels in Cholesterol-Rich Diet Rabbit Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielewski, M.; Gomułkiewicz, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Matuszewska, A.; Nowak, B.; Piórecki, N.; Trocha, M.; Szandruk-Bender, M.; Jawień, P.; Szeląg, A.; Dzięgiel, P.; Sozański, T. Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) Iridoid and Anthocyanin-Rich Extract Reduces Various Oxidation, Inflammation, and Adhesion Markers in a Cholesterol-Rich Diet Rabbit Model. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Transcription of Eukaryotic Protein-Coding Genes. Annu Rev Genet 2000, 34, 77–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, B.; Tjian, R. Orchestrated Response: A Symphony of Transcription Factors for Gene Control. Genes Dev 2000, 14, 2551–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielewski, M.; Matuszewska, A.; Szeląg, A.; Sozański, T. The Impact of Anthocyanins and Iridoids on Transcription Factors Crucial for Lipid and Cholesterol Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Liang, Y.; Broderick, C.L.; Oldham, B.A.; Beyer, T.P.; Schmidt, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Stayrook, K.R.; Suen, C.; Otto, K.A.; Miller, A.R.; Dai, J.; Foxworthy, P.; Gao, H.; Ryan, T.P.; Jiang, X.C.; Burris, T.P.; Eacho, P.I.; Etgen, G.J. Antidiabetic action of a liver x receptor agonist mediated by inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, M.; Gorski, J. Endothelial lipase: regulation and biological function. J Physiol Pharmacol 2022, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.A.; Kersten, S.; Qi, L. Lipoprotein Lipase and Its Regulators: An Unfolding Story. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2021, 32, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günenc, A.N.; Graf, B.; Stark, H.; Chari, A. Fatty Acid Synthase: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Subcell Biochem 2022, 99, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Nie, T.; Li, K.; Wu, W.; Long, Q.; Feng, T.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Gao, X.; Ye, D.; Yan, K.; Gu, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, K.; Loomes, K.M.; Lin, S.; Wu, D.; Hui, X. Hepatic CPT1A Facilitates Liver-Adipose Cross-Talk via Induction of FGF21 in Mice. Diabetes 2021, db210363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Wen, Y.; Jiao, J.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Tan, W.; Xia, Q.; Wu, H.; Kong, X. PARK7 deficiency inhibits fatty acid β-oxidation via PTEN to delay liver regeneration after hepatectomy. Clin Transl Med 2022, 12, e1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heverin, M.; Ali, Z.; Olin, M.; Tillander, V.; Joibari, M.M.; Makoveichuk, E.; Leitersdorf, E.; Warner, M.; Olivercrona, G.; Gustafsson, J.Å.; Björkhem, I. On the regulatory importance of 27-hydroxycholesterol in mouse liver. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2017, 169, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Fu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wang, N.; Guan, Y.; Tang, C.; Shyy, J.Y.; Zhu, Y. Laminar shear stress regulates liver X receptor in vascular endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008, 28, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høgmoen Åstrand, O.A.; Gikling, I.; Sylte, I.; Rustan, A.C.; Thoresen, G.H.; Rongved, P.; Kase, E.T. Development of new LXR modulators that regulate LXR target genes and reduce lipogenesis in human cell models. Eur J Med Chem 2014, 74, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Du, H.; Yin, M.; Zhang, L.; Mao, L.; Xiao, N.; Ren, G.; Zhang, C.; Pan, J. Effects of high dietary fat and cholesterol on expression of PPAR alpha, LXR alpha, and their responsive genes in the liver of apoE and LDLR double deficient mice. Mol Cell Biochem 2009, 323, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Torrejon, C.; Chang, C.L.; Hamai, H.; Worgall, T.S.; Deckelbaum, R.J. Fatty acids regulate endothelial lipase and inflammatory markers in macrophages and in mouse aorta: a role for PPARγ. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2012, 32, 2929–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhshandehroo, M.; Sanderson, L.M.; Matilainen, M.; Stienstra, R.; Carlberg, C.; de Groot, P.J.; Müller, M.; Kersten, S. Comprehensive analysis of PPARalpha-dependent regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism by expression profiling. PPAR Res 2007, 2007, 26839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovic, A.; Panzenboeck, U.; Wintersperger, A.; Kratzer, I.; Hammer, A.; Levak-Frank, S.; Frank, S.; Rader, D.J.; Malle, E.; Sattler, W. Regulated expression of endothelial lipase by porcine brain capillary endothelial cells constituting the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem 2005, 94, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Yu, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, X.; Xiang, Z. An integrated network pharmacology and cell metabolomics approach to reveal the role of rhein, a novel PPARα agonist, against renal fibrosis by activating the PPARα-CPT1A axis. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, E.N.; Wang, W.Y.; Albert, C.J.; Langhi, C.; Baldán, Á.; Ford, D.A. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α accelerates α-chlorofatty acid catabolism. J Lipid Res 2017, 58, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowska, P.; Mlyczyńska, E.; Dawid, M.; Jurek, M.; Klimczyk, D.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. Review: Vaspin (SERPINA12) Expression and Function in Endocrine Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibara, D.; Matsuo, K.; Yamano, S.; Matsusue, K. Vaspin is a novel target gene of hepatic CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein. Gene 2019, 721, 144113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majerczyk, M.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Puzianowska-Kuźnicka, M.; Chudek, J. Retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) as the causative factor and marker of vascular injury related to insulin resistance. Postepy Hig Med Dosw 2016, 70, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, X.R.; Ye, M.Y.; Xu, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Liu, H.; Huang, X.Z. RBP4 Is Associated With Insulin Resistance in Hyperuricemia-Induced Rats and Patients With Hyperuricemia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 653819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, B.; Iseli, T.; Ramezani-Moghadam, M.; Ho, V.; Wankell, M.; Sun, E.J.; Qiao, L.; George, J.; Hebbard, L.W. The role of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 in liver fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2018, 1864, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bermejo, A.; Botas-Cervero, P.; Ortega-Delgado, F.; Delgado, E.; García-Gil, M.M.; Funahashi, T.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Association of ADIPOR2 with liver function tests in type 2 diabetic subjects. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008, 16, 2308–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinjani, A.; Mesiano, T.; Andini, P.W.; Yugo, M.R.; Yunus, R.E.; Kurniawan, M.; Hidayat, R.; Rasyid, A.; Harris, S. Resistive index of internal carotid artery and common carotid artery In patients with cerebral small vascular disease. J Hypertens 2021, 39, e16–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharska, A.Z.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Piórecki, N.; Fecka, I. Iridoids, Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Edible Honeysuckle Berries (Lonicera caerulea var. kamtschatica Sevast.). Molecules 2017, 22, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Lei, P.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, J. Down-regulated of SREBP-1 in circulating leukocyte is a risk factor for atherosclerosis: a case control study. Lipids Health Dis 2019, 18, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimano, H. SREBP-1c and Elovl6 as Targets for Obesity-related Disorders. Yakuga Zasshi 2015, 135, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, D.; Miksztowicz, V.; Macri, V.; López, G.H.; Friedman, S.; Berg, G.; Zago, V.; Schreier, L. Overproduction of altered VLDL in an insulin-resistance rat model: Influence of SREBP-1c and PPAR-α. Clin Investig Arterioscler 2015, 27, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Bo, S.; Cassader, M.; De Michieli, F.; Gambino, R. Impact of sterol regulatory element-binding factor-1c polymorphism on incidence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and on the severity of liver disease and of glucose and lipid dysmetabolism. Am J