1. Introduction
Efforts to integrate haptic feedback into virtual reality/augmented reality (VR/AR)[
1] and teleoperation applications [
2] aim to expand sensory perception beyond the visual and auditory realms. Such integration of haptic feedback seeks to create an immersive experience. In this context, we propose the use of Pneumatic Unit Cell (PUC) as a novel and versatile pneumatically driven actuator for haptic applications.
Haptic feedback comprises two distinct modalities: kinesthetic feedback and tactile feedback. Kinesthetic feedback engages muscular and skeletal components to sense forces and torques, while tactile feedback employs the skin to perceive various attributes such as roughness, hardness, temperature, and friction [
3,
4,
5]. Among the multitude of haptic sensations, this paper narrows its focus to two specific types: static pressure and vibrotactile feedback.
Recent research on the use of static pressure feedback [
6] and vibrotactile feedback [
7] as alternatives to kinesthetic force feedback, has reported control stability benefits without a significant impact on task performance. Additionally, Pacchierotti et al. [
8] observed the advantages of providing both static pressure and vibrotactile feedback to accommodate the diverse subjective exploration strategies employed by humans.
Various actuator solutions have been investigated to incorporate static pressure and vibrotactile feedback. Pacchierotti et al. [
8] implemented the feedback by using servo motors and vibrotactile motors to individually address the desired feedback. The design of the haptic display offered control over the direction of the feedback but is limited by the lack of amalgamation of different actuations and is constrained by the design.
Alternatively, elastomeric actuators have shown potential in addressing these challenges [
9]. Dielectric elastomeric actuators [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13] and pneumatic actuators [
9,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19] have demonstrated their capacity to offer both static pressure and vibrotactile feedback. Dielectric elastomeric actuators, in particular, have exhibited potential for haptic applications, primarily due to their compactness and modularity. However, dielectric elastomeric actuators often demand high operating voltages and can require intricate fabrication procedures [
10,
11,
12,
13].
In the case of pneumatically driven actuators, the evolution of these actuators initially began with static pressure feedback. Primarily, the use of pin arrays [
20,
21], air jets [
22,
23], and inflatable structures [
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29], with the latter accommodating more actuator design freedom. In line with this topic, research by King et al. [
29,
30] explored the use of inflatable soft pneumatic actuators for static pressure feedback while incorporating modularity and scalability into the design. Recent investigations into soft pneumatic actuators have also revealed the potential of inflatable actuators for vibrotactile feedback, achieving frequencies of up to 250 Hz [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19].
Within pneumatic actuator designs, the primary objective is to localize deformation during inflation-deflation cycles by introducing contrast in the stiffness. The literature offers a range of solutions, with the most notable design approaches involving the use of fabric and silicone [
14,
15,
17,
18,
19], the bonding of soft elastomers to rigid substrates [
26,
27,
28], and the integration of elastomers between rigid components [
25].
In this paper, we are inspired to approach the design of soft pneumatic actuators that are further simplified and eliminate the need for fabric to introduce structural stiffness. Additionally, our focus extends to designing an actuator with a broad scope of application – one that is modular, scalable, and mountable on any surface.
Addressing these objectives, we have designed a Pneumatic Unit Cell (PUC) (
Figure 1). PUCs are entirely manufactured using silicone. The inherent simplicity of the PUC design makes it conducive to scalability while maintaining the generation of both static pressure and vibrotactile feedback. In addition, recent work presented in [
31] highlights the preference for PUC actuators as a haptic feedback option over traditional electromechanical vibration motors, particularly in simulating virtual button clicks.
The main objective of this paper is to characterize the performance of a single Pneumatic Unit Cell (PUC). The study focuses on investigating the influence of the top layer thickness of the PUC on the stiffness along with the influence of pressure and frequency on the performance of the PUC actuator. The study involves three distinct PUC designs with varying top-layer thicknesses: 0.6 mm, 0.9 mm, and 1.2 mm, which influence the stiffness. These different PUC designs are tested for manufacturing accuracy and evaluated for their performance under both static pressure and frequency conditions.
In the static pressure condition, all PUC designs are assessed for their top-layer free deflection and blocking force performance. The results of these tests provide insights into the linear free deflection operating range of PUCs for a given PUC design. The frequency condition, the free deflection of the top layer of the PUCs is studied. This offered insights into the effects of varying degrees of inflation-deflation cycles on the free deflection.
The structure of the paper goes as following:
Section 2 details the fabrication procedure, followed by an overview of dimensional measurements, discussions, and results related to the fabrication process.
Section 3 outlines the characterization of the PUC, with an overview of the hardware setup, methods used in the characterization study of PUC under static pressure and frequency conditions, along with discussions and results.
Section 4 presents the general discussions, and
Section 5 presents the final conclusion.
2. Fabrication of Pneumatic Unit Cells
This section describes the PUC fabrication, the dimensional evaluation of the top layer thickness and the statistical analysis of the measured data.
2.1. Design And Fabrication Steps
PUCs are cylindrical hollow structures with an 8 mm diameter and pneumatic inputs located at the bottom of the structure. They were fabricated using Dragon SkinTM 10 Medium (Smooth-On, United States) silicone. To localize the deformation to the top layer, the thickness of the top layer was kept relatively low compared to the rest of the PUC structure. For the scope of the current paper, PUCs with top layer thicknesses of 0.6 mm, 0.9 mm, and 1.2 mm were designed, while the side walls of the PUC were maintained at 1.5 mm.
PUCs were fabricated using the closed mold method. This method was chosen over the open mold method for its fabrication consistency. PUCs were produced in two halves: the upper and bottom parts (
Figure 2a-b). The molds necessary for PUC fabrication were created using Formlab’s Stereolithography (SLA) printers (Formlabs, United States), utilizing Rigid 10K resin. The molds were prepared and assembled for the injection of Dragon Skin
TM 10 Medium. Resin mixers (DM2X 400-01-60 manual dispenser, SAF-400-01-10-0 cartridge, and MFH-06-24T static mixer, procured from Siko BV, Netherlands) were employed to ensure consistent mixing (
Figure 2c). The molds were filled through injection and then placed in an oven and cured at 60°C for one hour. After curing, the parts were extracted from the molds and joined together using Dragon Skin
TM 10 Medium (
Figure 2d-f). The assembled PUC was returned to the oven for an additional hour at 60°C for curing.
2.2. Method For Dimensional Measurements
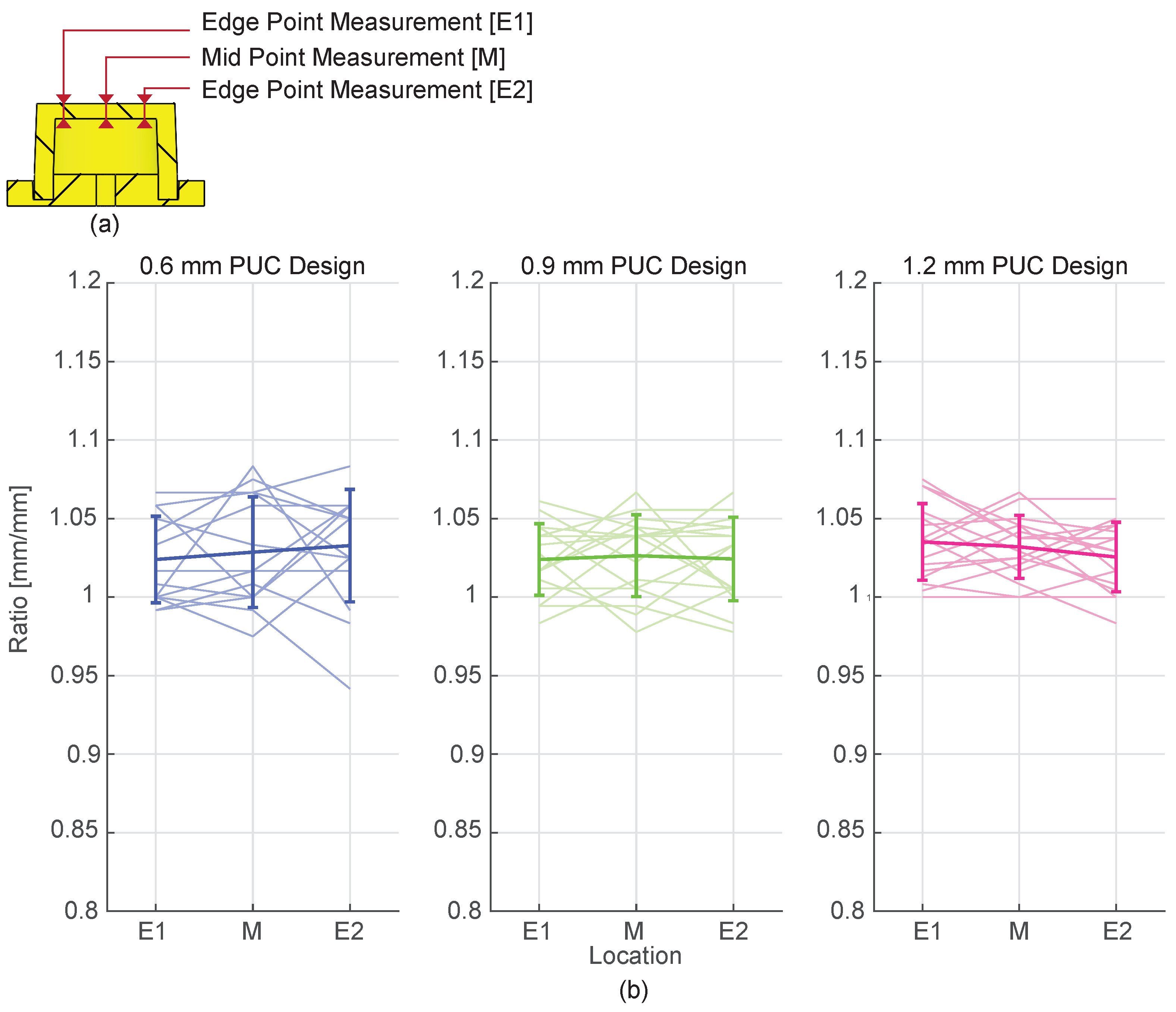
The top layer thickness of the fabricated PUCs was measured using an ISOMA Bienne Suisse microscope. Four batches of PUCs were fabricated for each design (0.6 mm, 0.9 mm, and 1.2 mm), with each batch producing four individual PUCs. To ensure a representative sample, two PUCs were randomly selected from each batch and sectioned along the coronal plane. The resulting halves of each PUC were used for thickness measurements. To assess the uniformity of the thickness, measurements were taken at three locations E1, M and E2, as shown in
Figure 3a. Location E1 and E2 represents the measurements at close to the edge and location M represent the measurement at the middle of the cross section. This resulted in 16 data points for each combination of measurement location and PUC design. Thickness ratios were calculated to compare the measured thickness to the target thickness. A two-way 3x3 ANOVA (PUC design x measurement location) was performed on the thickness ratios to study the uniformity of the thickness.
