Introduction
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) play a major role in associating specific genetic variants with common diseases and complex traits [
1,
2,
3]. Sometimes, researchers may have limited access to individuals’ genetic information with specific traits and large-scale genetic studies can be expensive and resource-intensive [
4]. Thus, with a small sample size in GWAS, the association test could have low power and may also increase the possibility of false-positive findings, especially for infrequent variants (i.e., MAF < 5%) [
5,
6].
The rapid development of sequencing technologies has promoted substantial advancement in GWAS, particularly in obtaining comprehensive genetic information from limited samples [
7,
8]. The integration of sequenced samples provides a great opportunity for identifying novel genetic associations and increasing the statistical power of single-variant association tests [
9]. Nevertheless, the challenges associated with integrating sequenced samples arise from various factors, such as the utilization of diverse sequencing platforms, variations in genotype calling procedures, the presence of population stratification, and so forth [
10]. In a single study, by incorporating sequenced samples from other studies as an external control sample, the power of single-variant tests can be significantly increased without incurring additional sequencing costs. However, the systematic differences (batch effect) between studies could inflate the type I error rates and increase the possibility of false-positive findings in association studies [
11].
Several methods have been proposed recently to address the systematic differences between genotyped data of internal and external sources using likelihood-based methods [
12]. Liu and Leal proposed a method SEQCHIP to correct bias for integrating genotype data in rare variant association studies [
13]. Derkach et al. proposed another method that substitutes the genotype calls by the expected values given observed sequence data to account for differential read depths between studies [
14]. Motivated by Derkach et al., Chen and Lin proposed regression calibration (RC) methods to account for differential sequencing errors between cases and controls [
15]. Although these methods are powerful, computing genotype probabilities and storing sequence reads data can be challenging and expensive for large-scale studies. Thus, ProxECAT incorporates external controls to estimate enrichment of rare variants using allele counts in case-control analysis [
16]. However, nonuse of the internal control samples potentially limits the power of the association test. iECAT allowed the incorporation of external controls in single variant association tests [
11]. And the batch effect between internal and external studies can be assessed by comparing odds ratio estimates of alleles using internal control samples and combined control samples from internal and external studies. Then an empirical Bayesian-type shrinkage estimator is constructed based on the degrees of odds ratios in the single-variant test. And it is demonstrated that this method can control type I error rates, as well as improve the power of the association test. However, this method cannot adjust for covariates such as age, gender, and so on [
11]. Based on the aforementioned method, Li and Lee proposed a novel score based test, which constructs a shrinkage score statistic using exclusively internal samples and external control samples, allowing for covariate adjustment [
17]. However, the power increase of this method in association testing by integrating external controls is limited for extremely unbalanced case-control studies.
In this study, we present a novel approach that integrates External Controls into Association Tests by Regression Calibration (iECAT-RC) to incorporate external control samples in case-control association studies. The objective of this research is to boost the statistical power of the single-variant association test by integrating external controls with the adjustment of batch effects. We propose an approach that adjusts the genotypes of an external control sample to approximate the same distribution as the genotypes in the internal control sample through regression calibration. Furthermore, we apply the Saddlepoint approximation [
18] and efficient resampling [
19] methods to control type I error rates with imbalanced case-control and low minor allele count (MAC) scenarios, respectively.
Materials and Methods
Consider a phenotype with case and control states. We code a case as 0 and control as 1. Assume that the internal study has the sample size with controls and cases and ; the external study has controls. For the subject, let be the dichotomous phenotype. Denote , and as the genotypes of the internal control sample, the internal case sample, and the external control sample at a genetic variant, respectively, with indicating the number of copies of the minor allele carried by the subject at that genetic variant. We denote be the first principal components of internal genotypes, and be the first principal components of external genotypes for the subject.
Motivated by the novel method iECAT-Score [
20], we propose a new method by integrating external controls into association tests to boost the statistical power. Our proposed method involves three steps. Step 1. adjusting the genotypes of external controls using regression calibration; Step 2. conducting single-variant association test; and Step 3. calibrating single-variant test using Saddlepoint approximation (SPA) [
18] and efficient resampling (ER) methods [
19], particular addressing scenarios of case-control imbalance and low minor allele count (MAC). By following these three steps, the iECAT-RC method effectively minimizes the impact of batch effects and improves the power of association testing.
