1. Introduction
In recent decades, the treatment of patients with bacterial infections has often been complicated by the multiple drug resistance (MDR) of causative agents to antibiotics. Among the causative agents, the World Health Organization (WHO) has identified 12 pathogens that pose a global threat to human health [
1]. This list includes ESKAPE pathogens and identifies three categories of pathogens depending on their hazard and the urgency of developing new antibacterial drugs.
Staphylococcus aureus that is resistant to methicillin and vancomycin (MRSA and VRSA) was assigned to the high priority group [
2]. Given the faster growth of MDR among nosocomial strains of
Staphylococcus epidermidis [
3] and its increased ability to form biofilms [
4,
5,
6], an assessment of the antibacterial activity of new drugs against both
S. aureus, S. epidermidis and other coagulase-negative staphylococci is required.
Among the promising drugs that can become an alternative or addition to antibiotics are bacteriophages. These viruses can specifically infect a bacterial pathogen and eliminate it from the organism. In most cases, phages are safe for the patient's microbiota and after elimination of the target pathogen are excreted naturally without disrupting the functioning of the excretory and immune systems [
7,
8,
9]. Phages can be used to treat infants, the elderly, and even cancer patients [
10,
11,
12]. Despite many advantages, the use of bacteriophages has a number of limitations. Only phages with a proven inability to a lysogenic lifestyle and with the absence of undesirable genes in the genome can be used in phage therapy. In addition, the phages used should have high lytic activity and at least two phages that are active against the pathogen should be used to avoid the development of phage resistance [
11,
13]. Moreover, the usual high specificity of phages requires the selection of personalized phages in each case or the use of phage polyvalent cocktails, which increases the impact on the immune system. Thus, lytic phages with a wide host spectrum and a short, easily annotated genome are preferred for phage therapy.
Phage enzymes capable of destroying bacterial surfaces have advantages over bacteriophages [
14,
15,
16,
17]. The phage lysins have a wider host spectrum and low bacterial resistance; they demonstrate clear bioavailability and pharmacokinetics [
18]. Importantly, standardized biotechnological methods can be used for their production. WHO has recently recognized phage lysins as promising therapeutics [
19].
There are three large groups of phage lysins: (1) tail-associated murein lytic enzymes (TAME) that provide genome DNA penetration when the phage adsorbs the host cell; (2) endolysins, which are produced inside the infected cell providing the release of new phage particles; and (3) depolymerases that are able to cleave polysaccharide chains [
20,
21,
22]. Notably, endolysins can hydrolyze peptidoglycans of the cell wall, being outside. This can be used in particular against gram-positive pathogens and biofilms formed by them. Most phage lysins have a domain structure. Endolysins of phages specific to gram-positive bacteria usually have one or two enzymatically active domains (EAD) and a cell-binding domain (CBD). CBD can be C-terminal or it can be located between two EADs. Many (but not all) endolysins from phages of gram-negative bacteria are small molecules (15 kDa – 20 kDa) and have one EAD or N-terminal CBD plus C-terminal EAD. Based on their lytic activity, all EADs can be divided into five classes: lytic transglycosylases (transferases), which cleave the N-acetylmuramoyl-β-1,4-N-acetylglucosamine bond and four classes of hydrolases, namely 1) N-acetyl-β-D muramidases (lysozymes), endo β-N-acetylglucosaminidases (glucosaminidases), N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidases, and endopeptidases [
23,
24]. Notably, the pentaglycine interpeptide bridge is a unique component of most
Staphylococcus strains that can be digested by the specific peptidoglycan hydrolases [
25]. Last years, efficacy of endolysins of phages of Gram-positive bacteria as antibacterial drugs has been demonstrated [
18,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30].
In this study, the S. epidermidis phage St_134 was isolated and characterized. This small podophage had the genome of 18,275 bp and was able to infect more than ten coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species and one strain from the Staphylococcus aureus complex. Two genes encoding different endolysins were found in the St_134 genome and one endolysin was able to destroy peptidoglycans from the cell walls of S. aureus, S. epidermidis, and Staphylococcus haemolyticus as well as their biofilms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
Escherichia coli strain XL1Blue was used for cloning the lysins genes in the expression plasmid pQE60. Production of the recombinant lysins was carried out in the
E. coli strain M15. A total of 461
Staphylococcus strains (24 species) that were obtained from the Collection of Extremophile Microorganisms and Type Cultures (CEMTC) of ICBFM SB RAS were used to test the host range of the St_134 (
Table S1). In addition,
S. aureus CEMTC 675,
S. aureus CEMTC 1685,
S. epidermidis CEMTC 2043,
S. epidermidis CEMTC 2058, and
S. haemolyticus CEMTC 3413 were used to investigate the antibacterial activity of lysins Lys-Ste134_1 and LysSte134_2.
Staphylococcus species was determined by sequencing the 16S rRNA gene fragment (~1400 bp). Antibiotic resistance has been previously tested using the disk-diffusion method (Oxoid™, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in accordance with the EUCAST recommendations [
3]. All bacterial strains were cultivated in Luria Bertani (LB) media/agar (1.5% w/v) (10 g/L peptone, 5 g/L yeast extract, 10 g/L NaCl, pH: 7.0, Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). The planktonic bacteria cells were grown in an orbital shaker incubator with 150 rpm at 37°C (Infors HT, Bottmingen, Switzerland).
2.2. Phage St_134 Isolation and Propagation
To isolate the phage, 1 mL of sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.5 was added to a swab and the obtained suspension was sterilized through a 0.22 μm filter (Wuxi Nest Biotechnology, Wuxi, China). Drops of the filtrate were placed onto freshly prepared lawns of various bacterial cultures in the top agar (Becton, Dickinson and Company Sparks Difco Laboratories, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey, USA). After overnight incubation at 37°C, phage plaques were found on a Petri dish with S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 that was considered the host strain. One plaque was cut from the agar, suspended in sterile PBS, and incubated with shaking overnight to extract phages from the agar. Then, serial ten-fold dilutions were dropped onto a fresh layer of S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 to obtain single plaques. The procedure with a single plaque was repeated four times. Both samples that contained phage and the host strain were collected during the study that was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Novosibirsk Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics (protocol 014/17-2 from 25 November 2011). Both patients whose samples were used to isolate the phage St_134 and its host strain provided informed consents.
To propagate the isolated phage St_134, exponentially growing in LB S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 was infected with St_134 and incubated with shaking at 37°C until the bacterial lysis occurred. The obtained bacterial lysate was clarified by centrifugation at 10,000g for 30 min and phage particles were isolated using precipitation with polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000 (AppliChem, Darmstadt, Germany) supplemented with NaCl with subsequent centrifugation. Phage precipitate was dissolved in a sterile STM buffer (0.59g of NaCl; 7.88g of Tris-HCl, pH 7.5; and 2.38g of MgCl2 per 1L).
2.3. Electron microscopy
Phage particles were visualized, using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Formvar-supported copper grid was coated with 109 pfu/mL of St_134 phage particles for 1 min. Uranyl acetate was used to contrast the grid with St_134 phage particles. TEM imaging was performed with a TEM JEM 1400 (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). To obtain digital pictures Veleta digital camera (Olympus SIS, Münster, Germany) was used.
2.4. Biological Properties and Host Range
To evaluate the biological properties of the St_134 phage,
S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 was used. All experiments were repeated twice, and each experiment had three replicates. Experiments on phage adsorption rate and burst size were carried out according to [
31,
32] with minor modifications [
33]. To determine the adsorption time, an exponentially growing host cell culture (10
8 CFU/mL) was infected with 10
5 pfu/mL of St_134 (multiplicity of infection, MOI = 0.001). The infected culture was incubated with shaking at 37°C and aliquots were taken every two minutes to determine the titer of free phages by immediate titration. For a one-step growth experiment, 10 mL of exponentially growing host cells were pelleted at 8000g for 10 min and suspended in 500 mkL of LB medium. Phage St_134 was added to the cells with a MOI of 0.001, suspension was incubated for 5 min without shaking at 37°C, and cells were centrifuged. To discard non-adsorbed phage particles, the supernatant was carefully removed and then, the bacterial pellet was resuspended in 10 mL of LB medium. The infected culture was incubated with shaking at 37°C; aliquots were taken and titrated immediately. The lytic activity of the St_134 phage was assessed as described previously [
26] with our modifications. Phage St_134 (10
7 pfu/mL) was mixed with
S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 culture being in the exponential growth phase with a MOI of 0.1 and incubated without shaking at 37 °C for 30 min to improve infection. Then, infected culture was incubated with shacking and aliquots were taken every 60 min, diluted, seeded on the LB agar and incubated overnight at 37 °C. The bacterial killing curve was evaluated based on counted CFU. To determine the host range for the St_134, phages a spot-assay [
34] was carried out using >450 strains belonging to 23
Staphylococcus species.
2.5. Phage DNA Purification and Complete Genome Sequencing
Genome DNA was isolated from a St_134 stock (10
7 PFU/mL) as described previously [
35]. Phage particles were precipitated using a PEG/NaCl solution and suspended in a STM-buffer (10 mМ NaCl, 50 mМ tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 10 mМ MgCl2). The obtained phage suspension was supplemented with 10-25 units DNase I (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in DNase I buffer (10 mM tris-HCl pH 7.5, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM CaCl2), up to 10-20 µg/mL RNase (Thermo Scientific), and incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. Then, SDS (final concentration of 0.5%), up to 20 mM of 0.5 M EDTA, pH 8.0, and Proteinase K (up to 100-200 µg/mL) were added followed by incubation at 55 °C for 2-3 hours or at 37 °C overnight. Phage DNA was purified using phenol chloroform extraction with following ethanol precipitation. A paired-end library of phage St_134 DNA was prepared using the NEBNext Ultra II DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (New England Biolabs, Inc., Ipswich, MA, USA). Sequencing was carried out using the MiSeq Benchtop Sequencer and MiSeq Reagent Kit v.2 (2 × 250 base reads). The genome was assembled de novo by SPAdes v.3.15.4 and resulted in one genomic contig with an average coverage of 152.
2.6. Comparative Analysis of the Phage St_134 Genome and Proteome
Linearized St_134 genome sequence was imported into online RAST server v. 2.0 [
26] to identify the putative ORFs. Functions of the identified ORFs were predicted by BLASTP (NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA), InterProScan, and HHpred algorithms. Predictions on the architecture of the domains and functional motives were made using CD-BLAST (NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA). In addition, the results of annotation were manually verified by checking all of the predicted proteins against the NCBI GenBank protein database (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed on 19 September 2022).
To compare the St_134 proteome, ViPTree analysis with default parameters [
36] was computed by tBLASTx based on genome-wide sequence similarities. ViPTree version 3.7 web server was used (
https://www.genome.jp/viptree, accessed on 3 August 23). Phylogenetic analysis of St_134 proteins was performed using Maximum Likelihood. Protein sequences were extracted from the NCBI’s protein database using St_134 proteins as query in BLASTp search. Amino acid sequences were aligned using M-Coffee in the T-Coffee program [
37]. Phylogenetic trees were constracted by the IQ-tree program v. 2.0.5 [
38] the best fit substitution model was applied according to ModelFinder [
39]. Branch support was evaluated using 1000 ultrafast bootstrap replicates [
40]. All trees were midpoint rooted and visualized in FigTree v1.4.1.
2.7. In Silico Identification and Structural Analysis of Putative Lysins
2.8. Cloning, Expression and Purification of Recombinant Lysins
The genes encoding LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2 lysins were obtained by PCR using Ste134 genomic DNA as a matrix and pairs of primers endolysin_StE134_1U/endolysin_StE134_1L and endolysin_ste134_2u/endolysin_StE134_2L, respectively (
Table 1). The expressing plasmid pQE-60 was cleaved using
NcoI and
BamHI (Sibenzyme, Novosibirsk, Russia) and ligated with the obtained PCR fragments that were
NcoI/
BamHI digested too. The obtained plasmids pQE-60/LysSte134_1 and pQE-60/LysSte134_2 were used to transform
E. coli XL1blue cells. To search
E. coli clones, containing the corresponding expression plasmids, PCR was performed using primers pQE60-SeqU and pQE60_SeqL (
Table 1). Positive clones were sequenced by Sanger sequencing using 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
To optimize the expression of recombinant lysins, E. coli M15 cells were transformed with pQE-60/LysSte134_1 or pQE-60/LysSte134_2 plasmids. E. coli M15-pQE-60/LysSte134_1 or E. coli M15-pQE-60/LysSte134_2 cells were grown on LB-agar with 50 mkg/mL ampicillin at 37°C overnight. To produce recombinant lysins LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2, fresh colonies of E. coli M15-pQE-60/LysSte134_1 or E. coli M15-pQE-60/LysSte134_2 were grown in LB medium with 50 mkg/mL ampicillin to reach OD600 0.6-0.7. Then, 0.1 mM isopropyl-β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added and cell cultures were grown overnight with shacking at 150 rpm at 12°C, 20°C, 30°C, and 37°C with shaking at 150 rpm. Then, cells were centrifuged for 10 min at 6000×g, resuspended in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, and lysed by sonication using an ultrasonic Sonopuls HD 2070 homogenizer (Bandelin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany). Expression level of recombinant proteins and proteins localization was analyzed using polyacrylamide gel (PAAG) with 12.5% SDS.
