1. Introduction
Comprehensive ocean exploration has emerged as a critical focus, garnering significant attentions within scientific, industrial, and military sectors. Key areas such as safety, weather monitoring, and marine commerce are heavily dependent on an in-depth understanding of the marine environment. Yet, exploring this complex terrain, particularly in deep ocean areas, is fraught with challenges. These include high costs, inherent dangers, and technical difficulties. In response to these challenges, there has been rapid advancement in technologies such as underwater wireless sensing, underwater imaging detection, and the development of both manned and unmanned underwater vehicles. Consequently, the demand for advanced underwater communication technology, capable of high-rate data transmission, has intensified. Such technology is essential for not only transmitting observational data but also for gaining a deeper understanding of the marine environment.
Underwater wireless communication is a pivotal technology in ocean exploration and operations. Electromagnetic wave, typically employed for communication, face significant attenuation in underwater environment due to the high electrical conductivity of seawater. As a result, sound waves have become the prevalent medium for underwater wireless communication. Despite their ability to cover distances of kilometers, acoustic systems are limited by their transmission bandwidth, typically only reaching speeds of a few Kbps. Moreover, the slow propagation speed of sound underwater poses substantial challenges for real-time, high-speed communication [
1]. Further complicating the issue, acoustic communication equipment often suffers from drawbacks such as large size and high energy consumption, which impedes its development and widespread adoption.
In contrast, underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) presents several advantages over traditional radio frequency, acoustic communication, and wired communication methods. UWOC is notable for its higher data transmission rates, lower latency, and greater flexibility [
2,
3,
4]. Capable of covering hundreds of meters and potentially achieving Gbps transmission rates, UWOC holds promising application potential in areas such as high-capacity data transmission in deep-sea environments, remote control and monitoring of underwater robotics, and deep-sea oil and gas exploration [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. These advantages position UWOC as a technology with significant potential for advancing the field of underwater communication.
The transmission of light through seawater channels is significantly influenced by dynamic seawater conditions. During transmission, light absorption reduces the total propagation energy, while scattering caused by water particles leads to increased pulse spread in the time domain of the optical signal [
10]. Additionally, multiple scatterings result in increased geometric loss in communication links [
11] So, the optical signal’s spatial and temporal distribution characteristics show strong randomness [
12]. The high cost of underwater measurements adds to the complexity of accurately modeling and analyzing the optical signal variation in underwater channels, a topic that has garnered global research interests [
13,
14,
15]. Traditional methods, such as the Beer-Lambert law and simple exponential analysis models, fall short in accuracy, particularly when the optical signal propagates in the scattering enhancement area and the random-walk area [
16].
In recent years, the Monte Carlo method has gained popularity for simulating underwater optical signal transmission [
17,
18,
19]. Gabriel C.’s analysis of underwater channel impulse response and time dispersion across various seawater types, link distances, and received apertures indicates that time dispersion is often negligible, reducing the likelihood of inter-symbol interference. The two-term Henyey–Greenstein Function (TTHG) has been employed for more accurate simulation of power distribution on the receiving surface [
20,
21]. Shijian Tang’s application of the Monte Carlo method, coupled with the two-term Gamma Function to represent impulse response curves, demonstrates that the two-term Gamma Function model is effective in scenarios with large attenuation lengths. This approach also suggests that use of equalization can significantly reduce bit error rates in UWOC systems [
22]. Qadar R characterizes the underwater light attenuation and bit error rate by analyzing the photons’ multiple scattering, the results show that the detector aperture and FOV have an effect on underwater communication, and the effect of FOV is more obvious when the detector aperture is larger [
23]. Jianlei Zhang’s extension of the multiple phase screen model integrates turbulence, absorption, and scattering effects into the Monte Carlo simulation framework, facilitating a comprehensive study of these combined effects on underwater channels [
24]. Lastly, Biao Han’s research using the Monte Carlo method explores the impact of backscattering on receivers in duplex UWOC systems [
25]. These diverse studies underscore the complexity and evolving nature of modeling and analyzing optical signals in underwater environments.
The existing literature primarily focuses on the characteristics of underwater optical transmission, including attenuation characteristics, impulse response, communication error rates, and backscattering effects. These studies often compare and analyze light transmission in various types of seawater, such as clear, coastal, and Harbor-II waters [
25,
26,
27]. However, there is a noticeable gap in research concerning the transmission characteristics of light in Harbor water, moreover, in-depth analysis of the transmission characteristics of light in Harbor water is also of great strategic significance for the construction of Global Marine Space-Time Frame Network [
28]. Addressing this gap, our paper utilizes the Monte Carlo method to simulate and analyze the changes in normalized power attenuation and time domain spread characteristics relative to various factors. These factors include attenuation length, transmitted divergence angle, received aperture, and received field of view (FOV) under specified light energy conditions.
