Submitted:
19 December 2023
Posted:
20 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Highlights
- MAPK are decisive for neuro-immunological interaction and synapses
- Imbalance of MAPK pathways disrupts neuronal immune-homeostasis
- Readjusting MAPKinome improves immuno-epigenetic response
- MAPK based clinical trials offer therapeutic advantage for AD
Introduction
Alzheimer’s Disease: Progressive Neurodegenerative Ailment
Beta Amyloid Specific Interventions for AD
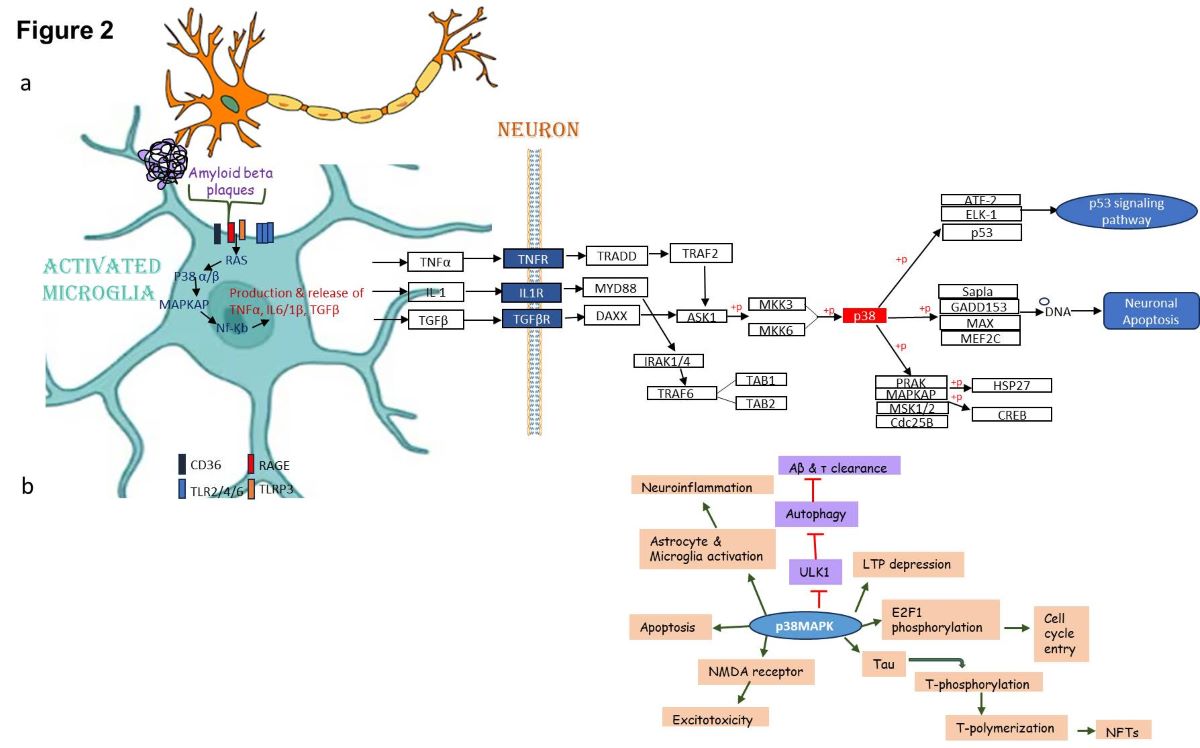
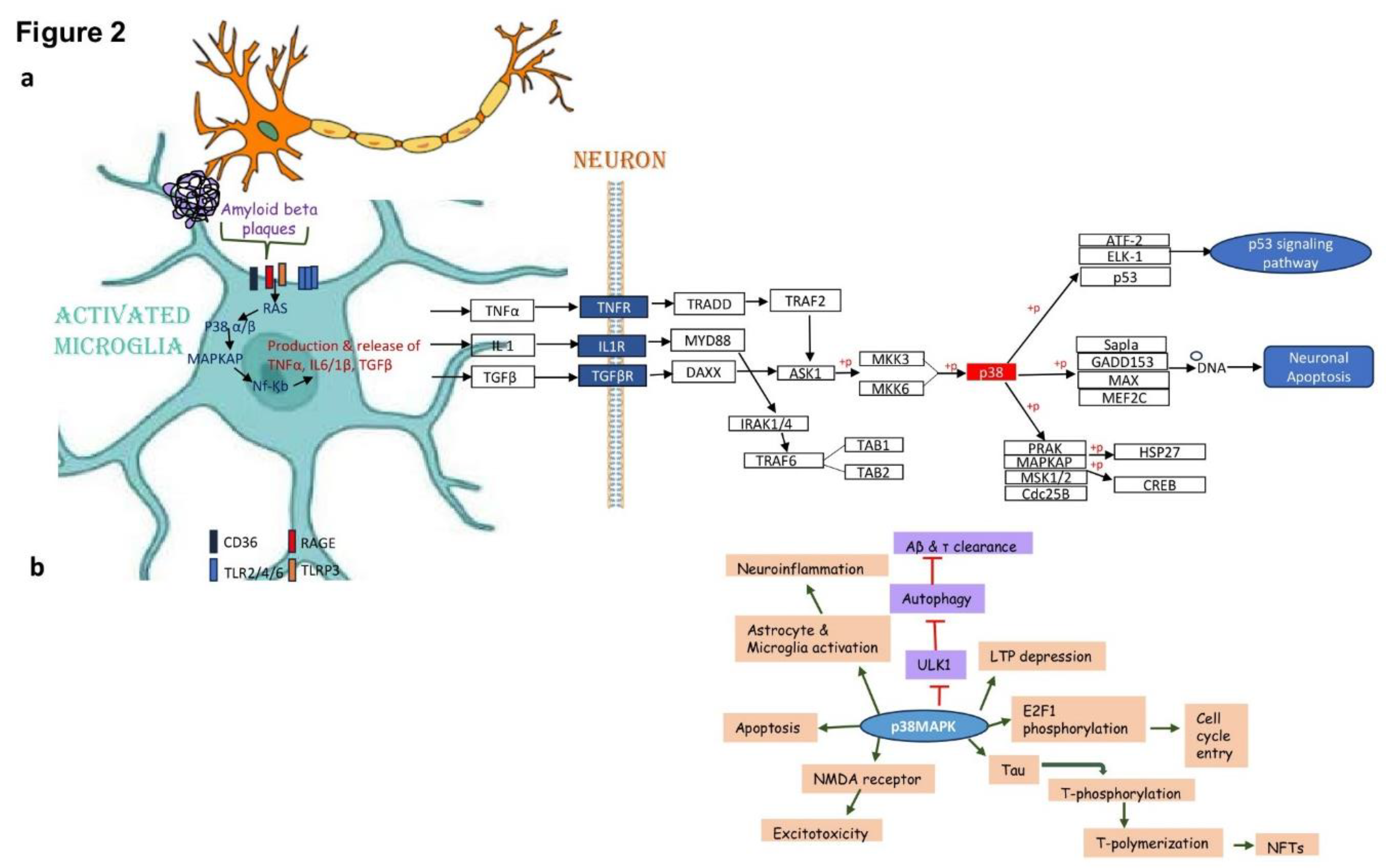
MAPK Based Intervention of Alzheimer Diseases
Redefining New Strategies for Managing AD
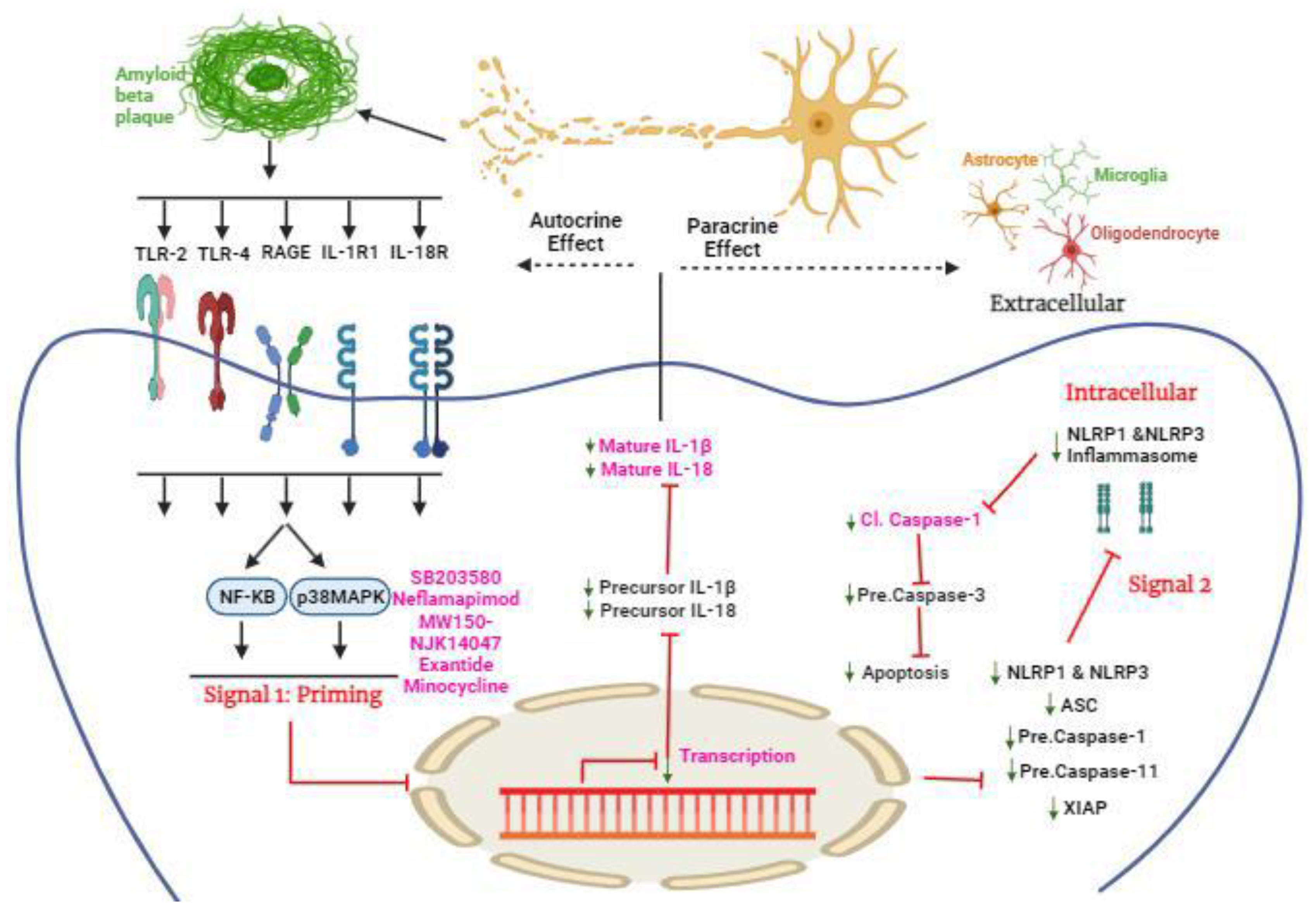
p38 inhibitors
Neflamapimod
SB203580
MW150-
NJK14047-
Exantide
Minocycline
Limitations/Bottlenecks
Conclusions
Abbreviation
| MAPK | Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| TNFR | Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor |
| IL1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL1R | Interleukin-1 Receptor |
| TGFβ | Transforming Growth Factor-Beta |
| TGFβR | Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Receptor |
| TRADD | TNFR1-Associated Death Domain Protein |
| MYD88 | Myeloid Differentiation Factor 88 |
| DAXX | Death Domain Associated Protein |
| TRAF | TNF Receptor-Associated Factor |
| ASK1 | Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1 |
| IRAK | Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase |
| MKK | Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Kinase |
| TAB | Transforming Growth Factor Beta-Activated Kinase 1-Binding Protein |
| CDC25B | Cell Division Cycle 25B |
| ATF | Activating Transcription Factor |
| ELK | ETS Like-1 Protein |
| SAPLA | Regulatory Subunit of Serine/Threonine-Protein Phosphotase 6 |
| GADD | Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-Inducible Protein |
| MAX | MYC Associated Factor X |
| MEF2C | Myocyte-Specific Enhancer Factor 2C |
| TLR | Toll-Like Receptors |
| RAGE | Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts |
| NF-KB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| XIAP | X-Linked inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein |
| ASC | Apoptosis-Associated Speck-Like Protein |
| NLRP1/3 | NLR Family Pyrin Domain Containing 1/3 |
| 5XFAD | Familiar Alzheimer Disease Mice Bear 5 AD-Linked Mutation |
References
- Cano, M.; Guerrero-Castilla, A.; Nabavi, S.M.; Ayala, A.; Argüelles, S. Targeting pro-senescence mitogen activated protein kinase (Mapk) enzymes with bioactive natural compounds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Wang, S.; Bowden, N.; Martin, J.; Head, R. Repurposing existing therapeutics, its importance in oncology drug development: Kinases as a potential target. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannaiyan, R.; Mahadevan, D. A comprehensive review of protein kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 18, 1249–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Zulfiqar, A.; Arguelles, S.; Rasekhian, M.; Silva, A.S.; Nabavi, S.M. Map kinase signaling as therapeutic target for neurodegeneration. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxford, A.E.; Stewart, E.S.; Rohn, T.T. Clinical Trials in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Hurdle in the Path of Remedy. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.H.; Lee, N.-R.; Gee, M.S.; Song, C.W.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.-K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kil Lee, J.; Inn, K.-S.; et al. Chemical Knockdown of Phosphorylated p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) as a Novel Approach for the Treatment of Alzheimer′s Disease. ACS Central Sci. 2023, 9, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcicchia, C.; Tozzi, F.; Arancio, O.; Watterson, D.M.; Origlia, N. Involvement of p38 MAPK in Synaptic Function and Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, S.; Sajadimajd, S.; Alaei, L.; Soheilikhah, Z.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Bahrami, G. Targeting Common Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Stroke and Alzheimer’s: a Comprehensive Review. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 1589–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, P.; Chakrabarti, S.; Goel, K.; Bhutani, K.; Chopra, T.; Bali, S. Neuronal cell death mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease: An insight. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 937133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.H.; Nagao, T.; Gouras, G.K. Plaque formation and the intraneuronal accumulation of β-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Pathology international 2017, 67, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kril, J.J.; Patel, S.; Harding, A.J.; Halliday, G.M. Neuron loss from the hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease exceeds extracellular neurofibrillary tangle formation. Acta neuropathologica 2002, 103, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, C.E.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I.; Gutierrez, A.; Moruno-Manchon, J.F.; McCullough, L.D. Age-related immune alterations and cerebrovascular inflammation. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.-Z.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, H.-Y.; Li, F.-J.; Xu, S.-G.; Gao, L.-C. The Role of Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease From the Perspective of Immune Inflammation and Iron Metabolism. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 888989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastira, I.; Bernhart, E.; Joshi, L.; Koyani, C.N.; Strohmaier, H.; Reicher, H.; Malle, E.; Sattler, W. MAPK signaling determines lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-induced inflammation in microglia. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2023. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions 2023, 9, e12385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.-J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Molecular Basis of Disease 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagiani, F.; Lanni, C.; Racchi, M.; Govoni, S. Targeting dementias through cancer kinases inhibition. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions 2020, 6, e12044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachstetter, A.D.; Van Eldik, L.J. The p38 MAP Kinase Family as Regulators of Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in Degenerative Diseases of the CNS. Aging Dis 2010, 1, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Germann, U.A.; Alam, J.J. P38α MAPK Signaling—A Robust Therapeutic Target for Rab5-Mediated Neurodegenerative Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origlia, N.; Bonadonna, C.; Rosellini, A.; Leznik, E.; Arancio, O.; Yan, S.S.; Domenici, L. Microglial Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Product-Dependent Signal Pathway Drives β-Amyloid-Induced Synaptic Depression and Long-Term Depression Impairment in Entorhinal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11414–11425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, G.R.; Ryou, M.-G.; Poteet, E.; Wen, Y.; He, R.; Sun, F.; Yuan, F.; Jin, K.; Yang, S.-H. Involvement of p38 MAPK in reactive astrogliosis induced by ischemic stroke. Brain Res. 2014, 1551, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, N.-F.; Chien, L.-N.; Ku, H.-L.; Hu, C.-J.; Chiou, H.-Y. Alzheimer disease and risk of stroke: a population-based cohort study. Neurology 2013, 80, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fann, D. Y.-W. et al. Evidence that NF-κB and MAPK signaling promotes NLRP inflammasome activation in neurons following ischemic stroke. Molecular neurobiology 2018, 55, 1082–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colié, S.; Sarroca, S.; Palenzuela, R.; Garcia, I.; Matheu, A.; Corpas, R.; Dotti, C.G.; Esteban, J.A.; Sanfeliu, C.; Nebreda, A.R. Neuronal p38α mediates synaptic and cognitive dysfunction in an Alzheimer’s mouse model by controlling β-amyloid production. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep45306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P. An exploratory clinical study of p38α kinase inhibition in Alzheimer’s disease. Annals of clinical and translational neurology 2018, 5, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, S.K.; Dobrikova, E.Y.; Shveygert, M.; Gromeier, M. p38α Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Depletion and Repression of Signal Transduction to Translation Machinery by miR-124 and -128 in Neurons. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, J.; Dou, J.; She, H.; Tao, K.; Xu, H.; Yang, Q.; Mao, Z. Phosphorylation of LAMP2A by p38 MAPK couples ER stress to chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Z.A.; Zhao, D.; Hussain, T.; Yang, L. The Role of Unfolded Protein Response and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Neurodegenerative Diseases with Special Focus on Prion Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, K.L.; Snider, B.; Mills, S.L.; Buckles, V.D.; Santacruz, A.M.; Bateman, R.J.; Morris, J.C. Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network: facilitating research and clinical trials. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2013, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph-Mathurin, N.; Llibre-Guerra, J.J.; Li, Y.; McCullough, A.A.; Hofmann, C.; Wojtowicz, J.; Park, E.; Wang, G.; Preboske, G.M.; Wang, Q.; et al. Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities in the DIAN-TU-001 Trial of Gantenerumab and Solanezumab: Lessons from a Trial in Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 92, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberlein, S.B.; Aisen, P.; Barkhof, F.; Chalkias, S.; Chen, T.; Cohen, S.; Dent, G.; Hansson, O.; Harrison, K.; von Hehn, C.; et al. Two Randomized Phase 3 Studies of Aducanumab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 9, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, J.; Blackburn, K.; Patrick, D. Neflamapimod: Clinical Phase 2b-Ready Oral Small Molecule Inhibitor of p38α to Reverse Synaptic Dysfunction in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis 2017, 4, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; Prins, N.; Lammertsma, A.; Yaqub, M.; Gouw, A.; Wink, A.M.; Chu, H.; van Berckel, B.N.M.; Alam, J. An exploratory clinical study of p38α kinase inhibition in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcicchia, C.; Tozzi, F.; Arancio, O.; Watterson, D.M.; Origlia, N. Involvement of p38 MAPK in Synaptic Function and Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-W.; Pan, Y.-Q.; Tang, M.-M.; Lin, W.-J. Blocking p38 Signaling Reduces the Activation of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines and the Phosphorylation of p38 in the Habenula and Reverses Depressive-Like Behaviors Induced by Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Imachi, H.; Yoshimoto, T.; Fukunaga, K.; Sato, S.; Ibata, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Dong, T.; Yonezaki, K.; Yamaji, N.; et al. SB 203580 is a specific inhibitor of a MAP kinase homologue which is stimulated by cellular stresses and interleukin-1. FEBS Lett. 1995, 364, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-W.; Pan, Y.-Q.; Tang, M.-M.; Lin, W.-J. Blocking p38 Signaling Reduces the Activation of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines and the Phosphorylation of p38 in the Habenula and Reverses Depressive-Like Behaviors Induced by Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Bachstetter, A.D.; Späni, C.B.; Roy, S.M.; Watterson, D.M.; Van Eldik, L.J. Retention of normal glia function by an isoform-selective protein kinase inhibitor drug candidate that modulates cytokine production and cognitive outcomes. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutigliano, G.; Stazi, M.; Arancio, O.; Watterson, D.M.; Origlia, N. An isoform-selective p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor rescues early entorhinal cortex dysfunctions in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 70, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, M.S.; Son, S.H.; Jeon, S.H.; Do, J.; Kim, N.; Ju, Y.-J.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, E.K.; Inn, K.-S.; Kim, N.-J.; et al. A selective p38α/β MAPK inhibitor alleviates neuropathology and cognitive impairment, and modulates microglia function in 5XFAD mouse. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, M.S.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, M.S.; Jin, H.K.; Bae, J.-S.; Inn, K.-S.; Kim, N.-J.; Kil Lee, J. A Novel and Selective p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibitor Attenuates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation in BV2 Microglia and a Mouse Model. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 2362–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.; Ke, S.; Liu, L.; Pan, X.; Chen, Z. Exenatide alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction and cognitive impairment in the 5×FAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 370, 111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liao, X.-X.; Liu, W.; Guo, R.-X.; Wu, Z.-Z.; Zhao, C.-M.; Chen, P.-X.; Feng, J.-Q. A novel role of minocycline: Attenuating morphine antinociceptive tolerance by inhibition of p38 MAPK in the activated spinal microglia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chico, L.K.; Van Eldik, L.J.; Watterson, D.M. Targeting protein kinases in central nervous system disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 892–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohyagi, Y. Intracellular Aβ42 activates p53 promoter: a pathway to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. The FASEB Journal 2005, 19, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Monte, S., Sohn, Y. K., Ganju, N. & Wands, J. R. P53-and CD95-associated apoptosis in neurodegenerative diseases. Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical methods and pathology 1998, 78, 401–411. [Google Scholar]
