1. Introduction
Forest ecosystems are the most structurally complex, widespread, and biologically diverse ecosystems on land. They not only provide shelter and habitat for many species, but also play important roles in climate mitigation and disaster resilience [
1,
2]. Soil is the most extensive organic matter pool in the terrestrial biosphere and therefore acts as the prime agent for material cycling in terrestrial ecosystems. It provides plants with essential nutrients for sustenance, growth, and development [
3,
4]. Soil stoichiometry, which serves as an indicator of soil conditions, is influenced by climate, moisture, litter inputs, and elevation [
5]. Soil stoichiometry directly impacts plant growth and distribution [
6]. However, plant distribution is also based on elevation, habitat conditions, moisture, and temperature. Harsh environmental conditions can impede plant growth and development. Increases in altitude have previously been identified as associated with increases in soil total nitrogen (TN), soil organic carbon (SOC), and the ratios of carbon to nitrogen (C/N), carbon to phosphorus (C/P), and nitrogen to phosphorus (N/P), although the difference in TN was not significant [
7]. Altitude-associated differences in SOC have been found to significantly affect the distribution of sweet chinkapin [
8]. An earlier study also showed that the most important environmental factors influencing secondary forest regeneration are soil nutrient status and dead wood thickness [
9].
Qinghai spruce (
Picea crassifolia) is predominantly found in pure forests in the Qi-lian Mountains. This endemic species is unique to northwest China. It serves as a crucial protector against wind and sand erosion and contributes to water conservation and local climate regulation [
10,
11]. However, the site is located in an ecologically fragile area with delicate natural conditions, a variable climate, and a monolithic forest structure. Structural integrity is extremely difficult to restore after it is compromised [
12]. Several studies have investigated the impacts of soil moisture and fertility on Qinghai spruce growth and development. For example, increased temperature and humidity facilitate earlier spruce growth, and a higher altitude postpones budding [
13]. The carbon density in the tree layer has been shown to decrease along with increasing altitude, whereas the carbon density in the soil layer first decreases, then increases; furthermore, the percentage of soil carbon density out of the total carbon density in-creases with altitude [
14]. There are significant positive correlations of elevation with soil organic carbon content and carbon density in the Qinghai spruce tree layer, and a significant negative correlation between elevation and mean summer air temperature [
15]. However, links between the natural regeneration features of Qinghai spruce and soil stoichiometric properties at varying elevations remain unexplored.
To address this gap in knowledge, we here examined the associations of three Qinghai spruce seedling bioindicators (density, basal diameter (BD), and plant height) with elevation and soil stoichiometric characteristics. The following hypotheses were addressed: (1) Qinghai spruce regeneration and soil stoichiometry would differ based on elevation; (2) regeneration density, BD, and plant height would show specific associations with soil stoichiometric parameters at each elevation; and (3) variations in soil stoichiometry would affect regeneration density, BD, and plant height across LAMs and various altitudinal gradients. This study was designed to provide new insights into the relationships between altitude, soil characteristics, and Qinghai spruce regeneration, providing valuable information for protection of this ecologically important species.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area was located in the Pailugou watershed in the Qilian Mountains National Park (100°17′0′′-100°18′30′′E, 38°32′0′′-38°33′30′′N). The mean annual temperature was 5.4 °C, ranging from a high monthly average of 12.2 °C in July to a low monthly average of -12.9 °C in January of the study year, 2022 [
16]. The region has a continental alpine mountain climate. The average annual precipitation is 416 mm, with an annual potential evaporation of 1011.3 mm and an annual sunshine duration of 1562.6 h [
17,
18]. There is an intricate topography with significant variations in altitude. The vegetation types are montane grassland, montane forest-steppe, subalpine scrub-meadow, and alpine snow and ice vegetation. The soil types vary by elevation and comprise, from lowest to highest altitude, mountain chestnut-calcium, mountain greyish-brown, alpine meadow, and alpine desert soil [
19]. The primary tree species dominating the area are Qinghai spruce and
Sabina przewalskii; the most abundant shrubs are
Caragana jubata,
Potentilla fruticosa,
Salix gilashanica, and
Potentilla glabra. The predominant herbaceous plants in the area are
Carex atrata,
Achnatherum splendens,
Potentilla chinensis, and
Polygonum viviparum [
16,
17].
2.2. Experimental Design
Based on the life history characteristics of Qinghai spruce, population size classification was performed [
20,
21]. Seedlings with a height of < 2 m and a diameter at breast height (DBH) of < 50 mm were categorized as seedlings. In 2022, experimental sample plots were selected at 2700 m, 3000 m, and 3300 m above sea level (a.s.l.) (
Figure 1). The soil type in each plot was a mountainous gray cinnamon soil; the texture was considered loam, with a sand content of 34–58% [
22]. The soil thickness was 50–80 cm. Six 20 × 20 m sample plots were selected at each altitude and the soil depth, aspect, and slope were recorded (
Table 1). Each sample plot was partitioned into 16 small squares of 5 × 5 m, three of which were selected at random for measurements of Qinghai spruce seedling density, BD, and plant height. Basic information concerning elevation, soil depth, aspect, and the slope of each plot was also recorded during field work (
Table 1).
Soil was collected from the four corners and center of each plot at a depth of 0–10 cm and uniformly mixed to form a single sample per plot. These served as representative samples of the overall soil composition. Soil moisture content (SMC) was measured using the drying method; soil pH was determined using the leaching electrode method; SOC was analyzed with the potassium dichromate method; TN was quantified using a Kjeldahl nitrogen meter; and total phosphorus (TP) was assessed using the acid solubilization-molybdenum antimony anti-stibnite colorimetric method [
23].
2.3. Data Processing
Normality was assessed for each indicator (density, BD, and height) with the Shapiro test. Differences in density, BD, plant height, and soil stoichiometric attributes across elevations were assessed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Multiple comparisons were conducted with Dunn’s test followed by detrended correspondence analysis (DCA), which revealed a first axis result of < 3. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was therefore selected to examine correlations between the three seedling indicators and soil stoichiometric properties. Adonis multivariate ANOVA was utilized to ex-amine differences in seedling indicators based on soil physicochemical characteristics at different elevations. The distance matrix was generated using Bray-Curtis distance and the Monte-Carlo permutation test was set to 999. Data were recorded and initially collated with Microsoft Excel 2019 software. Normality tests and ANOVA were con-ducted in Origin Pro 2022; RDA was performed with Canoco5; and Adonis multivariate ANOVA was conducted in RStudio v4.1.3.