Step 1. adjusting the genotypes of external controls by regression calibration
To adjust the genotype of external control samples for the batch effect, we propose to use the following procedure:
1). Without loss generality, we assume . We randomly choose individuals with genotypes from external control samples.
2). We assume a linear regression model for , where is the least square estimate of .
3). We repeat 1) and 2) times. We obtain and calculate the average value . Let for . When , we let take 0, where is determined such that the frequency of 0 in the internal control genotypes equals to the frequency of 0 in for . When , we let take 1, where is determined such that the frequency of 1 in the internal control genotypes equals to the frequency of 1 in for . When , we let take 2.
We repeat the above procedure till we obtain for . Then we perform the association test based on the internal case-control data and external control data with genotypes .
Step 2. Single-variant association test
We combine the internal samples and external control samples with the adjusted genotypes. is the vector of genotypes at a variant for subjects, where . Assume that there are covariates, then we relate the phenotype to the covariate , and genotype using the logistic regression model , where the phenotype follows a Bernoulli distribution. In this equation, is a vector of coefficients for covariates including the intercept, and is the genotype effect at the variant. Assessing whether the association exists between the phenotype and the genotype at a variant is equivalent to testing .
Let
and
be the maximum-likelihood estimate of
under
. In the score test, the score is given by
. where
,
is the covariate adjusted genotype vector and
[
2]. Under the null hypothesis of no genetic effect,
and
. Then the score test statistic
asymptotically follows the chi-square distribution with 1 degree of freedom, and the p-value can be obtained as
.
Step 3. Calibrating single-variant test using SPA and ER methods
The single-variant score test approximates the null hypothesis by normal distribution. The variance estimates based on such asymptotic test behaves well for common variants and balanced case-control studies. When allele frequency is extremely low resulting from low MAC, or when the case-control ratio is unbalanced, the underlying distribution of test statistic could be highly skewed. In such cases, the traditional asymptotic-based score test performs poorly with conservative or anticonservative results [
21,
22].
To account for scenarios of unbalanced case-control ratio, we apply the SPA method to obtain the p-value when the score estimates lie far from mean zero [
18]. When the MAC is low (
) either in the internal sample, combining sample, or external sample, we apply the ER method to obtain the p-values [
19].
1). SPA method
SPA is an improvement over the normal approximation which only uses the mean and variance to approximate the underlying distribution. SPA uses the entire cumulant-generating function (CGF). Given the score test statistic
, the estimation of the CGF of
is
. According to the SPA method, the distribution of
can be estimated by
where , , and are the estimations of the first- and second-order derivatives of , is the solution to the equation , and is the distribution of a standard normal distribution. The p-value can be obtained using the R package SPAtest.
1). ER method
ER method is used for rare variant association test with binary trait. Given phenotypes
, genotypes
, and covariates
, the p-value of ER method is defined as
where is the score test statistic from the original phenotype, is the number of individuals with minor alleles, and is the number of cases among individuals carrying a minor allele. The p-value can be obtained using the R package SKAT.
Simulations
In order to evaluate the performance of the proposed method iECAT-RC related to the type I error rates and power, we carry out simulation studies under a series of scenarios. We generate the binary phenotypes with cases and controls from a logistic regression model:
, where
is a continuous covariate generated from the standard normal distribution;
is a binary covariate taking values
and
with the probability of
;
is chosen such that the disease prevalence is
;
is the genotype at a variant generated from a binomial distribution
;
is the effect size of the variant; and
follows a standard normal distribution.
is sampled from the empirical Mini-Exome genotype data provided by the GAW17, which includes
variants in
genes introduced in Sha et al [
2].
To mimic the batch effect between internal and external control studies, we first define the differential variant size (DVS), that is the proportion of the variants subject to different MAFs between the internal and external control samples. For such variants, we set the MAFs of the external controls to be randomly generated based on the following two scenarios to mimic the level of batch effect: (1) and (2) , where is the MAF of the corresponding variants in the internal sample. Subsequently, we consider different numbers of cases and controls in the internal sample and the number of controls in the external controls. We set the following three ratios between the internal cases, internal controls and external controls : (1) , (2) , and (3) . Thus, we consider a total of six models. Model 1: the ratio is and MAF of the external sample is from ; Model 2: the ratio is and MAF of external sample is from ; Model 3: the ratio is and MAF of external sample is from ; Model 4: the ratio is and MAF of external sample is from ; Model 5: the ratio is and MAF of external sample is from ; and Model 6: the ratio is and MAF of external sample is from .