Clin Nutr 2013, 98, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, I.; Shimano, H.; Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Differential expression of exons 1a and 1c in mRNAs for sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 in human and mouse organs and cultured cells. J Clin Invest 1997, 99, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, T.; Takahashi, A.; Saito, R.; Sekiya, M.; Igarashi, M.; Iwasaki, H.; Miyahara, S.; Koyasu, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ishii, K.; Matsuzaka, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Yahagi, N.; Takekoshi, K.; Sone, H.; Yatoh, S.; Suzuki, H.; Yamada, N.; Shimano, H. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 determines plasma remnant lipoproteins and accelerates atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2011, 31, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Yamabe, N.; Noh, J.S.; Kang, K.S.; Tanaka, T.; Yokozawa, T. The beneficial effects of morroniside on the inflammatory response and lipid metabolism in the liver of db/db mice. Biol Pharm Bull 2009, 32, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamabe, N.; Noh, J.S.; Park, C.H.; Kang, K.S.; Shibahara, N.; Tanaka, T.; Yokozawa, T. Evaluation of loganin, iridoid glycoside from Corni Fructus, on hepatic and renal glucolipotoxicity and inflammation in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2010, 648, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Tanaka, T.; Yokozawa, T. Evaluation of 7-O-galloyl-D-sedoheptulose, isolated from Corni Fructus, in the adipose tissue of type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Fitoterapia 2013, 89, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Niu, D.; Wang, T.; An, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Bi, H.; Xue, X.; Kang, J. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction of total triterpenoid acids from Corni Fructus and hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of the extract in mice. Food Funct 2020, 11, 10709–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Cho, E.J.; Yokozawa, T. Protection against hypercholesterolemia by Corni fructus extract and its related protective mechanism. J Med Food 2009, 12, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsusue, K.; Gavrilova, O.; Lambert, G.; Brewer, H.B. Jr; Ward, J.M.; Inoue, Y.; LeRoith, D.; Gonzalez, F.J. Hepatic CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha mediates induction of lipogenesis and regulation of glucose homeostasis in leptin-deficient mice. Mol Endocrinol 2004, 18, 2751–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Lee, C.G.; Jeong, H.; Yeo, S.; Kim, J.A.; Jeong, S.Y. Antiadipogenic Effects of Mixtures of Cornus officinalis and Ribes fasciculatum Extracts on 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Shin, J.H.; Shin, T.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, N.J.; Kim, J.D. Anthocyanins from Cornus kousa ethanolic extract attenuate obesity in association with anti-angiogenic activities in 3T3-L1 cells by down-regulating adipogeneses and lipogenesis. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0208556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.L.; Jeon, Y.D.; Park, J.; Rim, H.K.; Jeong, M.Y.; Lim, H.; Ko, S.G.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Hong, S.H.; Um, J.Y. Corni Fructus Containing Formulation Attenuates Weight Gain in Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity and Regulates Adipogenesis through AMPK. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013, 2013, 423741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.E.; Nsengimana, J.; Bostock, J.A.; Cymbalista, C.; Futers, T.S.; Knight, B.L.; McCormack, L.J.; Prasad, U.K.; Riches, K.; Rolton, D.; Scarrott, T.; Barrett, J.H.; Carter, A.M. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha, beta and delta gene variants: associations with obesity related phenotypes in the Leeds Family Study. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2010, 7, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren. ; Guo, J.; Jiang, F.; Lu, J.; Ding, Y.; Li, A.; Liang, X.; Jia, W. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α is a crucial regulator of human fat mass and obesity associated gene transcription and expression. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014, 406909. [Google Scholar]
