Submitted:
13 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To propose an effective credit card fraud detection model that addresses the challenge of imbalanced datasets, where fraud occurrences are uncommon in comparison to genuine transactions.
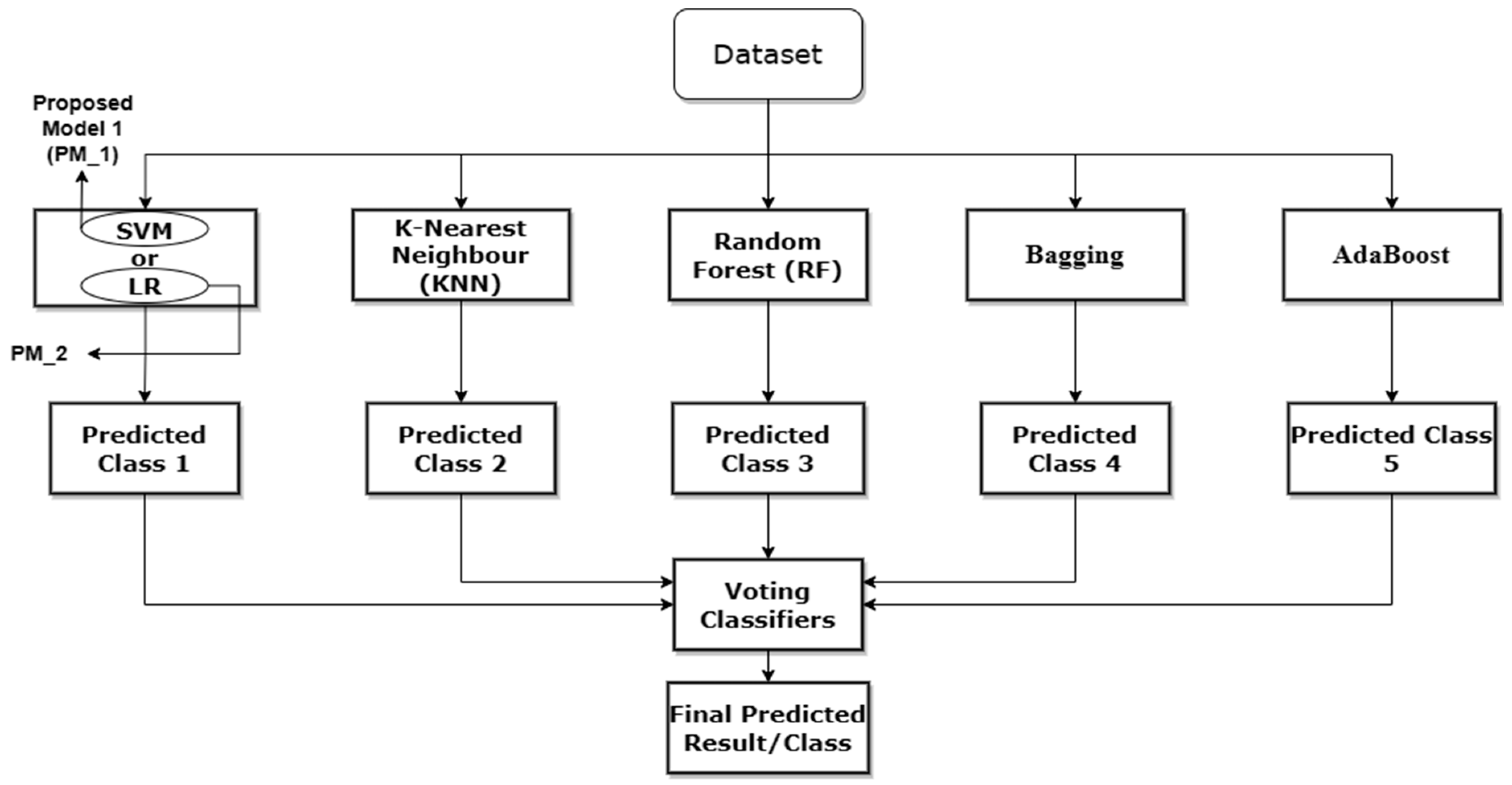
- To compare the performance of various machine learning models in identifying credit card fraud, such as Support Vector Machine (SVM), K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN), Random Forest (RF), Bagging, and Boosting.
- To benchmark the performance of the proposed model with existing credit card fraud detection models.
2. Related work
2.1. Statistical Methods
2.2. Deep Learning (DL) in Credit Card Fraud Detection
2.3. Machine Learning (ML) in Credit Card Fraud Detection
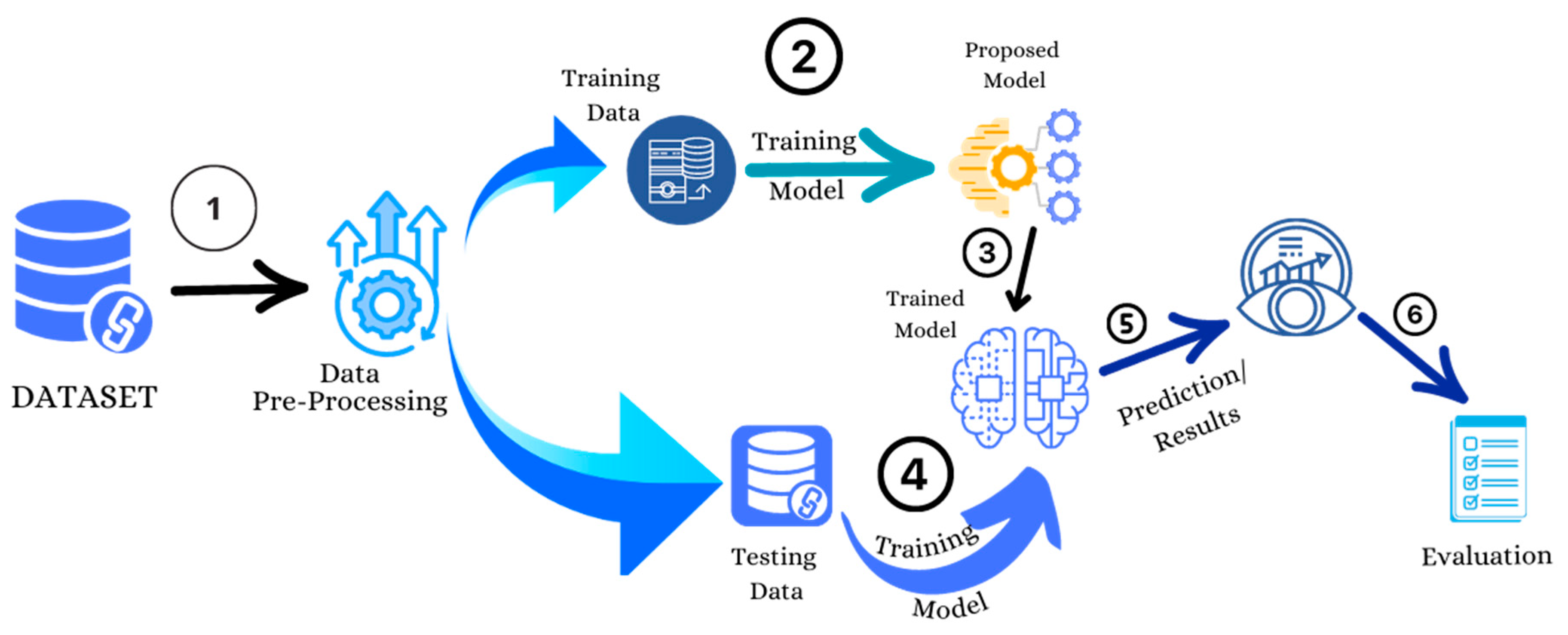
3. Methodology
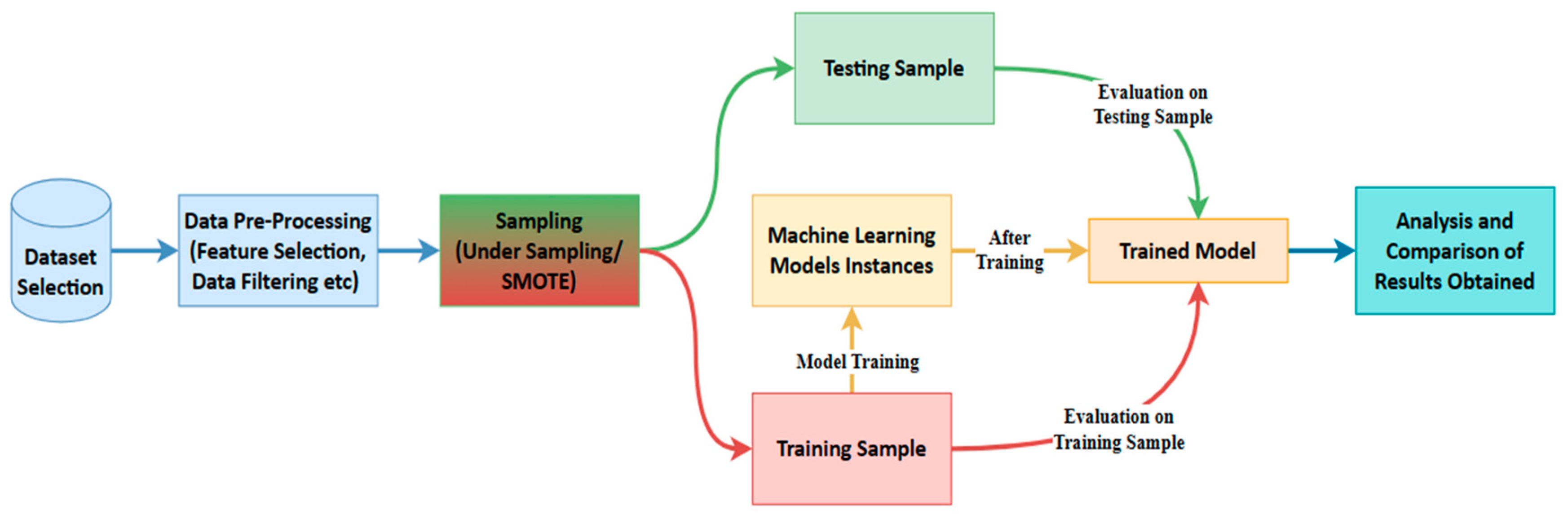
3.1. Dataset
3.2. The Proposed Model
3.3. Hardware and Platforms
3.4. Model Design
3.4.1. Data Pre-processing
- Finding and filling/removing any null values.
