Submitted:
21 December 2023
Posted:
22 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient selection
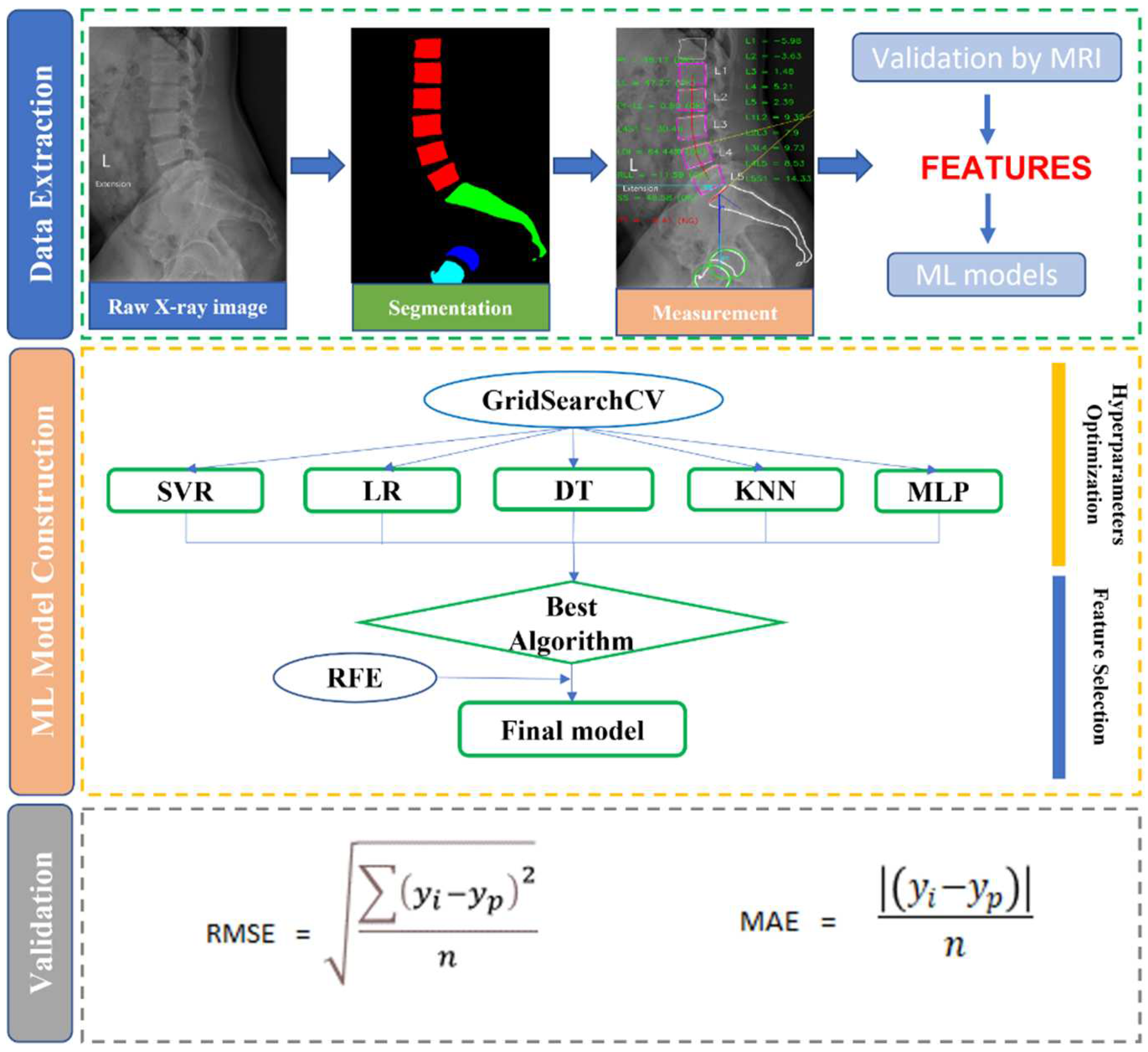
2.2. X-ray segmentation and feature extraction
2.3. ML implementation
2.3.1. Data preprocessing
2.3.2. Regression models
2.4. Statistical analysis and measurement metrics
3. Results
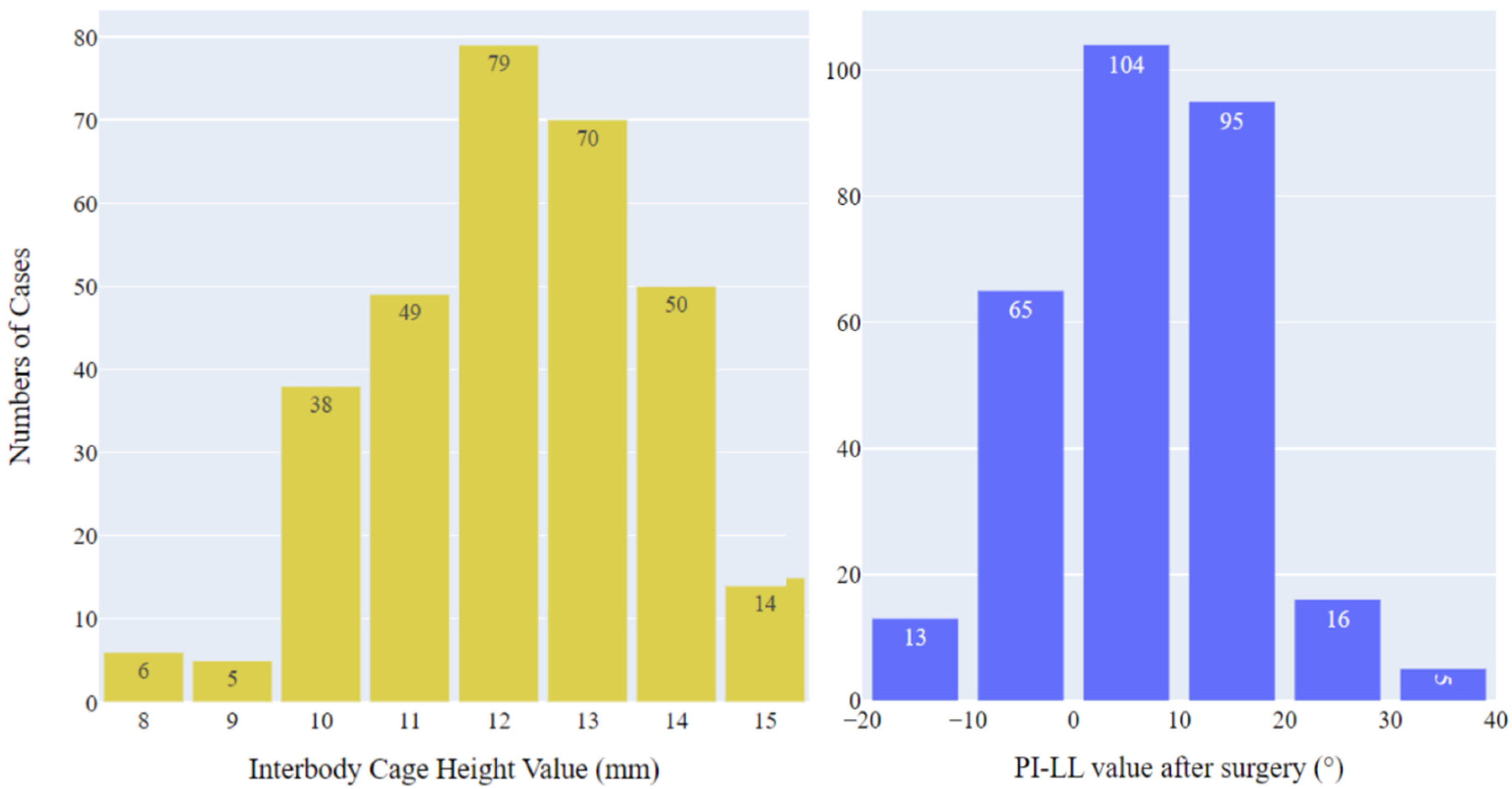
3.1. Patient characteristics
3.2. Performance of ML algorithms
3.3. Final model
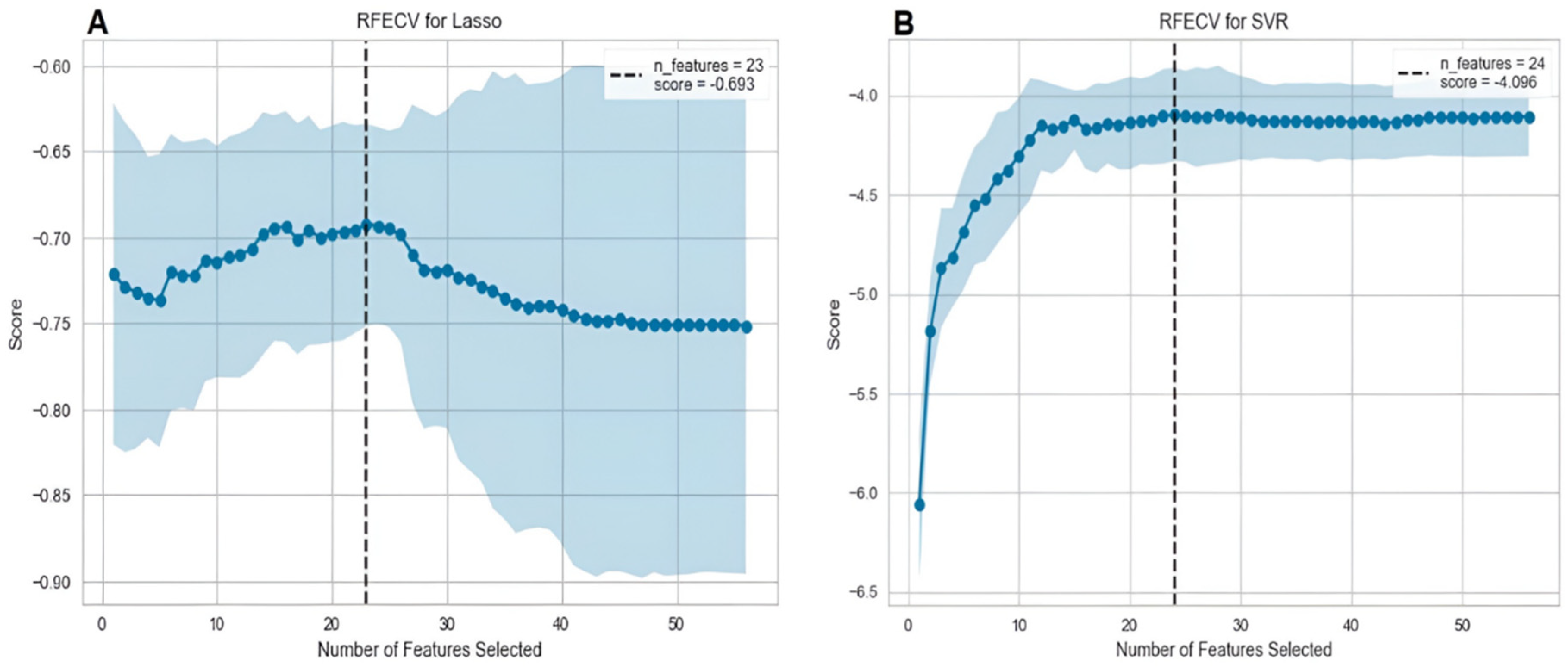
3.3.1. Feature selection
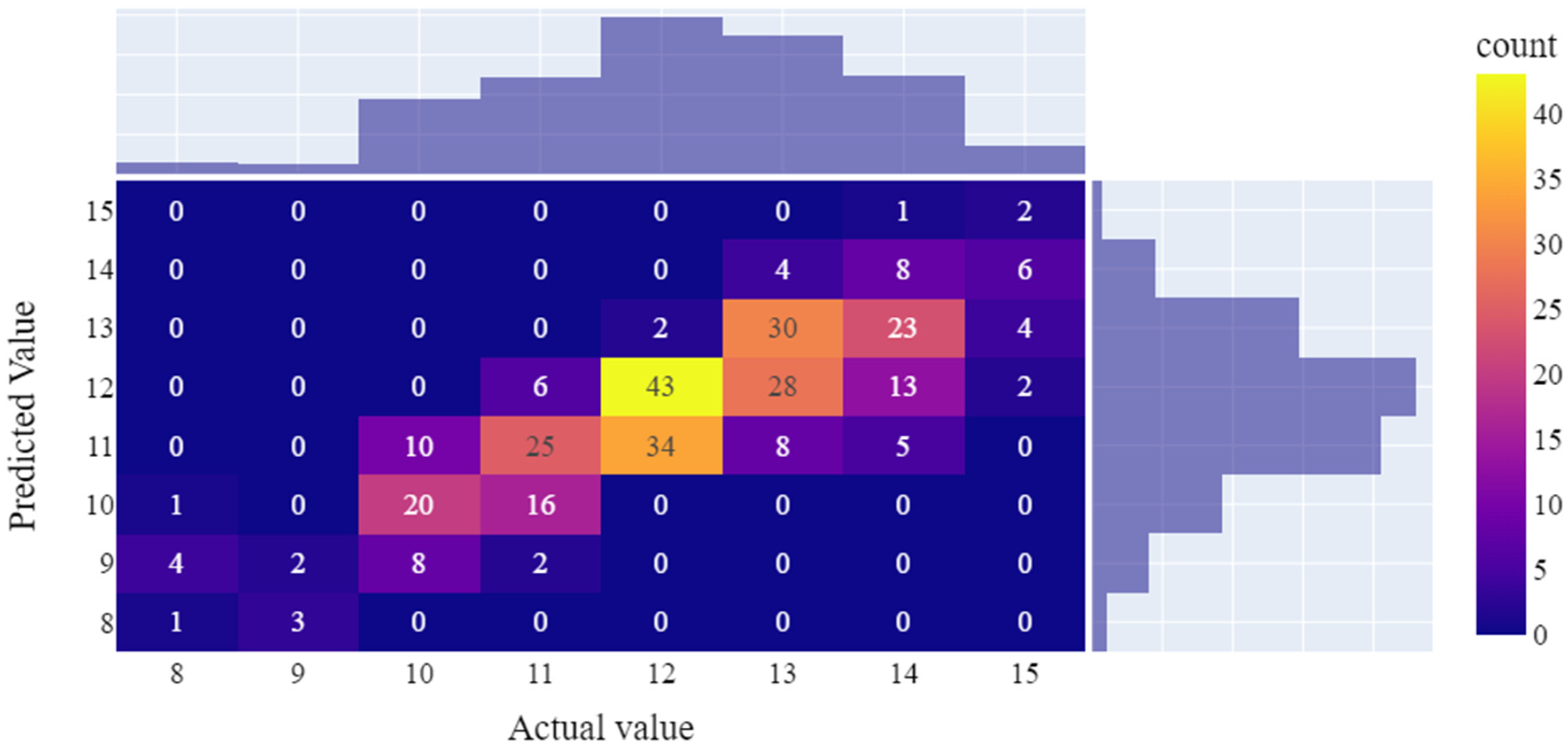
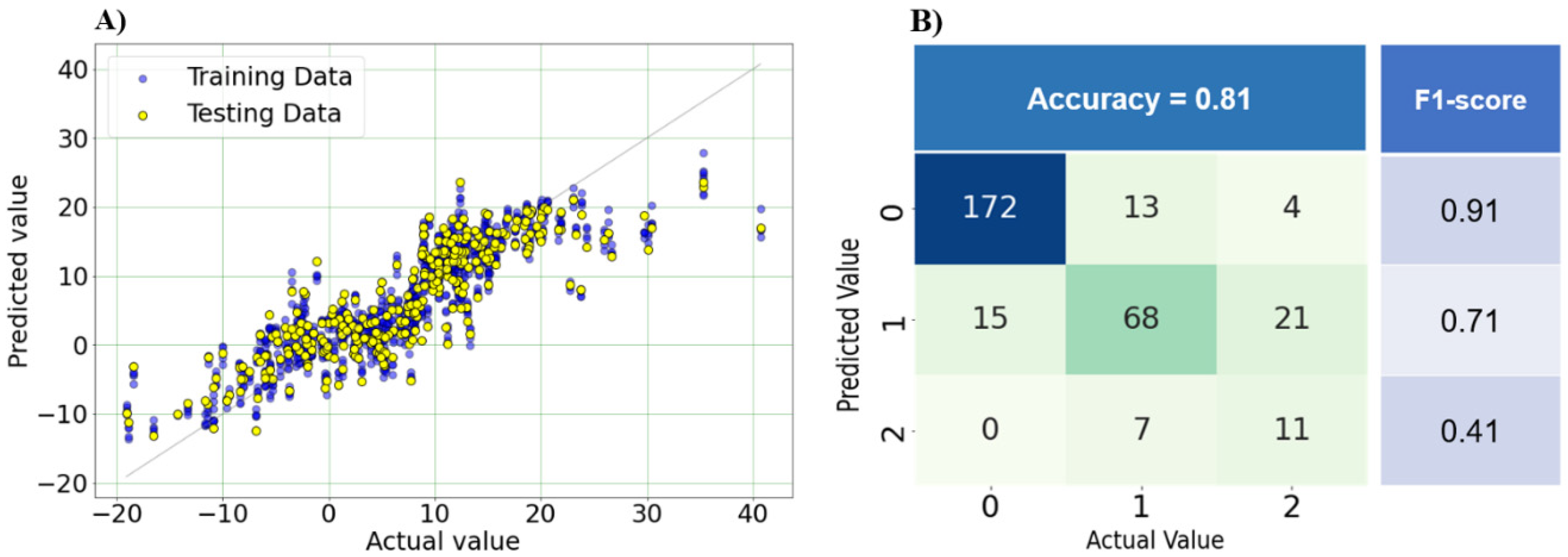
3.3.2. Optimal model performance
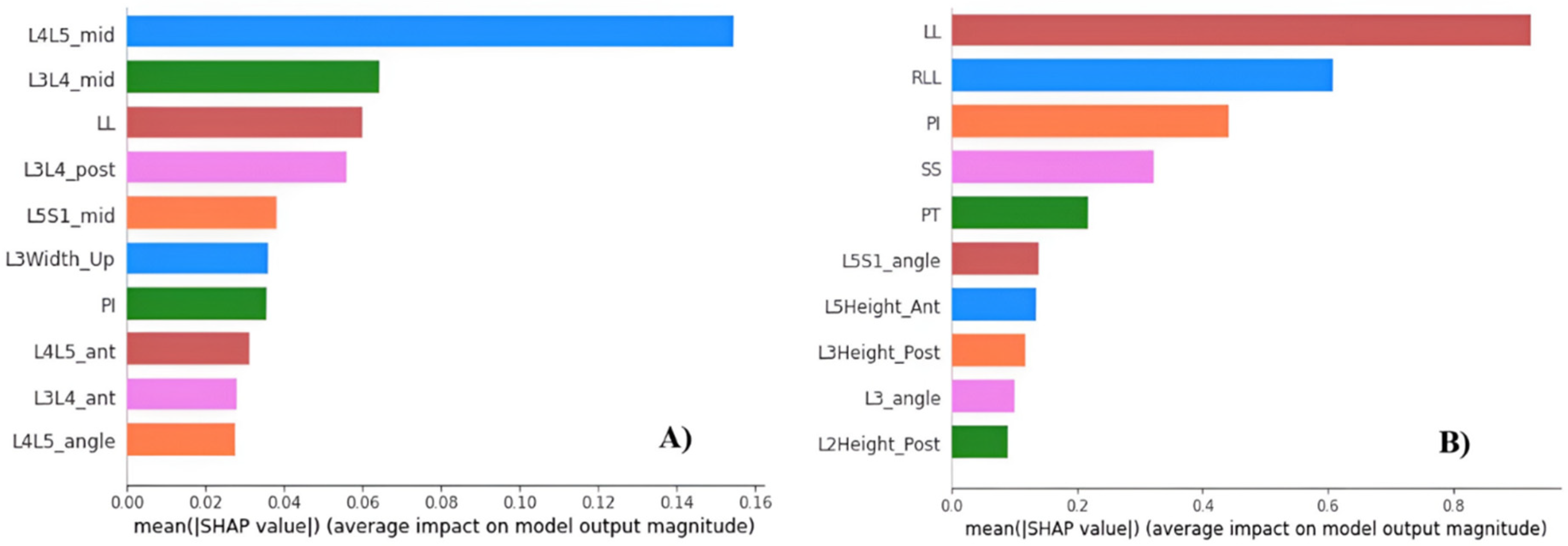
3.3.3. Feature importance.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mummaneni PV, Dhall SS, Eck JC, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 11: interbody techniques for lumbar fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. Jul 2014;21(1):67-74. [CrossRef]