- Cenini, G.; Sultana, R.; Memo, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Elevated levels of pro-apoptotic p53 and its oxidative modification by the lipid peroxidation product, HNE, in brain from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2008, 12, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NCT | Agent | Study title | Status/result | Target | Phase | study summary | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00890890 | Avagacestat | A Multicenter, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled, Safety and Tolerability Study of BMS-708163 in Patients With Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease | Terminated/ No | Gamma secretase inhibitor | II | The purpose of this study is to determine the safety and tolerability of BMS-708163 in patients with Prodromal Alzheimer’s disease over a treatment period of a minimum of 104- weeks. In addition patients will be seen for safety visits at 4 and 12 weeks post treatment. | Safety and tolerability of BMS-708163 in patients with Prodromal Alzheimer’s disease as measured by adverse events, vital signs, laboratory assessments, electrocardiograms (ECGs) and Safety Head Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings, Every 12 weeks up to week 220| |
| NCT00810147 | BMS-708163 | A Phase II, Multicenter, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Safety, Tolerability Study of BMS-708163 in Patients With Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease | Completed/No | 2 | The purpose of this study is to determine the safety and tolerability of BMS-708163 in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease over a treatment period of 12-weeks and the course of any potential effects during a 12-week wash-out period |
Adverse Events | |
| NCT01039194 | BMS-708163 | Drug-Drug Interaction to Study the Effect of BMS-708163 on Pharmacokinetics (PK) of Galantamine Extended Release (ER) |
Completed/No | 1 | The purpose of the study is to find out if the plasma concentration of galantamine extended release is changed when BMS-708163 is administered at the same time. |
Safety and tolerability | |
| NCT00726726 | BMS-708163 + Cooperstown Cocktail |
Drug Interaction Study With a Potential Alzheimer’s Disease Compound | Completed/No | 1 | The purpose of this study is to determine whether BMS-708163 will affect the pharmacokinetics of the commonly prescribed medicines midazolam, warfarin, caffeine, omeprazole and dextromethorphan |
Adverse events | |
| NCT01042314 | BMS-708163 | Drug-Drug Interaction Study With Aricept® (Donepezil) | Completed/No | 1 | The purpose of this study is to find out if the plasma concentration of donepezil is changed when BMS-708163 is administered at the same time |
Safety and tolerability | |
| NCT01079819 | BMS-708163 | Study to Evaluate the Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of BMS-708163 | Completed/No | 1 | The purpose of the study is to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of BMS-708163 administered as single and multiple doses in Chinese subjects |
Adverse events | |
| NCT01035138 | Semagacestat | A Study of Semagacestat for Alzheimer’s Patients | Completed/ yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 3 | The primary objective of the original study was to assess the safety of semagacestat in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients during 24 months of open-label treatment. Baseline for the efficacy measures is defined as the baseline for feeder studies LFAN (NCT00594568) and LFBC (NCT00762411). For all safety analyses (adverse events), baseline for patients will be week 0 of this study (LFBF). | semagacestat did not slow disease progression and was associated with worsening of clinical measures of cognition and the ability to perform activities of daily living. |
| Preliminary results from LFAN and LFBC showed Study drug was stopped in all studies. Very few participants from LFBC rolled over into LFBF (N = 9). Due to insufficient sample size, the data for LFBC participants who rolled into LFBF were not analyzed. | |||||||
| NCT00663026 | Bapineuzuma b | Study Evaluating Bapineuzumab In Alzheimer Disease Subjects | Completed/ yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 2 | The study will evaluate the safety and effectiveness of bapineuzumab for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer disease. Subjects will be in the study for six months and will receive subcutaneous injections once per week. |
Adverse events and serious adverse events. |
| NCT00676143 | Bapineuzuma b | Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Bapineuzumab in Alzheimer Disease Patients | Terminated / yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 3 | This is a study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of multiple doses of bapineuzumab in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease. Patients will receive either bapineuzumab or placebo. Each patient’s participation will last approximately 1.5 years. | Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale- Cognitive (ADAS-Cog)/11 Subscale Total Score at Week 78, |
| NCT00996918 | Bapineuzuma b | A Long-Term Safety And Tolerability Study Of Bapineuzumab In Alzheimer Disease Patients | Terminated / yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 3 | The purpose of this study is to assess the long- term safety and tolerability of bapineuzumab in subjects with Alzheimer Disease who participated in study 3133K1-3000 (NCT00667810). Over 250 sites will participate in over 26 countries. Subjects will receive bapineuzumab. Each subject’s participation will last approximately 4 years. |
Adverse events |