We compare our proposed method, iECAT-RC, with other three approaches for a single-variant association test: iECAT-N based on the naïve integrating the internal and external control samples; Internal using only the internal sample; and iECAT-Score proposed by Li and Lee [
20]. If the case-control ratio of the combined sample is unbalanced or MAC is low (< 10 is used in the simulation studies), iECAT-RC, iECAT-N, and Internal use SPA or ER to obtain the corresponding p-values, respectively.
To evaluate type I error rates, phenotypes are generated with . For each simulation, we generate data sets and use different significance levels , , , and for single-variant tests. To save computation time, we generate genotypes, then resample the disease phenotypes of internal samples times for each set, while keeping other data fixed in the type I error rate evaluation.
To evaluate power, the effect size in Model 3 and Model 6 is set to be . The effect size for other models is set to be . We generate data sets for each model to evaluate the empirical power at the significance level of .
Result
Type I error rates
To evaluate the Type I error rates, we simulate
data sets under the null hypothesis of no association.
Table 1 and
Table S1 provide a summary of the type I error rates of the four methods, iECAT-RC, iECAT-N, Internal, and iECAT-Score, at different significance levels under
, respectively. From these two tables, we can see that iECAT-RC, Internal, and iECAT-Score control Type I error rates very well. However, the Type I error rates of iECAT-N are significantly inflated when the internal samples and external control samples are naively integrated without adjusting the batch effect. For instance, as shown in
Table 1, the empirical Type I error rates of iECAT-N exceed the nominal significance level
by approximately 1000-fold when the internal and external samples are combined naively. Furthermore, we examine scenarios when the case, control, and external control ratio remains the same but the batch effect levels differ (Model 1 and Model 4). The performance of the four methods under Model 4 is consistent with those in Model 1. Under both models, the results show well-controlled Type I error rates across all methods except iECAT-N. Additionally, we consider scenarios with varying case, control, and external control ratio but the same batch effect level (Model 1-3). In these cases, iECAT-RC effectively controls the Type I error rates, even under extremely unbalanced case-control samples.
Power
To evaluate the performance of our proposed method, we consider different batch effect levels, different values of DVS, and different values of
. We compare the power of the three methods iECAT-RC, Internal, and iECAT-Score at an empirical significance level
. iECAT-N is ignored in the power comparison since this method inflates type I error rates.
