1. Introduction
The classical formulation of the theory of irreversible processes is essentially based on the Onsager-Machlup linear relation between fluxes and thermodynamic forces [
1,
2], further elaborated by Green and many other authors [
3,
4]. This theory is essentially grounded on parabolic transport equations for the concentration fields and to equilibrium Gaussian distributions. The intrinisc asymmetry of parabolic models in treating space and time variables (first order in time, second order in space) leads to the paradox of infinite propagation velocity, as immediately follows from the non-compactly supported nature of the diffusional Green function for any time
[
5].
This problem has bothered many scientists, as clearly addressed by Carlo Cattaneo who proposed a hyperbolic transport model to solve it, nowadays referred to as the Cattaneo heat equation [
5,
6]. The Cattaneo heat equation, independently of its intrinsic relevance, has represented a major stimulus in thermodynamic research in order to extend the theory beyond the assumptions of the parabolic models (corresponding to what is usually referred to as “the theory of irreversible processes” [
4]), generalizing the representation of entropy production rate beyond the equilibrium ansatz, thus developing a more general framework referred to as “Extended Thermodynamics” [
7,
8]. Specifically, the rate of entropy production has been generalized by Müller and Ruggeri to include an additional quadratic dependence on the fluxes that superimposes to the expression deriving from equilibrium thermodynamics, and of course vanishing at equilibrium.
While this extension has marked a major advance in thermodynamic modelling of a variety of physical phenomena, motivating the convinction that the hyperbolic theory is not only physically consistent (with the principles of relativity as regards the boundedness of propagation velocity), but also necessary in order to account for the experimental observations especially at microscale [
8,
9], the hyperbolic foundation of extended irreversible thermodynamics grounded on the Cattaneo equation is characterized by a conceptual and mathematical shortcoming, namely the lack of positivity of the Cattaneo heat equation in spatial dimensions higher than one. In the one-dimensional case Mark Kac proved the stochastic foundation of the Cattaneo model and thus its positivity [
10].
The issue of positivity has been pointed out in [
11,
12], and it has represented the main motivation for analyzing a stochastic interpretation of transport models in higher dimensions via the concept of Generalized Poisson-Kac (GPK) processes [
12,
13], that subsequently has been extended to encompass also anomalous diffusional effects [
14,
15].
The starting principle in the analysis by Giona et al. [
12] of transport models, referred to as
the principle of stochastic consistency is indeed simple: the transport models expressed in the form of integro-differential equations for the concentrations of the transported entities should indeed derive from the micro/mesoscopic stochastic equations of motion at the particle/molecular level, as their statistical description (generalized Fokker-Planck equations). In this way the fulfillment of positivity is automatically ensured from probability theory.
In the first part of the present article we carefully analyze the issue of positivity for transport operators associated with mass and heat transfer, as this represents a foundative principle in any thermodynamic theory of irreversible processes, at the same level of physical importance of the positivity of entropy production rates in out-of-equilibrium conditions.
Indeed positivity, or better to say the lack of positivity, is one of the most evident ringbell for the lack of a correct thermodynamic behavior. We address this issue with the aid of a problem raised by Uffink [
16] and further realaborated by Giona [
17] in connection with the analysis irreversibility and thermodynamic behavior developed by Mackey [
18,
19].
The stochastic alternative to the Cattaneo model in higher dimensions is expressed by GPK models [
12,
13,
20,
21] characterized by Markovian transition rates, that reduces to the Cattaneo equation in one-dimensional case assuming a two-velocity simplification. These class of models put forward a representation issue, consisting in the fact that the resulting concentration fields of continuous thermodynamic theories may be functions not only of space and time variables, but also of other internal degrees of freedom, such as velocities or velocity orientations, in order to account for the Markovian nature of the transition process. This situation bears similarities with the kinetic foundation of transport theory, grounded on the Boltzmann equation, in which the one-particle density function - the dynamics of the lower moments of which determines mass, momentum and energy balances - depends explictly on the particle velocity [
22].
The above observations bring attention to the representation issue in continuous theories irreversible thermodynamics, as in principle the concentration fields involved in these equations may depends also on additional internal variables, and this dependence cannot be neglected. The analysis of this topic represents the second part of this article where we consider two interesting case studies motivated by microfluidic applications and by the analysis of chemical physical processes at microscale. The first problem is represented by the interaction of a diffusing particles with a solid boundary where adsorption/chemical reaction takes place. If the hydrodynamic interactions are accounted for, the effective diffusion coefficient depends on the particle position and it vanishes as the particle approaches the surface [
23,
24]. But even if the diffusivity is assumed to be constant, a subtle issue of stochastic consistency of the parabolic model arises due to the interplay between a stochastic model possessing unbounded propagation velocity (the Wiener model associated with the parabolic diffusion equation) and ordinary reactive events possessing a finite transition rate and/or a finite probability of occurrence.
The second case study is represented by mass-transport phenomena in complex viscoelastic flows in which any consistent model for mass transport should necessarily account for the internal degrees of freedoms associated with the viscoelastic relaxation of the solvent fluid [
25,
26,
27].
The article is organized as follows.
Section 2 succintly reviews the problem of the positivity of the Cattaneo equation and its stochastic solution in terms of Generalized Poisson-Kac processes.
Section 3 addresses the issue of positivity in a broader thermodynamic context, providing a physical interpretation of the Uffink counterexample to the Mackey theory of irreversibility. The case of a one-dimensional Poisson-Kac dynamics (Cattaneo equation) under time-reversal is explicitly analyzed. The representation issue originated by the formulation of GPK processes is also analyzed.
This important aspect is further exemplified with the aid of problems deriving from chemical-physical/hydrodynamic phenomena at microscale.
Section 4 addresses the problems of diffusing particles undergoing adsorption or chemical reactions at a solid surface, as the parabolic model in this case suffers some delicate issues of stochastic consistency, in the meaning that it cannot be represented in a simple wat by means of a stochastic dynamics with ordinary annihilation rates. Conversely, hyperbolic models are intrinsically suited for handling elegantly these problems.
Section 5 addresses another physical problem leading to interesting representation issues for the continuous concentration fields, related to diffusion in viscoelastic fluids, the rheological properties of which are accounted for and impacting, via fluctuation-dissipation relations, to the transport properties of the diffusing solute.
2. The Cattaneo Equation: Positivity and Stochastic
Representation
Consider the Cattaneo equation for a concentration field
,
,
characterized by two parameters: the diffusivity
D [m
2/s], and the relaxation time
[s
−1], out of which the characteristic velocity
,
can be defined. The inclusion of the first term at the l.h.s. of eq. (
1) with
determines the hyperbolic character of eq. (
1) that is characterized by a constant propagation velocity
expressed by eq. (
2).
For one-dimensional spatial problems, eq. (
1) specializes as
. The reduction of eq. (
1) to eq. (
3) is mathematically trivial, but its physical implications are much subtler that it may seem.
For
, the Cattaneo equation reduces to the parabolic diffusion equation, which admits a simple interpretation in terms of stochastic dynamics: eq. (
1) corresponds, for
, to the Fokker-Planck equation for the probability density function (coinciding, modulo an irrelevant multiplicative factor, with the concentration
), associated with the Wiener-driven Langevin equation
where
is the particle position vector at time
t and
the increement in the time interval
of the 3-dimensional Wiener process
(we use capital letters, such as
for the process, and lower-case letters, say
, for a realization of it).
Motivated by this strong connection between stochastic models of motion and transport equations (we return to this issue in
Section 4) it has been natural to search for a stochastic interpretation of the Cattaneo equation. This was provided by M. Kac in 1974 [
10] (although the original manuscript dates the early ’50 and almost at the same time S. Goldstein published an analogous contribution on persistent random walks [
28,
29]), in terms of a simple process defined by the parity transition of an ordinary Poisson counting process
,
characterized by the transition rate
.
The stochastic model defined by eq. (
5) is characterized by a constant velocity
in which the direction of motion is inverted accordingly to the parity of
. Consequently, the transition time
, i.e. the time interval between two inversions in the direction of motion is itself a random variable characterized by an exponential distribution with density
,
. The position
of the particle at time
t is not a Markovian process, but a Markovian embedding of it can be achieved by considering the joint variable
with
attaining values
.