The recombinant LysSte134_1 protein was purified from the cytoplasm using Ni–NTA Sepharose chromatography (Qiagen, Venlo, Netherlands) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. LysSte134_1 was eluted with buffer A (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0) containing 100 mM imidazole and concentrated by Amicon Ultra-4 filter (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) with a cutoff threshold of 10 kDa. The buffer was replaced with a storage buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 300 mM NaCl) by dialysis. Concentration of purified recombinant endolysin was assessed using the Qubit protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) on a Qubit 4 fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.9. Zymography with Peptidoglycans from Staphylococcal Cells
Peptidoglycans from the cell walls of staphylococci were obtained in accordance with the previously described method [
45]. A fresh overnight culture of Staphylococcus spp. cells diluted 500 times, and cultured to OD600 = 1-1.5 in 1 L of LB medium at 37 °C, 150 rpm. The cells were centrifuged for 10 min at 6000×g or 8000×g (depending on the
Staphylococcus species), resuspended in 10 mL of 4 M LiCl, boiled in a water bath for 20 min and re-centrifuged. The precipitate was resuspended in mQ water, disrupted by ultrasonication (35% power) for 25 min using a Sonopuls HD 2070 homogenizer (Bandelin, Berlin, Germany), and centrifuged (12,000×g for 12 minutes). The obtained precipitate was resuspended in 12 mL of 4% SDS, boiled for 20 minutes and pelleted by centrifugation (12 minutes at 12,000×g). The precipitate was resuspended in 12 mL of 1M NaCl and pelleted by centrifugation (12 minutes, 12,000×g). This stage was repeated until the peptidoglycan precipitate became colorless. The resulting peptidoglycan precipitate was suspended in 1-2 mL of mQ water, re-centrifuged, dissolved in 2 mL of mQ water with 0.02% NaN3, and stored at a temperature of 4 °C. The concentration of peptidoglycan was determined using a SmartSpec Plus spectrophotometer (BioRad, Hercules, California, USA). OD
540 = 1.0 approximately corresponded to the concentration of peptidoglycan 1 mg/mL. To assess the hydrolytic activity, recombinant lysins were fractionated by electrophoresis using SDS-PAAG with purified peptidoglycans at a concentration of 0.1 mg/mL. After electrophoresis, the gel was gently washed with deionized water several times and transferred to a renaturing buffer containing 25 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.2 and 1% Triton X-100. After incubation at 37°C for 1 hour, the gel was washed several times with deionized water and stained with 1% methylene blue solution.
2.10. Biofilm Assay
To obtained biofilms, staphylococcal cells (2 × 108 CFU) of were resuspended in 200 µL of sterile 0.9% NaCl, mixed with 10 mL of LB medium, and placed in a Petri dish with a pre-sterilized coverslip. The cells were incubated for 5 days at 37°C. On the fifth day, biofilm was evaluated using a Zeiss Axio Imager A2 microscope (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). The formed biofilms were treated with purified endolysin at a concentration of 25 mkg/mL in PBS. PBS without endolysin was used as a negative control. Treated biofilms were incubated at 37°C and stained with 0.1% methyl violet.
2.11. Statistical Analyses
The statistical analysis was carried out by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using Statistica 10 software (StatSoft. Inc., USA). The differences between the groups were considered significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. St_134 Isolation, Plaques and Phage Particles Morphology
Phage St_134 was found in a skin wash sample that was obtained from a patient with psoriasis. The clinical strain S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 that was used as a bacterial host has been previously isolated from a purulent wound and kindly provided by our colleagues from the Novosibirsk Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics. Its taxonomy was confirmed by sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene (GenBank ID OP393915). On the fresh lawn of the host strain, the phage St_134 formed cloudy plaques with a diameter of 0.8–1 mm.
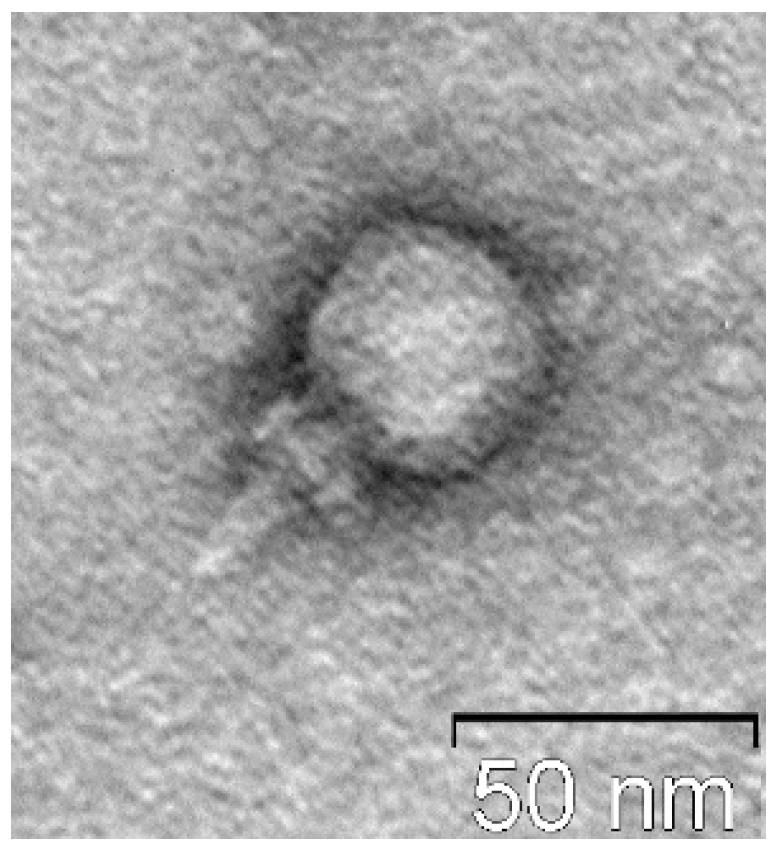
Electron microscopy indicated that St_134 is a relatively small podophage with icosahedral head (Ø 37–40 60 nm) connected to a short non-contractile tail (
Figure 1).
3.2. St_134 Biological Properties and Host Range
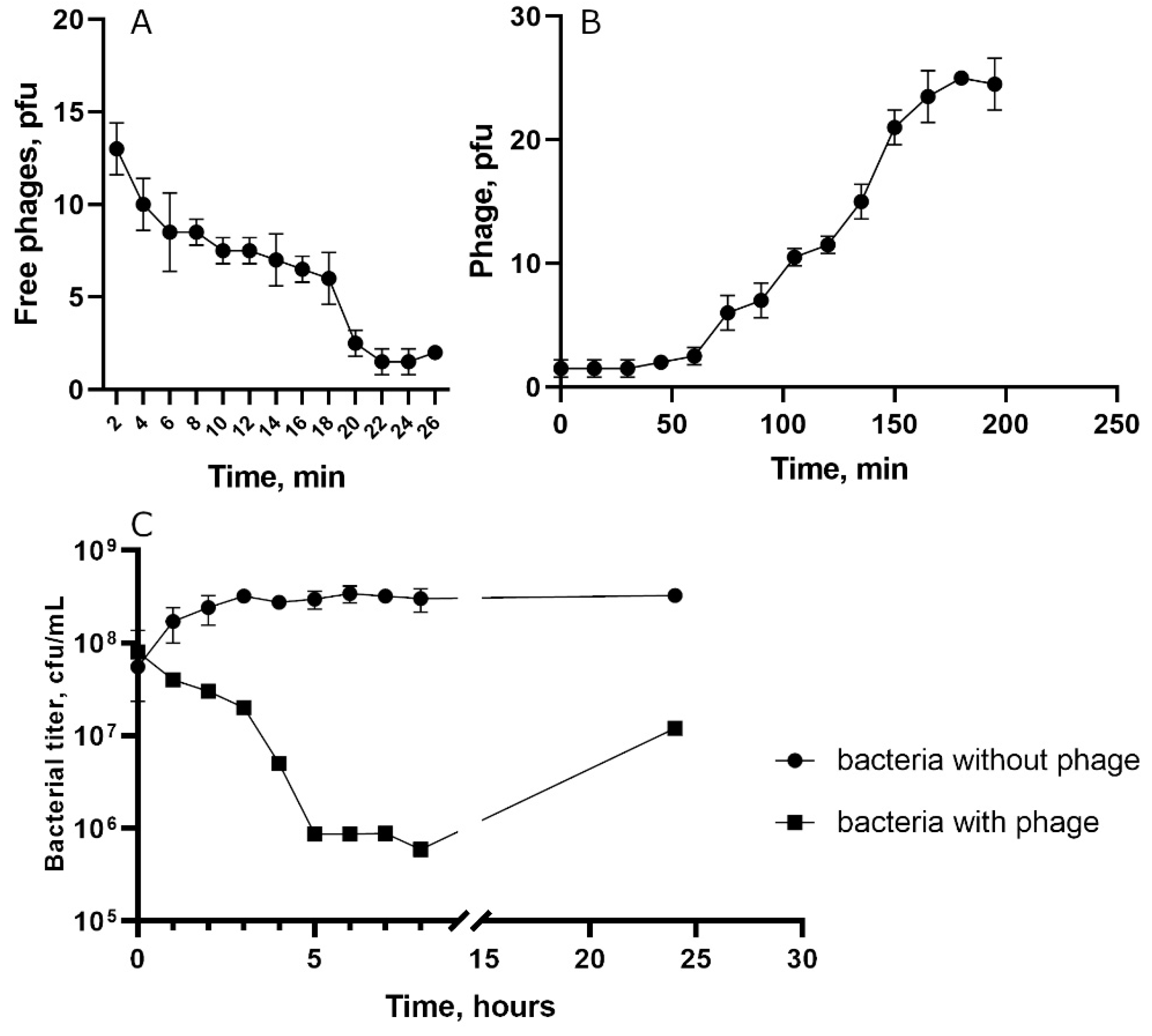
To characterize biological properties of the phage St_134, the host strain
S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 was used. Absorption experiment indicated that approximately 85% of St_134 phage particles attached to host cells within 22 min (
Figure 2A). One step growth assay showed that the latent period for St_134 was ~45 min and a burst size was ~12 phage particles per infected cell (
Figure 2B). The multistep bacterial killing experiments revealed that phage was not highly virulent (
Figure 2C).
To determine the phage host range, 461
Staphylococcus strains of 23 various species were used (
Table 2). Of them, 446 strains were obtained from clinical samples and 15 strains were obtained from pets. Among tested strains, 204 were coagulase-positive
S. aureus and
S. intermedius; however, only one strain (
S. roterodami/S. argenteus CEMTC 3692) was susceptible to St_134 infection. Other 357 strains were coagulase-negative
Staphylococcus, and 61 strains from them were St_134-sensitive, including six strains obtained from pets. (CEMTC number, resistance to antibiotics, and GenBank ID of all St_134-sensitive staphylococcal strains are presented in
Table S1). Most of the susceptible strains were
S. epidermidis and both antibiotic-sensitive and antibiotic-resistant (or even MDR) strains were identified among St_134-susceptible ones. Other 24 strains that were sensitive to St_134 included: three
S. haemolyticus strains with MDR; all tested
S. capitis,
S. caprae,
S. casei,
S. cohnii, and
S. lugdunensis (all of them were antibiotic-sensitive); and single strains from other species, some of which were antibiotic-resistant or even MDR (
Table 2,
Table S1).
