Introduction.
The physiologic absorption of Quanta of photons derived from light is deemed a prerequisite for multiple aspects of mammalian health, and as such, humans have always instinctively sought daylight for many sorts of illnesses including infectious illnesses, wound healing and other maladies.[
1,
2,
3] Of note, UV light irradiation following sunlight exposure has empirically been considered nature’s natural cure-all for many kinds of infectious illnesses for many generations of humankind.[
4,
5] Among the oldest references to the benefits of sun therapy were reported on or before 1500 B.C.[
3] Although the molecular mechanisms of these photon-mediated, light-derived effects have generally often remained unknown, unconfirmed, or speculative at best, emerging findings now point to a nuclear disruptive element that impedes further local replication of the infectious agent combined with enhancement of immune responses in the UV or sunlight-exposed host.[
5,
6] According to the laws of photobiology, light absorption requires the presence of a specific photo-acceptor molecule or complex that after photonic excitation could induce the downstream activation of biochemical or physiologic signaling pathways to bring about its desired healthful or other responses.[
6,
7] The blood protein hemoglobin (Hb) is recognized to be an efficient light absorbing photochemical capable of absorbing photons due to its unique electronic configurations which enable to undergo reversible taut vs relaxed states, and accommodate the efficient transport and release of life-giving oxygen to peripheral tissues in addition to its contributions to gas transport, buffering capacity, uptake of 2,3 deoxy diphosphoglycerate (2,3 DPG) and other critical biologic functions.[
8,
9,
10]
Aromatic amino acid residues, including tryptophan and tyrosine, are common constituents of most proteins including the peptide sidechain of hemoglobin. Both amino acids have absorption bands in the 260-290 nm range that can be reached via photonic excitation.[
8,
10] Excitation produces a broad fluorescence centered at 340 nm, a band that extends from 310 to 370nm. Fluorescence from RBCs however is centered nearer 480nm. While it is possible that tryptophan and tyrosine could be excited by the laser beam activity for the referenced aromatic amino acids, the excitation range is outside the typical range for hemoglobin. In addition, the fluorescence lifetime reported for tryptophan in proteins shows a small amplitude ~0.2 for the 0.5ns component and the two equally weighted major components with ~2ns and ~5ns lifetime, respectively. Thus, the difference in emission wavelength and fluorescence lifetime allows us to rule out tryptophan and tyrosine as the primary sources of the biophotonic RBC signal as the peak for hemoglobin is distant from the 260-290 nm range, and of greater magnitude and encompasses the 480 nm wavelength.[
10,
11]
Excessive radiation exposure can cause DNA damage and block cellular replication.
Both ionizing and non-ionizing radiation can cause mutations in DNA of cells, albeit through different molecular mechanisms. Strong ionizing radiation such as high-energy UV-C, X-rays, and gamma rays can cause single- and double-strand breaks in the nucleotide and nucleoside backbones through the formation of hydroxyl radicals and other biochemic events upon irradiation.[
12,
13] In contrast, exposure to non-ionizing radiation can induce the formation of dimers between two adjacent pyrimidine bases of RNA, and in both cases of ionizing or nonionizing exposure the usual consequence is the prevention of further
in vivo replication of the infectious agent.[
5,
14,
15] The consensus if that that the denaturation of the viral genetic material occurs, rather than denaturing or damage to the protein and lipid envelopes, is likely to be the primary and more efficacious target for irradiation-induced viral inactivation.[
14,
15,
16]
,
Controlled UV irradiation can deliver beneficial effects.
The more healthful biostimulation process produced via low level photonic emission generally promotes cell survival and proliferation in both
in vitro and
in vivo applications.[
3,
14] Emerging evidence supports a low-level laser stimulation action mediates increases in the generation of “good” or favorable metabolic reactive oxygen species (ROS).[
9] Favorable ROS are able to activate redox sensitive signal transduction pathways such as Nrf-2, NF-kB, ERK and which collectively can act as key redox checkpoints in cell survival processes and replication mechanisms.[
9,
17,
18] In addition, these signal transduction factors also contribute to the proliferation and tissue survival of affected tissues. The bio-stimulation process also improves peripheral oxygen delivery to tissues via a laser-induced photodissosiation of oxygen from oxyhemoglobin in cutaneous blood vessels, increasing blood pO2 saturation concentrations, and further contributing to the beneficial and supportive roles of oxygen in the biomedical processes of tissue healing and cellular regeneration.[
6,
7,
10,
15,
20].
