1. Introduction
Biofilm infections involving
Pseudomonas aeruginosa present a complex and persistent problem in clinical settings [
1]. As an opportunistic pathogen,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is known for its remarkable ability to form robust biofilms, which are structured communities of bacteria encased in a self-produced extracellular matrix [
2,
3]. This matrix provides essential structural support and protection, enabling the bacteria to adhere to surfaces, evade host immune responses, and exhibit resistance to conventional antimicrobial therapies [
3,
4].
The challenges posed by
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections are multifaceted. One key challenge is the inherent antibiotic resistance displayed by bacteria within biofilms. This resistance is attributed to limited drug penetration into the biofilm matrix and the altered physiological states of bacteria residing within the biofilm [
5]. Consequently, conventional antibiotic treatments often prove ineffective against biofilm-associated infections[
1].
A notable aspect of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections is their association with medical devices, such as catheters, implant, and ventilator tubes [
6,
7,
8,
9]. These devices provide ideal surfaces for biofilm formation, leading to impaired device function and an elevated risk of systemic infections [
10]. Biofilm formation on ventilator tubes poses a serious risk in healthcare settings, leading to ventilator associated pneumonia, increased patient morbidity, and healthcare costs [
9]. Research efforts are dedicated to unraveling the molecular mechanisms underlying
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and investigating potential targets for therapeutic intervention [
11,
12]. Understanding the role of quorum sensing, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production, and other virulence factors is paramount in devising effective strategies to disrupt biofilm development [
12].
Nanoparticles have emerged as promising tools in the battle against biofilm formation due to their unique physicochemical properties and versatile applications. These nanoscale materials exhibit a range of effects that interfere with various stages of biofilm development, offering innovative strategies to combat this persistent problem, and improve the efficacy of antimicrobial approaches. The effects of nano materials on preventing biofilm formation includes physical disruption, surface modification, release of antimicrobials, disruption of quorum sensing, electrostatic interactions, mechanical stress, photothermal effects, and enzymatic degradation [
13,
14].
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have garnered considerable scientific and technological interest in the past few decades [
14,
15]. In comparison with other nanoparticles, AuNPs are recognized for their exceptional stability and have been synthesized in diverse shapes and structures. Additionally, they exhibit adjustable and distinctive optical properties [
14,
16,
17]. Currently, AuNPs has been engineered for diverse applications in the medical and pharmaceutical domains. These applications encompass antibacterial and antibiofilm properties, among others [
17].
Glucosamine is a naturally occurring amino sugar that serves as a building block for various molecules within the body, including glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and proteoglycans. In recent years, glucosamine nanoparticles have gained attention for their potential applications in various fields, including medicine and material science [
12,
13,
14]. In the context of preventing biofilm formation, glucosamine nanoparticles have been investigated for their ability to inhibit initial bacterial adhesion. The functional groups on the surface of glucosamine can interact with bacterial cell surfaces, disrupting their attachment and colonization on surfaces. Additionally, glucosamine nanoparticles might interfere with quorum sensing systems that play a role in biofilm formation by inhibiting bacterial communication [
4,
15].
Previous studies have reported the synergistic antibiofilm effect of colistin+meropenem against
Myroides odoratimimus. However, combination involving meropenem, such as meropenem+ampicillin/sulbactam and meropenem+gentamicin did not exhibit antibiofilm activity against
Acinetobacter baumannii [
18,
19]. Leon-Buitimea A, et al., described potential combination therapy between antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents including nanoparticles to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria [
20]. The combination of antibiotics and AuNPs, particularly those functionalized with glucosamine has the potentially to exhibit synergistic antibiofilm effects. This approach involves leveraging the advantages of both antibiotics and AuNPs to enhance antibiofilm activity and overcome limitations associated with conventional antibiotic therapies. We aimed to investigate the effect of glucosamine nanoparticles, both alone and combination with meropenem, to prevent biofilm formation of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 on the endotracheal tube, serving as a model of ventilator associated pneumonia. Ex-vivo assessment of glucosamine nanoparticles against
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm was conducted using the tissue culture plate method and scanning electron microscope.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Endotracheal tube Pieces Preparation
The package of endotracheal tube (Life Resources) was opened under the biological safety cabinet. The endotracheal tube was cut with a sterile scalpel of around 0.5 cm per piece. A piece of sterile endotracheal tube was placed into an individual well of tissue culture plate for further experiment [
14].