3.3. St_134 Genome Characteristics and Comparative Analysis
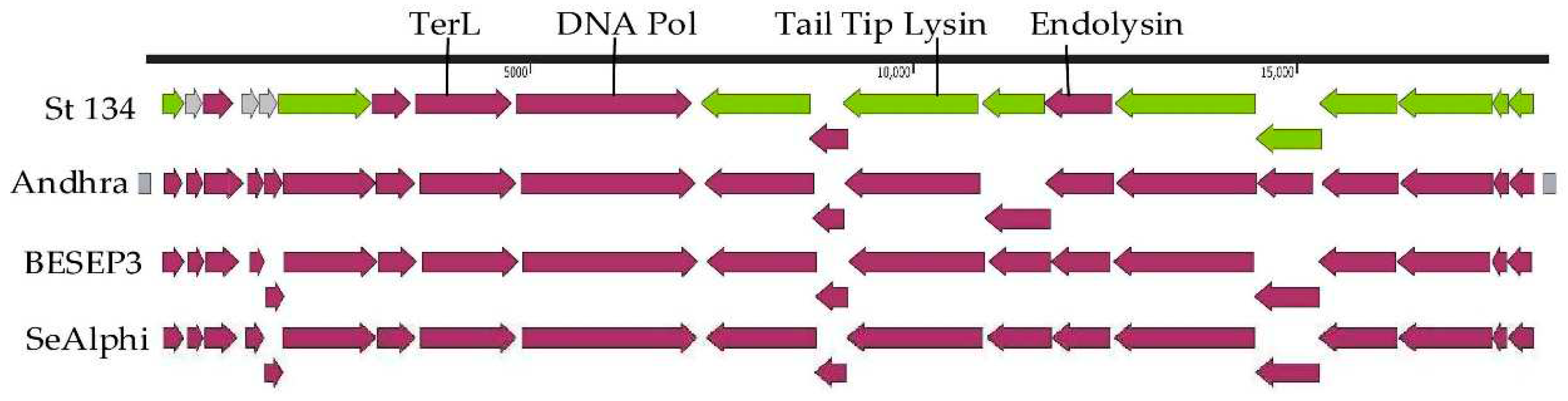
The St_134 genome is double-stranded linear DNA of 18,275 bp. Twenty putative ORFs were found and nine of them are oriented in the forward direction, whereas eleven ORFs are in opposite direction (
Figure 3). Among 20 ORFs, 17 ORFs encode proteins with predicted functions (
Table S2) and only three ORFs encode hypothetical proteins. The first block of ORFs contains the genes encoding the DNA polymerase, terminaze large subunit, several virion proteins, including virion-associated tail tip lysin, and three relatively small hypothetical proteins. The second block consists of genes encoding the holing, endolysin, and structural proteins (
Figure 3).
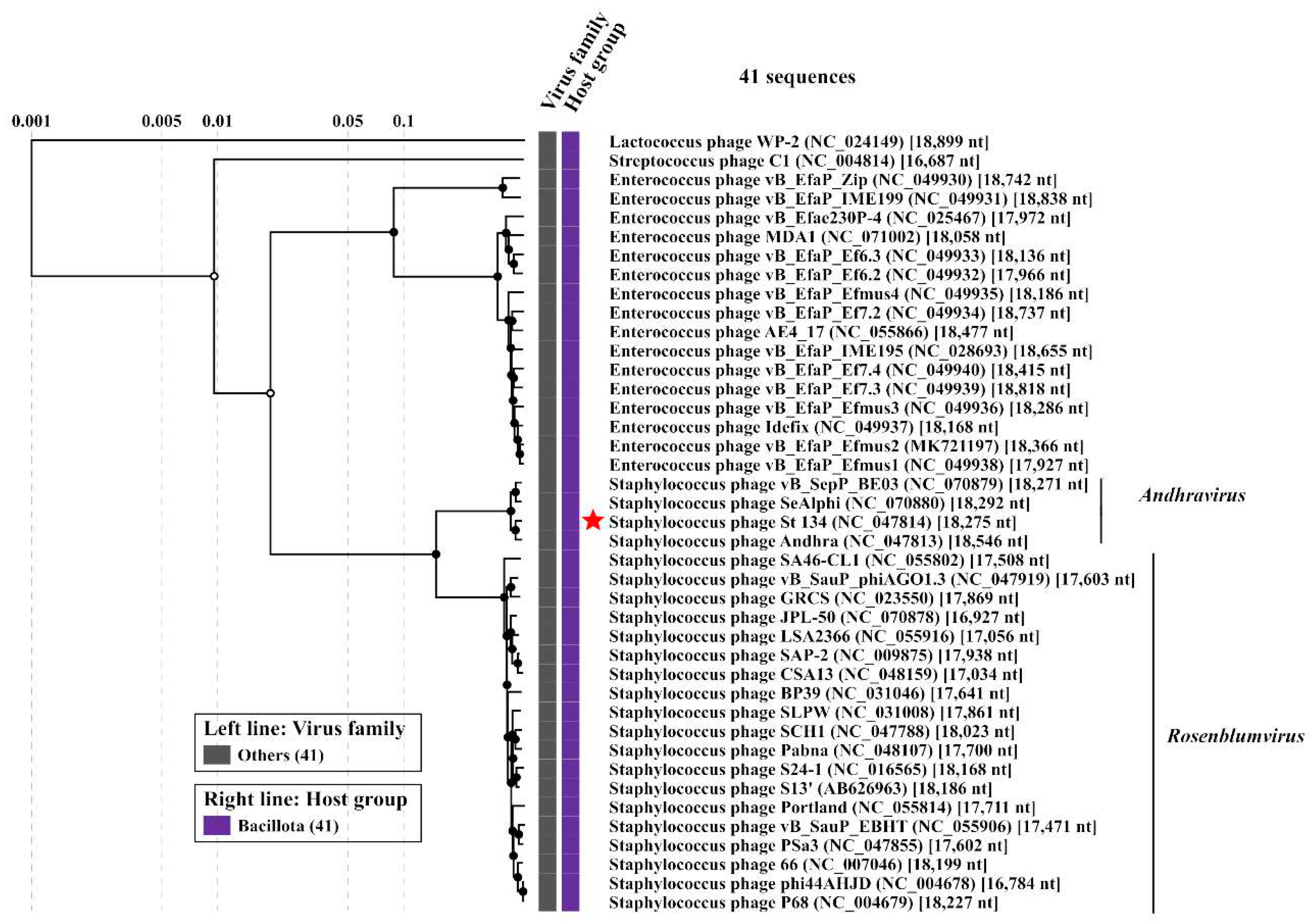
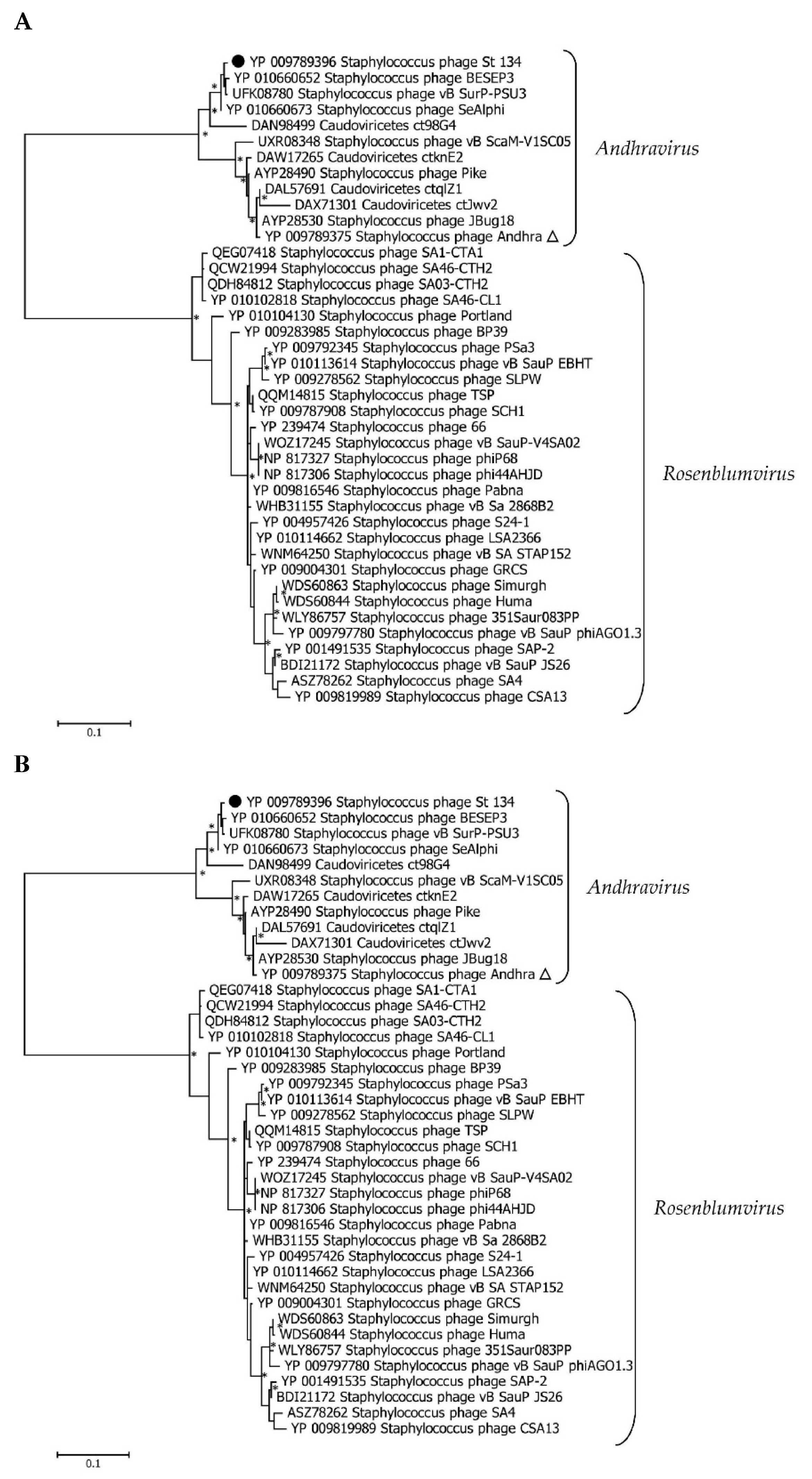
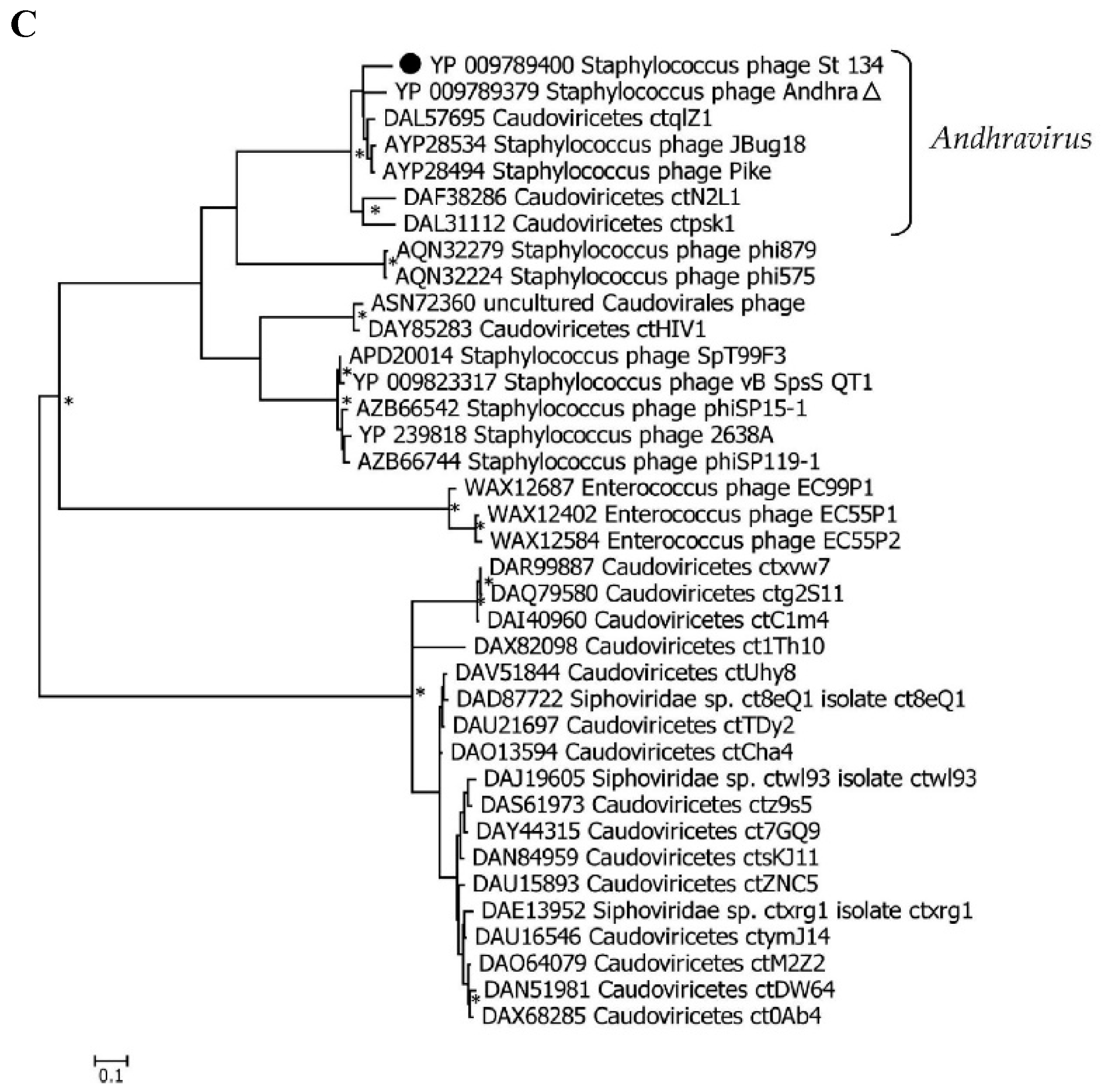
Comparative genome analysis indicated that the St_134 phage is a member of the
Andhravirus genus (
Rountreeviridae family). The genomes of all known phages from the
Andhravirus genus are similar in size (~18 kb) and their organization is similar too. All genomes contain 20 ORFs divided into the same two blocks according to the ORFs orientation (
Figure 3). Most genes are orthologous and located in the same positions in the genomes of the
Andhravirus species. ViPTree analysis confirmed taxonomy of St_134 (
Figure 4). Notably, all members of the
Andhravirus genus and neighbor
Rosenblumvirus genus infect
Staphylococcus spp.