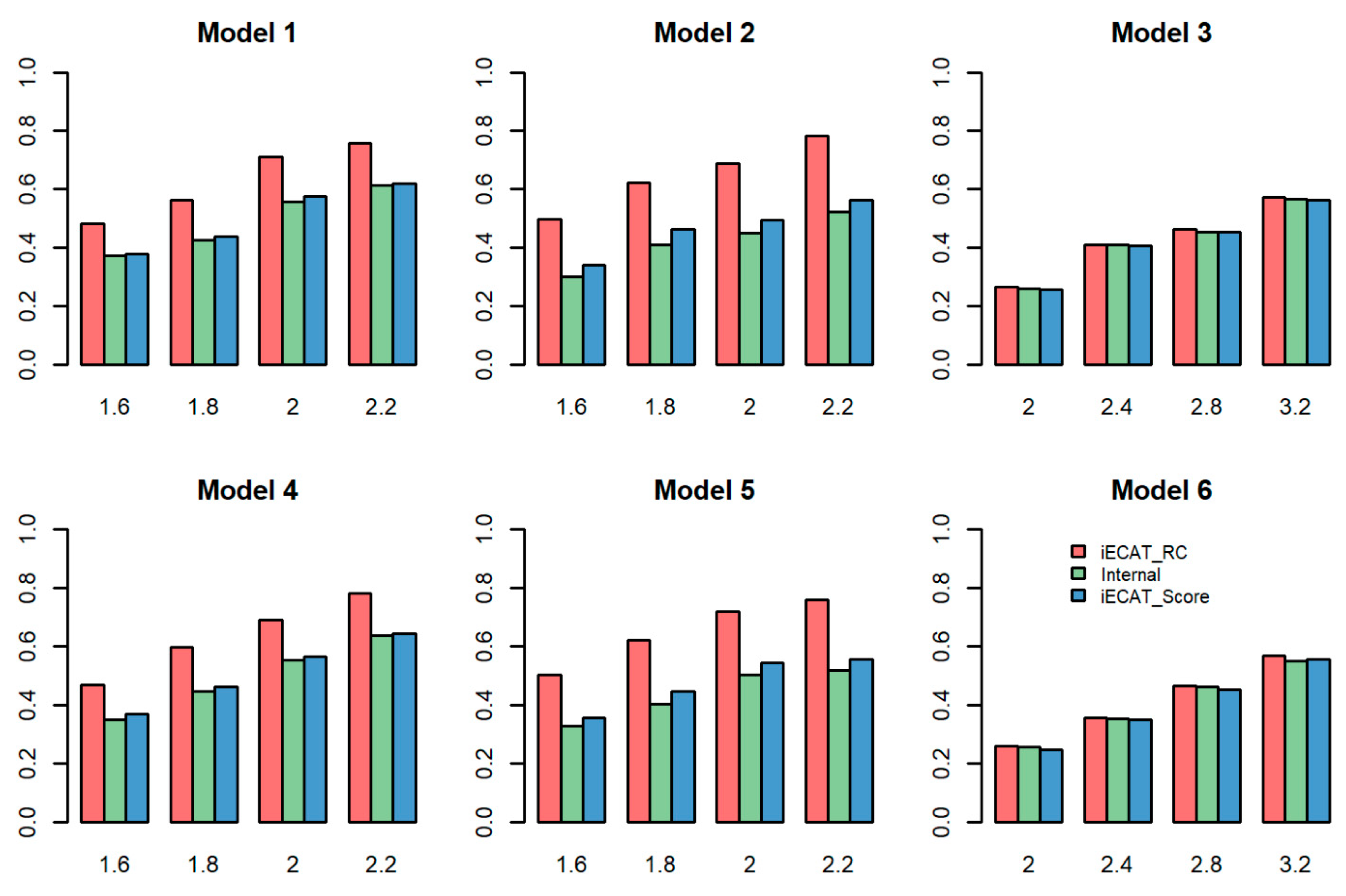
Figure 1 shows the power comparison of these three tests (iECAT-RC, Internal, and iECAT-Score) for different values of
when DVS is 0.03. As shown in the figure, in the case of both balance (Model 1 and model 4) and slightly unbalanced (Model 2 and Model 5) case control ratio in the internal samples, iECAT-RC is more powerful than the other two tests; Internal is the least powerful one due to a smaller sample size compared with other two methods. For the extremely unbalanced internal case-control ratio (Model 3 and Model 6), these three methods have a similar power performance. This is reasonable because there is slight inflation in the p-value for the extremely unbalanced case-control ratio after calibrating the score test by SPA [
18].
Power comparison of the three tests for DVS = 0.5 is showed in
Figure S1. The power patterns of the three methods are very similar between these two different DVS settings for Models 1, 2, 4, and 5. iECAT-RC is more powerful than the other two methods, iECAT is the second powerful method, and Internal is the least powerful method. For models 3 and 6, similar to the pattern for DVS = 0.03, iECAT-RC and Internal have similar power, but iECAT-Score has lower power than iECAT-RC and Internal.
Application to the UK Biobank Data
The UK Biobank dataset, which contains approximately
individuals with
variants from across the United Kingdom, provides a prospective cohort study for discovering more genetic associations and the genetic bases of complex traits with deep genetic and phenotypic data [
23,
24,
25]. In the UK Biobank dataset, genotypes are assayed using two genotyping calling procedures which are the Applied Biosystems UK BiLEVE Axiom Array (UKBL) and the UK Biobank Axiom Array (UKBB) [
26,
27]. However, the common practice of calling underlying genotypes and then treating the called values as known is prone to false positive findings, especially when genotyping errors are systematically different between cases and controls [
28]. Therefore, we apply our proposed method to the real data from the UK Biobank based on two genotype calling procedures and consider genotype calling as the batch effect. The genotype quality control is performed by PLINK 1.9
https://www.cog-genomics.org/plink/1.9/ with missing rate
, Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium exact test threshold
, and MAF greater than
[
29]. Then
variants are obtained after quality control. We consider the M72 Fibroblastic disorders as phenotype, and choose individuals from UKBL as internal data with
cases and UKBB with controls as the external data. The overlap variants in these two samples are used in real analysis. And the covariates age, sex, and the first
principal components are adjusted in the model. The descriptive statistics of subjects from internal and external studies are shown in
Table 2.
