1. Introduction
Prosthetic organs, e.g., hands [
1,
2], are a robotic system, which has the power generator, actuator, body, sensor, and controller [
3,
4]. One of the important challenges with prosthetic organs, e.g., hand, is to control the prosthetic hands from the patient brain. Specifically, given a task to be performed with the prosthetic hand, how the human intention or desire to accomplish the task is mapped to the actuator on the prosthetic hand is a challenge. A popular approach is to make use of Electromyography (EMG) signals to represent the patient intent to perform a task. Therefore, EMG-controlled prostheses are popular today, which incorporate embedded motors that move the fingers based on recorded electrical activities during muscle contraction that comes from the patient brain [
5]. These prostheses allow for multiple grip patterns and user-friendly interaction [
6]. However, a major challenge with EMG prosthetics is that it takes users many months of continuous training to achieve full mastery over EMG-controlled prosthetics [
7]. The training process takes place through repetitive exercises where the user learns to consciously control their muscle contraction. In practice, because of this strenuous training process, many users abandon the prosthesis before mastery is achieved. Another challenge with EMG-controlled prosthetic hand is an inherent difficulty to represent high resolution brain signals for task manipulation; often in practice the failure in grasping an object often happens, either the object being slipped out of the prosthetic hand or finger or the object being damaged due to too high force from the prosthetic hand [
8]. Several methods to enhance the EMG representation have been proposed, including Electroencephalography (EEG) [
9], eye tracking, transfer learning [
10,
11], and facial recognition. EMG along with its enhancing methods is limited because the desired resolution with the patient Brain signal (e.g., to grasp an object) increases far faster than the resolution of the representation of patient intent in brain, which can be achieved with the current technology such as EMG, EEG, and so on.
The other idea to overcome the limit is to make the prosthetic hand of highly autonomy, meaning that they can automatically perform the task of gripping an object. Hao et al. (2021) designed a low-cost soft prosthetic hand with embedded actuation and sensors, allowing for initial contact detection during gripping to prevent damage to objects [
12]. However, the inclusion of extra sensors increased the weight of the prosthetic hand and posed the risk of sensor degradation. Castro et al. (2022) presented a prototype incorporating EMG-based control and computer vision for seamless control of a prosthetic hand with different grip patterns [
13]. However, the paper did not address the control of grip pressure, which is crucial when handling delicate objects. Czimmermann et al. (2020) conducted a comprehensive review of defect detection technologies, emphasizing the resource requirements for effective training of neural networks [
14]. They also highlighted the challenges of parallelization when dealing with large datasets. Abbasi et al. (2019) used unsupervised learning techniques to analyze patterns in different grasp types, but their approach was deemed expensive and impractical [
15].
The motivation of the study presented in this paper was to advance the technology along the idea -- i.e., improving the autonomy of the prosthetic hand. The objective of this paper is to a train an agent (i.e., prosthetic hand) using three different algorithms—Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) [
16], Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) [
17], and Deep Q Networks (DQN)—to enable the prosthetic hand to autonomously grasp objects. To achieve the objective, the impact of each algorithm on the effectiveness of the gripping action will be evaluated [
18,
19] and an optimal model for a variety of objects will be tested, specifically investigating how the physical properties of the objects may significantly influence the capability of the prosthetic hand to grip them effectively.
This paper presents significant contributions to the field of Myo prosthetic hand development by leveraging computer vision and machine learning technologies. Also, this paper will provide an understanding of the impact of object properties on grasping success. These contributions are important in improving the development of more efficient and effective prosthetic grasping systems with low cost and high usability.
2. Experiment
This section covers the experimental setup in using the reinforcement learning [
20] to train the prosthetic arm gripper to be able to grip an object in minimum time and with optimal force.