3.3. Phylogenetic analysis of the St_134 Proteins
Phylogenetic analysis was performed for the St_134 terminaze large subunit, tail tip lysin, and endolisin (
Figure 5). In each case, 40 most similar sequences according to the BLASTp comparison were used for analysis. On the Maximum Likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of the St 134 terminate large subunit, phage sequences of the
Andhravirus genus form a monophyletic, highly supported clade (
Figure 5). Several unknown phage sequences from the metagenome assembled genomes (MAGs) are grouped with this clade. The remaining sequences belong to the
Rosenblumvirus genus and are clustered separately (
Figure 5A).
The topology of the ML tree containing the St_134 tail tip lysin is similar (
Figure 5B). Analysis of the St_134 tail tip lysin using BLASTp demonstrated that it has 89% similarity (100% coverage) with the Andhra phage protein gp10 (tail tip lysin gp10, YP_009789375.1). This lysin contains N-terminal glycosyl hydrolase (GyH) domain and C-terminal cysteine-histidine-dependent amidohydrolases/peptidases (CHAP) domain. A clade of sequences of the genus
Andhravirus is also formed with high reliability and divided into two subclades. The remaining sequences belong to the genus
Rosenblumvirus and are grouped separately. As for the endolysin phylogeny, only four sequences from the known
Andhraviruses, including the St_134 and Andhra phages, are found on the ML tree. St_134 endolysin (LysSte134_1) sequence showed 81% similarity (100% coverage) with the Andhra phage protein gp14 (N-acetylmuramuramoyl-L-alanine amidase, YP_009789379). Three additional sequences from MAGs are grouped with them. The remaining sequences have a low level of similarity with endolysin sequences from the
Andhravirus genus (
Figure 5C).
3.3. In Silico Characterization of St_134 lysins
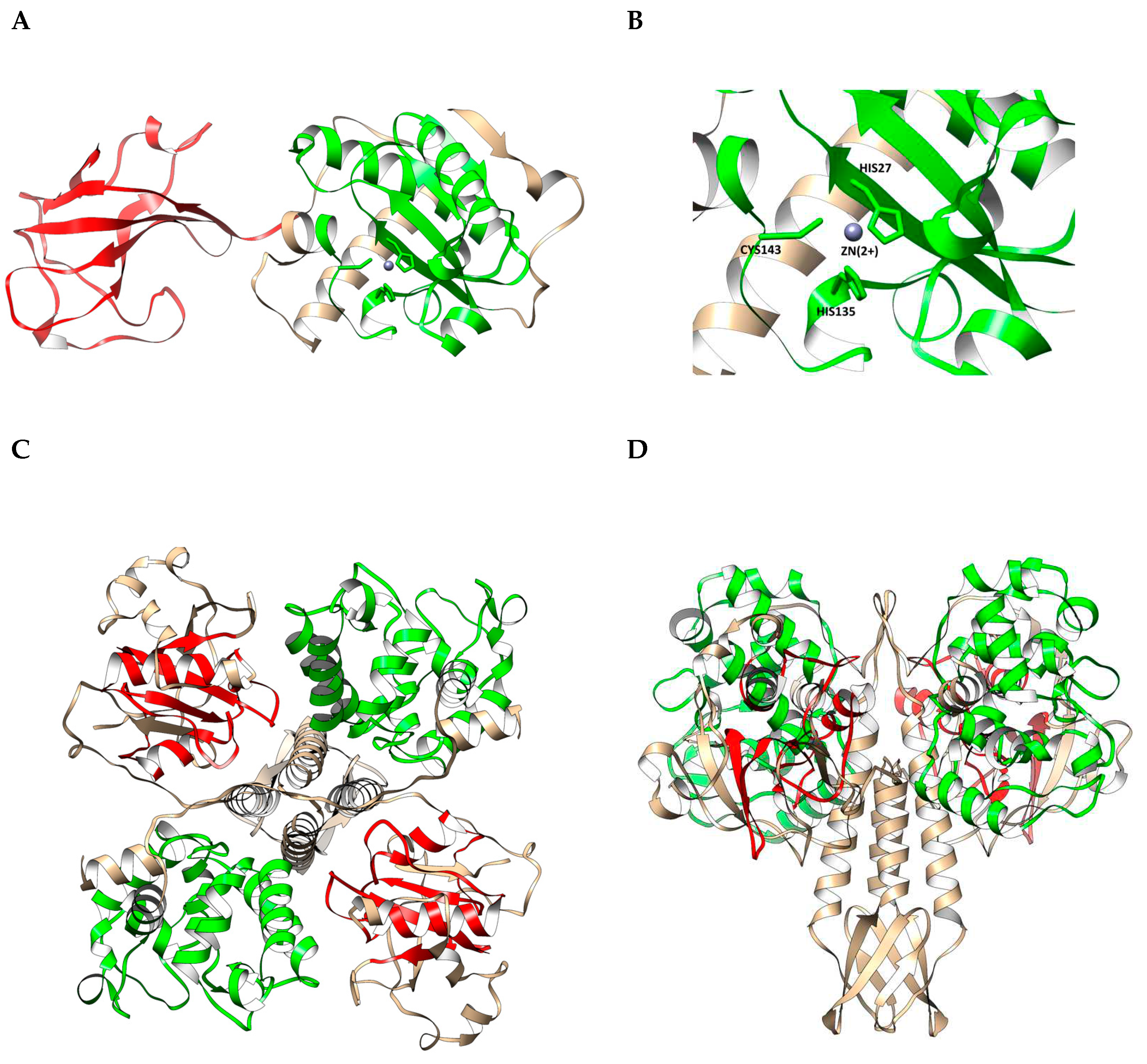
The putative endolysin LysSte134_1 consists of 295 amino acids (aa) with an isoelectric point (pI) of 9.21 and a predicted molecular weight of 35 kDa. InterPro software package (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence/, accessed 21.08.2023) was used to determine the LysSte134_1 domains. It was shown that LysSte134_1 belongs to the superfamily of N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase/peptidoglycan recognition proteins (Amidase/PGRP_sf) (IPR036505) and contains two domains. The N-terminal domain is the N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase-like type II (NALAA-2, EC 3.5.1.28, EC 3.5.1.28) domain (IPR002502). In the LysSte134_1 sequence, the NALAA-2-like catalytic domain (pfam01510) is located between 22 and 147 aa residues. The C-terminal region (190-295 aa) of LysSte134_1 has similarity with SH3 domains (G3DSA:2.30.30.40).
The putative structure of LysSte134_1 was predicted using AlphaFold2. It was confirmed that Lys Ste134_1 consists of two domains. The N-terminal globular core contains the predicted enzymatic NALAA-2-like domain that connects to the C-terminal globular SH3 domain via an unordered linker (
Figure 6). The N-terminal NAALA-2-like domain contains four α-helices and one β-sheet; the C-terminal domain consists of two β-sheets interlinked by flexible linkers. Ligand-binding site of LysSte134_1 was predicted using meta-server approach to protein-ligand binding site prediction COFACTOR. It was predicted that the catalytic zinc ion (Zn
2+) is coordinated with His27, His135, and Cys143 (
Figure 6).
The putative tail tip lysin LysSte134_2 contains 472 aa with pI of 8.91 and predicted molecular weight of 51.4 kDa. HHpred, InterPro (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence/, accessed 21.08.2023), and CDD database were used to identify the domain structure. It was indicated that LysSte134_2 belongs to the superfamily NLPC_P60 and contains two enzymatic domains: N-terminal GyH and C-terminal CHAP endopeptidase (IPR007921). The C-terminal domain is similar to CATH-Gene3D 3DSA:3.90.1720.10. The N-terminal GyH-like domain is located between 10 and 183 aa resides, whereas CHAP domain (Pfam PF05257) is located between 351 and 439 aa residues. The cysteine, histidine-dependent amidohydrolases/peptidases (CHAP) hydrolyze peptidoglycans in the bacterial cell wall.
AlphaFold2 showed that the putative 3D structure of LysSte134_2 is similar to the Andhra gp10 protein [
46]. In LysSte134_2, the N-terminal globular core contains the predicted enzymatic GyH-like domain and connects to the C-terminal globular CHAP domain via an ordered linker domain (middle linker). This linker domain consists of two α-helices and one β-sheet (
Figure 6). Probably, LysSte134_2 form homodimer like gp10 of the Andhra phage (
Figure 6). The N-terminal GyH-like domain contains eight α-helices; the C-terminal CHAP-like domain consists of two α-helices and one β-sheet.
Solubility of putative recombinant LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2 was assessed using SoluProt and Protein-sol bioinformatics tools. SoluProt demonstrated that both putative lysins have suitable solubility scores (> 0.5) to be produced in E. coli cells. However, analysis using Protein-sol indicated that while LysSte134_1 has solubility scores adequate (~ 0.45), LysSte134_2 has solubility scores insufficient for production in E. coli cells (much less than 0.45).
3.4. Cloning, Production and Purification of LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2
The genes encoding the lysins LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2 were inserted into the expression plasmid pQE-60. To produce the recombinant the lysins LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2 the constructed plasmids pQE-60-LysSte134_1 and pQE-60-LysSte134_2 were used to transform
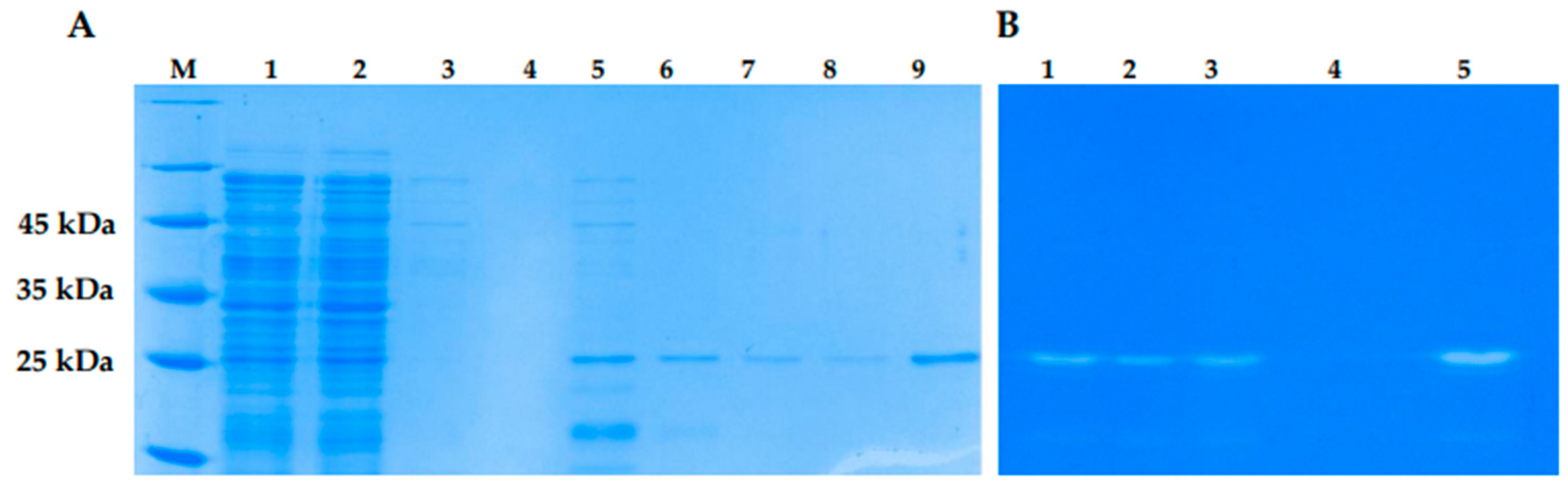
E. coli M15 cells. Various growth conditions were tested to increase solubility of the recombinant lysins. The localization and yield of LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2 were evaluated using PAAG electrophoresis (
Figure S1). LysSte134_1 was found in the soluble fraction of the cytoplasm only after cultivation of
E. coli M15/pQE-60-LysSte134_1 cells at 10°C and induction with 100 µM IPTG. LysSte134_1 was purified using Ni-NTA agarose from a soluble fraction of cytoplasm and its molecular weight was ~35 kDa, which corresponded to the predicted one (
Figure 7). The purity of LysSte134_1 after chromatography was evaluated using PAGE and it was ~95% (
Figure 7). The yield of LysSte134_1 production was 2 mg from 1 L of cell culture after all stages of purification and dialysis. The purified LysSte134_1 was stored at a concentration of more than 1 mg/ml in buffer S (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 300 mM NaCl) at 4°C.
