Submitted:
12 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and discussion
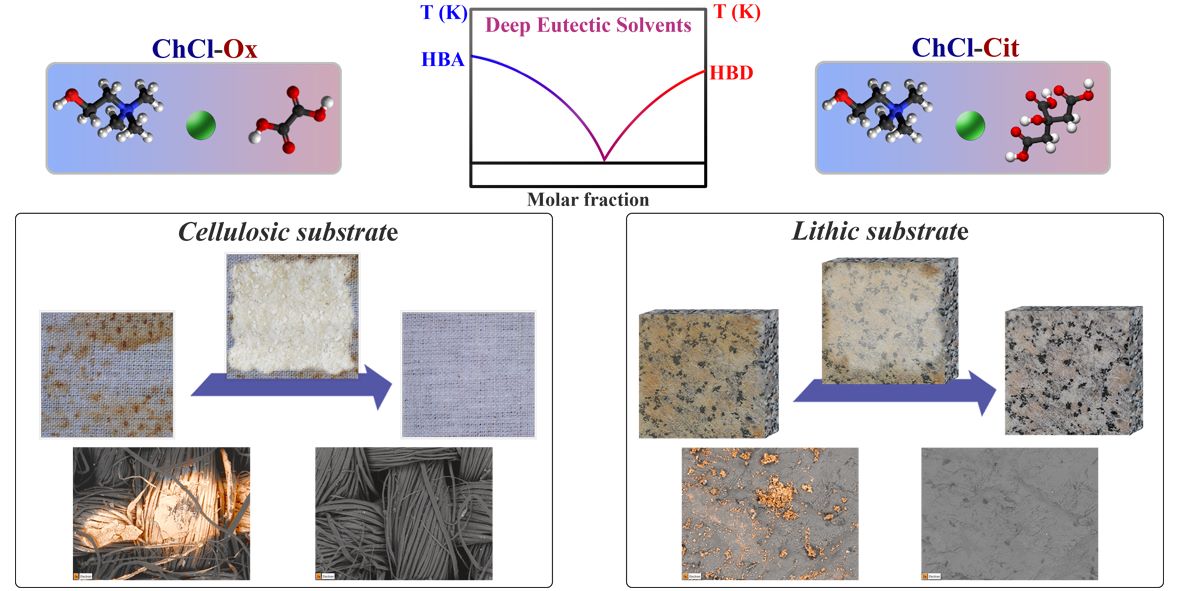
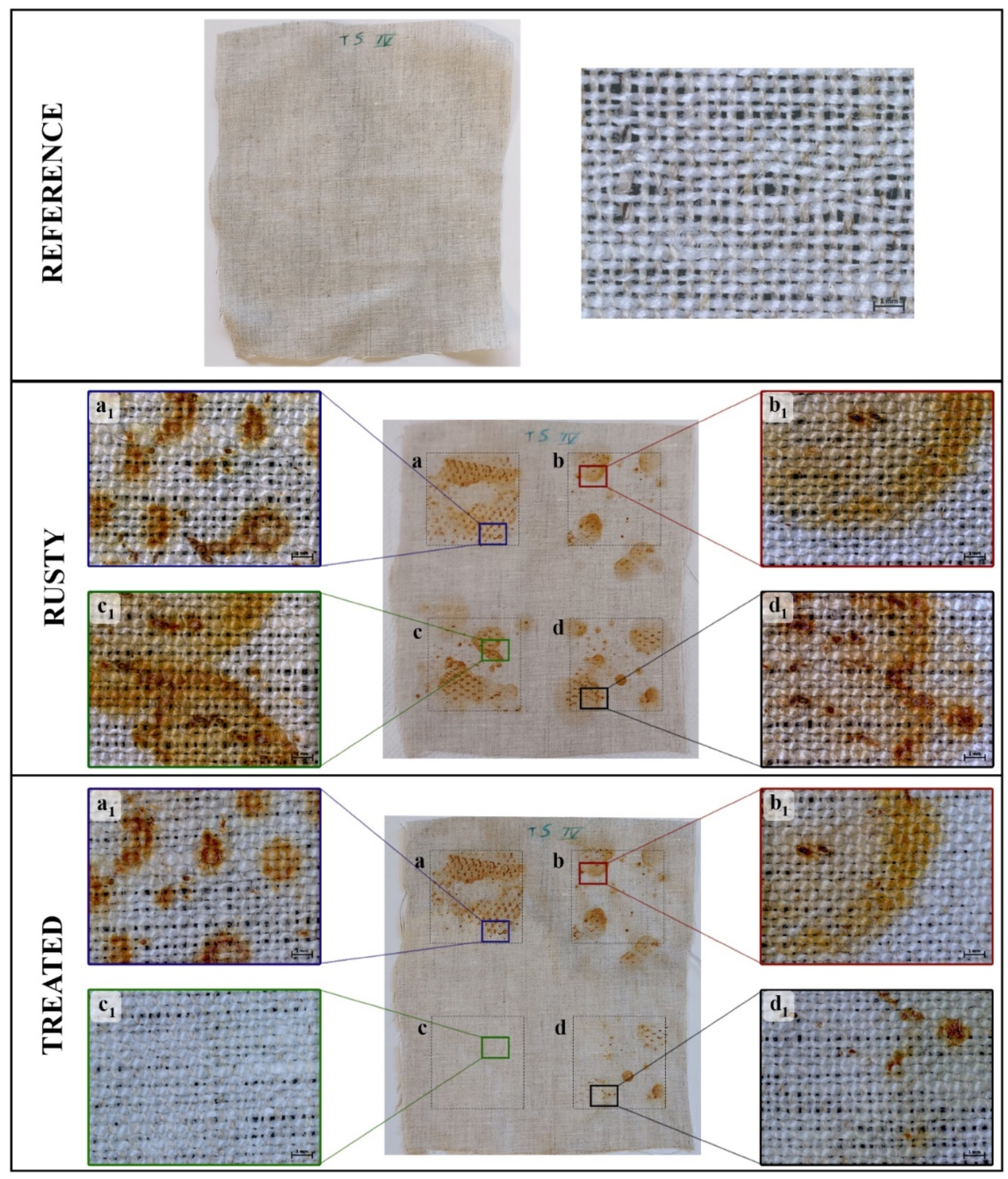
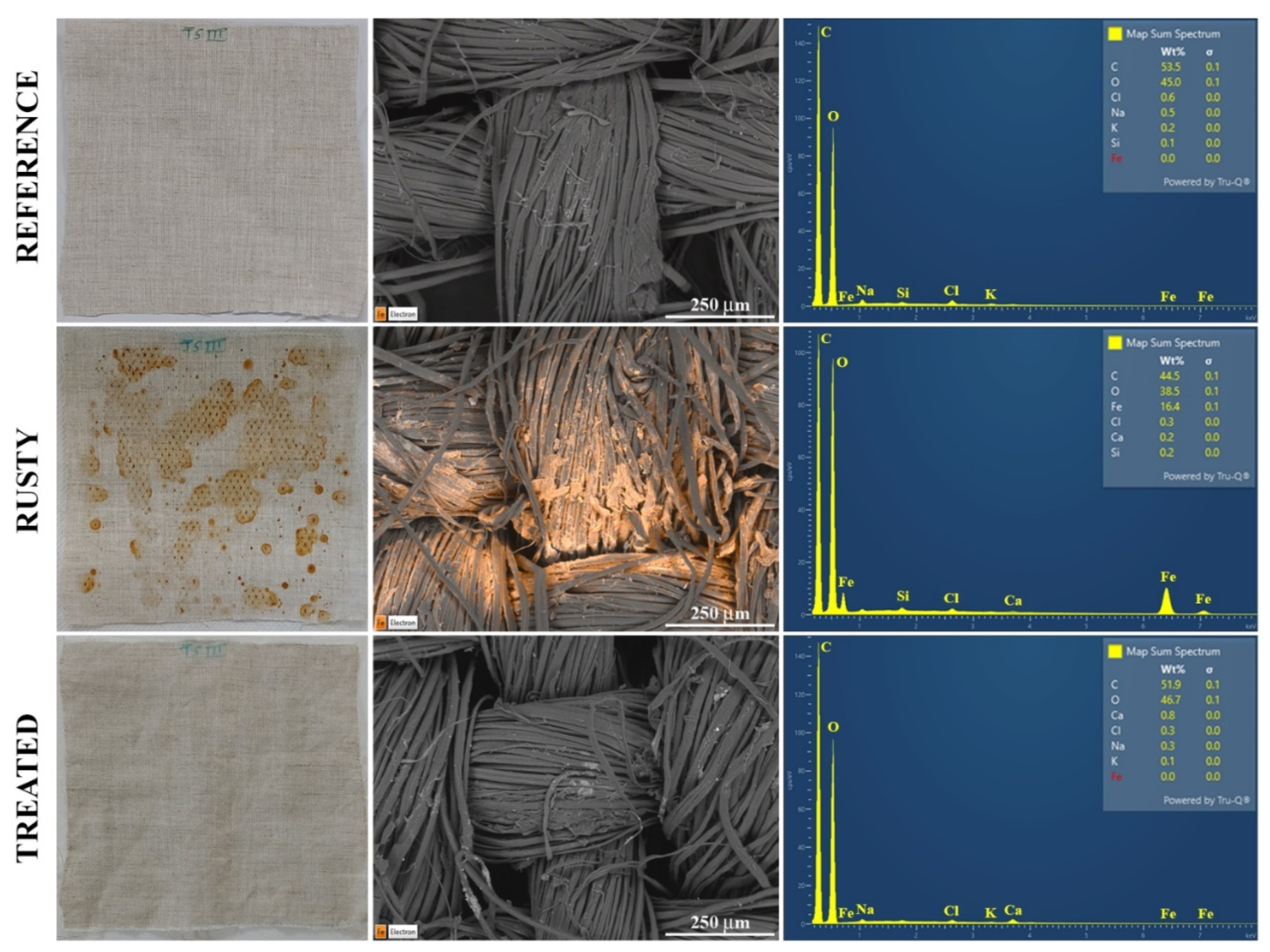
2.1. Canvas
SEM/EDS analysis
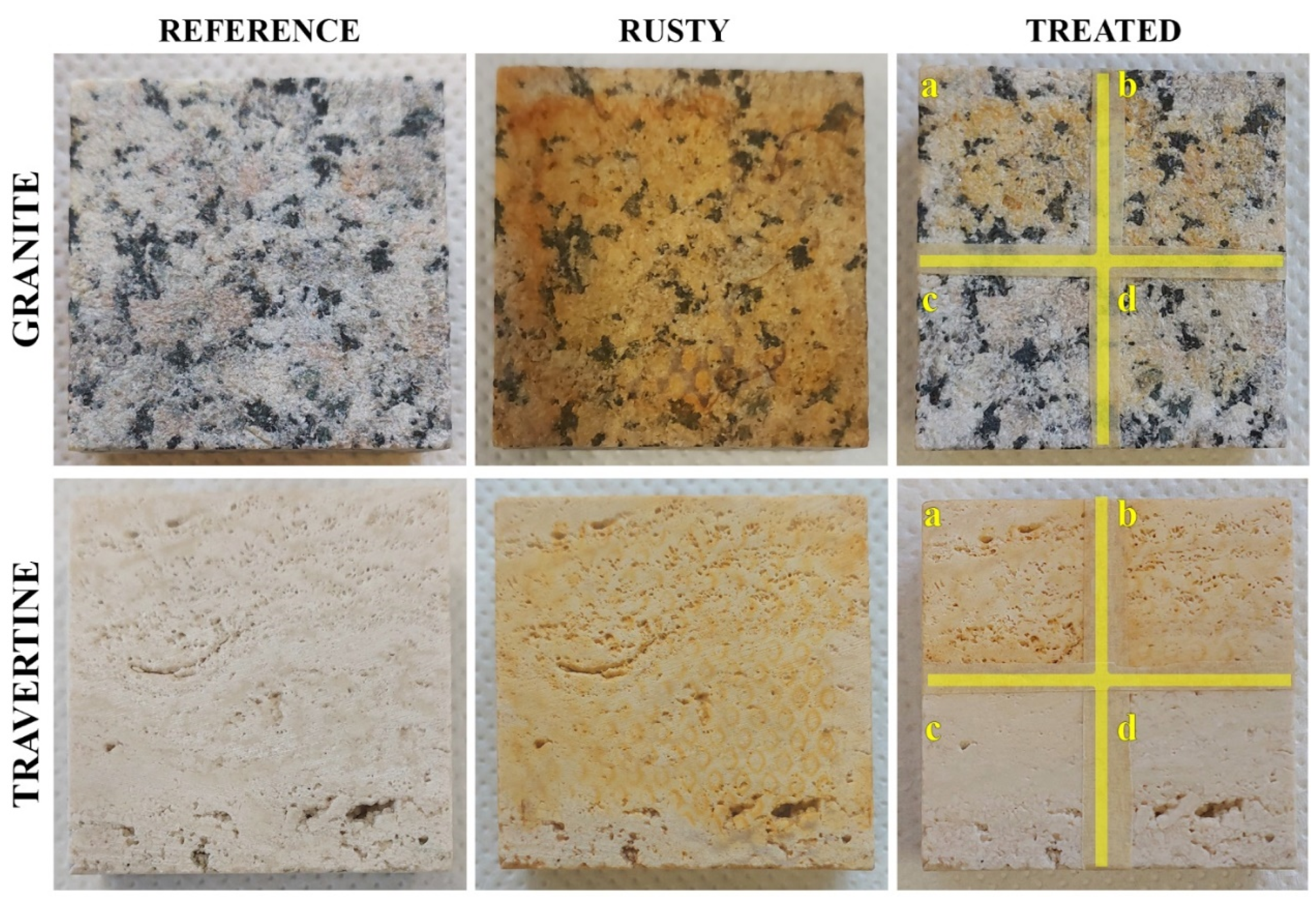
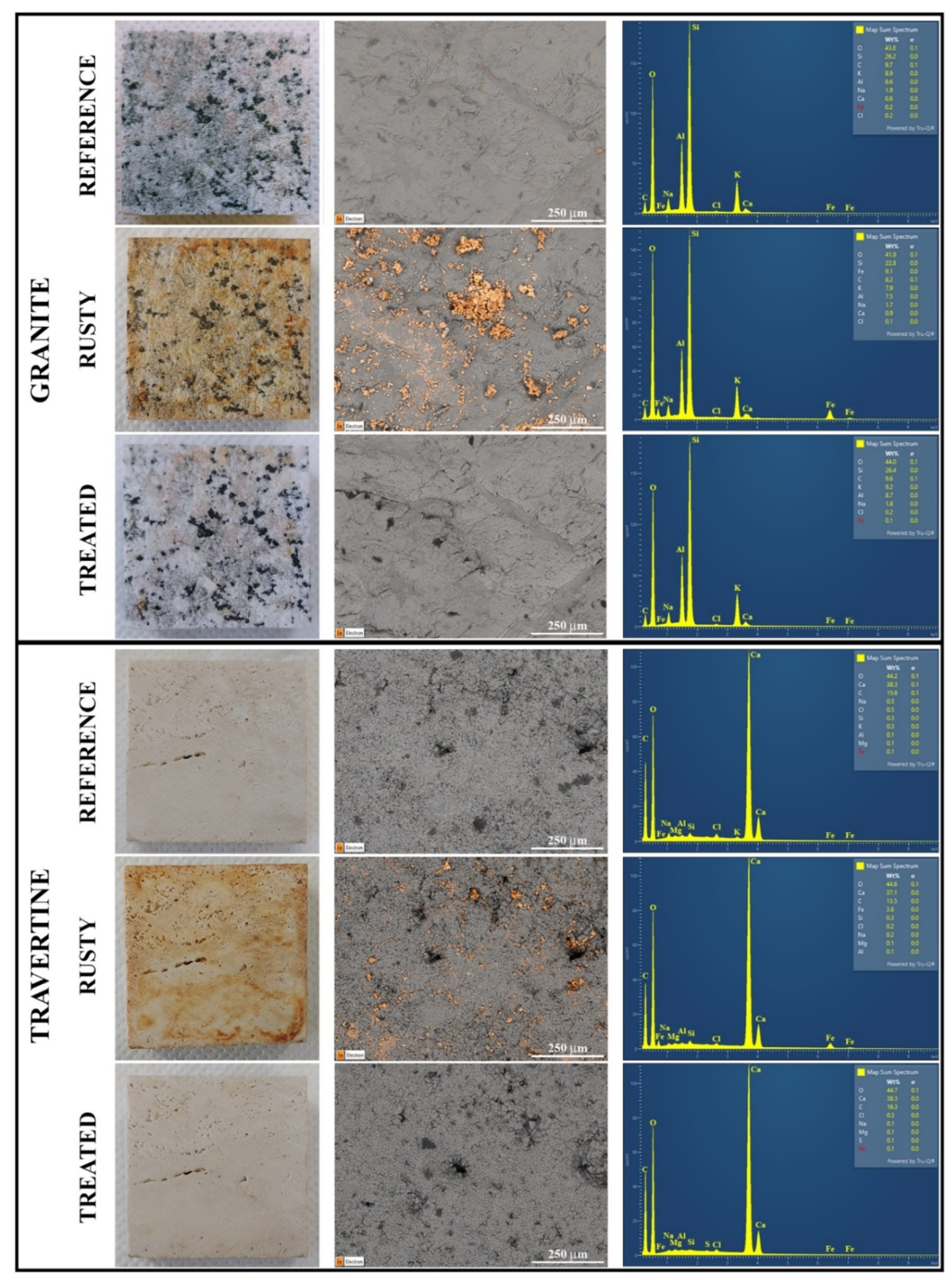
2.2. Stone
Photo and Colorimetry
SEM/EDS analysis
3. Materials and Methods
Materials
Staining of canvas and stone
DES preparation
DES application
Colorimetry
Stereomicroscope observations
SEM-EDS analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Comm. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, S. Deep eutectic solvents: syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Matias, A.A.; Duarte, A.R.C. How do we drive deep eutectic systems towards an industrial reality? Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 11, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and properties of deep eutectic solvents: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett., 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Gao, J; Zhang, Q.; Fanyu Kong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Sun, C.; Lv, S. Research progress on deep eutectic solvents and recent applications. Processes 2023, 11, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justyna Płotka-Wasylka, J.; de la Guardia, M.; Andruch, V.; Vilková, M. Deep eutectic solvents vs ionic liquids: Similarities and differences. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, M. Ionic Liquids Toxicity−Benefits and Threats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.T. Greener solvents: Room temperature ionic liquids from biorenewable sources. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 2938–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomba, L.; Ribate, M.P.; Sangüesa, E.; Concha, J.; Garralaga, M.