- Standardising the "Amount" column to make it easy for analysis.
- Removing the 'Time' Column from the dataset as it was not contributing much during training and evaluation.
- Checking and removing duplicate entries in the dataset.
3.4.2. Data Sampling
- Separate data entries based on labels (Legit/Fraud in this case)
- Apply the required sampling technique to specific data
- Concatenate all data to have all data in a single dataset
3.4.2.1. Under-Sampling
3.4.2.2. SMOTE (Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique)
3.4.3. Model Training
4. Results and Discussion
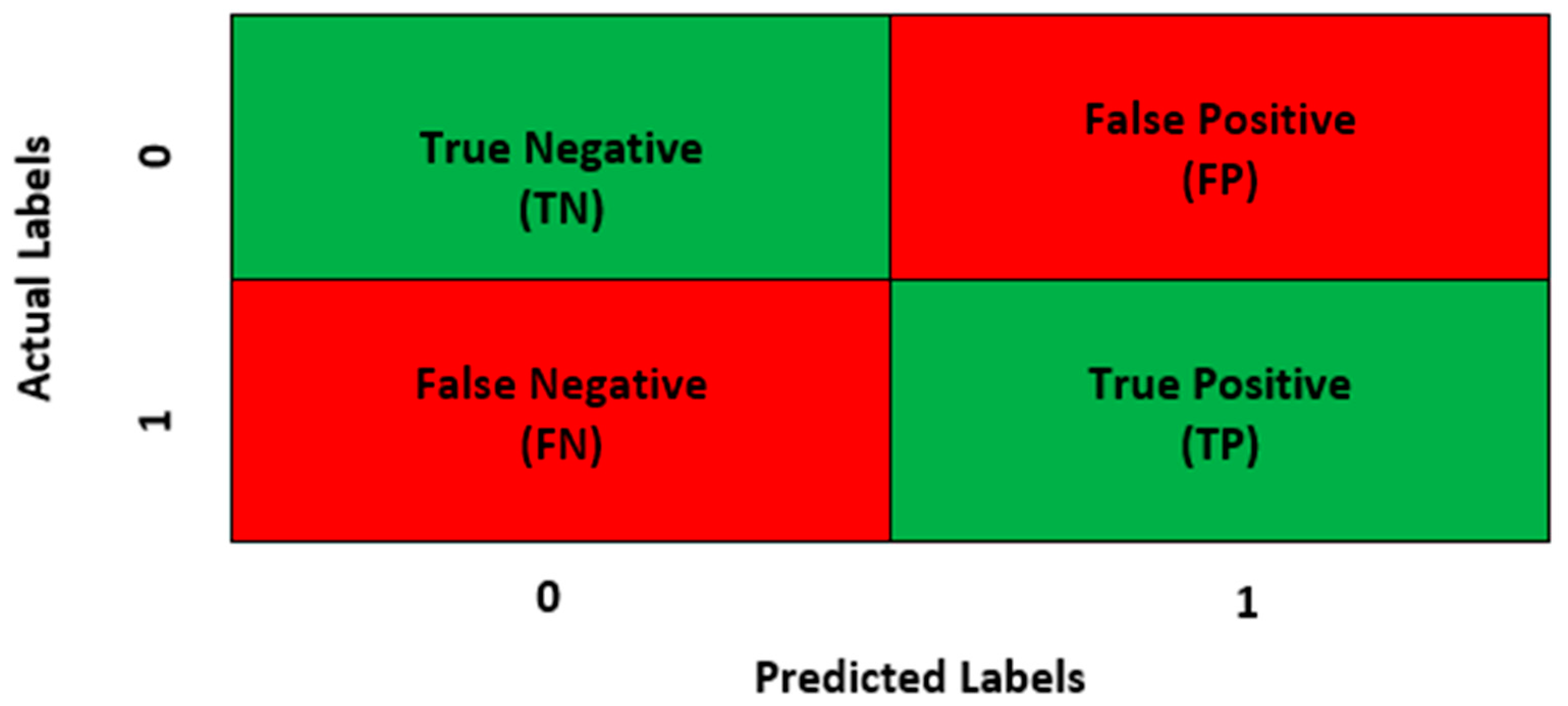
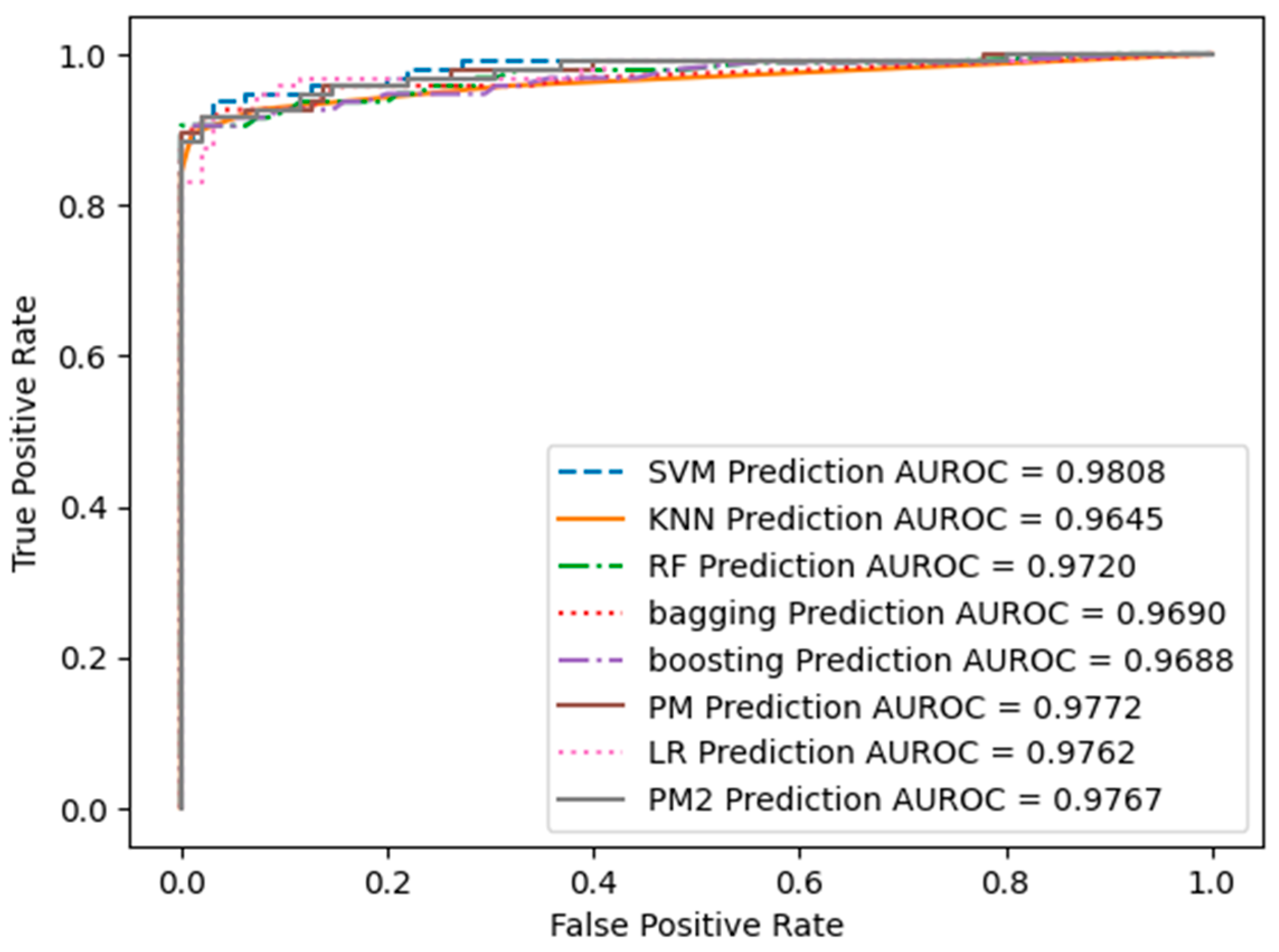
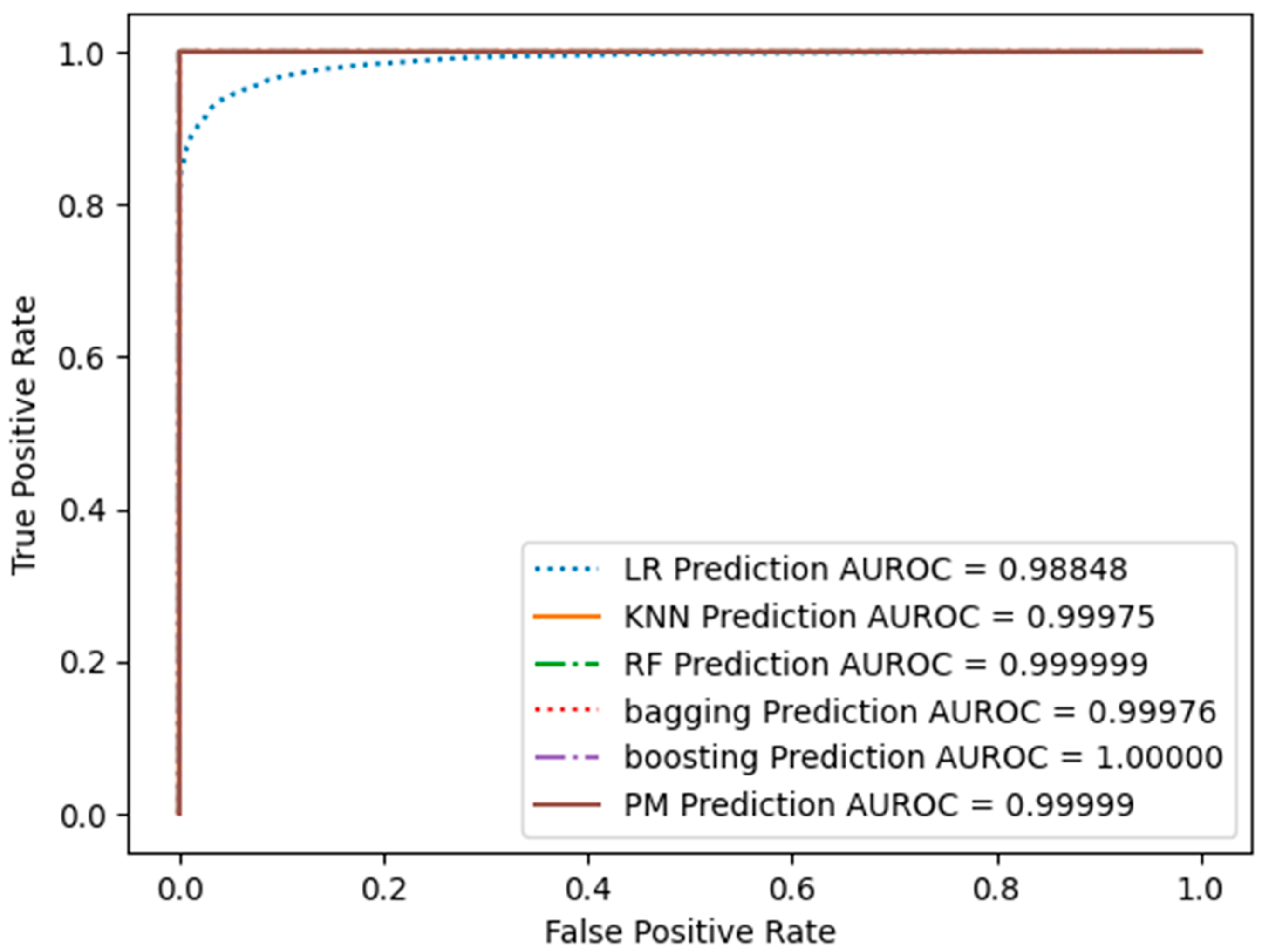
4.1. Performance Evaluation
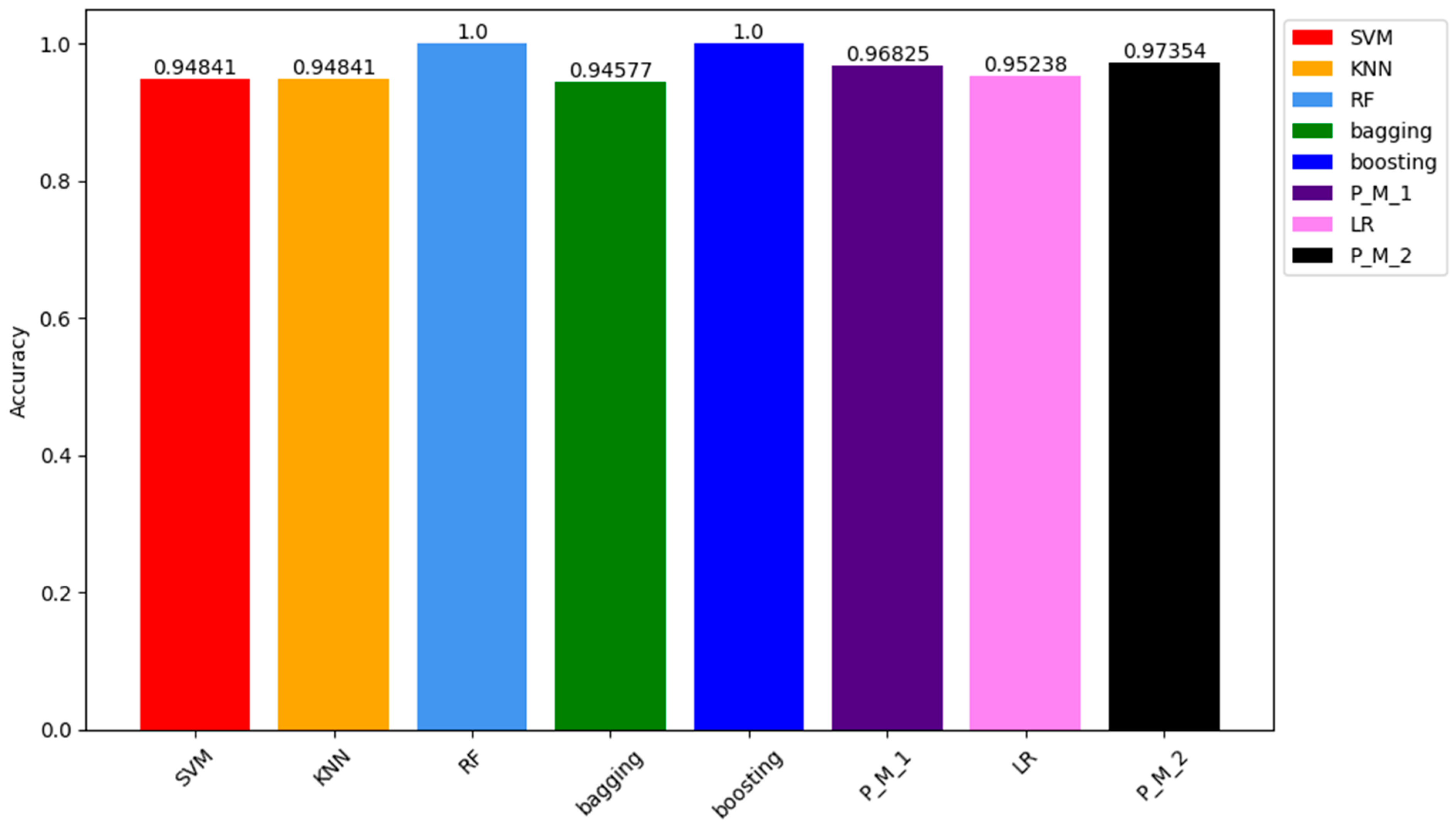
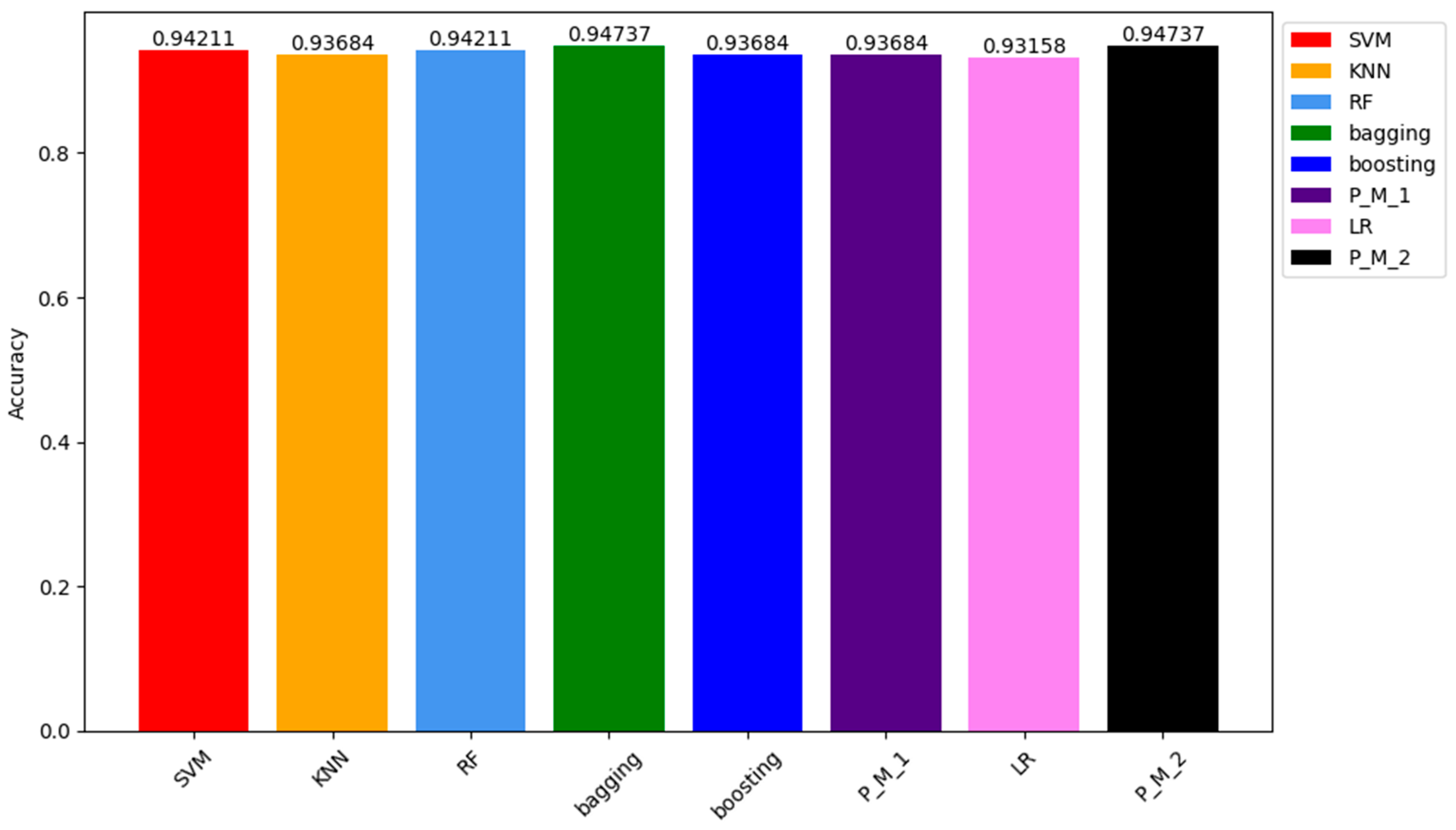
4.1.1. Under-Sampling Results