2.3. Results
Figure 3b presents the results of dimensional measurement of the top layer thickness, categorized by measurement location and design. For the 0.6 mm PUC design, the mean thickness ratio values at locations E1, M, and E2 are 1.024 ± 0.028 mm/mm, 1.029 ± 0.035 mm/mm, and 1.033 ± 0.036 mm/mm, respectively. For the 0.9 mm PUC design, the mean thickness ratio at locations E1, M, and E2 are 1.024 ± 0.023 mm/mm, 1.026 ± 0.026 mm/mm, and 1.024 ± 0.027 mm/mm, respectively. For the 1.2 mm PUC design, the mean thickness ratio at locations E1, M, and E2 are 1.035 ± 0.024 mm/mm, 1.032 ± 0.020 mm/mm, and 1.026 ± 0.022 mm/mm, respectively. A two-way 3x3 ANOVA analysis revealed no significant main effect of the measurement location (F(2,135) = 0.04, p = 0.96) or the design (F(2,135) = 0.59, p = 0.55) on the thickness ratio.
2.4. Discussion
The results of the dimensional measurement show the mean thickness ratios do not differ significantly between PUC designs. The results of a two-way ANOVA comparing the thickness ratio between PUC designs also revealed no significant main effect among the designs. This indicates that the closed mold fabrication process results in a consistent thickness ratio. Furthermore, the two-way ANOVA shows no significant main effect of measurement location on the thickness ratio. This suggests that the closed mold-fabricated PUCs also result in a uniform thickness ratio across the cross-section.
The proposed fabrication process produces PUCs that are approximately to thicker than the target thickness. This consistent deviation in the thickness ratio could be attributed to two factors: (a) Mating tolerance between the two pieces of the upper part mold, resulting in increased separation between both pieces of the upper part mold. (b) The proposed fabrication process consists of two stages of oven curing. In the first stage, the silicone is cured inside the mold, while in the second stage, both parts of the PUC are extracted from the molds and assembled. During the second stage of curing, the PUC has the freedom to expand and form new cross-links, likely resulting in a permanent but consistent deviation in the thickness ratio across different PUC designs.
3. Characterisation of PUCs
This section begins with an overview of the hardware setup, followed by a detailed description of PUC tests under static pressure conditions, results, and discussion. Subsequent subsections address the PUC tests under frequency conditions, results, and discussions.
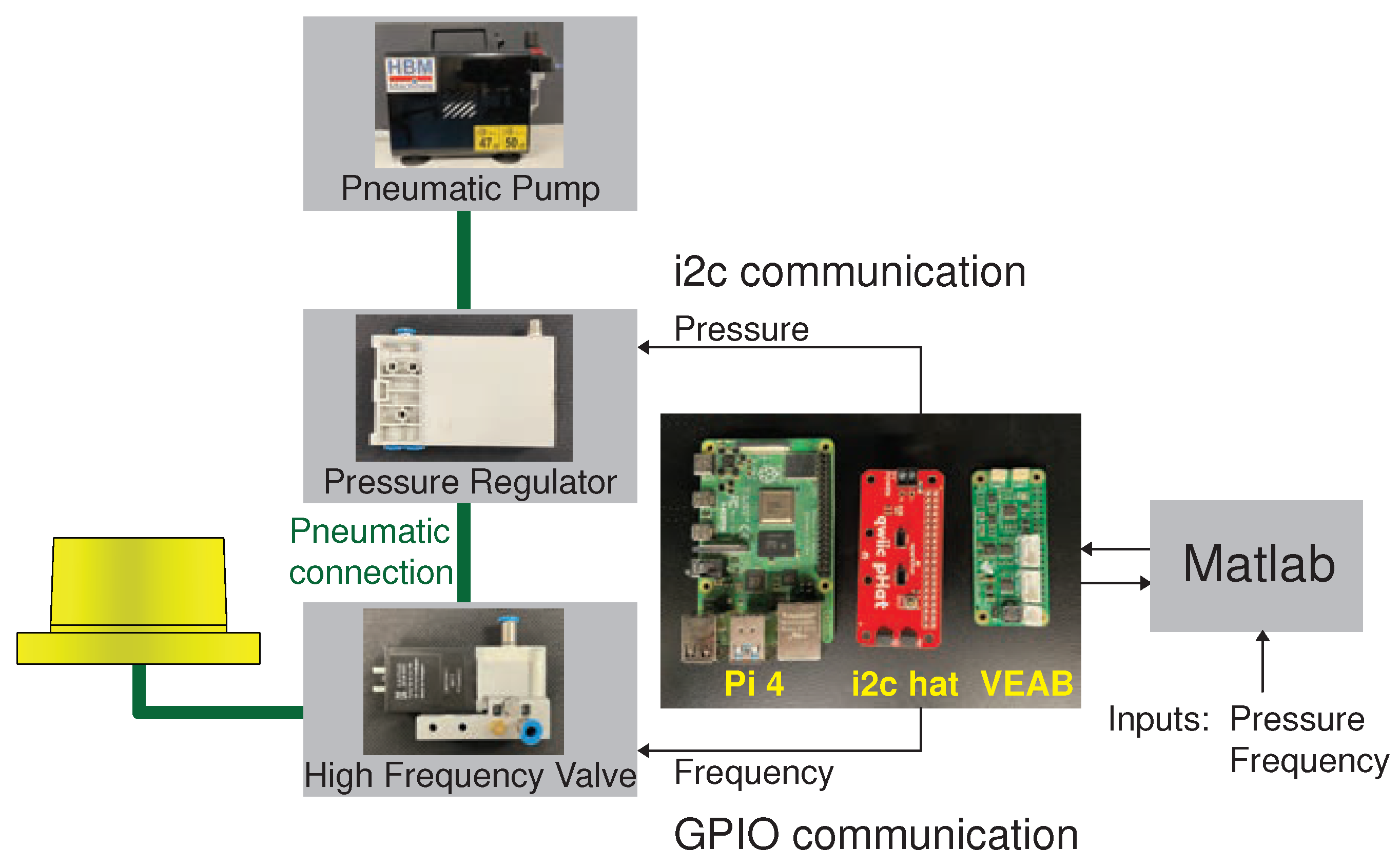
3.1. Hardware Setup
The control of pneumatic pressure and inflation-deflation frequencies was achieved using a customized desktop-sized platform powered by Raspberry Pi, as described in
Figure 4. The hardware setup comprises two types of peripherals: a proportional pressure control valve (VEAB-L-26-D13-Q4-V1-1R1, Festo, Germany) for regulating the pneumatic pressure, and a high frequency valve (MHP2-MS1H-3/2G-M5, Festo, Germany) for controlling the inflation-deflation rates. The desired pressure and frequencies were configured through Matlab and communicated to Raspberry Pi, which then initiated parallel processes to control the individual peripherals. For further details about the setup, see [
32].
In the static pressure condition, PUCs were inflated to a maximum pressure of 40 KPa to measure free deflection and 30 KPa to measure blocking force, respectively. In the frequency condition, PUCs were inflated to a maximum pressure of 30 KPa, and inflation-deflation rates ranging from 0.5 Hz to 100 Hz, including 1, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.8, 10, 12.5, 15, 25, 30, 31, 50, 55, 62, 71, and 83 Hz [
17,
19] at 30% duty cycle. see
Table 1 for an overview of the static pressure and frequency condition.
3.2. Static Pressure Condition - Free Deflection Measurement
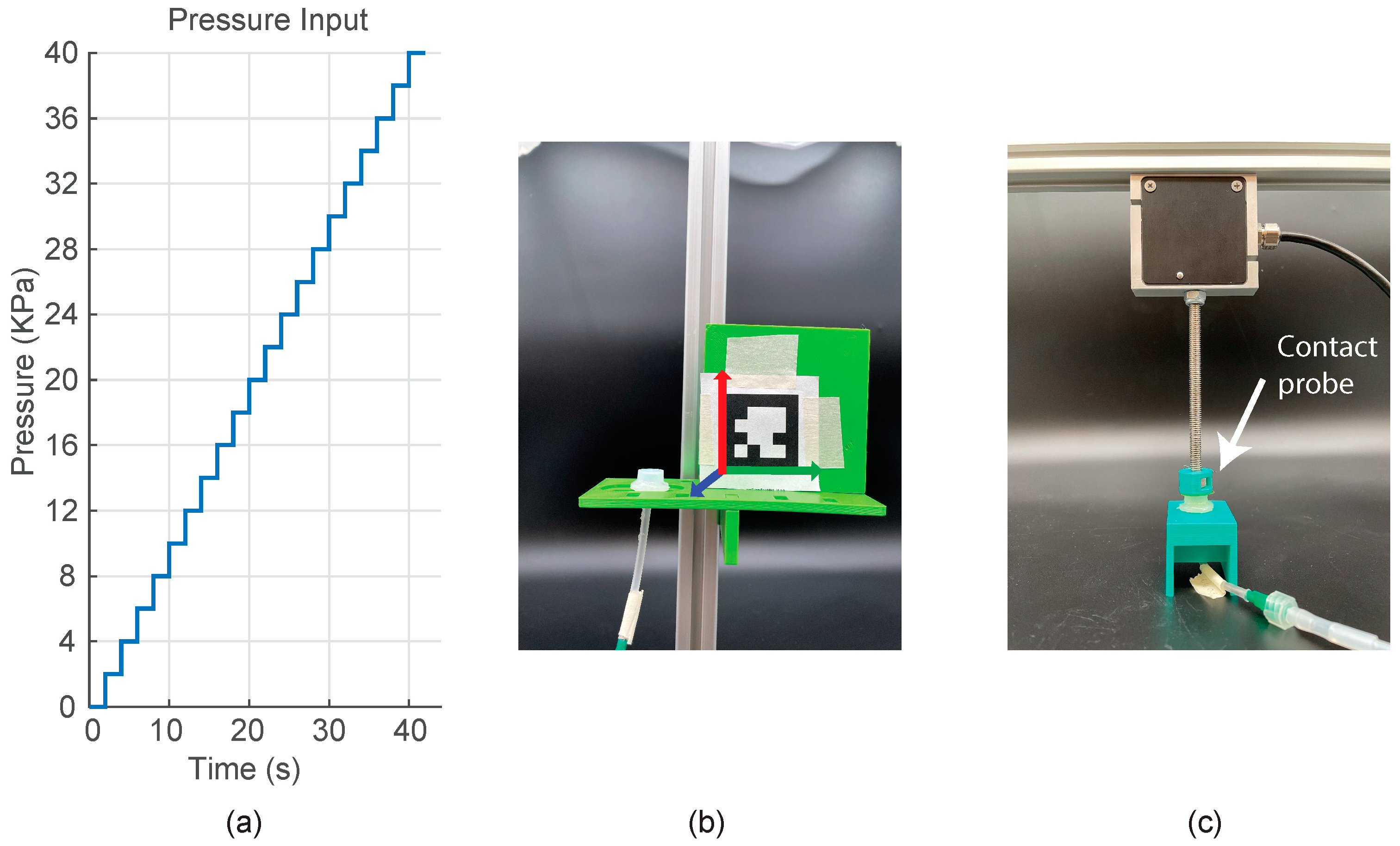
In this test, we investigated the top layer’s free deflection behavior of the PUC under varying inflation pressures for the three designs. The inflation pressures were increased from 0 KPa to 40 KPa in 2 KPa increments, with each increment maintained for 2 seconds.