- Noshchenko A, Hoffecker L, Lindley EM, Burger EL, Cain CM, Patel VV. Perioperative and long-term clinical outcomes for bone morphogenetic protein versus iliac crest bone graft for lumbar fusion in degenerative disk disease: systematic review with meta-analysis. J Spinal Disord Tech. May 2014;27(3):117-35. [CrossRef]
- Xiao Y, Li F, Chen Q. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with one cage and excised local bone. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. May 2010;130(5):591-7. [CrossRef]
- Ould-Slimane M, Lenoir T, Dauzac C, et al. Influence of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion procedures on spinal and pelvic parameters of sagittal balance. Eur Spine J. Jun 2012;21(6):1200-6. [CrossRef]
- Watkins RGt, Hanna R, Chang D, Watkins RG, 3rd. Sagittal alignment after lumbar interbody fusion: comparing anterior, lateral, and transforaminal approaches. J Spinal Disord Tech. Jul 2014;27(5):253-6. [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki K, Hoshino M, Omori K, et al. Risk Factors of Adjacent Segment Disease After Transforaminal Inter-Body Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Jan 15 2017;42(2):E86-e92. [CrossRef]
- Rothenfluh DA, Mueller DA, Rothenfluh E, Min K. Pelvic incidence-lumbar lordosis mismatch predisposes to adjacent segment disease after lumbar spinal fusion. Eur Spine J. Jun 2015;24(6):1251-8. [CrossRef]
- Aoki Y, Nakajima A, Takahashi H, et al. Influence of pelvic incidence-lumbar lordosis mismatch on surgical outcomes of short-segment transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. Aug 20 2015;16:213. [CrossRef]
- Senteler M, Weisse B, Snedeker JG, Rothenfluh DA. Pelvic incidence-lumbar lordosis mismatch results in increased segmental joint loads in the unfused and fused lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. Jul 2014;23(7):1384-93. [CrossRef]