The findings from this study are anticipated to be significantly beneficial for the design and development of UWOC systems operating in Harbor water conditions. Additionally, this research offers an accurate and efficient approach for the long-distance simulation of UWOC, potentially advancing the understanding and capabilities in this domain.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The optical parameters of the underwater channel
The interaction between photons and particles within seawater is both frequent and intense. When a laser beam travels through water, its light is absorbed by various elements such as water molecules, phytoplankton, dissolved organic matter, and organic debris. Concurrently, the light undergoes scattering caused by particles suspended in the seawater [
29]. To mathematically describe these effects, two wavelength-dependent optical characteristic parameters are utilized: the absorption coefficient, denoted as a(λ), and the scattering coefficient, denoted as b(λ). Consequently, the attenuation coefficient, c(λ), which represents the cumulative effect of both absorption and scattering, can be expressed as [
30]:
In Equation (1), λ represents the wavelength of light. The ratio of the scattering coefficient b(λ) to the attenuation coefficient c(λ) is known as the albedo, symbolized as ω
0. This ratio, detailed in Equation (2), indicates the proportion of scattering loss relative to the total loss [
31]. For the purpose of this study, which aims to analyze the impact of water turbidity on UWOC, Harbor water is categorized into four distinct types: Harbor-I, Harbor-II, Harbor-III, and Harbor-IV. A communication wavelength of 532 nm is chosen for analysis.
Table 1 presents the absorption coefficient (a), scattering coefficient (b), attenuation coefficient (c), and albedo (ω
0) for these four types of Harbor water. The optical parameters for Harbor-II seawater are sourced from Petzold’s report [
32]. For the remaining three Harbor water types, their optical parameters are extrapolated using the same albedo ω
0 while varying the attenuation coefficients c(λ).
2.2. Selection of appropriate scattering phase function
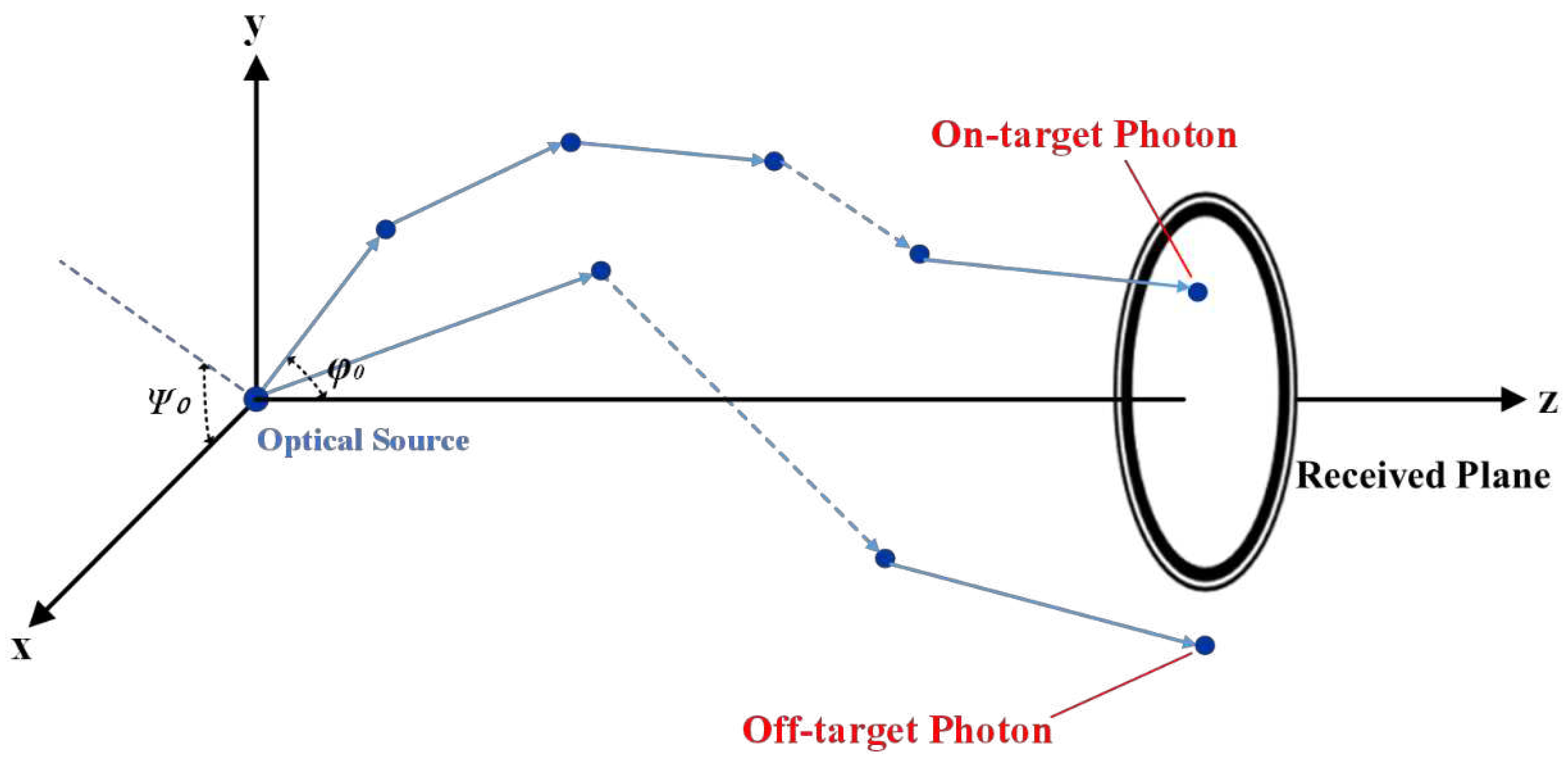
The transmission dynamics of photons in underwater channels are illustrated in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. Photons emitted from the light source undergo multiple scatterings by particles within the water, following various trajectories. Some of these photons, termed ‘On-target photons,’ reach the photosensitive surface of the receiver and are absorbed. Others, known as ‘Off-target photons,’ deviate from the receiver’s aperture and field of view (FOV) after multiple scatterings, as depicted in
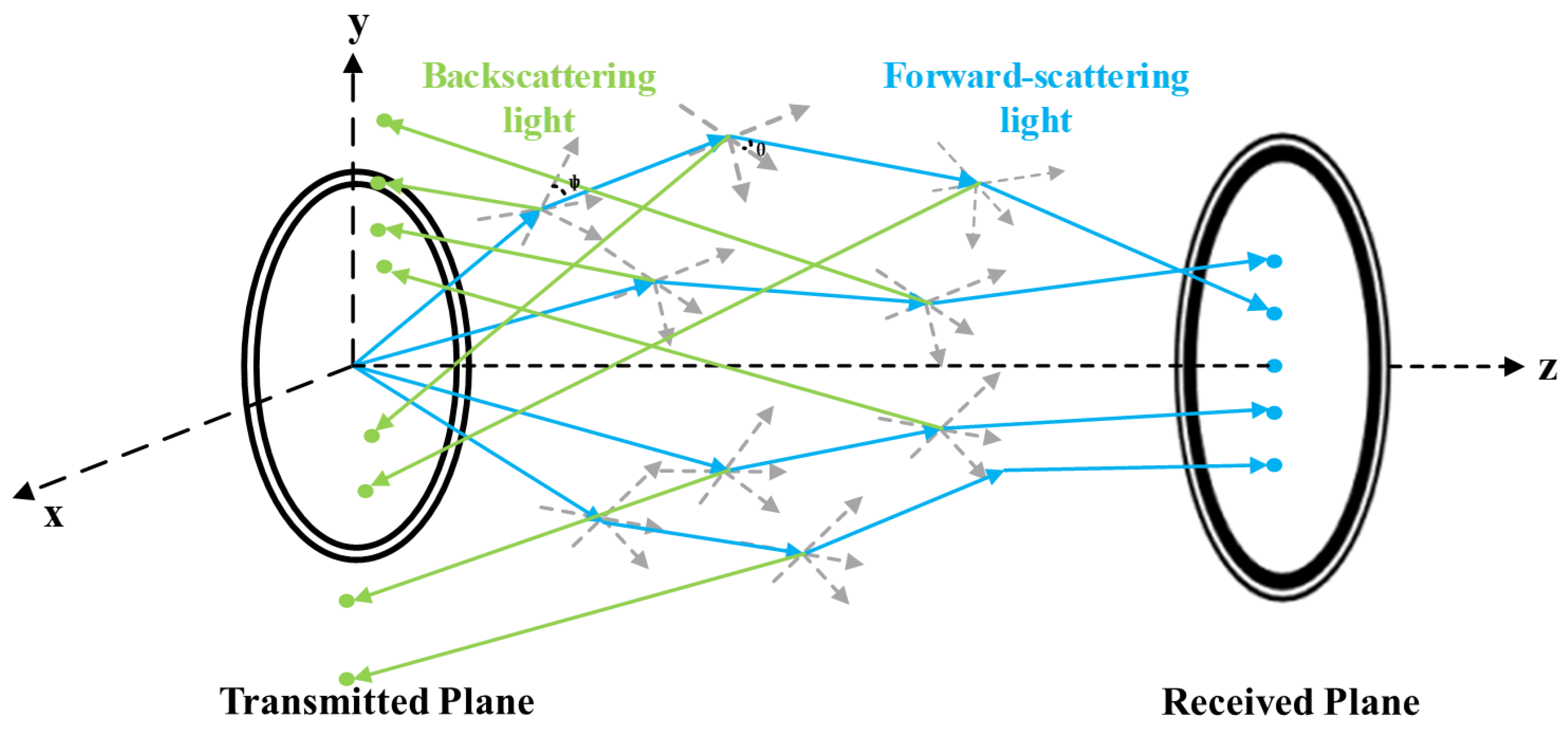
Figure 1. Additionally, the interaction between seawater particles and photons results in two distinct types of light: Forward-scattering light and Backscattering light, as shown in
Figure 2. Forward-scattering light influences the time domain characteristics of the received signal, whereas Backscattering light tends to decrease the optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) of the communication signal [
24]. A thorough analysis of both Forward-scattering and Backscattering light is crucial to understand their impact on UWOC systems.
In underwater environments, the scattering direction of a photon post-collision with seawater particles is generally random. To evaluate the distribution of light energy following such scatterings, the volume scattering phase function is employed [
34]. In this study, this function is denoted as β(φ). The relationship between the volume scattering phase function and the scattering coefficient b(λ) is articulated in Equation (3) [
35]. Here,
represents the scattering phase function, which plays a crucial role in determining how light is redistributed after interacting with particles in seawater.
To date, several scattering phase functions have been proposed to study the light transmission characteristics in underwater channels. Notable among these are the Henyey–Greenstein Function (HG) [
36], the two-term Henyey–Greenstein Function (TTHG) [
37], and the Fournier–Forand Function (FF) [
38,
39]. The FF scattering phase function, in particular, has been shown to align well with the characteristics of Petzold Harbor water, as indicated in relevant literature [
40].
Further supporting the use of the FF function, simulation results have demonstrated its similarity to the measured data of Petzold Harbor water, especially when specific parameters are applied: a slope (μ) of 3.5835 and a seawater refractive index (n) of 1.13 [
41]. Given these findings, this paper adopts the FF scattering phase function for its simulation analysis. The expression for the FF scattering phase function is provided in Equation (4). In this expression, ѱ represents the azimuth angle of the photons, and φ denotes their scattering angle. The variables υ and δ are intermediate variables without direct physical significance, with δ
180 representing the value of δ when the scattering angle φ equals 180°.
2.3. The process of Monte Carlo numerical simulation
2.3.1. The initial parameters of photon packets
The Monte Carlo method is a stochastic simulation technique used to model the propagation of light in seawater. This method involves tracking the random propagation paths of numerous photons, thereby facilitating statistical analysis and calculation. In this approach, the light source is modeled as a collection of photon packets, each characterized by specific distribution properties. The simulation process is guided by the optical and water quality parameters pertinent to the communication system. The photon scattering angle, determined by the volume scattering phase function, plays a crucial role in this process. By tracking the trajectory of each photon, the method enables a detailed analysis of their motion paths. Ultimately, this simulation allows for the accumulation and analysis of data regarding the number of photons received and their distribution characteristics. Such comprehensive data are crucial for understanding and optimizing underwater communication systems.