Figure 5a represents the input signal used during the measurement. We utilized the hardware setup described in
Section 3.1. To capture the free deflection behavior, PUC samples were positioned within a desktop photo studio next to an April tag (
Figure 5b), which marked the coronal plane of the PUC. An Exilim Ex-F1 camera was used to record the free deflection behavior at a frame rate of 600 frames per second. Prior to the experiment, we measured the intrinsic characteristics of the Exilim Ex-F1 camera using the OpenCV toolkit [
33].
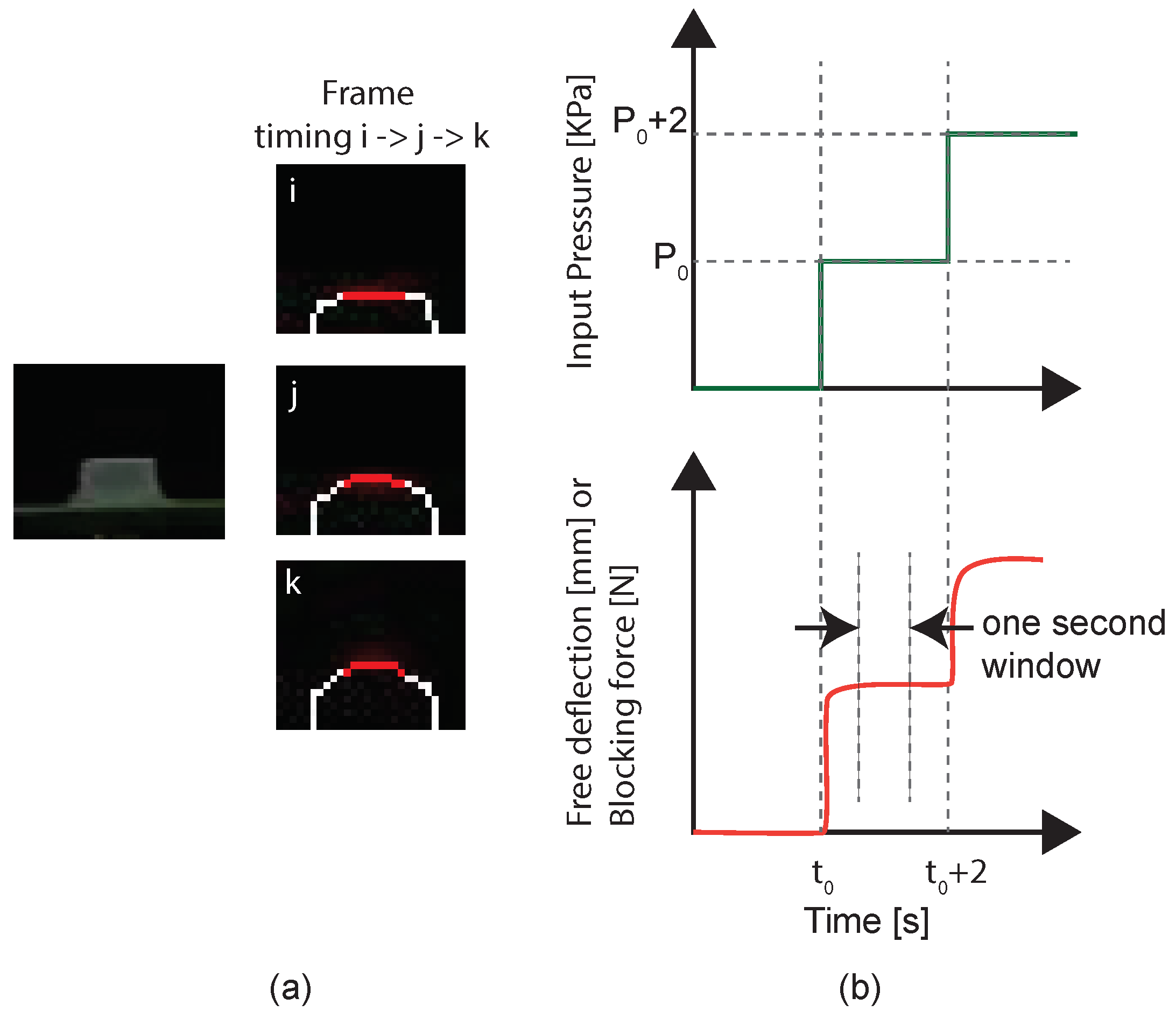
The recorded data from the Exilim Ex-F1 camera were analyzed frame-by-frame to measure free deflection. For each frame, the edge information of the PUC was extracted, as illustrated in
Figure 6a. Specifically, the middle 9 pixels corresponding to the top layer of the PUC were identified and highlighted in red, as shown in
Figure 6a. In this paper, the mean vertical position of these red pixels was used to determine the top layer’s position. The vertical position information in pixels was converted into millimeters using the intrinsic characteristics of the camera and the April tag.
To calculate the mean free deflection for a given pressure, we excluded the initial and final half a second of data points (
Figure 6b). This exclusion ensured that we considered only data points representing the fully deformed state of the PUC while avoiding capturing any dynamic transition responses. The mean free deflection of a PUC at the specific pressure was then calculated using the remaining one-second long data.
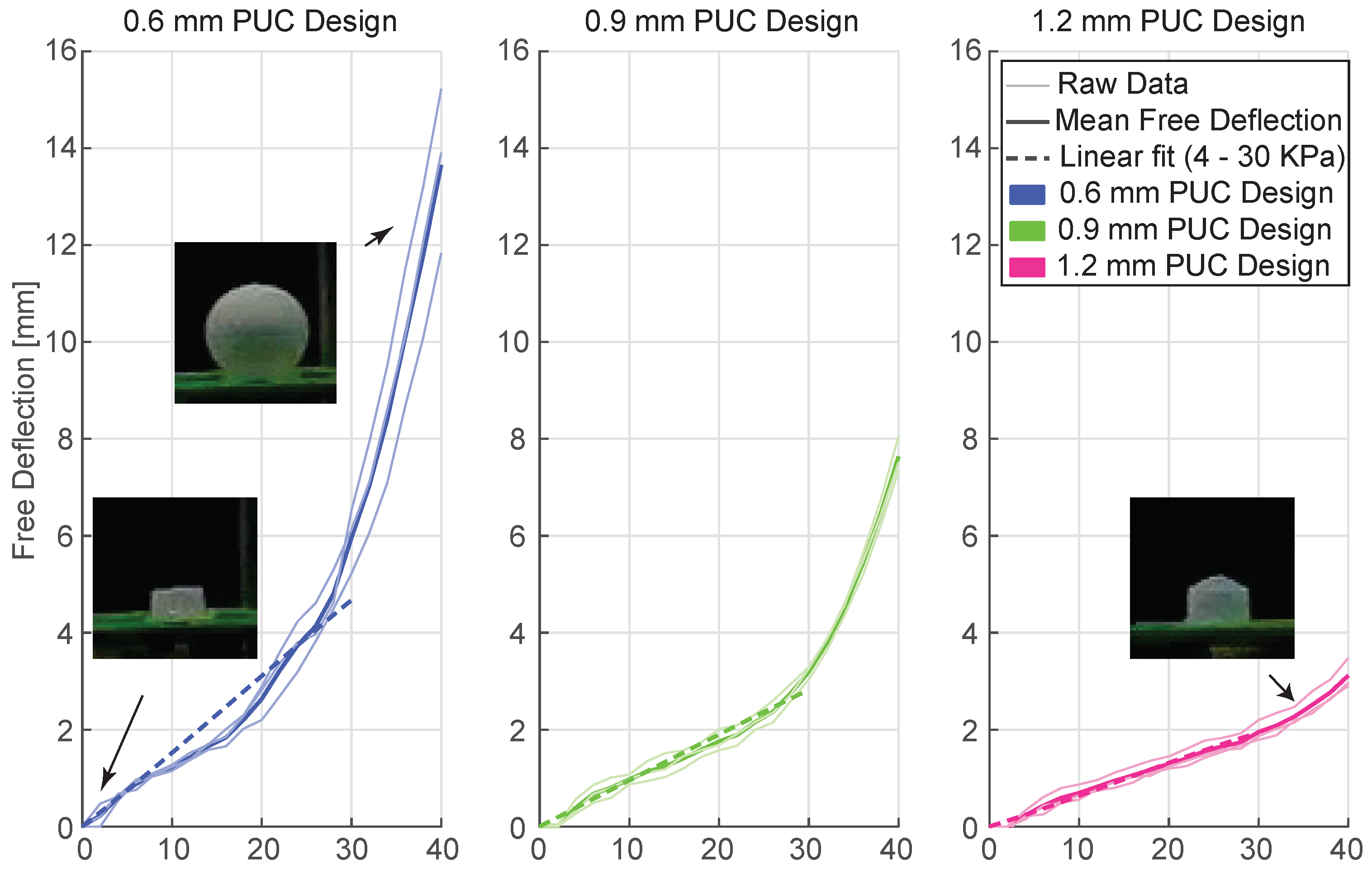
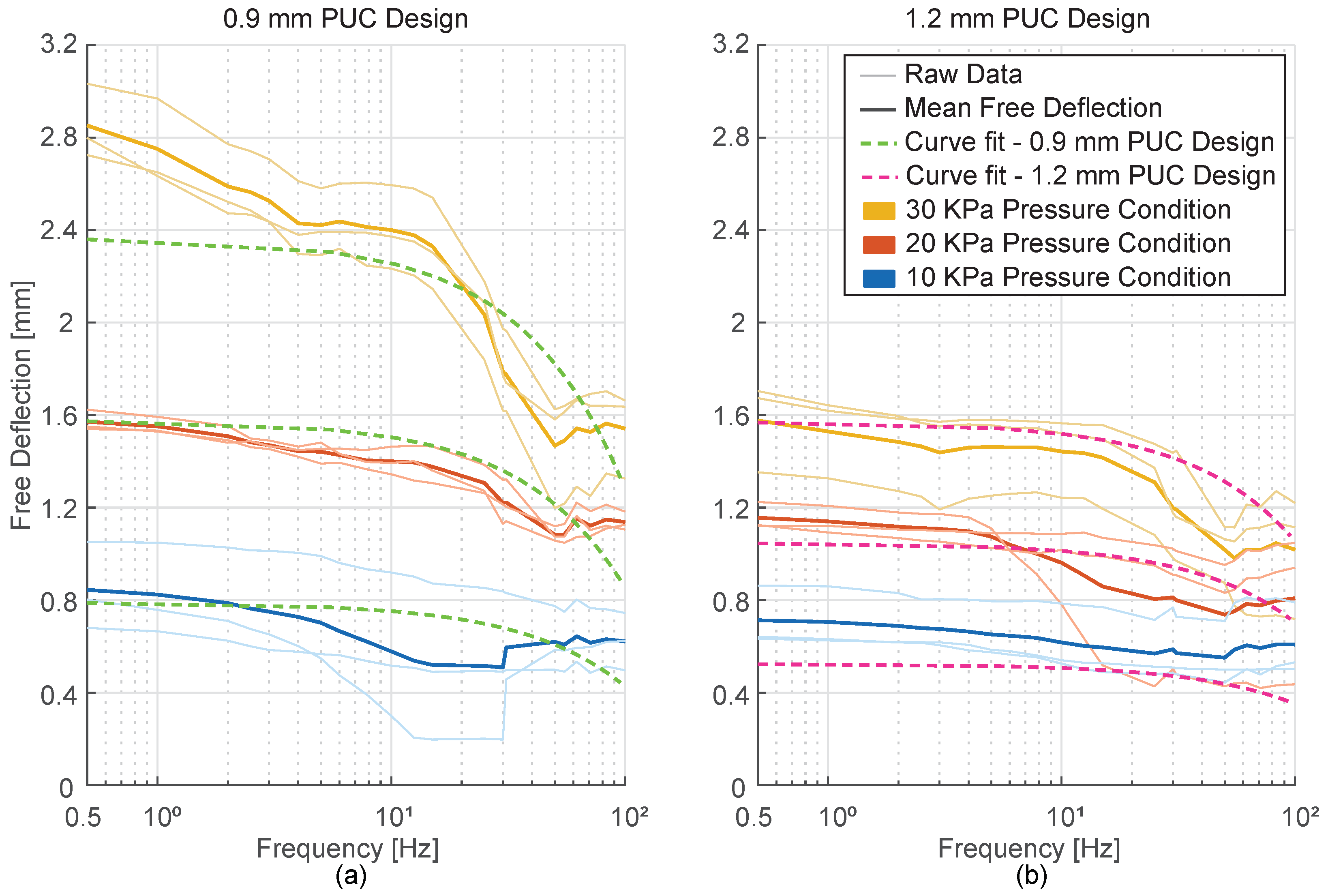
3.2.1. Results
Figure 7 presents the free deflection behavior of PUCs under static pressure conditions. In this experiment, three newly fabricated PUC samples per design were used to measure the free deflection. The measurements revealed that PUCs with top layer thicknesses of 0.6 mm, 0.9 mm, and 1.2 mm exhibited mean free deflections of 13.66 ± 1.71 mm, 7.63 ± 0.37 mm, and 3.11 ± 0.31 mm, respectively, under a maximum pressure of 40 KPa. To examine the linear relationship between free deflection and pressure, the data were fitted to Equation 1.
The term "Pressure" represents the inflation pressure and the term "Free Deflection" represents the resulting motion of the top layer. The term ’’ is the coefficient in the linear relation between free deflection and pressure.
Two curve fits were performed to identify the pressure range that describes the relation between inflation pressure and free deflection using Equation 1, with least root mean square error. The fits consisted of one that covered free deflection measurements for pressures between 4 and 40 KPa (not shown in
Figure 7) and another that covered measurements for pressures between 4 and 30 KPa (shown in
Figure 7). The results, including the slope ’
’ and root mean square error from all the fits, are presented in
Table 2.
To note, we excluded free deflection data at 0 KPa and 2 KPa due to limitations in the hardware setup’s ability to deliver consistent 2 KPa pressure.
3.2.2. Discussion
Within the scope of the current paper and based on the free deflection behaviour presented in