In this way, defining the partial densities
,
the Chapman-Kolmogorov equation applied to
permits to derive the balance equations for
,
The Cattaneo equation eq. (
3) for the overall density
is recovered from eq. (
7) setting
,
. Due to its stochastic origin, the one-dimensional Cattaneo equation is consistent with the positivity requirement in the meaning that, if
, then
, solution of eq. (
3), is non-negative for any
.
The extension of this property to higher dimensions is not possible. In spatial dimensions higher that 1, the Cattaneo equation does not admit any stochastic interpretation in the meaning that there is no stochastic process possessing the Cattaneo equation as the evolution equation for its probability density function. Moreover, it has been shown by Körner and Bergmann [
11] that, starting from two-dimensional spatial problems, the Green function of the Cattaneo equation attains negative values.
This result can be easily checked by considering the fundamental solution of the one-dimensional
, and of three-dimensional
Cattaneo equation, corresponding to the response of the Cattaneo equation to an impulsive forcing both in space and time [
30]. In one-dimensional spatial problems, the Cattaneo equation eq. (
3) admits the fundamental solution [
30]
where
is the modified Bessel function of the first kind and order 0, and
the Heaviside step function of arguments
. In a similar way, the fundamental solution of the Cattaneo equation (
1) in
is given by [
30]
where
is the modified Bessel function of the first kind and order 1 of argument
, and
represents the continuous, nonimpulsive part of the fundamental solution.
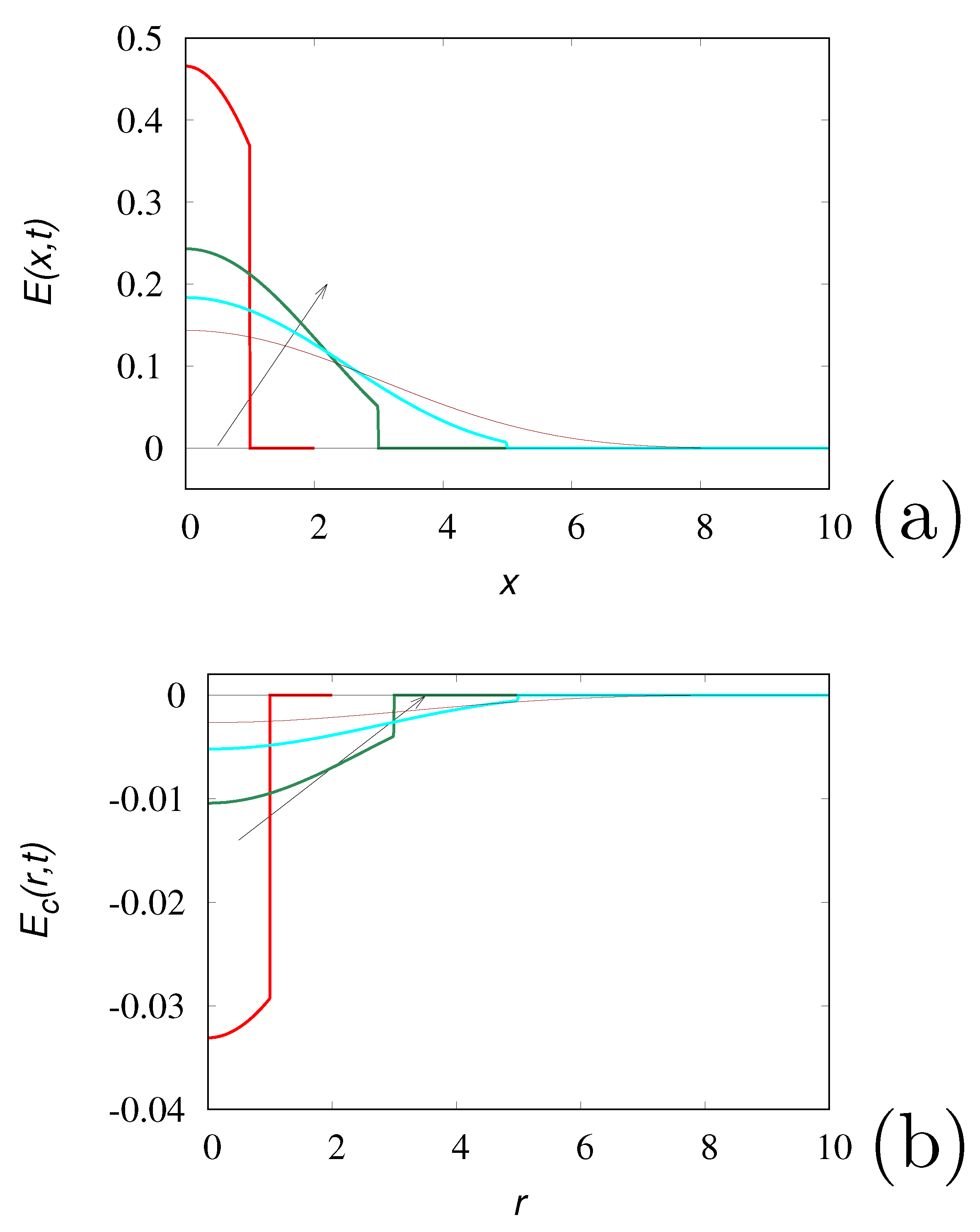
Figure 1 depicts the fundamental solutions of the Cattaneo equation in one and three dimensions. In the one-dimensional case
is always non-negative, consistently with the positivity requirement (panel a). Conversely, the regular, non-impulsive part of the three-dimensional fundamental solution
in
displays negative values (panel b).
The lack of positivity is a major physical problem in all the situations in which the concentration
corresponds to the specific content of intriniscally non-negative physical entities, such as in mass and thermal transport problem. The only exception in represented by momentum transfer, i.e. the equations of hydrodynamics, as the hydrodynamic mean field velocity is the first-order moment of a probability distribution function (see e.g. the classical kinetic analysis based on the Boltzmann equation), and consequently no requirement of positivity for the momentum-transfer equations is dictated by fundamental principles. In the case of momentum transfer, the natural extension of the Newtonian paradigm is to consider constitutive equations of viscoelastic nature for the shear stress tensor as a function of the deformation tensor, characterized by finite nonvanishing relaxation times [
31,
32]. In this way, the finite propagation velocity of the shear stresses can be accounted for, as discussed in [
27] (se also [
26]). Nevertheless, in dealing with hydrodynamics, this represents a second-order problem with respect to the commonly assumed hypothesis of incompressibility for liquid flows, corresponding to the solenoidal condition for the velocity field, as the latter implies an infinite convective velocity in the propagation of density and pressure perturbations (infinite sound velocity). A way for overcoming this issue is addressed in [
33] where a dynamic formulation of the pressure contribution is proposed.
3. Positivity Constraint and Irreversibility
As addressed above, the condition of positivity is structural and fundamental whenever mass and thermal balances are concerned. To perform a mass balance means essentially to count the number of molecules (particles) that are present in infinitesimal volume elements. A negative number of atoms (and similarly a negative value of a probability or a probability density) is an alarm-bell that something in the theory is deeply incorrect, and it can hardly be justified as acceptable even in a non-classical quantum interpretation of fluctuations (as claimed e.g. by R. Feynman [
34]).
The positivity of the evolution equations for mass/temperature is therefore a fundamental constraint in the balance equations of any theory of irreversible phenomena. In the remaninder we attempt to explain why the positivity constraint is in principle as fundamental as the fulfillment of the second principle of thermodynamics dictating the positivity of entropy production rates. Specifically we consider the Mackey theory of irreversibility [
18,
19].
In series of works [
18,
19] Mackey addressed in detail the properties a dynamical system should possess in order to exhibit a thermodynamic behavior. The analysis is based on the Markov operator associated with the dynamics, mapping densities into densities. For instance if one considers the Langevin dynamics eq. (
4), the evolution equation for densities is the parabolic diffusion equation
, and the corresponding Markov operator
, continuously parametrized with respect to
, is
such that
. The proper space for studying the properties of Markov operators is the space of functions
in the domain
(corresponding to the physical region where transport occurs), equipped with the
-norm
. In general, a Markov operator is any linear operator
, parametrized with respect to time
, such that for any
,
the following conditions are met:
probability conservation,
The time-domain of definition of the Markov operator can be either in the case of invertible systems, or for non-invertible ones.