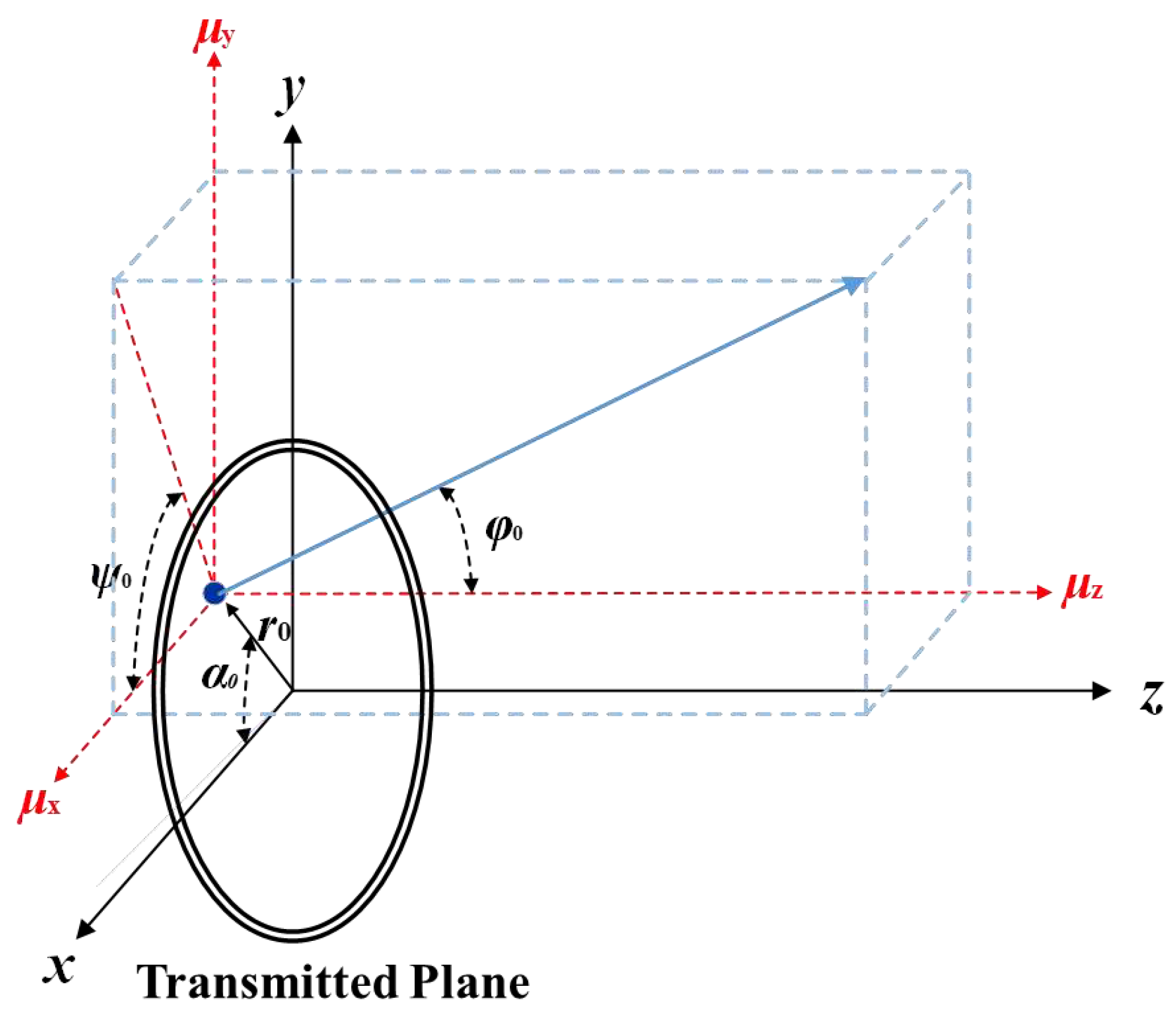
In the Monte Carlo simulation, the initial parameters of a photon are defined by its initial coordinates
on the Transmitted Plane and the directional components
of the photon’s direction vector along the x, y, and z axes, respectively. These directional components, commonly referred to as Direction Cosines, determine the photon’s propagation direction, while the coordinates indicate its current position. As illustrated in
Figure 3, we assume that the photon packet travels along the z-axis and lies on the Transmitted Plane.
The distance between the photon packet’s current position and the center of the light source is denoted as r0. Additionally, the initial polarization angle (α0), azimuth angle (ψ0), and elevation angle (φ0) of the photon are specified. The photon’s initial weight is set to ω=1.
The initial coordinates of the photon
and the Direction Cosines
are derived using trigonometric functions, as shown in Equations (5) and (6).
Given that the light source and beam in Monte Carlo simulations are typically radially symmetric, the initial polarization angle (α
0) and the initial azimuth angle (ψ
0) can be randomly determined. This random selection is guided by Equation (7), where R represents a random value within the normalized interval [0, 1]. This method ensures that the angles are uniformly distributed, aligning with the radial symmetry of the light source and beam configuration.
The energy distribution of the laser beam in the simulation follows Gaussian distribution characteristics. This distribution is crucial for determining the radius r
0 on the Transmitted Plane, which represents the distance between a given photon and the center of the light source. The calculation of r
0 is based on the Gaussian distribution, as outlined in Equation (8). In this equation,
represents the waist radius of the laser beam, and R is a random value drawn from the normalized interval [0, 1].
The initial elevation angle φ
0 of each photon is derived based on the initial divergence half-angle (
) of the beam, the beam waist radius (
), and the radius (r
0) on the Transmitted Plane. The specific relationship among these parameters is articulated in Equation (9). This equation ensures that the elevation angle of each photon is accurately aligned with the beam’s divergence characteristics and its position relative to the center of the light source.
2.3.2. The movement and scattering of the photon
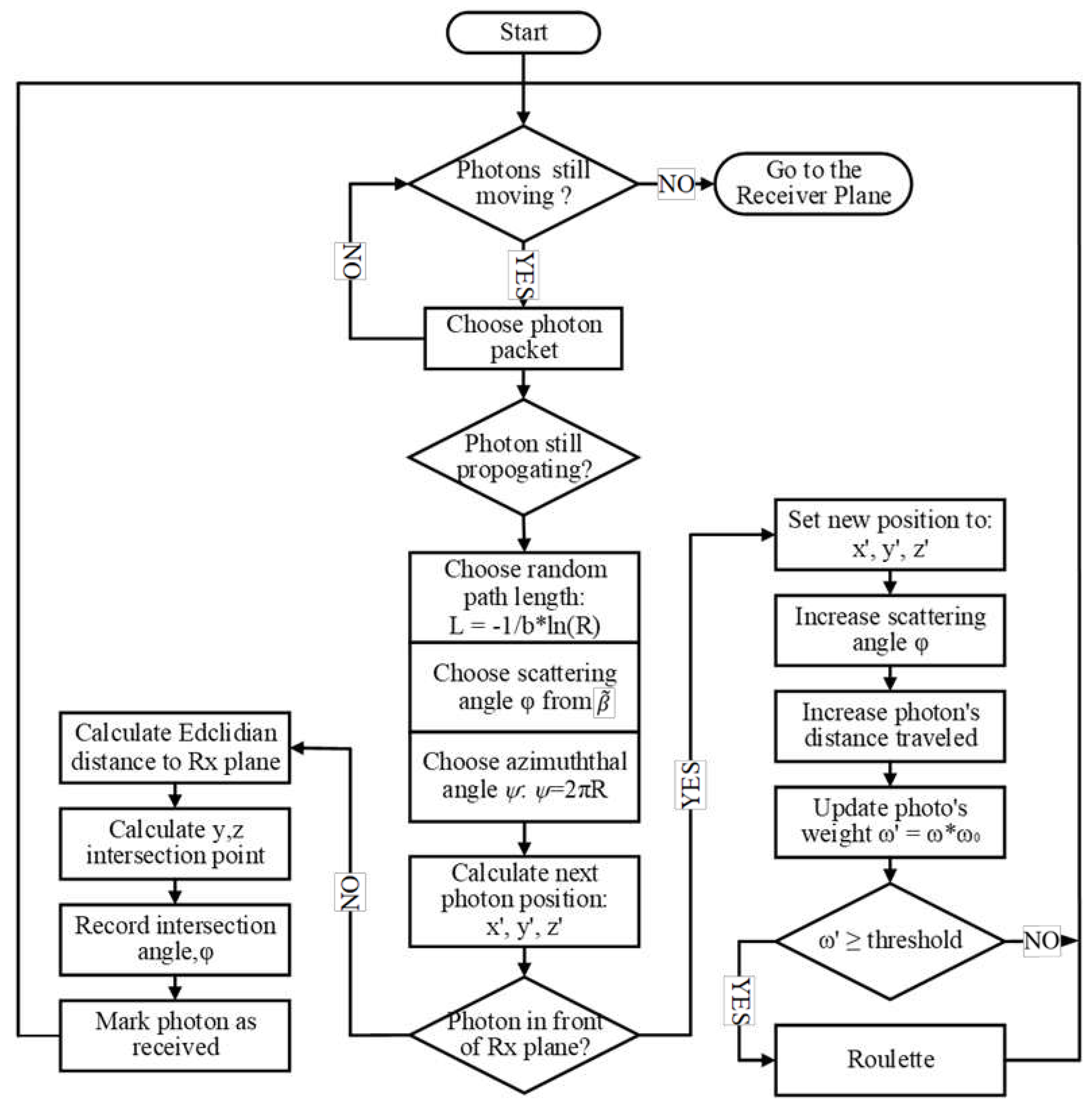
The Monte Carlo simulation process is comprehensively illustrated in
Figure 4, which presents a detailed flowchart. A critical aspect of this simulation involves determining the random scattering path length (L), scattering angle (φ), and azimuth angle (ψ) for each photon during its movement through the simulated environment. The scattering path length L is defined as the distance a photon travels between two consecutive scattering events. This length is crucial as it influences the photon’s trajectory and the overall simulation accuracy. The scattering angle (φ) of the photon is calculated using Equation (3). Equation (10) then provides further detail on how this angle is determined, with φ’ representing the specific scattering angle chosen during a scattering event. These steps are integral to accurately simulating the random paths of photons through water, crucial for understanding light behavior in underwater communication channels.
When the random scattering path length L, scattering angle φ and azimuth angle ψ of the photon are confirmed, the position of the photon can be updated as [x′, y′, z′] in Equation (11), where μ
x, μ
y, and μ
z are the Direction Cosine of the photon in the current state, the scattering path length is selected randomly as L= -In(R)/b [
42,
43].