- Ailon T, Scheer JK, Lafage V, et al. Adult Spinal Deformity Surgeons Are Unable to Accurately Predict Postoperative Spinal Alignment Using Clinical Judgment Alone. Spine Deform. Jul 2016;4(4):323-329. [CrossRef]
- Lafage V, Schwab F, Vira S, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP. Spino-pelvic parameters after surgery can be predicted: a preliminary formula and validation of standing alignment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Jun 2011;36(13):1037-45. [CrossRef]
- Lafage R, Pesenti S, Lafage V, Schwab FJ. Self-learning computers for surgical planning and prediction of postoperative alignment. Eur Spine J. Feb 2018;27(Suppl 1):123-128. [CrossRef]
- Abbushi A, Cabraja M, Thomale UW, Woiciechowsky C, Kroppenstedt SN. The influence of cage positioning and cage type on cage migration and fusion rates in patients with monosegmental posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterior fixation. Eur Spine J. Nov 2009;18(11):1621-8. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Wang H, Zhu Y, Ding W, Wang Q. Incidence and risk factors of posterior cage migration following decompression and instrumented fusion for degenerative lumbar disorders. Medicine (Baltimore). Aug 2017;96(33):e7804. [CrossRef]
- Aoki Y, Yamagata M, Nakajima F, et al. Examining risk factors for posterior migration of fusion cages following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a possible limitation of unilateral pedicle screw fixation. J Neurosurg Spine. Sep 2010;13(3):381-7. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Chen W, Jiang J, Lu F, Ma X, Xia X. Analysis of the correlative factors in the selection of interbody fusion cage height in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. Jan 12 2016;17:9. [CrossRef]
- Makino T, Honda H, Fujiwara H, Yoshikawa H, Yonenobu K, Kaito T. Low incidence of adjacent segment disease after posterior lumbar interbody fusion with minimum disc distraction: A preliminary report. Medicine (Baltimore). Jan 2018;97(2):e9631. [CrossRef]
- Landham PR, Don AS, Robertson PA. Do position and size matter? An analysis of cage and placement variables for optimum lordosis in PLIF reconstruction. Eur Spine J. Nov 2017;26(11):2843-2850. [CrossRef]
- Cho BH, Kaji D, Cheung ZB, et al. Automated Measurement of Lumbar Lordosis on Radiographs Using Machine Learning and Computer Vision. Global Spine J. Aug 2020;10(5):611-618. [CrossRef]
- Tran V, Lin H-Y, Liu H-W, Jang F-J, Tseng C-H. BiLuNet: A Multi-path Network for Semantic Segmentation on X-ray Images. 2021:10034-10041. [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. the Journal of machine Learning research. 2011;12:2825-2830.