4.1.2. SMOTE Results
| Training Sample of SMOTE Dataset | ||||||
| LR | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | PM | |
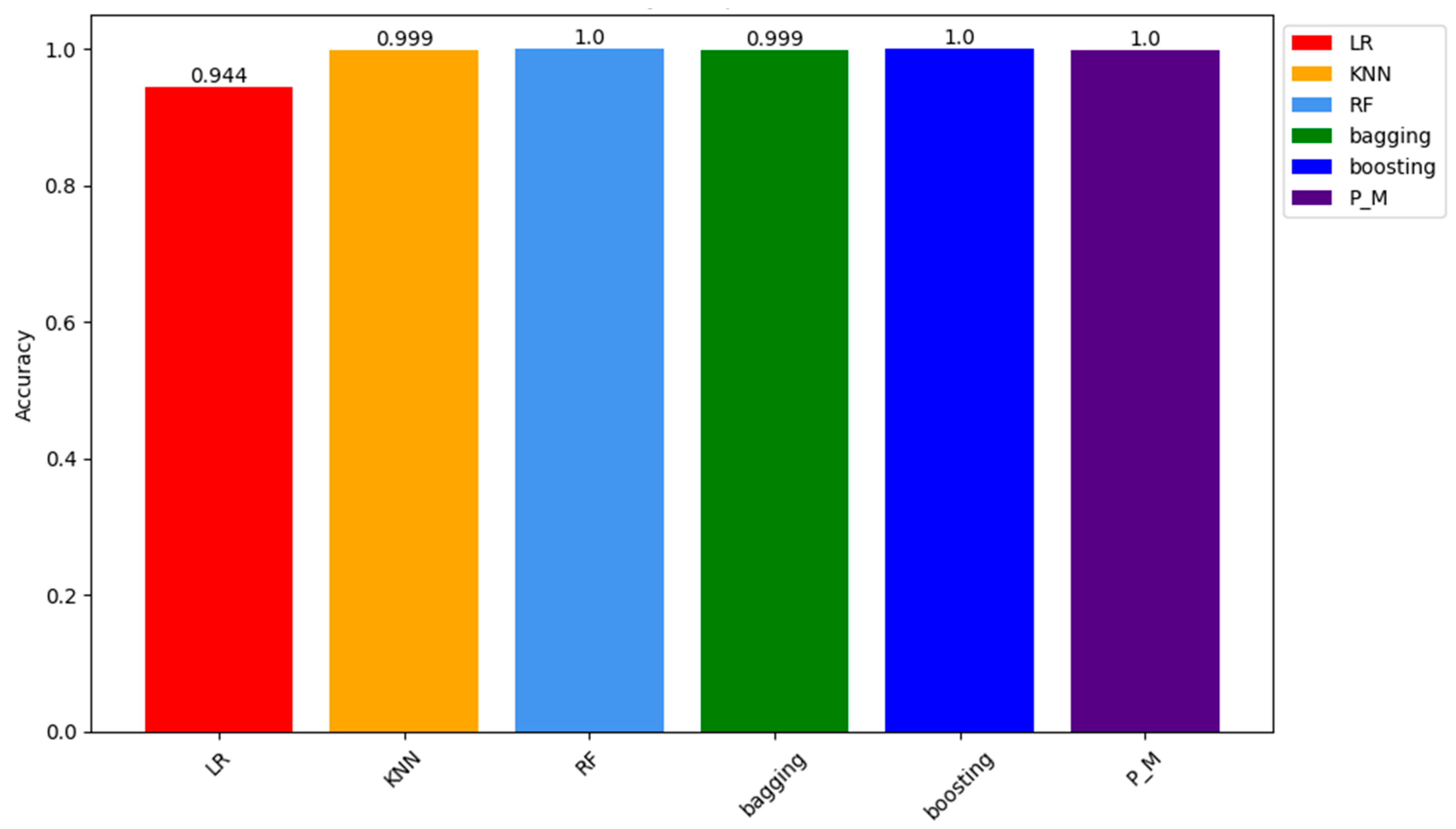
| Accuracy | 0.94443 | 0.999354 | 1 | 0.9993 | 1 | 0.99983 |
| Testing Sample of SMOTE Dataset | ||||||
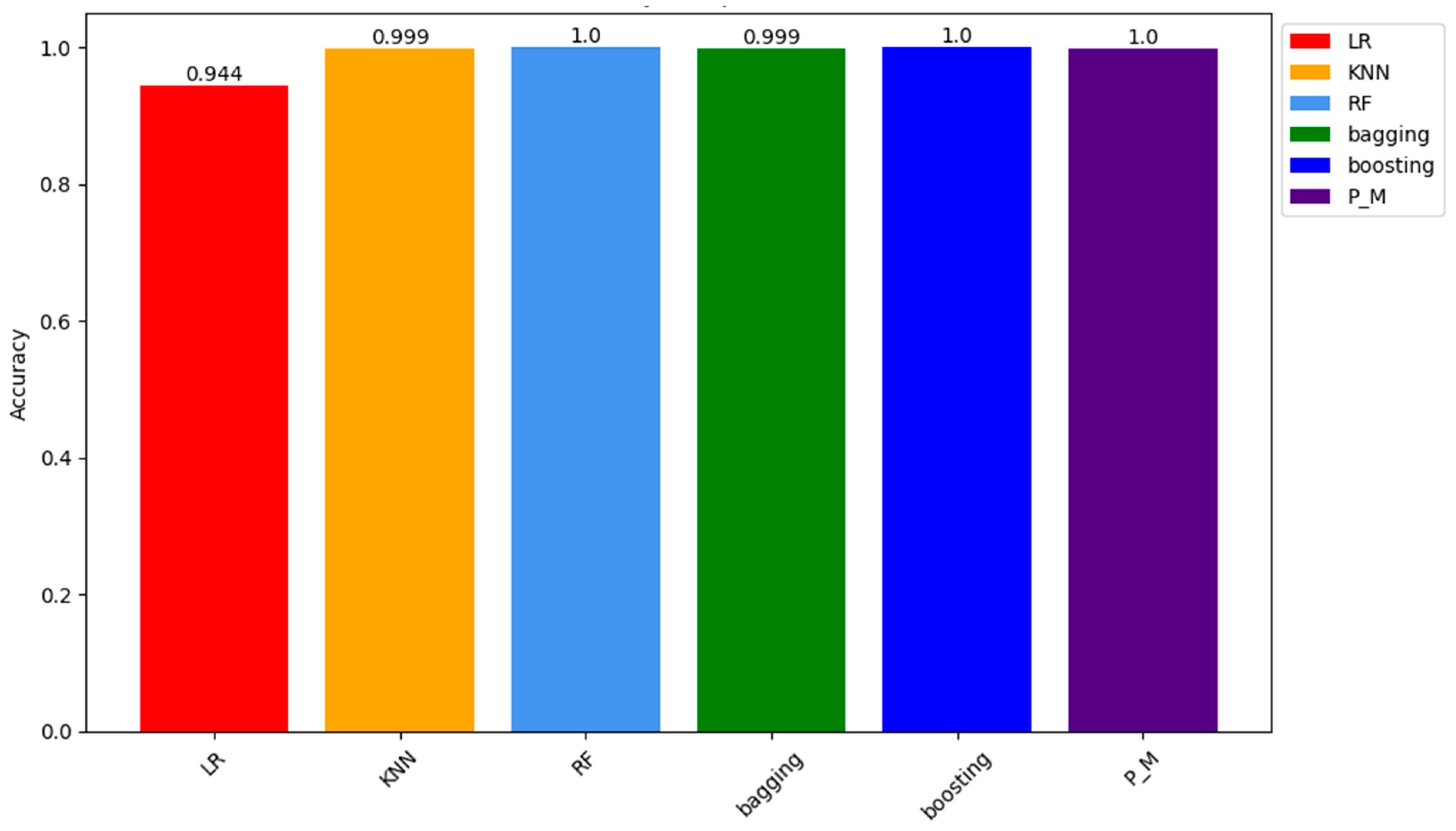
| Accuracy | 0.944256 | 0.999173 | 0.99989 | 0.999 | 0.999092 | 0.9996 |
| LR | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | PM | |
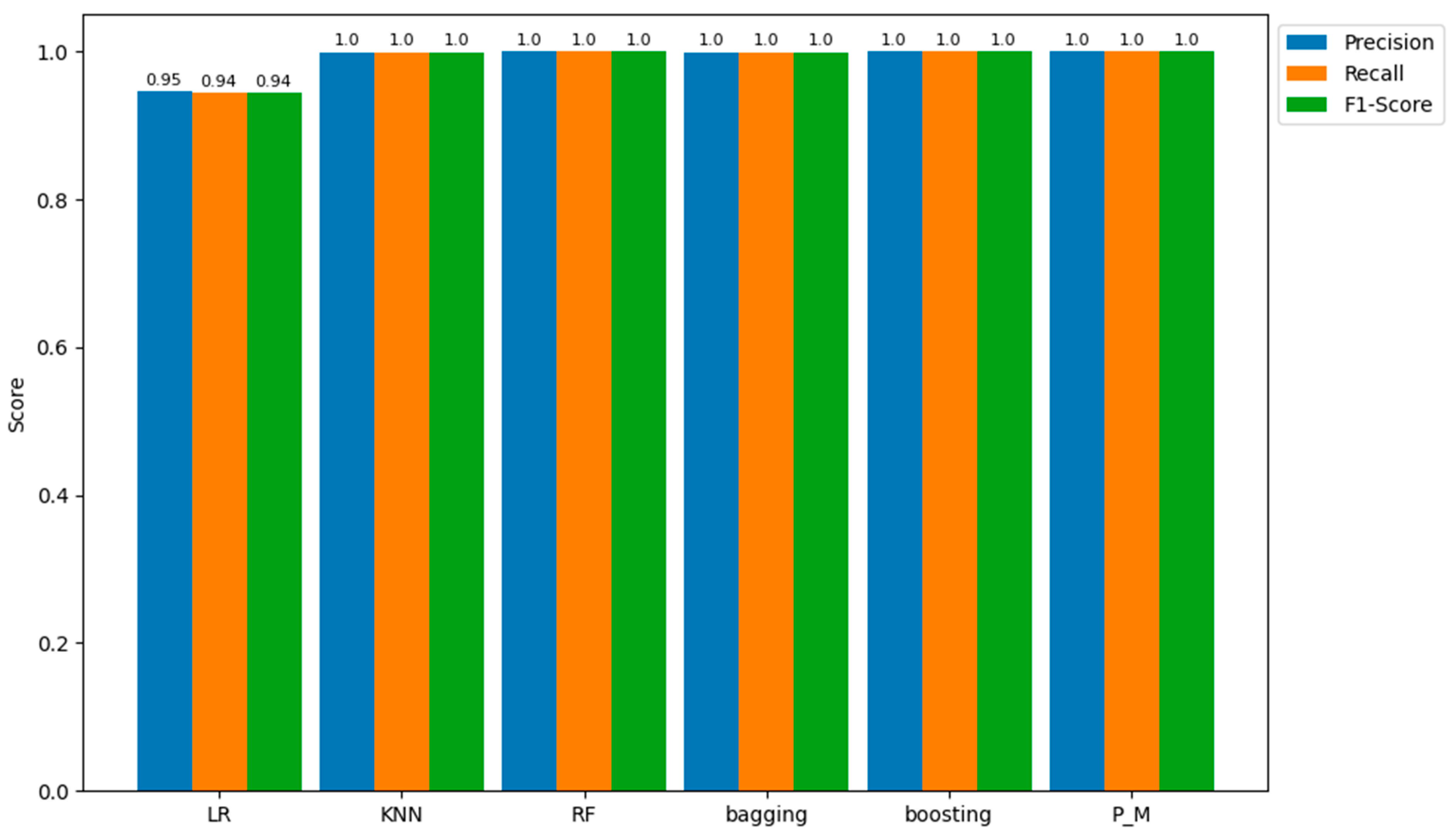
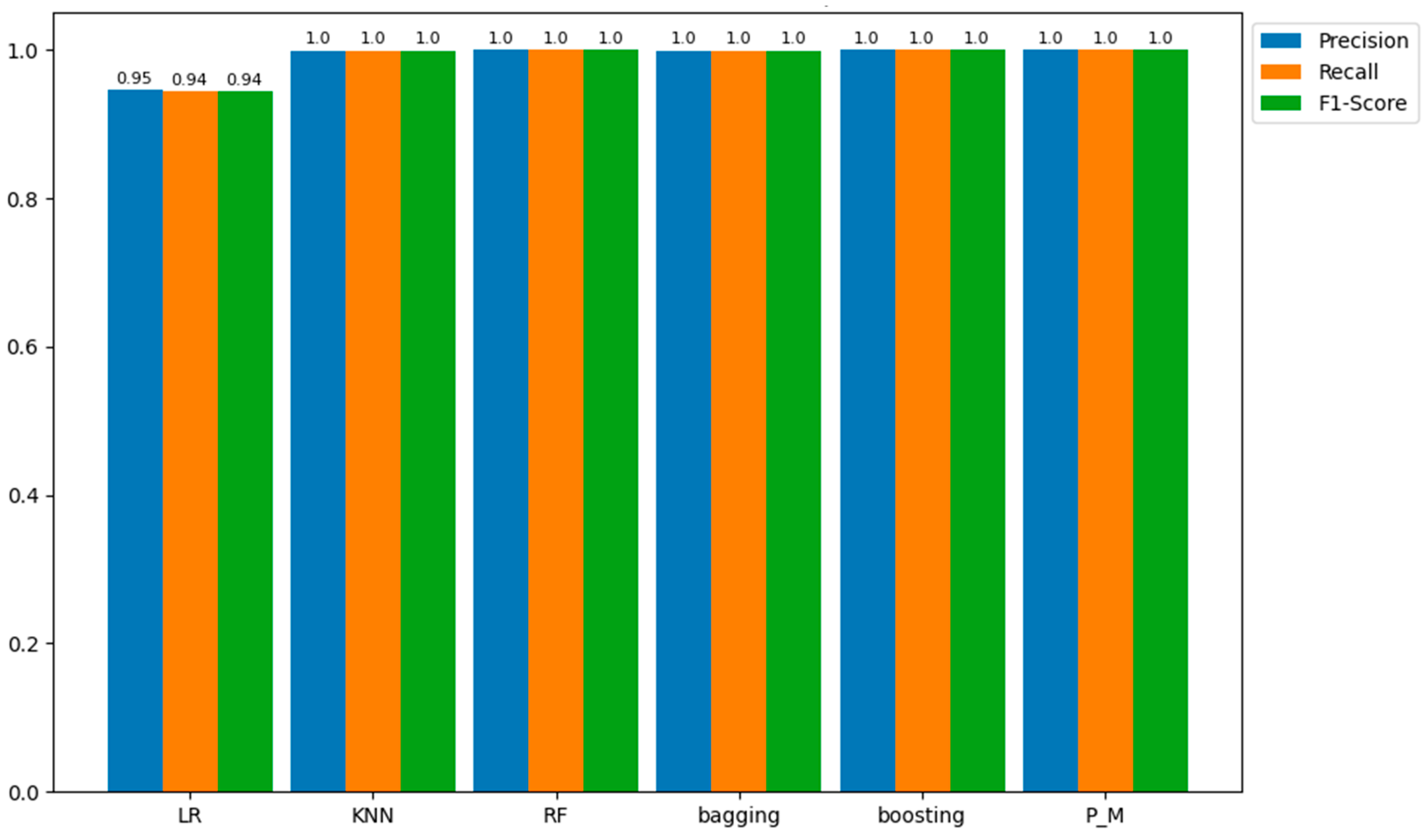
| Precision | 0.945938 | 0.999174 | 0.999891 | 0.999 | 0.999092 | 0.999601 |
| Recall | 0.944256 | 0.999173 | 0.99989 | 0.999 | 0.999092 | 0.9996 |
| F1-score | 0.944204 | 0.999173 | 0.99989 | 0.999 | 0.999092 | 0.9996 |
4.2. Comparison with Existing Models
| . | [17] | [28] |
PM (SMOTE) |