As a criterion for a proper thermodynamic behavior, Mackey chose the increase of the Kullback conditional entropy with respect to the equilibrium density. More precisely, assume that the Markov operator admit an equilibrium density
, such that
. The conditional entropy
of
with respect to
is defined by
and, according to Mackey, a system possesses a proper thermodynamic behavior if the conditional entropy
is a monotonically increasing function of
t, vanishing at equilibrium. Based on this reasonable definition, Mackey was able to show that if the Markov operator is invertible then
i.e. the conditional entropy does not increase, remaining constant at the value dictated by the initial density
. This is the case of a dynamical system defined by a system of ordinary differential equations. Consequently, “nonivertibility in system dynamics, as reflected in an evolution of densities via a nonivertible Markov operator, is necessary for the entropy to increase as the system evolves” (p. 33 in [
19]).
This formulation has been questioned by Uffink [
16], and elaborated further in [
17]. Specifically, Uffink considered a 2-state Markov chain, which, as well known, possesses a proper thermodynamic behavior. Indicating with
and
the probability of the two states, and
, we have
with
. In this case
, and since
possesses bounded eigenvalues
,
, the inverse operator
,
can be defined, and consequently
is invertible, apparently in contradiction with the Mackey’s result. More specifically, consider the forward dynamics eq. (13) up to a given time
, and then define
.
A similar situation arises in the case of Poisson-Kac processes as well as in the case of any GPK or Extended Poisson-Kac process [
15] possessing Einsteinian (the mean square displacement is in the long-term a linear function of time) or anomalous diffusive behavior (the mean quare displacement is in the long-term a nonlinear function of time). The reason for this essentially lies in the spectral properties of these processes [
17,
35], as the eigevalues of their evolution operators possess bounded real part (in the case of parabolic models, the real part of the ordered eigenvalue sequence diverges to minus infinity causing
to be a semigroup with respect to time
t, and thus a non invertible operator).
In order to make a concrete example consider the simplest two-velocity Poisson-Kac model in nondimensional form defined in a closed domain
, equipped with periodic boundary conditions. The dynamics for the partial densities
corresponds to eq. (
7) with
. The Poisson-Kac process possesses a proper thermodynamic behavior. The entropy function in this case can be defined as
By making use of eq. (
7) in the case
equipped with periodic boundary conditions and unit values for
and
(simply corresponding to the nondimensional formulation of the Poisson-Kac process) one obtains
and the definition of the entropy
is analogous, modulo an additive constant, to the Kulback conditional entropy as the equilibrium partial densities
are uniform in
.
In this case,
, the eigenfunctions of
are simply the periodic Fourier imaginary exponentials
, with the associated eiganvalues
,
, where
,
for
and
, for
,
, with
. The closed form solution of eq. (
7) in this case takes the expression
where the expressions for
,
are reported in the Appendix.
As for Markov chains, the dynamics of Poisson-Kac processes is invertible: by considering the time reversal
and inverting the direction of the velocity, which corresponds to the transformation
where
refer to the time-reversal dynamics satisfying the equations
As in the case of the Markov chain, integrate the dynamics up to a given time instant
, and then, starting from the profiles at
, perform the time-reversal to obtain
,
.
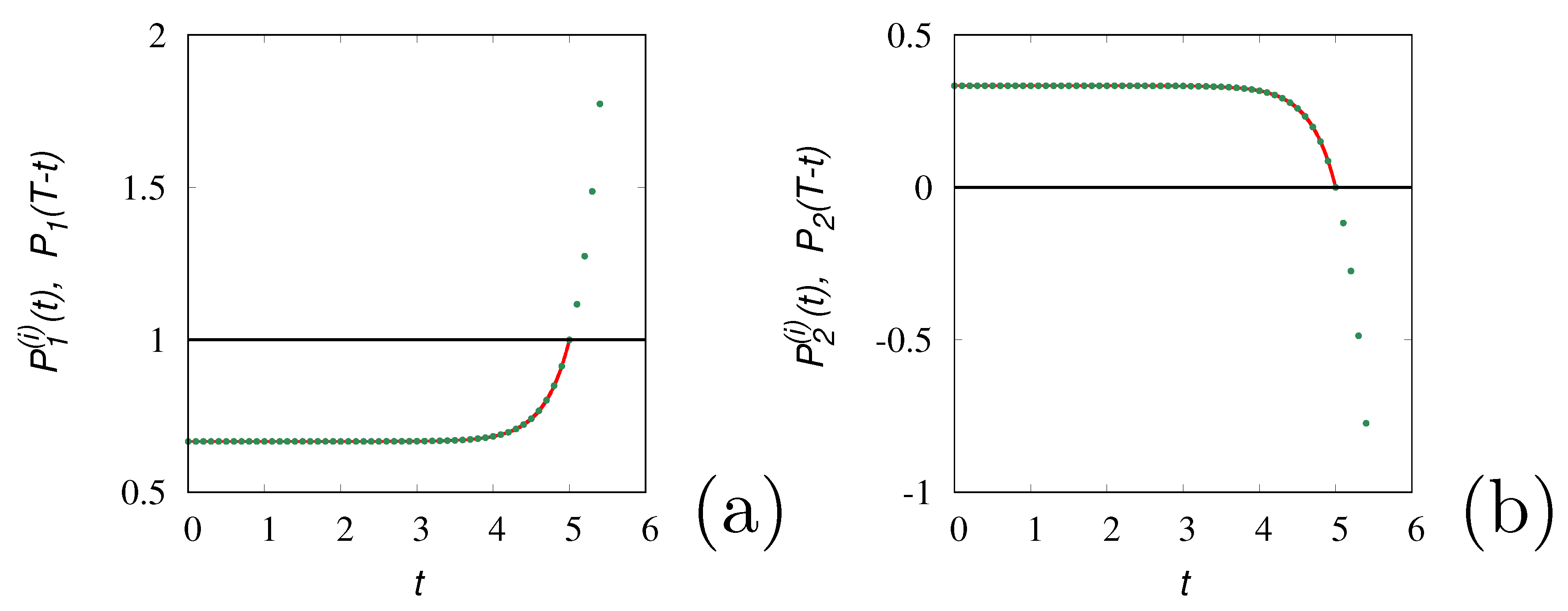
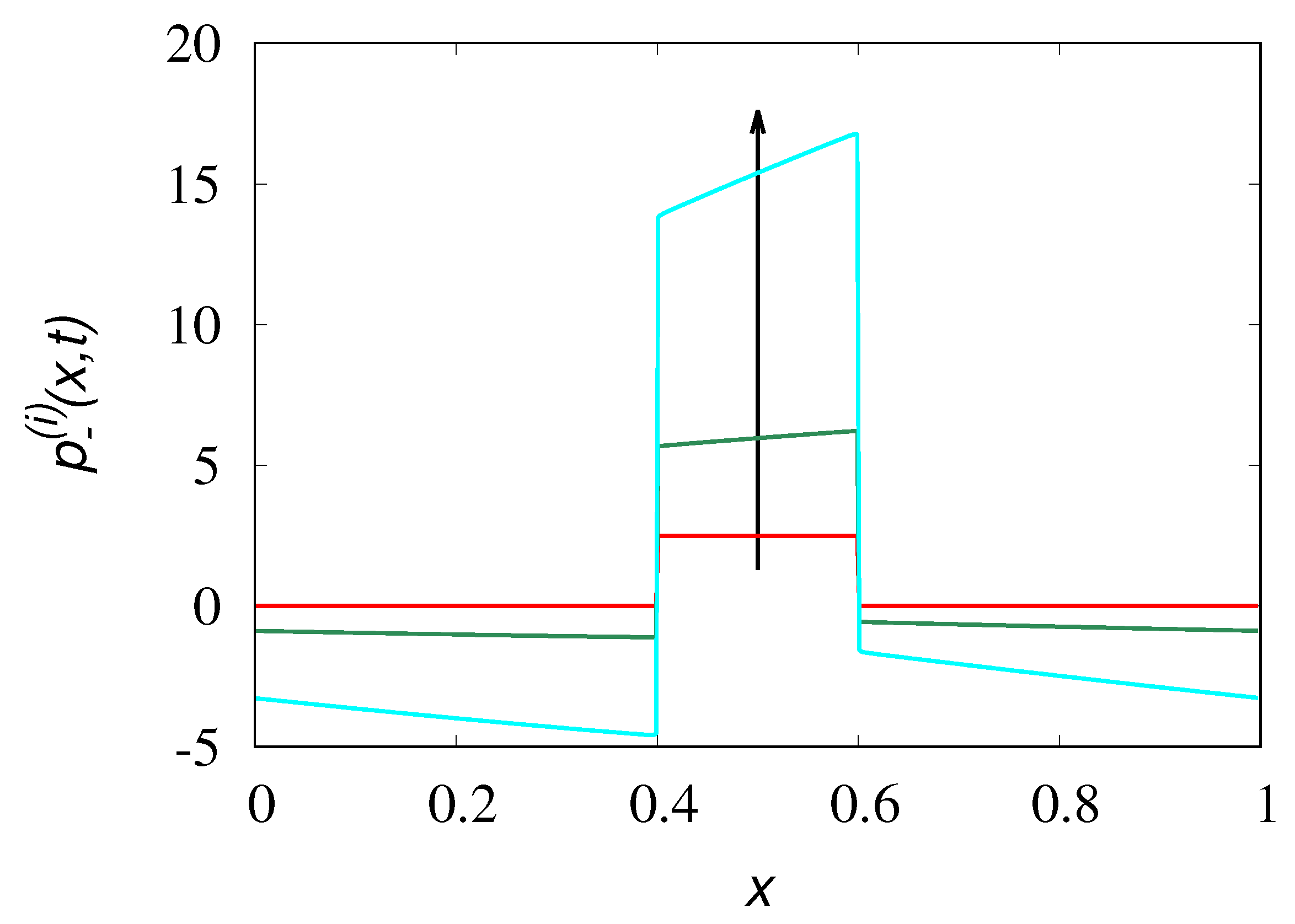
Figure 2 depicts the result of the time-reversal operation i.e. the quantities
,
, for the 2-state Markov chain starting from
,
,
,
, integrating up to
.