ª.P.; Errazquin, D.; García, C.B.; Giner, B. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Are They Safe? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joarder, S.; Bansal, D.; Meena, H.; Kaushik, N.; Jaya Tomar, J.; Kumari, K.; Bahadur, I.; Choi, E.H.; Kaushik, N.K.; Singh, P. Bioinspired green deep eutectic solvents: preparation, catalytic activity, and biocompatibility. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 376, 121355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R. Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Geert-Jan Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents − Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henni Vanda, H.; Dai, Y.; Wilson, E.G.; Robert Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Green solvents from ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents to natural deep eutectic solvents. C. R. Chim. 2018, 21, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural deep eutectic solvents: Properties, applications, and perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, Z.; Sharma, M.; Tripathi, M.; Lukk, T.; Karpichev, Y.; Nicholas Gathergood, N.; Singh, B.N.; Thakur, V.K.; Tabatabaei, M.; Gupta, V.K. Biobased natural deep eutectic system as versatile solvents: Structure, interaction and advanced applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastiras, O.-E.; Samanidou, V. Applications of deep eutectic solvents in sample preparation and extraction of organic molecules. Molecules 2022, 27, 7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, M.; Butt, F.W.; Akram, S.; Ashraf, R.; Ahmed, D. Deep eutectic liquids as tailorable extraction solvents: A review of opportunities and challenges. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2022. Published online: 23 September 2022. . [CrossRef]