3. Results
3.1. Regeneration Characteristics of Qinghai Spruce at Varying Elevations
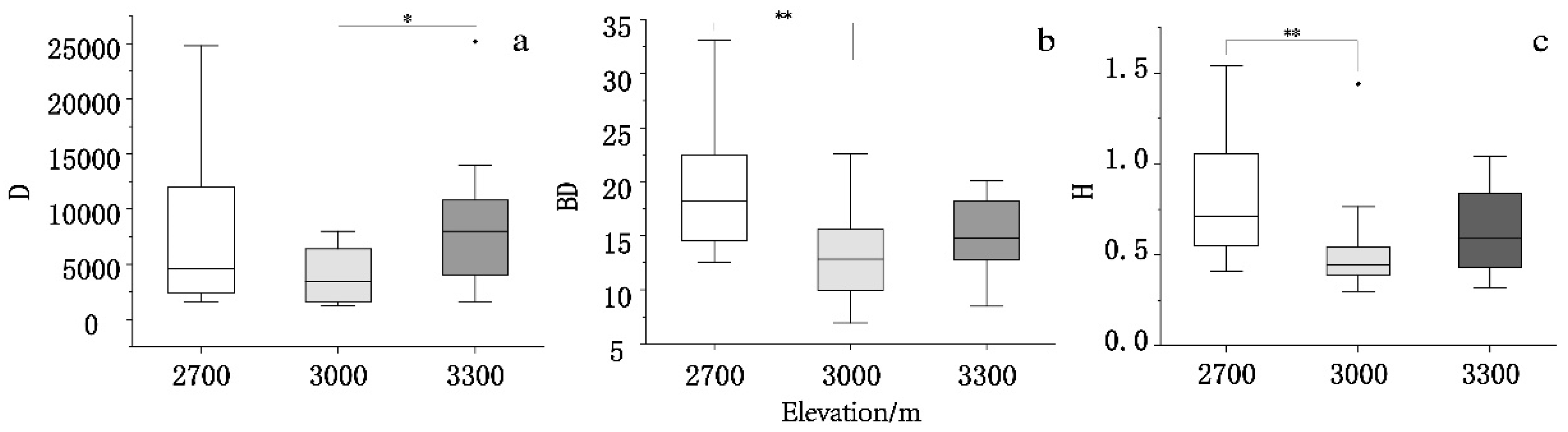
We first compared regenerated seedling density, BD, and plant height across elevations (
Figure 2). Generally, seedling density was higher and more scattered at 2700 m, but lower and more concentrated at 3000 m. There were significant differences in regenerated seedling density at 3000 m compared to 3300 m (
p < 0.05). Furthermore, the regenerated seedling density was significantly higher at a single 3300-m plot than at other plots at the same elevation. This was likely due to the relatively gentle slope of this plot, which could have had a concentrating effect on Qinghai spruce seeds. Overall, seedling BD was highest at 2700 m, with a more dispersed distribution than at the other elevations. There were significant differences between altitudes; seedlings at 3000 m had a lower average diameter than those at 3300 m. The latter exhibited diameters ranging from those found at 2700 m to those found at 3000 m, with a concentrated distribution. The difference in BD between seedlings regenerated at 2700 m and those regenerated at 3000 m was highly significant (
p < 0.01). Seedlings at 2700 m exhibited a greater overall height with a more dispersed distribution; those at 3000 m had a lower overall height with a more centralized distribution. There were significant differences in height between seedlings at 2700 m compared to 3000 m (
p < 0.01). Seedlings at 2700 m were taller but had a more dispersed height distribution, whereas seedlings at 3000 m were shorter with a more distributed height (
p < 0.01). Seedlings in one plot at 3000 m were significantly taller than those from other plots at the same altitude. However, this finding was not distinctive and was sustained. Overall, the three seedling indicators decreased among seedlings at 3000 m compared to 2700 m, then increased again at 3300 m.
3.2. Characteristics of Soil Stoichiometry at Each Elevation
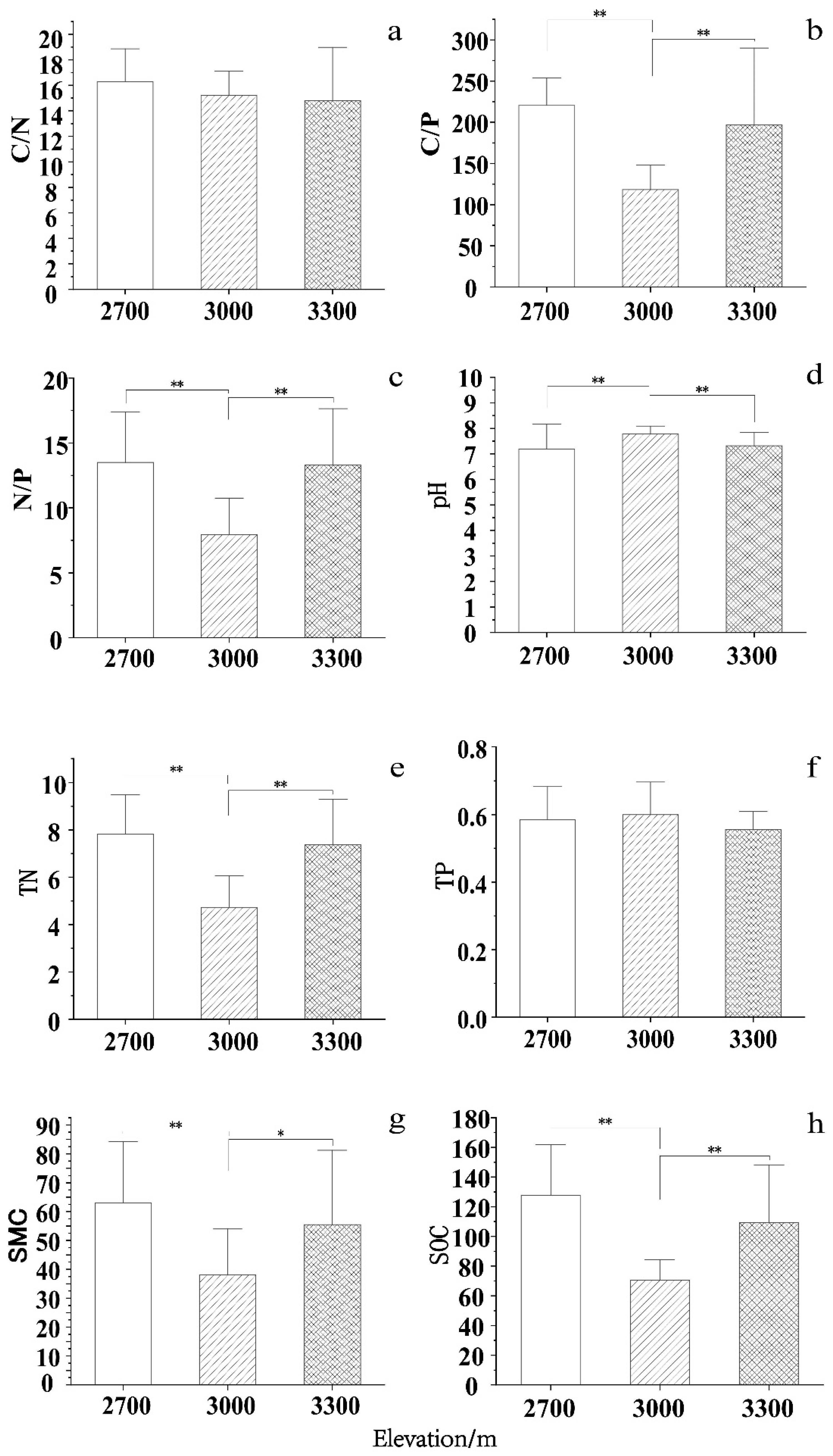
We next examined variations in soil nutrients in the Qinghai spruce forest across the three elevations (