P_M_1 | P_M_2 |
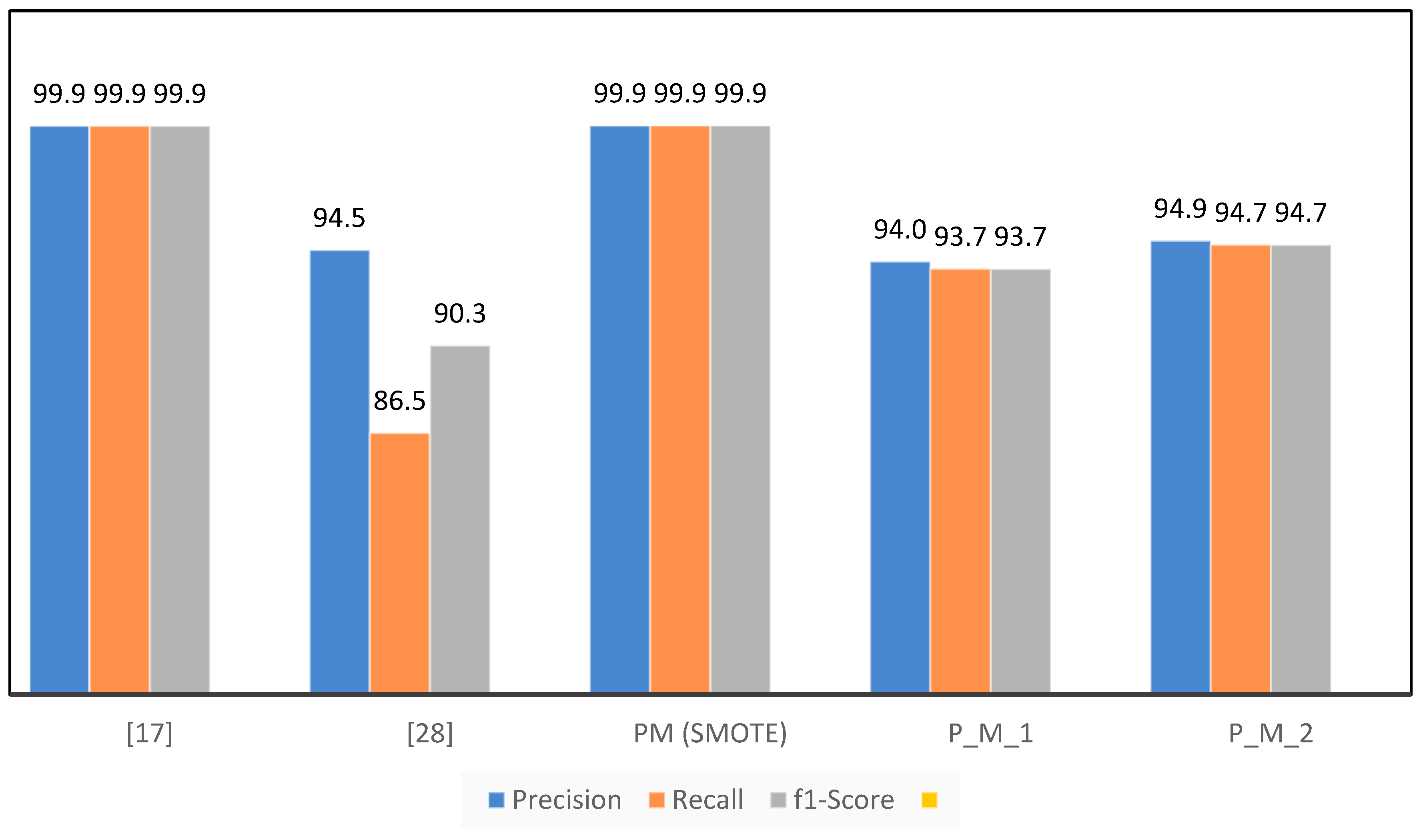
| Accuracy | 99.9455 | 83.83 | 99.9591 | 93.684 | 94.737 |
| Precision | 99.947 | 94.5 | 99.9591 | 93.996 | 94.916 |
| Recall | 99.9455 | 86.47 | 99.9591 | 93.684 | 94.737 |
| F1-Score | 99.9462 | 90.31 | 99.9591 | 93.673 | 94.731 |
Future Work
Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Crime Agency (NCA), "Fraud and Economic Crime." Accessed: May 11, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.nationalcrimeagency.gov.uk/what-we-do/crime-threats/fraud-and-economic-crime.
- Federal Trade Commission, "CSN-Data-Book-2022," no. February 2023, Accessed: Mar. 11, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/CSN-Data-Book-2022.pdf.
- A. Sudjianto, S. Nair, M. Yuan, A. Zhang, D. Kern, and F. Cela-D\’\iaz, "Statistical methods for fighting financial crimes," Technometrics, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 5–19, 2010. [CrossRef]