2.1. Sensor Setup
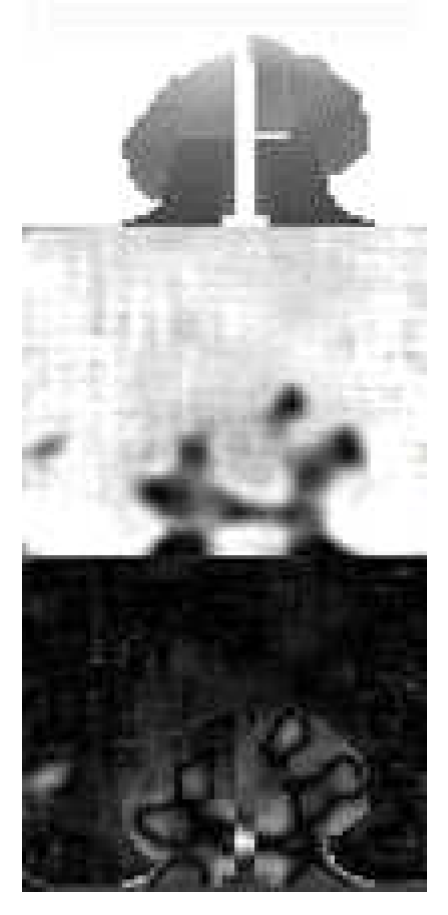
The sensor in the task represents a camera mounted at the midpoint of the gripper’s base which records observations captured in discrete steps. The observations captured by the sensor represent the state space in the Markov decision process. In an approach like (Baris, 2020), we implemented a perception pipeline using RGBD observations captured by the camera (
Figure 1).
RGBD stands for Red, Green, Blue, and Depth and refers to a type of imaging technology that combines traditional RGB color data with depth information. The method to preprocess the RGBD data before feeding it into the convolutional neural network is like the method implemented in [
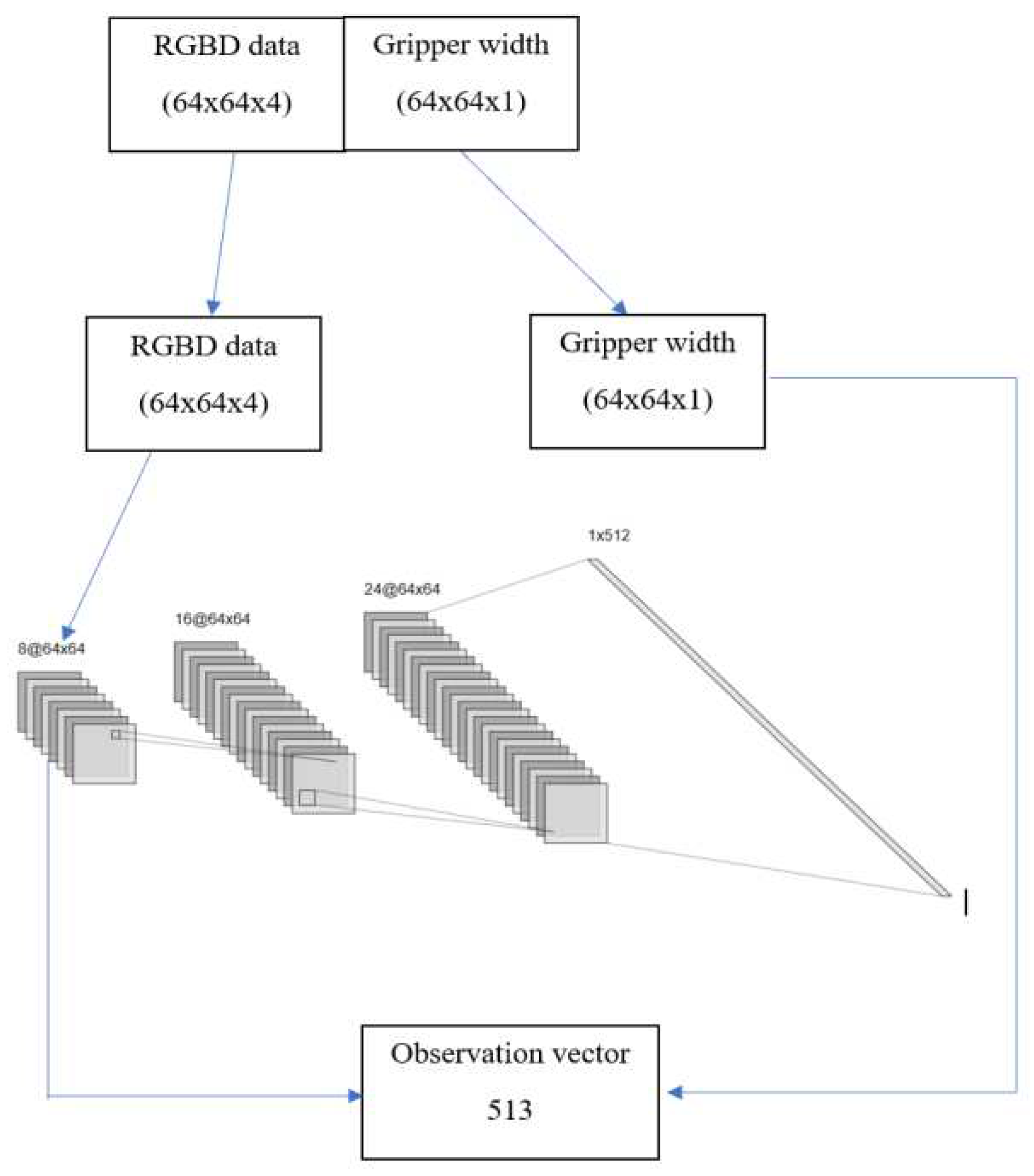
21]. Since our task involves a gripper with a certain width, we need to include this information in our processing of the sensor output. To achieve this, we pad the gripper width information into a three-dimensional array that has the same shape as the sensor data (i.e., 64x64x1 or 64x64x4). This extra information is added as an extra “layer” to the sensor data, which we call a “channel”.
By doing this, we can make sure that the width information of the actuator is included in the processing of the sensor data without changing the way we process it. During training, we remove this extra channel so that the robot can learn how to use the sensor data to control its movements, considering the width of the gripper. By including the gripper width information in this way, we can ensure that the robot can use this information to perform the task as we want it to do.
The RGBD data is then fed into a convolutional neural network to learn meaningful features and representations of the scene, which is used as input to the agent’s decision-making process. The output is passed through one or more fully connected layers, which are also sometimes called dense layers. The output of the last fully connected layer can then be flattened into a one-dimensional array. The difference in the CNN architecture from the work of [
22] and the one used in this study, is the introduction of dropout layers [