The applications and effectiveness of biophotonic therapy in the treatment of infectious illness have been noted for nearly a century.[
3,
5,
14] Like sunlight, biophotonics can deliver a controllable source of photons to damaged or infected tissues and function an adjunct in the immunogenic responses during recovery from numerous illnesses.[
5,
16]
, Until recently the biophysiologic mechanisms that contribute to biophotonic therapy were unclear, while the overall healthful effects were more widely documented.[
3,
4,
16] It is now clear that the multiple events connected to UV irradiation may induce both beneficial or damaging effects on tissue viability. The UV effects are dependent on the wavelengths encountered, the intensity and duration of the exposure, and the tissues exposed weather applied
in vivo or as an extracorporeal exposure typically of freshly obtained whole blood.[
5,
10,
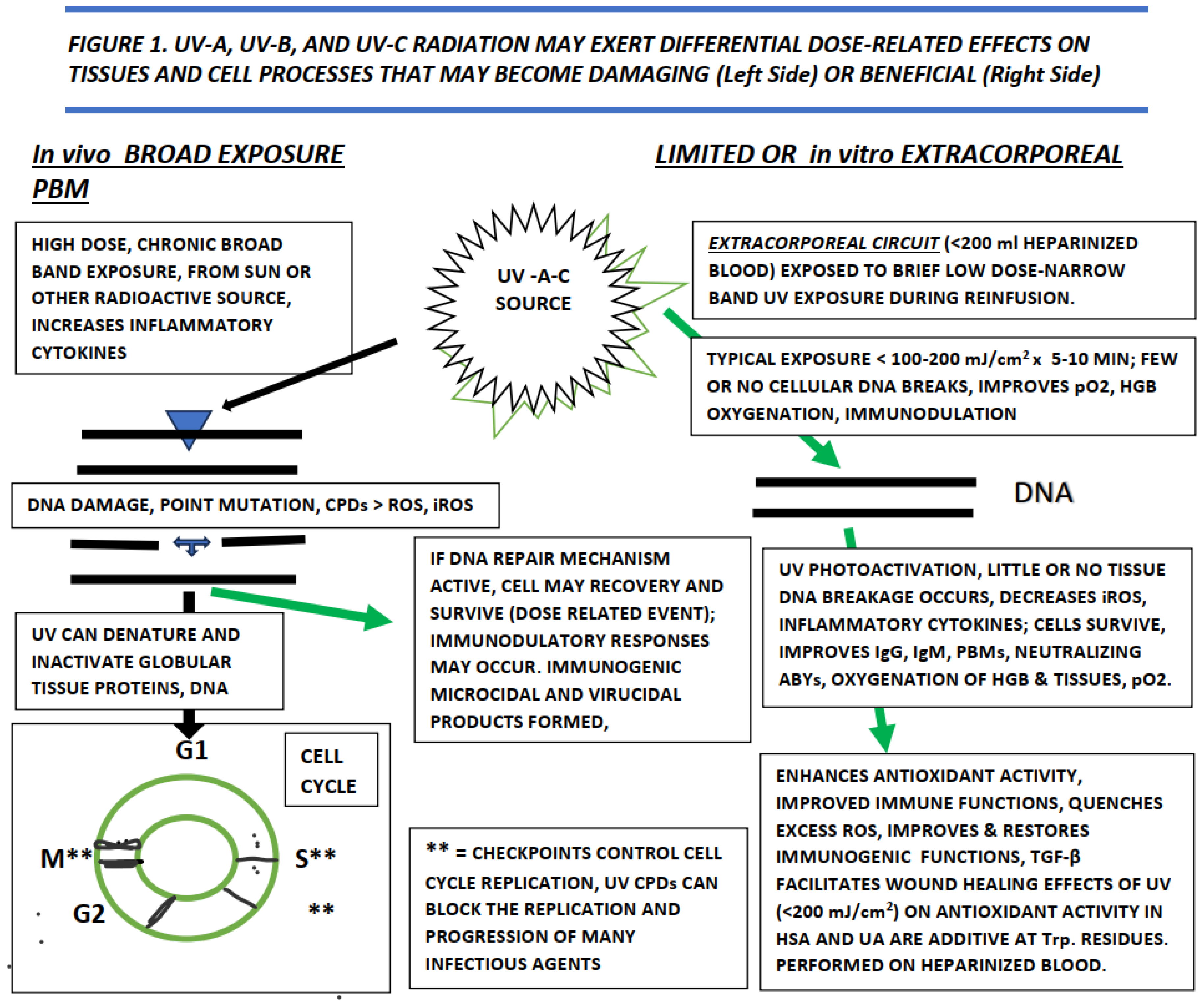
13] A summary of the effects of UV and the biophotonic and biophotomodulatory actions on cells, tissues and infectious agents is depicted in
Figure 1 below. The potentially damaging effects of extreme exposure as may be caused by excess solar exposure is summarized on the left side of the diagram, and the effects of extracorporeal biophotonic exposure depicted on the right side of the figure. For the extracorporeal approach, the blood is typically diluted in sterile, normal saline and re-infused immediately after UV exposure, and within 30 minutes of its initial removal from the subject.[
5,
14]
Biophotonic UV treatment improves peripheral blood oxygen saturation and cell survival.
The biostimulation process via low level photonic emission generally promotes cell survival and proliferation both
in vitro and
in vivo. Emerging evidence supports a low-level laser stimulation action to mediates increases in the generation of “good” reactive oxygen species, that can activate redox sensitive signal transduction pathways such as Nrf-2, NF-kB, ERK and which collectively can act as key redox checkpoints in cell survival and replication mechanisms and in proliferation and survival of affected tissues.[
10,
12,
17,
18]