- S. Data, "Descriptive statistics," Birth, vol. 30, p. 40, 2012.
- W. H. Walters, "Survey design, sampling, and significance testing: Key issues," The Journal of Academic Librarianship, vol. 47, no. 3, p. 102344, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee and H. K. Kim, "Adsas: Comprehensive real-time anomaly detection system," in Information Security Applications: 19th International Conference, WISA 2018, Jeju Island, Korea, August 23–25, 2018, Revised Selected Papers 19, 2019, pp. 29–41.
- M. Somvanshi, P. Chavan, S. Tambade, and S. V Shinde, "A review of machine learning techniques using decision tree and support vector machine," in 2016 international conference on computing communication control and automation (ICCUBEA), 2016, pp. 1–7.
- R. Shah, "Introduction to K-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) Algorithm," https://ai.plainenglish.io/introduction-to-k-nearest-neighbors-knn-algorithm-e8617a448fa8.
- S. D. Jadhav and H. P. Channe, "Comparative study of K-NN, naive Bayes and decision tree classification techniques," International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 1842–1845, 2016.
- K. Randhawa, C. K. Loo, M. Seera, C. P. Lim, and A. K. Nandi, "Credit card fraud detection using AdaBoost and majority voting," IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 14277–14284, 2018. [CrossRef]
- O. S. Yee, S. Sagadevan, and N. H. A. H. Malim, "Credit card fraud detection using machine learning as data mining technique," Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering (JTEC), vol. 10, no. 1–4, pp. 23–27, 2018.