Figure 3). With the exceptions of soil pH and TN, all of the soil parameters first decreased, then increased along with the altitude; SMC, TN, C/P, N/P, and SOC peaked at 2700 m and reached minima at 3000 m. C/N also exhibited the maximum value at 2700 m but remained virtually unchanged at 3000 m and 3300 m. The pH was highest at 3000 m and lowest at 2700 m. In contrast, TN was lowest at 3300 m and highest at 3000 m. The differences in soil pH, TN, C/P, N/P, SOC, and SMC were significant between 2700 m and 3000 m and between 3000 m and 3300 m (
p < 0.01); in contrast, the differences between 2700 m and 3300 m were not statistically significant. There were no significant differences in C/N or TP between altitudes.
3.3. Relationships Between Seedling Indicators and Soil Physicochemical Characteristics
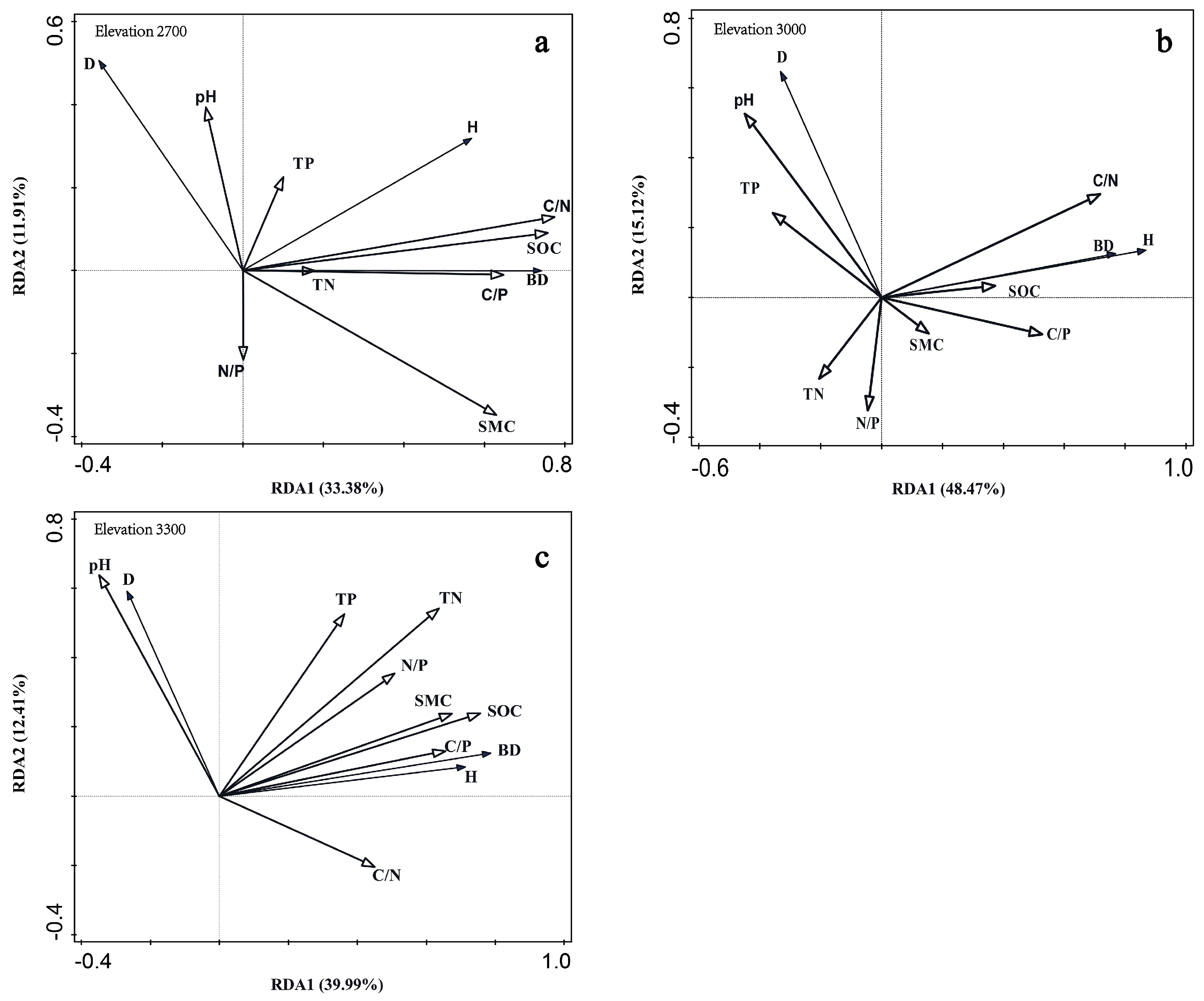
RDAs were next conducted for seedling density, BD, and plant height with the analyzed soil parameters (
Figure 4). At 2700 m, the eight soil parameters accounted for 52.3% of soil variability; the first two axes accounted for 33.4% and 11.9%, respectively. The angles indicated that seedling density was positively correlated with pH and negatively correlated with C/N, C/P, and SMC; BD was positively correlated with C/N, SOC, C/P, and SMC; and plant height was positively correlated with C/N, SOC, C/P, and TN and negatively correlated with N/P. At 3000 m, the eight soil parameters ac-counted for 64.9% of the soil variance, with the first two axes explaining 48.5% and 15.1% of the variance, respectively. Seedling density was positively correlated with the pH and TN but negatively correlated with the C/P and N/P ratios. Furthermore, BD was positively correlated with C/N, C/P, and SOC and negatively correlated with TN, TP, and pH. Plant height was positively correlated with C/N, C/P, N/P, and SOC, and negatively correlated with TN, TP, and pH. At 3300 m, seedling density was positively correlated with pH and TN and negatively correlated with C/N. BD was positively associated with C/N, C/P, N/P, TN, TP, SOC, and SMC. Plant height was positively correlated with C/N, C/P, N/P, TN, TP, SOC, and SMC.