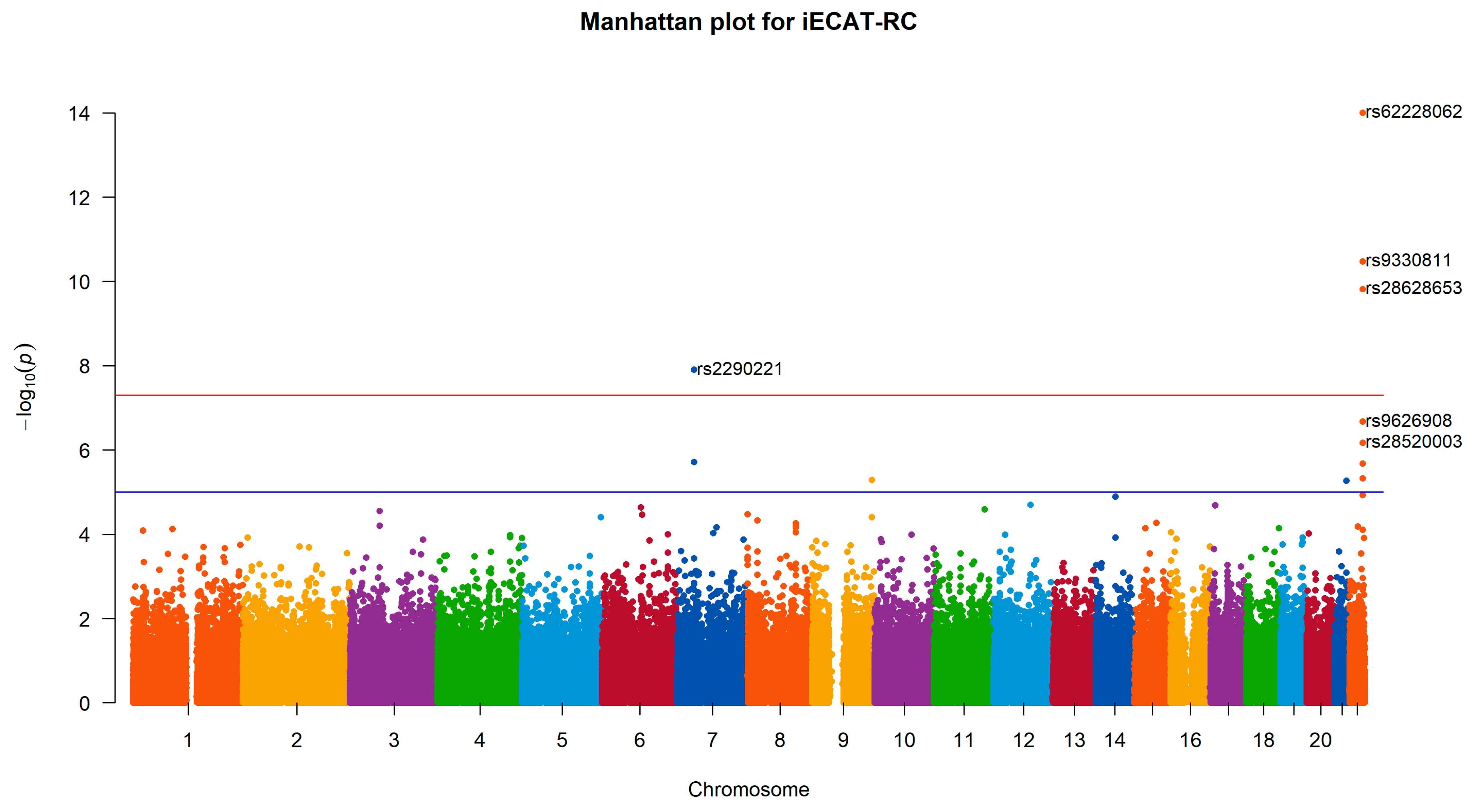
We apply iECAT-RC, Internal, and iECAT-Score to analyze M72 Fibroblastic disorders for two genotyping calling procedures in the UK Biobank. Four SNPs are detected to be associated with Fibroblastic disorders by all three methods at the significance level
(
Table 3 and
Figure 2). iECAT-RC detect these three SNPs with smaller p-values. Among the four SNPs, SNP rs62228062 locates in gene WNT7B. A recent transcriptome study identified WNT7B as amongst the most enriched transcripts in anterior capsule tissue in patients undergoing arthroscopic capsulotomy surgery for frozen shoulder (tissue disorder) suggesting WNT7B as a potential causal gene at the locus [
30]. SNP rs2290221 on chromosome 7 is identified for association with Fibroblastic disorders, and shows the strongest association signal with a p-value of
by iECAT-RC. This SNP is in the intronic of the genes secreted frizzled-related protein 4 (SFRP4) and ependymal related protein 1 (zebrafish) (EPDR1). And it is detected to be associated with Dupuytren’s disease which has a large overlap with frozen shoulder-associated loci [
31,
32].