23] which determines the fraction of the input units to drop out during the training of a neural network. The importance of this is to avoid overfitting which is a reoccurring problem in machine learning. We also employed an Exponential Linear Unit because of its success in speeding up learning compared to other LUs and in dealing with sparse data. After the tensor output has been flattened into a one-dimensional array, the unpadded gripper width information is then concatenated to the RGBD tensor array, to form the observation vector. This process is represented with the schematic shown in
Figure 2.
2.2. Reward Function
The reward function implemented for this task is a custom-shaped reward function designed to incentivize the gripper’s behaviour in the environment. The aim of the reward function is to incentivize the agent to grasp the object efficiently and to lift it to the desired height quickly, while penalizing the agent for taking too long to complete the task. The reward function consists of several parameters that influence the reward value and can be summarized with
Table 1. Whether an object has been grasped is detected by checking the gripper width after the robot runs a close gripper event.
2.3. Training Process
The agent was trained using three existing policies, SAC, DQN and PPO. The choice of these algorithms was based on their proven effectiveness and wide usage in the field [
22]. By leveraging the strengths of SAC, DQN, and PPO, it was anticipated that the agent could benefit from their advantages in terms of stability, sample efficiency, and performance.
Training begins at the reset state where the objects have the spawned on the table and the gripper also spawned midair. For each of the algorithms, we defined the reward function that provides positive feedback when the agent takes actions to move it closer to the goal, and negative feedback when it takes actions to move it further away from the goal. Next, the agent is run through a series of episodes in timesteps of 1000 in the environment. Each episode consists of the agent taking actions and receiving rewards. The agent’s goal is to maximize the cumulative reward over all episodes. During each episode, the agent observes the current state of the environment, chooses an action based on its current policy, and receives a reward based on the outcome of the action. The agent then updates its policy based on the observed rewards and the current state of the environment.