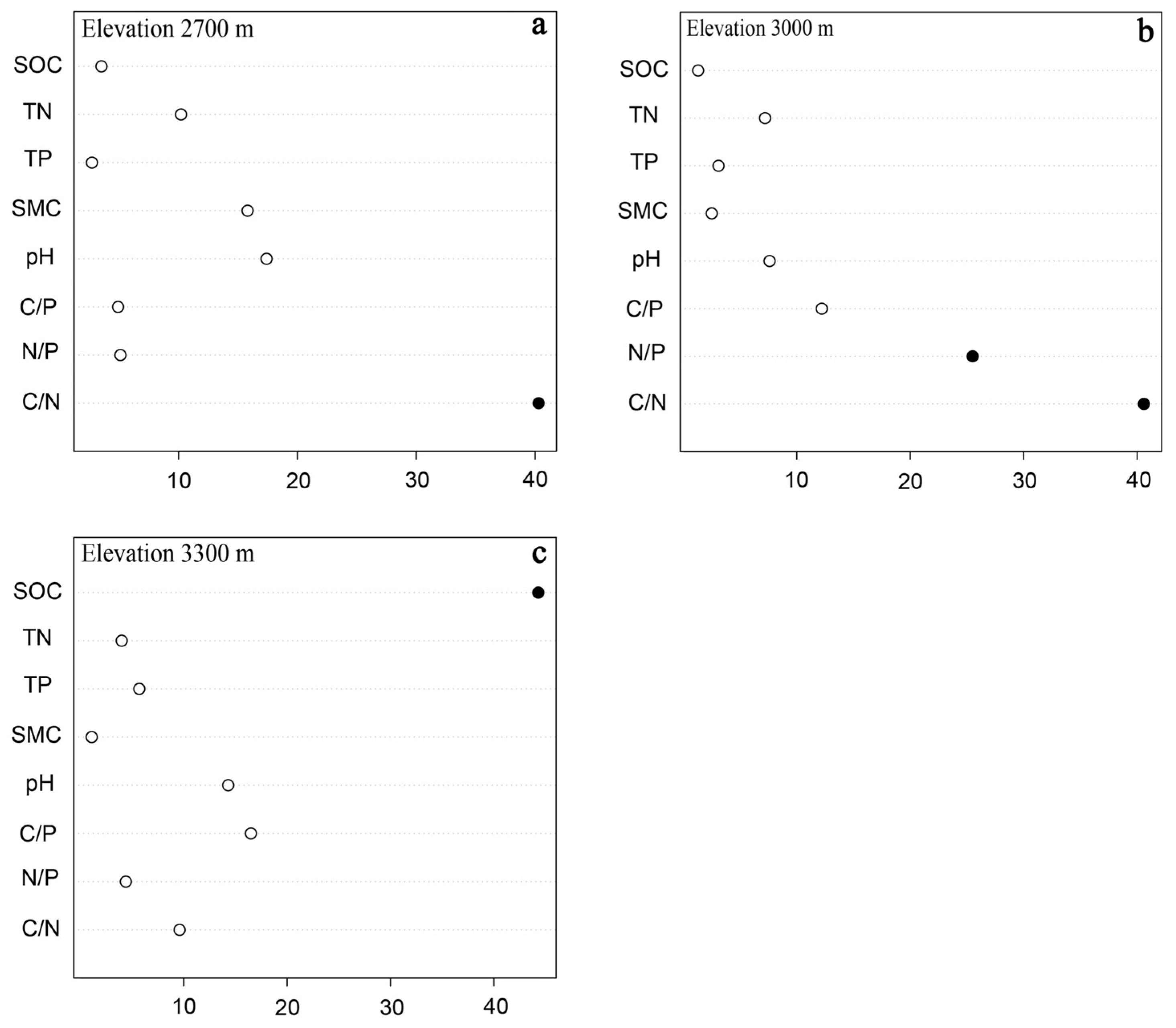
RDA was also used to rank the contribution rates of soil parameters to soil varia-bility at each altitude (
Figure 5). At 2700 m, C/N contributed 40.3% to the observed variations in soil stoichiometric characteristics (
p < 0.05), whereas the other indicators showed no significant contributions. At 3000 m, C/N also contributed 40% to variations in soil stoichiometric characteristics. At 3300 m, SOC was responsible for 44.3% of the variation in soil stoichiometric characteristics (
p < 0.05). Additionally, N/P contributed 25.5% to variations in soil stoichiometric characteristics (
p < 0.05), with a 40.6% overall contribution rate (
p < 0.05).
None of the soil indicators had significant impacts on seedling density at each elevation (
Table 2). However, pH, SOC, and C/N had significant effects on BD across elevations, with R
2 values of 0.161, 0.245, and 0.0690, respectively. Of these three variables, SOC had the greatest effect and C/N had the smallest. There were also significant effects of pH, SOC, C/N, and C/P on plant height (R
2 = 0.117, 0.201, 0.134, and 0.08, respectively). Here again, SOC had the greatest effect, whereas C/P had the smallest effect. Overall, the effects of SOC were strongest and the effects of C/N on regenerating spruce indicators were the weakest.
