Submitted:
13 December 2023
Posted:
14 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
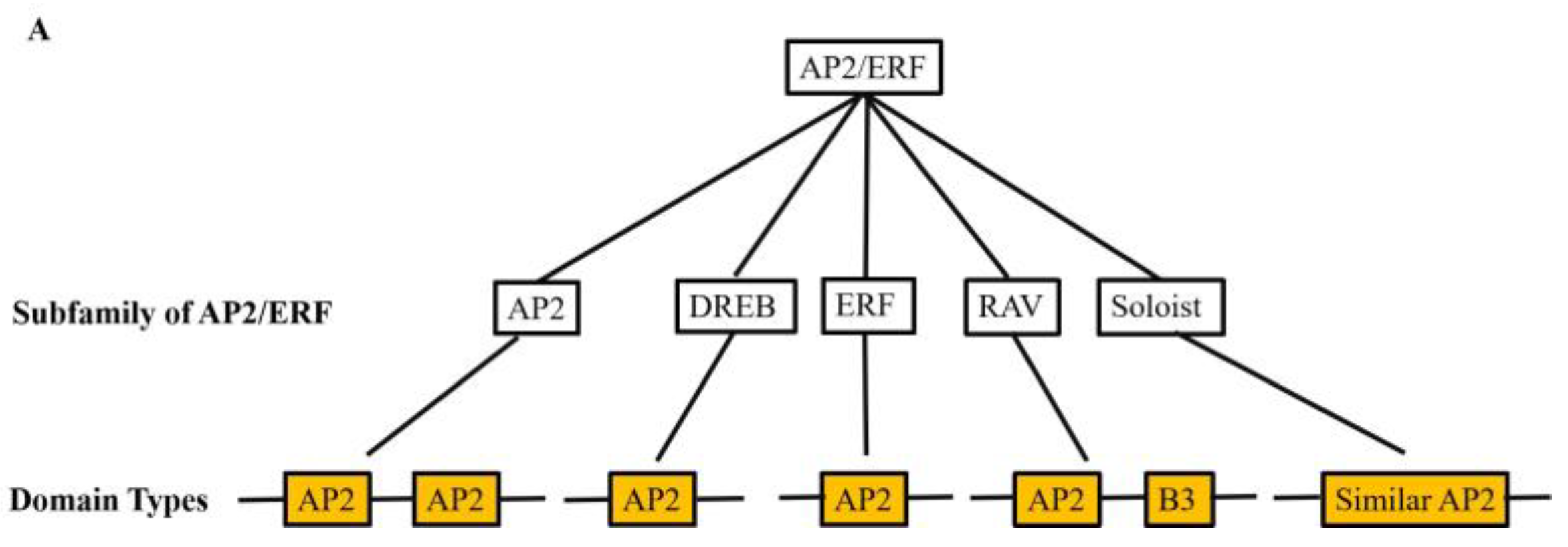
1.1. Classification and structural classification of AP2/ERF transcription factors
1.2. Cis-acting elements recognized by AP2/ERF transcription factors
2. AP2/ERF transcriptional regulation and interacting protein under abiotic stresses
2.1. AP2/ERF transcriptional regulation under abiotic stresses
2.2. AP2/ERF interacting protein under abiotic stresses
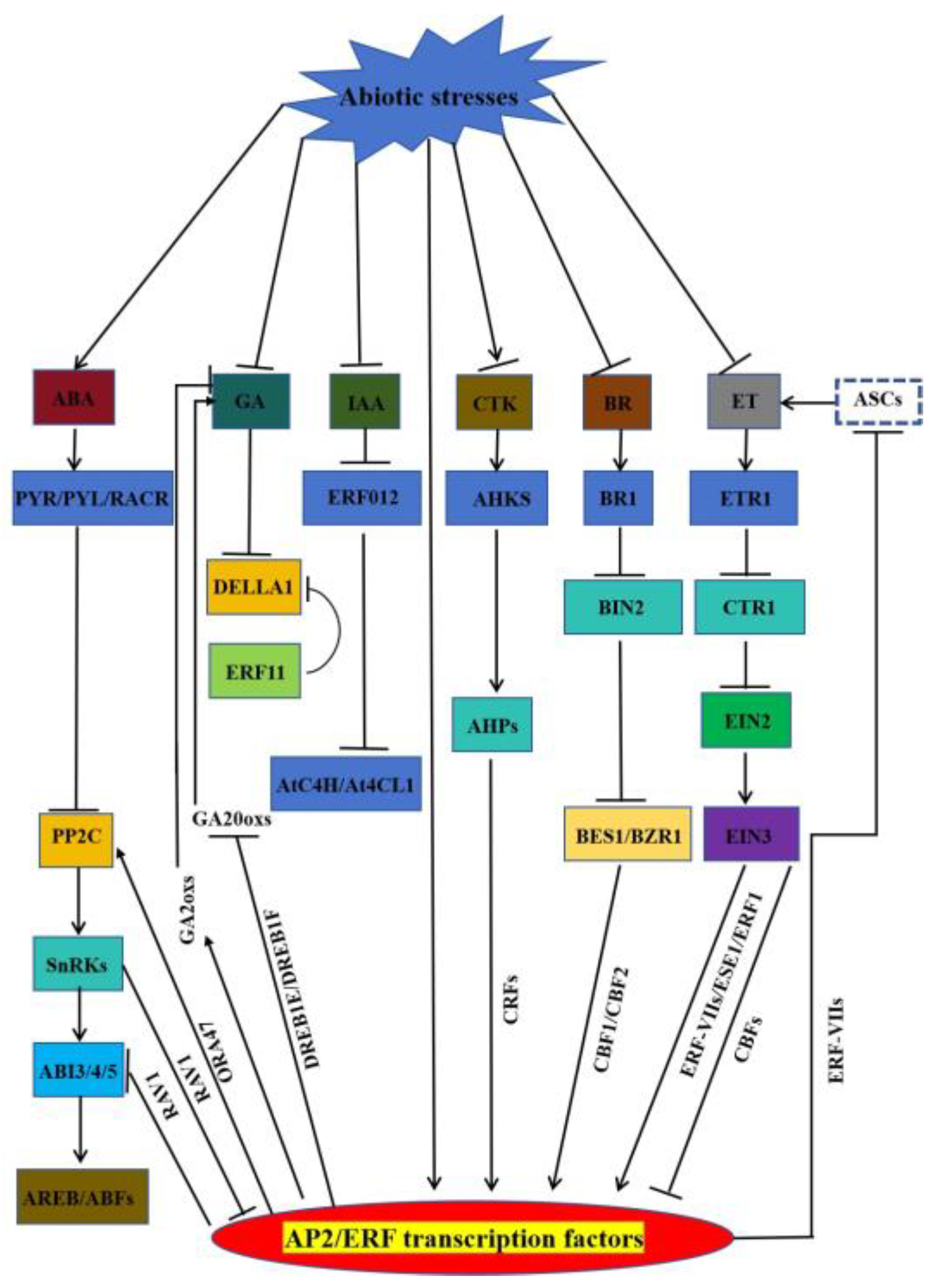
3. AP2/ERF by participating in the regulation of hormone-mediated abiotic stresses
3.1. AP2/ERF involved in ABA-mediated stress response
3.2. AP2/ERF involved in GA-mediated stress response
3.3. AP2/ERF involved in IAA-mediated stress response
3.4. AP2/ERF involved in ET-mediated stress response
3.5. AP2/ERF involved in BR-mediated stress response
3.6. AP2/ERF involved in CTK-mediated stress response
4. Role of AP2/ERF transcription factors in response to abiotic stresses(Not depend on hormone signalling pathway)
4.1. AP2/ERF transcription factors in response to drought stress
4.2. Molecular mechanisms of AP2/ERF associated with salt stress
4.3. AP2/ERF involved in plant response to temperature stress
4.3.1. AP2/ERF and high temperature stress
4.3.2. AP2/ERF and low temperature stress
4.4. Role of Plant AP2/ERF in Response to Nutritional element stress
4.5. AP2/ERF Involved in Plant Response to heavy metals stress
5. Conclusion and Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, B.; Shrestha, J. Editorial: Abiotic stress adaptation and tolerance mechanisms in crop plants. Front Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1278895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, L. MicroRNA: A Dynamic Player from Signalling to Abiotic Tolerance in Plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 11364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R.; Zandalinas, SI.; Fichman, Y.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species signalling in plant stress responses. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombage, R.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. Melatonin and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Yuan, L. ERF Gene Clusters: Working Together to Regulate Metabolism. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakabayashi, R.; Saito, K. Integrated metabolomics for abiotic stress responses in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015, 24, 10–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadarajah, K.; Abdul, H.; Abdul, R.N. SA-Mediated Regulation and Control of Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Rice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibpourmehraban, F.; Atwell, B.J.; Haynes, P.A. Unique and Shared Proteome Responses of Rice Plants (Oryza sativa) to Individual Abiotic Stresses. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 15552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibpourmehraban, F.; Wu, Y.; Masoomi-Aladizgeh, F.; Amirkhani, A.; Atwell, B.J.; Haynes, P.A. Pre-Treatment of Rice Plants with ABA Makes Them More Tolerant to Multiple Abiotic Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat Rev Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, J.C.; Park, S.; Lee, H.S.; Kwak, S.S. Molecular characterization of two ethylene response factor genes in sweetpotato that respond to stress and activate the expression of defense genes in tobacco leaves. J Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1112–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Gene networks involved in drought stress response and tolerance. J Exp Bot. 2007, 58, 221–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The Multiple Roles of Ascorbate in the Abiotic Stress Response of Plants: Antioxidant, Cofactor, and Regulator. Front Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 598173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.R.; Kumari, S.; Nazir, F.; Khanna, R.R.; Gupta, R.; Chhillar, H. Defensive Role of Plant Hormones in Advancing Abiotic Stress-Resistant Rice Plants. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, Y.; Loo, E.P. Plant immunity in signal integration between biotic and abiotic stress responses. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Lim, C.W.; Lee, S.C. Role of pepper MYB transcription factor CaDIM1 in regulation of the drought response. Front Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1028392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Tian, H.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Hussain, H.; Lin, R.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, S. AtbZIP62 Acts as a Transcription Repressor to Positively Regulate ABA Responses in Arabidopsis. Plants (Basel). 2022, 11, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemiatkowska, B.; Chiara, M.; Badiger, B.G.; Riboni, M.; D'Avila, F.; Braga, D.; Salem, M.A.A.; Martignago, D.; Colanero, S.; Galbiati, M.; Giavalisco, P.; Tonelli, C.; Juenger, T.E.; Conti, L. GIGANTEA Is a Negative Regulator of Abscisic Acid Transcriptional Responses and Sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2022, 63, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanitha, P.A.; Vijayaraghavareddy, P.; Uttarkar, A.; Dawane, A.; Sujitha, D.; Ashwin, V.; Babitha, K.C.; Niranjan, V.; Sheshshayee, M.S.; Anuradha, C.V.; et al. Novel small molecules targeting bZIP23 TF improve stomatal conductance and photosynthesis under mild drought stress by regulating ABA. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 6058–6077. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, O.; Krahmer, J.; Galbier, F.; Lagier, M.; Galvão, V.C.; Ince, Y.