| NCT03639987 | Aducanumab | A Study of Aducanumab in Participants With Mild Cognitive |
Terminated/ yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
2 | The primary objective of the study is to assess the safety impact of continuing aducanumab |
Number of Participants with Clinically Impactful Amyloid-related Imaging |
| NCT02484547 | Aducanumab | 221AD302 Phase 3 Study of Aducanumab (BIIB037) in Early |
Terminated/ yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
3 | The primary objective of the study is to evaluate the efficacy of monthly doses of |
Change From Baseline in Clinical Dementia Rating Scale - Sum of Boxes |
| NCT02477800 | Aducanumab | 221AD301 Phase 3 Study of Aducanumab (BIIB037) in Early |
Terminated/ yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
3 | The primary objective of the study is to evaluate the efficacy of monthly doses of |
Change From Baseline in Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes (CDR- |
| NCT05108922 | Aducanumab | A Study of Donanemab (LY3002813) Compared With Aducanumab in |
Active not recruiting/ No |
Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
3 | The main purpose of this study is to compare donanemab to aducanumab on amyloid plaque |
|
| NCT01677572 | Aducanumab | Multiple Dose Study of Aducanumab (BIIB037) (Recombinant, Fully |
TERMINATED/ No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
1 | The primary objective of this study is to evaluate the safety and tolerability of multiple |
Number of Participants with Adverse Events, Baseline to week 518 |
| NCT01397539 | Aducanumab | Single Ascending Dose Study of BIIB037 in Participants With |
COMPLETED/ No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
1 | The primary objective of the study is to evaluate the safety and tolerability of a range |
Number of Participants with Adverse Events as a Measure of Safety and |
| NCT05310071 | Aducanumab | A Study to Verify the Clinical Benefit of Aducanumab in Participants With |
RECRUITING/ No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
3 | The primary objective of this study is to verify the clinical benefit of monthly doses of |
Change From Baseline in CDR-SB Score at Week 78, impairment. Positive |
| NCT02782975 | Aducanumab | Absolute Bioavailability of a Single, Fixed Subcutaneous Dose of |
COMPLETED/ No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
1 | The primary objectives of this study are to evaluate the absolute bioavailability of a single, |
PK parameter of SC dose of aducanumab: Absolute Bioavailability, |
| NCT04241068 | Aducanumab | A Study to Evaluate Safety and Tolerability of Aducanumab in participants With Alzheimer’s |
ACTIVE_NOT_RECR UITING/ No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers |
3 | The primary objective is to evaluate the safety and tolerability of aducanumab over 100 weeks of treatment after a wash-out period imposed |
Number of Participants with Adverse Events (AEs) and Serious Adverse Events (SAEs): Number of Participants |
| NCT02434718 | Aducanumab | Single and Multiple Ascending Dose Study of Aducanumab (BIIB037) in Japanese Participants With Alzheimer’s Disease | COMPLETED/ No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 1 | The primary objective of the study is to evaluate the safety and tolerability of single and multiple intravenous (IV) infusions of Aducanumab in Japanese participants with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). The secondary objectives of this study are as follows: To evaluate the serum pharmacokinetics (PK) of Aducanumab after single and multiple intravenous (IV) infusions of Aducanumab; To evaluate the effect of single and multiple IV infusions of Aducanumab on immunogenicity. |
Incidence and nature of adverse events (AE) / serious adverse events(SAE), Up to week 42 abnormalities in neurological and physical examinations, Up to week 42|Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings to assess amyloid- related imaging abnormalities (ARIA), including incidence of ARIA-E (edema) or ARIA-H (hemosiderosis), Up to week 42 |
| NCT01767311 | Lecanemab | A Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Lecanemab in Subjects With Early Alzheimer’s Disease | Active not | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 2 | This is a multinational, multicenter, double- blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study using a Bayesian design with response adaptive randomization across placebo or 5 active arms of lecanemab to determine clinical efficacy and to explore the dose response of lecanemab using a composite clinical score (ADCOMS). | adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs) |
| Recruiting/No | |||||||
| NCT03887455 | Lecanemab | A Study to Confirm Safety and Efficacy of Lecanemab in Participants With Early Alzheimer’s Disease | Active_not_recruitin g/ No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 3 | This study will be conducted to evaluate the efficacy of lecanemab in participants with early Alzheimer’s disease (EAD) by determining the superiority of lecanemab compared with placebo on the change from baseline in the Clinical Dementia Rating-Sum of Boxes (CDR- SB) at 18 months of treatment in the Core Study. This study will also evaluate the long- term safety and tolerability of lecanemab in participants with EAD in the Extension Phase and whether the long-term effects of lecanemab as measured by the CDR-SB at the end of the Core Study is maintained over time in the Extension Phase. | Adverse event that emerges during treatment or within 30 days of the last dose of study drug. Worsens in severity during treatment relative to the pretreatment state, when the adverse event was continuous |
| NCT04468659 | Lecanemab | AHEAD 3-45 Study: A Study to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of Treatment With Lecanemab in Participants With Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease and Elevated Amyloid and Also in Participants With Early Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease and Intermediate Amyloid | Recruiting/No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 3 | The primary purpose of this study is to determine whether treatment with lecanemab is superior to placebo on change from baseline of the PACC5 at 216 weeks of treatment (A45 Trial) and to determine whether treatment with lecanemab is superior to placebo in reducing brain amyloid accumulation as measured by amyloid (PET) at 216 weeks of treatment (A3 Trial). |
Preclinical Alzheimer Cognitive Composite 5 (PACC5) Score at Week 216 |