The process of updating the policy varies depending on which algorithm was being tried but follows a similar update rule (1). During training, the agent explores the environment to learn the optimal policy. The training process continues until the agent has the maximum number of episodes which is predefined.
is the estimate of the action-value function at time t, is the reward received at time t, ∝ is the learning rate, γ is the discount factor, and is the maximum value over all actions that can be taken in the next state.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Algorithm-Specific Success Rate
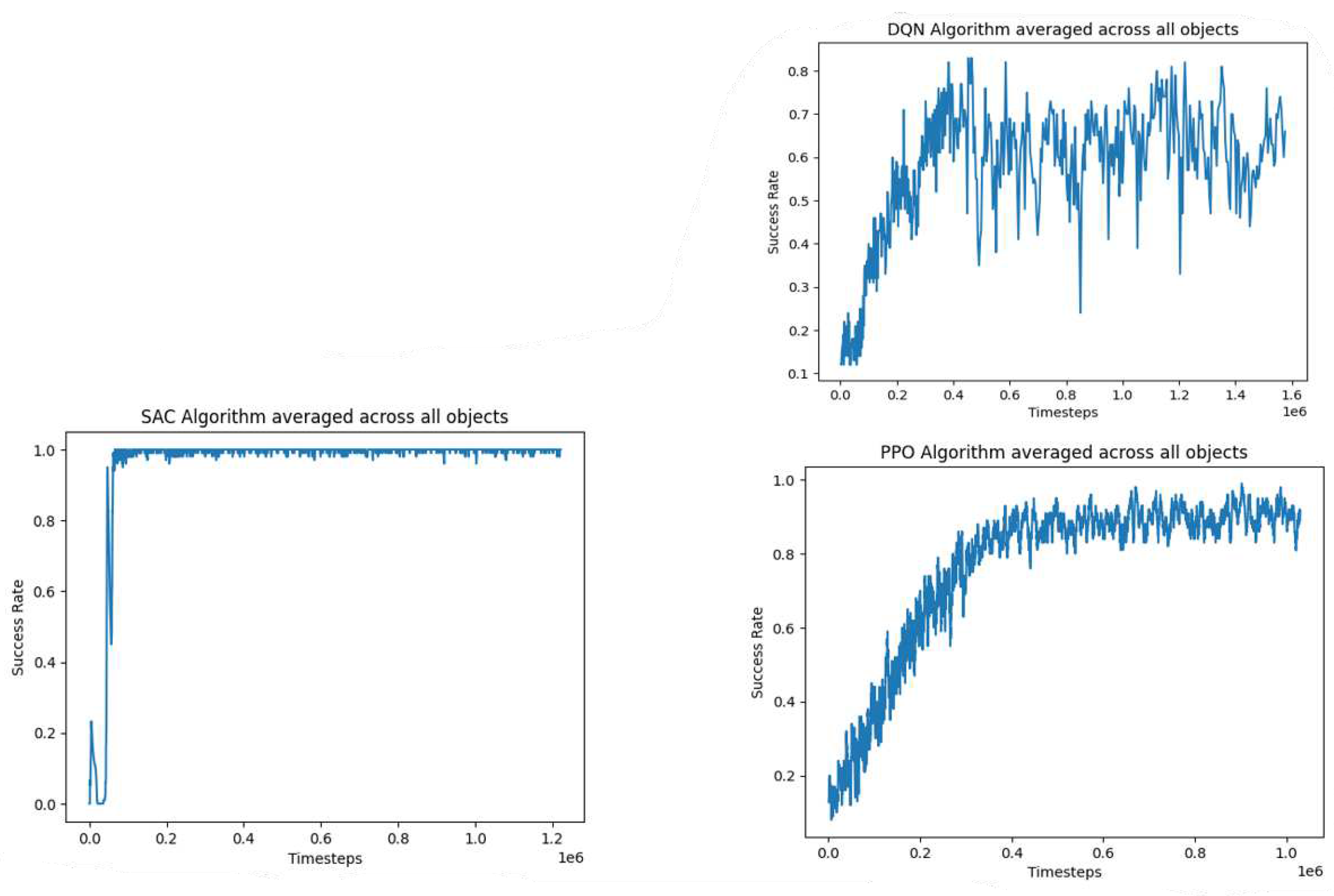
Three different algorithms were tested during training: DQN, SAC and PPO. The training went on for 1,000,000 timesteps and the performance of each algorithm by success rate is shown in
Figure 3.