- Bowen, H.; Durrani, R.; Delavault, A.; Durand, E.; Chenyu, J; Yiyang, L.; Lili, S.; Jian, S.; Weiwei, H.; Fei, G. Application of deep eutectic solvents in protein extraction and purification. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 912411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.K.U.; Hadinoto, K. Deep eutectic solvent as green solvent in extraction of biological macromolecules: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Verma, M.; Bharti, R.; Sharma, R. Recent advances in utilization of deep eutectic solvents: An environmentally friendly pathway for multi-component synthesis. Curr. Org. Chem., 2022, 26, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, S.; Messa, F.; Troisi, L.; Salomone, A. N-, O- and S-Heterocycles synthesis in deep eutectic solvents. Molecules 2023, 28, 3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javahershenas, R. Recent advances in the application of deep eutectic solvents for the synthesis of Spiro heterocyclic scaffolds via multicomponent reactions. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 385, 122398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długosz, O. Natural deep eutectic solvents in the synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles. Mater. 2023, 16, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, B.; Li, X. Can deep eutectic solvents be the best alternatives to ionic liquids and organic solvents: A perspective in enzyme catalytic reactions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taklimi, S.M.; Divsalar, A.; Ghalandari, B.; Xianting Ding, X.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Omar, K.A.; Saboury, A.A. Effects of deep eutectic solvents on the activity and stability of enzymes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowska-Kopczyńska, I.; Nowosielski, B.; Warmińska, D. Deep eutectic solvents: Properties and applications in CO2 separation. Molecules 2023, 28, 5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, J. CO2 capture mechanism by deep eutectic solvents formed by choline prolinate and ethylene glycol. Molecules 2023, 28, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qader, I.B.; Prasad, K. Recent developments on ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents for drug delivery applications. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Duan, L.; Lin, Y.; Cui, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. Deep eutectic systems as novel vehicles for assisting drug transdermal delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, Q.; Yang, G. Deep eutectic solvents - Recent advances in fabrication approaches and pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 622, 121811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Frisch, G.; Gurman, S.J.; Hillman, A.R.; Hartley, J.; Holyoak, F.; Ryder, K.S. Ionometallurgy: designer redox properties for metal processing. Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 10031–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, J.; Jones, P.T. Solvometallurgy: An emerging branch of extractive metallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 570–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.I.; García-Díaz, I.; López, F.A. Properties and perspective of using deep eutectic solvents for hydrometallurgy metal recovery. Miner. Eng. 2023, 203, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep eutectic solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Pandey, A.; Pant, K.K.; Mishra, B. Investigating the