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Stoichiometry and Regeneration Indices Associated With Qinghai Spruce Across Elevations
Prior studies have demonstrated that altitude impacts the temperature, light, and moisture of a forest environment. These factors in turn affect the stand structure, veg-etation distribution, and species diversity. As a result, there is extensive spatial variation in the vegetation of a given community, as indicated by various biological factors and the physicochemical properties of the understory soil [
24,
25]. For example, altitude influences
Tetracentron sinense Oliv. distribution by affecting environmental factors including temperature and moisture. This reflects the plant’s ecological characteristics and environmental responses [
26]. Seedlings in
Pinus tabulaeformis forests show differing responses to the environment depending on the elevation; increases in altitude are associated with gradual increases in density [
27]. Elevation determines numerous eco-system properties and processes in the mountains of subtropical China, with changes in altitude strongly impacting soil stoichiometry [
28]. The present study highlights variations in Qinghai spruce regeneration indicators and in soil stoichiometry based on altitudinal shifts. Specifically, we identified significant differences between seedling density at 3000 m and 3300 m during regeneration. In addition, there were significant differences in both BD and plant height between 2700 m and 3000 m. However, soil stoichiometric properties were more sensitive than plant indicators were to altitude, with increases in altitude showing positive effects on soil pH, SMC, TN, C/P, N/P, and SOC. There were statistically significant differences in N/P and SOC between 2700 m and 3000 m and between sites at 3000 m and at 3300 m.
Prior studies have shown that soil microorganism activities have direct impacts on plant apoplastic material decomposition rates. Therefore, altitude-related temperature changes directly affect soil stoichiometric characteristics. In contrast, plants possess self-regulatory capacities and can therefore adjust their growth strategies to differences in temperature. As a result, differences in altitude had relatively insignificant effects on seedlings compared to the effects on soil stoichiometric characteristics [
29]. The seedling density, BD, and plant height initially decreased, then increased along with the altitude. These trends were consistent with those of TN, SMC, SOC, C/P, and N/P. Better hydrothermal conditions at 2700 m appear to have resulted in higher forest stand biomass and a relatively large amount of material transported to the soil by plants; these conditions are known to enhance soil microbial activity and accelerate the rate of apo-plastic material decomposition by soil microbes [
30]. In contrast, worse hydrothermal conditions at 3000 m resulted in lower forest stand biomass and increased intraspecies competition; this favored larger age classes of spruce, minimizing the Qinghai spruce regeneration status. Soil stoichiometry was still worse at 3300 m due to inferior hydrothermal conditions, which reduced soil microbial activity and the rate of apomictic decomposition. However, a significant reduction in older spruce at this elevation resulted in weakened intraspecific competition by these species, improving the Qinghai spruce regeneration status and soil parameters [
31].
4.2. Relationships Between Qinghai Spruce Regeneration and Soil Stoichiometry
Forest regeneration is impacted by various factors, including species specific biology, faunal behavior, microhabitat characteristics, and the abundance of older plants. Soil stoichiometry slightly influences regenerating seedling growth, development, and distribution patterns [
32,
33]. A prior study of renewal characteristics and influencing factors in mixed forests of the Qinling Mountains found that SMC is the primary factor influencing the distribution of oil pine seedlings, and that SOC and quick-acting phosphorus have the most significant impacts on Hua shan pine seedlings [
34]. Another study of soil nutrient impacts on spruce secondary forest regeneration discovered a significant positive correlation between soil pH and the number of spruce seedlings [
35]. These prior results are comparable to the findings of the present study. We here found a positive correlation of Qinghai spruce seedling density with pH and a negative correlation with C/N at all three elevations. This suggested that indigenous Qinghai spruce regeneration favored either neutral or slightly alkaline soils. This preference may have been influenced by microtopographical factors. For example, on gentle slopes where organic matter and plant seeds accumulate [
36], soil with sufficient aeration and microbial activity supports good soil structure in tandem with the biogenic root system. This combination makes it harder for salty ions to be washed away by water flow and for a higher pH to form [
37].
Qinghai spruce regeneration may have varied between elevations due to environmental changes [
37]. Regenerated Qinghai spruce BD also varied with elevation, and there was a slight elevation-based difference in the relationship between the number and degree of soil indicators [
38]. There were also positive relationships be-tween C/N, C/P, and SOC. At 2700 m and 3000 m, C/N appeared to significantly affect seedlings, as did N/P at 3000 m. Furthermore, SOC had a significant effect on seedlings at 3300 m. SOC serves as a source of nutrients for plant-associated microorganisms and enhances soil physicochemical and biological properties by influencing soil bulk density, increasing porosity, promoting soil aggregation structure, and enhancing soil water absorption, water holding, and aeration [
39,
40]. SOC thus plays a crucial role in plant growth, particularly under adverse environmental conditions, but also when conditions are generally conducive to plant growth. Furthermore, the soil C/N and C/P statuses offer valuable insights into the behavior of soil microorganisms; microbial decomposition of apoplastic matter improves plant nutrient absorption and stimulates growth. Additionally, the processes of plant growth and decay contribute materials and energy to the soil, highlighting the pivotal roles of soil microorganisms in promoting plant succession [
41,
42].
Plant regeneration strategies and the factors that influence biological indicators can differ between sites even at the same elevation due to variations in topography, hydrothermal conditions, and other factors, which result in different nutrient inputs to the soil and cause variations in soil stoichiometry [
43]. Although pH was here correlated with regenerated Qinghai spruce seedling density at various altitudes, we found no significant impacts of soil parameters on seedling density at any elevation. However, soil pH, SOC, and C/N significantly influenced elevation-specific differences in BD. Additionally, soil pH, SOC, C/N, and C/P all had significant impacts on differences in plant height between elevations. Overall, Qinghai spruce seedling regeneration is impacted by a range of factors beyond soil stoichiometric properties. Previously identified factors of this nature include the distance from cohorts of older plants, surface temperature, light exposure, slope orientation and inclination, anthropogenic activities, and competition with other plant types such as shrubs [
44,
45,
46,
47]. Light conditions and the forest window environment are also known to strongly affect regeneration density [
48,
49]. This explains the relatively small role of soil variations in affecting regeneration density at each elevation. The correlations between seedling growth (BD and height) and soil nutrients are predominantly linked to density [
50]. Nutrient absorption directly from the soil is essential for plant growth and development. Thus, differing levels of soil nutrients can have a significant impact on seedling growth, affecting both BD and height to produce diverse growth patterns. This consequently leads to differences in seedling BD and height between altitudes.