2.2. Bacterial Isolate
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 was used in this study. The isolates from fresh agar plates were inoculated in 5 mL of trypticase soy broth and were kept for incubation at 37oC for 24 hours. The 108 CFU/mL of inoculum was used for biofilm formation assay on the endotracheal tube.
2.3. AuNPs Preparation
The preparation of AuNPs with average sizes of 10 nm was conducted as previously described with slight modification [
21,
22]. Briefly, 1 mL of 0.1% m/v HAuCl
4.3H
2O and 49 mL water were added to 4 mL of 0.02%, 0.04%, and 0.06% (m/v) Na
3-citrate solution with continuous stirring at 60
oC and 800 rpm for 45 minutes. Subsequently, the mixture was cooled to room temperature before the addition of glucosamine phosphate.
2.4. Conjugation of Glucosamine Phosphate and AuNPs (GlcN-AuNPs)
The different concentrations of GlcN-AuNPs were generated as previously described [
22]. Appropriate amounts of glucosamine phosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) were added into a cylindrical flask with a flat bottom containing 5 mL of AuNPs at a designated flow rate (0.150 mL/min). The mixture was stirred at 800 rpm in room temperature. The final concentration of GlcN-AuNPs were 0.008%, 0.012%, 0.016%, 0.020%, and 0.024%. Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (ThermoScientific Genesys 150) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) (JOEL JEM-1400) of GlcN-AuNPs were performed prior to usage for characterization and quality assurance purposes. The TEM images were obtained at the TEM service unit in the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
2.5. Ex-Vivo Assessment of GlcN-AuNPs against Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 Biofilms