Unlike LysSte134_1, the recombinant LysSte134_2 was insoluble under any cultivation conditions. Several attempts were made to refold LysSte134_2 from the insoluble cytoplasm fraction as described previously [
47]. During dialysis, LysSte134_2 precipitated when the concentration of urea in the re-coagulation buffer was below 1 M. So, a purified soluble preparation of this protein was not obtained and the insoluble fraction of the cytoplasm was used to assess the enzymatic activity of the protein.
3.5. Enzymatic activity of LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2
The lytic activity of LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2 lysins was assessed by zymographic assay using cell wall peptidoglycans of various
Staphylococcus strains as substrates. It was shown that LysSte134_1 hydrolyzed peptidoglycan from the cell wall of
S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 that is a host strain of St_134 phage (
Figure 7). In addition, LysSte134_1 was able to digest peptidoglycans from other coagulase-negative strains, namely
S. epidermidis СEMTC 2043 (insensitive to St_134 strain with MDR),
S. haemolyticus СEMTC 3413 (MDR), and
S. warneri СEMTC 2062 (weak activity) (
Figure 8). However, it could not cleave peptidoglycans isolated from the cell wall of
S. warneri СEMTC 4154 and both tested
S. saprophyticus strains СEMTC 3872 and СEMTC 6829. Notably, the parental St_134 phage did not infect all tested
S. warneri and
S. saprophyticus strains (
Table 2,
Table S1).
It is worth noting that LysSte134_1 hydrolyzed peptidoglycans from the cell wall of the coagulase-positive strains
S. aureus CEMTC 675 and
S. aureus CEMTC 1685 (
Figure 8).
S. aureus CEMTC 675 is resistant to cefoxitin, gentamicin, erythromycin, and clindamycin (strain with MDR), whereas
S. aureus CEMTC 1685 is resistant to lincomycin and vancomycin (VRSA) and both
S. aureus strains are not susceptible to St_134 infection. The obtain results demonstrated that LysSte134_1 is able to hydrolyze peptidoglycan from various pathogenic the cell wall of the
Staphylococcus strains despite their resistance to antibiotics and sensitivity to the parental phage St_134 (
Figure 8). LysSte134_2 did not hydrolyze any of the investigated peptidoglycans isolated from various
Staphylococcus cells walls.
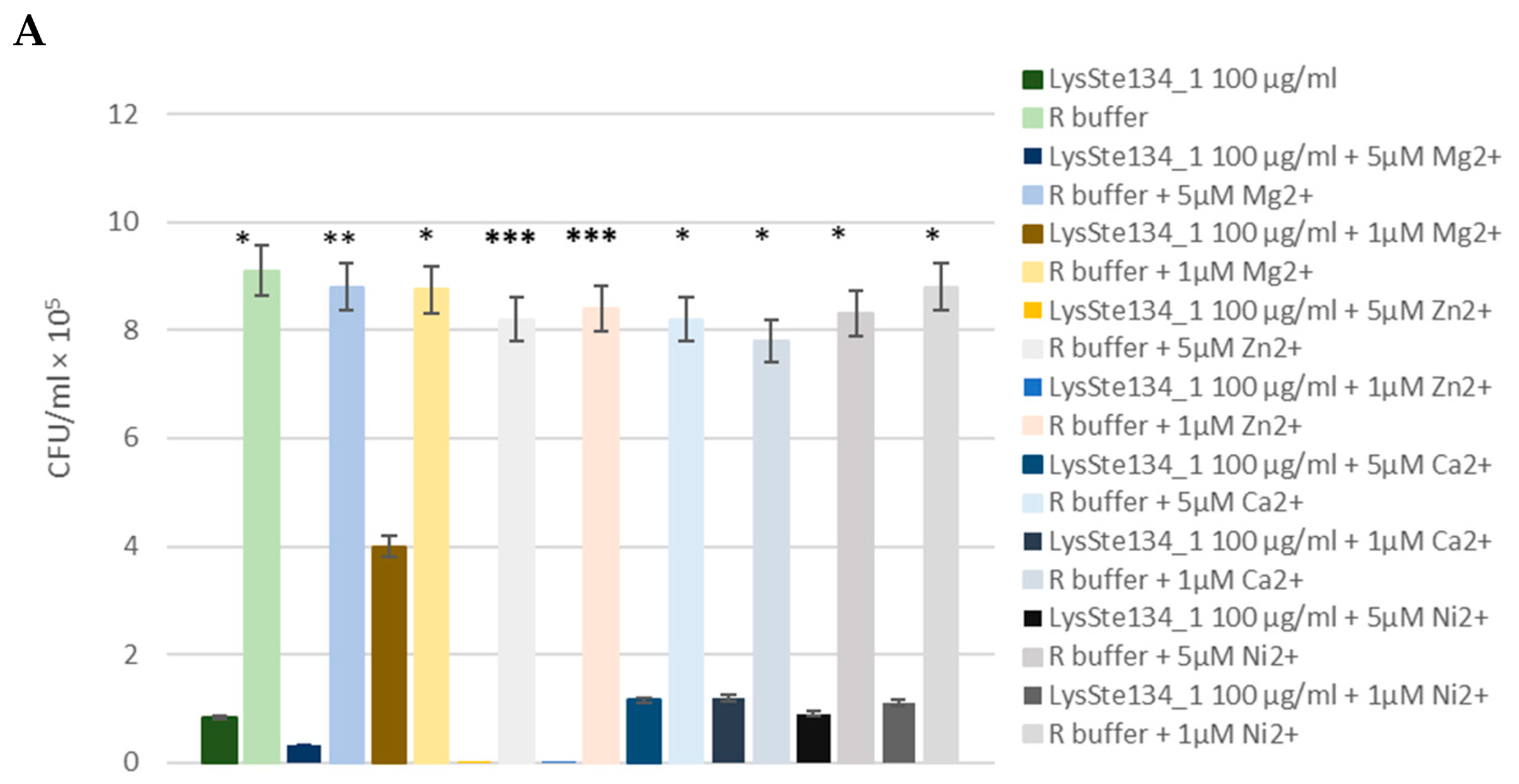
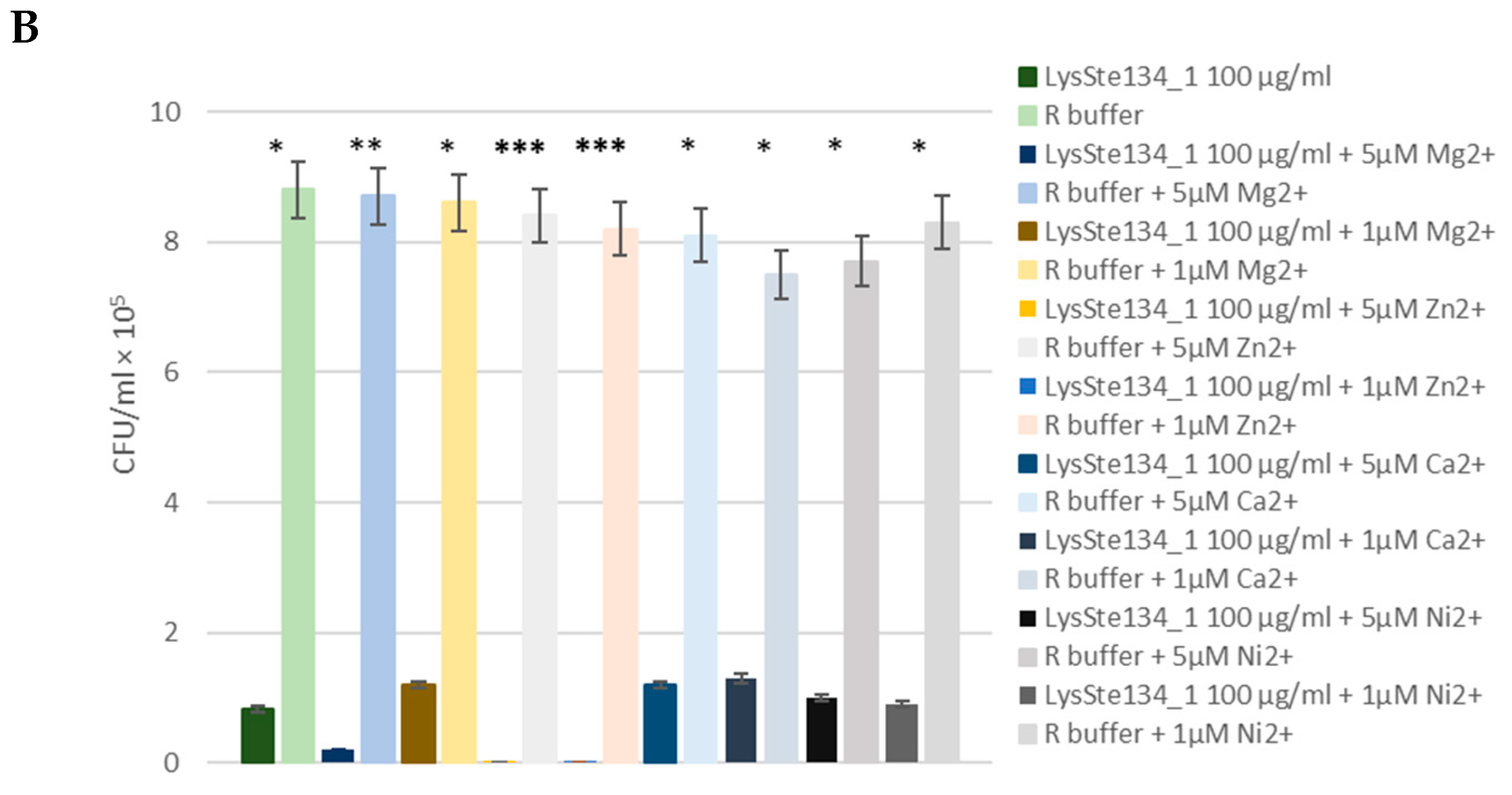
3.6. Anti-Staphylococcal Activity of LysSte134_1
The antibacterial activity of LysSte134_1 was assessed against a planktonic culture
S. aureus CEMTC 1685 and
S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058. It was demonstrated that treatment of
S. aureus СEMTC 1685 or
S. epidermidis strain СEMTC 2058 cells with LysSte134_1 (25 µg/ml) resulted in a 50-fold decrease in CFU (
Figure 9). Then, the effect of different concentrations of bivalent ions (Ca
2+, Mg
2+, Zn
2+, and Ni
2+) on effectivity of LysSte134_1 was studied. When
S. aureus CEMTC 1685 and
S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 were treated with LysSte134_1 that was supplemented with ZnCl
2 at concentrations of 1 µM and 5 µM, lytic activity of LysSte134_1 against these strains increased up to 100-fold and 1000-fold, respectively (
Figure 9). Notably, Ca
2+, Mg
2+, and Ni
2+ did not significantly affect the hydrolytic activity of LysSte134_1 against both tested S
taphylococcus strains.