Figure 7, we decided to operate within the linear range of PUC actuators to avoid undesired plastic deformation. These cautionary conditions were not met by the 0.6 mm PUCs within the early stages of inflation and by the 0.9 mm PUCs for pressures close to 30 KPa. As a result, for all further experiments, the 0.6 mm PUCs were excluded from consideration, and the maximum inflation pressure was capped at 30 KPa. Due to the limitations of the proportional pressure control valve (VEAB-L-26-D13-Q4-V1-1R1, Festo, Germany) in generating consistent 2 KPa pressure, the free deflection data for the pressure 2 KPa is also excluded and not considered for the linear curve fit.
The coefficient ’’ dimensionally represents the ratio of mm to KPa, indicating the deformation characteristics of the PUC’s top layer. Essentially, the coefficient serves as a measure of the PUC’s top layer compliance, which inversely relates to its stiffness. The stiffness of the top layer is influenced by various factors, including span, thickness, and material. Given that the top layer thickness is the sole variable between PUC designs, it is expected to be the primary factor affecting the magnitude of the coefficient ’.’ With increase in thickness, the stiffness is expected to increase. The results of the linear curve fitting, based on free deflection measurements, estimate the value of the coefficient as 0.094 mm/KPa for the 0.9 mm PUC design and 0.065 mm/KPa for the 1.2 mm PUC design. These findings affirm our expectations, illustrating that PUCs with greater top layer thickness are less compliant (stiffer) compared to PUCs with thinner top layer thickness.
3.3. Static Pressure Condition - Blocking Force Measurement
The aim of the blocking force test was to measure the maximum force exerted by a PUC for a given inflation pressure. The blocking force behaviour of the PUC was characterised using the setup described in the
Figure 5c. The test setup involved placing a PUC on a rigid mounting platform, while a force transducer (KAP-E 20 N, Angewandte System Technik, Germany) with a rigid contact probe was positioned directly above the PUC’s top layer. Before inflating the PUC samples, the force transducer zeroed.
The PUCs were inflated in steps of 2 KPa from 0 to 30 KPa (
Figure 5a). The pressure inside the PUCs was maintained for two seconds, and force data from the transducer were recorded at a sampling rate of 20 Hz. Within this time frame, we excluded the initial and final half a second of force data, calculating the mean of the remaining measured force data to determine the effective blocking force for the specific constant inflation pressure.
Figure 6b shows the input-output response and data points used for mean blocking force calculation.
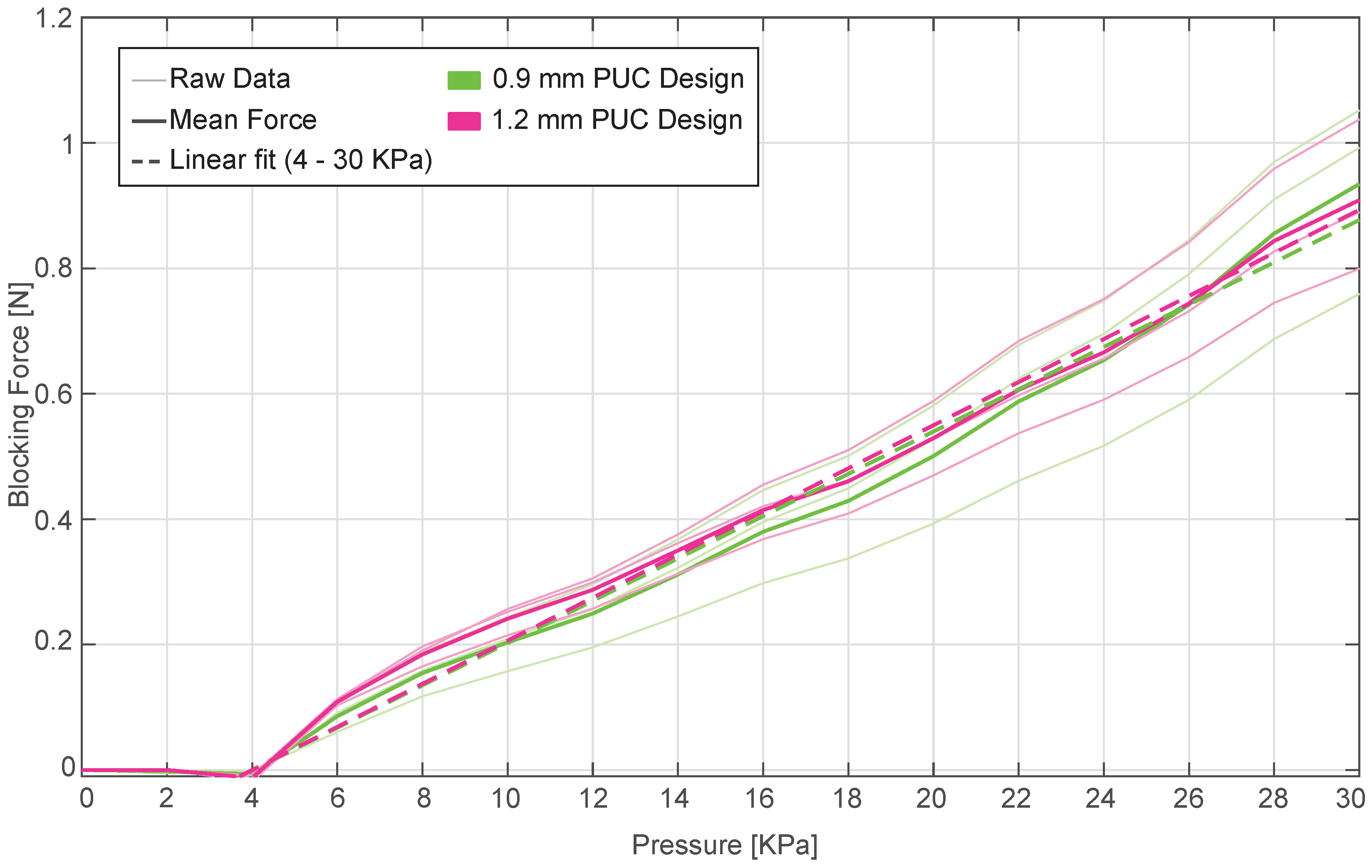
3.3.1. Results
Figure 8 presents the blocking force performance of 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs under static pressure condition. In this experiment, three newly fabricated PUC samples per design were used for the blocking force measurement. The measurements revealed that PUCs with thicknesses of 0.9 mm, and 1.2 mm exhibited mean blocking force of 0.93 ± 0.15 N and 0.90 ± 0.12 N, respectively, under a maximum pressure of 30 KPa.