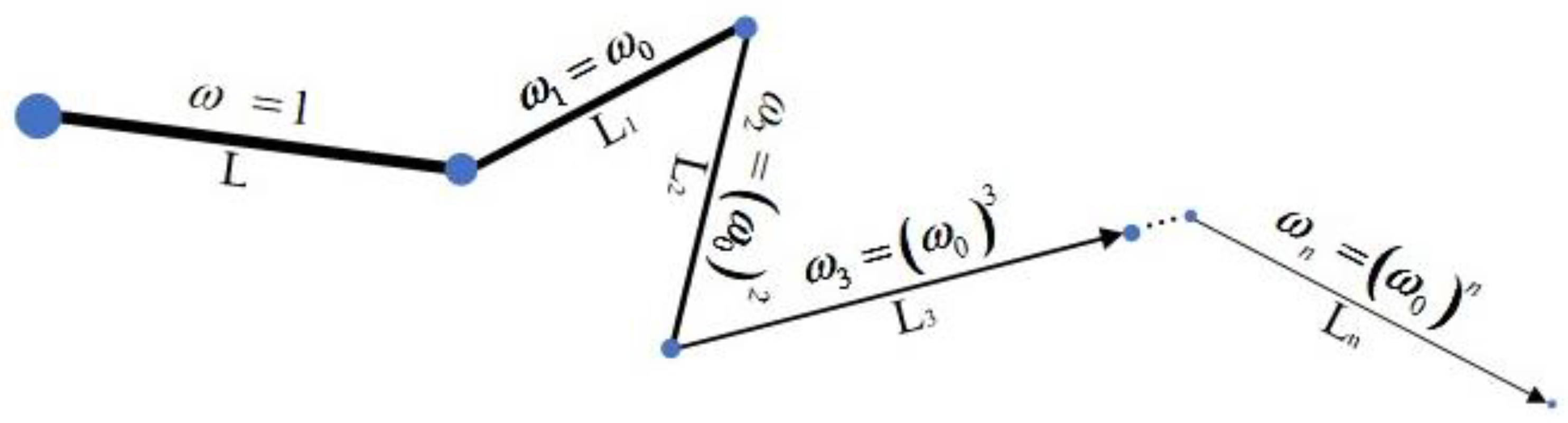
The photon packet’s new weight ω
n is obtained further, its weight decays exponentially as shown in Equation (12) and
Figure 5.
When the photon’s new position is determined and is still in front of the Received Plane, it is still possible to be absorbed by the receiver. The scattering angle and azimuth angle of the photon are re-selected to obtain the new Direction Cosine
in Equation (13), where
, φ’ and ѱ’ are the new scattering angle and azimuth angle of the photon, respectively.
2.3.3. Termination of photon motion or reception of photon
In the simulation, the termination of a photon’s motion is defined under two specific conditions. First, a photon is considered absorbed by the particles in the Harbor water if its weight decreases to a threshold of 10-6 or less. Second, the photon’s transmission is deemed to have ended once it reaches the receiver’s photosensitive surface.
Throughout the photon tracking process, key attributes of each photon are recorded, including its position, received angle, weight, and propagation distance. A photon is classified as ‘Received’ if it falls within the bounds of the receiver’s photosensitive surface and if it’s received angle is within the specified Field of View (FOV). If either of these conditions is not met, the photon is considered ‘not Received,’ and its tracking is discontinued.
This methodical approach allows for precise determination of photon reception, facilitating an accurate assessment of the efficiency and effectiveness of the underwater wireless optical communication system in various Harbor water conditions.
3. The simulation results and discussion
In this paper, we primarily investigate the characteristics of UWOC with varying communication distances in four distinct types of Harbor water. To facilitate this study, certain parameters of the transmitter and receiver are predetermined and held constant, with the main variable parameters being the Transmitted full divergence angle, the Received aperture size, and the Received Field of View (FOV).
Reflecting the focus of our research, we have established a set of initial fixed parameters for use in our simulation model. These parameters, detailed in
Table 2, include the laser wavelength, the number of photons transmitted, the energy per photon, and the total transmitted light energy.
This approach ensures a consistent baseline for analyzing the impact of the aforementioned variable parameters on the performance of UWOC systems in different Harbor water conditions.
The specific settings for the Transmitted full divergence angle, as outlined in
Table 3, include values of 0.5 mrad, 5 mrad, 10 mrad, and 100 mrad. Corresponding to these full divergence angles, the Transmitted beam waist diameter for each setting is calculated using Equation (9). In the analysis of how these varying Transmitted full divergence angles affect the communication system, both the Received aperture and the Received Field of View (FOV) are held constant. These are fixed at 200 mm for the Received aperture and π/2 rad for the Received FOV. This methodical approach allows for a focused investigation into the impact of the Transmitted full divergence angle on UWOC system performance, ensuring that other variables do not confound the results.
The specific settings for the Received Field of View (FOV) and aperture are detailed in
Table 4. The Received aperture sizes are set at 25 mm, 50 mm, 100 mm, 200 mm, and 400 mm. The values for the Received FOV are varied and include π/90 rad, π/30 rad, π/22.5 rad, π/15 rad, π/7.5 rad, π/2 rad, π/1.5 rad, and π rad. In the analysis that focuses on the impact of these variable Received apertures and FOVs on the communication system, the Transmitted full divergence angle is consistently fixed at 0.5 mrad. This approach enables a targeted examination of how changes in the Received aperture and FOV affect the performance of the UWOC system, isolating these variables to understand their specific contributions.
3.1. Analytical Examination of the Full Divergence Angle in Transmission
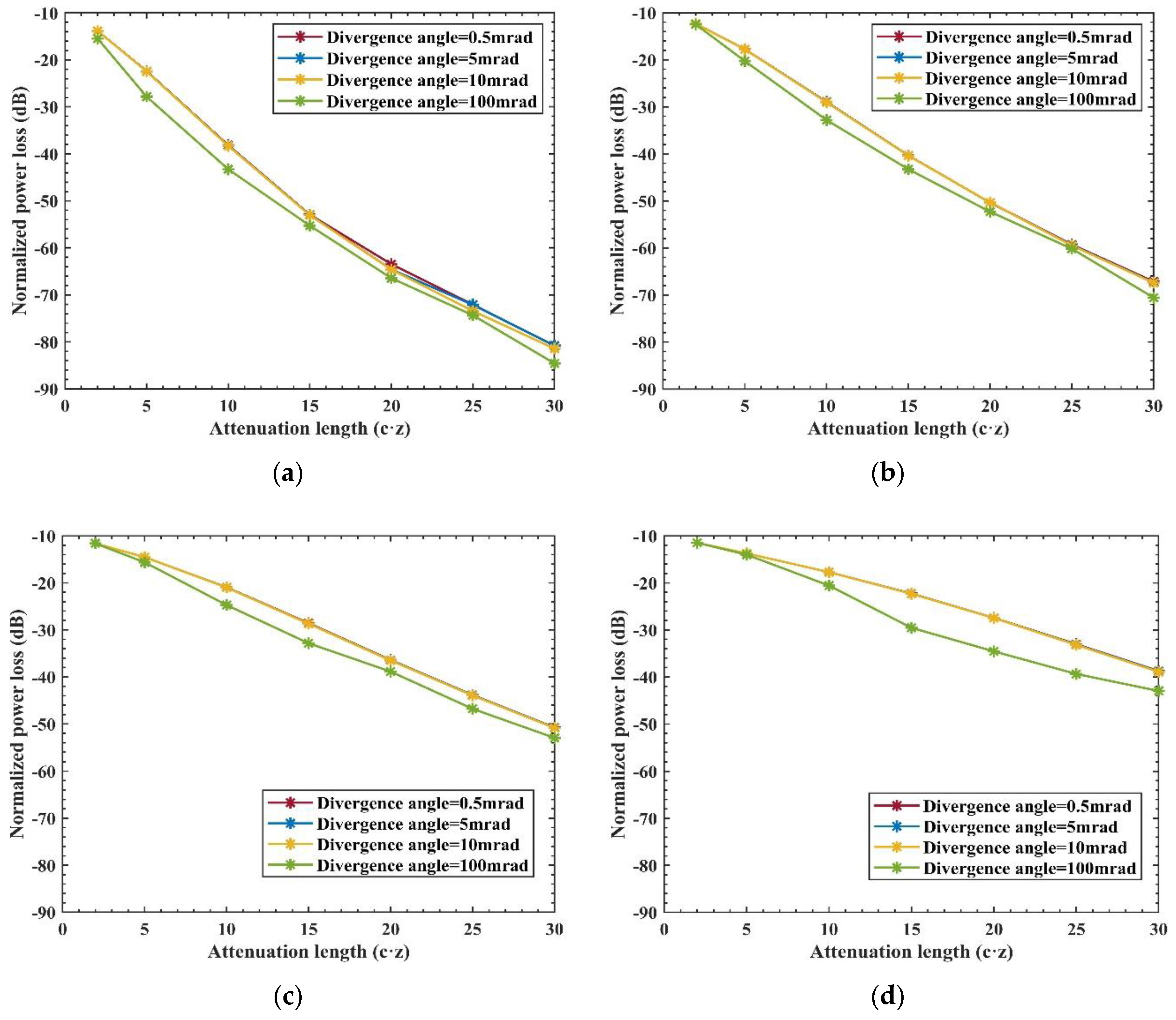
In this study, we analyze the variation characteristics of laser power in relation to both the attenuation length and the divergence angle.
Figure 6 illustrates the normalized power loss received as a function of the attenuation length (AL) and the Transmitted full divergence angle. The attenuation length AL is defined as the product of the attenuation coefficient c(λ) and the communication distance z, expressed mathematically as AL=c(λ)×z.
Simulation results indicate a consistent trend across all four types of Harbor water: as AL increases, there is a corresponding increase in the attenuation loss of received power. Notably, the attenuation of received optical power initially occurs at a rapid rate and then stabilizes. This pattern is attributed to the gradual divergence of the light beam, which leads to a swift attenuation of light energy over a short distance. As the transmission distance extends, the light beam enters a state of full scattering. In this phase, the proportion of energy attenuation due to light scattering gradually diminishes, making absorption the predominant factor affecting light transmission. This trend is particularly evident in
Figure 6(a), highlighting the dynamic interplay between scattering and absorption in determining the attenuation characteristics of UWOC.
