Submitted:
22 December 2023
Posted:
22 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
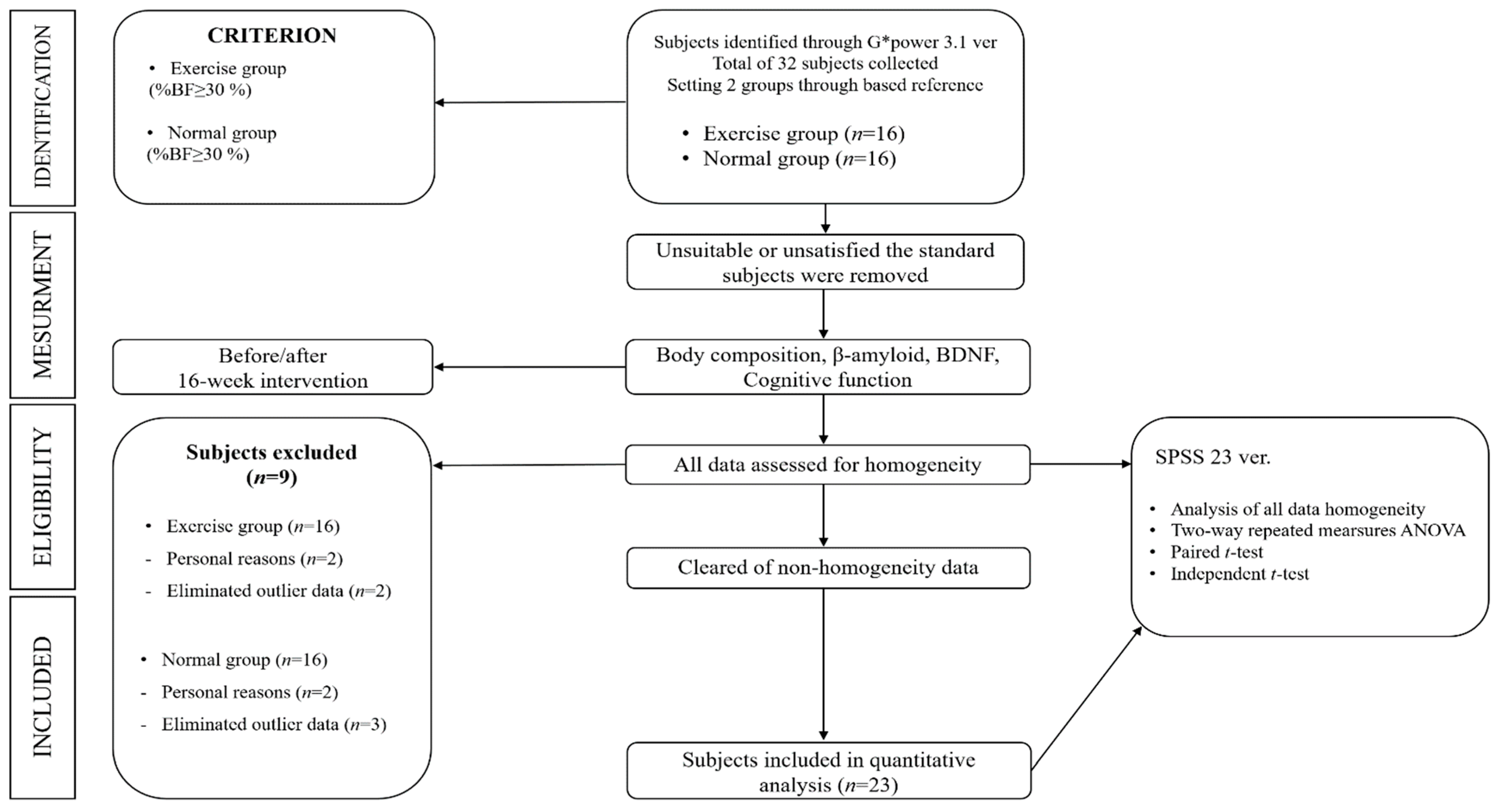
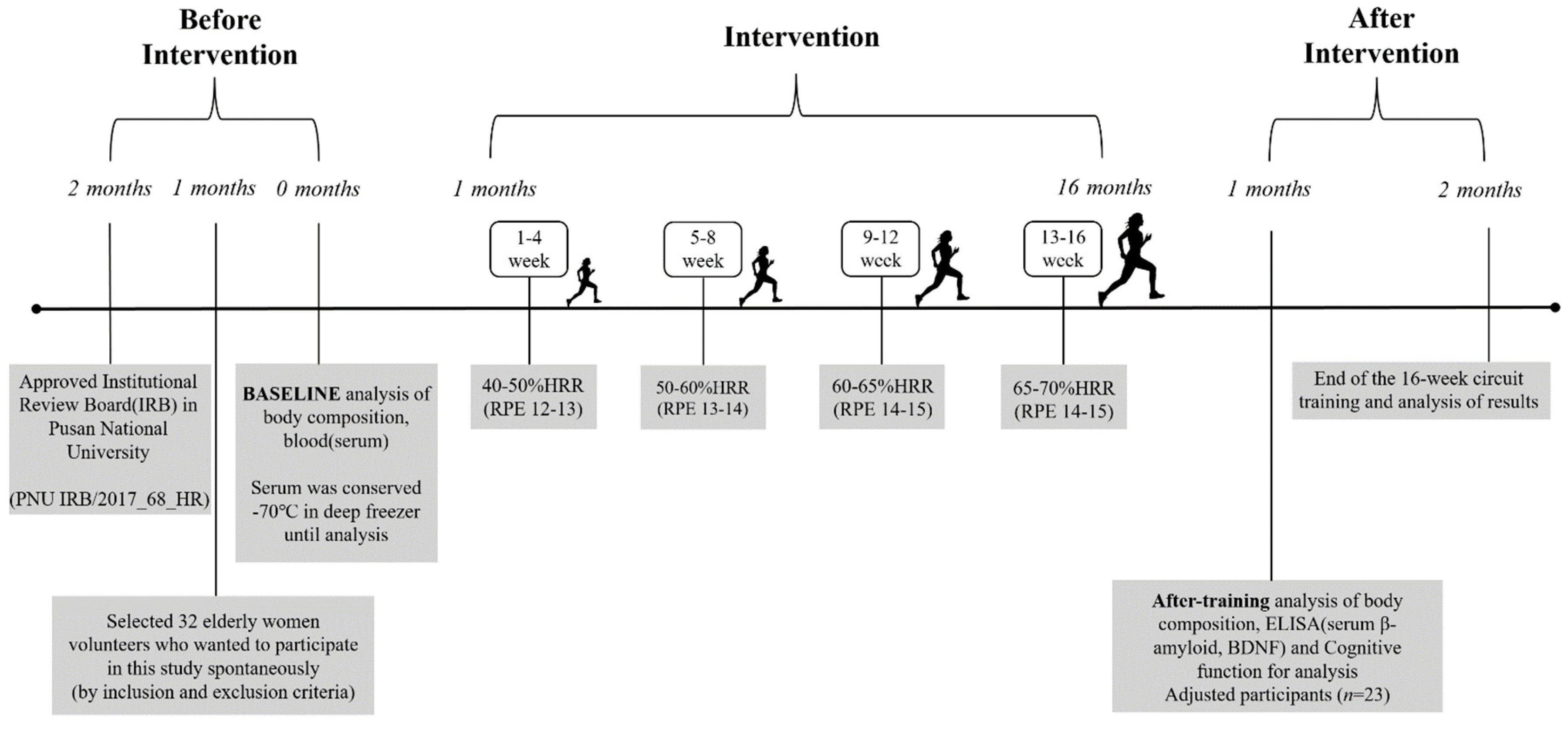
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Circuit Training Program
2.3. Measurement Items and Analytical Method
2.3.1. Body Composition
2.3.2. Blood Analysis
2.3.3. Cognitive Function
2.3.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. β-amyloid