Ç.; Trevisan, M.; Knerova, J.; Dickinson, P.; Hibberd, J.M.; Zeeman, S.C.; Fankhauser, C. Abscisic acid modulates neighbor proximity-induced leaf hyponasty in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, R.R.; Lynch, T.J. Overexpression of ABI5 Binding Proteins Suppresses Inhibition of Germination Due to Overaccumulation of DELLA Proteins. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Upadhyay, RK.; Prabhakar, R.; Tiwari, N.; Garg, R.; Sane, V.A.; Sane, A.P. SlDREB3, a negative regulator of ABA responses, controls seed germination, fruit size and the onset of ripening in tomato. Plant Sci. 2022, 19, 111249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Jin, Y.M.; Wu, T.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Du, X. OsDREB2B, an AP2/ERF transcription factor, negatively regulates plant height by conferring GA metabolism in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1007811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wu, T.; Huang, K.; Jin, Y.M.; Li, Z.; Chen, M.; Yun, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; et al. A Novel AP2/ERF Transcription Factor, OsRPH1, Negatively Regulates Plant Height in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Sun, F.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Huang, Y.; Feng, Y.Q.; Luo, X.; Yang, J. Rice ethylene-response AP2/ERF factor OsEATB restricts internode elongation by down-regulating a gibberellin biosynthetic gene. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 216–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaish, M.W.; El-Kereamy, A.; Zhu, T.; Beatty, P.H.; Good, A.G.; Bi, Y.M.; Rothstein, S.J. The APETALA-2-like transcription factor OsAP2-39 controls key interactions between abscisic acid and gibberellin in rice. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.M.; Zhou, M.L.; Wang, D.; Tang, Y.X.; Lin, M.; Wu, Y.M. Overexpression of the lotus corniculatus soloist gene LcAP2/ERF107 enhances tolerance to salt stress. Protein Peptide Lett. 2016, 23, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiri, R.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Maziah, M.; Yusof, Z.N.B.; Atabaki, N.; Sahebi, M.; Valdiani, A.; Kalhori, N.; Azizi, P.; Hanafi, M. M. Role of ethylene and the APETALA 2/ethylene response factor superfamily in rice under various abiotic and biotic stress conditions. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2017, 134, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Ding, C.; Hu, H.; Dong, G.; Zhang, G.; Qian, Q.; Ren, D. Molecular Events of Rice AP2/ERF Transcription Factors. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; Yu, J.H.; Kim, S.Y. Isolation and functional characterization of CE1 binding proteins. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.Y. AtERF15 is a positive regulator of ABA response. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritonga, F.N.; Ngatia, J.N.; Wang, Y.; Khoso, M.A.; Farooq, U.; Chen, S. AP2/ERF, an important cold stress-related transcription factor family in plants: A review. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021, 27, 1953–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboledo, G.; Agorio, A.; Ponce, D.L.I. Moss transcription factors regulating development and defense responses to stress. J Exp Bot. 2022, 73, 4546–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Shabbir, R.; Ali, A.; Afzal, I.; Zaheer, U.; Gao, S.J. Transcription Factors in Plant Stress Responses: Challenges and Potential for Sugarcane Improvement. Plants (Basel). 2020, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, R.; Asaf, S.; Numan, M.; Lubna; Kim, K.-M. Plant Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis and Transcriptional Regulation in Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stress Conditions. Agronomy. 2021, 11, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Q.; Asim, M.; Zhang, R.; Khan, R.; Farooq, S.; Wu, J. Transcription Factors Interact with ABA through Gene Expression and Signaling Pathways to Mitigate Drought and Salinity Stress. Biomolecules. 2021, 11, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasch, P.; Fundinger, M.; Müller, J.T.; Lee, T.; Bailey, S.J.; Mustroph, A. Redundant ERF-VII Transcription Factors Bind to an Evolutionarily Conserved cis-Motif to Regulate Hypoxia-Responsive Gene Expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2016, 28, 160–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.S.; Go, Y.S.; Suh, M.C. Cuticular wax biosynthesis is positively regulated by WRINKLED4, an AP2/ERF-type transcription factor, in Arabidopsis stems. Plant J. 2016, 88, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Hsieh, E.J.; Cheng, M.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lin, T.P. ORA47 (octadecanoid-responsive AP2/ERF-domain transcription factor 47) regulates jasmonic acid and abscisic acid biosynthesis and signaling through binding to a novel cis-element. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hwang, E.Y.; Seok, H.Y.; Tarte, V.N.; Jeong, M.S.; Jang, S.B.; Moon, Y.H. Arabidopsis AtERF71/HRE2 functions as transcriptional activator via cis-acting GCC box or DRE/CRT element and is involved in root development through regulation of root cell expansion. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 223–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Mizoi, J.; Yoshida, T.; Fujita, Y.; Nakajima, J.; Ohori, T.; Todaka, D.; Nakashima, K.; Hirayama, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. An ABRE promoter sequence is involved in osmotic stress-responsive expression of the DREB2A gene, which encodes a transcription factor regulating drought-inducible genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 2136–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Liao, H.T.; Charng, Y.Y. The role of class A1 heat shock factors (HSFA1s) in response to heat and other stresses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 738–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owji, H.; Hajiebrahimi, A.; Seradj, H.; Hemmati, S. Identification and functional prediction of stress responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors in Brassica napus by genome-wide analysis. Comput Biol Chem. 2017, 71, 32–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoi, J.; Kanazawa, N.; Kidokoro, S.; Takahashi, F.; Qin, F.; Morimoto, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Heat-induced inhibition of phosphorylation of the stress-protective transcription factor DREB2A promotes thermotolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem. 2019, 294, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.P.; Agarwal, M.; Ohta, M.; Guo, Y.; Halfter, U.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.K. Role of an Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP-type transcriptional repressor in abscisic acid and drought stress responses. Plant Cell. 2005, 17, 2384–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfluger, J.; Wagner, D. Histone modifications and dynamic regulation of genome accessibility in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 645–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rando, O.J.; Ahmad, K. Rules and regulation in the primary structure of chromatin. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 250–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, R.J.; Bird, A.P. Genomic DNA methylation: the mark and its mediators. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006, 31, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemach, A.; Grafi, G. Methyl-CpG-binding domain proteins in plants: interpreters of DNA methylation. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 80–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavas, M.; Kizildogan, A.; Gökdemir, G.; Baloglu, M.C. Genome-wide investigation and expression analysis of AP2-ERF gene family in salt tolerant common bean. EXCLI J. 2015, 14, 1187–206. [Google Scholar]
- Jisha, V.; Dampanaboina, L.; Vadassery, J.; Mithöfer, A.; Kappara, S.; Ramanan, R. Overexpression of an AP2/ERF Type Transcription Factor OsEREBP1 Confers Biotic and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Rice. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0127831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.B.; Belachew, A.; Ma, S.F.; Young, M.; Ade, J.; Shen, Y.; Marion, C.M.; Holtan, H.E.; Bailey, A.; Stone, J.K.; Edwards, L.; Wallace, A.D.; Canales, R.D.; Adam, L.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Repetti, P.P. The EDLL motif: a potent plant transcriptional activation domain from AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant J. 2012, 70, 855–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.P.; Galbraith, D.W. AtSAP18, an orthologue of human SAP18, is involved in the regulation of salt stress and mediates transcriptional repression in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2006, 60, 241–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; López-Vidriero, I.; Carrasco, J.L.; Godoy, M.; Vera, P.; Solano, R. DNA-binding specificities of plant transcription factors and their potential to define target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014, 111, 2367–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waadt, R.; Seller, C.A.; Hsu, P.K.; Takahashi, Y.; Munemasa, S.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Nolan, T.M.; Jiang, H.; Yin, Y. AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Regulatory Networks in Hormone and Abiotic Stress Responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 2019, 28, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Seo, D.H.; Shin, H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, C.M.; Jang, G. The Role of Stress-Responsive Transcription Factors in Modulating Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Agronomy. 2020, 10, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B. Genomic architecture of promoters and transcriptional regulation of candidate genes in rice involved in tolerance to anaerobic germination. Curr. Plant Biol. 2022, 29, 100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, P.J.; Rashotte, A.M. Interactions between cytokinin signalling and abiotic stress responses. J Exp Bot. 2015, 66, 4863–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yan, T.; Shen, Q.; Lu, X.; Pan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, M.; Jiang, W.; Lv, Z.; Shi, P.; Ma, Y.N.; Hao, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Tang, K. GLANDULAR TRICHOME-SPECIFIC WRKY 1 promotes artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sheerin, D.J.; von Roepenack-Lahaye., E.; Stahl, M.; Hiltbrunner, A. The phytochrome interacting proteins ERF55 and ERF58 repress light-induced seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, H.; Todorovska, E.; Li, Z. OsERF71 confers drought tolerance via modulating ABA signaling and proline biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2018, 270, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; An, L.; Li, F.; Ahmad, W.; Aslam, M.; Ul Haq, M.Z.; Yan, Y.; Ahmad, R.M. Wide-Range Portrayal of AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family in Maize (Zea mays L.) Development and Stress Responses. Genes (Basel) 2023, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.; Chu, Z.; Peng, X.; Cui, G.; Li, W.; Dong, L. Transcript-wide identification and expression pattern analysis to comprehend the roles of AP2/ERF genes under development and abiotic stress in Trichosanthes kirilowii. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wei, L.; Wansee, S.; Rabbani Nasab, H.; Chen, L.; Kang, Z.; Wang, J. TaAP2-10, an AP2/ERF transcription factor, contributes to wheat resistance against stripe rust. J Plant Physiol. 