Tissue culture plate method was carried out to investigate the biofilm formation of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 on the endotracheal tube [
23]. A piece of ETT was placed in a well of individual wells of 24 well-flat bottom polystyrene (Biologix Europe GmbH). Individual wells of 24 well-flat bottom polystyrene (Biologix Europe GmbH) were filled with 200 μL of 10
8 CFU/ml
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 inoculums into 200 μL trypticase soy broth-glucose medium. The uninoculated medium, serving as the negative control, was added to each well to ensure that the medium was sterile. After the plates were incubated for eight hours at 37 °C, the broth medium was carefully pipetted out of the wells. Plates were washed twice with 200 μL of phosphate buffer saline (pH 7.2). The ETT was moved to a new individual wells of 24 well-flat bottom polystyrene. The individual wells were filled with 200 μL of trypticase soy broth (without glucose) for further experiments described in
Table 1.
Plates then were incubated at 37
oC for 24 hours. After 24 hours incubation, plates were washed twice with 200 μL of phosphate buffer saline (pH 7.2) and incubated at 37
oC for an hour. The plates were stained with 200 μL of 0.1% crystal violet for 10 min. Excess stain was removed by washing twice with deionized water and the plates were kept for drying. 200 μL of 33% glacial acetic acid was added to the wells. Optical density (OD) of the isolates were determined using micro-ELISA auto reader (BIORAD) at a wavelength of 570 nm. The experiment was performed quadruplets per group. The analysis of optical density data for identifying biofilm formation referred to