3.1.1. The Results for Intra-Group and Inter-Group Analysis of Changes and Interactions of β-amyloid are Shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
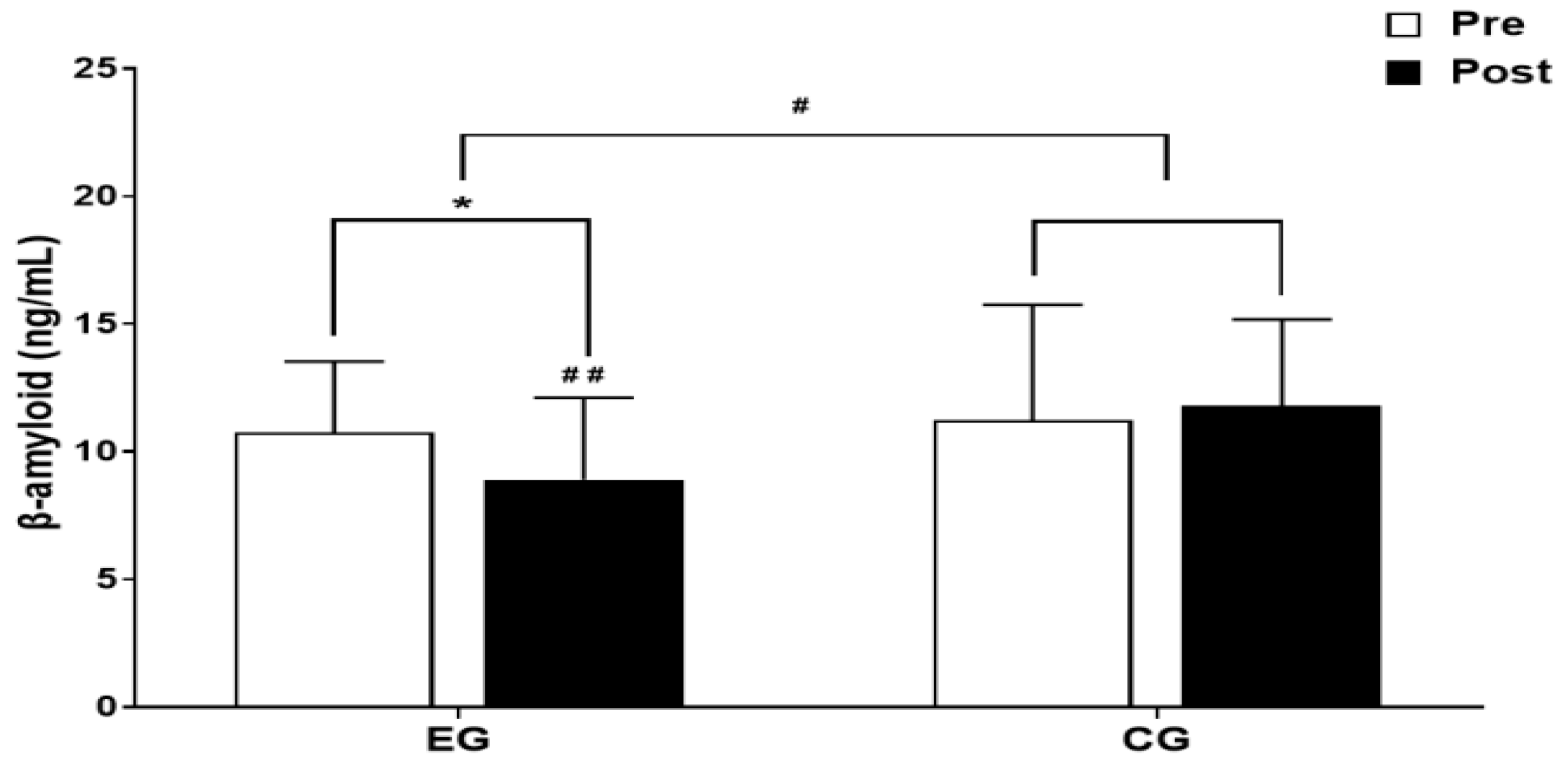
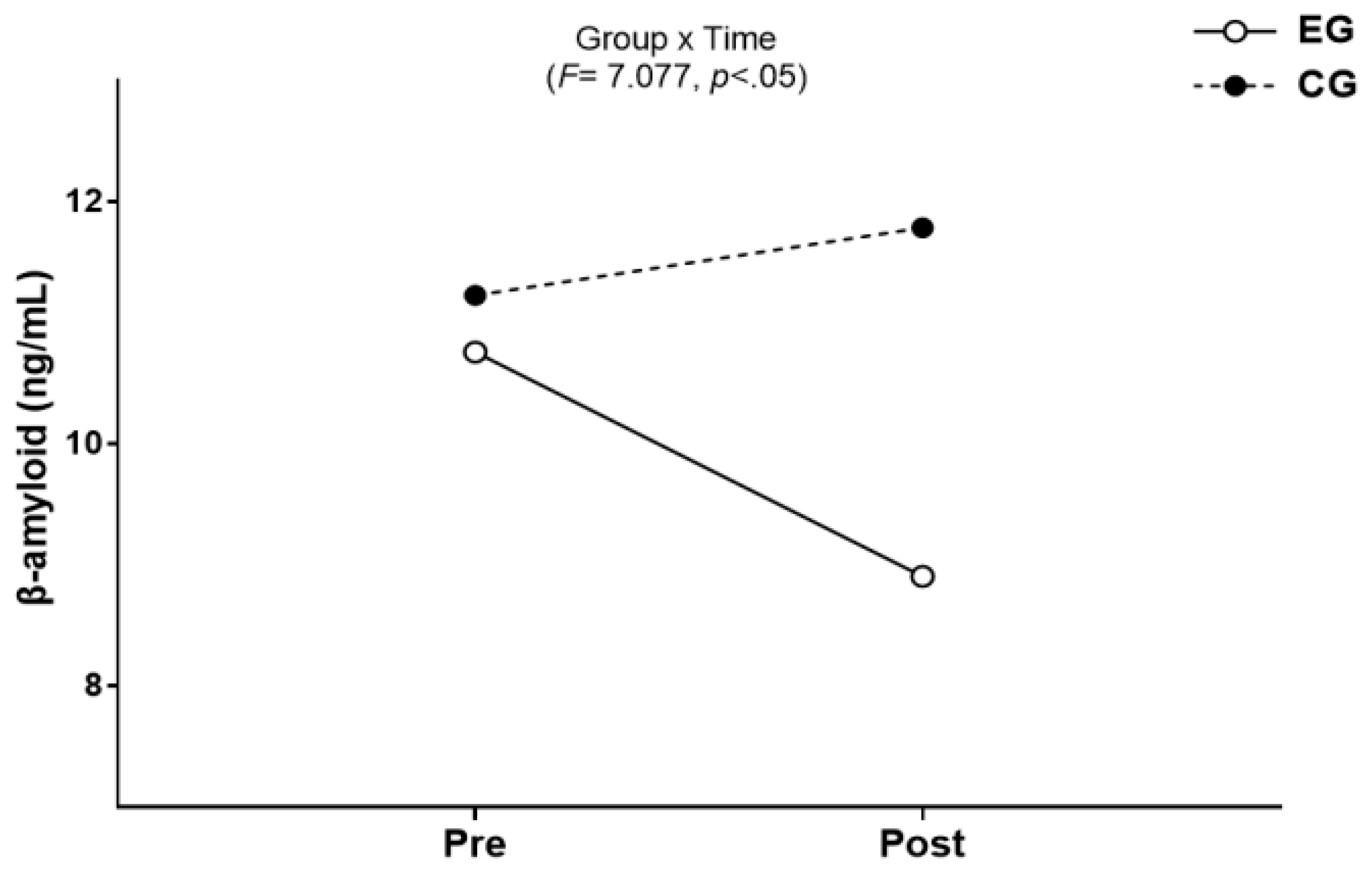
3.2. BDNF
3.2.1. The results for Intra-Group and Inter-Group Analysis of Changes and Interactions of BDNF are Shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
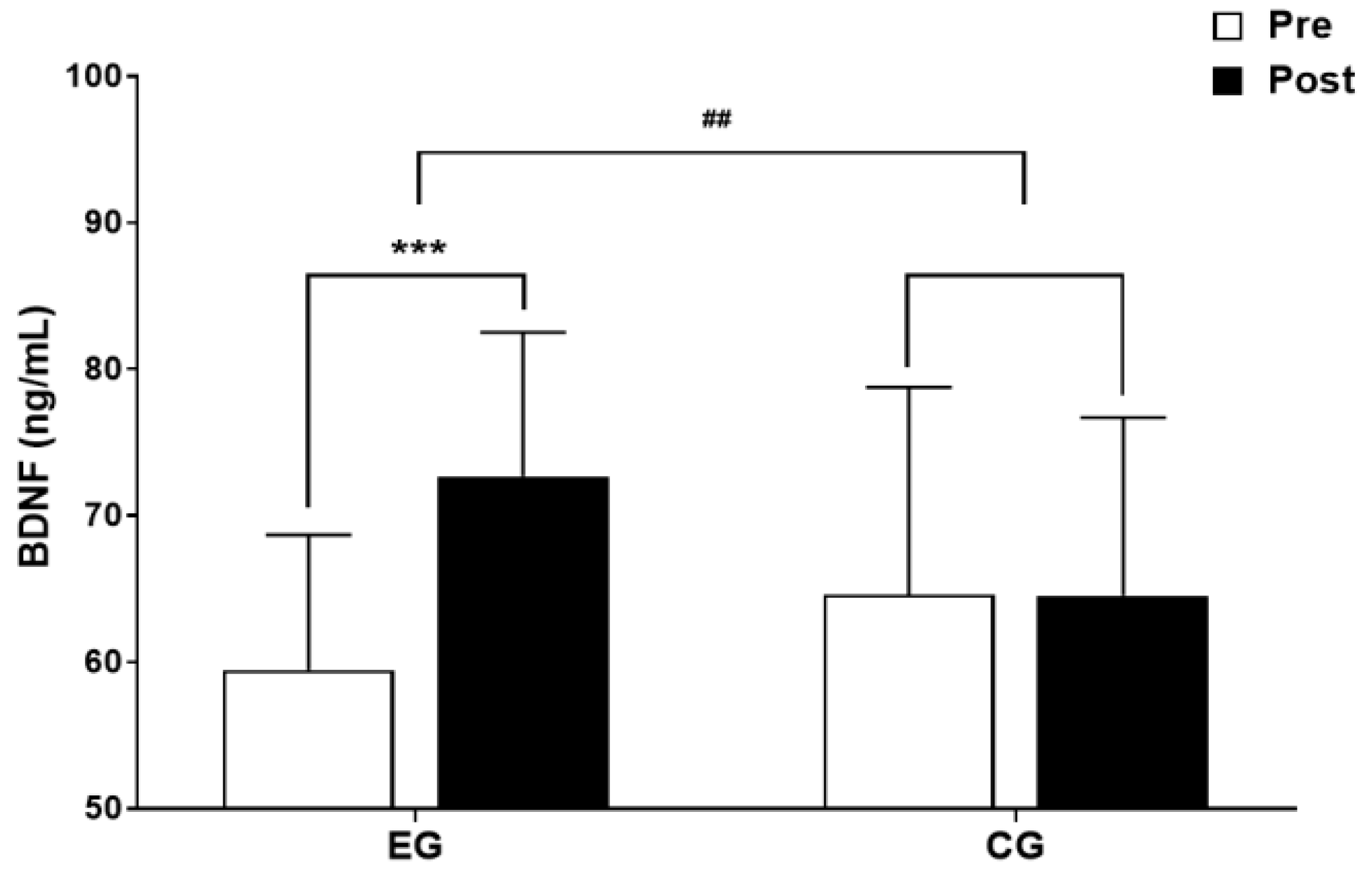

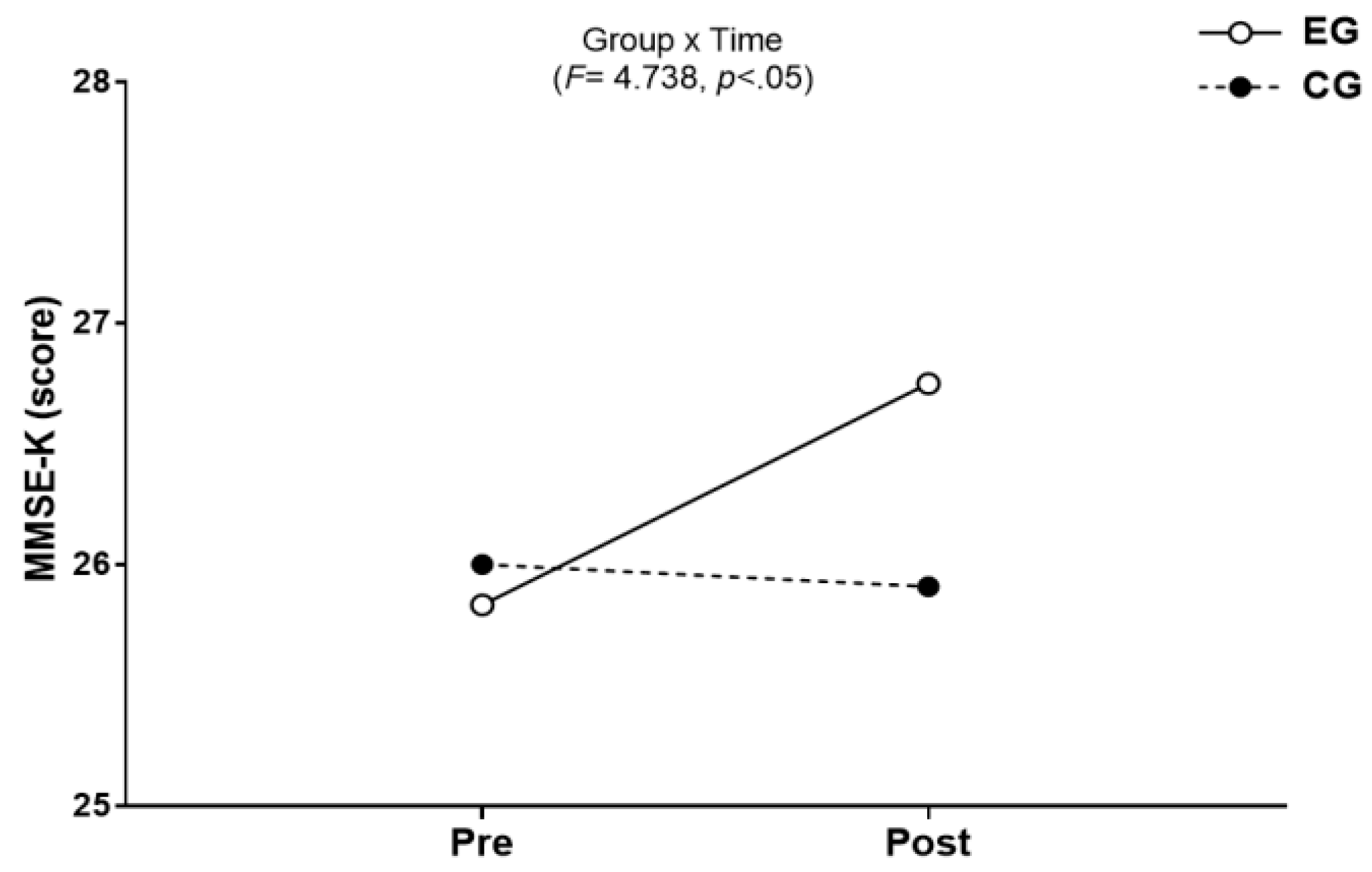