Furthermore, our analysis reveals that a larger transmitted full divergence angle correlates with greater normalized received optical power attenuation loss. This trend holds consistently across the four types of Harbor water. However, it’s observed that as the quality of Harbor water deteriorates, the normalized power loss decreases. The underlying reason for this is that the received optical power is more strongly influenced by the communication distance z than by water quality. Therefore, the common approach in many studies of directly deriving communication distance by dividing the attenuation coefficients of two different water types proves to be inapplicable in the context of Harbor water. This finding underscores the complexity of the relationship between water quality, communication distance, and light attenuation in underwater optical communication, challenging assumptions that may hold true in other types of aquatic environments.
Additionally, our findings indicate that the differences in normalized power loss among smaller divergence angles, specifically 0.5 mrad, 5 mrad, and 10 mrad, are relatively minor compared to a larger angle like 100 mrad. The primary reason for this is that a smaller transmitted full divergence angle confines the light spot within a more limited range. This confinement results in reduced geometric loss and diminishes the likelihood of photons being scattered by particles in the water. Consequently, a smaller divergence angle ensures that a higher number of photons can reach the photosensitive surface of the receiver and be effectively absorbed. This observation underscores the significance of divergence angle control in minimizing power loss in underwater optical communication, particularly in environments with scattering particles.
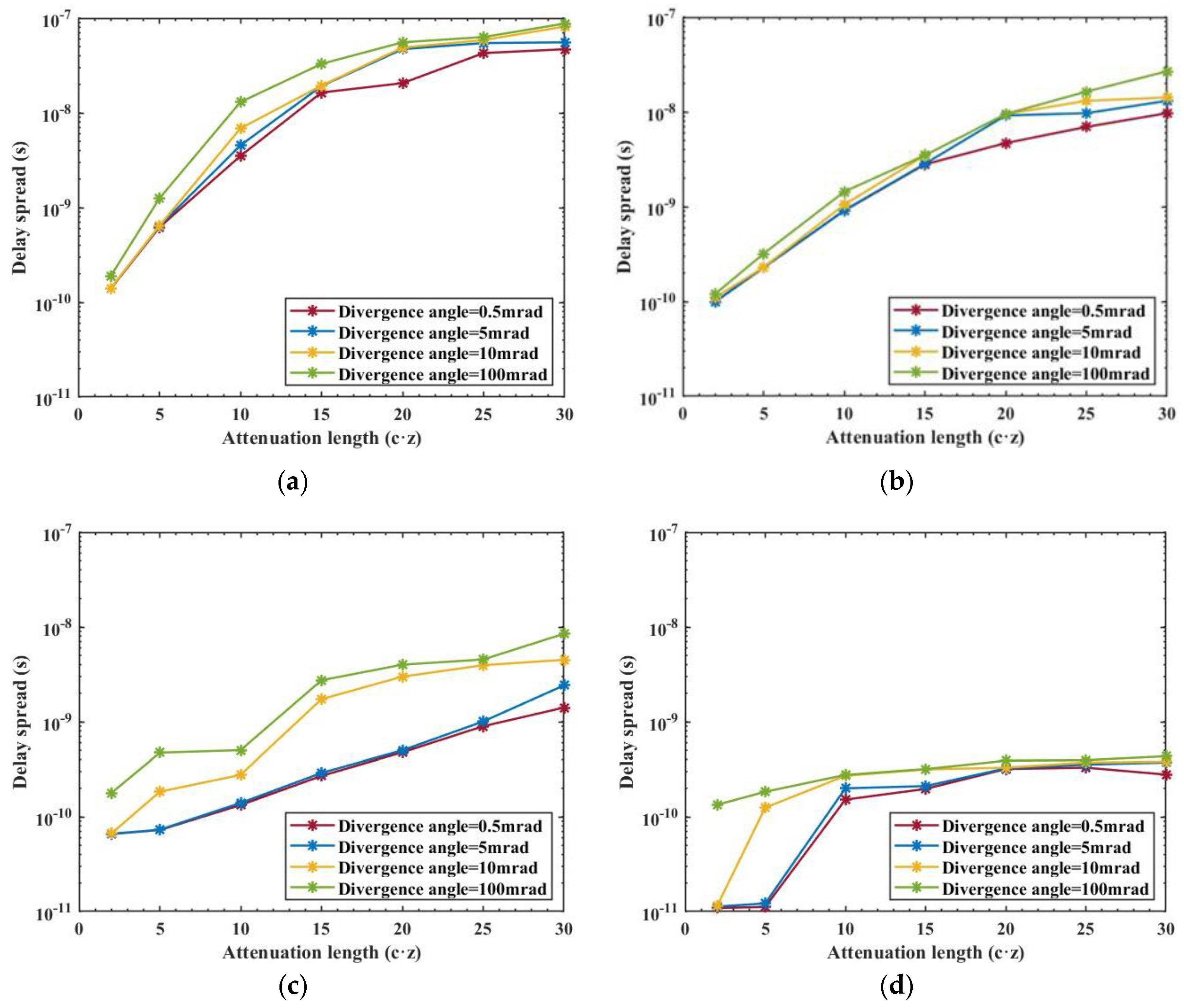
In our final analysis, we examine the time delay spread in relation to both the attenuation length (AL) and the Transmitted full divergence angle across the four types of Harbor water, as depicted in
Figure 7. We observe that under identical Harbor water conditions, the time delay spread increases with both the increase in AL and the Transmitted full divergence angle. Conversely, for a given AL and Divergence angle, the time delay spread decreases as the quality of Harbor water deteriorates. This trend mirrors the observed behavior in received normalized power loss, indicating that the time delay spread is more closely associated with communication distance z than with water quality. Additionally,
Figure 7(d) highlights a specific scenario where the AL ranges from 2-5 and the Transmitted full divergence angle is between 0.5 mrad and 5 mrad. In this case, the time delay spread is notably low, ranging only from 1.09×10
-11s-1.22×10
-11s. This minimal spread can be attributed to the relatively short transmission distance, approximately 0.45m to 1.14m, which is insufficient to contribute significantly to the time delay spread. This finding emphasizes the importance of considering both the transmission distance and beam divergence characteristics when assessing the time delay in underwater optical communication.
3.2. Analytical Evaluation of the Received Aperture and FOV
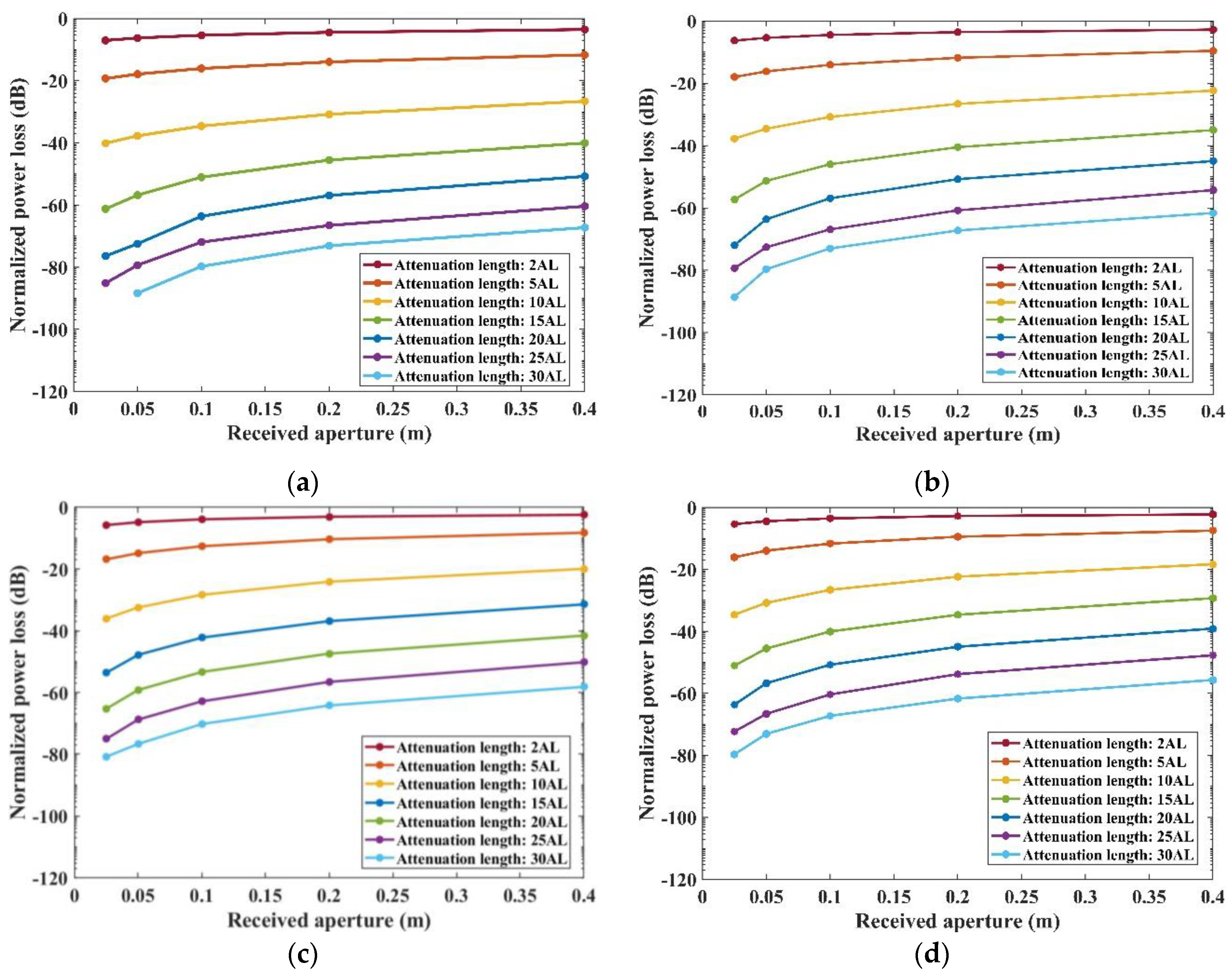
The study also examines how received normalized power loss correlates with the attenuation length (AL) and the size of the Received aperture at the receiver’s end, as illustrated in
Figure 8. Our simulations reveal a consistent relationship between these variables across the four types of Harbor water. Notably, as the size of the Received aperture increases, the received normalized power loss decreases. However, the rate of this decline slows and eventually stabilizes. This trend is attributed to the fact that a larger Received aperture can capture more scattered photons, thus enhancing the absorption efficiency of the receiver.