From the results above, we can see that SAC outperformed the other two algorithms in terms of success rate by converging the quickest in just under 200000 timesteps. On the DQN algorithm, the agent never fully learns the optimal policy required for the grasping task. We can see it reaches a peak success rate of 80% in about 450,000 timesteps then stays at equilibrium at that point. There are several possible reasons why SAC performed better than the other two algorithms. First, SAC is an off-policy actor-critic algorithm that uses a soft value function to estimate the Q-value of actions. This soft value function provides a smoother estimate of the Q-value than the hard value function used in DQN and PPO, which can lead to better performance in the action spaces. SAC also uses a stochastic policy that is updated using a combination of maximum entropy reinforcement learning and entropy regularization. This encourages the policy to explore the state space more thoroughly, which can lead to better performance in environments with sparse rewards, such as the object picking task in our study. DQN might have performed badly because it is an on-policy algorithm that suffers from instability when learning from action spaces.
From the results, the SAC algorithm performed the best with a mean success rate of 0.990. This is significantly higher than the mean success rate of the DQN algorithm (0.602) and the PPO algorithm (0.821). The high success rate achieved by the SAC algorithm can be attributed to its inherent advantages in handling high-dimensional action spaces.
On the other hand, the DQN algorithm performed the worst, with a mean success rate of 0.602. The lower success rate achieved by the DQN algorithm can be attributed to the fact that the Q-learning architecture employed by the DQN algorithm is known to have stability issues when applied to continuous control tasks, as it tends to overestimate the Q-values and leads to suboptimal policies. This result is summarised in
Table 2.
MANOVA test was further conducted on the success rates of the three algorithms: DQN, SAC, and PPO, to investigate whether there were significant differences in their performance. The results are shown in
Table 3. Based on the results of the MANOVA analysis, there is strong evidence to suggest that there are significant differences between the three different algorithms in terms of their performance. The Pillai’s trace statistic of 0.57982 and the highly significant p-value (< 2.2e-16) indicate that the different algorithms have a substantial impact on the success rate of the gripper. The approximate F-value of 2040.7 further supports the presence of a significant effect. These findings indicate that the choice of algorithm significantly influences the observed differences in performance of the prosthetic gripper.
3.2. Comparative Analysis of SAC, PPO and DQN for Object Grasping – Hyperparameter Exploration
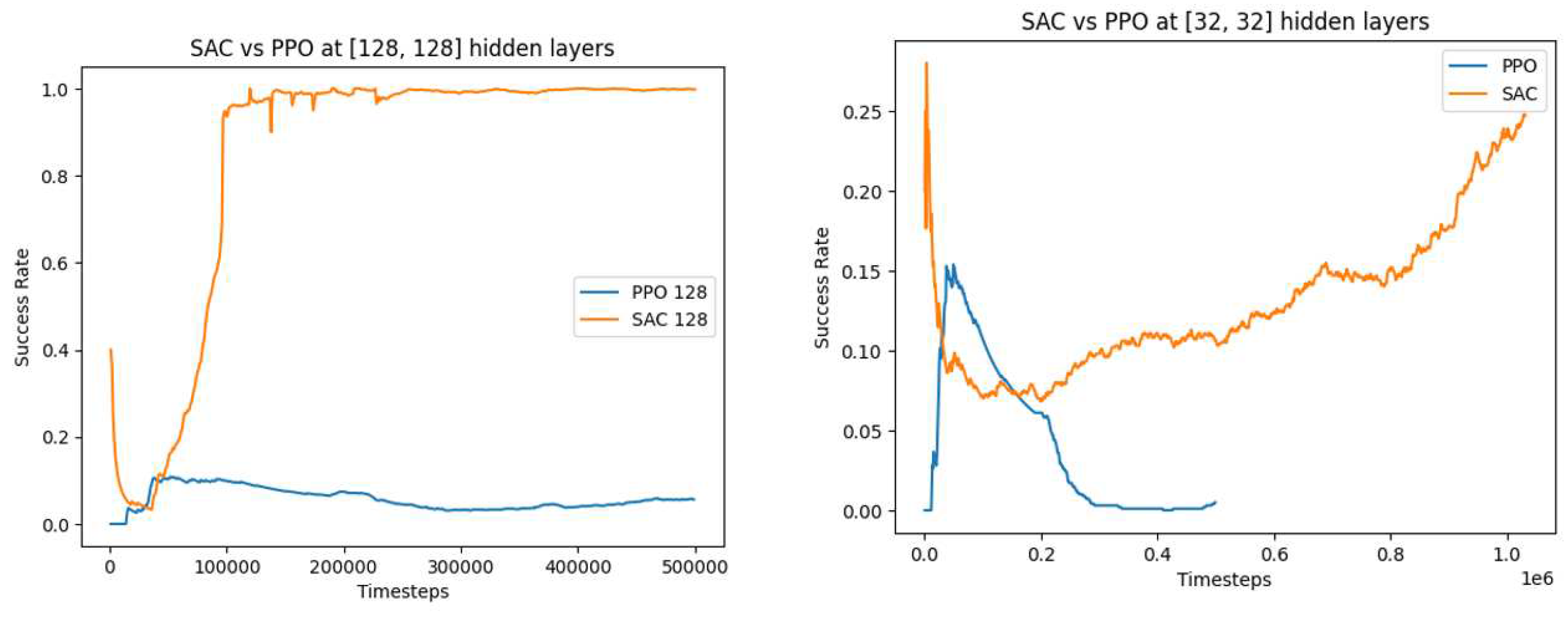
Increasing the batch size to 128 had a positive effect on the convergence speed of the SAC algorithm, enabling it to converge quickly after just 100,000 time-steps (
Figure 4). This performs much better than the SAC with RGBD presented in (Baris, 2020).