As expected for
the inverse dynamics correctly reproduce back the forward trajectory up to he initial configuration. For
, quantities
either attains negative values or values greater than 1. A similar situation occurs for the Poisson-Kac dynamics.
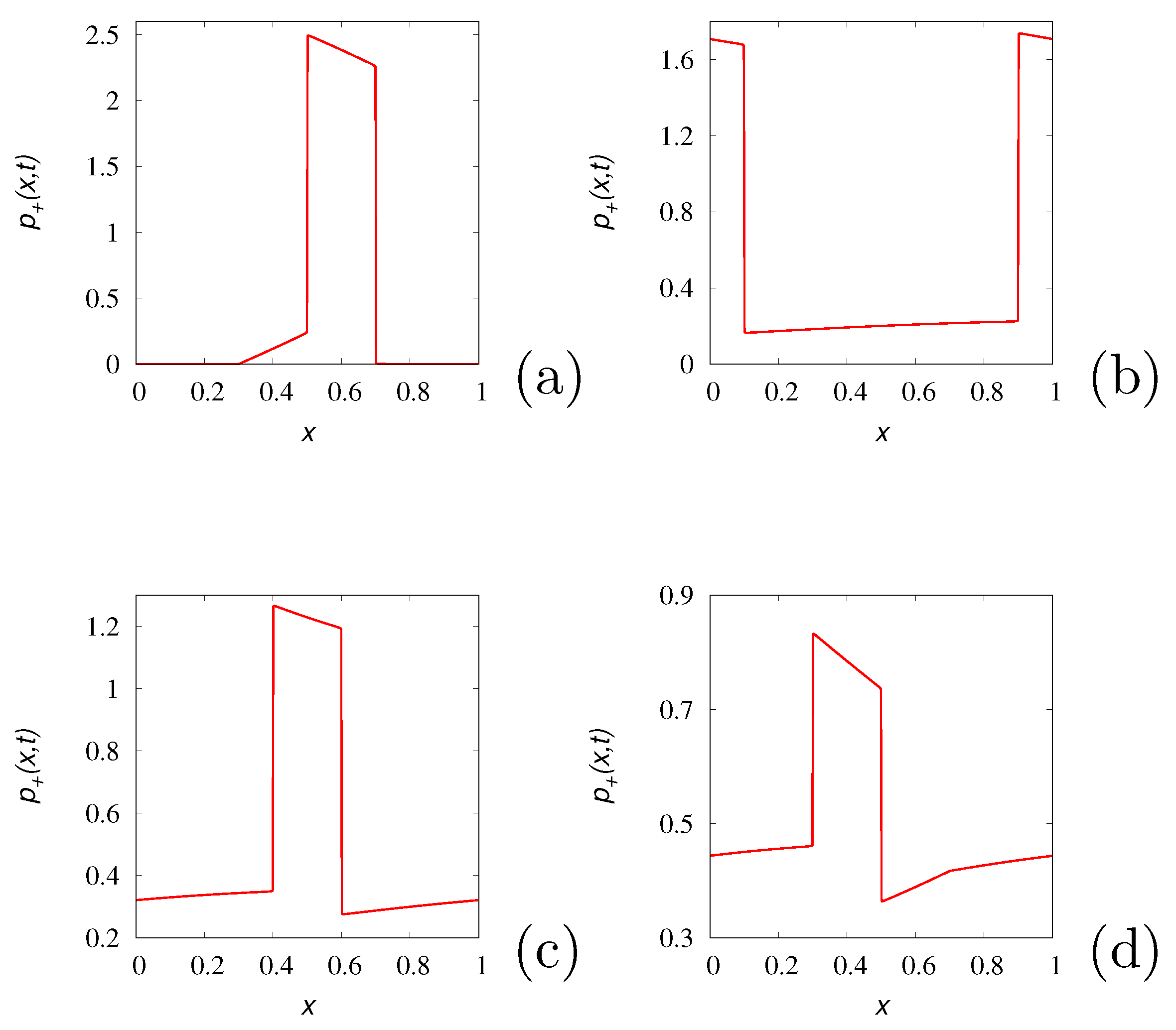
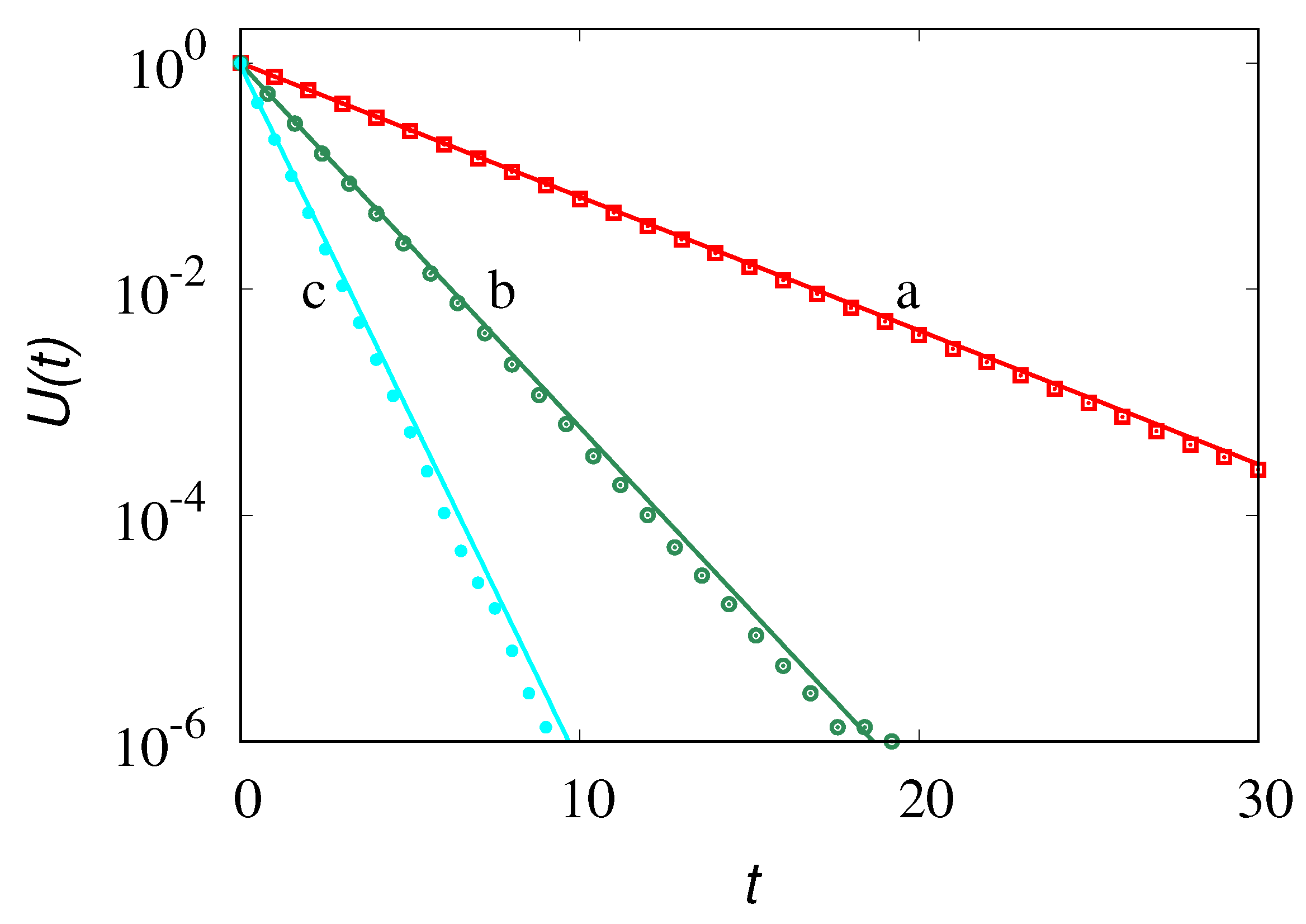
Figure 3 displays the partial density
obtained from eq. (
18) starting from the initial distributions
for
and zero otherwise with
and
at various time instants. The stopping time has been set equal to
.