Additionally, it is evident that larger AL values correspond to greater received normalized power losses. This relationship underscores the significant impact of communication distance and beam attenuation characteristics on the efficiency of photon reception in underwater optical communication systems.
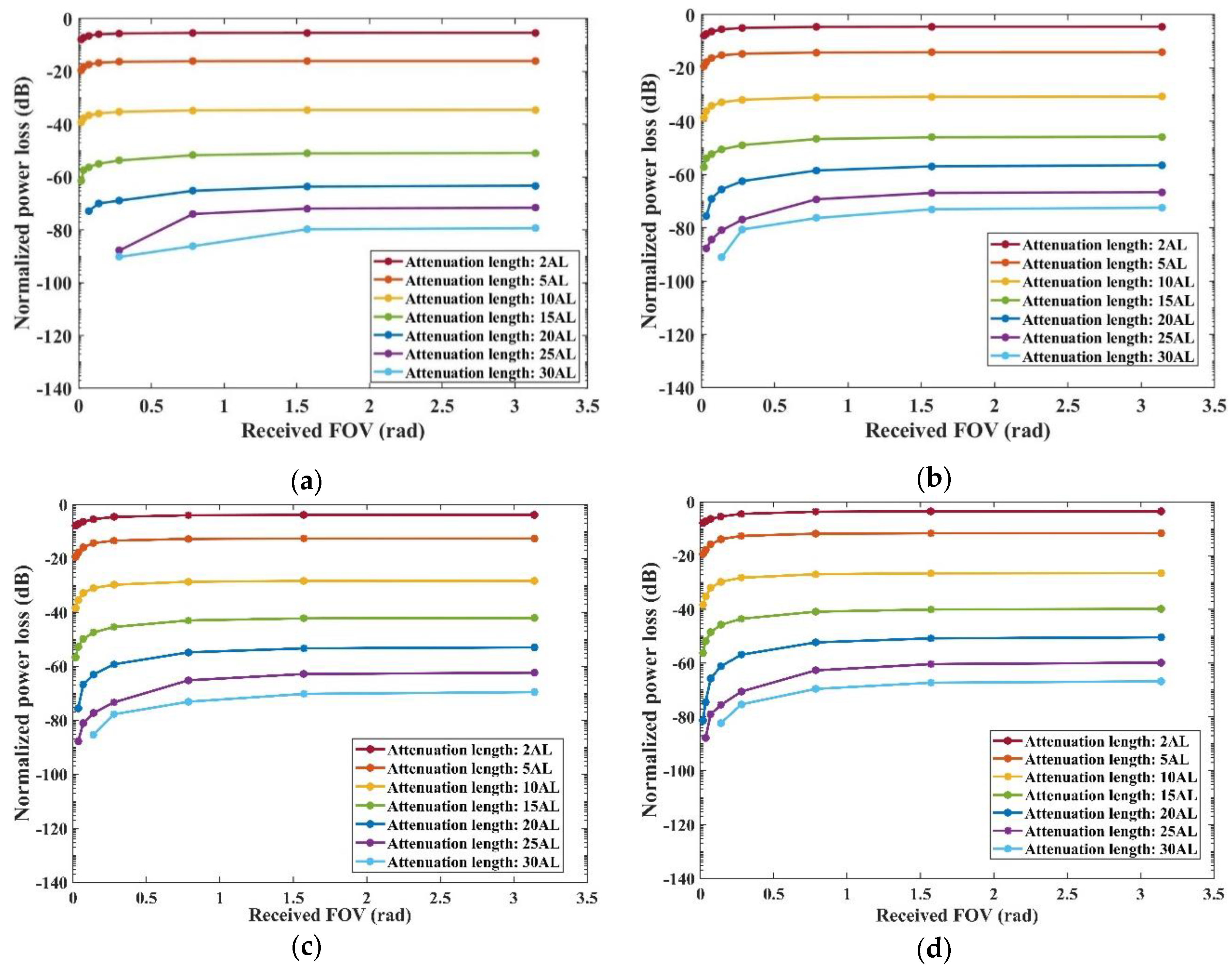
The relationship between received normalized power loss, attenuation length (AL), and the Field of View (FOV) at the receiving end is further explored in
Figure 9, focusing on the four types of Harbor water. Simulation results indicate that the trends in received normalized power loss correspond closely with both AL and the Received FOV across these water types. In scenarios where the Received FOV is relatively small (< 0.2793 rad), there is a noticeable decrease in received normalized power loss as the FOV increases. This decrease is attributed to the fact that a larger FOV allows more photons, particularly those deviating from the optical axis, to become On-target photons and be absorbed by the receiver. However, as the Received FOV continues to expand beyond this point, the impact on normalized power loss diminishes. This plateau in the effect is due to the large FOV eventually encompassing almost the entire peak intensity region of the Gaussian beam on the Received plane. Consequently, further increases in FOV do not significantly affect the proportion of photons captured, thereby stabilizing the received normalized power loss.
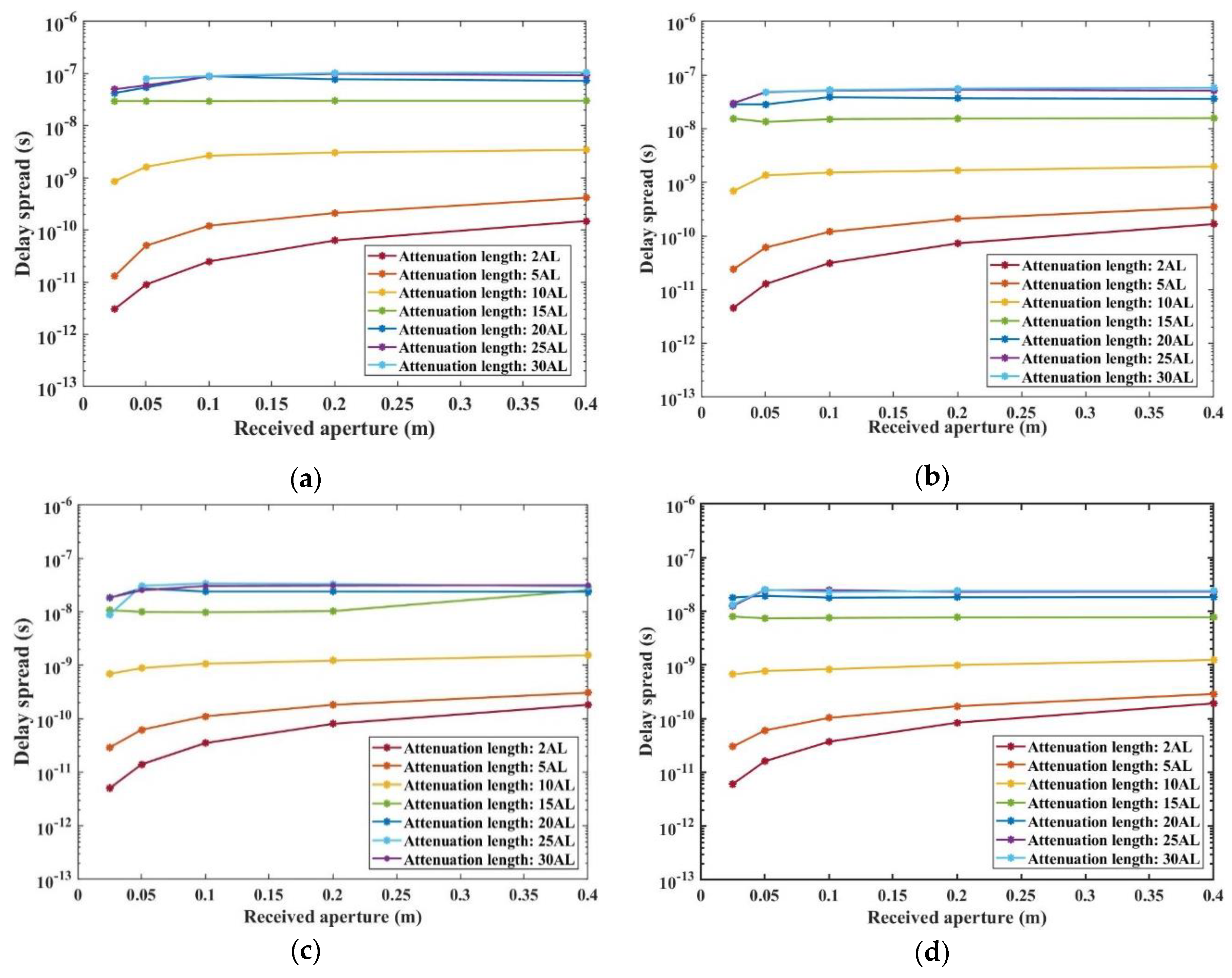
In our concluding analysis, we examine the time delay spread at the receiving end in relation to AL, the size of the Received aperture, and the Received FOV across the four types of Harbor water. This analysis is illustrated in
Figure 10 and
Figure 11. Our findings indicate that, under constant Harbor water conditions, the time delay spread increases with the rising AL. In the range of shorter ALs (2AL-10AL), as shown in
Figure 10, the time delay spread enlarges with an increase in the size of the Received aperture. This trend is attributed to the fact that a larger aperture increases the likelihood of capturing multiple-scattered photons. However, in scenarios involving larger ALs (15AL-30AL), the time delay spread exhibits minimal variation in response to changes in the Received aperture size, remaining within the range of 1.05×10
-7s to 7.39×10
-9s. The primary reason for this is that at longer communication distances, most scattered photons become Off-target photons due to multiple scatterings, and thus they are unlikely to be absorbed by the receiver. Consequently, in the range of 15AL-30AL, the time delay spread remains relatively constant.