With a larger batch size, the SAC algorithm benefits from an increased sample efficiency. More data is available for each update step, allowing for better estimation of the policy gradient and reducing the impact of noise or outlier experiences. This increased data diversity enhances the stability of the learning process and facilitates faster convergence towards an optimal policy. Increasing the batch size increases the amount of information available for each update, and this significantly increases the agent’s training time.
The performance of the DQN algorithm drops at both the batch size of 32 and 128, compared to the initial analysis at batch size 64 (
Figure 3). We can infer that at batch size 64, there is an optimal balance between sample efficiency and computational overhead. Deviations from this batch size, either lower or higher, lead to a diminished performance due to limitations in data availability or computational inefficiencies.
We observe a similar pattern, as shown in
Figure 5, when varying the number of hidden layers for the SAC and PPO algorithms. The SAC algorithms benefit from an increase in the number of hidden layers while the PPO algorithm performs poorly in both cases at 500000 timesteps and would possibly take a longer time to converge. Based on these results, we can make an inferred comparison of these three algorithms, as shown in
Table 4.
3.3. Object-Specific Success Rate
Using SAC as the preferred algorithm, the agent was once again trained to grasp three different types of objects – remote controller, soap bar and mug Figures 6 and 7). This is to determine how the object shape and size affect the agent convergence at an optimal policy.
The results show that the mug was the easiest object for the agent to grasp, as it converged the fastest, achieving a success rate of over 0.9 after 200,000 timesteps. The remote controller was the second easiest object to grasp, with a success rate of over 0.8 after 250,000 timesteps. However, the soap bar was the most challenging object for the agent, as it failed to converge, with a success rate that remained between 0.0 and 0.008 throughout the training process.
These results are consistent with our understanding of the properties of these objects. The remote controller and mug are both easy to grip with well-defined shapes and surfaces that the agent can easily detect and grasp. On the other hand, the soap bar has a smooth surface and is difficult to grip, making it challenging for the agent to learn a successful grasping policy.
These results can also be explained in terms of the exploration-exploitation trade-off. The agent’s task is to maximize its reward, which in this case is the success rate of grasping an object. To do this, the agent must explore different grasping strategies to find the one that maximizes its reward. However, if the exploration process is too extensive, the agent may fail to converge to an optimal policy. On the other hand, if the agent exploits the same grasping strategy without exploring others, it may miss out on better strategies.
In the case of the soap bar, the slippery surface and difficult-to-grip nature of the object may have made it more challenging for the agent to explore different grasping strategies. As a result, the agent may have become stuck in a suboptimal policy that did not lead to successful grasping.