| NCT05738486 | Donanemab | A Study of Different Donanemab (LY3002813) Dosing Regimens in Adults With Early Alzheimer’s Disease (TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 6) | RECRUITING/No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | This study will investigate different donanemab dosing regimens and their effect on the frequency and severity of ARIA-E in adults with early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and explore participant characteristics that might predict risk of ARIA. | Percentage of Participants with Any Occurence of Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormality-Edema/Effusion (ARIA-E), 24 Weeks | |
| NCT05108922 | Donanemab | A Study of Donanemab (LY3002813) Compared With Aducanumab in Participants With Early Symptomatic Alzheimer’s Disease (TRAILBLAZER- ALZ 4) |
ACTIVE_NOT_RECR UITING/No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | The main purpose of this study is to compare donanemab to aducanumab on amyloid plaque clearance in participants with early symptomatic Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). | ||
| NCT05508789 | Donanemab | A Study of Donanemab (LY3002813) in Participants With Early Symptomatic Alzheimer’s Disease (TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 5) | RECRUITING/No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | The reason for this study is to assess the safety and efficacy of donanemab in participants with early Alzheimer’s disease. The study duration including screening and follow-up is up to 93 weeks. |
Change from Baseline on the Integrated Alzheimer’s Disease Rating Scale (iADRS), Change from Baseline on the iADRS in at least one of ’the low medium tau pathology population or |
|
| NCT05026866 | Donanemab | A Donanemab (LY3002813) Prevention Study in Participants With Alzheimer’s Disease (TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 3) | RECRUITING/No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of donanemab in participants with preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). | Time to clinical progression as measured by Clinical Dementia Rating Global Score (CDR-GS), participant’s stage on the spectrum of AD dementia., Estimated Up to Week 182 | |
| NCT04640077 | Donanemab | A Follow-On Study of Donanemab (LY3002813) With Video Assessments in Participants With Alzheimer’s Disease (TRAILBLAZER- EXT) | ACTIVE_NOT_RECR UITING/No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | The main goals of this study are to further determine whether the study drug donanemab is safe and effective in participants with Alzheimer’s disease and to validate video scale assessments. | Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale Cognitive Subscale (ADAS-Cog13). A summary of serious and other non- serious adverse events regardless of causality is located in the Reported Adverse Events module., Up to 72 Weeks | |
| NCT04437511 | Donanemab | A Study of Donanemab (LY3002813) in Participants With Early Alzheimer’s Disease (TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2) | ACTIVE_NOT_RECR UITING/No | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | The reason for this study is to see how safe and effective the study drug donanemab is in participants with early Alzheimer’s disease. | Change from Baseline on the integrated Alzheimer’s Disease Rating Scale (iADRS), Change from Baseline on the iADRS in participants with early symptomatic AD in at least one of ’the low-medium tau pathology population or the overall population’., Baseline, Up to Week 76 | |
| Additional participants will be enrolled to an addendum safety cohort. The participants will be administered open-label donanemab. | |||||||
| NCT01224106 | Ganteneruma b |
A Study of Gantenerumab in Participants With Prodromal |
Completed/Yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ |
3 | This multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel-group study. |
Adverse Events (AEs) or Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) |
| NCT02051608 | Ganteneruma b | A Study of Gantenerumab in Participants With Mild Alzheimer Disease | Completed/Yes | Monoclonal antibodies to Aβ or its oligomers or fibrils | 3 | Part 1 is a multicenter, randomized, double- blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study will evaluate the efficacy and safety of gantenerumab in participants with mild Alzheimer disease. Participants will be randomized to receive either gantenerumab subcutaneously every 4 weeks or placebo subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Approved Alzheimer medication is allowed if on stable dose for 3 months prior to screening. Part 2 is an open-label extension (OLE). | Adverse Events (AEs) or Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) |
| NCT01998841 | Crenezumab | Completed/Yes | 2 | Study evaluates the efficacy and safety of Crenezumab versus Placebo in participants who carry the PSEN1 E280A autosomal- dominant mutation and do not meet the criteria for mild cognitive impairment due to AD or dementia due to AD and are thus, in a preclinical phase of AD. |
Adverse Events (AEs) and Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) | ||
| NCT01723826 | Crenezumab | Completed/Yes | 2 | study will evaluate the long-term safety and tolerability of crenezumab in participants with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease who have participated in and completed the treatment period of the Phase II Study ABE4869g (NCT01343966) or ABE4955g (NCT01397578). Participants who received placebo in Study ABE4869g (NCT01343966) or ABE4955g (NCT01397578) will receive crenezumab. Anticipated time on study treatment is 144 weeks. |
Adverse Events (AEs) | ||
| NCT02760602 | Solanezumab | A Study of Solanezumab (LY2062430) in Participants With Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease | Terminated/yes | 3 | The main purpose of this study is to investigate the safety and efficacy of the study drug solanezumab in participants with prodromal Alzheimer’s disease (AD). |
Alzheimer´s Disease Assessment Scale- Cognitive Subscale (ADAS- Cog14) Score | |
| NCT01900665 | Solanezumab | Progress of Mild Alzheimer’s Disease in Participants on Solanezumab Versus Placebo | Terminated/yes | 3 | To test the idea that solanezumab will slow the cognitive decline of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) as compared with placebo in participants with mild AD. |
ADAS-Cog14 | |