effect of mono di carboxylic acids as hydrogen bond donor on solvation of copper in choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 383, 122142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.R.; Machiels, L.; Binnemans, K. p-Toluenesulfonic acid-based deep-eutectic solvents for solubilizing metal oxides. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3940–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Fedorov, A.Y.; Milevskii, N.A.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Dissolution of metal oxides in a choline chloride–sulphosalicylic acid deep eutectic solvent. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2021, 55, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. New chloroacetic acid-based deep eutectic solvents for solubilizing metal oxides. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 118393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateli, I.M.; Thompson, D.; Alabdullah, S.S.M.; Abbott, P.A.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Hartley, J.M. The effect of pH and hydrogen bond donor on the dissolution of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem., 2020, 22, 5476–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Novel diglycolic acid-based deep eutectic solvents and their applications as a rust remover. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spile, S.; Suzuki, T.; Bendix, J.; Simonsen, K.P. Effective cleaning of rust stained marble, Herit. Sci. 2016 4 12. [CrossRef]
- Maravelaki, P.N. Surface cleaning: Implications from choices & future perspectives, in: Conserving Stone Heritage. Cultural Heritage Science, Gherardi, F., Maravelaki, P.N., Eds.; Springer, Cham, Switzerland, 2022, pp. 37–74. [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, F.; Casieri, C.; Spreti, N. Reducing-chelating efficacy of chitosan-carboxylic acid hydrogels for removing rust from various lithic surfaces. J. Cult. Herit. 2023. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N. , Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the synthesis and properties of deep eutectic solvents based on cholinium chloride and carboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafie, M.H.; Yusof, R.; Gan, C.-Y. Synthesis of citric acid monohydrate-choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents (DES) and characterization of their physicochemical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 111081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, N.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Solvometallurgical recovery of cobalt from lithium-ion battery cathode materials using deep-eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzigrigoriou, A.; Karapanagiotis, I.; Poulios, I. Superhydrophobic coatings based on siloxane resin and calcium hydroxide nanoparticles for marble protection. Coatings 2020, 10, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, F.; Ranaldi, R.; Bruno, L.; Casieri, C.; Rugnini, L.; Spreti, N. Biodeterioration of stone monuments: studies on the influence of bioreceptivity on cyanobacterial biofilm growth and on the biocidal efficacy of essential oils in natural hydrogel. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.R.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kollau, L.J.B.M.; Kroon, M.C.; Binnemans, K. Degradation of deep-eutectic solvents based on choline chloride and carboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11521–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNI EN 15886:2010. Conservation of cultural property - Test methods – Color measurement of surfaces.