To examine the linear relationship between force and pressure, the blocking force data were fitted to Equation 2. The term ’Blocking Force’ and ’Pressure’ represent the measured mean blocking force for an inflation pressure and inflation pressure, respectively. The term ’
’ represents the slope of the linear relationship. The fits are performed per PUC design. The results, including the slope ’
’ and root mean square error from all the fits, are presented in
Table 3.
3.3.2. Discussion
The blocking force measurement showed a similar blocking force-pressure relation for both 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs, implying that there is no noticeable effect of the top layer thickness. This is also reinforced in the linear curve fit results, where the slope term resulted in similar magnitudes for both the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs.
Similar to the observation in the
Section 3.2.2, the measured blocking force data for 2 KPa pressure are excluded for curve fitting due to the limitations of the proportional pressure control valve. It is also observed, the considered force transducer (KAP-E 20 N, Angewandte System Technik, Germany) is not sensitive to measure the blocking force at 4 KPa pressure. To avoid underestimation of the pressure-blocking force relation, the pressure term in Equation 2 is off set by 4 KPa.
Dimensionally, the term represents the effective contact area of the PUC with the force sensor. Considering a PUC with an 8 mm diameter, this effective contact area is expected to correspond to the top layer’s surface area, which is approximately 50.27 . However, the results from the linear curve fit reveal that the magnitude of for the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUCs is approximately 33.7 and 34.4 , respectively.
This discrepancy can be attributed to two contributing factors. First, the non-uniform distribution of force applied by the PUC onto the force transducer. In the case of PUCs, the force magnitude increases from zero at the edge, where there is no force applied in the normal direction, to its maximum at the center. This gradient in force significantly impacts the effective contact area. Second, PUCs are fabricated using Dragon SkinTM 10 Medium, a viscoelastic material, which introduces an element of energy loss.
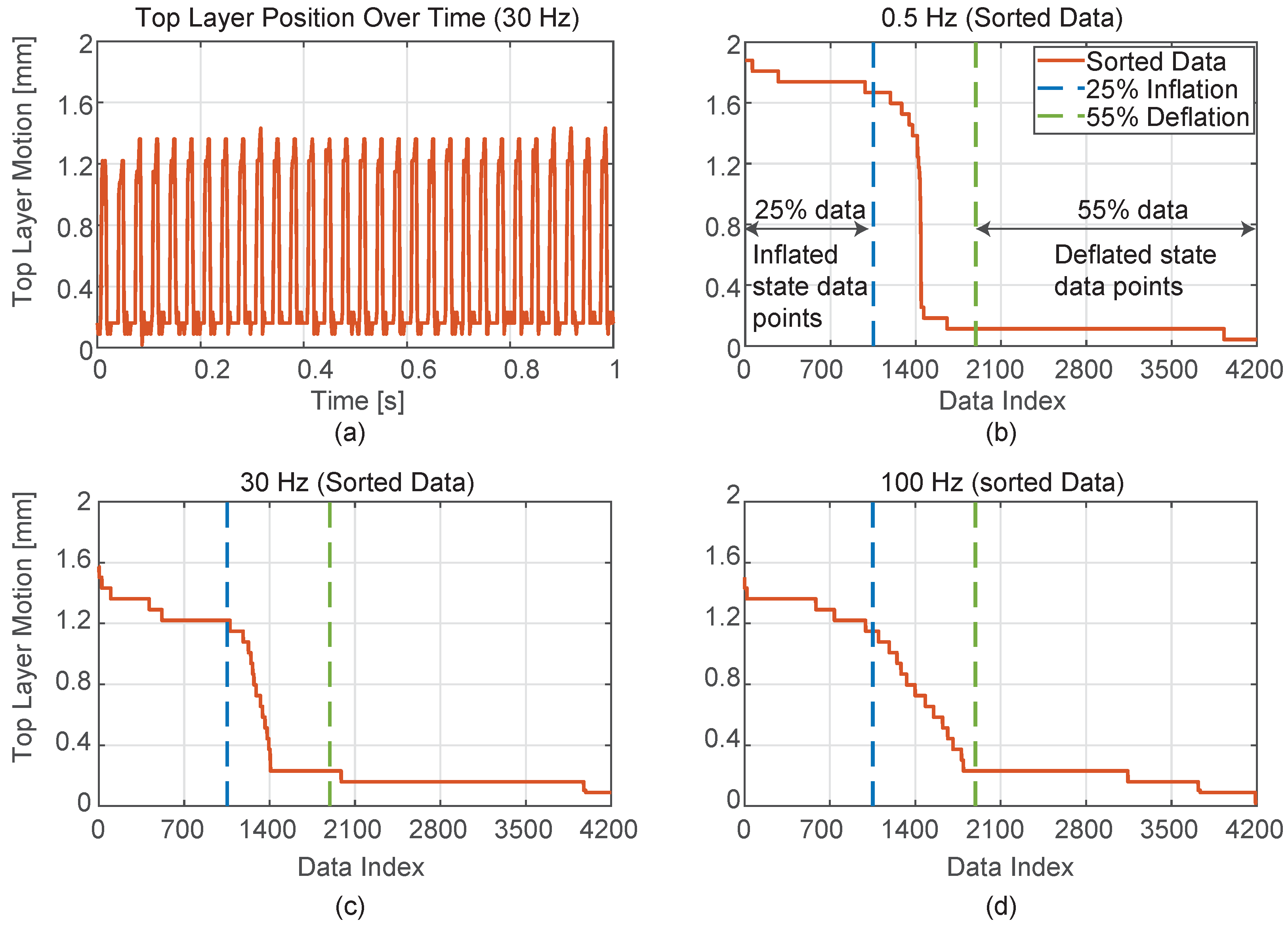
3.4. Frequency Condition - Free Deflection Measurement
The frequency condition aimed to examine the PUC’s free deflection behavior under various inflation and deflation rates. PUC samples were exposed to a range of frequencies (inflation-deflation rates) spanning from 0.5 Hz to 100 Hz, with variations in pressure. Specifically, the frequency sweep covered inflation-deflation cycles at 10 KPa, followed by 20 KPa, and then 30 KPa pressures. Each frequency was evaluated for its free deflection behavior during a 7-second measurement period, followed by a 3-second resting period. For this condition, three newly fabricated PUCs per design were used for the free deflection measurements.
The same hardware setup as described in
Section 3.2 was employed for the frequency test. However, additional steps were implemented to extract the free deflection magnitude during the frequency condition. Initially, the mean position of the top layer for a given frame was determined (
Figure 9a), following the steps described in
Section 3.2. The extracted position data per frame were then sorted in descending order, as shown in
Figure 9b-d.
The initial 25% of the sorted positions were regarded as representing the inflated state of the PUC, while the final 55% of the sorted positions were treated as the deflated state. These specific percentages were chosen to account for the 30% duty cycle. To accommodate data points capturing the inflation-deflation transition states, percentages of 25% and 55% were used for inflated and deflated states, respectively. The free deflection for each frequency and pressure was determined by taking difference between the means of the data points corresponding to the inflated and deflated states.
3.4.1. Results
Figure 10 presents the mean free deflection of 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs across inflation-deflation frequencies ranging from 0.5 Hz to 100 Hz at pressures of 10 KPa, 20 KPa, and 30 KPa. For this condition, three newly fabricated PUCs per design were tested for their free deflection behavior.
All tested PUC samples exhibited their maximum mean free deflection at 30 KPa and 0.5 Hz, with 0.9 mm PUC measuring 2.85 ± 0.16mm and 1.2 mm PUC measuring 1.57 ± 0.19mm. The minimum mean free deflection for all PUCs occurred at 10 KPa and 100 Hz, with the 0.9 mm PUC measuring 0.62 ± 0.12mm and the 1.2 mm PUC measuring 0.6 ± 0.15mm.
At a given pressure, free deflection magnitude decreased with increasing frequency, with a more significant drop as pressure increased. For 0.9 mm PUCs, at 10 KPa pressure, mean free deflection decreased by , while at 30 KPa pressure, it dropped by . In the case of 1.2 mm PUCs, at 10 KPa and 30 KPa pressures, mean free deflection decreased by and , respectively.