5. Conclusions
We here found initial decreases in Qinghai spruce seedling density, basal diameter (BD), and height along with elevation, followed by increases in the same parameters at a higher altitude. These trends mirrored patterns observed in soil total nitrogen(TN), soil moisture content(SMC), soil organic carbon(SOC), carbon to nitrogen ratio(C/P), and nitrogen to phosphorus ratio(N/P). Varying elevations showed notable discrepancies in regenerated seedling density, basal diameter (BD), and height, in addition to differences in most of the measured soil parameters. Notably, soil stoichiometric characteristics were much more susceptible to elevation-induced changes than seedling density, BD, or plant height were.
The relationships of Qinghai spruce seedling density, basal diameter (BD), and plant height with soil stoichiometric features differed slightly between elevations. However, some trends were consistent, including positive correlations of seedling density with soil pH, spruce basal diameter (BD) and plant height, and soil carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N). At 2700 m, C/N significantly impacted carbon to nitrogen ratio(C/P) and soil organic carbon(SOC). At 3000 m and 3300 m, both C/N and C/P affected SOC. Differences in soil chemistry resulting from changes in elevation influenced regenerated seedling BD and height to varying degrees across elevations. None of the soil parameters affected regenerated seedling density at any elevation. However, the soil pH, SOC, and C/N were correlated with seedling BD at various elevations, whereas pH, SOC, C/N, and C/P were correlated with differences in seedling height. Overall, these results shed new light on the factors influencing new Qinghai spruce seedlings growth across altitudes in the Qilian Mountain region of China, contributing valuable in-formation for conservation and management efforts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W.(Xiurong WU) and P.C.(Peifang CHONG); methodology, W.Z.(Weijun ZHAO); S.W.(Shunli Wang); software, W.J. and R.W.(Wenmao JING and Rongxin Wang); investigation, X.W.(Xiurong WU), W.Z.(Weijun ZHAO), J.Z.(jingzhong ZHAO), X.M.(Xuee MA); data curation, W.Z.(Weijun ZHAO); writing—original draft preparation, X.W.(Xiurong WU); writing—review and editing, X.W.(Xiurong WU), P.C.(Peifang CHONG) and W.Z.(Weijun ZHAO); supervision, E.X.(Erwen XU); project administration, E.X.(Erwen XU); All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20468、32060247), the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province(22JR5RG1030) and the central government of Gansu Province guides local science and technology development funds(22ZY2QG001).
Data Availability Statement
Not available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Costanza, R.; De Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S. J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R. K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Global environmental change,2014,26,152-158. [CrossRef]
- Pauli, G.; Grabherr, M.; Gottfriedand, H. Climate effects on mountain plants. Nature, 1994,369,447-450. [CrossRef]
- Bussotti, F., Pollastrini, M., Holland, V., Brüggemann, W. Functional traits and adaptive capacity of European forests to climate change. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2015,111,91-113. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Xiao, C; Li Y. Effects of climate factors and soil properties on soil nutrients and elemental stoichiometry across the Huang–Huai–Hai River Basin, China. J Soils Sediments 2020,20(17),1970–1982. [CrossRef]
- Alves, L. F.; Vieira, S. A.; Scaranello, M. A.; Camargo, P. B.; Santos, F. A. M.; Joly, C. A.; Martinelli, L. A. Forest structure and live aboveground biomass variation along an elevational gradient of tropical atlantic moist forest (brazil). Forest Ecology and Management,2010,260(5):679-691. [CrossRef]
- Wang,X.; Fang, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, Biao. Climatic control of primary forest structure and DBH-height allometry in Northeast China. Forest ecology and management,2006,234(1-3):264-274. [CrossRef]
- Hu, C; Li, F; Xie Y.; Deng Z.; Hou Z.; Li X. Spatial distribution and stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus along an elevation gradient in a wetland in China. European Journal of Soil Science,2019,70(6):1128-1140. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q; Liu, S; Chen, K; Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Li, J; Lin, Y. Change characteristics and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in Castanopsis eyrei natural forests at different elevation in Wuyishan Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(13):5328-5339. (In Chinese)). [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, j. M.; Chazdon, R. L. Interacting effects of canopy gap, understory vegetation and leaf litter on tree seedlings recruitmentand composition in tropical secondary forests. Forest Ecology and Management,2008,255(11):3716-3725. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Gao, C.; Xie, H.; Qiao, Y; Gao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Ge, L.; Zhang, G. Effects of environmental variables on seedlings -sapling distribution of Qinghai spruce (Picea crassifolia) along altitudinal gradients. Forest Ecology and Management.2017,384:54-64. [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zhang, F; Gou, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, J.; Wu, X. Different responses of radial growth of Picea crassifolia to climate warming in the middle and eastern Qilian Mountains. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2022,44(1):14-23. (In Chinese).
- Song, X.; Yan, C.; Xie, J.; Li S. Assessment of changes in the area of the water conservation forest in the Qilian Mountains of China’s Gansu province, and the effects on water conservation. Environ Earth Sci,2012,66,2441–2448. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wilmking, M. Divergent growth responses and increasing temperature limitation of Qinghai spruce growth along an elevation gradient at the northeast Tibet Plateau. Forest Ecology and Management,2010,260(6),1076-1082. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Webb, A. A; Li, Z.; Tian, X; Han, Z.; Wang S.; Yu, P. Influence of climatic and geographic factors on the spatial distribution of Qinghai spruce forests in the dryland Qilian Mountains of Northwest China. Science of the Total Environment,2018,612,1007-1017. [CrossRef]
- Zeng ,L.; Lei, L; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, W.; Liu, X., Jing, W. Effect of altitudinal variation on carbon density in arbor layer and soil layer of Picea crassifolia forest in Qilian Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(20),7168-7177. [CrossRef]
- Wan,Y.; Yu, P.; Wang,Y., Wang, B; Yu Y., Wang Xo, Liu Z., Liu X., Wang S., Xiong W. The Variation inWater Consumption by Transpiration of Qinghai Spruce among Canopy Layers in the Qilian Mountains, Northwestern China. Forests,2020,11(8):845. [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yu, P.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X; Wang, S. Seasonal pattern of stem diameter growth of Qinghai spruce in the Qilian mountains, northwestern China. Forests,2020,11(5),494. [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Zhao, W.; He, Z. Radial pattern of sap flow and response to microclimate and soil moisture in Qinghai spruce (Picea crassifolia) in the upper Heihe River basin of arid northwestern china. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2014,187,14-21. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W.; Ma, J. Phenology of five shrub communities along an elevation gradient in the Qilian Mountains, China.Forests,2018,9(2),58. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, X. Biomass change of middle aged forest of Qinghai spruce along an altitudinal gradient on the north slope of Qilian Mountains. Sci. Silva. Sin. 2015,51, 4-10. [CrossRef]
- Ta, F; Liu, X., Liu, R., Zhao, W., Jing, W., Ma, J; Wu, X., Zhao, J., Ma,X. Spatial distribution patterns and association of Picea crassifolia population in Dayekou Basin of Qilian Mountains, northwestern China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020,44,1172-1183. (In Chinese).