. In addition, the bio-stimulation process also improves peripheral oxygen delivery to tissues via a laser-induced photodissosiation of oxygen from oxyhemoglobin in cutaneous blood vessels, thereby increasing blood SpO2 saturation concentrations, and further contributing to its role in biomedical processes of tissue healing and regeneration. The duration of the photodissociation effect remains unclear.[
2,
3,
6]
The biophysiologic or molecular mechanism through which biostimulation may deliver its beneficial effects remains speculative but is likely dependent on the presence of potential light absorbing elements such as aromatic structures in the peripheral tissues. Tryptophan, a common residue to most proteins including the beta chain of hemoglobin, has an absorption band in the 260-290 nm range that can be reached via photonic excitation.[
7,
9,
10,
21] Excitation of tryptophan produces a broad fluorescence centered at 340 nm that extends from 310 to 370 nm, similar to that of tyrosine. Fluorescence from RBCs is centered near 480nm, however, beyond the tryptophan or typrosine excitable range. While it is possible that tryptophan and/or tyrosine could be excited by the photonic laser, little or no fluorescence would likely become detected given the 310 to 370nm spectra for aromatic amino acids The fluorescence lifetime reported for tryptophan in proteins shows a small amplitude ~0.2 for the 0.5ns component and the two equally weighted major components with ~2ns and ~5ns lifetime, respectively. [
10]. The difference in emission wavelength and fluorescence lifetime between tryptophan and blood components allows us to rule out tryptophan as the primary source of the 480 nm RBC signal.[
21]
Legend to
Figure 1. Summary of the effects of
in vivo and extracorporeal UV radiation exposure on tissues and cells. UV = ultraviolet light; UV-A = wavelength 320-400 nm; UV-B= 280-320 nm; UV-C = wavelength 200-280 nm; mJ = millijoules; cm = centimeter; in vivo = in the live organism or subject; CPDs = cyclobutene dimes; ROS = Reactive Oxygen Species; iROS = inflammatory reactive oxygen species; DNA = deoxynucleic acid; RNA = ribonucleic acid; G1, S, G2 and M = phases of the cell cycle; PBMs = photobiomodulation products; IgG = immunoglobulin G; IgM = immunoglobulin M; ABYs = antibodies; TGF-β = tissue growth factor- beta; pO2 = percent oxygen saturation in whole blood; USA = human serum albumin; UA = uric acid; Trp = tryptophan. Modified from [
16,
26].