3.3. Cognitive Function
3.3.1. The Results for Intra-Group and Inter-Group Analysis of Changes and Interactions of Cognitive Function are Shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
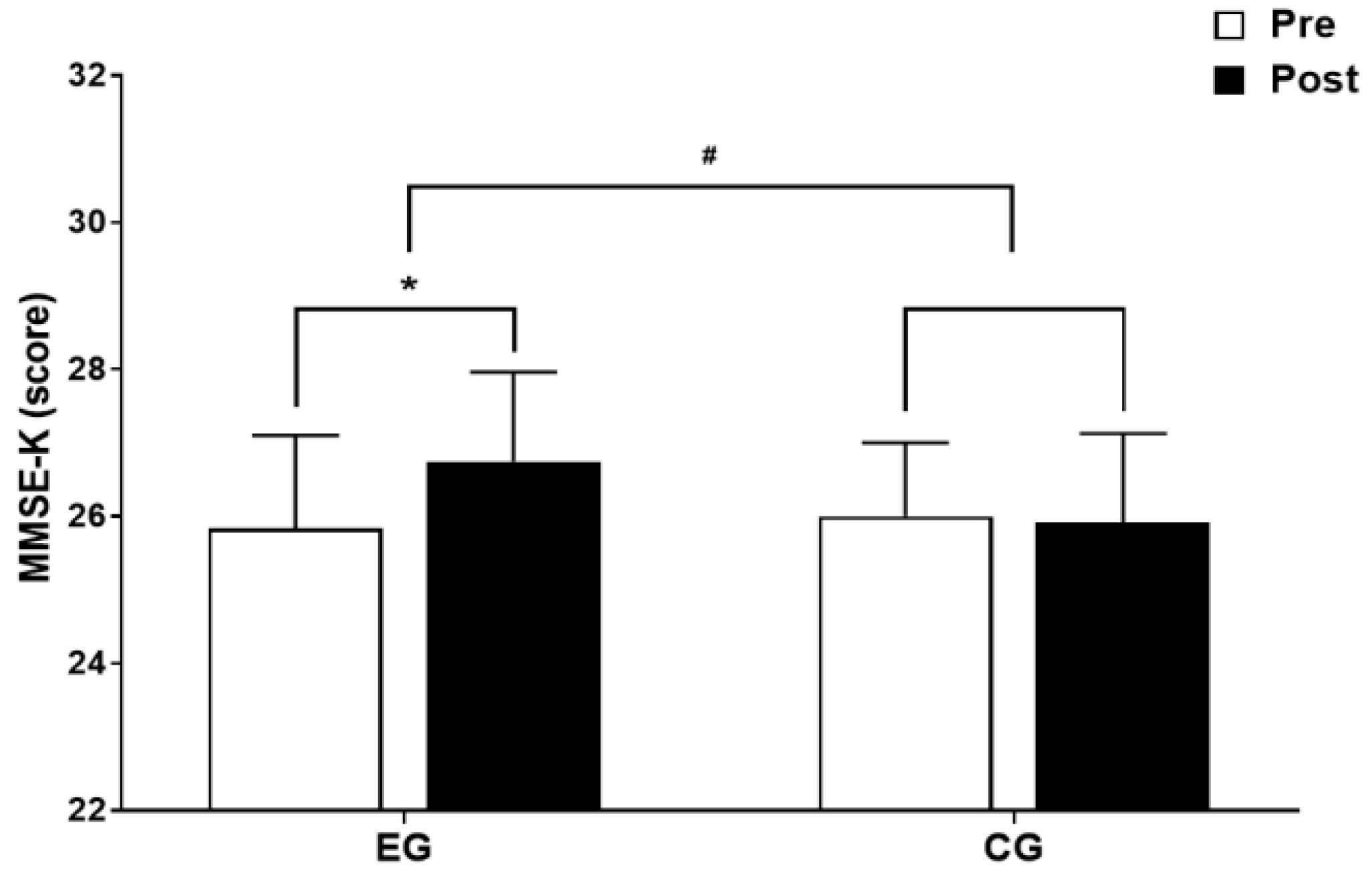
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
References
- National Institute of Dementia. Global Trends of Dementia Policy 2020; National Medical Center National Institute of Dementia: Seoul, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S. Relationships between cognitive function and quality of life of elderly stroke patients. IJACT. 2018, 6, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Dementia. National Institute of Dementia Annual Report 2021; National Medical Center National Institute of Dementia: Seoul, Korea, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.; Kim, S.J.; Hong, S.P.; Kim, Y.S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease utilizing amyloid and tau as fluid biomarkers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.M.; Dalmolin, G.D.; Bär, J.; Karpova, A.; Mello, C.F.; Kreutz, M.R.; Rubin, M.A. Inhibition of the polyamine system counteracts β-amyloid peptide-induced memory impairment in mice: involvement of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors. PLOS ONE. 2014, 9, e99184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, M.H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Eisch, A.J. Dynamic expression of TrkB receptor protein on proliferating and maturing cells in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Hippocampus. 2008, 18, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.S. The effects of dementia perception and attitude on aging anxiety. JKEIA. 2020, 14, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoul National University Hospital. Nationwide Study on the Prevalence of Dementia in Korea Elders; Seoul, Korea, 2008.