- Repa, J.J.; Liang, G.; Ou, J.; Bashmakov, Y.; Lobaccaro, J.M.; Shimomura, I.; Shan, B.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXRalpha and LXRbeta. Genes Dev 2000, 14, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, H.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S.; Liang, G. LXR-SREBP-1c-phospholipid transfer protein axis controls very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) particle size. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 6801–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z. Yin-xing-tong-mai decoction attenuates atherosclerosis via activating PPARγ-LXRα-ABCA1/ABCG1 pathway. Pharmacol Res 2021, 169, 105639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.; Cai, C.; Zhong, L.; Yu, H.; Shen, W. LXRɑ participates in the mTOR/S6K1/SREBP-1c signaling pathway during sodium palmitate-induced lipogenesis in HepG2 cells. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2018, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramji, D.P.; Foka, P. ; CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J 2002, 365(Pt 3), 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, P.; Shen, Z.; Xu, K.; Wu, C.; Tian, F.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Li, P. Morroniside Promotes PGC-1α-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux in Sodium Palmitate or High Glucose-Induced Mouse Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Biomed Res Int 2021, 2021, 9942152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, M. ABCA1 and ABCG1 as potential therapeutic targets for the prevention of atherosclerosis. J Pharmacol Sci 2022, 148, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, F.; Farhat, D.; Gursu, G.; Samnani, S.; Lee, J.Y. Snapshots of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8: A Sterol’s Journey to Cross the Cellular Membranes. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 24, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Ding, H. Role of ABCA1 in Cardiovascular Disease. J Pers Med 2022, 12, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobo-Albavera, L.; Domínguez-Pérez, M.; Medina-Leyte, D.J.; González-Garrido, A.; Villarreal-Molina, T. The Role of the ATP-Binding Cassette A1 (ABCA1) in Human Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22(4), 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarling, E.J. Expanding roles of ABCG1 and sterol transport. Curr Opin Lipidol 2013, 24, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, Ż.; Bereta, J. Rola zjawiska “wytrenowanej odporności” w patogenezie miażdżycy. Acta Mygenica 2020, 17, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bekkering, S.; Quintin, J.; Joosten, L.A.; van der Meer, J.W.; Netea, M.G.; Riksen, N.P. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces long-term proinflammatory cytokine production and foam cell formation via epigenetic reprogramming of monocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2014, 34, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Mechanisms of foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J Mol Med (Berl) 2017, 95, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Cao, H.; Shen, D.; Li, S.; Yan, L.; Chen, C.; Xing, S.; Dou, F. Quercetin protects against atherosclerosis by regulating the expression of PCSK9, CD36, PPARγ, LXRα and ABCA1. Int J Mol Med 2019, 44, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.S.; Ricote, M.; Akiyama, T.E.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Glass, C.K. PPARgamma and PPARdelta negatively regulate specific subsets of lipopolysaccharide and IFN-gamma target genes in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 6712–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Fitzgerald, M.L.; Freeman, M.W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in macrophage biology: Friend or foe? Curr Opin Lipidol 2001, 12, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.E.; Han, S.Y.; Wolfson, B.; Zhou, Q. The role of endothelial lipase in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and cancer. Histol Histopathol 2018, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.Y.; Steiner, J.M.; Cridge, H. Lipases: it’s not just pancreatic lipase! Am J Vet Res 2022, 83, ajvr.22.03.0048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersten, S. Physiological regulation of lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1841, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.L. Lipoprotein lipase: new roles for an ‘old’ enzyme. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2019, 22, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, M.; Horinishi, A.; Saito, M.; Ebara, T.; Endo, Y.; Kaku, K.; Murase, T.; Eto, M. A novel complex deletion-insertion mutation mediated by Alu repetitive elements leads to lipoprotein lipase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 2007, 92, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viljoen, A.; Wierzbicki, A.S. Diagnosis and treatment of severe hypertriglyceridemia. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2012, 10, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Farooqui, K.J.; Bano, T.; Khandelwal, M.; Gill, H.; Mithal, A. Heparin and insulin in the management of hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis: case series and literature review. Arch Endocrinol Metab 2017, 61, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Fillmore, J.J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Moore, I.K.; Pypaert, M.; Lutz, E.P.; Kako, Y.; Velez-Carrasco, W.; Goldberg, I.J.; Breslow, J.L.; Shulman, G.I. Tissue-specific overexpression of lipoprotein lipase causes tissue-specific insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, 7522–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Eckel, R.H. Lipoprotein lipase: from gene to obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2009, 297, E271–E288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khetarpal, S.A.; Vitali, C.; Levin, M.G.; Klarin, D.; Park, J.; Pampana, A.; Millar, J.S.; Kuwano, T.; Sugasini, D.; Subbaiah, P.V.; Billheimer, J.T.; Natarajan, P.; Rader, D.J. Endothelial lipase mediates efficient lipolysis of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. PLoS Genet 2021, 17, e1009802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, M.E.; Lamarche, B. Endothelial lipase: its role in cardiovascular disease. Can J Cardiol 2006, 22 (Suppl B), 31B–34B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen-Urstad, A.P.; Semenkovich, C.F. ; Fatty acid synthase and liver triglyceride metabolism: housekeeper or messenger? Biochim Biophys Acta 2012, 1821, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Sales, E.; Ebrahimi-Kalan, A.; Alipour, M.R. Preventive effect of trans-chalcone on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Improvement of hepatic lipid metabolism. Biomed Pharmacother 2019, 109, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.S.; Latasa, M.J.; Griffin, M.J.; Sul, H.S. Suppression of fatty acid synthase promoter by polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Lipid Res 2002, 43, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latasa, M.J.; Moon, Y.S.; Kim, K.H.; Sul, H.S. Nutritional regulation of the fatty acid synthase promoter in vivo: sterol regulatory element binding protein functions through an upstream region containing a sterol regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 10619–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, P. Regulation of renal lipid deposition in diabetic nephropathy on morroniside via inhibition of NF-KB/TNF-a/SREBP1c signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact 2023, 385, 110711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liang, G.; Ou, J.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Central role for liver X receptor in insulin-mediated activation of Srebp-1c transcription and stimulation of fatty acid synthesis in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 11245–11250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Zhang, C.; Cao, X.; Feng, B.; Li, X. Intestinal Population in Host with Metabolic Syndrome during Administration of Chitosan and Its Derivatives. Molecules 2020, 25, 5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, R.S.; Lokanatha, O.; Muni Swamy, G.; Venkataramaiah, C.; Muni Kesavulu, M.; Appa Rao, C.; Badri, K.R.; Balaji, M. Anti-Obesity and Lipid Lowering Activity of Bauhiniastatin-1 is Mediated Through PPAR-γ/AMPK Expressions in Diet-Induced Obese Rat Model. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 704074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, I.R.; Joshi, M. CPT1A-mediated Fat Oxidation, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Potential. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqz046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, B.; Xu, T.; Wang, J.; Wei, D. Canagliflozin Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Inhibiting Inflammation through Induction of Autophagy. Yonsei Med J 2022, 63, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K. Mitochondrial CPT1A: Insights into structure, function, and basis for drug development. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1160440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondevila, M.F.; Fernandez, U.; Heras, V.; Parracho, T.; Gonzalez-Rellan, M.J.; Novoa, E.; Porteiro, B.; Alonso, C.; Mayo, R.; da Silva Lima, N.; Iglesias, C.; Filliol, A.A.; Senra, A.; Delgado, T.C.; Woodhoo, A.; Herrero, L.; Serra, D.; Prevot, V.; Schwaninger, M.; López, M.; Dieguez, C.; Millet, O.; Mato, J.M.; Cubero, F.J.; Varela-Rey, M.; Iruzubieta, P.; Crespo, J.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Schwabe, R.F.; Nogueiras, R. Inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A in hepatic stellate cells protects against fibrosis. J Hepatol 2022, 77, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Alimujiang, M.; Hu, L.; Liu, F.; Bao, Y.; Yin, J. Berberine alleviates lipid metabolism disorders via inhibition of mitochondrial complex I in gut and liver. Int J Biol Sci 2021, 17, 1693–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, G.; Du, X.; Shi, Z.; Jin, M.; Sha, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Expression patterns of hepatic genes involved in lipid metabolism in cows with subclinical or clinical ketosis. J Dairy Sci 2019, 102, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thering, B.J.; Bionaz, M.; Loor, J.J. Long-chain fatty acid effects on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha-regulated genes in Madin-Darby bovine kidney cells: optimization of culture conditions using palmitate. J Dairy Sci 2009, 92, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ge, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, N.; Gu, Y.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, R. Integrative lipidomic and transcriptomic study unravels the therapeutic effects of saikosaponins A and D on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm Sin B 2021, 11, 3527–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.W.; Jo, H.K.; Chung, S.H. Ginseng seed oil ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation in vitro and in vivo. J Ginseng Res 2018, 42, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Byun, S.; Choi, S.; Xiao, Z.; Iwamori, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Ge, K.; Kemper, B.; Kemper, J.K. Fasting-induced JMJD3 histone demethylase epigenetically activates mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation. J Clin Invest 2018, 128, 3144–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Panserat, S.; Kamalam, B.S.; Aguirre, P.; Véron, V.; Médale, F. Insulin regulates lipid and glucose metabolism similarly in two lines of rainbow trout divergently selected for muscle fat content. Gen Comp Endocrinol 2014, 204, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, J. Vaspin: a novel serpin with insulin-sensitizing effects. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2008, 17, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöting, N.; Berndt, J.; Kralisch, S.; Kovacs, P.; Fasshauer, M.; Schön, M.R.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M. Vaspin gene expression in human adipose tissue: association with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 339, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, O.G.; Sadik, N.A. Vaspin gene in rat adipose tissue: relation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Mol Cell Biochem 2013, 373, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.R.; Caminos, J.E.; Vázquez, M.J.; Garcés, M.F.; Cepeda, L.A.; Angel, A.; González, A.C.; García-Rendueles, M.E.