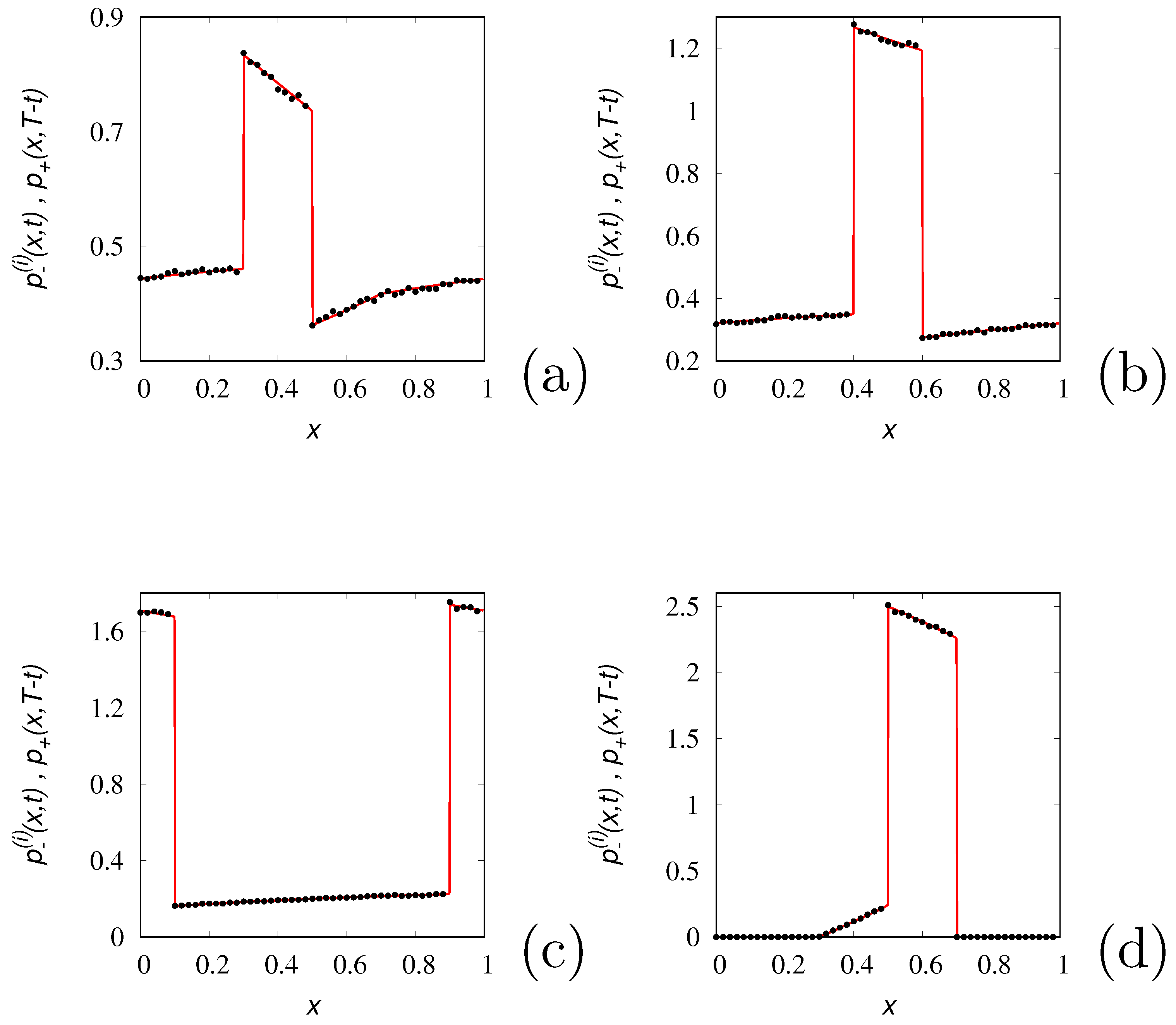
The profiles of the time-reversed dynamics
(lines) at several values of time
are depicted in
Figure 3 against the results of stochastic simulations (symbols) for
. As expected from the spectral structure of the Poisson-Kac processes the time-reversed dynamics correctly reproduces backwardly the concentration patterns up to
. At later times the concentration profiles attain negative values, as depicted in
Figure 4, reproducing perfectly the initial profile at
.
This result is not surprising, and provides a conclusive answer to the Uffink’s objection to Mackey theory. For
the time-reversal defines an operator
that is no longer a Markov operator, as the positivity condition eq. (
11) is not met. In both the cases considered, as well as in all the cases in which the eigenvalues of the Markov operator possess bounded real part, is the positivity constraint (or better to say its failure for the time-reversed operator
), that indicates that the time-reversed dynamics does not exist as a probabilistic model (i.e. that
exists as mathematical operator but it is not a Markov operator), and moreover that the theory developed by Mackey fully and beautifully applies to all this cases.
The above analysis clearly indicates the thermodynamic importance of the positivity constraints, and how it can be applied to discriminate between thermodynamic and non-thermodynamic behavior of dynamical systems.
For this reason, in developing higher-dimensional transport models generalizing the Cattaneo heat transfer equation and ensuring the positivity constraint, a safe approach is to obtain them from micro/mesoscopic stochastic models of motion. If one generalizes the original Kac’s approach from one-dimensional to higher dimensional problems, the natural mass/heat transport model is represented (in the linear case) by Generalized Poisson-Kac processes the probabilistic description of which involves the joint probability density
, parametrized with respect to particle velocity
and defined by the integro-differential equation
with
, and
,
. Eq. (
20) corresponds to a linear Boltzmann equation, and an open question is to obtain simplified evolution equations for the marginal density
other than the long-term parabolic diffusion equation. This means that thermodynamic theories and transport equations should necessarily include in their formulations the presence of additional degrees of freedom (in this case, the velocity variable
) and develop the theory accordingly. Of course the model may include additional physical effects becoming nonlinear in the densities
[
9,
13]. Another even more drastic representation issue emerges in the study of mass transport in complex fluids, as outlined in
Section 5.