- Wu, M.S.; Lan, T.H.; Chen, C.M.; Chiu, H.C.; Lan, T.Y. Socio-demographic and health-related factors associated with cognitive impairment in the elderly in Taiwan. BMC Public Health. 2011, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritz-Silverstein, D.; Von Mühlen, D.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Bressel, M.A.B. Isoflavones and cognitive function in older women: the SOy and Postmenopausal Health In Aging (SOPHIA) Study. Menopause. 2003, 10, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.K.; Koh, B.R.; Lee, J.Y. The relationship between sleep-related factors and dementia-related factors in middle-aged women with exercise intensity. J. Korean Soc. Wellness. 2018, 13, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Yan, R. A close look at BACE1 inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease treatment. CNS Drugs. 2019, 33, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, R.J.; Beach, T.G.; Yaari, R.; Reiman, E.M. Alzheimer’s disease a century later. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2006, 67, 1784–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Farr, S.A. The role of amyloid-beta in the regulation of memory. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Dementia Association. Dementia: A Clinical Approach; Daehan Medical: Seoul, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.H.; Cheon, J.U. Effects of 16-week Combined Exercise on Dementia, Depression, and Cognitive Function in Elderly Women. J. Korean Appl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 36, 456–467. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Duan, B.Y.; Zhou, X.P.; Gong, J.X.; Luo, Z.G. Calpain activation promotes BACE1 expression, amyloid precursor protein processing, and amyloid plaque formation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27737–27744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Zingler, D.; Schuhbaeck, K.; Schloetcke, K.; Zingler, C.; Schuff-Werner, P.; Virchow, J.C. The impact of age, weight and gender on BDNF levels in human platelets and plasma. Neurobiol. Aging. 2005, 26, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J. The cognition, balance, and quality of life in the elderly. J. Korean Biol. Nurs. Sci. 2011, 13, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Friedland, R.P.; Fritsch, T.; Smyth, K.A.; Koss, E.; Lerner, A.J.; Chen, C.H.; Petot, G.J.; Debanne, S.M. Patients with Alzheimer’s disease have reduced activities in midlife compared with healthy control-group members. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001, 98, 3440–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.H.; Kim, K.H. The effect of Health Promotion exercise on Alzheimer's dementia-related factors and cognitive function in elderly women. The Korean J. Sports Sci. 2018, 27, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, H.S.; Kim, D.H. The effects of band resistance exercise and circuit exercise program on body composition and bone mineral density in elderly women with osteopenia. Korean Health Fundam. Med. Sci. Soc. 2021, 14, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Culture Sports and Tourism. National Life Sports Survey; Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism: Sejong, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Amarya, S.; Singh, K.; Sabharwal, M. Health consequences of obesity in the elderly. J. Clin. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2014, 5, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayabe, T.; Ohya, R.; Kondo, K.; Ano, Y. Iso-α-acids, bitter components of beer, prevent obesity-induced cognitive decline. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.; Masaki, K.; Xue, Q.L.; Peila, R.; Petrovitch, H.; White, L.R.; Launer, L.J. A 32-year prospective study of change in body weight and incident dementia: the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Hyang-Beum; Kim, Y. W. A study on the influence of combined training of dance sports and resistance exercise on motor abilities and sarcopenia indicators in old women. The J. Korean Dance. 2017, 35, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.M.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.H. Effects of circuit exercise on functional fitness, estradiol, serotonin, depression and cognitive function in elderly women. Journal of Korean Association of Physical Education and Sport for Girls and Women. 2017, 31, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.; Jung, J.W. Validity of Borg’s category ratio 10 scale during maximal-graded exercise testing. Exerc. Sci. 2016, 25, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winocur, G.; Wojtowicz, J.M.; Sekeres, M.; Snyder, J.S.; Wang, S. Inhibition of neurogenesis interferes with hippocampus-dependent memory function. Hippocampus. 2006, 16, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.K.; Kwang, I.H.; Kim, W.S. The effects of sensory integration exercise on β-amyloid, DHEAs, BDNF in older female. Korea Society for Wellness. 2012, 7, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Drollette, E.S.; Scudder, M.R.; Raine, L.B.; Moore, R.D.; Saliba, B.J.; Pontifex, M.B.; Hillman, C.H. Acute exercise facilitates brain function and cognition in children who need it most: an ERP study of individual differences in inhibitory control capacity. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, N.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, T.D. The effect of aquarobics exercise on the prefrontal EEG alpha Wave Activation and dementia related factors in elderly women. Korean J. Sport Sci. 2017, 26, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.D.; Kim, W.K. Effects of taekwondo poomsae training on body composition, β-amyloid and dheas concentration in elderly women. The Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2009, 48, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.A.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, D.J. The effects of the physical activity program on body composition, depression and risk factors of dementia in the elderly women. J. Life Sci. 2011, 21, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Woo, J.; Shin, K.O.; Roh, H.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Yoon, B.K.; Park, C.H. Effects of exercise type on β-amyloid, BDNF and cognitive function in Type 2 diabetic mice. J. Korean Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 37, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.H.; Kim, J.; Davis, J.M.; Blair, S.N.; Cho, H.C. Association among basal serum BDNF, cardiorespiratory fitness and cardiovascular disease risk factors in untrained healthy Korean men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, L.T.; Williams, J.S.; Shen, C.L. The effect of acute exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and cognitive function. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.W.; Kim, J.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kim, D.Y. Effects of resistance training using elastic band on myokine in obese elderly women. Korean J. Sport Sci. 2021, 30, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinoff, A.