Results.
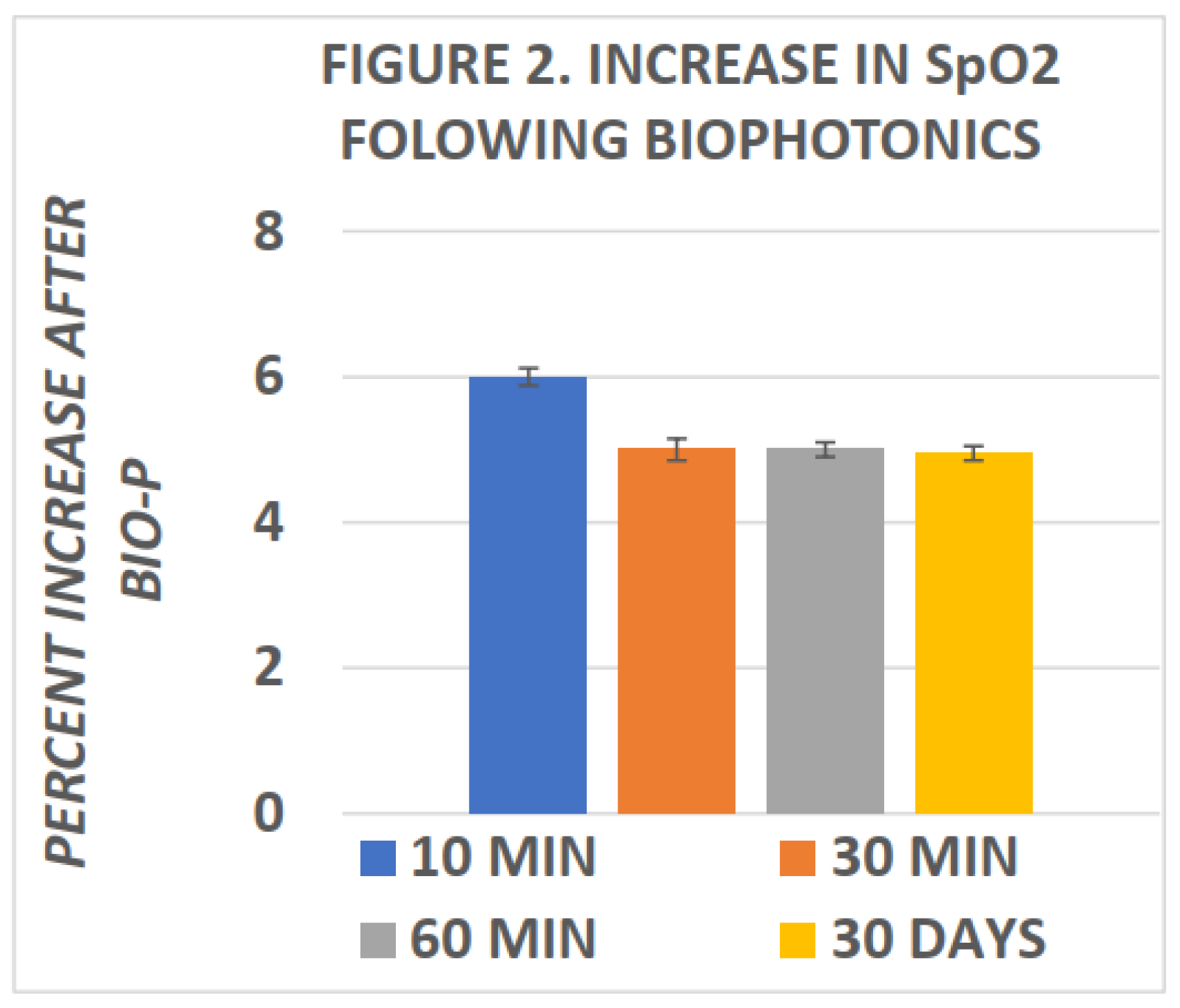
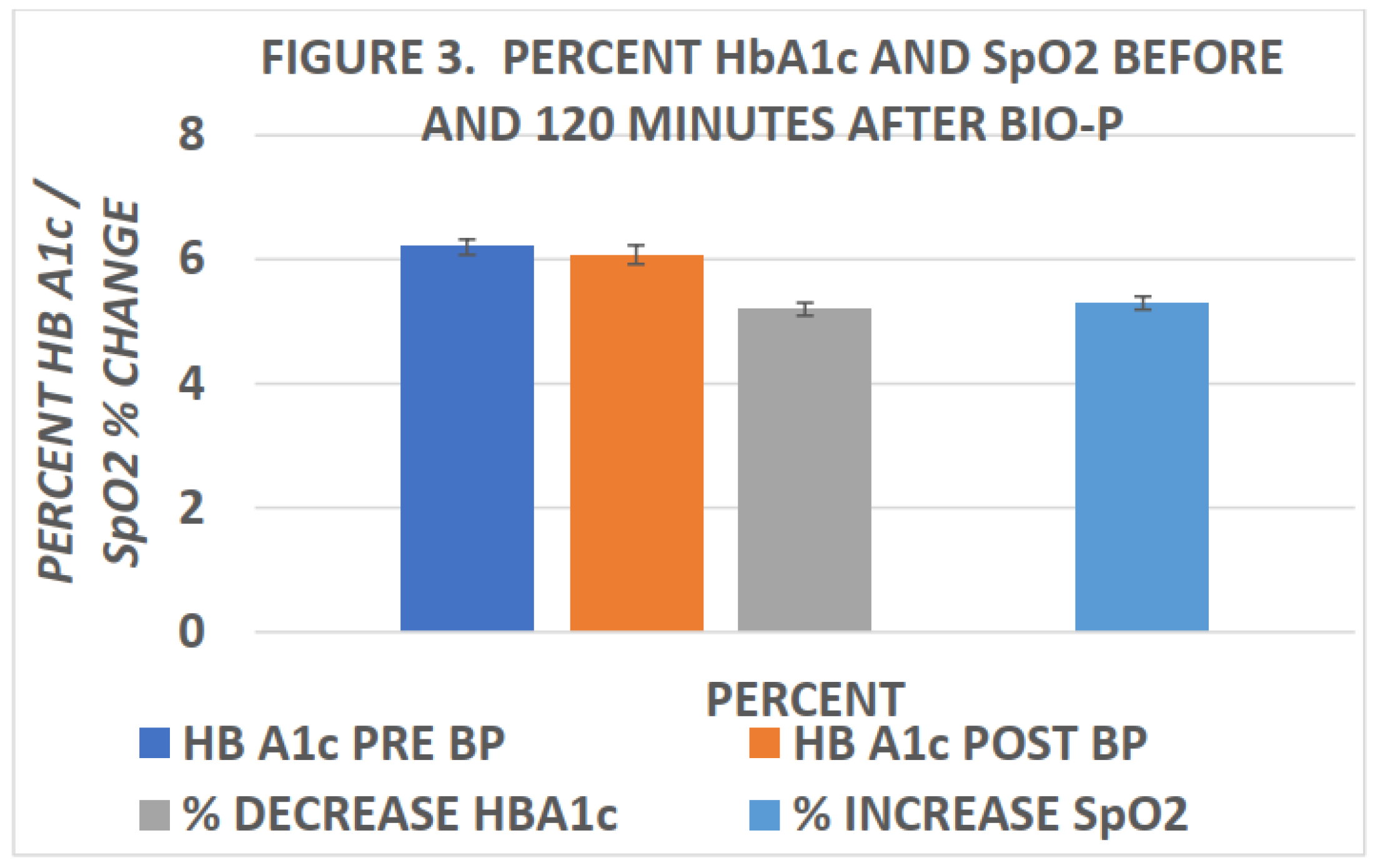
Miley was among the first to report changes in blood SpO2 following biophotonic treatment.[
15] In his studies, he reported elevations in SpO2 within ten minutes of completion of biophotonic exposure and which improvements in SpO2 were found to persist for many weeks following the photonic treatments. More recently, Tulp et al and Bently[
16,
22] confirmed the elevations in blood SpO2 within 120 minutes of completing biophotonc treatment. The effects of biophotonic treatments on SpO2 and HbA1c are depicted in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 below, and indicate that the effects on blood oxygen saturation persist for up to 4 weeks or more following treatment (
Figure 2). In
Figure 3, the effects of biophotonic treatment on HbA1c are depicted following the treatment and indicated that HbA1c became significantly decreased when measured just 120 minutes