- Shalabi LA, Shaaban Z, Kasasbeh B. Data Mining: A Preprocessing Engine. Journal of Computer Science. 2006;2(9). [CrossRef]
- Lundberg SM, Lee S-I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Advances in neural information processing systems. 2017;30.
- Koo TK, Li MY. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J Chiropr Med. Jun 2016;15(2):155-63. [CrossRef]
- Schwab F, Ungar B, Blondel B, et al. Scoliosis Research Society-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: a validation study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). May 20 2012;37(12):1077-82. [CrossRef]
- Kong LD, Zhang YZ, Wang F, Kong FL, Ding WY, Shen Y. Radiographic Restoration of Sagittal Spinopelvic Alignment After Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. Clin Spine Surg. Mar 2016;29(2):E87-92. [CrossRef]
- Glassman SD, Berven S, Bridwell K, Horton W, Dimar JR. Correlation of radiographic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Mar 15 2005;30(6):682-8. [CrossRef]
- Weisz G, Houang M. Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Jul 1 2005;30(13):1558-9; author reply 1559. [CrossRef]
- Lafage V, Schwab F, Skalli W, et al. Standing balance and sagittal plane spinal deformity: analysis of spinopelvic and gravity line parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Jun 15 2008;33(14):1572-8. [CrossRef]
- Legaye J, Duval-Beaupère G, Hecquet J, Marty C. Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J. 1998;7(2):99-103. [CrossRef]
- Chou D. Commentary: Retrospective Review of Immediate Restoration of Lordosis in Single-Level Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Comparison of Static and Expandable Interbody Cages. Operative Neurosurgery. 2020;18(5):E153-E154. [CrossRef]
- McMordie JH, Schmidt KP, Gard AP, Gillis CC. Clinical and Short-Term Radiographic Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion With Expandable Lordotic Devices. Neurosurgery. Feb 1 2020;86(2):E147-e155. [CrossRef]
- Porche K, Dru A, Moor R, Kubilis P, Vaziri S, Hoh DJ. Preoperative Radiographic Prediction Tool for Early Postoperative Segmental and Lumbar Lordosis Alignment After Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Cureus. Sep 2021;13(9):e18175. [CrossRef]
- Schwab F, Lafage V, Patel A, Farcy JP. Sagittal plane considerations and the pelvis in the adult patient. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Aug 1 2009;34(17):1828-33. [CrossRef]
- Inami S, Moridaira H, Takeuchi D, Shiba Y, Nohara Y, Taneichi H. Optimum pelvic incidence minus lumbar lordosis value can be determined by individual pelvic incidence. Eur Spine J. Nov 2016;25(11):3638-3643. [CrossRef]
- Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP, Lafage V. Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Dec 1 2010;35(25):2224-31. [CrossRef]
- Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S, et al. Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a prospective multicenter analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Jun 1 2013;38(13):E803-12. [CrossRef]
- Berjano P, Aebi M. Pedicle subtraction osteotomies (PSO) in the lumbar spine for sagittal deformities. Eur Spine J. Jan 2015;24 Suppl 1:S49-57. [CrossRef]
- Brink RC, Colo D, Schlösser TPC, et al. Upright, prone, and supine spinal morphology and alignment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017;12:6. [CrossRef]
- Salem W, Coomans Y, Brismée JM, Klein P, Sobczak S, Dugailly PM. Sagittal Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Profiles in Upright Standing and Lying Prone Positions Among Healthy Subjects: Influence of Various Biometric Features. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Aug 1 2015;40(15):E900-8. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi H, Suguro T, Yokoyama Y, Iida Y, Terashima F, Wada A. Effect of cage geometry on sagittal alignment after posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative disc disease. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). Aug 2010;18(2):139-42. [CrossRef]