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; López, M.; Bravo, S.B.; Nogueiras, R.; Diéguez, C. Regulation of visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor by nutritional status, metformin, gender and pituitary factors in rat white adipose tissue. J Physiol 2009, 587(Pt 14) Pt 14, 3741–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, K.; Wada, J.; Eguchi, J.; Zhang, H.; Baba, M.; Seida, A.; Hashimoto, I.; Okada, T.; Yasuhara, A.; Nakatsuka, A.; Shikata, K.; Hourai, S.; Futami, J.; Watanabe, E.; Matsuki, Y.; Hiramatsu, R.; Akagi, S.; Makino, H.; Kanwar, Y.S. Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor: a unique insulin-sensitizing adipocytokine in obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 10610–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, G.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Han, W.; Lv, Y.; Sun, C. Vaspin promotes 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2015, 240, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieger, K.; Weiner, J.; Krause, K.; Schwarz, M.; Kohn, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M.; Heiker, J.T. Vaspin suppresses cytokine-induced inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via inhibition of NFκB pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2018, 460, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Chen, X.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y. Vaspin contributes to autophagy and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition via PI3K-/AKT-mTOR pathway. Acta Histochem 2022, 124, 151881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, Y.M.; Lee, Y.L.; Yoon, H.K.; Kang, S.W.; Lee, W.J.; Park, J.Y. Vaspin inhibits cytokine-induced nuclear factor-kappa B activation and adhesion molecule expression via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2014, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhao, S.; Yang, K.; Chen, X.; Zheng, C. Vaspin inhibited proinflammatory cytokine induced activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and its downstream molecules in human endothelial EA.hy926 cells. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014, 103, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbarrino, K.; Hafiane, A.; Zheng, H.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Intensive Statin Therapy Compromises the Adiponectin-AdipoR Pathway in the Human Monocyte-Macrophage Lineage. Stroke 2019, 50, 3609–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, N.; Song, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Ren, J.; Chen, H.; Zhan, T.; Tian, J.; Ma, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B. A novel small molecule AdipoR2 agonist ameliorates experimental hepatic steatosis in hamsters and mice. Free Radic Biol Med 2023, 203, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin receptors: a review of their structure, function and how they work. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014, 28, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.D. Adiponectin: Role in Physiology and Pathophysiology. Int J Prev Med 2020, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yuan, W.; Peng, X.; Wang, M.; Xiao, J.; Wu, C.; Luo, L. PPAR γ/Nnat/NF-κB Axis Involved in Promoting Effects of Adiponectin on Preadipocyte Differentiation. Mediators Inflamm 2019, 2019, 5618023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awazawa, M.; Ueki, K.; Inabe, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Kaneko, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Bardeesy, N.; Ohnishi, S.; Nagai, R.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin suppresses hepatic SREBP1c expression in an AdipoR1/LKB1/AMPK dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009, 382, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Morais, A.; Lebrun, V.; Abarca-Quinones, J.; Brichard, S.; Hue, L.; Guigas, B.; Viollet, B.; Leclercq, I.A. Prevention of steatohepatitis by pioglitazone: implication of adiponectin-dependent inhibition of SREBP-1c and inflammation. J Hepatol 2009, 50, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oku, H.; Matsuura, F.; Koseki, M.; Sandoval, J.C.; Yuasa-Kawase, M.; Tsubakio-Yamamoto, K.; Masuda, D.; Maeda, N.; Ohama, T.; Ishigami, M.; Nishida, M.; Hirano, K.; Kihara, S.; Hori, M.; Shimomura, I.; Yamashita, S. Adiponectin deficiency suppresses ABCA1 expression and ApoA-I synthesis in the liver. FEBS Lett 2007, 581, 5029–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Gao, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Impact of 