after completion of the treatment. While the decreases in HbA1c were quantitatively small, the decreases were consistent among all recipients of the treatment; no subjects experienced an increase in HbA1c. Moreover, the percent decreases in HbA1c were of similar proportion to the percent increase in SpO2 in the same blood specimens when taken 2 hours after completion of the biophotonic procedure. In
Figure 3 the HbA1c measures are depicted in the left panel of the figure and the percent increase in blood SpO2 in the right panel. While a direct link or absolute mechanism resulting in the changes in HbA1c, SpO2 and the biophotonic exposure cannot be determined from the observations reported, the coincidence is striking.
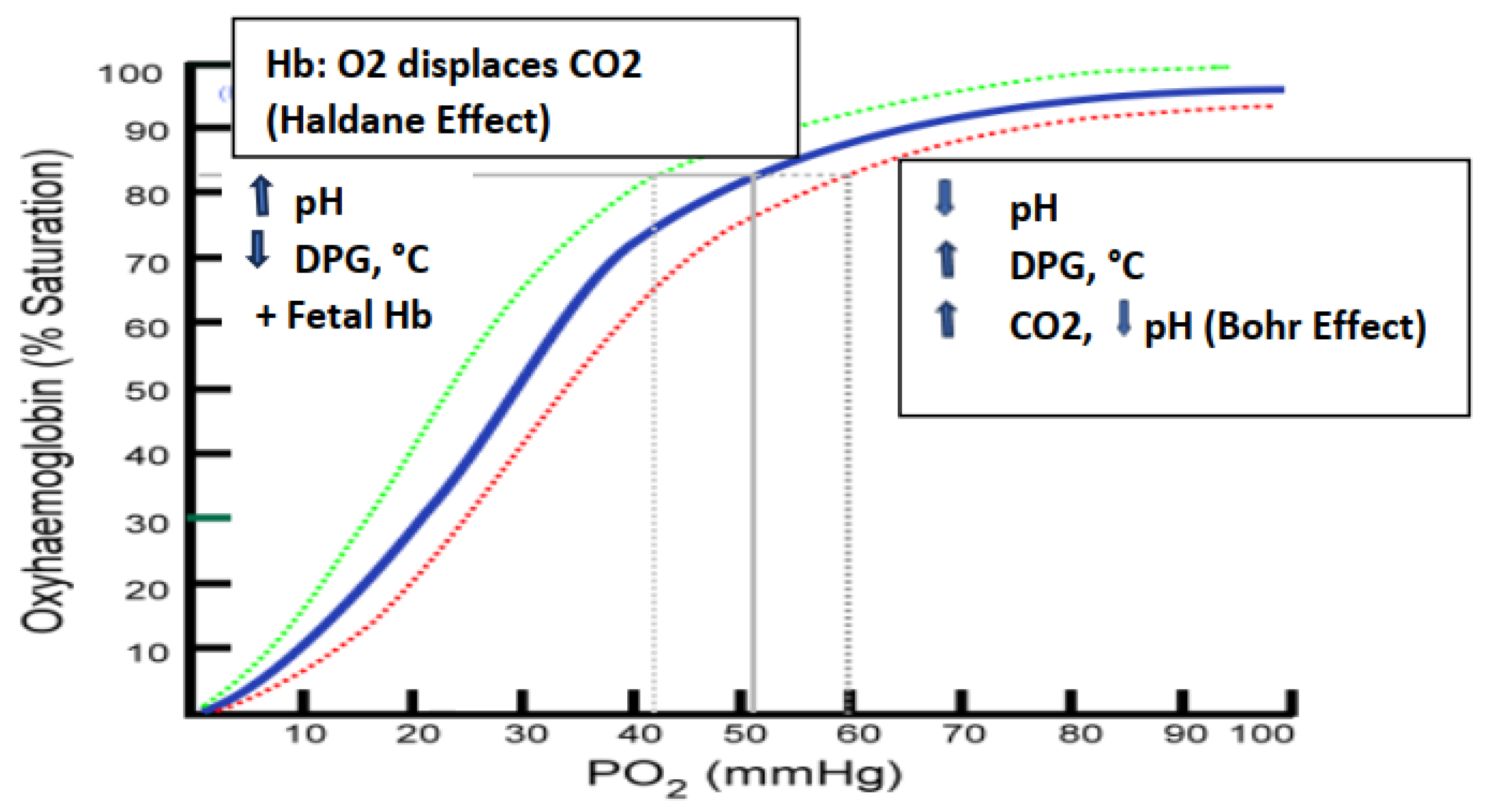
Discussion. The strength by which oxygen binds to hemoglobin is affected by several factors and can be represented as a shift to the left or right in the oxygen dissociation curve depicted in