Similar to the static pressure condition discussed in
Section 3.2, free deflection magnitude is influenced by applied pressure, with the extent of influence varied with frequency. For the 0.9 mm PUC design, free deflection increased by
at 0.5 Hz and
at 100 Hz when pressure increased from 10 KPa to 30 KPa. In the case of the 1.2 mm PUC design, free deflection increased by
at 0.5 Hz and
at 100 Hz for the same increase in the pressure. We further analyzed the measured free deflection data by fitting it to Equation 3.
The terms "Pressure" and "Frequency" represent the pressure and the rate of inflation and deflation applied to a PUC, while the term "Free Deflection" represents the measured motion of the top layer of the PUC. The terms ’
’ and ’
’ are fitted coefficients defined in the Equation 3. Separate fits were performed for the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs, and the results are reported in
Table 4.
3.4.2. Discussion
Under frequency condition, the free deflection is influenced by both pressure and frequency. The observed behaviour suggests an inverse relation between free deflection and frequency. The reduction in free deflection from 0.5 Hz to 100 Hz becomes more pronounced with an increase in pressure. This observation may be attributed to challenges related to fluid flow inherent in pneumatically driven actuators. The extent of this fluid flow challenge is expected to increase as we transition from low-pressure and low-frequency conditions to high-pressure and high-frequency conditions. In such cases, the PUCs may not reach the intended pressure, potentially causing reduced free deflection performance. For a clear understanding of the behavior of PUCs during frequency conditions, an investigation that includes real-time sensing of pressure inside the PUCs is considered for future work.
The second term, in Equation 3, accounts for fluid flow limitations, which can be viewed as a penalty term. This penalty is affected by both frequency and pressure, with higher frequency and high pressure imposing a greater penalty on the free deflection. The estimated magnitudes of for the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs are in the order of and .
Accounting for the similar internal volume of the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs and the identical operating conditions, curve fitting to Equation 3 should result in coefficient term with identical magnitudes. However, this is not observed. The estimated magnitudes of differ between the designs and fall within distinct confidence bounds. This suggests the influence of an unaccounted parameter on . Since both PUC designs only differ by the compliance of their top layer, it is recommended to repeat the fitting with the introduction of a compliance term to the penalty term.
Root mean square errors (RMSE) of the curve fits for the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs are approximately 0.22 mm and 0.20 mm, respectively. Notably, in the case of the 0.9 mm PUC design at 30 KPa, a significant deviation between the measured free deflection and curve fit contributes to the RMSE. This deviation can be attributed to the 0.9 mm PUC design’s operation at the threshold of nonlinear deformation. This characteristic is also observable in the free deflection behavior under static pressure conditions (
Figure 7). Given that the
term in Equation 3 accounts solely for linear free deflection behavior, the deviation between the curve fit expectation and the measured free deflection can be justified.
Two instances of PUC behavior are also noteworthy contributors to the RMSE: one in a 0.9 mm PUC at a 10 KPa pressure (
Figure 10a) and the other in a 1.2 mm PUC sample at a 20 KPa pressure (
Figure 10b). In both cases, the PUCs faced challenges in exhausting and taking in air input, possibly due to airflow obstructions caused by dust particles or tubing kinks. While the exact cause remains uncertain, we are considering a thorough inspection of the test setup and the potential implementation of rapid exhaust valves in future studies to prevent similar issues.
4. General Discussion
The primary focus of this research paper is to report on the manufacturing and behavior of Pneumatic Unit Cell (PUC) actuators. The study demonstrates that the closed mold fabrication method consistently produces PUC actuators with uniform top-layer thickness, with an overshoot of approximately 2% to 3% compared to the target thickness.
The characterization of different PUC designs with varying top-layer thicknesses reveals their performance under both static pressure and frequency conditions. Under static pressure conditions, PUC designs with top-layer thicknesses of 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm exhibit a linear relationship between input pressure and free deflection. Notably, the 0.9 mm PUC design shows a greater range of free deflection compared to the 1.2 mm design. Blocking force tests under similar static pressure conditions (up to 30 KPa) demonstrate identical force performance for both the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs.
In the frequency condition characterization, the study shows that PUCs exhibit free deflection at inflation-deflation frequencies of up to 100 Hz at 30 KPa pressure. Specifically, the 0.9 mm PUCs demonstrate a wider range of free deflection compared to the 1.2 mm PUCs under identical input conditions.
The measured free deflection behavior of the PUCs under static pressure condition and frequency condition was fitted to Equation 1 and Equation 3, respectively. Both equations were selected to relate the input conditions to the free deflection. As discussed in
Section 3.2.2, the coefficient
in Equation 1 is influenced by the compliance of the PUC’s top layer. Similarly, in Equation 3, the coefficient
is expected to exhibit similar characteristics to
from Equation 1. Despite the similarity of the coefficients
and
, the curve fits reported in the
Table 2 and
Table 4 show estimates of the coefficients with confidence bounds (interval) do not overlap.
The difference in the estimation of the coefficients can be attributed to the nature of the data used during curve fitting. For coefficient , the free deflection magnitude is measured by maintaining a constant pressure for a duration of two seconds. In contrast, coefficient is determined under dynamic conditions, with a maximum duration of 0.6 seconds for inflation at 0.5 Hz and a 30% duty cycle.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, we test the physical performance of Pneumatic Unit Cells (PUCs) as potential soft actuators for applications in the field of haptics, primarily due to their capacity to generate static pressure and vibrotactile feedback. The design we introduce is selected for its simplicity in design.
The paper presents a comprehensive account of the fabrication methods for PUCs. A particular focus is placed on investigating the top layer thickness, revealing that close mold fabrication effectively produces soft actuators with uniform thickness.
Within the paper’s scope, PUCs with top layer thicknesses of 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm were tested for free deflection under both static pressure and frequency conditions, as well as blocking force under static pressure condition. The experimental outcomes highlighted the PUC’s exhibit a linear relationship between input pressure and output free deflection and blocking force under static pressure conditions. The results also demonstrate that PUCs can rapidly inflate and deflate at 30 KPa pressure up to 100 Hz, making them desirable as haptic actuators capable of generating multiple forms of feedback.
This research lays a foundational groundwork for the integration of PUCs into haptic devices, with initial investigations already showing encouraging results [
31]. In the future, the exploration will expand to encompass PUCs of diverse forms and sizes, enabling the examination of their distinct characteristics and their potential to evoke varying degrees and forms of human perception.
In conclusion, this study establishes Pneumatic Unit Cells as promising soft actuators for haptic applications, showcasing their fabrication flexibility and capacity to generate both static pressure and vibrotactile feedback.
References
- Escobar-Castillejos, D.; Noguez, J.; Neri, L.; Magana, A.J.; Benes, B. A Review of Simulators with Haptic Devices for Medical Training. Journal of Medical Systems 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enayati, N.; De Momi, E.; Ferrigno, G. Haptics in Robot-Assisted Surgery: Challenges and Benefits. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering 2016, 9, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederman, S.J.; Klatzky, R.L. Haptic perception: A tutorial. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics 2009, 71, 1439–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, S.; Nagano, H.; Yamada, Y. Psychophysical Dimensions of Tactile Perception of Textures. IEEE Transactions on Haptics 2013, 6, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Ohnishi, K.; Xu, W. Multimodal Haptic Display for Virtual Reality: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2020, 67, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prattichizzo, D.; Pacchierotti, C.; Rosati, G. Cutaneous Force Feedback as a Sensory Subtraction Technique in Haptics. IEEE Transactions on Haptics 2012, 5, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massimino, M.; Sheridan, T. Sensory Substitution for Force Feedback in Teleoperation. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 1992, 25, 109–114, 5th IFAC Symposium on Analysis, Design and Evaluation of Man-Machine Systems (MMS’92), The Hague, The Netherlands, 9-11 June 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacchierotti, C.; Prattichizzo, D.; Kuchenbecker, K.J. Cutaneous Feedback of Fingertip Deformation and Vibration for Palpation in Robotic Surgery. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2016, 63, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, S.; Shepherd, R. Elastomeric Haptic Devices for Virtual and Augmented Reality. Advanced Functional Materials 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.; Hinchet, R.; Shea, H. Multimode Hydraulically Amplified Electrostatic Actuators for Wearable Haptics. Advanced Materials 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.; Shea, H. Hydraulically Amplified Electrostatic Taxels (HAXELs) for Full Body Haptics. Advanced Materials & Technologies 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, G.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H. Fully 3D-Printed, Stretchable, and Conformable Haptic Interfaces. Advanced Functional Materials 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.H.; Mun, H.; Kyung, K.U. A Wearable Soft Tactile Actuator With High Output Force for Fingertip Interaction. IEEE Access 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Kim, H.; Talhan, A.; Jeon, S. A Pneumatically-Actuated Mouse for Delivering Multimodal Haptic Feedback. Applied Sciences 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaroto, J.J.; Suarez, E.; Krebs, H.; Marasco, P.; Vela, E. A Soft Pneumatic Actuator as a Haptic Wearable Device for Upper Limb Amputees: Toward a Soft Robotic Liner. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonar, H.; Gerratt, A.P.; Lacour, S.; Paik, J. Closed-Loop Haptic Feedback Control Using a Self-Sensing Soft Pneumatic Actuator Skin. Soft Robotics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhan, A.; Kumar, S.; Kim, H.; Hassan, W.; Jeon, S. Multi-mode soft haptic thimble for haptic augmented reality based application of texture overlaying. Displays 2022, 74, 102272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.S.; Joolee, J.B.; Hassan, W.; Jeon, S. Soft Pneumatic Fingertip Actuator Incorporating a Dual Air Chamber to Generate Multi-Mode Simultaneous Tactile Feedback. Applied Sciences 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhan, A.; Kim, H.; Jeon, S. Tactile Ring: Multi-Mode Finger-Worn Soft Actuator for Rich Haptic Feedback. IEEE Access 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, G.; Wagner, C.; Fearing, R. A compliant tactile display for teletaction. Proceedings 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37065) 2000. [CrossRef]
- Ujitoko, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Sakurai, S.; Hirota, K. Development of Finger-Mounted High-Density Pin-Array Haptic Display. IEEE Access 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Air jet driven force feedback in virtual reality. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Ha, T.; Oakley, I.; Woo, W.; Ryu, J. Air-jet button effects in AR. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yun, K.S. Three-Axis Pneumatic Haptic Display for the Mechanical and Thermal Stimulation of a Human Finger Pad. Actuators 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frediani, G.; Carpi, F. Tactile display of softness on fingertip. Scientific Reports 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Kappers, A.M.; Fujiwara, M.; Sano, A. A Pneumatic Tactile Ring for Instantaneous Sensory Feedback in Laparoscopic Tumor Localization. IEEE Transactions on Haptics 2018, 11, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathna, C.P.; Ruhunage, I.; Chathuranga, D.S.; Lalitharatne, T.D. Haptic Feedback System for an Artificial Prosthetic Hand for Object Grasping and Slip Detection: A Preliminary Study. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), 2018, pp. 2304–2309. [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.C.; Lee, H.K.; Doh, E.; Yun, K.S.; Park, J. Tactile display with tangential and normal skin displacement for robot-assisted surgery. Advanced Robotics 2014, 28, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.H.; Franco, M.; Culjat, M.O.; Higa, A.T.; Bisley, J.W.; Dutson, E.; Grundfest, W.S. Fabrication and Characterization of a Balloon Actuator Array for Haptic Feedback in Robotic Surgery. Journal of Medical Devices 2008, 2, 041006. https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/medicaldevices/article-pdf/2/4/041006/5809375/041006_1.pdf. [CrossRef]
- King, C.; Culjat, M.; Franco, M.; Bisley, J.; Dutson, E.; Grundfest, W. Optimization of a Pneumatic Balloon Tactile Display for Robot-Assisted Surgery Based on Human Perception. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, F.E.; Bisschop, Q.P.I.; Kuling, I.A. Validation of a soft Pneumatic Unit Cell (PUC) in a VR experience: a comparison between vibrotactile and soft pneumatic haptic feedback. IEEE Transactions on Haptics 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caasenbrood, B.J.; Van Beek, F.E.; Chu, H.K.; Kuling, I.A. A Desktop-sized Platform for Real-time Control Applications of Pneumatic Soft Robots. 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Soft Robotics, RoboSoft 2022. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2022, pp. 217–223. [CrossRef]
- OpenCV: Camera Calibration — docs.opencv.org. Available online: https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/dc/dbb/tutorial_py_calibration.html (accessed on 22 August 2023).