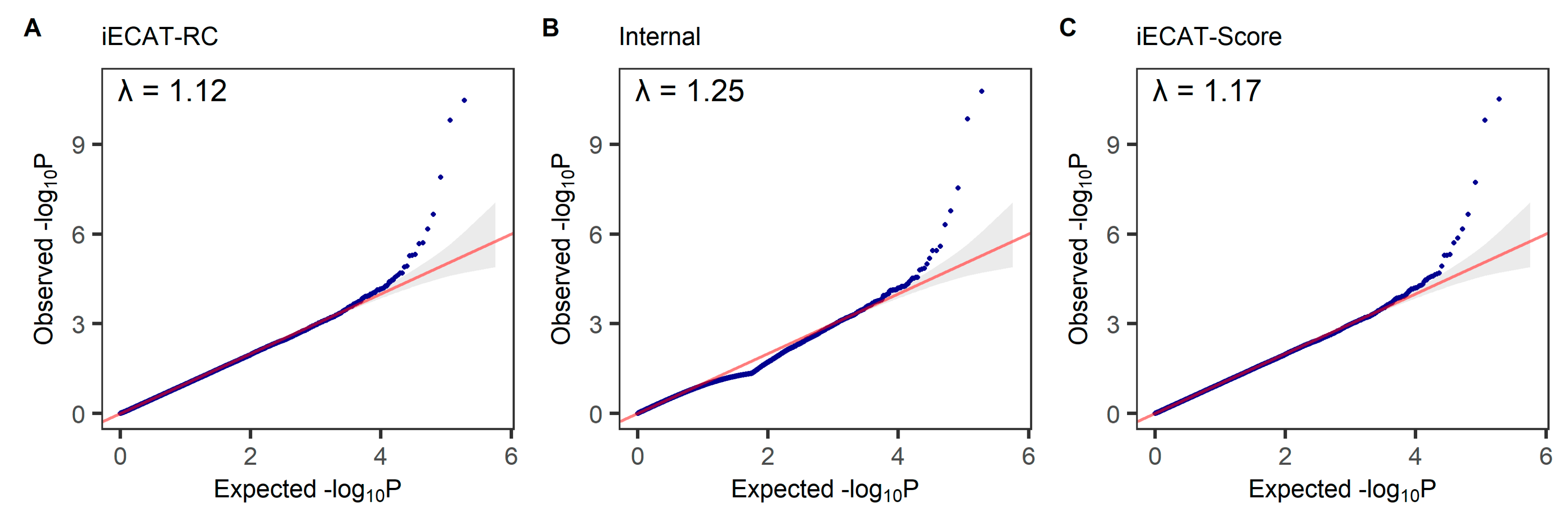
The Q-Q plot is used to assess the number and magnitude of observed associations between SNPs and the disease under study, compared to the association statistics expected under the null hypothesis of no association. The −log10 p-values calculated from each method are ranked in order from smallest to largest on the y-axis and plotted against the distribution that would be expected under the null hypothesis of no association on the x-axis. We test for association between the disease status of M72 Fibroblastic disorders and a SNP, adjusting for age, sex, and the first 10 principal components. The QQ plots from the tests integrating external control samples using the iECAT-RC method, Internal method, and iECAT-Score method are shown in
Figure 3. We observe the similarity between the patterns of the three QQ plots, which are both close to the 45-degree line and show that all three methods can control Type I error rates well in this analysis.