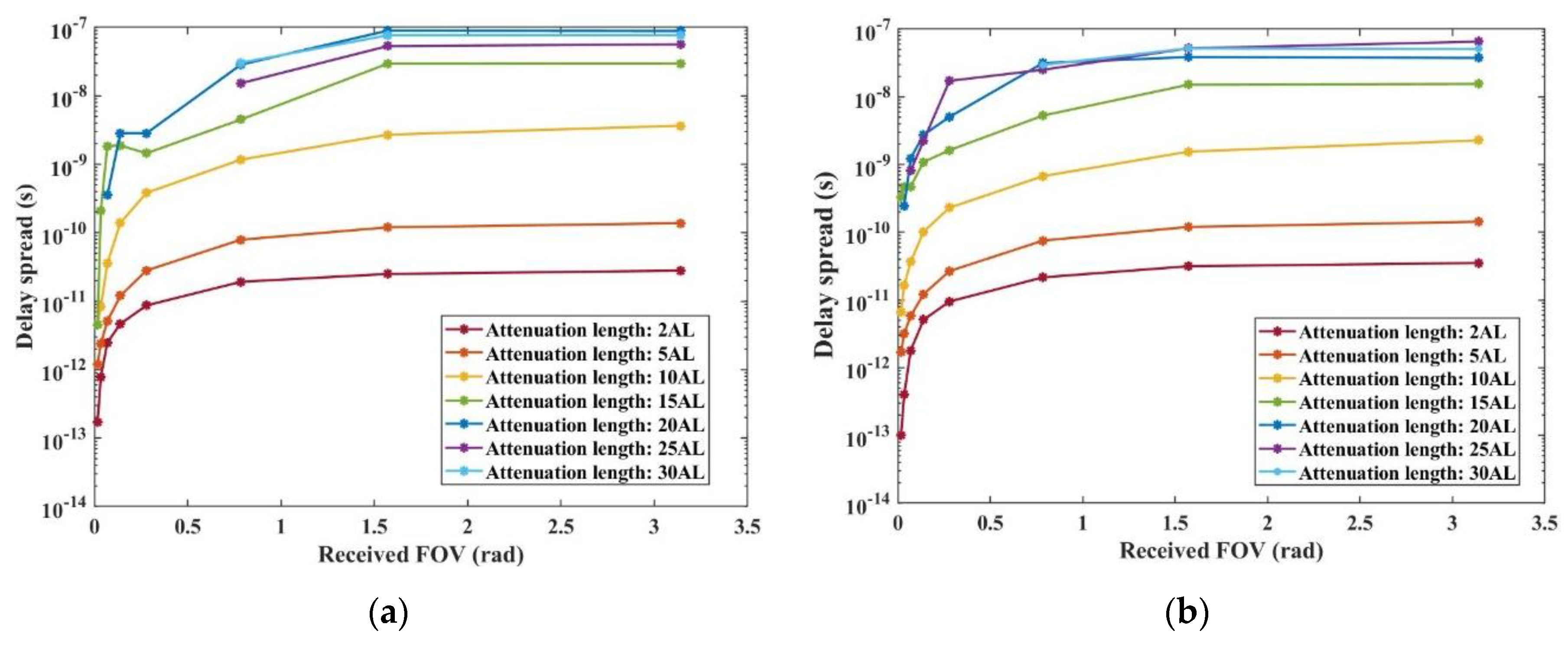
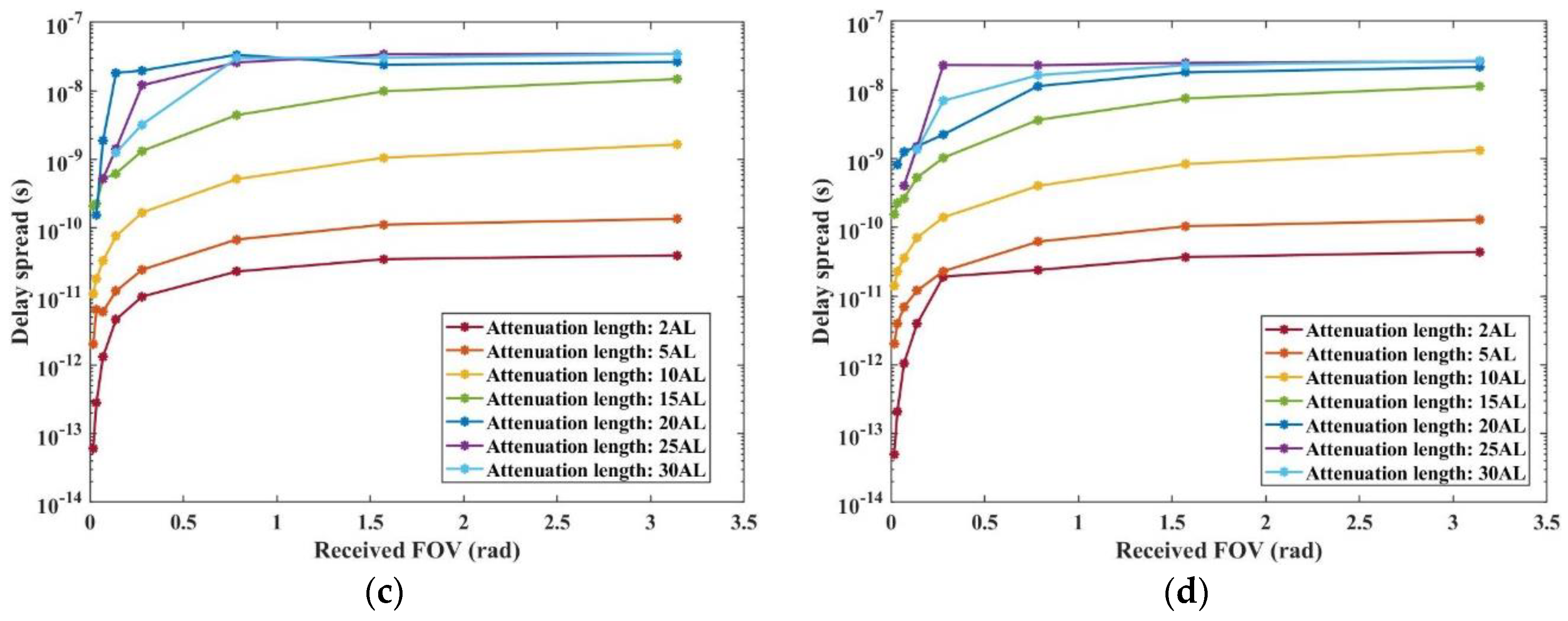
In the case of a small Received FOV (less than 0.8 rad), as depicted in
Figure 11, there is a noticeable increase in the time delay spread as the FOV gradually expands. This pattern arises because a larger Received FOV enhances the receiver’s capability to capture a greater number of multiple-scattered photons. As a result, the time delay spread grows with the increasing FOV.
However, beyond a certain point, the rate of increase in time delay spread significantly slows down. This slowdown occurs because a larger FOV eventually encompasses most of the multiple-scattered photons within the Received plane. Therefore, further increases in the FOV do not substantially add to the number of photons captured, leading to only marginal changes in the time delay spread. This finding illustrates the intricate balance between FOV size and the efficiency of photon capture in determining the time delay characteristics of underwater optical communication systems.
4. Conclusions
This study has critically examined the nuances of Underwater Wireless Optical Communication (UWOC) within four distinct types of Harbor water, employing the Monte Carlo method to simulate photon behavior and analyze key communication parameters. Our findings reveal that the transmitted full divergence angle, received aperture size, and Field of View (FOV) profoundly affect the UWOC system’s performance. Notably, increased attenuation length (AL) and divergence angle lead to higher received normalized power loss and time delay spread, with these effects being more pronounced in clearer water types. The research also underscores that larger received apertures and FOVs enhance the reception of multiple-scattered photons, thus reducing power loss. However, beyond certain thresholds, the advantages plateau due to the full coverage of the scattered photons within the received plane. Additionally, the study establishes critical termination conditions for photon motion, highlighting the significance of photon weight and alignment with the receiver’s photosensitive surface. These insights pave the way for more efficient design and optimization of UWOC systems, particularly in challenging Harbor water environments, by providing a detailed understanding of the interplay between light scattering, absorption properties, and system configuration. Further, the analysis results of time delay spread provides a strong theoretical support and technical basis for optical timing, ranging and positioning technology based on UWOC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C. and X.X.; methodology, X.H.; software, G.L.; validation, P.L. (Peng Li); formal analysis, W.N. and P.L. (Peixuan Liao); writing—review and editing, C.C.; visualization, C.L.; su-pervision, W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key R&D Program, grant number 2021YFC2800504 and National Key R&D Program, grant number 2022YFC2806000
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
The study did not involve humans.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the support from the State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Urick R.J. Principles of Underwater Sound. Los Altos, CA, USA: Peninsula, 1983.