Table 2. Additionally, the percentage of biofilm inhibition was determined using the following formula [
19]:
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscope
Scanning electron microscope preparation was conducted following the previous described method [
25]. Initially, the suspensions containing a piece of ETT in each well of the tissue culture microplate were discarded. Subsequently, each ETT piece underwent two gentle rinses with 1% sterile phosphate-buffered saline (Merck, USA) and was fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 2 hours. The fixed ETT pieces were then washed again with PBS and dehydrated through a series of graded ethanol solutions. Finally, the ETT pieces were removed from the wells, dried overnight, and gold-coated before imaging. The examination was performed using a scanning electron microscope (Hitachi TM 3000, Japan) at the Laboratory of Bioscience, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of GlcN-AuNPs
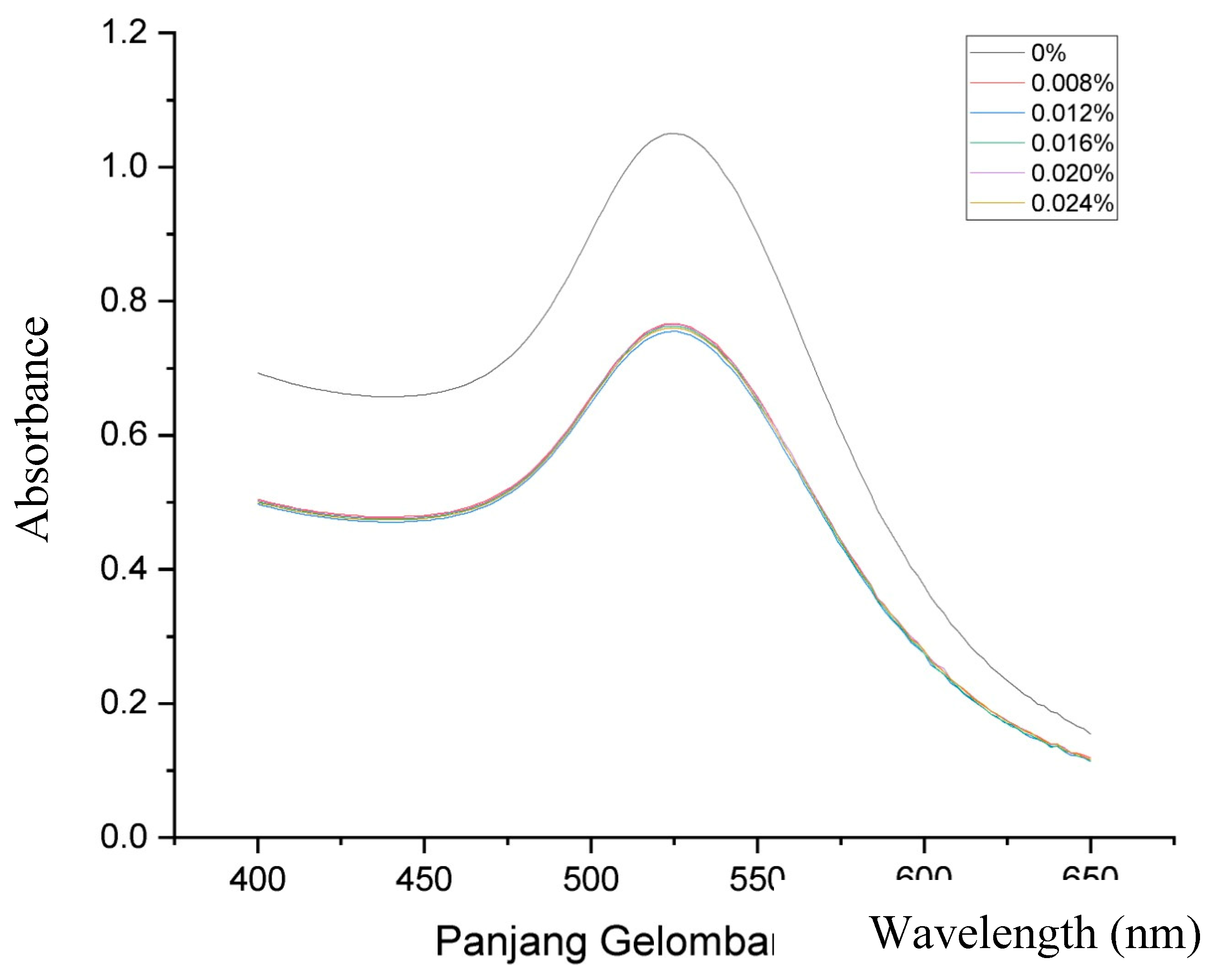
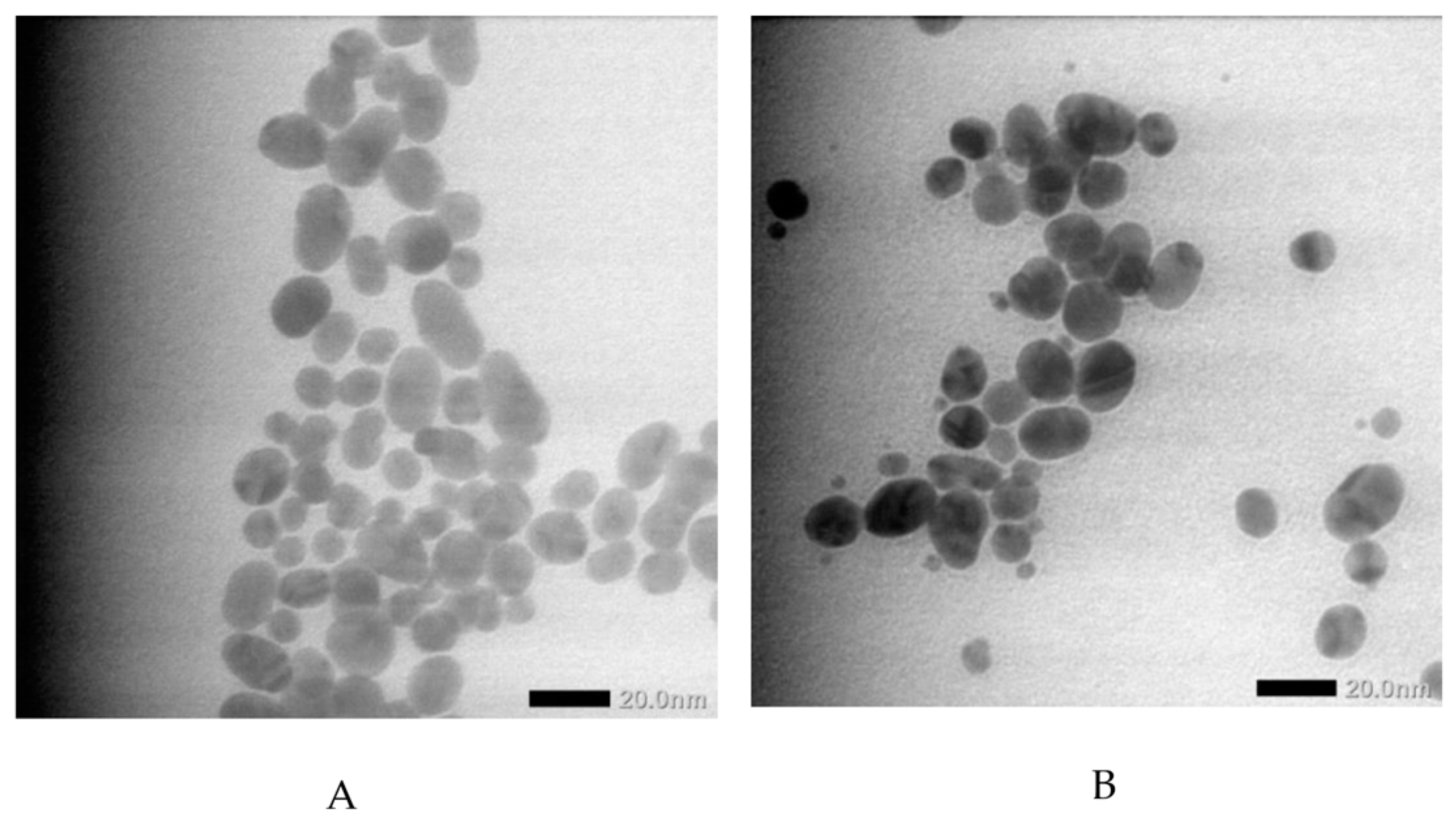
Figure 1 displays the ultraviolet-visible spectra of both AuNPs and GlcN-AuNPs, revealing a distinctive absorption band in the range of approximately 500-550 nm. The AuNPs (0%) showed an absorption band at 525 nm, this presence signifies the formation of AuNPs. The functionalized of GlcN-AuNPs in difference concentrations including 0.008%, 0.012%, 0.016%, 0.020%, and 0.024% (m/v) resulted the similar absorption bands at 525 nm, reflecting the similar size, shape, and surface of the nanoparticles. In addition, the morphology and particle size of AuNPs and GlcN-AuNPs were characterized by TEM. Both AuNPs and GlcN-AuNPs were found to have a spherical shape and exhibited an average size of less than 100 nm (
Figure 2).