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, C.S.; Sherman, C.; Chan, S.; Lanctôt, K.L. The effect of exercise training on resting concentrations of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): A meta-analysis. PLOS ONE. 2016, 11, e0163037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Cheon, J.U. The effect of 16-weeks combined exercise on the β-amyloid and BDNF among the elderly women. ksw. 2016, 11, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.I. The change of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1(IGF-1) and working-memory in adolescents by aerobic exercise intensity for 12 weeks. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2013, 52, 753–763. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, C.P.; Kuys, S.S.; Brauer, S.G. The effect of aerobic exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor in people with neurological disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 4716197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.G.; Yoon, H.K. The effects of aerobic and thera-band combined exercise on cerebral blood flow, BDNF, and aging-related hormone in elderly women. The Korean J. Growth Dev. 2013, 21, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Bus, B.A.A.; Tendolkar, I.; Franke, B.; de Graaf, J.; den Heijer, M.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Oude Voshaar, R.C.O. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor: determinants and relationship with depressive symptoms in a community population of middle-aged and elderly people. World J. Biol. Psychiatry. 2012, 13, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Poo, M.M. Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maass, A.; Düzel, S.; Brigadski, T.; Goerke, M.; Becke, A.; Sobieray, U.; Neumann, K.; Lövdén, M.; Lindenberger, U.; Bäckman, L.; et al. Relationships of peripheral IGF-1, VEGF and BDNF levels to exercise-related changes in memory, hippocampal perfusion and volumes in older adults. NeuroImage. 2016, 131, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.Y.; Kang, S.; Park, J.Y.; Park, K.M. Effects of myokine factors on exercise types in obese women. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 26, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterness, A.K.; Wiebe, E.; Kwasnica, A.; Keyes, G.; Christie, B.R. Voluntary exercise does not enhance long-term potentiation in the adolescent female dentate gyrus. Neuroscience. 2011, 183, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, E.; Mandel, R.J.; Klein, R.L.; Muzyczka, N.; Lindvall, O.; Kokaia, Z. Suppression of insult-induced neurogenesis in adult rat brain by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 177, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, K.; Yamamoto, W.; Tadokoro, M.; Takagi, N.; Sasakawa, K.; Nitta, A.; Furukawa, S.; Takeo, S. Alterations in hippocampal GAP-43, BDNF, and L1 following sustained cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2002, 935, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.; Lee, N.H. Effects of combined exercise on neurotrophic factors and cognitive function in elderly women. Journal of Korean Physical Education Association for Girls and Women. 2012, 26, 173–189. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, E.B.; Wang, L.; Bowen, J.D.; McCormick, W.C.; Teri, L.; Crane, P.; Kukull, W. Exercise is associated with reduced risk for incident dementia among persons 65 years of age and older. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 144, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karssemeijer, E.G.A.; Aaronson, J.A.; Bossers, W.J.; Smits, T.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.M.; Kessels, R.P.C. Positive effects of combined cognitive and physical exercise training on cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: A meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gelder, B.M.; Tijhuis, M.A.R.; Kalmijn, S.; Giampaoli, S.; Nissinen, A.; Kromhout, D. Physical activity in relation to cognitive decline in elderly men: the FINE Study. Neurology. 2004, 63, 2316–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Oh, S.H. A meta-analytic approach to the effects of exercise intervention on cognitive function in elderly women. Journal of Korean Association of Physical Education and Sport for Girls and Women. 2018, 32, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.Y.; Han, J.Y. The effect of exercise on cognitive function in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Korean Data Inf. Sci. Soc. 2016, 27, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.; Marshall, S.J.; Patterson, R.E.; Marinac, C.R.; Natarajan, L.; Rosenberg, D.; Wasilenko, K.; Crist, K. Objectively measured physical activity is related to cognitive function in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2013, 61, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Howard, V.J.; Wadley, V.G.; Hutto, B.; Blair, S.N.; Vena, J.E.; Colabianchi, N.; Rhodes, D.; Hooker, S.P. Association between objectively measured physical activity and cognitive function in older adults-the reasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, P.M. Alzheimer’s disease, amnestic mild cognitive impairment, and age-associated memory impairment: current understanding and progress toward integrative prevention. Altern. Med. Rev. 2008, 13, 85–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Kang, H. Relation between objectively measured physical activity levels and cognitive function decline risk factors in community dwelling women elderly. The Korean J. Growth Dev. 2017, 25, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkul, C.; Guclu-Gunduz, A.; Irkec, C.; Fidan, I.; Aydin, Y.; Ozkan, T.; Yazici, G. Effect of combined exercise training on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, suppressors of cytokine signaling 1 and 3 in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 316, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaffe, K.; Barnes, D.; Nevitt, M.; Lui, L.Y.; Covinsky, K. A prospective study of physical activity and cognitive decline in elderly women: women who walk. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Merrill, D.A.; Coppola, G.; Tsukada, S.; Schroeder, B.E.; Shaked, G.M.; Wang, L.; Blesch, A.; Kim, A.; Conner, J.M. Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent and primate models of Alzheimer's disease. Nat. Med. 2020, 15, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CG(n=11) | EG(n=12) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |
| Age(yr) | 67.97±1.73 | 66.97±1.63 | ||
| Height(cm) | 154.73±3.69 | 152.55±4.19 | ||
| Weight(kg) | 55.49±4.44 | 55.75±4.72 | 57.33±6.61 | 57.24±6.59 |
| BMI(kg/㎡) | 24.45±1.70 | 24.58±2.00 | 24.67±2.38 | 24.62±2.31 |
| SMM(kg/㎡) | 19.09±1.40 | 18.99±1.34 | 19.68±1.85 | 19.98±1.87** |
| BFM(kg/㎡) | 19.82±2.79 | 19.95±2.71 | 20.35±4.12 | 19.79±3.96 |
| %BF(%) | 35.55±3.12 | 35.65±2.45 | 35.37±3.31 | 34.33±3.45** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