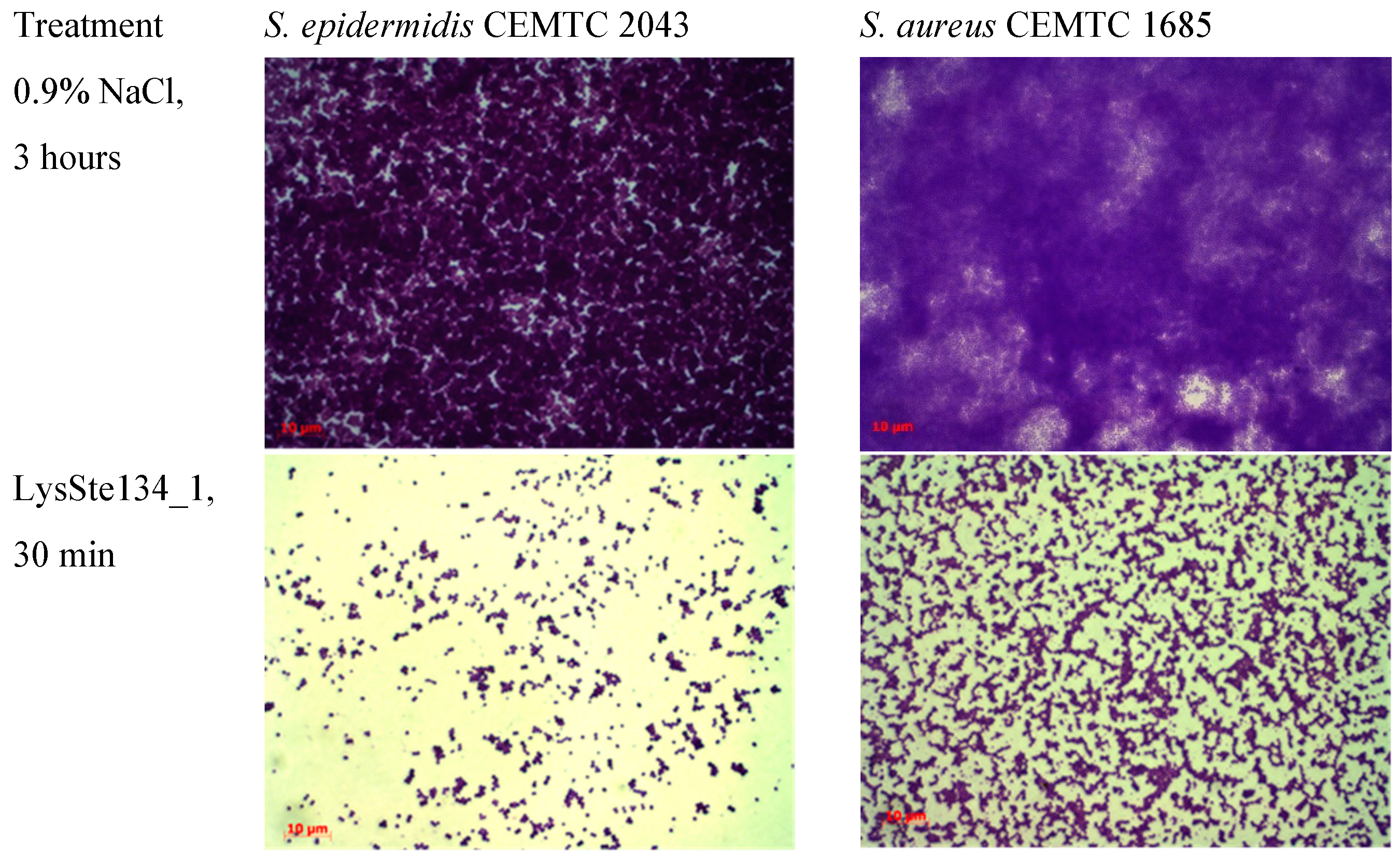
3.7. Biofilm Disruption Activity of LysSte134_1
LysSte134_1 activity against staphylococcal biofilms was evaluated using biofilms formed by
S. epidermidis CEMTC 2043 and
S. aureus CEMTC 1685. Both strains are insensitive to St_134 infection and
S. epidermidis CEMTC 2043 is resistant to cefixime, erythromycin, ciprofloxacin/levofloxacin, chloramphenicol, and vancomycin, whereas
S. aureus CEMTC 1685 is a VRSA strain. Biofilms were grown on the surface of coverslips in LB medium. When biofilms were formed, they were treated with purified LysSte134_1 at a concentration of 25 μg/mL in PBS. Sterile PBS was added as a control. Biofilms with LysSte134_1 were incubated at 37°C for 30 min and 120 min, while biofilms with PBS were incubated for ~180 minutes. In
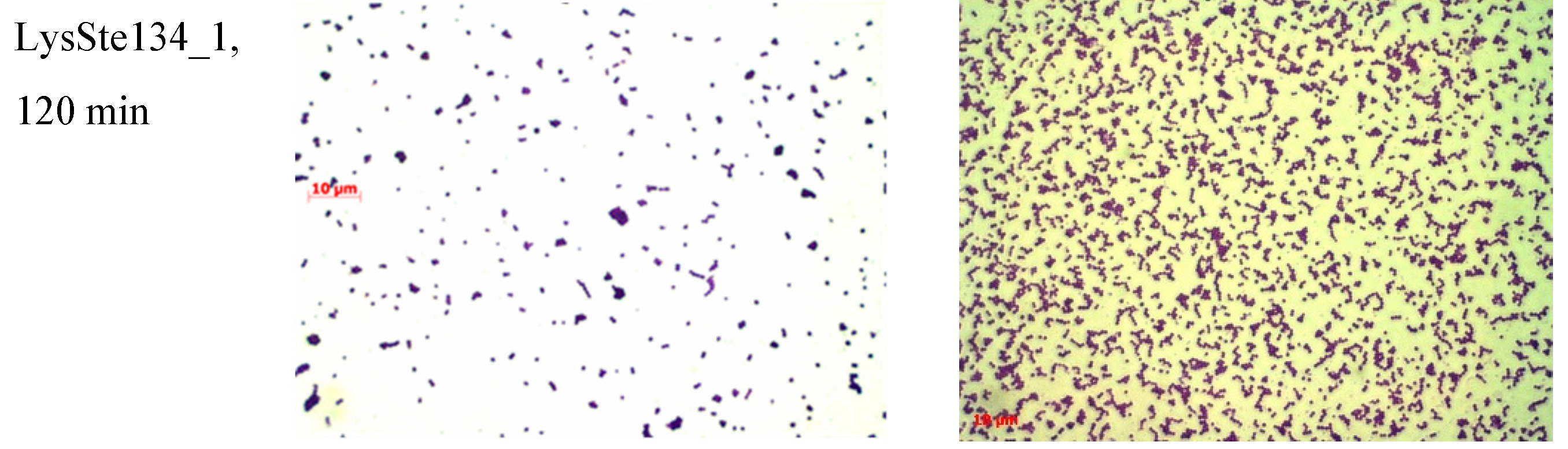
S. epidermidis biofilm treated with LysSte134_1, only small remains of biofilm matrix and cells were observed after incubation for 30 min (
Figure 10). LysSte134_1 was not so active against biofilm formed by
S. aureus cells; however, even this biofilm was sustantualy disrupted within 30 min. In control biofilms, a tight matrix of stained bacteria was observed (
Figure 10)
4. Discussion
Phage-encoded lysins are promising agents against drug-resistant bacterial pathogens. In this study, the functional and in silico structural analysis of recombinant lysins LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2 was performed. The genes encoding these lysins were cloned using the genome of the lytic
Staphylococcus epidermidis phage St_134. This small podophage is a typical member of the
Andhravirus genus (
Rountreeviridae family). Like its close relatives, namely
Staphylococcus phages Andhra [
46,
48], BESEP3 (GenBank: MT596500.1), and SeAlphi (NCBI: NC_070880.1), the bacterial host of St_134 is
S. epidermidis. Several other coagulase-negative
Staphylococcus species were sensitive to St_134, including
S. haemolyticus. However, we did not find
S. saprophyticus and
S. warneri strains that can be infected with St_134 as well as coagulase-positive
S. aureus and
S. intermidius strains, despite the fact that >200 strains were tested. Nevertheless, one coagulase-positive strain (CEMTC 3692) was found to be susceptible to St_134 infection. It was a member of the
S. aureus complex. Sequencing of its 16S rRNA gene fragment (1364 bp) indicated high nucleotide identity (NI) with
Staphylococcus roterodami (NI = 100%) and
Staphylococcus argenteus (NI = 99.93%). These two species are part of the
S. aureus complex and were isolated from a human foot infection and hip joint infection [
49,
50]. So, we can conclude that the phage St_134 has a relatively wide host range.
The genes encoding both types of lysins were found in the St_134 genome: Lys-Ste134_1 that is produced in the host cell cytoplasm providing the release of new phage particles (endolysin) and LysSte134_2, which cleaves the cell walls peptidoglycans after phage adsorption (tail-associated lysin). Endolysin LysSte134_1 belongs to the N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase/peptidoglycan recognition proteins (Ami-dase/PGRP_sf) superfamily. It contains N-terminal NALAA-2-like catalytic domain and C-terminal SH3 domain. Usually, amidases from the NALAA-2 group are Zn2+-dependent enzymes that cleaved the amide linkage between N-acetylmuramoyl and L-amino acids in the bacterial cell wall [
51]. In the endolysin LysSte134_1, Zn2+ presumably bound with His28, His130, and Cys138. The tail-associated lysin LysSte134_2 consists of the N-terminal GyH-like domain connected to the C-terminal CHAP domain via linker domain (structured linker), that formed dimer structure of LysSte134_2.
Despite the fact that solubility of LysSte134_1 was predicted as acceptable for production in E. coli cells, this protein was produced in a soluble form only when E. coli culture was grown at 10°C. Unfortunately, our attempts to obtain enzimaticaly active LysSte134_2 were unsuccessful. Zymographic assay, using peptidoglycans from various Staphylococcus cells revealed that LysSte134_1 hydrolyzed peptidoglycans from both coagulase-positive (S. aureus) and coagulase-negative (S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, and one S. warneri) Staphylococcus spp. In addition, LysSte134_1 showed antibacterial activity against both S. aureus and S. epidermidis. Moreover, the ability of LysSte134_1 to disrupt biofilms formed by S. aureus and S. epidermidis was confirmed.
Phylogenetic analysis indicated that the most similar lysins to the studied LysSte134_1 and LysSte134_2 are well-characterized lysins of the Andhra phage [
46,
48]: Andhra_gp10, which that is a homologue of LysSte134_2 and Andhra_gp14 that is a homologue of LysSte134_1. It was shown that Andhra_gp1 had moderate hydrolytic activity and Andhra_gp10 demonstrated strong hydrolytic activity against peptidoglycans
in vitro. In the growth inhibition test, both gp10 and gp14 proteins suppressed the growth of
S. epidermidis and
Staphylococcus intermedius strains, with little or no effect on the growth rate of
S. aureus [
46]. Such differences are probably due to the fact that although Andhra_gp14 and LysSte134_1 are similar proteins, their similarity rate is only 80%. The largest number of substitutions in both endolysins is located in the NALAA-2 and SH3 domains, which probably leads to an increase in the spectrum of lytic activity of LysSte134_1. Unfortunately, the hydrolytic activity of LysSte134_1 against peptidoglycans from
S. intermedius and planctonic culture was not tested, which is a limitation of this study. It should be done in future.
Both
S. aureus and
S. intermedius are coagulase-positive staphylococci; however, they belong to different complexes. Usualy, strains from the
S. aureus complex can cause various severe infections in humans including meningitis and sepsis, whereas strains from the
S. intermedius complex are mainly causative agents of veterinary infections and can be transmitted to humans through contacts with animals [
52,
53,
54]. High lytic activity of LysSte134_1 against planktonic cultures of
S. aureus and biofilms that were formed by
S. aureus is an advantage of the LysSte134_1 endolysin. Notably, LysSte134_1 showed even higher efficacy against
S. epidermidis cells and biophilms that against
S. aureus ones. Although it is believed that
S. epidermidis is a less virulent pathogen than
S. aureus, in recent years the proportion of
S. epidermidis strains with MDR is significantly higher than that for
S. aureus at least in some regions [
3]. In addition,
S. epidermidis, being a normal skin commensal, is capable of forming biofilms, which is a serious problem in intensive care units and especially in surgery.
In conclusion, taking into consideration hydrolytic activity of LysSte134_1 against both coagulase-positive S. aureus and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp., we can consider this endolysin as a promising antibacterial agent that is able to remove staphylococcal biofilms. In addition, such phage lysins can be used in combination with antibiotics, as they can digest and destroy the biofilm matrix, which facilitates antibiotics to reach the target cells and, in turn, can lead to a decrease in the dosage of antibiotics.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1. Staphylococcus spp. strains sensitive to the St_134 phage. Table S2. Open reading frames (ORFs) found in the genome of the St_134 phage. Figure S1: SDS PAAG electrophoreses (A): 1 - lysates of E. coli M15-pQE-60/LysSte134_1 cells, producing recombinant LysSte134_1; 2 – insoluble cytoplasm of E. coli M15- pQE-60/LysSte134_1; 3 –soluble cytoplasm of E. coli M15- pQE-60/LysSte134_1. (B): 1 - lysates of E. coli M15-pQE-60/LysSte134_2 cells, producing recombinant LysSte134_2; 2 – insoluble cytoplasm of E. coli M15- pQE-60/LysSte134_1; 3 – soluble cytoplasm of E. coli M15- pQE-60/LysSte134_2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L.M. and N.V.T.; methodology V.V.M., A.L.M. and Y.N.K.; validation, N.N.G., I.V.B., Y.A.K., A.L.M., and E.A.P.; data curation, N.N.G., V.V.M., and A.L.M.; formal analysis, N.N.G., A.L.M., V.V.M., E.A.P., E.V.Z. and Y.A.K.; funding acquisition, A.Y.T.; investigation, T.A.U., N.N.G., E.I.R., Y.N.K., E.A.P., E.V.Z., A.L.M., and A.Y.T.; visualization, N.N.G., Y.N.K., E.I.R., T.A.U., I.V.B., and A.L.M.; writing—original draft, Y.A.K. A.L.M., and N.V.T.; writing—review and editing, Y.A.K., N.V.T., and A.Y.T.; supervision, N.V.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian state-funded project for ICBFM SB RAS (grant number 122110700002-2).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Samples that contained phage and the host strain were collected during the study that was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Novosibirsk Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics (protocol 014/17-2 from 25 November 2011).