| NCT01127633 | Solanezumab | Continued Safety Monitoring of Solanezumab (LY2062430) in Alzheimer’s Disease | Terminated/yes | 3 | This study is an open-label extension study in Alzheimer’s patients who have completed participation in either solanezumab Clinical Trial H8A-MC-LZAM (NCT00905372) or H8A-MC LZAN (NCT00904683). | A summary of serious and other non- serious adverse events regardless of causality is located in the Reported Adverse Events module., Baseline through Week 104 | |
| NCT01739348 | Verubecestat | An Efficacy and Safety Trial of Verubecestat (MK-8931) in Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease (P07738) |
Terminated/yes | BACE1 inhibitor | 02-Mar | This study assesses the efficacy and safety of verubecestat (MK-8931) compared with placebo administered for 78 weeks in the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). |
ADAS-Cog11 |
| NCT01953601 | Verubecestat | Efficacy and Safety Trial of Verubecestat (MK-8931) in Participants With Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease (MK-8931-019) | Terminated/yes | 3 | The study assesses the efficacy and safety of verubecestat (MK-8931) compared with placebo administered for 104 weeks in the treatment of amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) due to Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), also known as prodromal AD. |
Adverse events | |
| NCT02910739 | Verubecestat | An Open-Label Study Investigating MK-8931 in Participants With Mild and Moderate Hepatic Insufficiency (MK-8931-016) | Complete/yes | 1 | The purpose of this study is to compare the plasma pharmacokinetics of verubecestat (MK- 8931) following administration of a single oral dose of 40 mg MK-8931 to participants with moderate hepatic insufficiency (HI) to that of healthy matched controls. | ||
| NCT02569398 | Atabecestat | An Efficacy and Safety Study of Atabecestat in Participants Who Are Asymptomatic at Risk for Developing Alzheimer’s Dementia | Terminated/No | 2/3 | The purpose of this study is to evaluate whether treatment with atabecestat slows cognitive decline compared with placebo treatment, as measured by a composite cognitive measure, the Preclinical Alzheimer Cognitive Composite (PACC), in amyloid- positive participants who are asymptomatic at risk for developing Alzheimer’s dementia. |
||
| NCT02972658 | Lanabecestat | A Study of Lanabecestat (LY3314814) in Early Alzheimer’s Disease |
Terminated/Yes | 3 | This study is an extension of study I8D-MC- AZES (NCT02245737), the AMARANTH study. |
ADAS-Cog13 | |
| NCT02783573 | Lanabecestat | A Study of Lanabecestat (LY3314814) in Participants With Mild Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia | Terminated/Yes | 3 | The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of the study drug known as lanabecestat in participants with mild Alzheimer’s disease (AD) dementia. |
ADAS-Cog13 | |
| NCT02245737 | Lanabecestat | An Efficacy and Safety Study of Lanabecestat (LY3314814) in Early Alzheimer’s Disease | Terminated/Yes | 2/3 | The purpose of this study is to assess the efficacy and safety of lanabecestat compared with placebo administered for 104 weeks in the treatment of early Alzheimer´s disease. | ADAS-Cog13 |
| DRUG | PHASE | TARGET | No of participant |
duration | OUTCOME |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibits the activation of microglia | |||||
| Masatinib | 3 | TKI | 600 | 24 weeks | Recovered spetial learning performance and synaptic markers (10) |
| AL002 | 2 | TREM 2Antibody | 265 | 96 weeks | Diminished dystrophic neurites, lowered filamentous Aβ plaques, and encouraged microglia activation and Aβ phagocytosis |
| Monoclonal IgG1 antibody | |||||
| NE3107 | 3 | NFkB/ERK/ MAPK pw inhibitor | 316 | 30 weeks | Decreasing hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and mediation of insulin resistance (12) |
| BCG | 2 | Immunomodulator | 15 | 364 days | BCG vaccination prevented cognitive impairment, raised circulating IFNγ, attracted macrophages to cerebral Aβ plaques, and boosted cerebral anti-inflammatory cytokines in a transgenic mouse model of AD (17) |
| Semaglutide | 3 | GLP-1 agonist | 1840 | 173 weeks | Anti-inflammatory in AD (cummings) |
| Baricitinib | 1-2 | JAK STAT inhibitor | 20 | 24 weeks | CSF concs of basatinib, CCL2 |
| Canakimumab | 2 | Anti-interlukin 1b antibody | 90 | 24 weeks | Change in NTB total score |
| Daratumumab | 2 | Anti-CD38 antibody | 15 | 24 weeks | ADAS-cog11 |
| Dasatinib+quercetin | 2 | SER kinase inhibitor and upregulator of SIRT1 and senolytics |
48 | 48 weeks | Adverse/serious events |
| 20 | 11 weeks | Safety and tolerability | |||
| 12 | 12 weeks | Neuro vascular, coupling, executive function, Gait speed | |||
| Sagramostim | 2 | Synthetic GM-CSF | 42 | 24 weeks | Adverse events |
| Senicapoc | 2 | KCA3,1 inhibitor | 55 | 52 weeks | ADAS-cog13 scores csf markers |
| Rapamycin | 2 | mTOR Inhibitor | 10-40 | 8weeks/ 12months |
BBB penetration, adverse events, metabolic pannel |
| Proleukin | 2 | Recombinant human interleukin 2 |
45 | 18 months | CDR |
| Pepinemab | 01-Feb | Anti-SEMA4D antibody | 40 | 40 weeks | Adverse events |
| Montelukast | 2 | Leukotriene antagonist | 70 | 26 weeks | Global neuro physiological test battery |
| L-serine | 2 | Reduces inflammation | 40 | 12 months | Cognitive assessment, health check (blood tests), adverse events |
| Lenatidomide | 2 | Proinflammatory cytokines inhibitor |
30 | 18months | ADAS-COG, ADAS-ADL |
| TB006 | 2 | Anti-galactin 3 antibody | 140 | 104 days | Severity of dementia |
| T-Dap vaccine | 01-Feb | immunomodulator | 50 | 6 months | Change in abeta42/40 ratio and tau in plasma |
| Valacyclovir | 2 | HSV antiviral | 120 | 18months | |
| XProl 595 | 2 | s-TNF inhibitor | 201 | 23 weeks | |
| CpG 1018 | 1 | Actives TLR9 | 39 | 18 weeks | Adverse events, rheumatoid factor, anti-nuclear antibody, and anti-neutrophil ab in their blood |
| Emtricitabine | 1 | NRTI for HIV | 35 | 8 months | Adverse events |
| IBC-ab002 | 1 | PD 1 inhibitor | 40 | 48 weeks | Abnormalities in brain, suicidal thoughts, vital signs, significant changes in hematology |
| Salsalate | 1 | P300/CBP inhibitor | 40 | 12 months | Adverse events |
| VT301 | 1 | Regulatory T cells | 12 | 3 | Adverse events |
| SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY DRUGS |
|||||
| Blarcamesine | 02-Mar | Sigma 1/ muscarinic agonist | 500 | 48 weeks | |
| Simufilam | 3 | Binds to filamin to prevent interaction of abeta and A7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor |
750 | 52 weeks | |
| AGB101 | 02-Mar | SB2A INHIBITOR | 164 | 78 weeks | CDRSB |
| Fosgonimeton | 02-Mar | Hepatocyte growth factor/MET activator |
475 | 26 weeks | |
| Bryostatin | 2 | PKC activator | 100 | 30 days | SIB, safety |
| AL001 | 01-Feb | GSK3 beta inhibitor | 72 | 14 days | Safety and toleralibity |