- Zhang, L.; Shi, H.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Pan, S.; Wang, B.; Tian, H. Divergent growth responses to warming between stand-grown and open-grown trees in a dryland montane forest in Northwestern China. Forests 2019, 10, 1133. [CrossRef]
- Zhang,Y., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Yuan, X., Li, Y., Wang, K. Ecological stoichiometry and interrelation of Cynodon dactylon and soil in the three Gorges hydro⁃fluctuation zone under different slopes.Acta Ecologica Sinica,2023,43(11):4798⁃4811. (In Chinese).
- Wang, L., Wang, P., Sheng, M., Tian, J. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, southwest China. Global ecology and conservation,2018,16,e00449. [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A., Macdonald, S., Quideau, S. Understory plant community composition is associated with fine-scale above-and below-ground resource heterogeneity in mature lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) forests. PloS one,2016,11(3), e0151436. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., Duan, F., Li, Y., Wang, Q., Lu, X., Gan, X., Tang, J. Population structure and quantitative characteristics of Tetracentron sinense (Trochodendraceae) in Leigong mountain nature reserve, China. Botanical Sciences,2020,98(1),86-100. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., Cao, Y. Response of tree regeneration and understory plant species diversity to stand density in mature Pinus tabulaeformis plantations in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Ecological engineering,2014,73,238-245. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hou, E.; Liu, Y; Wen,D. Altitudinal patterns and controls of plant and soil nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry in subtropical China. Scientific reports,2016,6(1),24261. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N., He, N., Wang, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, R., Xu, Z., Yu, G. The altitudinal patterns of leaf C∶N∶P stoichiometry are regulated by plant growth form, climate and soil on Changbai Mountain, China. PloS one,2014,9(4), e95196. [CrossRef]
- Janet, A., Jan, M. Impact of pyrolysis and hydrothermal biochar on gas-emitting activity of soil microorganisms and bacterial and archaeal community composition. Applied Soil Ecology,2015,96:225-239. [CrossRef]
- Körner, C., Paulsen, J. A. World-Wide Study of High Altitude Treeline Temperatures. Journal of Biogeography,2004,31(5):713-732. [CrossRef]
- Davis, E. L., Hager, H. A., Gedalof, Z. E. Soil properties as constraints to seedlings regeneration beyond alpine treelines in the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research,2018,50(1),e1415625. [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, N. J., Ndangalasi, H. J., McEntee, J. P., Howe, H. F. Disperser limitation and recruitment of an endemic African tree in a fragmented landscape. Ecology,2009,90(4),1030-1041. [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z., & Wang, D. Environmental influences on the successful regeneration of pine-oak mixed forests in the Qinling Mountains, China. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research,2016,31(4),368-381. [CrossRef]
- Van Breugel, M., Craven, D., Lai, H. R., Baillon, M., Turner, B. L., Hall, J. S. Soil nutrients and dispersal limitation shape compositional variation in secondary tropical forests across multiple scales.Journal of Ecology, 2018,107(2):565-1-581. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Sun X.; Ye,Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lei, P; Chen, B; Guan, Q. Effect of micro⁃topography on the saplings regeneration in the coniferous (Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis) and broadleaf mixed forest in the Wuyishan, Jiangxi Province.Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022,42(6):2357⁃2367. [CrossRef]
- Cui, J., Holden, N. M. The relationship between soil microbial activity and microbial biomass, soil structure and grassland management. Soil and Tillage Research,2015,146,32-38. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q., He, Z., Xiao, S., Peng, X. , Ding, A. , Lin, P. Response of stem radial growth of qinghai spruce (picea crassifolia) to environmental factors in the Qilian mountains of china. Dendrochronologia,2017,44,76-83. Response of stem radial growth of qinghai spruce (picea crassifolia) to environmental factors in the Qilian mountains of china. [CrossRef]
- Yang, F. , Zhang, G. L. , Yang, J. L. , Li, D. C. , Zhao, Y. G. , Liu, F. , Yang, R.; Fan Yang. Organic matter controls of soil water retention in an alpine grassland and its significance for hydrological processes. Journal of Hydrology,2014,519:3086-3093. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; I., Xu, J.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J. Dynamic Relationship Between Biologically Active Soil Organic Carbon and Aggregate Stability in Long-Term Organically Fertilized Soils, Pedosphere,2012,22(5):616-622. [CrossRef]
- Tkacz, A.; Cheema, J.; Chandra, G.; Grant, A.; Poole, P. Stability and succession of the rhizosphere microbiota depends upon plant type and soil composition. The ISME journal,2015,9(11),2349-2359. [CrossRef]
- Lozano, Y.; Hortal, S.; Armas, C.; Pugnaire, F. Interactions among soil, plants, and microorganisms drive secondary succession in a dry environment. Soil biology and biochemistry,2014,78, 298-306. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qiu, K.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Cui, L.; Wang S.; Bao, P. Geographical, Climatic and Soil Factors Control Over The Altitudinal Pattern of Rhizosphere Microbial Diversity And its Driving Effect on Root Zone Soil Multifunctionality In Mountain Ecosystems. Available at SSRN 4510902. [CrossRef]
- Doroski, D.;Felson, A.; Bradford, M.; Ashton, M. P.; Oldfield, E. E.; Hallett, R. A.; Kuebbing, S. E. Factors driving natural regeneration beneath a planted urban forest. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2018,29,238-247. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lian, J.; Lin, G.; Cao, H.; Huang, Z.; Guan, D. Forest dynamics and its driving forces of sub-tropical forest in South China. Sci Rep,2016,6,22561. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; He, F. Half-century evidence from western Canada shows forest dynamics are primarily driven by competition followed by climate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2015,112(13),4009-4014. [CrossRef]
- Tinya, F.; Márialigeti, S.; Bidló, A.; Ódor, P. Environmental drivers of the forest regeneration in temperate mixed forests. Forest Ecology and Management,2019,433,720-728. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lu, D.; Zhang, W. Effects of gaps on regeneration of woody plants: a meta-analysis. Journal of Forestry Research, 2014,25(3),501-510. [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A., Sidari, M., Mercurio, R. Influence of gap size on organic matter decomposition, microbial biomass and nutrient cycle in Calabrian pine (Pinus laricio, Poiret) stands. Forest Ecology and Management,2007,242(2-3),412-418. [CrossRef]
- Sumida, A. The diameter growth–height growth relationship as related to the diameter–height relationship. Tree physiology, 2015,35(10),1031-1034. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Digital elevation model (DEM) of the study area showing the locations of Qinghai spruce plots. P1–P3 represent the locations of three plots at elevations of 2700 m, 3000 m, and 3300 m above sea level, respectively.