Informed Consent Statement
Both patients whose samples were used to isolate the phage St_134 and its host strain provided informed consents.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank their colleagues from the Novosibirsk Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics the strain and clinical sample provided.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, in writing the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2020, 33(3), e00181-19. [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L., Carmeli, Y. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2018, 18(3), 318–327. [CrossRef]
- Bardasheva, A.; Tikunov, A.; Kozlova, Y.; Zhirakovskaia, E.; Fedorets, V.; Fomenko, N.; Kalymbetova, T.; Chretien, S.; Pavlov, V.; Tikunova, N.; Morozova, V. Antibiotic Resistance and Pathogenomics of Staphylococci Circulating in Novosibirsk, Russia. Microorganisms 2021, 9(12), 2487. [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2014, 27(4), 870–926. [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis Pathogenesis. Methods Mol Biol 2014, 1106, 17–31. [CrossRef]
- Paharik, A.E.; Horswill, A.R. The Staphylococcal Biofilm: Adhesins, Regulation, and Host Response. Virulence Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogens 2016, 50, 529–566. [CrossRef]
- Morozova, V.V.; Vlassov, V.V.; Tikunova, N.V. Applications of Bacteriophages in the Treatment of Localized Infections in Humans. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9, 1696. [CrossRef]
- Petrovic Fabijan, A.P; Lin, R.C.Y.; Ho, J.; Maddocks, S.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Iredell, R. Safety of bacteriophage therapy in severe Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat Microbiol 2020, 5(3), 465–472. 3. [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, Z.; Majewska, J.; Milczarek, M.; Owczarek, B.; Dąbrowska, K. Circulation of Fluorescently Labelled Phage in a Murine Model. Viruses. 2021;13(20), 297. [CrossRef]
- Chanishvili, N. Bacteriophages as Therapeutic and Prophylactic Means: Summary of the Soviet and Post-Soviet Experiences. Curr Drug Deliv 2016, 13, 309–323. [CrossRef]
- Schooley, R.T.; Biswas, B.; Gill, J.J.; Hernandez-Morales, A.; Lancaster, J.; Lessor, L.; Barret J.J. Development and Use of Personalized Bacteriophage-Based Therapeutic Cocktails To Treat a Patient with a Disseminated Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infection [published correction appears in Antimicrob Agents Chemother. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017; 61(10), e00954-17. [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.; Turner, P.E.; Kim, S.; Mojibian, H.R.; Elefteriades, J.A.; Narayan, D. Phage treatment of an aortic graft infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Evol Med Public Health. 2018, 2018(1), 60–66. [CrossRef]
- Morozova, V.; Kozlova, Y.; Ganichev, D.; Tikunova, N. Bacteriophage Treatment of Infected Diabetic Foot Ulcers. In: Methods in Molecular Biology, Joana Azeredo and Sanna Sillankorva (Eds): Bacteriophage Therapy, 2018, 1693, 151–158. [CrossRef]
- Schmelcher, M.; Donovan, D.M.; Loessner, M.J. Bacteriophage endolysins as novel antimicrobials. Future Microbiol 2012, 7(10), 1147–1171. [CrossRef]
- Gondil, V.S.; Harjai, K.; Chhibber, S. Endolysins as Emerging Alternative Therapeutic Agents to Counter Drug-Resistant Infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105844. [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, F.; Easwaran, M.; Daramola, O.; Ragab, S.; Lynch, S.; Oduselu,T.J.; Khan, F.M.; Ayobami, A.; Adnan, F.; Torrents, E.; Sanmukh, S.; El-Shibiny1, A. Phage-Encoded Endolysins Antibiotics (Basel) 2021, 10(2), 124. [CrossRef]
- Murray, E.; Draper, L.A.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. The Advantages and Challenges of Using Endolysins in a Clinical Setting. Viruses 2021, 13, 680. [CrossRef]
- Harhala, M.A.; Gembara, K.; Nelson, D.C.; Miernikiewicz, P.; Dabrowska, K. Immunogenicity of Endolysin PlyC. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 966. [CrossRef]
- WHO. 2020 Antibacterial Agents in Clinical and Preclinical Development; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; 76p. 76p.
- Adhya, S.; Merril, C.R.; Biswas, B. Therapeutic and Prophylactic Applications of Bacteriophage Components in Modern Medicine. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a012518. [CrossRef]
- São-José, C. Engineering of Phage-Derived Lytic Enzymes: Improving Their Potential as Antimicrobials. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 29. [CrossRef]
- Latka, A.; Maciejewska, B.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Briers, Y.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Bacteriophage-Encoded Virion-Associated Enzymes to Overcome the Carbohydrate Barriers during the Infection Process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3103–3119. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rubio, L.; Gerstmans, H.; Thorpe, S.; Mesnage, S.; Lavigne, R.; Briers, Y. DUF3380 Domain from a Salmonella Phage Endolysin Shows Potent N -Acetylmuramidase Activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4975–4981. [CrossRef]
- Höltje, J.V.; Mirelman, D.; Sharon, N.; Schwarz, U. Novel Type of Murein Transglycosylase in Escherichia Coli. J. Bacteriol. 1975, 124, 1067–1076. [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, M.; Walker, S. Envelope Structures of Gram-Positive Bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017, 404, 1–44. [CrossRef]
- Gilmer, D. B.; Schmitz, J. E.; Thandar, M.; Euler, C.W.; Fischetti, V.A. The Phage Lysin PlySs2 Decolonizes Streptococcus suis from Murine Intranasal Mucosa. PloS one 2017, 12(1), e0169180. [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D., Garrido, V., Fernández, L., Portilla, S., Rodríguez, A., Grilló, M. J., García, P. Phage Lytic Protein LysRODI Prevents Staphylococcal Mastitis in Mice. Frontiers in microbiology 2020, 11, 7. [CrossRef]
- Miernikiewicz, P.; Barylski, J.; Wilczak, A.; Dragoš, A.; Rybicka, I.; Bałdysz, S.; Szymczak, A.; Dogsa, I.; Rokush, K.; Harhala, M.A.; Ciekot, J.; Ferenc, S.; Gnus, J.; Witkiewics, W.; Dabrowska, K. New Phage-Derived Antibacterial Enzyme PolaR Targeting Rothia spp. Cells 2023, 12, 1997. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Seo, J. A Novel Strategy to Identify Endolysins with Lytic Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5772. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Nyaruaba, R.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.; Wei, H.A. Highly Active Chimeric Lysin with a Calcium-Enhanced Bactericidal Activity against Staphylococcus aureus In Vitro and In Vivo. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021, 19, 461. [CrossRef]
- Pajunen, M.; Kiljunen, S.; Skurnik, M. Bacteriophage phiYeO3-12, specific for Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3, is related to coliphages T3 and T7, J Bacteriol, 2000, 182, 5114–5120. [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M. Measurement of the rate of attachment of bacteriophage to cells. In: Bacteriophages: methods and protocols, Clokie M.R.J., Kropinski, A.M.; Humana Press; New York, USA, 2009; pp. 151-155. [CrossRef]
- Morozova, V.; Kozlova, Y.; Jdeed, G.; Tikunov, A.; Ushakova, T.; Bardasheva, A.; Zhirakovskaia, E.; Poletaeva, Y.; Ryabchikova, E.; Tikunova, N. A Novel Aeromonas popoffii Phage AerP_220 Proposed to Be a Member of a New Tolavirus Genus in the Autographiviridae Family. Viruses 2022, 14, 2733. [CrossRef]
- Kutter, E. Phage host range and efficiency of plating. In: Bacteriophages: methods and protocols, Clokie M.R.J., Kropinski, A.M.; Humana Press; New York, USA, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 141–149. [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, S.; Coffey, A.; Edwards, R.; Meaney, W.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P. Genome of staphylococcal phage K: a new lineage of Myoviridae infecting gram-positive bacteria with a low GC content. J Bacteriol 2004, 186, 2862–2871. [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kuronishi, M.; Uehara, H.; Ogata, H.; Goto, S. Viptree: The viral proteomic tree server. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2379–2380. [CrossRef]
- Notredame, C.; Higgins, D.G.; Heringa, J. T-Coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 205–217. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [CrossRef]
- Hebditch, M.; Carballo-Amador, M.A.; Charonis, S.; Curtis, R.; Warwicker, J. Protein–Sol: A web tool for predicting protein solubility from sequence. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3098–3100. [CrossRef]
- Hon, J.; Marusiak, M.; Martinek, T.; Kunka, A.; Zendulka, J.; Bednar, D.; Damborsky, J. SoluProt: Prediction of soluble protein expression in Escherichia coli. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 23–28. [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schutze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. Colab-Fold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25(13), 1605–1612. [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Sekiguchi, J. Zymographic Techniques for the Analysis of Bacterial Cell Wall in Bacillus. Methods Mol Biol. 2016, 1440, 87-98. [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, N. C., Kizziah, J. L., Hatoum-Aslan, A., Dokland, T. Structure and host specificity of Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriophage Andhra. Science advances, 2022, 8(48), eade0459. [CrossRef]
- Matveev,A., Khlusevich, Y., Golota, O., Kravchuk, B., Tkachev, S., Emelyanova, L., Tikunova, N. Tick-borne encephalitis nonstructural protein NS1 expressed in E. coli retains immunological properties of the native protein. Protein expression and purification, 2022, 191, 106031. [CrossRef]
- Cater, K., Dandu, V. S., Bari, S. M., Lackey, K., Everett, G. F., Hatoum-Aslan, A. A Novel Staphylococcus Podophage Encodes a Unique Lysin with Unusual Modular Design. mSphere, 2017, 2(2), e00040-17. [CrossRef]
- Schutte, A. H. J., Strepis, N., Zandijk, W. H. A., Bexkens, M. L., Bode, L. G. M., Klaassen, C. H. W. Characterization of Staphylococcus roterodami sp. nov., a new species within the Staphylococcus aureus complex isolated from a human foot infection. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology 2021, 71(9). [CrossRef]
- Tong, S. Y. C., Schaumburg, F., Ellington, M. J., Corander, J., Pichon, B., Leendertz, F., Bentley, S. D., Parkhill, J., Holt, D. C., Peters, G., Giffard, P. M. Novel staphylococcal species that form part of a Staphylococcus aureus-related complex: the non-pigmented Staphylococcus argenteus sp. nov. and the non-human primate-associated Staphylococcus schweitzeri sp. nov. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology, 2015, 65(Pt 1), 15–22. [CrossRef]
- Vermassen, A.; Leroy, S.; Talon, R.; Provot, C.; Popowska, M.; Desvaux, M. Cell Wall Hydrolases in Bacteria: Insight on the Diversity of Cell Wall Amidases, Glycosidases and Peptidases Toward Peptidoglycan. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 331. [CrossRef]
- Somayaji, R.; Priyantha, M.A.; Rubin, J.E.; Church, D. Human infections due to Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, an emerging zoonosis of canine origin: report of 24 cases. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016, 85, 471–476. [CrossRef]
- Darlow, C.A.; Paidakakos, N.; Sikander, M.; Atkins, B. A spinal infection with Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2017221260. [CrossRef]
- Magleby, R.; Bemis, D.A.; Kim, D.; Carroll, K.C.; Castanheira, M.; Kania, S.A.; Jenkins, S.G.; Westblade, L.F. First reported human isolation of Staphylococcus delphini. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019, 94, 274–276. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Electron micrograph of St_134 phage particle negatively stained with 1% uranyl acetate.
Figure 1.
Electron micrograph of St_134 phage particle negatively stained with 1% uranyl acetate.
Figure 2.
Biological properties of the phage St 134: (A) phage adsorption to host cells; (B) burst size experiments; (C) bacterial lytic curve.
Figure 2.
Biological properties of the phage St 134: (A) phage adsorption to host cells; (B) burst size experiments; (C) bacterial lytic curve.
Figure 3.
Genome maps of the St_134 phage and Staphylococcus phages from the Andhravirus genus. Terminal repeats of the genome of the phage Andhra are marked with gray squares. ORFs encoding structural and hypothetical proteins are marked with green and grey, respectively.
Figure 3.
Genome maps of the St_134 phage and Staphylococcus phages from the Andhravirus genus. Terminal repeats of the genome of the phage Andhra are marked with gray squares. ORFs encoding structural and hypothetical proteins are marked with green and grey, respectively.