2023, 288, 154078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qu, G.; Chen, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiles of C-Repeat Binding Factor Transcription Factors in Betula platyphylla under Abiotic Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chai, Z.; Lin, P.; Huang, C.; Huang, G.; Xu, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors in sugarcane (Saccharum spontaneum L.). BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Meng, X.P.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Wang, X.P. Over-expression of OsDREB genes lead to enhanced drought tolerance in rice. Biotechnol Lett. 2008, 30, 2191–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Shen, Q.; Xu, D.; Wang, Q. Maize transcription factor ZmEREB20 enhanced salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021, 159, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Han, H.; Chen, D.; Qiu, D.; Yang, Y. Transcriptome-wide analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors involved in regulating taxol biosynthesis in Taxus× media. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J.; Jia, B.; Sun, X.; Sun, M. A comprehensive investigation of the regulatory roles of OsERF096, an AP2/ERF transcription factor, in rice cold stress response. Plant Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, H.; Tang, N.; Shi, L.; Xu, F.; Wang, S. Arabidopsis ERF012 Is a Versatile Regulator of Plant Growth, Development and Abiotic Stress Responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Xia, D.N.; Li, W.Q.; Cao, X.Y.; Ma, F.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhan, X.Q.; Hu, T.X. Overexpression of a tomato AP2/ERF transcription factor SlERF.B1 increases sensitivity to salt and drought stresses. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 304, 111332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan, K. Diverse roles of jasmonates and ethylene in abiotic stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 219–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.H.; Seo, Y.S.; Walia, H.; Cao, P.; Fukao, T.; Canlas, P.E.; Amonpant, F.; Bailey-Serres, J.; Ronald, P.C. The submergence tolerance regulator Sub1A mediates stress-responsive expression of AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 1674–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Castro, J.M.; van, Zanten. M.; Lee, S.C.; Patel, M.R.; Voesenek, L.A.; Fukao, T.; Bailey-Serres, J. Expression of rice SUB1A and SUB1C transcription factors in Arabidopsis uncovers flowering inhibition as a submergence tolerance mechanism. Plant J. 2011, 67, 434–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, M.; Wilson, I.W.; Yang, J.; Buerstenbinder, K.; Llewellyn, D.; Dennis, E.S.; Sauter, M.; Dolferus, R. Arabidopsis RAP2.2: an ethylene response transcription factor that is important for hypoxia survival. Plant Physiol 2010, 153, 757–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamura, M.M.; Piacentini, D.; Della Rovere., F.; Fattorini, L.; Falasca, G.; Betti, C. New Paradigms in Brassinosteroids, Strigolactones, Sphingolipids, and Nitric Oxide Interaction in the Control of Lateral and Adventitious Root Formation. Plants (Basel) 2023, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Liu, K.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, S. ERF72 interacts with ARF6 and BZR1 to regulate hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot. 2018, 69, 3933–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, A.J.; Folsom, J.J.; Jikamaru, Y.; Ronald, P.; Walia, H. SUB1A-mediated submergence tolerance response in rice involves differential regulation of the brassinosteroid pathway. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurepa, J.; Shull, T.E.; Smalle, J.A. Friends in Arms: Flavonoids and the Auxin/Cytokinin Balance in Terrestrialization. Plants (Basel). 2023, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Guo, Z.H.; Hao, P.P.; Wang, G.M.; Jin, Z.M.; Zhang, S.L. Multiple regulatory roles of AP2/ERF transcription factor in angiosperm. Bot Stud. 2017, 58, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawlong, I.; Ali, K.; Tyagi, A. Cloning and characterization of a water deficit stress responsive transcription factor gene from Oryza sativa L. Indian J Exp Biol. 2016, 54, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Rashotte, A.M.; Mason, M.G.; Hutchison, C.E.; Ferreira, F.J.; Schaller, G.E.; Kieber, J.J. A subset of Arabidopsis AP2 transcription factors mediates cytokinin responses in concert with a two-component pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006, 103, 11081–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striberny, B.; Melton, A.E.; Schwacke, R.; Krause, K.; Fischer, K.; Goertzen, L.R.; Rashotte, A.M. Cytokinin Response Factor 5 has transcriptional activity governed by its C-terminal domain. Plant Signal Behav. 2017, 12, e1276684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, P.J.; Robinson, B.R.; Risley, M.G.; Rashotte, A.M. Cytokinin response factor 6 negatively regulates leaf senescence and is induced in response to cytokinin and numerous abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 971–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, P.J.; De Clercq, I.; Howton, T.C.; Hallmark, H.T.; Hurny, A.; Keshishian, E.A.; Parish, A.M.; Benkova, E.; Mukhtar, M.S.; Van, Breusegem. F.; Rashotte, A.M. Cytokinin Response Factor 6 Represses Cytokinin-Associated Genes during Oxidative Stress. Plant Physiol 2016, 172, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, P.J.; Compton, M.A.; Adams, C.I.; Rashotte, A.M. Cytokinin response factor 4 (CRF4) is induced by cold and involved in freezing tolerance. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 573–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golldack, D.; Li, C.; Mohan, H.; Probst, N. Tolerance to drought and salt stress in plants: Unraveling the signaling networks. Front Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Lee, E.; Tripathi, P.; Heo, S.; Kim, K.H. Root Response to Drought Stress in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhang, S.; Song, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, X. Transcriptomic Identification of Wheat AP2/ERF Transcription Factors and Functional Characterization of TaERF-6-3A in Response to Drought and Salinity Stresses. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarambasa, T.; Regon, P.; Jyoti, S.Y.; Gupta, D.; Panda, S.K.; Tanti, B. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the Pisum sativum (L.) APETALA2/ethylene-responsive factor (AP2/ERF) gene family reveals functions in drought and cold stresses. Genetica 2023, 151, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Tewari, K.; Garg, N.K.; Changan, S.S.; Tyagi, A. Isolation and characterization of drought and ABA responsive promoter of a transcription factor encoding gene from rice. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022, 28, 1813–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.M.T.; Hossain, M.S.; Bashar, K.K.; Honi, U.; Ahmed, B.; Emdad, E.M.; Alam, M.M.; Haque, M.S.; Islam, M.S. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of AP2/ERF superfamily genes under stress conditions in dark jute (Corchorus olitorius L.). Ind. Crops Prod 2021, 166, 113469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Song, Q.; Wei, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, M.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Luo, K. The AP2/ERF transcription factor PtoERF15 confers drought tolerance via JA-mediated signaling in Populus. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 1848–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litalien, A.; Zeeb, B. Curing the earth: A review of anthropogenic soil salinization and plant-based strategies for sustainable mitigation. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ma, Z.; Hu, L.; Huang, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, W.; Wu, T.; Du, X. Involvement of rice transcription factor OsERF19 in response to ABA and salt stress responses. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021, 167, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licausi, F.; van Dongen, J.T.; Giuntoli, B.; Novi, G.; Santaniello, A.; Geigenberger, P.; Perata, P. HRE1 and HRE2, two hypoxia-inducible ethylene response factors, affect anaerobic responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2010, 62, 302–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Seok, H.Y.; Woo, D.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Tarte, V.N.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, C.H.; Moon, Y.H. AtERF71/HRE2 transcription factor mediates osmotic stress response as well as hypoxia response in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011, 414, 135–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, H.Y.; Tran, H.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Moon, Y.H. AtERF71/HRE2, an Arabidopsis AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Gene, Contains Both Positive and Negative Cis-Regulatory Elements in Its Promoter Region Involved in Hypoxia and Salt Stress Responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, B.C.; Kariyawasam, B.C.; Bramley, H.; Coast, O.; Richards, R.A.; Reynolds, M.P.; Trethowan, R.; Atkin, O.K. Exploring high temperature responses of photosynthesis and respiration to improve heat tolerance in wheat. J Exp Bot. 2019, 70, 5051–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guan, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Zha, Z.; Guo, Y.; Jiao, C.; Cai, H. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Dynamic and Rapid Transcriptional Reprogramming Involved in Heat Stress and Identification of Heat Response Genes in Rice. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 14802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tang, Y.; Luan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Tao, J.; Zhao, D. Herbaceous peony AP2/ERF transcription factor binds the promoter of the tryptophan decarboxylase gene to enhance high-temperature stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 2729–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemal, R.; Khoudi, H. The barley SHN1-type transcription factor HvSHN1 imparts heat, drought and salt tolerances in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021, 164, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidokoro, S.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Transcriptional regulatory network of plant cold-stress responses. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Gu, L.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Z. Identification of AP2/ERF transcription factors in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum revealed the specific roles of ERF46 under cold stress. Front Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 936602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; You, X.; Yu, H.; Guo, R.; Zhao, X. Genome-Wide Identification of AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes in Juglans mandshurica and Expression Analysis under Cold Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 15225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, X.R.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Zhang, M.X.; Li, S.J.; Liu, X.F.; Shi, Y.N.; Grierson, D.; Chen, K.S. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR39-MYB8 complex regulates low-temperature-induced lignification of loquat fruit. J Exp Bot. 2020, 71, 3172–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Quan, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yin, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, R. Overexpression of ClRAP2.4 in Chrysanthemum enhances tolerance to cold stress. Funct Plant Biol. 2023, 50, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahaya, S.M.; Mahmud, A.A.; Abdullahi, M.; Haruna, A. Recent advances in the chemistry of N, P, K as fertilizer in soil: A review. Pedosphere. 2022, 35, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Waqas, M.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Geilfus, C.M. Feeding the world sustainably: Efficient nitrogen use. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, V.; Joshi, M.; Penalosa, A. Comparative analysis of tissue-specific transcriptomic responses to nitrogen stress in spinach (Spinacia oleracea). PLoS One. 2020, 15, e0232011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, M.R.; Wang, Q.; Stolz, P.; Folgmann, J.; Frances, L.; Katzer, K.; Li, X.; Heckmann, A.B.; Wang, T.L.; Downie, J.A.; Klingl, A.; de Carvalho-Niebel, F.; Xie, F.; Parniske, M. The ERN1 transcription factor gene is a target of the CCaMK/CYCLOPS complex and controls rhizobial infection in Lotus japonicus. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezek, M.; Allan, A.C.; Jones, J.J.; Geilfus, C.M. Why do plants blush when they are hungry? New Phytol. 2023, 239, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Xie, Q.; Xia, Y.; Lu, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, G.; Long, S.; Cai, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, E.; Jiang, Y. Control of arbuscule development by a transcriptional negative feedback loop in Medicago. Nat Commun. 2023, 14, 5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Qin, J.; Tong, S.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Y. One AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Positively Regulates Pi Uptake and Drought Tolerance in Poplar. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parakkunnel, R.; Naik, K.B.; Vanishree G, C.S.; Purru, S.; Bhaskar, K.U.; Bhat, K.V.; Kumar, S. Gene fusions, micro-exons and splice variants define stress signaling by AP2/ERF and WRKY transcription factors in the sesame pan-genome. Front Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1076229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Ruzicka, D.; Shin, R.; Schachtman, D.P. The Arabidopsis AP2/ERF transcription factor RAP2.11 modulates plant response to low-potassium conditions. Mol Plant 2012, 5, 1042–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Chien, T.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Chiang, M.H.; Lai, M.H.; Chang, M.C. Overexpression of a Novel ERF-X-Type Transcription Factor, OsERF106MZ, Reduces Shoot Growth and Tolerance to Salinity Stress in Rice. Rice (N Y) 2021, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilescu, M. Enhancing phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy metals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 74, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chot, E.; Reddy, M.S. Role of Ectomycorrhizal Symbiosis Behind the Host Plants Ameliorated Tolerance Against Heavy Metal Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 855473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgher, M.; Rehaman, A.; Islam, S.N.u.; Arshad, M.; Khan, N.A. Appraisal of Functions and Role of Selenium in Heavy Metal Stress Adaptation in Plants. Agriculture. 2023, 13, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Zori´c, L.; Sun, T.; Karanovi´c, D.; Fang, P.; Borišev, M.; Wu, X.; Lukovi´c, J.; Xu, P. The Anatomical Basis of Heavy Metal Responses in Legumes and Their Impact on Plant-Rhizosphere Interactions. Plants. 2022, 11, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanja, B.K.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, M.; M'mbone Muleke, E.; Dong, J.; Liu, L. Genome-wide characterization of the AP2/ERF gene family in radish (Raphanus sativus L.): Unveiling evolution and patterns in response to abiotic stresses. Gene 2019, 718, 144048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, Z.; Luo, D.; Jia, R.; Lu, H.; Tang, M.; Hu, Y.; Yue, J.; Huang, Z. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals key genes and pathways in two different cadmium tolerance kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) cultivars. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Meng, L.; He, T.; He, G. Identification of StAP2/ERF genes of potato (Solanum tuberosum) and their multiple functions in detoxification and accumulation of cadmium in yest: Implication for Genetic-based phytoremediation. Sci Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Ravindran, P.; Kumar, P.P. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takino, J.; Kozaki, T.; Ozaki, T.; Liu, C.; Minami, A.; Oikawa, H. Elucidation of biosynthetic pathway of a plant hormone abscisic acid in phytopathogenic fungi. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2019, 83, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, R. Abscisic Acid synthesis and response. Arabidopsis Book. 2013, 11, e0166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, S.K.; Reddy, K.R.; Li, J. Abscisic Acid and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants. Front Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Kong, Y.H.; Wu, W.H.; Chen, Y.F. Arabidopsis RAV1 transcription factor, phosphorylated by SnRK2 kinases, regulates the expression of ABI3, ABI4, and ABI5 during seed germination and early seedling development. Plant J. 2014, 80, 654–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magome, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Hanada, A.; Kamiya, Y.; Oda, K. dwarf and delayed-flowering 1, a novel Arabidopsis mutant deficient in gibberellin biosynthesis because of overexpression of a putative AP2 transcription factor. Plant J. 2004, 37, 720–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.L.; Park, J.; Tyler, L.; Yusuke, J.; Qiu, K.; Nam, E.A.; Lumba, S.; Desveaux, D.; McCourt, P.; Kamiya, Y.; Sun, T.P. The ERF11 Transcription Factor Promotes Internode Elongation by Activating Gibberellin Biosynthesis and Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2760–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Li, L.; Aluru, M.; Aluru, S.; Yin, Y. Mechanisms and networks for brassinosteroid regulated gene expression. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 545–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ye, K.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S. BZR1 Positively Regulates Freezing Tolerance via CBF-Dependent and CBF-Independent Pathways in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant. 2017, 10, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.J.; Chen, H.W.; Ma, B.; Zhang, W.K.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, J.S. The Role of Ethylene in Plants Under Salinity Stress. Front Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Shen, Z.; Huang, S.S.; Schmitz, R.J.; Urich, M.A.; Briggs, S.P.; Ecker, J.R. Processing and subcellular trafficking of ER-tethered EIN2 control response to ethylene gas. Science. 2012, 338, 390–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Ethylene Response Factors: A Key Regulatory Hub in Hormone and Stress Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Hsu, F.C.; Li, J.P.; Wang, N.N.; Shih, M.C. The AP2/ERF transcription factor AtERF73/HRE1 modulates ethylene responses during hypoxia in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 202–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Deng, K.; Liu, D.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, C.; Song, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Ectopic Expression of DREB Transcription Factor, AtDREB1A, Confers Tolerance to Drought in Transgenic Salvia miltiorrhiza. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 1593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012, 1819, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Tian, A.G.; Luo, G.Z.; Gong, Z.Z.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y. Soybean DRE-binding transcription factors that are responsive to abiotic stresses. Theor Appl Genet. 2005, 110, 1355–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Di, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, J.; Cao, A. Overexpression of ERF1-V from Haynaldia villosa Can Enhance the Resistance of Wheat to Powdery Mildew and Increase the Tolerance to Salt and Drought Stresses. Front Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Li, J.; Long, S.; Wei, S. A DREB1 gene from zoysiagrass enhances Arabidopsis tolerance to temperature stresses without growth inhibition. Plant Sci. 2019, 278, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; Jia, C.; Qin, J.; Pan, H. Functional Analysis of the Maize C-Repeat/DRE Motif-Binding Transcription Factor CBF3 Promoter in Response to Abiotic Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2015, 16, 12131–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Chen, L.; Xiao, W.; Yu, J. ZmEREB46, a maize ortholog of Arabidopsis WAX INDUCER1/SHINE1, is involved in the biosynthesis of leaf epicuticular very-long-chain waxes and drought tolerance. Plant Sci. 2022, 321, 111256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Tian, C.; Aslam, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W.; Zou, H. Overexpression of ZmEREBP60 enhances drought tolerance in maize. J Plant Physiol. 2022, 275, 153763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Xin, H.; Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Li, J.; Tran, L.S.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Qin, F. Genome-wide analysis of ZmDREB genes and their association with natural variation in drought tolerance at seedling stage of Zea mays L. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liang, K.; Fang, T.; Zhao, H.; Han, X.; Cai, M.; Qiu, F. A group VII ethylene response factor gene, ZmEREB180, coordinates waterlogging tolerance in maize seedlings. Plant Biotechnol J. 2019, 17, 2286–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Lumbreras, V.; Lopez, C.; Dominguez-Puigjaner, E.; Kizis, D.; Pagès, M. Maize DBF1-interactor protein 1 containing an R3H domain is a potential regulator of DBF1 activity in stress responses. Plant J. 2006, 46, 747–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ren, Z.; Abou-Elwafa, S.F.; Pu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, D.; Su, H.; Cheng, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, E.; Shao, R.; Ku, L. ZmERF21 directly regulates hormone signaling and stress-responsive gene expression to influence drought tolerance in maize seedlings. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wan, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, B.; Zhou, C.; Pan, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Jing, R.; Xu, Y.; Han, M.; Wu, F.; Lei, C.; Guo, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, H.; Wan, J. Transcriptional activation and phosphorylation of OsCNGC9 confer enhanced chilling tolerance in rice. Mol Plant. 2021, 14, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, D.D.; Barros, P.M.; Cordeiro, A.M.; Serra, T.S.; Lourenço, T.; Chander, S.; Oliveira, M.M.; Saibo, N.J. Seven zinc-finger transcription factors are novel regulators of the stress responsive gene OsDREB1B. J Exp Bot. 2012, 63, 3643–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Chen, C. Colinearity and similar expression pattern of rice DREB1s reveal their functional conservation in the cold-responsive pathway. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e47275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.H.; Li, X.P.; Zhou, H.L.; Zhang, J.S.; Gong, Z.Z.; Chen, S.Y. OsDREB4 Genes in Rice Encode AP2-Containing Proteins that Bind Specifically to the Dehydration-Responsive Element. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2005, 47, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.; Chu, C. Overexpression of a rice OsDREB1F gene increases salt, drought, and low temperature tolerance in both Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biol. 2008, 67, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- "Zhou, X.Y.; Jenks, M.A.; Liu, J.; Liu, A.L.; Zhang, X.W.; Xiang, J.H.; Zou, J.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.B. Overexpression of Transcription Factor OsWR2 Regulates Wax and Cutin Biosynthesis in Rice and Enhances its Tolerance to Water Deficit. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 719–731. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.K.; Jung, H.; Jang, G.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Ha, S.H.; Do, C.Y.; Kim, J.K. Overexpression of the OsERF71 Transcription Factor Alters Rice Root Structure and Drought Resistance. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 575–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Yu, J.; Miao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Fu, B.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Ali, J.; Li, Z. Natural Variation in OsLG3 Increases Drought Tolerance in Rice by Inducing ROS Scavenging. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramegowda, V.; Basu, S.; Krishnan, A.; Pereira, A. Rice GROWTH UNDER DROUGHT KINASE is required for drought tolerance and grain yield under normal and drought stress conditions. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1634–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Li, C. JcDREB2, a Physic Nut AP2/ERF Gene, Alters Plant Growth and Salinity Stress Responses in Transgenic Rice. Front Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, T.S.; Figueiredo, D.D.; Cordeiro, A.M.; Almeida, D.M.; Lourenço, T.; Abreu, I.A.; Sebastián, A.; Fernandes, L.; Contreras-Moreira, B.; Oliveira, M.M.; Saibo, N.J. OsRMC, a negative regulator of salt stress response in rice, is regulated by two AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant Mol Biol. 2013, 82, 439–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Schippers, J.H.; Mieulet, D.; Watanabe, M.; Hoefgen, R.; Guiderdoni, E.; Mueller-Roeber, B. SALT-RESPONSIVE ERF1 is a negative regulator of grain filling and gibberellin-mediated seedling establishment in rice. Mol Plant. 2014, 7, 404–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Tao, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Pu, L.; Huang, R.; Chen, T. INDETERMINATE SPIKELET1 Recruits Histone Deacetylase and a Transcriptional Repression Complex to Regulate Rice Salt Tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, J.; Guo, Z. The rice ERF transcription factor OsERF922 negatively regulates resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae and salt tolerance. J Exp Bot. 2012, 63, 3899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Abiotic Stress Type | AP2/ERF transcription factors | Species | Reference |
| Drought | AtDREB1A | Arabidopsis thaliana L. | [141] |
| Cold | DREB1/CBF | Arabidopsis thaliana L. | [142] |
| Cold | DREB2 | Arabidopsis thaliana L. | [142] |
| Cold, salt, drought | GmDREBa | Soybean (Glycine max L.) | [143] |
| Cold, salt, drought | GmDREBc | Soybean (Glycine max L.) | [143] |
| Drought | ERF1-V | Wheat (Triticum aestivum) | [144] |
| Temperature | ZjDREB1.4 | Zoysiagrass (Zoysia japonica S.) | [145] |
| Cold, salt, drought | ZmEREB3 | Maize (Zea mays L.) | [146] |
| Salt | ZmEREB20 | Maize (Zea mays L.) | [70] |
| Drought | ZmEREB46 | Maize (Zea mays L.) | [147] |
| Drought | ZmEREB60 | Maize (Zea mays L.) | [148] |
| Drought | ZmEREB137 | Maize (Zea mays L.) | [149] |
| Waterlogging | ZmEREB180 | Maize (Zea mays L.) | [150] |
| Osmotic | ZmEREB204 | Maize (Zea mays L.) | [151] |
| Drought | ZmEREB240 | Maize (Zea mays L.) | [152] |
| Cold | OsDREB1A | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [153] |
| Temperature | OsDREB1B | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [154] |
| Cold, salinity | OsDREB1D | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [155] |
| Drought | OsDREB1E | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [155] |
| Drought | OsDREB1G; OsDREB1I | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [69] |
| Drought | OsDREB2B | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [69] |
| Salt, drought, temperature | OsDREB4-1 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [156] |
| Salt, drought, temperature | OsDREB1F | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [157] |
| Temperature | OsWR2 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [158] |
| Drought | OsERF71 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [159] |
| Drought | OsLG3; OsERF62; OsRAF | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [160] |
| Drought | OsAP37 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [161] |
| Salt | OsAP23 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [162] |
| Salt, drought, temperature | OsEREBP2 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [163] |
| Salt | SERF1 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [164] |
| Salt | OsIDS1 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [165] |
| Salt | OsERF922 | Rice (Oryza sativa) | [166] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