- S. Sengupta et al., "A review of deep learning with special emphasis on architectures, applications and recent trends," Knowl Based Syst, vol. 194, p. 105596, 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. B. Muppalaneni, M. Ma, S. Gurumoorthy, P. R. Vardhani, Y. I. Priyadarshini, and Y. Narasimhulu, "CNN data mining algorithm for detecting credit card fraud," Soft computing and medical bioinformatics, pp. 85–93, 2019.
- A. Roy, J. Sun, R. Mahoney, L. Alonzi, S. Adams, and P. Beling, "Deep learning detecting fraud in credit card transactions," in 2018 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS), 2018, pp. 129–134. [CrossRef]
- U. Fiore, A. De Santis, F. Perla, P. Zanetti, and F. Palmieri, "Using generative adversarial networks for improving classification effectiveness in credit card fraud detection," Inf Sci (N Y), vol. 479, pp. 448–455, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Y. Prasad, A. S. Chowdary, C. Bavitha, E. Mounisha, and C. Reethika, "A Comparison Study of Fraud Detection in Usage of Credit Cards using Machine Learning," in 2023 7th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), 2023, pp. 1204–1209. [CrossRef]
- G. L. Sahithi, V. Roshmi, Y. V. Sameera, and G. Pradeepini, "Credit Card Fraud Detection using Ensemble Methods in Machine Learning," in 2022 6th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), 2022, pp. 1237–1241. [CrossRef]
- R. Qaddoura and M. M. Biltawi, "Improving Fraud Detection in An Imbalanced Class Distribution Using Different Oversampling Techniques," in 2022 International Engineering Conference on Electrical, Energy, and Artificial Intelligence (EICEEAI), 2022, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- D. Tanouz, R. R. Subramanian, D. Eswar, G. V. P. Reddy, A. R. Kumar, and C. H. V. N. M. Praneeth, "Credit Card Fraud Detection Using Machine Learning," in 2021 5th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), 2021, pp. 967–972. [CrossRef]
- R. Sailusha, V. Gnaneswar, R. Ramesh, and G. R. Rao, "Credit Card Fraud Detection Using Machine Learning," in 2020 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), 2020, pp. 1264–1270. [CrossRef]
- I. Sadgali, N. Sael, and F. Benabbou, "Performance of machine learning techniques in the detection of financial frauds," Procedia Comput Sci, vol. 148, pp. 45–54, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Raghavan and N. El Gayar, "Fraud Detection using Machine Learning and Deep Learning," in 2019 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Knowledge Economy (ICCIKE), 2019, pp. 334–339. [CrossRef]
- A. Saputra and others, "Fraud detection using machine learning in e-commerce," International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. 10, no. 9, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Jain, N. Tiwari, S. Dubey, and S. Jain, "A comparative analysis of various credit card fraud detection techniques," International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 402–407, 2019.
- H. Naik and P. Kanikar, "Credit card fraud detection based on machine learning algorithms," Int J Comput Appl, vol. 182, no. 44, pp. 8–12, 2019.
- D. Varmedja, M. Karanovic, S. Sladojevic, M. Arsenovic, and A. Anderla, "Credit Card Fraud Detection - Machine Learning methods," in 2019 18th International Symposium INFOTEH-JAHORINA (INFOTEH), 2019, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- A. Thennakoon, C. Bhagyani, S. Premadasa, S. Mihiranga, and N. Kuruwitaarachchi, "Real-time Credit Card Fraud Detection Using Machine Learning," in 2019 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), 2019, pp. 488–493. [CrossRef]
- D. Prusti and S. K. Rath, "Fraudulent Transaction Detection in Credit Card by Applying Ensemble Machine Learning Techniques," in 2019 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), 2019, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Machine Learning Group - ULB, "Credit Card Fraud Detection Dataset," https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/mlg-ulb/creditcardfraud.
- Binh Vu, "Fraud ecommerce Dataset." 2018.
- I. University of California, "KDD CUP 99 Intrusion Dataset." Accessed: Jun. 08, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://kdd.ics.uci.edu/databases/kddcup99/kddcup99.html.
- I-Cheng Yeh, "Dataset," no. 2016. [CrossRef]
- G. Niveditha, K. Abarna, and G. V Akshaya, "Credit card fraud detection using random forest algorithm," Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 301–306, 2019.
- J. Graser, S. K. Kauwe, and T. D. Sparks, "Machine learning and energy minimisation approaches for crystal structure predictions: a review and new horizons," Chemistry of Materials, vol. 30, no. 11, pp. 3601–3612, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Teemu Kanstrén, "A Look at Precision, Recall, and F1-Score." https://towardsdatascience.com.