| Tertomotide | 3 | Telomerase RT mimic | 936 | 6 month | Sib, CDRSB |
| CY6463 | 2 | Positive allostreric modulator of guanylate cyclase |
30 | 14 days | Safety and tolerability |
| Endonerpic | 2 | Specific target under defined may be collapsin response mediator protein 2 |
200 | 78 weeks | Change in CSF p Tau 181 |
| Dalzanemdor | 2 | N methyl d aspartate receptor, allosteric modulator |
150 | 84 days | |
| Elayta CT1812 | 2 | Sigma 2receptor antagonist | 450 | 18 months | CDRSB |
| X039 | 2 | Enhance n methyl d aspartate receptor activity |
120 | 28 weeks | |
| ExPlas | 2 | Human plasma with multiple constituents |
60 | 1 year | Adverse events |
| Levetiracetam | 2 | SV2A inhibitor | 85 | 5 months | |
| 65 | 1 year | ||||
| 30 | 4 weeks | Hippocampal function | |||
| MW150 | 2 | MAPK P38alpha inhibitor | 24 | 84 days | Safety measures |
| Neflamapimod | 2 | MAPK P38alpha inhibitor | 40 | 12 Weeks | Brain inflammation by translocator protein tracer |
| Centella asiatica | 1 | Multimiodel herb derives traditional Chinese medicine | 48 | 6 weeks | Brain AA/CR ratio assessed by MR spectroscope |
| Drug | Phase | Study title | Target | NCT | Study status/result | Study summary | Outcome measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neflamapimod | 2 | Proof-of-Concept Study of a Selective p38 MAPK Alpha Inhibitor, Neflamapimod, in Subjects With Mild Alzheimer’s Disease |
P38 MAPK inhibitor |
NCT03402659 | Completed/ yes | This is a phase 2b, double-blind, placebo controlled proof-of-concept study of a an oral small molecule selective inhibitor of p38 alpha kinase, neflamapimod, administered for 24 weeks in subjects with mild Alzheimer’s disease. The primary objective is to demonstrate significant improvement relative to placebo-treatment in episodic memory function, as assessed by the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test. Secondary endpoints include Clinical Dementia Rating scale (CDR), Wechsler Memory Scale (WMS), Mini- Mental-Status-Examination (MMSE) and Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers of AD disease activity and progression. | Total and Delayed Recall on the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test - Revised (HVLT-R), Combined change from baseline in z-scores of total and delayed recall on the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test - Revised (HVLT-R) in neflamapimod-treated subjects compared to placebo. The primary endpoint was analyzed using Mixed Model for Repeated Measures (MMRM) with fixed effects for treatment, background AD- specific therapy, CDR-Global Score of 0.5 versus 1.0, scheduled visit (nominal) and scheduled visit by treatment interaction, random effect for subject and baseline Z-score as a covariate.For baseline total and delayed recall, a z- score for each subject is defined by z=(x-m)/s where x is the subject’s recall at baseline, and m and s are the overall mean and overall standard deviation of recall at baseline across all subjects. A composite baseline z-score for each subject is calculated using equal weighting in the following way: Z=0.5\*z-score for total recall at baseline + 0.5\*z- score for delayed recall at baseline. For HVLT-R, higher score indicates improvement., Baseline and 24 weeks |
| VX-745 | 2 | Clinical Pharmacology of p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitor, VX- 745, in Mild Cognitive Impairment Due to Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) or Mild AD |
P38 MAPK inhibitor |
NCT02423200 | Completed/ yes | This study will assess the effects of VX-745 on markers of disease in the central nervous system of patients with MCI due to AD or with mild AD. The study will also evaluate the safety and tolerability of VX-745 in these patients during 6 weeks of dosing, as well as the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of VX- 745 during dosing. | Percent Change From Baseline to End of Treatment in Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Cytokines, Cytokines: Of nine cytokines assessed, only CSF IL-8 quantifiable at all time points. And so, only IL-8 levels are being reported herein. The analysis was exploratory and no statistical analysis was performed., Baseline and Day 42 of dosing with VX-745 |
| VX-745 | 2 | A PET Study of the Effects of p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitor, VX- 745, on Amyloid Plaque Load in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | P38 MAPK inhibitor |
NCT02423122 | Completed/ yes | This study will assess the effects of administration of VX-745 for 12 weeks on amyloid plaque burden in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Subjects who meet entry criteria will undergo 11C-PiB (Carbon-11-labeled Pittsburgh Compound B) positron emission tomography (PET) at baseline and after 45 days of dosing with VX-745. Cognitive testing will also be conducted at baseline and day 45. | Percent Change From Baseline in Amyloid Plaque Burden by 11C-PiB PET, Percent change in global cortical amyloid specific PET signal (BPND), Baseline compared to following 12 weeks’ dosing with VX-745|Number of 11C-PiB Responders, Number of patients meeting protocol pre- specified definition of response: \> 7% reduction in global cortical BPND, Day 84 |
| Exantide | 2 | A Pilot Clinical Trial of Exendin-4 in Alzheimer’s Disease | P38 MAPK inhibitor |
NCT01255163 | terminated | Researchers were interested in studying the safety and comparing the effects of Exendin-4 with placebo on cognitive performance, clinical progression of dementia, various chemicals measured in blood and cerebrospinal fluid, and brain MRI, in individuals with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease or MCI. Objectives were to determine the safety and tolerability of twice daily administration of Exendin-4, as well as to acquire preliminary evidence for effects on cognitive performance, clinical progression of dementia, various chemicals measured in blood and cerebrospinal fluid, and brain MRI, in individuals with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment. * Eligible participants were divided into two groups (double-blind randomization). One group received Exendin-4 SC twice daily, and the other will received a placebo. Participants kept a medication diary and scheduled for additional study visits 1 and 2 weeks after the start of the treatment. Participants had regular followup visits with blood tests, cognitive tests, imaging studies, and other examinations 6, 12, and 18 months after the start of the treatment. Another lumbar puncture was performed optionally at the 18- month followup visit. | Number of Participants With Incidence of Nausea, Tolerability of exenatide (nausea is the most common expected adverse event of exenatide), 18 months |