Figure 4.
ViPTree analysis of the Staphylococcus phage St 134 that is marked with a red asterisk.
Figure 4.
ViPTree analysis of the Staphylococcus phage St 134 that is marked with a red asterisk.
Figure 5.
Maximum Likelihood phylogenetic trees of the St_134 terminase large subunit (A), tail tip lysin (B), and endolysin (C) generated using IQ-tree software. Corresponding sequences of the St_134 phage are marked with black circles; sequences of Staphylococcus phage Andhra are marked with triangles. Nodes with 95% statistical significance calculated from 1000 ultrafast bootstrap replicates are marked with asterisks. The scale bar represents the number of substitutions per site.
Figure 5.
Maximum Likelihood phylogenetic trees of the St_134 terminase large subunit (A), tail tip lysin (B), and endolysin (C) generated using IQ-tree software. Corresponding sequences of the St_134 phage are marked with black circles; sequences of Staphylococcus phage Andhra are marked with triangles. Nodes with 95% statistical significance calculated from 1000 ultrafast bootstrap replicates are marked with asterisks. The scale bar represents the number of substitutions per site.
Figure 6.
(A) Ribbon representation of the predicted 3D structure of the endolysin LysSte134_1 in complex with Zn2+ ion; EAD and SH3 are marked in red and green, respectively. (B) Ribbon representation of the putative zinc-binding site of LysSte134_1; His27, His135, and Cys143) are shown in a stick representation. (C) Ribbon representation (top view) of the predicted 3D dimer structure of the lysin LysSte134_2; GyH and CHAP are marked in green and red, respectively. (D) Ribbon representation (side view) of the predicted 3D dimer structure of the lysin LysSte134_2; GyH and CHAP are marked in green and red, respectively. The molecular coordinates of the predicted 3D structure of St_134 lysins were rendered using UCSF Chimera molecular visualizer, version 1.15.
Figure 6.
(A) Ribbon representation of the predicted 3D structure of the endolysin LysSte134_1 in complex with Zn2+ ion; EAD and SH3 are marked in red and green, respectively. (B) Ribbon representation of the putative zinc-binding site of LysSte134_1; His27, His135, and Cys143) are shown in a stick representation. (C) Ribbon representation (top view) of the predicted 3D dimer structure of the lysin LysSte134_2; GyH and CHAP are marked in green and red, respectively. (D) Ribbon representation (side view) of the predicted 3D dimer structure of the lysin LysSte134_2; GyH and CHAP are marked in green and red, respectively. The molecular coordinates of the predicted 3D structure of St_134 lysins were rendered using UCSF Chimera molecular visualizer, version 1.15.
Figure 7.
SDS PAAG electrophoreses (A): 1 - lysates of E. coli M15-pQE-60/LysSte134_1 cells producing recombinant LysSte134_1; 2 – soluble cytoplasm of E. coli M15- pQE-60/LysSte134_1; 3 – eluate from Ni-NTA agarose after washing with buffer A (50 mM NaH2PO4, pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 5 mM Tris-HCl); 4 – 9 - eluate from Ni-NTA agarose after elution with buffer A, containing 50 mM, 100 mM, 150 mM, 200 mM, 250 mM and 350 mM imidazole, correspondingly. (B) Zymographic assay of eluate from Ni-NTA agarose after elution with buffer A, containing 100 mM (1); 150 mM (2) ; 200 mM (3), 250 mM (4) and 350 mM (5) M- protein ladder Precision Plus Protein™ Standards (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). PAGE (12,5%) containing 0.5 mg of peptidoglycan from S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058.
Figure 7.
SDS PAAG electrophoreses (A): 1 - lysates of E. coli M15-pQE-60/LysSte134_1 cells producing recombinant LysSte134_1; 2 – soluble cytoplasm of E. coli M15- pQE-60/LysSte134_1; 3 – eluate from Ni-NTA agarose after washing with buffer A (50 mM NaH2PO4, pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 5 mM Tris-HCl); 4 – 9 - eluate from Ni-NTA agarose after elution with buffer A, containing 50 mM, 100 mM, 150 mM, 200 mM, 250 mM and 350 mM imidazole, correspondingly. (B) Zymographic assay of eluate from Ni-NTA agarose after elution with buffer A, containing 100 mM (1); 150 mM (2) ; 200 mM (3), 250 mM (4) and 350 mM (5) M- protein ladder Precision Plus Protein™ Standards (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). PAGE (12,5%) containing 0.5 mg of peptidoglycan from S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058.
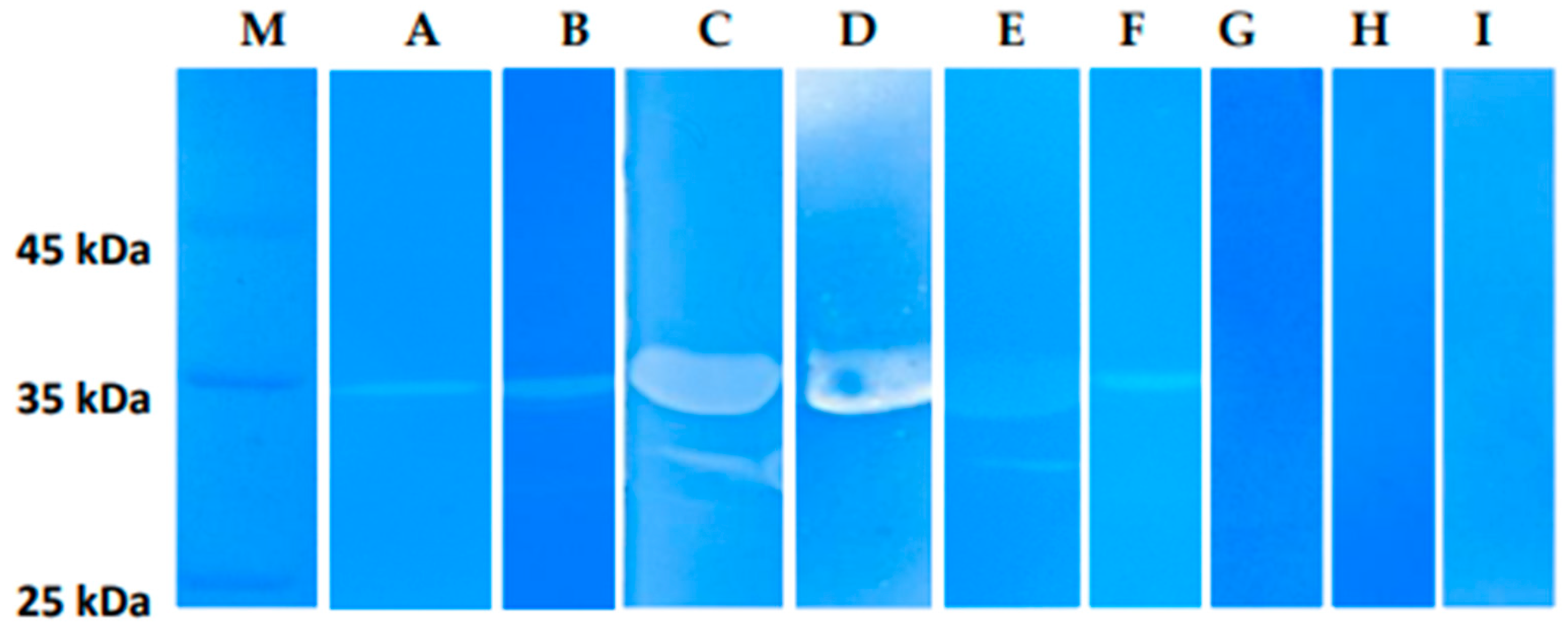
Figure 8.
Zymographic analysis of recombinant LysSte134_1. PAGE (12,5%) containing 0.5 mg of peptidoglycan from S. aureus СEMTC 675 (A), S. aureus СEMTC 1685 (B), S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 (C), S. epidermidis СEMTC 2043 (C), S. haemolyticus СEMTC 3753 (E), S. warneri СEMTC 2062 (F), S. warneri СEMTC 4154 (G), S. saprophyticus СEMTC 3872 (H), S. saprophyticus СEMTC 6829 (H), stained with methylene blue. M - protein ladder Precision Plus Protein™ Standards (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Figure 8.
Zymographic analysis of recombinant LysSte134_1. PAGE (12,5%) containing 0.5 mg of peptidoglycan from S. aureus СEMTC 675 (A), S. aureus СEMTC 1685 (B), S. epidermidis СEMTC 2058 (C), S. epidermidis СEMTC 2043 (C), S. haemolyticus СEMTC 3753 (E), S. warneri СEMTC 2062 (F), S. warneri СEMTC 4154 (G), S. saprophyticus СEMTC 3872 (H), S. saprophyticus СEMTC 6829 (H), stained with methylene blue. M - protein ladder Precision Plus Protein™ Standards (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Figure 9.
Antibacterial activity of LysSte134_1 against S. aureus CEMTC 1685 (A) and S. epidermidis СEMTC 2043. LysSte134_1 (100 µg/ml) was added to staphylococcal cells with or without CaCl2, MgSO4, ZnCl2, or NiSO4 and the obtained suspensions were incubated for two hours before viable colonies counting. Cell cultures with only CaCl2, MgSO4, ZnCl2, or NiSO4 were used as controls. Experiments were performed in triplicate. *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05.
Figure 9.
Antibacterial activity of LysSte134_1 against S. aureus CEMTC 1685 (A) and S. epidermidis СEMTC 2043. LysSte134_1 (100 µg/ml) was added to staphylococcal cells with or without CaCl2, MgSO4, ZnCl2, or NiSO4 and the obtained suspensions were incubated for two hours before viable colonies counting. Cell cultures with only CaCl2, MgSO4, ZnCl2, or NiSO4 were used as controls. Experiments were performed in triplicate. *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05.
Figure 10.
LysSte134_1 activity against biofilms that were formed by S. epidermidis CEMTC 2043 and S. aureus CEMTC 1685. Bacterial cells were stained with methylene blue.
Figure 10.
LysSte134_1 activity against biofilms that were formed by S. epidermidis CEMTC 2043 and S. aureus CEMTC 1685. Bacterial cells were stained with methylene blue.
Table 1.
Primers used for cloning and sequencing.
Table 1.
Primers used for cloning and sequencing.
| Primer title |
Primer sequence |
| endolysin_StE134_1U |
5`-GGGAACCATGGGAATGAAAAATATTTATTCAAACCACATTAAAGG-3` |
| endolysin_StE134_1L |
5`-GGGATGGATCCGTCAACCTCCAATTTTCCCCAAAGA-3` |
| endolysin_StE134_2U |
5`-CCGAATCATGAATGATAAAGAAAAAATTGACAAGTTTATACAT-3` |
| endolysin_StE134_2L |
5`-CCCAAGGATCCCTTAATACCACTAAAAAACATAATATTATCCCCTG-3` |
| pQE60-SeqU |
5’ - GATTCAATTGTGAGCGGATAAC-3` |
| pQE60_SeqL |
5` - ATCCAGATGGAGTTCTGAGGTC-3` |
Table 2.
Staphylococcus strains tested for their sensitivity to the St_134 phage.
Table 2.
Staphylococcus strains tested for their sensitivity to the St_134 phage.
| № |
Species |
Number of tested strains |
Number of strains sensitive to St_134 |
| Coagulase-positive Staphylococcus spp. |
| 1 |
S. aureus |
178 |
0 |
| 2 |
S. aureus complex (S. roterodami/S. argenteus)
|
1 |
1 |
| 3 |
S. intermedius |
25 |
0 |
| Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. |
| 4 |
S. epidermidis |
136 |
37 (27.2%) |
| 5 |
S. auricularis |
5 |
1 |
| 6 |
S. borealis |
2 |
0 |
| 7 |
S. capitis |
4 |
4 |
| 8 |
S. caprae |
5 |
5 |
| 9 |
S. carnosus |
2 |
0 |
| 10 |
S. casei |
2 |
2 |
| 11 |
S. coagulans |
8 |
1 |
| 12 |
S. cohnii |
5 |
2 |
| 13 |
S. devriesei |
4 |
1 |
| 14 |
S. equorum |
4 |
2 |
| 15 |
S. felis |
6 |
0 |
| 16 |
S. haemolyticus |
28 |
3 (10.7%) |
| 17 |
S. hominis |
22 |
0 |
| 18 |
S. lugdunensis |
2 |
2 |
| 19 |
S. pasteuri |
1 |
0 |
| 20 |
S. saprophyticus |
2 |
0 |
| 21 |
S. simulans |
8 |
0 |
| 22 |
S. succinus |
1 |
0 |
| 23 |
S. ureilyticus |
1 |
1 |
| 24 |
S. warneri |
9 |
0 |
| |
Total |
461 |
62 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).