Figure 5 below. While a direct link between the UV-associated changes in HbA1c, SpO2 and the biophotonic exposure cannot be determined from the observations reported, the likelihood that the parameters are related to one or more factors remains strong. The oxygenation of hemoglobin is influenced by numerous factors, including the presence of 2,3 bisphosphate gluconate (2,3 DPG or 2,3 BPG) in erythrocytes, local pH, the blood concentration of CO2, the magnitude of hemoglobin glycation, the Taut vs the Relaxed Hb configuration, and the Bohr effect.[
23,
24,
25] A rightward shift of the curve indicates that hemoglobin has a decreased affinity for oxygen and enables the release of oxygen to myoglobin more favorable, thus, under a rightward shift oxygen can more actively unload from hemoglobin. A shift to the left however indicates an increased oxygen-hemoglobin affinity and an increased reluctance to release oxygen to peripheral tissues from adult (α2β2) but not fetal (a2γ2) hemoglobin. When the intracellular pH becomes decreased however, CO2 production and 2,3 DPG can become increased, followed by the oxygen saturation curve shifting to the right. As the saturation curve moves to the right, the affinity to bind oxygen becomes decreased, resulting in a decreased affinity for reversible oxygenation and deoxygenation of hemoglobin. This inverse relationship is known as the ‘Bohr’ effect and is evident when metabolically active tissue oxidizes glucose and oxygen into CO2, water and organic acids. As the oxidation of glucose increases, pH decreases, 2,3 DPG increases, and hemoglobin then exhibits a reduced affinity for oxygen which facilitates its more efficient delivery to peripheral tissues via the Bohr effect.[
22,
25] In contrast, in the Haldane effect on hemoglobin oxygenation, oxygen displaces CO2 resulting in a shift of the hemoglobin oxygen saturation curve to the left with a greater affinity between oxygen and hemoglobin.[
25].