| Minocycline | 2 | Minocycline in Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease | P38 MAPK inhibitor |
NCT01463384 | completed | Cognitively normal individuals, patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) or Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) will undergo clinical screening, neuropsychological tests, blood and urine analyses, quantitative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and proton (1H ) and carbon 13 (13C) magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Each individual will receive minocycline oral administration for 4 weeks initially, after which MRI, MRS and neuropsychological results will be recorded. If no adverse side effects occur, subjects will continue minocycline administration for an additional 5 months. | Values are reported below for Baseline, averaged for 1-3 months, and averaged for 4-6 months during minocycline administration., Baseline values, 1-3 Months Values (averaged), 4-6 Months Values (averaged)|Hippocampal Volumes Measured in three Groups: Alzheimer Disease (AD), Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Normal, Age- matched Controls (NC)., Using magnetic resonance images acquired, hippocampal volume was measured monthly for 6 months. Biomarkers NAA/mI Measured in Three Groups: Alzheimer Disease (AD), Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Normal, Age-matched Controls (NC).two biomarkers, N acetylaspartate (NAA, a neuronal marker) and myo-inositol (mI, a glial marker) were quantified and then used to calculate NAA/mI (an index currently widely used for AD and MCI diagnosis). Scale of MRS biomarkers for aged- matched controls: NAA = 1.43, mI = 0.60, NAA/mI = 2.38. Any value lower than NAA/mI of 2.38 are considered not normal. |
| MW150 | 2 | MW150 Stress Kinase Inhibitor in Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease | P38 MAPK inhibitor |
NCT05194163 | Not yet recruiting | This study is a phase 2a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, study, in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease, of the oral investigational drug MW150, a p38alphaMAPK kinase inhibitor. The primary goals of this study are to investigate the safety and tolerability, and drug movements in the body. The secondary goals of the study are to investigate the effects of the drug on cognitive performance, activities of daily living, and behavior, and the biological effects of the drug on blood biomarkers. |
Drug Safety- Blood tests, Number of participants with |
| treatment-related adverse events as assessed by laboratory test abnormalities., 84 days treatment|Drug Safety- Electrocardiographic, Number of participants with emergent abnormal electrocardiograms., 84 days treatment|Drug Safety- C-SSRS, Development of any suicidality on COLUMBIA-SUICIDE SEVERITY RATING SCALE (C-SSRS) score (minimum 0, no maximum, higher number worse)., 84 days treatment|Drug Tolerability- Adverse events, Incidence of adverse events (AE)., 84 days treatment. | |||||||
| Mastinib | 3 | Masitinib in Patients With Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease |
TKI | NCT05564169 | Not yet recruiting/N o | Masitinib is an orally administered tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets activated cells of the neuroimmune system (mast cells and microglia). Study AB21004 will evaluate masitinib as an adjunct to cholinesterase inhibitor and/or memantine in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. | Absolute change from baseline in ADAS-Cog-11 score, Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale - cognitive subscale (ADAS-cog) (scores range from 0 to 70, with higher scores indicating worse dementia), 24 weeks|Absolute change from baseline in ADCS-ADL score, Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Activities of Daily Living Inventory scale (ADCS-ADL) (scores from 0 to 78, with lower scores indicating worse function), 24 weeks |
| Nilotinib | 3 | Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Nilotinib BE in Subjects With Early Alzheimer’s Disease |
TKI | NCT05143528 | Not yet recruiting/N o | This study will investigate the safety and efficacy of a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) called Nilotinib BE (bioequivalent) in individuals with Early Alzheimer’s disease (EAD). This is a multi-center double blinded, Phase 3 study, that will enroll patients for three years in approximately 50 centers nationwide. The total duration of the study will be for five years. | Changes From Baseline in Clinical Dementia Rating Scale - Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB) Score at Week 72 [ Time Frame: Baseline, Week 72], CDR-SB integrates assessments from 3 domains of cognition (memory, orientation, judgment/problem-solving) and 3 domains of function (community affairs, home/hobbies, personal care). Following a systematic patient examination, the rater assigns a score describing the participant’s current performance level in each of these domains of life functioning. Prespecified severity anchors range from none = 0, questionable = 0.5, mild = 1, moderate = 2 to severe = 3 (the personal care domain omits the 0.5 score). "Sum of boxes" scoring methodology sums the score for each of the 6 domains and provides a value ranging from 0 to 18 that can change in increments of 0.5 or greater. Higher scores indicate greater disease severity. A positive change from baseline indicates clinical decline., 72 weeks |
| Bumetanide | 2 | Bumetanide in Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease | NCT06052163 | Not yet recruiting/No | Bumetanide is a potent diuretic administered orally and is FDA approved for the treatment of edema and hypertension. Repurposing bumetanide as a medication for AD has been proposed based on data that demonstrated its ability to "flip" the APOE genotype-dependent transcriptomic signatures in AD mouse and cell culture models. Critically, this discovery was subsequently explored in Electronic Health Record cohorts, which revealed that among individuals over the age of 65, bumetanide exposure was significantly associated with a lower prevalence of AD in three independent datasets. |
Incidence of Treatment-Related Adverse Events, Number of participants with adverse events including clinical signs and symptoms, change in vital signs, ECGs, laboratory safety tests, and suicidality assessments., 6 months |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