4. Coupling Transport with Interfacial Phenomena: Stochastic Consistency at Work
The requirement of stochastic consistency can be used to explore another class of chemical-physical problems, involving the occurrence of chemical reactions at an interface, the prototypical model of which is represented by a diffusing solute performing a chemical reaction at an interface possessing zero measure. This simple problem highligts a subtle pathology of the parabolic models when considered in the light of a microscopic stochastic model for the process.
Consider a solute, the concentration of which is
, diffusing in a closed domain, say
, and performing at
a surface chemical reaction (modeled as a first-order reaction), while the other boundary,
, is impermeable to mass transport. Assuming the classical parabolic model for diffusion, we have
equipped with the boundary condition
where the constant
(isothermal conditions are considered) accounts for “the rate” of the surface chemical reaction. This meaning of
is further addressed in the remainder. The initial condition is unform inside the system,
.
In a nondimensional setting,
,
,
, we have,
where
represents the mass-transfer Biot number. For the sake of notational simplicity, we will indicate the non-dimensional variables
and
simply as
x and
t. Eq. (
24) is a linear problem admitting a closed form solution
where
,
are the roots of the cardinal eigenvalue equation,
. The fraction of solute
within the system at time
t is given by
The non-dimensional concentration
can be interpreted probabilistically as the probability density of finding the solute particles in the system, the dynamics of which is expressed by the simple Langevin equation
where
is the increment of a Wiener process in the time interval
. While the boundary condition at
corresponds to a reflection in particle motion, problems arise in expressing the reactive bondary condition at
for finite and non-vanishing values of
(and consequently of
). This stems from the fact that
is not strictly speaking a rate, as it possesses the physical dimension of a velocity [m/s]. Consequently, the reactive boundary condition does not correspond to an ordinary Markov process for a solute particle touching the reactive boundary and being annihilated at it.
As well known [
36,
37] it is possible to provide an algorithmic solution to this problem. Consider the numerical simulation of eq. (
26) adopting a time step
, i.e.,
, where
, and
,
are independent and identically distributed random variables sampled from a normal distribution (with zero mean and unit variance). If
touches or crosses the reactive boundary at
the particle reacts (it is annihilated) with probability
(in the nondimensional formulation
), otherwise it is reflected back.
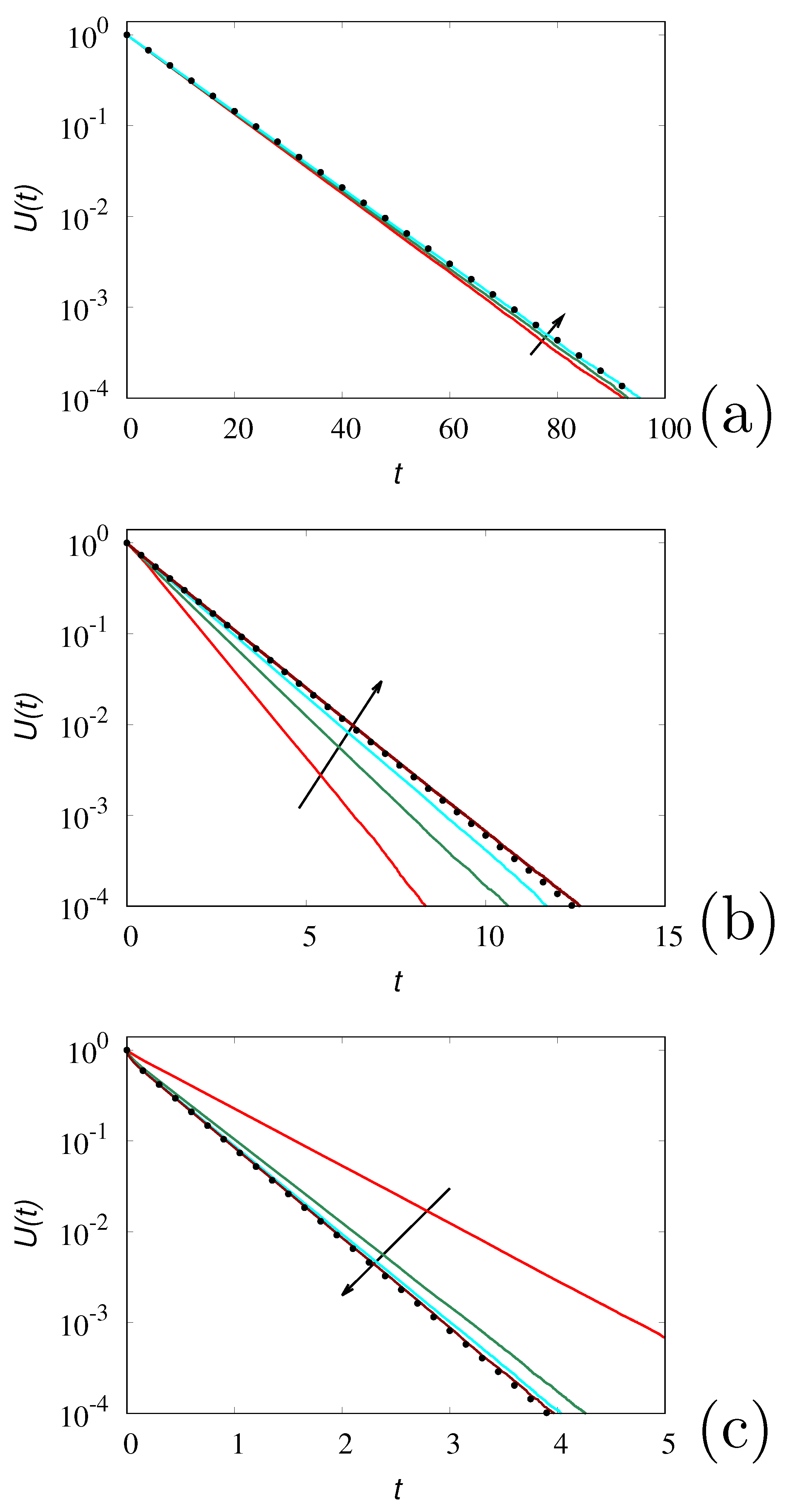
Figure 6 shows the results of stochastic simulations using eq. (
27) for an ensemble of
particles with
compared with the analytical result for
eq. (
25).
But the application of eq. (
27) to the discretized approximation of the Langevin equation (
26) represents an algorithmic solution of the dynamics that does not correspond, strictly speaking, to any stochastic process evolving in a continuous space-time and performing ordinary reactive events (i.e. possessing a finite rate). For this reason, we can state that the parabolic model of a diffusing species performing a surface chemical reaction at a solid interface violates the requirement of stochastic consistency, providing a pathological situation that can be referred to as
the paradox of surface chemical reactions.
In point of fact this paradox finds a simple explanation if one consider the properties of the trajectories of Wiener processes, and their intersections with lower dimensional manifolds (in this case the reactive interface): if a Wiener process crosses an interface at time
, in the neighbourhood of
a Cantor set (Cantor dust) of intersections occurs the fractal dimension of which is
[
38], justifying the rescaling of
by the factor
.
This problem finds a straightforward and elegant solution considering models of transport possessing finite propagation velocity. For simplicity consider the case of a Poisson-Kac process
where
,
, so that the effective diffusivity
equals 1, equipped with the initial and boundary conditions at
The reactive events occurring at
are described by means of the probability
corresponding to the annihilation probability for a particle touching the reactive interface. Consequently, the reactive boundary condition at
becomes in the hyperbolic setting
indicating that a fraction
of the incoming flux of particles
is reflected back. Eq. (
28) equipped with the boundary conditions eqs. (
29)-(
30) admits a consistent stochastic representation, independent of the algorithmic temporal resolution
.