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 on TG content in liver of rats with type 2 diabetes. Acta Cir Bras 2018, 33, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishak, N.A.; Ismail, M.; Hamid, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Abd Ghafar, S.A. Antidiabetic and Hypolipidemic Activities of Curculigo latifolia Fruit:Root Extract in High Fat Fed Diet and Low Dose STZ Induced Diabetic Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013, 2013, 601838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meex, R.C.R.; Watt, M.J. Hepatokines: linking nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2017, 13, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilicarslan, M.; de Weijer, B.A.; Simonyté Sjödin, K.; Aryal, P.; Ter Horst, K.W.; Cakir, H.; Romijn, J.A.; Ackermans, M.T.; Janssen, I.M.; Berends, F.J.; van de Laar, A.W.; Houdijk, A.P.; Kahn, B.B.; Serlie, M.J. RBP4 increases lipolysis in human adipocytes and is associated with increased lipolysis and hepatic insulin resistance in obese women. FASEB J 2020, 34, 6099–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrame, S.; Zhao, A.; Merrow, T.; Klimis-Zacas, D. The effects of wild blueberry consumption on plasma markers and gene expression related to glucose metabolism in the obese Zucker rat. J Med Food 2015, 18, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, R.; Nishimura, N.; Hoshino, H.; Isa, Y.; Kadowaki, M.; Ichi, T.; Tanaka, A.; Nishiumi, S.; Fukuda, I.; Ashida, H.; Horio, F.; Tsuda, T. Cyanidin 3-glucoside ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity due to downregulation of retinol binding protein 4 expression in diabetic mice. Biochem Pharmacol 2007, 74, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, C.; Nie, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, L.; Fan, M.; Qian, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. A novel regulatory mechanism of geniposide for improving glucose homeostasis mediated by circulating RBP4. Phytomedicine 2022, 95, 153862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viazzi, F.; Leoncini, G.; Derchi, L.E.; Pontremoli, R. Ultrasound Doppler renal resistive index: a useful tool for the management of the hypertensive patient. J Hypertens 2014, 32, 149–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N.; Maeda, R.; Ozono, R.; Nakano, Y.; Higashi, Y. Common Carotid Artery Flow Parameters Predict the Incidence of Hypertension. Hypertension 2021, 78, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscemi, S.; Verga, S.; Batsis, J.A.; Cottone, S.; Mattina, A.; Re, A.; Arnone, M.; Citarda, S.; Cerasola, G. Intra-renal hemodynamics and carotid intima-media thickness in the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2009, 86, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, D.; Meyerhans, A.; Bundi, B.; Schmid, H.P.; Frauchiger, B. Prediction of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: comparison of the internal carotid artery resistive index with the common carotid artery intima-media thickness. Stroke 2006, 37, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNaughton, D.A.; Abu-Yousef, M.M. Doppler US of the liver made simple. Radiographics 2011, 31, 161–188, Erratum in: Radiographics 2011, 31(3), 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
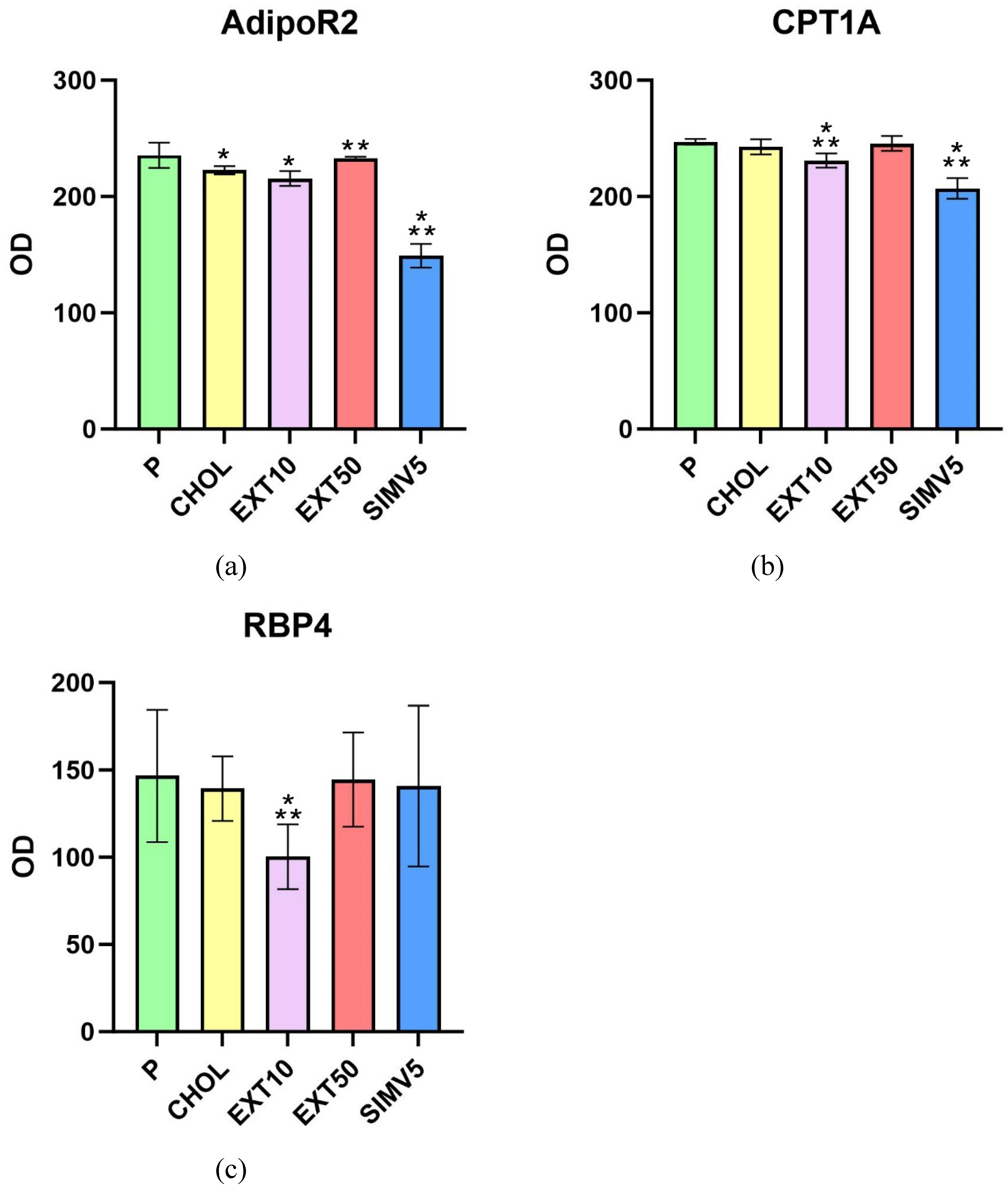
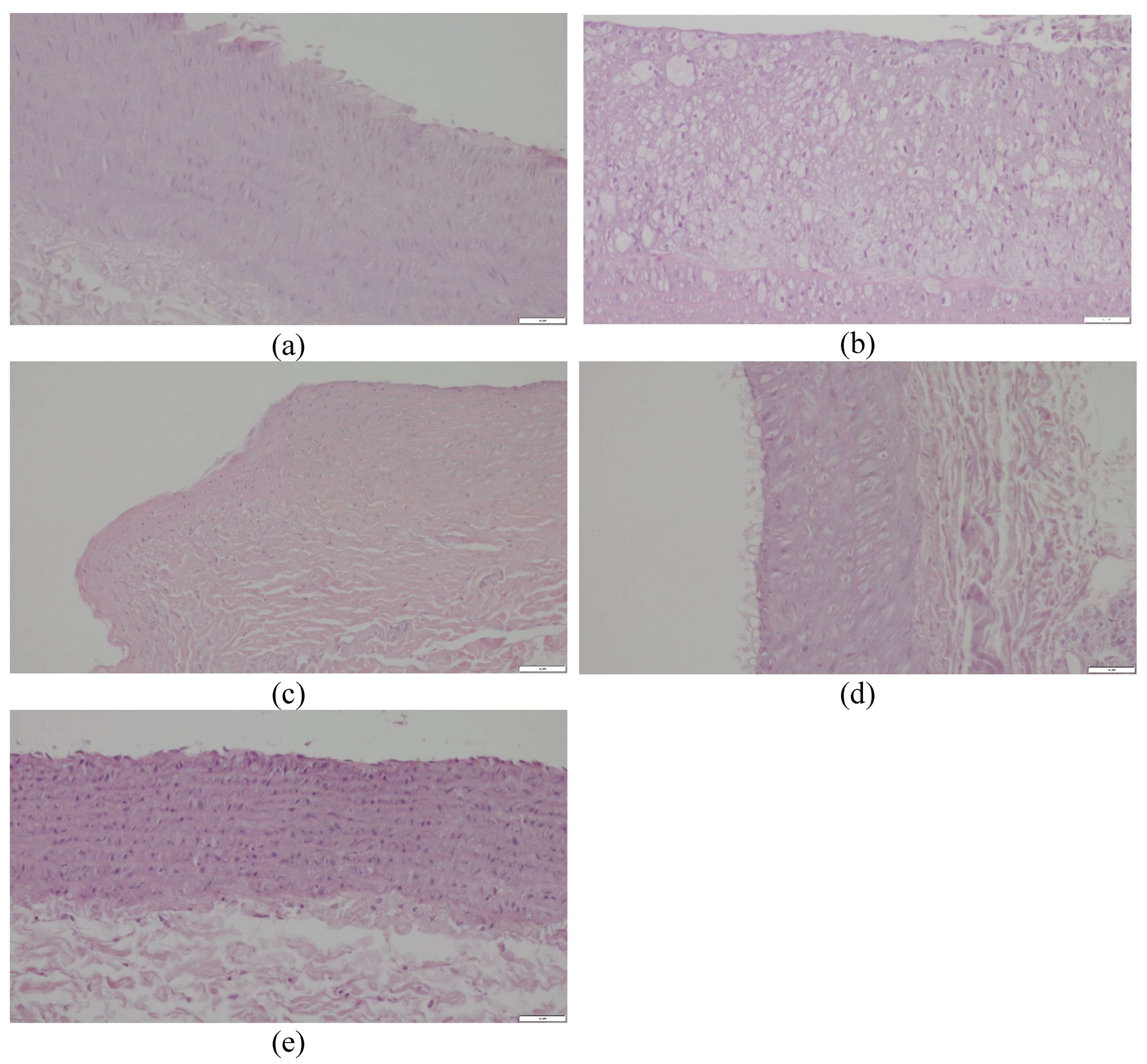
| Experimental group | P | CHOL | EXT10 | EXT50 | SIMV5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCA RI | 0.685 ± 0.090 | 0.735 ± 0.054 | 0.747 ± 0.104 | 0.707 ± 0.093 | 0.741 ± 0.080 |
| Aorta RI | 0.795 ± 0.099 | 0.840 ± 0.084 | 0.763 ± 0.069 | 0.738 ± 0.085 | 0.650 ± 0.119 |
| Experimental group | P | CHOL | EXT10 | EXT50 | SIMV5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCA Evaluation | 0.444 ± 0.527 | 3.625 ± 1.408 | 0.700 ± 1.059 | 0.556 ± 0.726 | 0.222 ± 0.441 |
| Experimental group | P | CHOL | EXT10 | EXT50 | SIMV5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chow | standard chow (sc) | sc + 1% cholesterol | sc + 1% cholesterol | sc + 1% cholesterol | sc + 1% cholesterol |
| Tested substance | - (normal saline solution) |
- (normal saline solution) |
cornelian cherry extract 10 mg/kg/b.w. |
cornelian cherry extract 50 mg/kg/b.w. |
simvastatin 5 mg/kg/b.w. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