In contrast, the well-defined edges and surface of the remote controller and mug may have made it easier for the agent to explore different grasping strategies, leading to faster convergence to an optimal policy. Also, the fact that the success rate of these objects continued to improve over time suggests that the agent was able to find better grasping strategies through exploration without getting stuck in a suboptimal policy.
MANOVA test was further conducted on the success rates of the three objects: mug, remote controller, and bar of soap, to investigate whether the type of object significantly affects the performance of the SAC algorithm. The results are shown in
Table 5.
Based on the results of the MANOVA analysis, there is strong evidence to suggest that the type of object (remote controller, soap, mug) has a significant effect on the success rates of the prosthetic gripper. The Pillai’s trace statistic of 0.6888 and the highly significant p-value (< 2.2e-16) indicate that the different object types contribute significantly to the variation in the success rate of the agent. The approximate F-value of 552.9 further supports the presence of a substantial effect. These findings suggest that different objects cause the RL agent to exhibit distinct performance levels in task completion.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the superiority of the SAC algorithm over DQN and PPO for training prosthetic hands to grasp objects effectively in terms of force and contact point. Importantly, the physical properties of the object, including shape and texture, significantly influence the success of prosthetic grasping. Recognizing these elements offers insights into creating robust prosthetic systems that prevent slippage or damage.
This research contributes significantly to the domain of Myo prosthetic hand development and emphasizes the advancing role of computer vision and machine learning technologies in this field. Notably, it highlights the influence of object physical properties, such as shape and texture, on prosthetic grasping. The study also refines traditional autoencoder models like those presented by Breyer, et al., (2019), introducing an innovative approach to sparse data handling in EMG-based applications by optimizing the learning rate for each parameter.
Future work, first, the Myo armband’s second channel has hinted at significant muscle activities, warranting a deeper investigation. Understanding the distinct role of these muscles, detected by this specific channel, can unveil crucial insights. By identifying the prominence of this channel’s captured activities, there’s potential to refine prosthetic algorithms, enhancing grip accuracy and responsiveness based on the underlying muscular dynamics. Second, a Post Hoc analysis, potentially employing methods like pairwise comparisons or interaction effect reviews, can be performed to shed light on how different algorithms perform across various objects. Considering that objects can differ in attributes such as shape, texture, and weight, it is essential to pinpoint which algorithms work best with each attribute. Understanding this can help us choose the right algorithm for specific tasks, making prosthetics work better in different real-life situations. Third, the robustness and resilience of the method will be studied. While robustness may be well known, resilience refers to whether a method still works if underlying conditions are changed, see the definition or resilience in literature [
24,
25].
Author Contributions
Writing – original draft preparation, J.O.; writing – review and editing, J.O., A.O. and W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu S., Zhang H., Yin R., Chen A., Zhang W.J., 2017. Finite Element Analysis and Application of a Flexure Hinge Based Fully Compliant Prosthetic Finger. In: Fei M., Ma S., Li X., Sun X., Jia L., Su Z. (eds) Advanced Computational Methods in Life System Modeling and Simulation. ICSEE 2017, LSMS 2017. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol. 761. Springer, Singapore.
- S.Q. Liu, H. B. Zhang, R. X. Yin, A. Chen, and W. J. Zhang, “Flexure hinge based fully compliant prosthetic finger,” in SAI Intelligent Systems Conference 2016, London, UK, September 2016.
- Chen, A.; Yin, R.; Cao, L.; Yuan, C.; Ding, H.; Zhang, W. Soft robotics: Definition and research issues. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP),, Auckland, New Zealand, 21–23 November 2017; pp. 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, A.; Rasouli, A.; Farahinia, A.; Wells, G.; Zhang, H.; Achenbach, S.; Yang, S.M.; Sun, W.; Zhang, W. Toward a Soft Microfluidic System: Concept and Preliminary Developments. 2021 27th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP). pp. 755–759.
- Waris, A.; Niazi, I.K.; Jamil, M.; Englehart, K.; Jensen, W.; Kamavuako, E.N. Multiday Evaluation of Techniques for EMG-Based Classification of Hand Motions. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2018, 23, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Zheng, L. Cao, Z. Q. Qian, A. Chen, and W. J. Zhang, “Topology optimization of a fully compliant prosthetic finger: design and testing,” in proceedings of the 6th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob 2016), Singapore, Jun 2016, pp. 1037-1042.