| Year | Authors |
Ensemble ML Models |
Under-Sampling | SMOTE | Comprehensive Evaluation |
| 2019 | Naik Kanikar [25] | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ |
| 2019 | Jain Tiwari et al. [24] | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ |
| 2019 | Saputra Suharjito [23] | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ |
| 2019 | Raghavan Gayar [22] | ✓ | × | ✓ | × |
| 2019 | Sadgali Benabbou [21] | ✓ | × | ✓ | × |
| 2020 | Sailusha Gnaneswar et al. [20] | ✓ | × | ✓ | × |
| 2021 | Tanouz Subramanian et al. [19] | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ |
| 2022 | Qaddoura, Biltawi [18] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 2022 | Sahithi Roshmi et al. [17] | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ |
| 2023 | Prasad Chowdary et al. [16] | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ |
| 2023 | Our Proposed Model | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Algorithm | Credit Card Fraud Detection using Ensemble Machine Learning Models |
| Input: | Credit_Card_Fraud_Dataset |
| Output: | Trained_Machine_Learning_Models |
| 1. | dataset ← Load_CreditCard_Fraud_Dataset() |
| 2. | processed_data ← PreprocessedData(dataset) |
| 3. | labels ← (processed_data) |
| 4. | under_sampled_data ← (labels) |
| 5. | smote_data ← (labels) |
|
6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. |
for model_type in [‘SVM’, ‘RF’, ‘Bagging’, ‘Boosting’, ‘LR’, ‘P_M_1’, ‘P_M_2’]: training_data, testing_data ← TrainTestSplit(under_sampled_data) if model_type == model: model ← model_type elif model_type == ‘Proposed_model’ models.append(mode_type) |
|
12. 13. 14. 15. |
for model_type, model in models: testing_data_features ← tresting_data.drop(‘Class’) testing_data_labels ← testing_data[‘Class’] confusion_matrix ← Evaluate_model(model, testing_data_features, testing_data_labels) |
| 16. | endif |
| 17. | end for |
| 18. | return display_results ← (confusion_matrix, model_type) |
| SVM | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | P_M_1 | LR | P_M_2 | |
| True Positive | 345 | 345 | 378 | 344 | 378 | 354 | 349 | 358 |
| True Negative | 372 | 372 | 378 | 371 | 378 | 378 | 371 | 378 |
| False Positive | 33 | 33 | 0 | 34 | 0 | 24 | 29 | 20 |
| False Negative | 6 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| SVM | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | P_M_1 | LR | P_M_2 | |
| True Positive | 87 | 86 | 86 | 87 | 86 | 85 | 87 | 87 |
| True Negative | 92 | 92 | 93 | 93 | 92 | 93 | 90 | 93 |
| False Positive | 8 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 8 |
| False Negative | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| Training Sample of Under-Sample Dataset | ||||||||
| SVM | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | P_M_1 | LR | P_M_2 | |
| Accuracy | 0.96 | 0.951 | 1 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.97 | 0.955 | 0.97 |
| Testing Sample of Under-Sample Dataset | ||||||||
| Accuracy | 0.9421 | 0.9368 | 0.937 | 0.9473 | 0.9368 | 0.9368 | 0.9315 | 0.9473 |
| SVM | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | P_M_1 | LR | P_M_2 | |
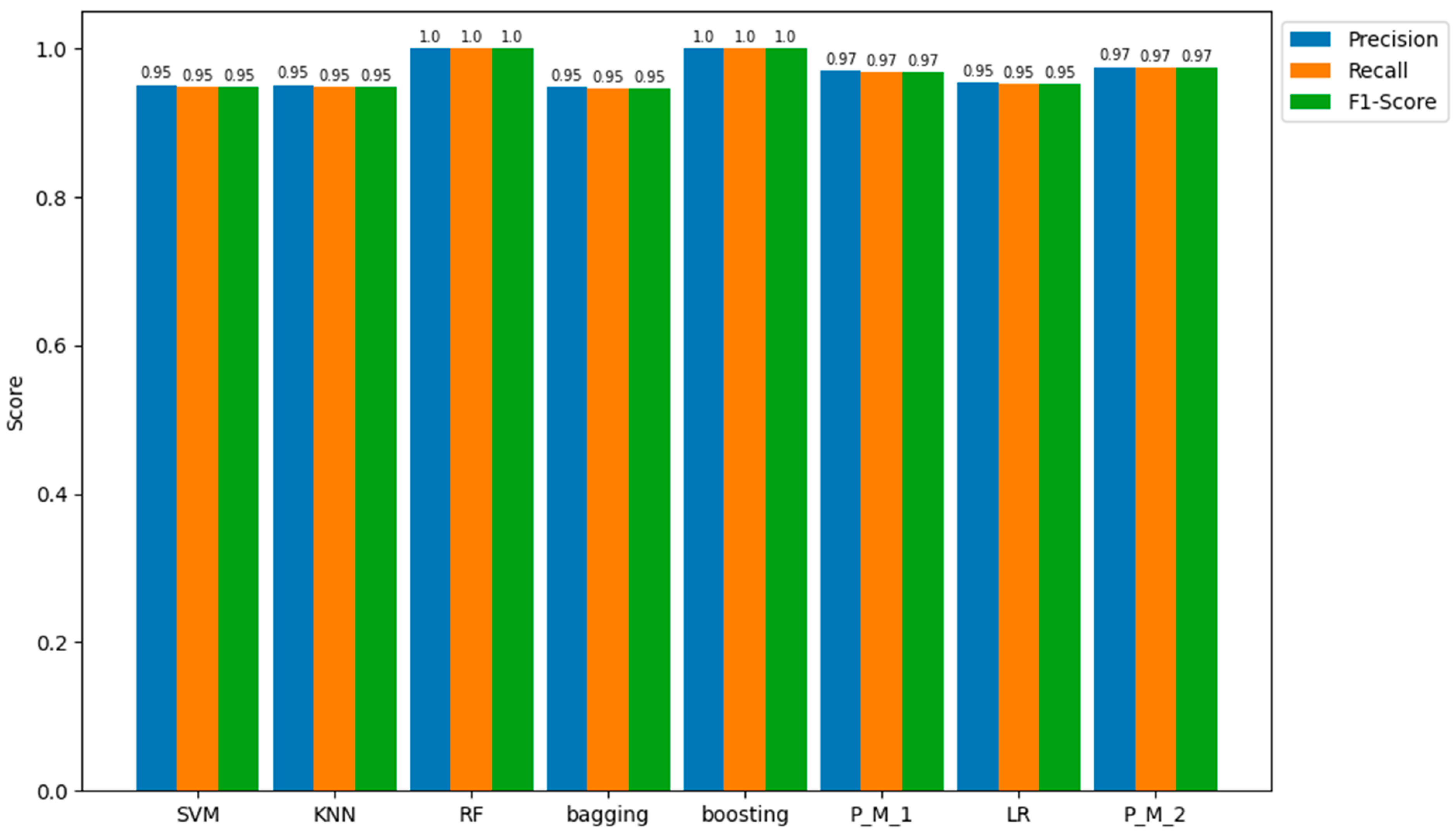
| Precision | 0.961 | 0.955 | 1 | 0.953 | 1 | 0.971 | 0.957 | 0.971 |
| Recall | 0.96 | 0.951 | 1 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.97 | 0.955 | 0.97 |
| F1-score | 0.96 | 0.951 | 1 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.97 | 0.955 | 0.97 |
| SVM | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | P_M_1 | LR | PM2 | |
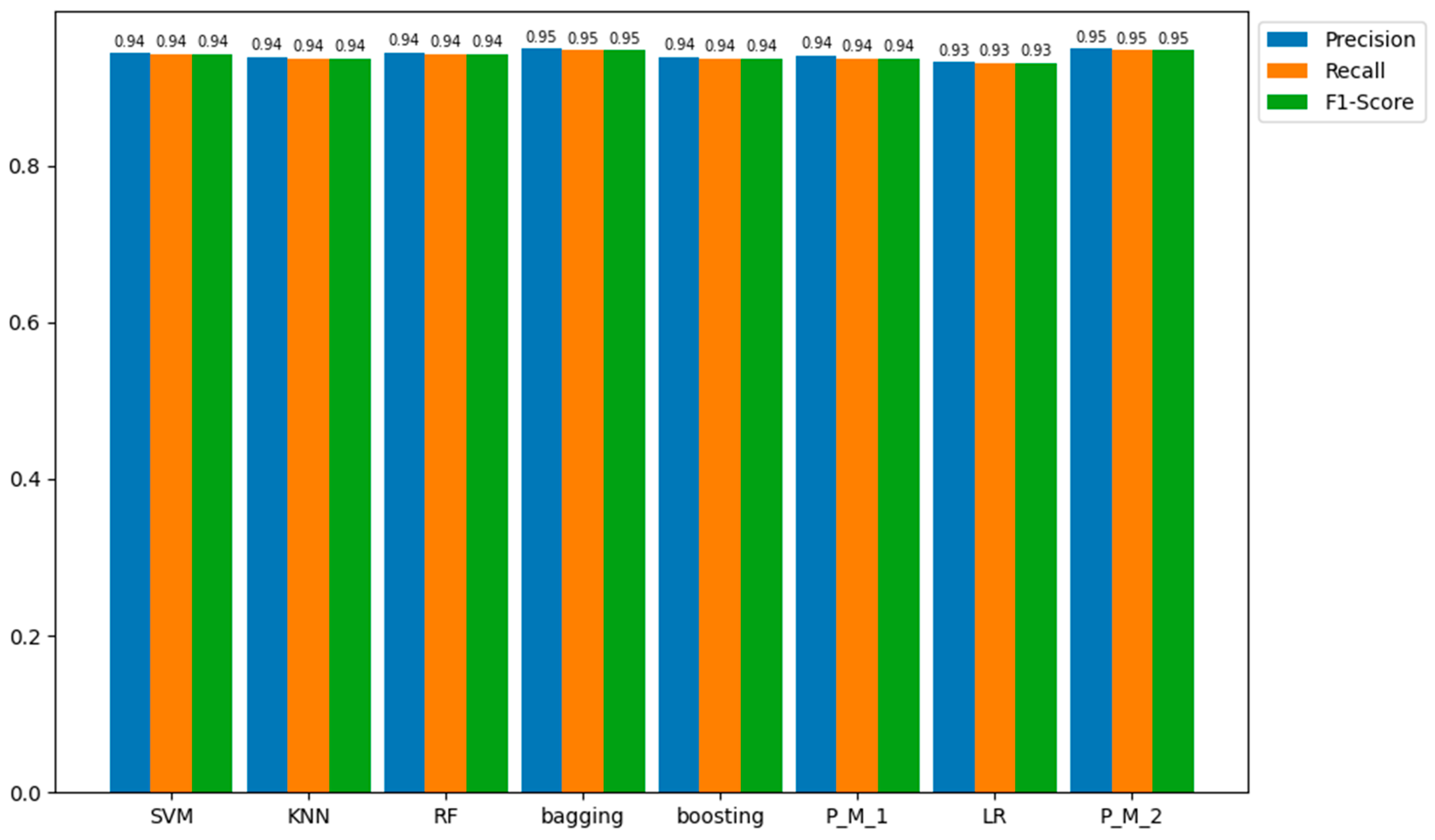
| Precision | 0.942 | 0.945 | 0.939 | 0.939 | 0.945 | 0.945 | 0.948 | 0.949 |
| Recall | 0.942 | 0.942 | 0.937 | 0.937 | 0.942 | 0.942 | 0.947 | 0.947 |
| F1-score | 0.942 | 0.942 | 0.937 | 0.937 | 0.942 | 0.942 | 0.947 | 0.947 |
| LR | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | P_M | |
| True Positive | 201231 | 220152 | 220152 | 220152 | 220152 | 220152 |
| True Negative | 214606 | 219868 | 220152 | 219864 | 220152 | 220082 |
| False Positive | 18921 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| False Negative | 5546 | 284 | 0 | 288 | 0 | 70 |
| LR | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | P_M | |
| True Positive | 50280 | 55038 | 55038 | 55038 | 55038 | 55038 |
| True Negative | 53660 | 54947 | 55028 | 54941 | 55028 | 54993 |
| False Positive | 4758 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| False Negative | 1378 | 91 | 10 | 97 | 10 | 45 |
| Prediction Results on Training Sample of SMOTE Dataset | ||||||
| LR | KNN | RF | Bagging | Boosting | PM | |
| Precision | 0.94607 | 0.999355 | 1 | 0.9993 | 1 | 0.99983 |
| Recall | 0.94443 | 0.99954 | 1 | 0.9993 | 1 | 0.999831 |
| F1-score | 0.94438 | 0.99954 | 1 | 0.9993 | 1 | 0.999831 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