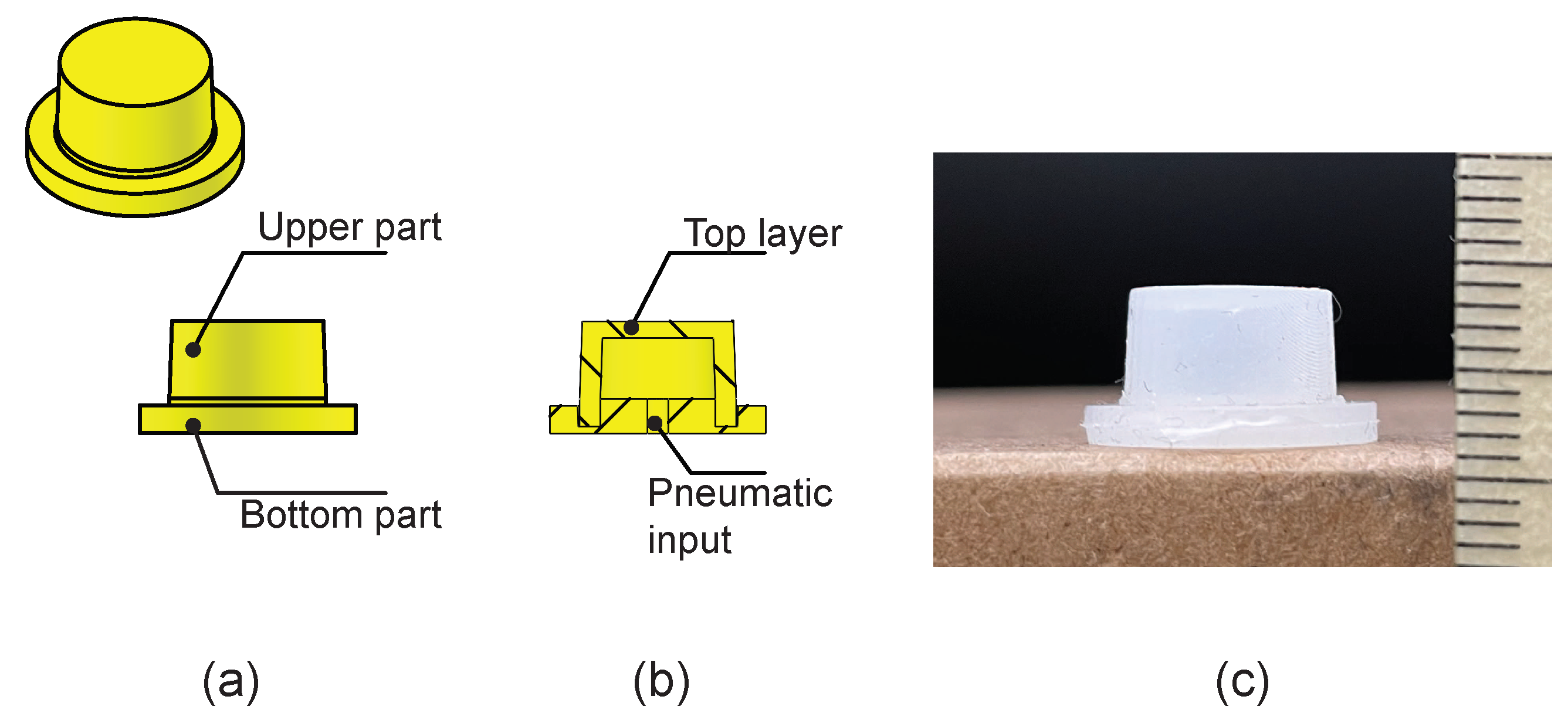
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic and nomenclature used in describing Pneumatic Unit Cell (PUC). (b) Section view of PUC along coronal plane. (c) Pneumatic Unit Cell next to a scale for size reference.
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic and nomenclature used in describing Pneumatic Unit Cell (PUC). (b) Section view of PUC along coronal plane. (c) Pneumatic Unit Cell next to a scale for size reference.
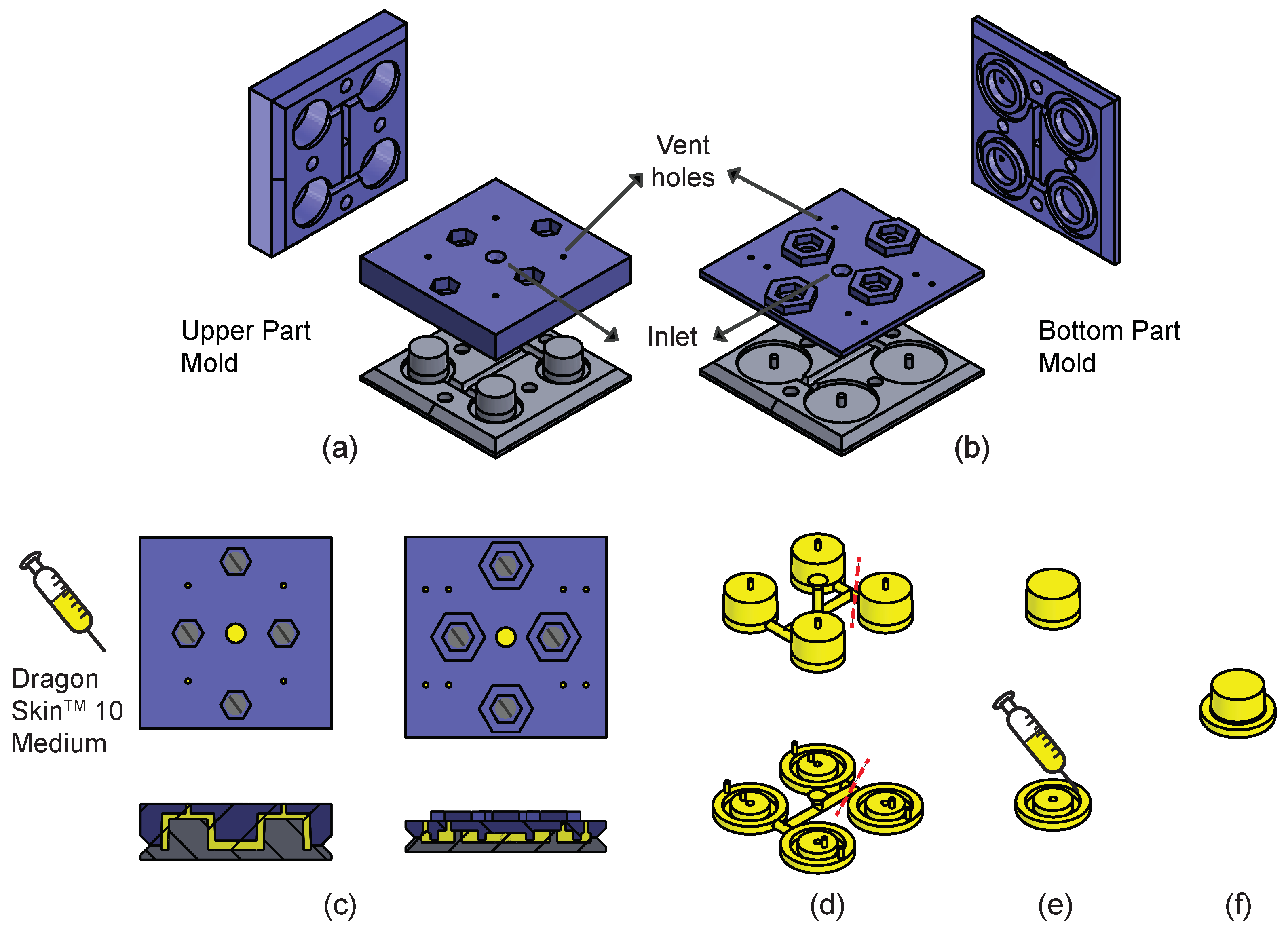
Figure 2.
Fabrication steps of Pneumatic Unit Cells (PUC): (a) Mold used for the fabrication of the upper part of the PUC. (b) Mold used for the fabrication of the bottom part of the PUC. (c) Top view and cross section view of the mold assembly. Injection of Dragon SkinTM 10 Medium into the molds through the inlets. (d) The extracted upper and bottom parts of PUCs from their respective molds. (e) Gluing of the upper and bottom parts of the PUC using Dragon SkinTM 10 Medium, (f) fully assembled PUC.