- van der Riet, D.; Stopforth, R.; Bright, G.; Diegel, O. An overview and comparison of upper limb prosthetics. AFRICON 2013; pp. 1–8.
- Kyberd, P., Wartenberg, C., Sandsjö, L., Jönsson, S., Gow, D., Frid, J., Sperling, L. (2007). Survey of Upper-Extremity Prosthesis Users in Sweden and the United Kingdom. JPO: Journal of Prosthetics and Orthotics, 19(2). Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/jpojournal/Fulltext/2007/04000/Survey_of_Upper_Extremity_Prosthesis_Users_in.6.aspx.
- Mihajlovic, V.; Grundlehner, B.; Vullers, R.; Penders, J. Wearable, Wireless EEG Solutions in Daily Life Applications: What are we Missing? IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2014, 19, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, C.; Yang, G.; Dy, J. A fuzzy logics clustering approach to computing human attention allocation using eyegaze movement cue. Int. J. Human-Computer Stud. 2009, 67, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Watson, L. Using eye movement parameters for evaluating human–machine interface frameworks under normal control operation and fault detection situations. Int. J. Human-Computer Stud. 2003, 59, 837–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyberd, P., Wartenberg, C., Sandsjö, L., Jönsson, S., Gow, D., Frid, J., Sperling, L. (2007). Survey of Upper-Extremity Prosthesis Users in Sweden and the United Kingdom. JPO: Journal of Prosthetics and Orthotics, 19(2). Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/jpojournal/Fulltext/2007/04000/Survey_of_Upper_Extremity_Prosthesis_Users_in.6.aspx.
- Castro, M.C.F.; Pinheiro, W.C.; Rigolin, G. A Hybrid 3D Printed Hand Prosthesis Prototype Based on sEMG and a Fully Embedded Computer Vision System. Front. Neurorobotics 2022, 15, 751282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czimmermann, T.; Ciuti, G.; Milazzo, M.; Chiurazzi, M.; Roccella, S.; Oddo, C.M.; Dario, P. Visual-Based Defect Detection and Classification Approaches for Industrial Applications—A SURVEY. Sensors 2020, 20, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Noohi, E.; Parastegari, S.; Zefran, M. Grasp Taxonomy for Robot Assistants Inferred from Finger Pressure and Flexion. 2019 International Symposium on Medical Robotics (ISMR); pp. 1–7.
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Djenouri, Y. DRL-Based URLLC-Constraint and Energy-Efficient Task Offloading for Internet of Health Things. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2023, PP, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Park, S.W.; Jin, S.-M. Toward a Fully Automated Artificial Pancreas System Using a Bioinspired Reinforcement Learning Design: In Silico Validation. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2020, 25, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Lv, Y.; Lv, D.; Gu, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W.; Gupta, M.M. A New Approach to Polyp Detection by Pre-Processing of Images and Enhanced Faster R-CNN. IEEE Sensors J. 2020, 21, 11374–11381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Jing, W.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, W. Automatic Polyp Detection by Combining Conditional Generative Adversarial Network and Modified You-Only-Look-Once. IEEE Sensors J. 2022, 22, 10841–10849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhong, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X. Automatic detection of surface defects based on deep random chains. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch Dueling Deep Q-Networks for Robotics Applications. Master’s Thesis. 2020.
- Breyer, M.; Furrer, F.; Novkovic, T.; Siegwart, R.; Nieto, J. Comparing Task Simplifications to Learn Closed-Loop Object Picking Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, Nitish & Hinton, Geoffrey & Krizhevsky, Alex & Sutskever, Ilya & Salakhutdinov, Ruslan. (2014). Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. Journal of Machine Learning Research. 15. 1929-1958.
- Han, B.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W. A Method to Measure The Resilience of Algorithm for Operation Management. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Wang, J.W.; Nayak, A.; Tiwari, M.K.; Han, B.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, W.J. Measuring the Resilience of Supply Chain Systems Using a Survival Model. IEEE Syst. J. 2014, 9, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).