- Kepler CK, Rihn JA, Radcliff KE, et al. Restoration of lordosis and disk height after single-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Orthop Surg. Feb 2012;4(1):15-20. [CrossRef]
- Faundez AA, Mehbod AA, Wu C, Wu W, Ploumis A, Transfeldt EE. Position of interbody spacer in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: effect on 3-dimensional stability and sagittal lumbar contour. J Spinal Disord Tech. May 2008;21(3):175-80. [CrossRef]
- Gambhir S, Wang T, Pelletier MH, Walsh WR, Ball JR. How Does Cage Lordosis Influence Postoperative Segmental Lordosis in Lumbar Interbody Fusion. World Neurosurg. Jun 2019;126:e606-e611. [CrossRef]
- Uribe JS, Harris JE, Beckman JM, Turner AW, Mundis GM, Akbarnia BA. Finite element analysis of lordosis restoration with anterior longitudinal ligament release and lateral hyperlordotic cage placement. Eur Spine J. Apr 2015;24 Suppl 3:420-6. [CrossRef]
- Smith JS, Bess S, Shaffrey CI, et al. Dynamic changes of the pelvis and spine are key to predicting postoperative sagittal alignment after pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a critical analysis of preoperative planning techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). May 1 2012;37(10):845-53. [CrossRef]
- Legaye J, Duval-Beaupère G. Sagittal plane alignment of the spine and gravity: a radiological and clinical evaluation. Acta Orthop Belg. Apr 2005;71(2):213-20.
- Langella F, Villafañe JH, Damilano M, et al. Predictive Accuracy of Surgimap Surgical Planning for Sagittal Imbalance: A Cohort Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Nov 15 2017;42(22):E1297-e1304. [CrossRef]
- Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Sep 15 2005;30(18):2024-9. [CrossRef]
- Lafage V, Schwab F, Patel A, Hawkinson N, Farcy JP. Pelvic tilt and truncal inclination: two key radiographic parameters in the setting of adults with spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Aug 1 2009;34(17):E599-606. [CrossRef]
| ML algorithm | Hyperparameter ranges | Optimal values for cage height prediction | Optimal values for PI-LL prediction |
|---|---|---|---|
| LR | Alpha = [0, 1], interval = 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
| DT | Criterion = [squared_error, friedman_mse, absolute_error, poisson] min_samples_split = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] min_samples_leaf = [5, 10, 20, 30, 40] |
poisson 30 20 |
squared_error 50 5 |
| SVR | kernels = [poly, linear, rbf, sigmoid] C = [0.1, 1, 10, 100] gamma = [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1] |
sigmoid 10 0.001 |
linear 0.1 1 |
| MLP | hidden_layer_sizes = [(50, 50, 50), (100, 100, 100), (200, 200, 200)] activation = [tanh, relu] solver = [sgd, adam, lbfgs] alpha = [0.0001, 0.001, 0.05] |
(200, 200, 200) relu lbfgs 0.05 |
(200, 200, 200) tanh sgd 0.0001 |
| KNN | n_neighbors = [5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50] metric = [euclidean, manhattan, minkowski] weights = [uniform, distance] |
20 euclidean uniform |
5 euclidean distance |
| Algorithm | Cage height | Postoperative PI-LL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | |
| DT | 1.12 | 0.85 | 7.05 | 5.39 |
| LR | 1.06 | 0.76 | 5.42 | 4.2 |
| SVR | 1.09 | 0.77 | 5.4 | 4.15 |
| MLP | 1.16 | 0.87 | 6.36 | 4.84 |
| KNN | 1.25 | 0.498 | 6.98 | 5.21 |
| Baseline model performance | Optimal model performance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | |
| Cage height prediction | 1.06 | 0.76 | 1.01 | 0.7 |
| Postoperative PI-LL prediction | 5.5 | 4.15 | 5.19 | 3.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