Figure 7 depicts the temporal evolution for
obtained from the stochastic simulations of the above hyperbolic model (
,
) for several values of the annihilation probability
. The stochastic simulation is rather simple: initially the particle are randomly and uniformly distributed in
, with equal probability of positive and negative velocity direction. Each particle performs a Poisson-Kac dynamics
, where
is a Poisson counting process with transition rate
. If a particle reaches
it is reflected back, if it reaches
it is annihilated (removed from the ensemble) with probability
.
By varying from to the whole spectrum of physical situations is described, from complete reflection () to total annihilation once the reactive boundary is touched ().
The parabolic model eq. (
23) can be recovered in the Kac-limit letting
be arbitrarily large, still assuming
, and defining the annihilation probability
in terms of
and the Biot number
. To obtain this relation, consider the expression
fo the flux in the hyperbolic model. Enforcing the reactive boundary condition eq. (
30) we have
In the Kac limit (
,
),
, where
is the overall density, so that eq. (
31) provides
This boundary condition should be compared with the boundary condition eq. (
23) of the parabolic model, indicating that the group
should coincide with
, i.e.,
that corresponds to the fact that
decreases as
to vanishing values in the Kac limit. Eq. (
33) is clearly indicating the intrinsic pathology of the parabolic Kac limit in the presence of interfacial effects (surface chemical reactions, adsorption phenomena). Given
, for large but finite
’s the annihilation probability
progressively decreases, still attaining non vanishing values (ensuring the occurrence of the chemical reaction). Hovewer in the limit
we have
(and
means that the incoming flux at the interface is totally reflected and no reaction occurs), indicating that the Kac limit is a singular limit in the presence of interfacial phenomena. In this sense the parabolic model is a singular, and physically pathological limit, of the hyperbolic Poisson-Kac dynamics.
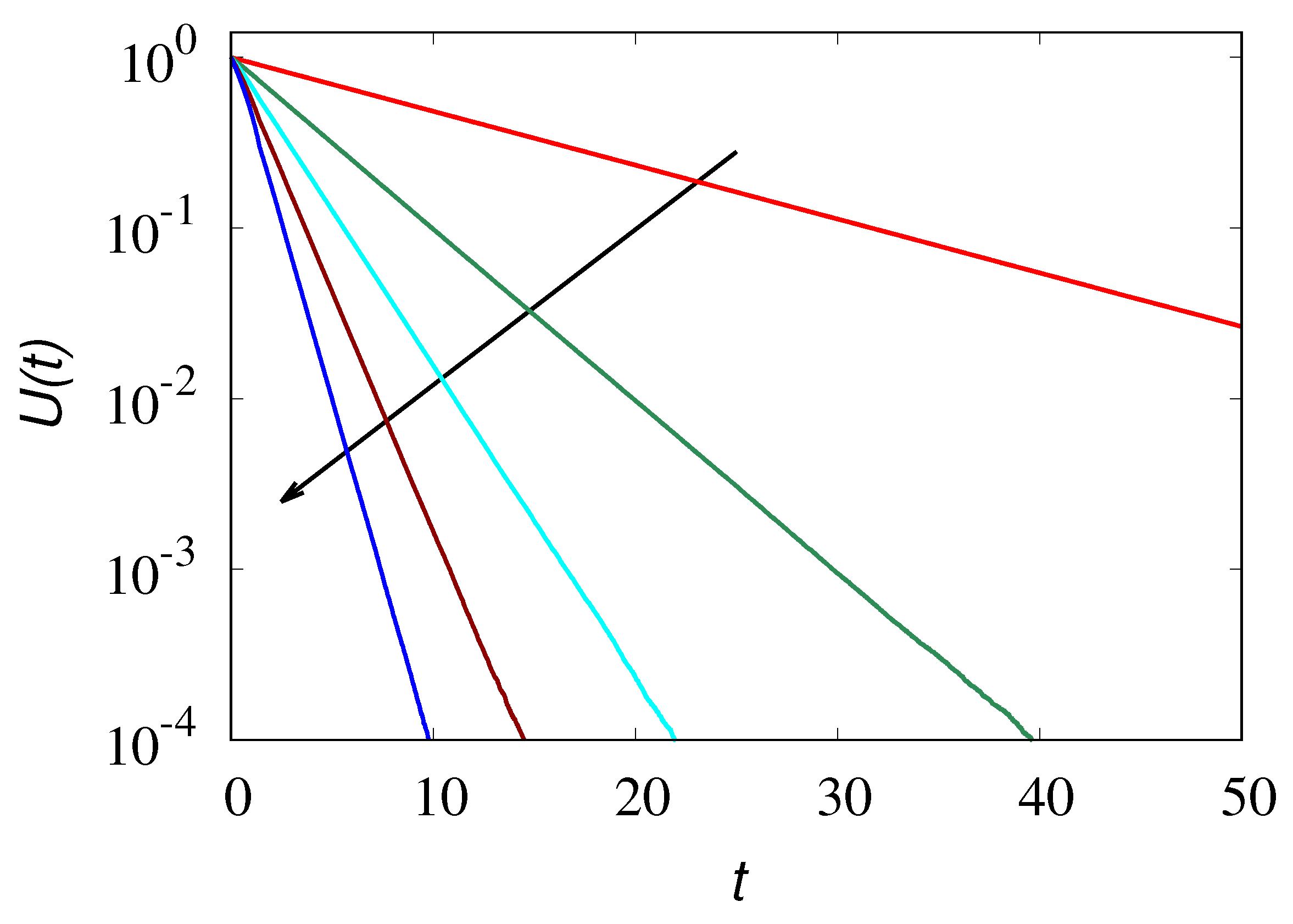
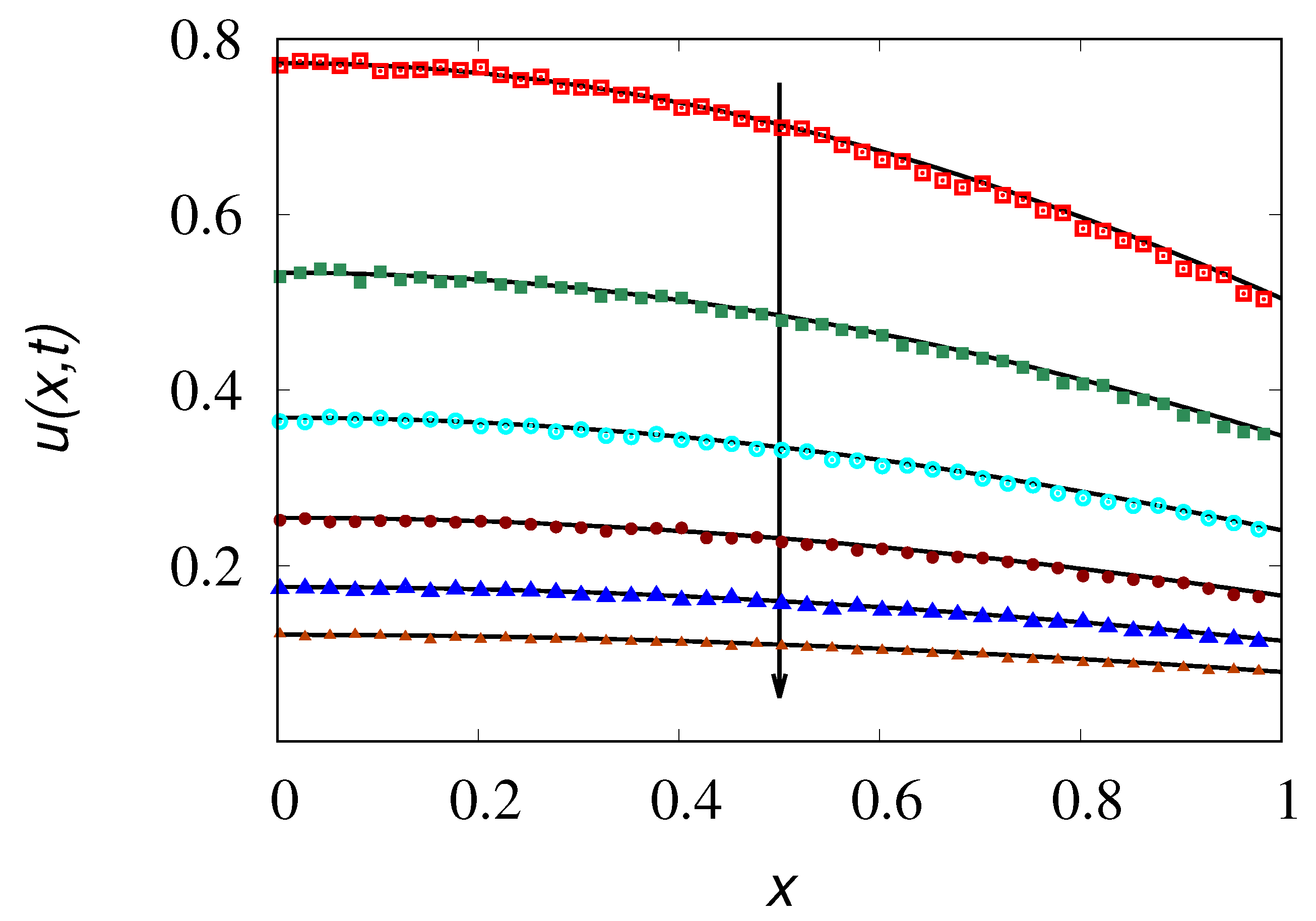
To exemplify of the above analysis of the Kac limit for large but finite values of
,
Figure 8 depicts the behaviour of
obtained from the stochastic simulations of the hyperbolic transport model at three different values of
for increasing values of
, compared with the corresponding results of the parabolic model eq. (
25). The behaviour of the concetration profiles at different time instants for
is depicted in
Figure 9 compared with the parabolic result eq. (
24).