- Xu J. Underwater wireless optical communication: why, what, and how? Chin Opt Lett 2019, 17(10): 100007.
- Zhu S.; Chen X.; Liu X.; Zhang G.; Tian P. Recent progress in and perspectives of underwater wireless optical communication. Prog Quant Electron 2020, 73: 100274. [CrossRef]
- Ali M.F.; Jayakody D.N.K.; Chursin Y.A.; Affes S.; Dmitry S. Recent advances and future directions on underwater wireless communications. Arch Comput Method E 2020, 27: 1379-1412. [CrossRef]
- Ma L.; Zhou S.; Qiao G.; Liu S.; Zhou F. Superposition coding for downlink underwater acoustic OFDM. IEEE J Oceanic Eng 2016, 42(1): 175-187. [CrossRef]
- Tian P.; Liu X.; Yi S.; Huang Y.; Zhang S.; Zhou X.; Hu L.; Zheng L.; Liu R. High-speed underwater optical wireless communication using a blue GaN-based micro-LED. Opt. Express 2017, 25(2): 1193-1201. [CrossRef]
- Kao C.C.; Lin Y.S.; Wu G.D.; Huang C.J. A comprehensive study on the internet of underwater things: applications, challenges, and channel models. Sensors 2017, 17(7): 1477. [CrossRef]
- Sun X.; Kang C.H.; Kong M.; Alkhazragi O.; Guo Y.; Ouhssain M.; Yang W.; et al. A review on practical considerations and solutions in underwater wireless optical communication. J Lightwave Technol 2020, 38(2): 421-431.
- Wang J.; Yang X.; Lv W.; Yu C.; Wu J.; Zhao M.; Qu F.; Xu Z.; Han J.; Xu J. Underwater wireless optical communication based on multi-pixel photon counter and OFDM modulation. Opt. Commun 2019, 451: 181-185. [CrossRef]
- Wei W.; Zhang X.; Rao J.; Wang W. Time domain dispersion of underwater optical wireless communication. Chin Opt Lett 2011, 9(3): 030101.
- Li J.; Luo J.; Li S.; Yuan X. Centroid drift of laser beam propagation through a water surface with wave turbulence. Appl Optics 2020, 59(20): 6210-6217. [CrossRef]
- Cox Jr W.C. Simulation, Modeling, and Design of Underwater Optical Communication Systems. North Carolina State University. 2012.
- Shen C.; Guo Y.; Oubei H.M.; Ng T.K.; Liu G.; Park K.H.; Ho K.T.; Alouini M.S.; Ooi B.S. 20-meter underwater wireless optical communication link with 1.5 Gbps data rate. Opt. Express 2016, 24(22): 25502-25509. [CrossRef]
- Sahu S.K.; Shanmugam P. A theoretical study on the impact of particle scattering on the channel characteristics of underwater optical communication system. Opt. Commun 2018, 408: 3-14. [CrossRef]
- Cochenour B.M.; Mullen L.J.; Laux A.E. Characterization of the beam-spread function for underwater wireless optical communications links. IEEE J Oceanic Eng 2008, 33(4): 513-521. [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos V. Going deeper than microscopy: the optical imaging frontier in biology. Nat. Methods 2010, 7(8): 603-614. [CrossRef]
- Li J.; Ma Y.; Zhou Q.; Zhou B.; Wang H. Channel capacity study of underwater wireless optical communications links based on Monte Carlo simulation. J Optics-UK 2011, 14(1): 015403. [CrossRef]
- Kodama T.; Sanusi M.A.B.A.; Kobori F.; Kimura T.; Inoue Y.; Jinno M. Comprehensive analysis of time-domain hybrid PAM for data-rate and distance adaptive UWOC system. IEEE Access 2021, 9: 57064-57074. [CrossRef]
- Gjerstad K.I.; Stamnes J.J.; Hamre B.; Lotsberg J.K.; Yan B.; Stamnes K. Monte Carlo and discrete-ordinate simulations of irradiances in the coupled atmosphere-ocean system. Appl Optics 2003, 42(15): 2609-2622. [CrossRef]
- Gabriel C.; Khalighi M.A.; Bourennane S.; Leon P. Rigaud V. Channel modeling for underwater optical communication. In Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM Workshops of the Conference. IEEE, 2011: 833-837. [CrossRef]
- Mobley C.D. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters. Academic Press 1994.
- Tang S.; Dong Y.; Zhang X. Impulse response modeling for underwater wireless optical communication links. IEEE T Commun 2013, 62(1): 226-234. [CrossRef]
- Qadar R.; Kasi M.K.; Ayub S.; Kakar F.A. Monte Carlo–based channel estimation and performance evaluation for UWOC links under geometric losses. Int J Commun Syst 2018, 31(6): e3527. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J.; Kou L.; Yang Y.; He F.; Duan Z. Monte-Carlo-based optical wireless underwater channel modeling with oceanic turbulence. Opt. Commun 2020, 475: 126214. [CrossRef]
- Han B.; Zhao W.; Meng J.; Zheng Y.; Yang Q. Study on the backscattering disturbance in duplex underwater wireless optical communication systems. Appl Optics 2018, 57(29): 8478-8486. [CrossRef]
- Qin J.; Fu M.; Sun M. Zhen C.; Ji R.; Zheng B. Simulation of beam characteristics in long-distance underwater optical communication. In Proceedings of the Global Oceans of the Conference,Singapore–US Gulf Coast. IEEE, 2020: 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Boluda-Ruiz R.; Rico-Pinazo P.; Castillo-Vázquez B.; García-Zambrana A.; Qaraqe K. Impulse response modeling of underwater optical scattering channels for wireless communication. IEEE Photonic J 2020, 12(4): 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Liu J.; Chen G.; Zhao J.; Gao K.; Liu Y. Development and trends of marine space-time frame network. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2019, 44(1): 17-37. [CrossRef]
- Gabriel C.; Khalighi M.A.; Bourennane S.; Léon P.; Rigaud V. Monte-Carlo-based channel characterization for underwater optical communication systems. J Opt Commun Netw 2013, 5(1): 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Jiang R.; Sun C.; Zhang L.; Tang X.; Wang H.; Zhang A. Deep learning aided signal detection for SPAD-based underwater optical wireless communications. IEEE Access 2020, 8: 20363-20374. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L.; Tang X.; Sun C.; Chen Z.; Li Z.; Wang H.; Jiang R.; Shi W.; Zhang A. Over 10 attenuation length gigabits per second underwater wireless optical communication using a silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) based receiver. Opt. Express 2020, 28(17): 24968-24980. [CrossRef]
- Hu S.; Mi L.; Zhou T.; Chen W. 35.88 attenuation lengths and 3.32 bits/photon underwater optical wireless communication based on photon-counting receiver with 256-PPM. Opt. Express 2018, 26(17): 21685-21699. [CrossRef]
- Mobley C.D.; Gentili B.; Gordon H.R.; Jin Z.; Kattawar G.W.; Morel A.; Reinersman P.; Stamnes K.; Stavn R.H. Comparison of numerical models for computing underwater light fields. Appl Optics 1993, 32(36): 7484-7504. [CrossRef]
- Sahu S.K.; Shanmugam P. A study on the effect of scattering properties of marine particles on underwater optical wireless communication channel characteristics. In Proceedings of the OCEANS of the Conference, Aberdeen, 2017: 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Cochenour B, Mullen L, Laux A, et al. Effects of multiple scattering on the implementation of an underwater wireless optical communications link. In Proceedings of the OCEANS of the Conference, IEEE, 2006: 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Cox W.; Muth J. Simulating channel losses in an underwater optical communication system. JOSA A 2014, 31(5): 920-934. [CrossRef]
- Petzold T.J. Volume scattering functions for selected ocean waters. 1972.
- Haltrin V.I. One-parameter two-term Henyey-Greenstein phase function for light scattering in seawater. Appl Optics 2002, 41(6): 1022-1028. [CrossRef]
- Fournier G R, Forand J L. Analytic phase function for ocean water. In Proceedings of the Ocean Optics XII of the Conference, 1994, 2258: 194-201. [CrossRef]
- Freda W.; Piskozub J. Improved method of Fournier-Forand marine phase function parameterization. Opt. Express 2007, 15(20): 12763-12768. [CrossRef]
- Mobley C.D.; Sundman L.K.; Boss E. Phase function effects on oceanic light fields. Appl Optics 2002, 41(6): 1035-1050. [CrossRef]
- Jaruwatanadilok S. Underwater wireless optical communication channel modeling and performance evaluation using vector radiative transfer theory. IEEE J Sel Area Comm 2008, 26(9): 1620-1627. [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru A. Wave propagation and scattering in random media. New York: Academic press, 1978.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).