Figure 2.
Fabrication steps of Pneumatic Unit Cells (PUC): (a) Mold used for the fabrication of the upper part of the PUC. (b) Mold used for the fabrication of the bottom part of the PUC. (c) Top view and cross section view of the mold assembly. Injection of Dragon SkinTM 10 Medium into the molds through the inlets. (d) The extracted upper and bottom parts of PUCs from their respective molds. (e) Gluing of the upper and bottom parts of the PUC using Dragon SkinTM 10 Medium, (f) fully assembled PUC.
Figure 3.
The top layer thickness. (a) Illustration representing the thickness measurement locations across the cross section of the top layer (b) The plots depict mean thickness ratios with errors for different PUC designs (0.6 mm in blue, 0.9 mm in green, and 1.2 mm in pink) and measurement locations.
Figure 3.
The top layer thickness. (a) Illustration representing the thickness measurement locations across the cross section of the top layer (b) The plots depict mean thickness ratios with errors for different PUC designs (0.6 mm in blue, 0.9 mm in green, and 1.2 mm in pink) and measurement locations.
Figure 4.
Schematic of the hardware setup used to set the pressure on the Festo pressure regulator (model number: VEAB-L-26-D13-Q4-V1-1R1) and Festo high-frequency valve (model number: MHP2-MS1H-3/2G-M5) through Raspberry Pi 4 and Matlab.
Figure 4.
Schematic of the hardware setup used to set the pressure on the Festo pressure regulator (model number: VEAB-L-26-D13-Q4-V1-1R1) and Festo high-frequency valve (model number: MHP2-MS1H-3/2G-M5) through Raspberry Pi 4 and Matlab.
Figure 5.
Input pressure signal and test setups used for measuring the free deflection of the top layer and blocking force of the PUCs under inflation: (a) Input pressure signal used during the static pressure test. (b) The test setup used for measuring the free deflection. The picture illustrates the mounting platform for the PUC and an April tag marking the coronal plane of the PUCs. The setup was placed inside a desktop photo studio.(c) The test setup used for measuring the blocking force of the PUC. PUCs were sandwiched between the mounting platform and a rigid contact plate. The contact plate was fixed to the force transducer probe.
Figure 5.
Input pressure signal and test setups used for measuring the free deflection of the top layer and blocking force of the PUCs under inflation: (a) Input pressure signal used during the static pressure test. (b) The test setup used for measuring the free deflection. The picture illustrates the mounting platform for the PUC and an April tag marking the coronal plane of the PUCs. The setup was placed inside a desktop photo studio.(c) The test setup used for measuring the blocking force of the PUC. PUCs were sandwiched between the mounting platform and a rigid contact plate. The contact plate was fixed to the force transducer probe.
Figure 6.
Steps followed for extracting the free deflection of the top layer and blocking force of the PUCs under inflation: (a) Shows a frame of an image captured using the Exilim Ex-F1 camera and the extracted edge data of the PUCs at different stages of inflation. Each frame was taken from a different time stamp. Red pixels represent the midpoints of the PUC. The vertical position of the PUC’s top layer for a given frame is calculated by taking the average of the vertical position of the red pixels. (b) Illustrates the steps followed in calculating the mean free deflection/blocking force at a constant pressure. Each data point represents the measured free deflection or blocking force at a given frame. The window represents the set of data points that were used to calculate the mean free deflection or blocking force for a given inflation pressure.
Figure 6.
Steps followed for extracting the free deflection of the top layer and blocking force of the PUCs under inflation: (a) Shows a frame of an image captured using the Exilim Ex-F1 camera and the extracted edge data of the PUCs at different stages of inflation. Each frame was taken from a different time stamp. Red pixels represent the midpoints of the PUC. The vertical position of the PUC’s top layer for a given frame is calculated by taking the average of the vertical position of the red pixels. (b) Illustrates the steps followed in calculating the mean free deflection/blocking force at a constant pressure. Each data point represents the measured free deflection or blocking force at a given frame. The window represents the set of data points that were used to calculate the mean free deflection or blocking force for a given inflation pressure.
Figure 7.
Static Pressure vs. Free Deflection performance of 0.6 mm (blue), 0.9 mm (green), and 1.2 mm (pink) PUC designs. Thin lines represent the free deflection data of the individual PUC samples. Solid bold lines represent the mean free deflection for each PUC design, while dashed bold lines represent the linear curve-fitted results using the 4 to 30 KPa pressure range free deflection data.
Figure 7.
Static Pressure vs. Free Deflection performance of 0.6 mm (blue), 0.9 mm (green), and 1.2 mm (pink) PUC designs. Thin lines represent the free deflection data of the individual PUC samples. Solid bold lines represent the mean free deflection for each PUC design, while dashed bold lines represent the linear curve-fitted results using the 4 to 30 KPa pressure range free deflection data.
Figure 8.
Static pressure vs block force performance of 0.9 mm (green) and 1.2 mm (pink) PUC designs. Thin lines represent individual PUC sample data, bold solid lines show the mean blocking force, and dashed lines represent linear fits for the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs.
Figure 8.
Static pressure vs block force performance of 0.9 mm (green) and 1.2 mm (pink) PUC designs. Thin lines represent individual PUC sample data, bold solid lines show the mean blocking force, and dashed lines represent linear fits for the 0.9 mm and 1.2 mm PUC designs.
Figure 9.
Steps followed in measuring free deflection in frequency test: (a) Recording of the top layer motion of a 0.9 mm PUC design at 20 KPa pressure and 30 Hz frequency for one second within a seven-second block. (b - d) Sorted free deflection data of the 0.9 mm PUC at 20 KPa pressure for frequencies of 0.5 Hz, 30 Hz, and 100 Hz. Dashed lines indicate the threshold lines used to distinguish data points representing inflated and deflated states.
Figure 9.
Steps followed in measuring free deflection in frequency test: (a) Recording of the top layer motion of a 0.9 mm PUC design at 20 KPa pressure and 30 Hz frequency for one second within a seven-second block. (b - d) Sorted free deflection data of the 0.9 mm PUC at 20 KPa pressure for frequencies of 0.5 Hz, 30 Hz, and 100 Hz. Dashed lines indicate the threshold lines used to distinguish data points representing inflated and deflated states.
Figure 10.
Free deflection results for (a) 0.9 mm and (b) 1.2 mm PUC designs at different inflation-deflation frequencies and pressure (10 KPa in blue, 20 KPa in red, 30 KPa in yellow). Thin lines represent the free deflection data of individual PUC samples, bold solid lines show the mean free deflection data, and dashed lines represent curve fit results for 0.9 mm (green) and 1.2 mm (pink) PUC design.
Figure 10.
Free deflection results for (a) 0.9 mm and (b) 1.2 mm PUC designs at different inflation-deflation frequencies and pressure (10 KPa in blue, 20 KPa in red, 30 KPa in yellow). Thin lines represent the free deflection data of individual PUC samples, bold solid lines show the mean free deflection data, and dashed lines represent curve fit results for 0.9 mm (green) and 1.2 mm (pink) PUC design.
Table 1.
Detailed information on the experimental conditions used in the characterisation of Pneumatic Unit Cells.
Table 1.
Detailed information on the experimental conditions used in the characterisation of Pneumatic Unit Cells.
| Experiment |
Measuring |
Design |
Pressure |
Frequency |
| Static Pressure Condition |
Free Deflection |
0.6 mm |
0 to 40 KPa |
- |
| 0.9 mm |
0 to 40 KPa |
- |
| 1.2 mm |
0 to 40 KPa |
- |
| Static Pressure Condition |
Blocking Force |
0.6 mm |
- |
- |
| 0.9 mm |
0 to 30 KPa |
- |
| 1.2 mm |
0 to 30 KPa |
- |
| Frequency Condition |
Free Deflection |
0.6 mm |
- |
- |
| 0.9 mm |
10, 20 , 30 KPa |
0.5 to 100 Hz |
| 1.2 mm |
10, 20 , 30 KPa |
0.5 to 100 Hz |
Table 2.
Results of curve fitting for free deflection under static pressure conditions using Equation 1.
Table 2.
Results of curve fitting for free deflection under static pressure conditions using Equation 1.
| Design |
Pressure Range [KPa] |
Coefficient [mm/KPa] |
Confidence Bounds [mm/KPa] |
RMSE [mm] |
| 0.6 mm |
4 to 40 KPa |
0.23 |
(0.21, 0.25) |
1.96 |
| 4 to 30 KPa |
0.16 |
(0.15, 0.17) |
0.58 |
| 0.9 mm |
4 to 40 KPa |
0.13 |
(0.12, 0.14) |
0.93 |
| 4 to 30 KPa |
0.094 |
(0.09, 0.098) |
0.21 |
| 1.2 mm |
4 to 40 KPa |
0.068 |
(0.066, 0.07) |
0.19 |
| 4 to 30 KPa |
0.065 |
(0.062, 0.067) |
0.14 |
Table 3.
Results of curve fitting for blocking force under static pressure conditions using Equation 2.
Table 3.
Results of curve fitting for blocking force under static pressure conditions using Equation 2.
Top Layer
Thickness |
Pressure Range
[KPa] |
Coefficient
[] |
Confidence Bounds
[] |
RMSE
[N] |
| 0.9 mm |
4 to 30 |
33.7 |
(32.04, 35.4) |
0.08 |
| 1.2 mm |
4 to 30 |
34.4 |
(33.18, 35.54) |
0.058 |
Table 4.
Results of curve fitting for free deflection under frequency conditions using Equation 3.
Table 4.
Results of curve fitting for free deflection under frequency conditions using Equation 3.
| Design |
Pressure |
Frequency |
Coefficient |
Confidence Bound |
RMSE |
| [KPa] |
[] |
[mm/KPa] |
[mm*S/KPa] |
[mm/KPa] |
[mm*S/KPa] |
[mm] |
| 0.9 mm |
10, 20, 30 |
0.5 to 100 |
0.079 |
0.36 |
(0.077, 0.081) |
(0.3, 0.4) |
0.22 |
| 1.2 mm |
10, 20, 30 |
0.5 to 100 |
0.052 |
0.17 |
(0.05, 0.054) |
(0.1, 0.2) |
0.20 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).