Figure 1.
Digital elevation model (DEM) of the study area showing the locations of Qinghai spruce plots. P1–P3 represent the locations of three plots at elevations of 2700 m, 3000 m, and 3300 m above sea level, respectively.
Figure 2.
Distribution of seedlings indicator values across altitudes. Seedlings were measured to assess (a) density (D), (b) basal diameter (BD), and (c) plant height (H). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (one-way analysis of variance)
Figure 2.
Distribution of seedlings indicator values across altitudes. Seedlings were measured to assess (a) density (D), (b) basal diameter (BD), and (c) plant height (H). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (one-way analysis of variance)
Figure 3.
Soil stoichiometric characteristics at each altitude. Soil samples were assessed to determine the (a) carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N), (b) carbon to phosphorus ratio (C/P), (c) nitrogen to phosphorus ratio (N/P), (d) pH, (e) total nitrogen (TN), (f) total phosphorus, (g) soil moisture content (SMC), and (h) soil organic carbon (SOC). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
Figure 3.
Soil stoichiometric characteristics at each altitude. Soil samples were assessed to determine the (a) carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N), (b) carbon to phosphorus ratio (C/P), (c) nitrogen to phosphorus ratio (N/P), (d) pH, (e) total nitrogen (TN), (f) total phosphorus, (g) soil moisture content (SMC), and (h) soil organic carbon (SOC). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
Figure 4.
Relationships between seedling regeneration indices. density(D), basal diameter (BD), and plant height (H) and soil stoichiometry at three elevations. Samples were collected at (a) 2700 m, (b) 3000 m, and (c) 3300 m. TP, total phosphorus; TN, total nitrogen; N/P, nitrogen to phosphorus ratio; SMC, soil moisture content; SOC, soil organic carbon; C/P, carbon to phosphorus ratio; C/N, carbon to nitrogen ratio.
Figure 4.
Relationships between seedling regeneration indices. density(D), basal diameter (BD), and plant height (H) and soil stoichiometry at three elevations. Samples were collected at (a) 2700 m, (b) 3000 m, and (c) 3300 m. TP, total phosphorus; TN, total nitrogen; N/P, nitrogen to phosphorus ratio; SMC, soil moisture content; SOC, soil organic carbon; C/P, carbon to phosphorus ratio; C/N, carbon to nitrogen ratio.
Figure 5.
Contribution rates of soil stoichiometry parameters at each elevation to renewal indices. Samples were collected at (a) 2700 m, (b) 3000 m, and (c) 3300 m. Renewal indices were seedling density, basal diameter, and height. TP, total phosphorus; TN, total nitrogen; N/P, ni-trogen to phosphorus ratio; SMC, soil moisture content; SOC, soil organic carbon; C/P, carbon to phosphorus ratio; C/N, carbon to nitrogen ratio.
Figure 5.
Contribution rates of soil stoichiometry parameters at each elevation to renewal indices. Samples were collected at (a) 2700 m, (b) 3000 m, and (c) 3300 m. Renewal indices were seedling density, basal diameter, and height. TP, total phosphorus; TN, total nitrogen; N/P, ni-trogen to phosphorus ratio; SMC, soil moisture content; SOC, soil organic carbon; C/P, carbon to phosphorus ratio; C/N, carbon to nitrogen ratio.
Table 1.
Basic characteristics of the three Qinghai spruce regeneration seedlings plots (mean value ± standard deviation).
Table 1.
Basic characteristics of the three Qinghai spruce regeneration seedlings plots (mean value ± standard deviation).
| Plots |
Coordinates |
Elevation
(m above sea leve) |
Soil
thickness
(cm) |
Aspect
(°) |
Slope
(°) |
Seedlings
density
(Trees·ha−1) |
Average
basal diameter (mm) |
Average
seedlings height
(m) |
| P1 |
E 100°17′10.3″ N 38°33′19.9″ |
2700 |
70 |
NE30 |
27 |
7267±6436 |
19.39±5.50 |
0.81±0.31 |
| P2 |
E 100°18’4.8’’
N 38°32’31.8’’ |
3000 |
60 |
NE24 |
25 |
41333±2505 |
12.91±3.89 |
0.52±0.26 |
| P3 |
E 100°18’15.5” N 38°32’8.5” |
3300 |
50 |
NE32 |
34 |
9044±7280 |
15.05±3.29 |
0.64±0.22 |
Table 2.
Effects of soil stoichiometry at each elevation on seedling regeneration indicators.
Table 2.
Effects of soil stoichiometry at each elevation on seedling regeneration indicators.
| |
Density |
Basal diameter (BD) Hight |
| R2
|
F |
R2
|
F |
R2
|
F |
| pH |
0.006 |
0.344 |
0.161** |
14.972 |
0.117** |
11.455 |
| SOC |
0.026 |
1.432 |
0.245** |
22.766 |
0.201* |
19.671 |
| TN |
0.054 |
2.954 |
0.014 |
1.315 |
0.006 |
0.571 |
| TP |
0.017 |
0.912 |
0.001 |
0.068 |
0.001 |
0.054 |
| C/N |
0.007 |
0.393 |
0.069* |
6.360 |
0.134** |
13.093 |
| C/P |
0.027 |
1.476 |
0.023 |
2.148 |
0.08* |
7.810 |
| N/P |
0.005 |
0.279 |
0.001 |
0.087 |
0.002 |
0.213 |
| SMC |
0.037 |
2.047 |
0.001 |
0.083 |
0.001 |
0.081 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).