The case-control ratio of the combined samples has a significant impact on the performance of these three methods (iECAT-RC, Internal, and iECAT-Score), particularly in extremely unbalanced case-control studies, as observed in the simulation studies. Our method demonstrates increased statistical power when the case-control ratio is small. To assess the model's performance in real data analysis, we randomly select a subset from the real dataset while maintaining a value of
is
. This allows us to compare the probabilities of detecting potentially significant SNPs using different methods. Specifically, we conduct
random samples, with each sample comprising
internal cases,
internal controls, and
external controls. Then we implement different methods and the proportion of detected significant SNPs among the 10,000 samples is presented in
Table S2. The proposed method, iECAT-RC, demonstrates a higher probability of detecting significant SNPs. For instance, the relative frequency of detecting SNP rs62228062 is
, surpassing that of the other two methods.
Discussion
In case-control studies, it is cost-effective to boost statistical power by increasing the sample size of case-control study. However, integrating external controls without considering systematic differences (batch effect) between studies, such as the differences in sequencing platforms, genotype calling procedures, population stratification, and so forth, may lead to inflated Type I error rates. In this paper, we propose an approach to integrate external control samples and allows for covariate adjustment. The proposed method, iECAT-RC, effectively addresses potential batch effects by calibrating bias using a regression model.
Simulation studies revealed that iECAT-RC can control for Type I error rates very well and boost power in the presence of batch effect. Specifically, we consider different simulation scenarios, including varying the batch effect level, DVS, and case-control ratios. Comparing iECAT-RC with three referenced methods, Internal, iECAT-Score, and iECAT-N, we demonstrate that all other methods could maintain Type I error rates except iECAT-N which naively combine internal and external samples without adjusting for the batch effects. Additionally, the simulation studies show that iECAT-RC has a higher power compared with other methods under different batch effect mechanisms.
In the real data analysis, we apply iECAT-RC, Internal, and iECAT-Score to genetic data from approximately 500,000 individuals with 784,256 SNPs across the United Kingdom. These individuals are used to identify the association between SNPs and M72 Fibroblastic disorders, while considering the genotype calling as the batch effect. Although all of the three methods, iECAT-RC, Internal, and iECAT-Score, identify four SNPs that are significantly associated with the disease, our proposed method has a higher probability of detecting these disease-associated SNPs compared to the other two methods when the case-control ratio is 1:3.
In conclusion, the proposed iECAT-RC method can integrate external control samples and at the same time, control type I error rate and boos statistical power. Through the linear regression calibration, we effectively reduce the batch effects arising from different platforms. Additionally, we employ SPA [
18] and ER [
19] methods to accurately calibrate p-values in scenarios of unbalanced case-control ratios and low MAFs. Our method provides a robust and effective improvement in score tests, ultimately contributing to a better understanding of the genetic architecture of complex diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis and methodology: LZ, JS, XC, SZ, and QS; Data curation and visualization: LZ and XC; Writing original draft: LZ and SZ; writing review and editing: LZ, JS, XC, SZ, and QS.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Part of this research has been conducted using the UK Biobank Resource under application number 102999. The Genetic Analysis Workshops are supported by NIH grant R01 GM031575 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Preparation of GAW 17 data was supported, in part, by NIH R01 MH059490 and used data from the 1000 Genomes Project (
www.1000genomes.org).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Price AL, Spencer CC, Donnelly P. Progress and promise in understanding the genetic basis of common diseases. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2015, 282, 20151684. [Google Scholar]
- Sha Q, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang S. Detecting association of rare and common variants by testing an optimally weighted combination of variants. Genetic epidemiology 2012, 36, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visscher PM, Wray NR, Zhang Q, Sklar P, McCarthy MI, Brown MA, Yang J. 10 years of GWAS discovery: biology, function, and translation. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2017, 101, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschhorn JN, Daly MJ. Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nature reviews genetics 2005, 6, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang S, Zhang S, Sha Q. Literature reviews on methods for rare variant association studies. Hum Genet Embryol. 2016, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Homann J, Osburg T, Ohlei O, Dobricic V, Deecke L, Bos I, Vandenberghe R, Gabel S, Scheltens P, Teunissen CE, Engelborghs S. Genome-wide association study of Alzheimer’s disease brain imaging biomarkers and neuropsychological phenotypes in the European medical information framework for Alzheimer’s disease multimodal biomarker discovery dataset. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2022, 14, 840651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin DY, Tang ZZ. A general framework for detecting disease associations with rare variants in sequencing studies. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2011, 89, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shendure J, Ji H. Next-generation DNA sequencing. Nature biotechnology 2008, 26, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skotte L, Korneliussen TS, Albrechtsen A. Association testing for next-generation sequencing data using score statistics. Genetic epidemiology 2012, 36, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini J, Howie B. Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nature Reviews Genetics 2010, 11, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee S, Kim S, Fuchsberger C. Improving power for rare-variant tests by integrating external controls. Genetic epidemiology 2017, 41, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmayer SJ, Evans KS, Zdraljevic S, Andersen EC. Evaluating the power and limitations of genome-wide association studies in Caenorhabditis elegans. G3 2022, 12, jkac114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu DJ, Leal SM. SEQCHIP: a powerful method to integrate sequence and genotype data for the detection of rare variant associations. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach A, Chiang T, Gong J, Addis L, Dobbins S, Tomlinson I, Houlston R, Pal DK, Strug LJ. Association analysis using next-generation sequence data from publicly available control groups: the robust variance score statistic. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen S, Lin X. Analysis in case–control sequencing association studies with different sequencing depths. Biostatistics 2020, 21, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricks AE, Billups SC, Pike HN, Farooqi IS, Zeggini E, Santorico SA, Barroso I, Dupuis J. ProxECAT: Proxy External Controls Association Test. A new case-control gene region association test using allele frequencies from public controls. PLoS genetics 2018, 14, e1007591. [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Lee S. Integrating external controls in case–control studies improves power for rare-variant tests. Genetic Epidemiology 2022, 46, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey R, Schmidt EM, Abecasis GR, Lee S. A fast and accurate algorithm to test for binary phenotypes and its application to PheWAS. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2017, 101, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee S, Fuchsberger C, Kim S, Scott L. An efficient resampling method for calibrating single and gene-based rare variant association analysis in case–control studies. Biostatistics 2016, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Lee S. Novel score test to increase power in association test by integrating external controls. Genetic epidemiology 2021, 45, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee S, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M, Lin X. Rare-variant association analysis: study designs and statistical tests. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2014, 95, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma C, Blackwell T, Boehnke M, Scott LJ, GoT2D Investigators. Recommended joint and meta-analysis strategies for case-control association testing of single low-count variants. Genetic epidemiology 2013, 37, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bycroft C, Freeman C, Petkova D, Band G, Elliott LT, Sharp K, Motyer A, Vukcevic D, Delaneau O, O’Connell J, Cortes A. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuirl MR, Pattillo Smith S, Sandstede B, Ramachandran S. Hierarchical clustering of gene-level association statistics reveals shared and differential genetic architecture among traits in the UK Biobank. bioRxiv 2019. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Z, Bi W, Zhou W, VandeHaar P, Fritsche LG, Lee S. UK Biobank whole-exome sequence binary phenome analysis with robust region-based rare-variant test. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2020, 106, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen R, Paul JS, Albrechtsen A, Song YS. Genotype and SNP calling from next-generation sequencing data. Nature Reviews Genetics 2011, 12, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tängdén T, Gustafsson S, Rao AS, Ingelsson E. A genome-wide association study in a large community-based cohort identifies multiple loci associated with susceptibility to bacterial and viral infections. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu YJ, Liao P, Johnston HR, Allen AS, Satten GA. Testing rare-variant association without calling genotypes allows for systematic differences in sequencing between cases and controls. PLoS genetics 2016, 12, e1006040. [Google Scholar]
- Liang X, Cao X, Sha Q, Zhang S. HCLC-FC: A novel statistical method for phenome-wide association studies. Plos one 2022, 17, e0276646. [Google Scholar]
- Green HD, Jones A, Evans JP, Wood AR, Beaumont RN, Tyrrell J, Frayling TM, Smith C, Weedon MN. A genome wide association study of frozen shoulder identifies a common variant of WNT7B and diabetes as causal risk factors. medRxiv 2020, 2020-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou L, Lermusiaux JL, Teyssedou JP, Bardin T, Beaudreuil J, Petit-Teixeira E. Genetics of Dupuytren's disease. Joint Bone Spine 2012, 79, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green HD, Jones A, Evans JP, Wood AR, Beaumont RN, Tyrrell J, Frayling TM, Smith C, Weedon MN. A genome-wide association study identifies 5 loci associated with frozen shoulder and implicates diabetes as a causal risk factor. PLoS genetics 2021, 17, e1009577. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).