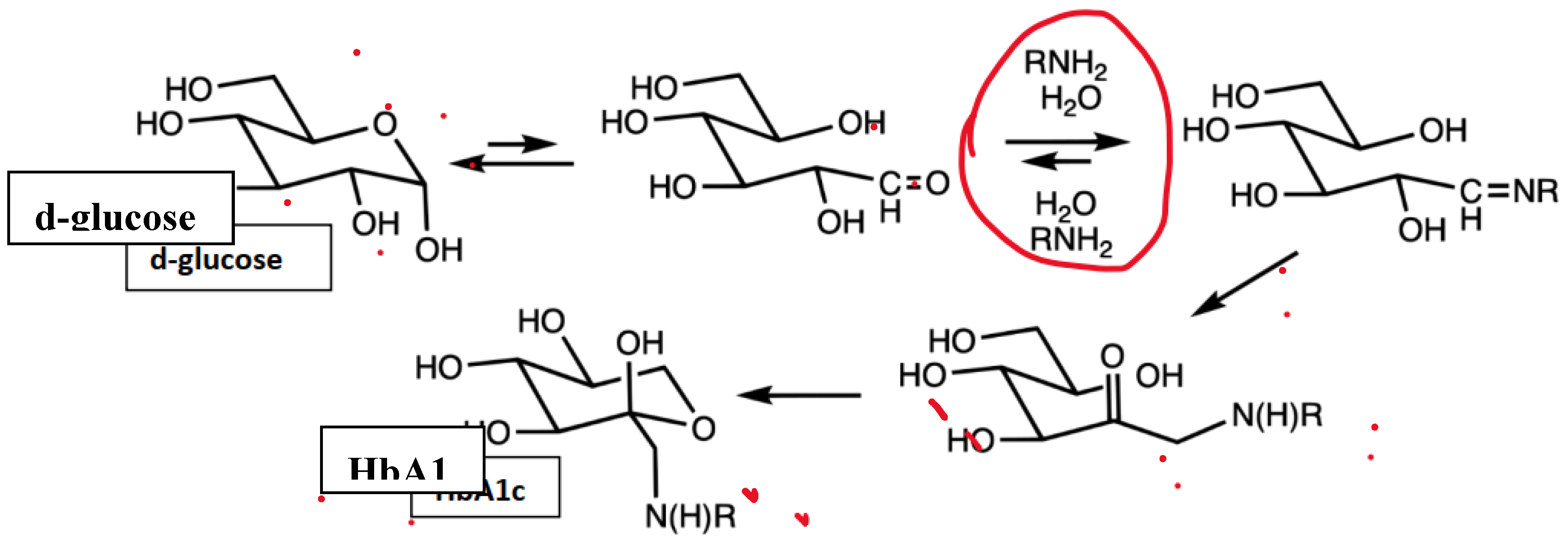
Figure 4.
Glycation pathway from d-glucose via Amadori rearrangement (in HbA1c, R is typically an N-terminal valine).
[[
14]
].
Figure 4.
Glycation pathway from d-glucose via Amadori rearrangement (in HbA1c, R is typically an N-terminal valine).
[[
14]
].
Figure 5.
Effects of DPG , pH and Temperature on the oxygen saturation curve. Modified from (9,25,27).
Figure 5.
Effects of DPG , pH and Temperature on the oxygen saturation curve. Modified from (9,25,27).
The mechanism for the biophotonic-mediated alterations in hemoglobin glycation remain speculative however, and may be due to a pH induced reversal or limitation at the level of the committed step in the glycation process as depicted in
Figure 4 as a result of the biophotonic excitation. The committed step is indicated in the encircled area and reflects the most likely locus in the glycation process where the potential reversal could occur. As the percent of glycation becomes decreased, parameters of glycemic may also become improved.[
28] Once the glycation reaction matures beyond the encircled step, it likely remains glycated for the remaining duration of the lifespan of the hosting erythrocyte. There was no clinical indication that red cells were removed via other biochemical processes linked to the photonic therapy, and no clinical evidence of RBC destruction has yet been observed. In a diabetic ob/ob mouse model, the biophotomodulation also resulted in improvements in glycemic status in association with improvements nf muscle metabolism.[
28] Regardless of the biochemical mechanisms involved, the proportion of decreased glycation was similar to the proportional increases in blood oxygenation in the reviewed study. The studies of Miley suggest that the beneficial effects of biophotonic therapy may remain well beyond the immediate responses, and increases in oxygen availability surely contribute to the cellular repair and tissue regeneration reported elsewhere. Oxygen availability in combination with ‘good’ ROS responses is a crucial component of a healthy wellbeing and immune responses, and are important constituents of the broad spectrum of beneficial effects of UV- biophotonic therapy, and signal the reemergence of an old and reliable treatment for both old and emerging diseases.