The number of particles used in the stochastic simulations reported in
Figure 8 is
, while
for the concentration profiles depicted in
Figure 9.
As expected the results of the hyperbolic model converge to those of its parabolic limit and, by taking large, enough the difference between the two settings becomes immaterial.
5. From the Equations of Motion to Continuous Models of Transport
In classical transport theories as well in the extended formulation of thermodynamic theories of irreversible phenomena we are used to consider concentration fields of transported entities as smooth functions of spatial and temporal t coordinates, and consequently to develop thermodynamic analysis of their consistency starting from this formal setting.
However, there are situations in which a coherent and accurate formulation of the transport equations requires the introduction of additional internal variables, the dynamics of which accounts for the physical response of the system. This phenomena have been briefly discussed in
Section 3 in relation to hyperbolic model of transport associated with GPK processes in order to enforce the requirement of finite propagation velocity. In this Section we consider an even more fundamental situation associated with the constitutive properties of a fluid medium. This is indeed the case of transport phenomena in viscoelastic and polymeric fluid possessing non-Newtonian rheological properties. The parabolic modeling of transport is explicitly considered, in order to focus on the strictly rheological nature of problem. The extension to the hyperblic setting is straightforward. Macroscopic transport equations in generic fluids can be developed from micro/mesoscopic stochastic equations of motion. Indeed the basic paradigm of this approach is expressed by the theory of Brownian motion: i) express particle dynamics accounting for mean-field hydrodynamic interactions and stochastic thermal flucuations, ii) define the intensity of velocity fluctuations from equilibrium properties at constant temperature, and finally iii) make of the overdamped approximation so that the statistical description of the process can be expressed exclusively in terms of the spatial concentration
of the diffusing species, without any account to the particle velocities.
The same approach can be extended to transport in any real complex fluid, once its rheological properties are specified [
31]. Below we consider the case of a viscoelastic fluid, neglecting for simplicity the effects of fluid inertia on particle hydromechanics [
27]. In the linear viscoelastic case, the particle equations of motion can be written in terms of a friction kernel
, accounting for the memory effects in the viscoelastic response [
25]
where
represents the stochastic thermal forcing. Setting
,
,
,
. Particle motion is described by the system of equations
where “*” indicates convolution. The kernel
can be obtained from the rheological properties of the fluid medium, and in general it can be expressed as the linear combination of exponentially decaying functions of time [
31,
32]
characterized by the relaxation rates
,
. Setting
, eq. (
35) can be rewritten as
where
,
, are distributional derivatives of independent Wiener processes. Observe, that in eq. (
37) the thermal forcing term entering eq. (
35) has been redistributed amongst the internal
-degrees of freedom. In eq. (
37) the coefficients
should be determined from fluctuation-dissipation relations and from the equilibrium property
. After some algebra, this provides the values of
[
39]
From the above analysis, it follows that the Fokker-Planck equation associated with eqs. (
35)-(
37) represents the rational and correct way to express mass balance in the viscoelastic medium. Specifically, the associated Fokker-Planck equation involves the joint density
and it takes the form
There is no way to reduce eq. (
39) for
e.g. via an overdamped approximation, to an equation exclusively expressed with respect to the marginal concentration field
This means that a correct formulation of the transport problem in a viscoelastic medium should involve the solution of the
-dimensional parabolic model equipped with suitable boundary conditions describing the specific case study under consideration. The problem of mass transport in viscoelastic media, treated rigorously starting from the equations of motion coupled with fluctuation-dissipation relations, opens up interesting issues as regards the representation formalism in thermodynamic theories and the possibility of obtaining reduced models, It indicates the need of introducing additional variables accounting for the history of the process (the
variables), that cannot be projected out in a simple and consistent way. If
N is sufficiently large,
, the direct solution of eq. (
39) becomes unfeasible and the only way to study the process is to return to the direct simulation of the stochastic Lagrangian equations (
35)-(
37).
6. Concluding Remarks
There are two main issues addressed in this article. First of all the physical relevance of the positivity condition for the evolution equations of concentrations, without which any analysis of irreversibility based on entropic constraints looses its meaning.
The example of the statistical properties of Poisson-Kac processes under time reversal is paradigmatic, as this process is irreversible. This process is ireversible, not because the time-reversed operator , , of its Markov operator cannot be defined ( exists in a mathematical and physical sense), but because is no longer a Markov operator due to its lack of positivity: does not map (positive) densities into (positive) densities. The backward evolution of starting from any initial distribution traces back its previous history up to a given time instance , corresponding to the time instant at which either the forward or the backward densities attain at some point vanishing values, and afterwards the densities start to become negative. One the densities become negative any definition of entropy based on the average of their logarithms looses its meaning. This case study clearly shows the significance of ensuring the positivity condition, and this can be safely achieved if the macroscopic transport model admits a stochastic interpretation, i.e. if it represents the statistical description of some micro/mesoscopic stochastic model of motion or interaction. This leads for processes possessing finite propagation velocity and Markovian or semi-Markovian transitions to a statistical description expressed in the form of integro-differential evolution equations for the associated densities.
The second main issue, involving either stochastic consistency and representation problems, originates by the description of microscopic phenomena espressed e.g. in the form of chemical-physical interactions (surface chemical reactions) or hydrodynamic models (as in the case of particle motion in complex viscoelastic fluids).
The case of simple surface reactions is particlarly interesting as it shows that parabolic transport models can hardly copes with event-based phenomena as surface reactions occurring at in interface. Indeed, it is possible to provide an algorithmic strategy to address this class of problems in numerical simulations, assuming kinetic processes to be dependent of the time resolution adopted in the particle motion, but this strategy leads to a singular limit for . For these problems, the hyperbolic approach provides a consistent formal setting for accomodating interfacial events occurring with finite rate and non-vanishing probabilities. This indicates once again that bounded velocities implies also finite transition rates in order to avoid the occurrence of singular limits.
In terms of the thermodynamic represenation of the evolution equations, an even harder problem is provided by transport (diffusion) processes in complex fluids. The case of viscoelastic fluids has been analyzed starting from the Brownian motion rationale in order to derive the transport equations from the microscopic/mesoscopic dynamics. In this case, due to the memory effects associated with the complex response of the fluid medium, it is practically impossible to project out the relaxation degrees of freedom of the medium in order to obtain transport equations expressed exclusively in term of the concentration fields of the diffusing species. This leads to higher-dimensional transport models, that necessarily account also for the evolution of the memory degrees of freedom in the particle dynamics (the variables
,
introduced in
Section 5) the solution of which, for
N sufficiently large, becomes unfeasible, leaving to the direct stochastic simulations the only reasonable alternative to tackle these problems.