| L* | a* | b* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF | 80±1 | 2.6±0.1 | 5.8±0.3 | ||
| RUSTY | ∆L* | ∆a* | ∆b* | ∆E* | |
| a1 | -10.9±0.1 | 3.46±0.01 | 7.40±0.02 | 13.6±0.1 | |
| b1 | -13.8±0.2 | 7.4±0.1 | 16.0±0.1 | 22.4±0.3 | |
| c1 | -15.2±0.3 | 7.8±0.2 | 14.7±0.2 | 22.5±0.4 | |
| d1 | -18.1±0.3 | 9.98±0.01 | 18.64±0.05 | 27.8±0.2 | |
| TREATED | ∆L* | ∆a* | ∆b* | ∆E* | |
| a1 | -11.1±0.1 | 3.61±0.02 | 7.0±0.1 | 13.6±0.1 | |
| b1 | -12.4±0.1 | 7.26±0.01 | 17.48±0.03 | 22.65±0.06 | |
| c1 | 0.9±0.5 | 0.54±0.02 | -0.54±0.04 | 1.2±0.4 | |
| d1 | -8.6±0.3 | 4.71±0.02 | 11.71±0.02 | 15.3±0.2 |
| Weight, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Ref | Rusty | Treated |
| C | 53.1±0.4 | 44±3 | 51.9±0.2 |
| O | 45.7±0.7 | 40±2 | 46.9±0.5 |
| Fe | 0.0±0.1 | 16±4 | 0.0±0.1 |
| GRANITE | TRAVERTINE | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* | ||||
| REF | 69±2 | 0.1±0.7 | 2±1 | 80±2 | 3.8±0.3 | 10±1 | |||
| RUSTY | ∆L* | ∆a* | ∆b* | ∆E* | ∆L* | ∆a* | ∆b* | ∆E* | |
| a | -11±5 | 11±5 | 27±6 | 32 | -7±1 | 7±2 | 19±4 | 21 | |
| b | -8±3 | 8±2 | 22±4 | 25 | -8±2 | 8±1 | 23±1 | 25 | |
| c | -6±2 | 8±2 | 22±3 | 24 | -7±3 | 8±2 | 22±8 | 25 | |
| d | -8±5 | 9±3 | 22±6 | 32 | -8±1 | 8±1 | 23±4 | 26 | |
| TREATED | ∆L* | ∆a* | ∆b* | ∆E* | ∆L* | ∆a* | ∆b* | ∆E* | |
| a | -5±2 | 3±3 | 9±7 | 11 | -5±1 | 5.1±0.7 | 14±3 | 15 | |
| b | -2±2 | 2±1 | 6±2 | 7 | -6±1 | 5.9±0.6 | 15±2 | 17 | |
| c | 2±2 | 0.1±0.3 | -1.3±0.8 | 2.0 | 0±1 | 1.1±0.3 | 2.9±0.8 | 3.1 | |
| d | -2±2 | 1.3±0.9 | 3±3 | 3.7 | 0±1 | 1.0±0.4 | 2.2±0.4 | 2.5 | |
| Weight, % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Ref | Rusty | Treated | |
| Granite | Si | 28±5 | 26±5 | 29±6 |
| Al | 7±3 | 6±3 | 7±3 | |
| Fe | 1±1 | 8±1 | 1±1 | |
| Travertine | Ca | 36±2 | 36±1 | 36±2 |
| C | 17±1 | 13.8±0.4 | 20±3 | |
| Fe | 0.1±0.1 | 5±1 | 0.1±0.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