3.2. Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 on an Endotracheal Tube
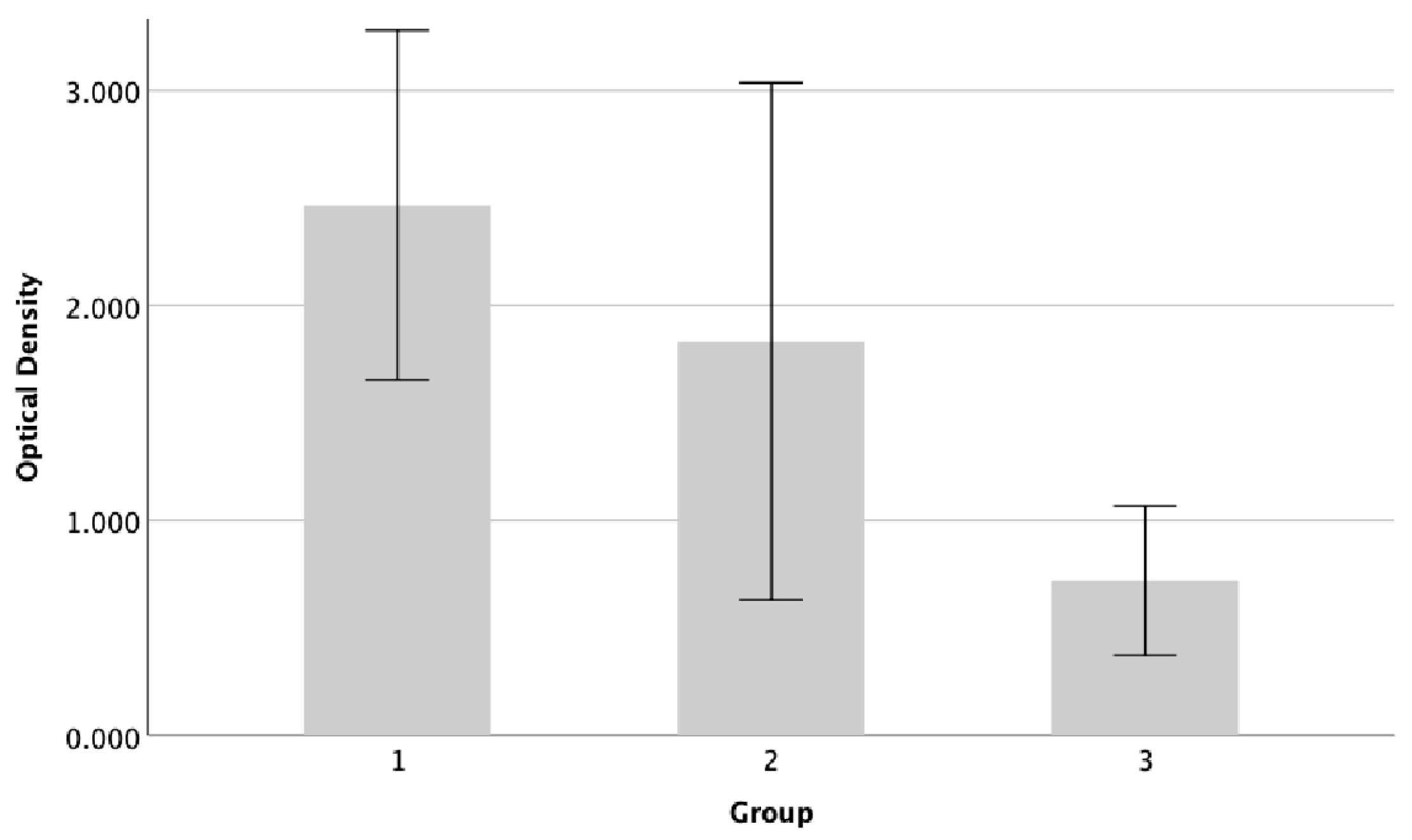
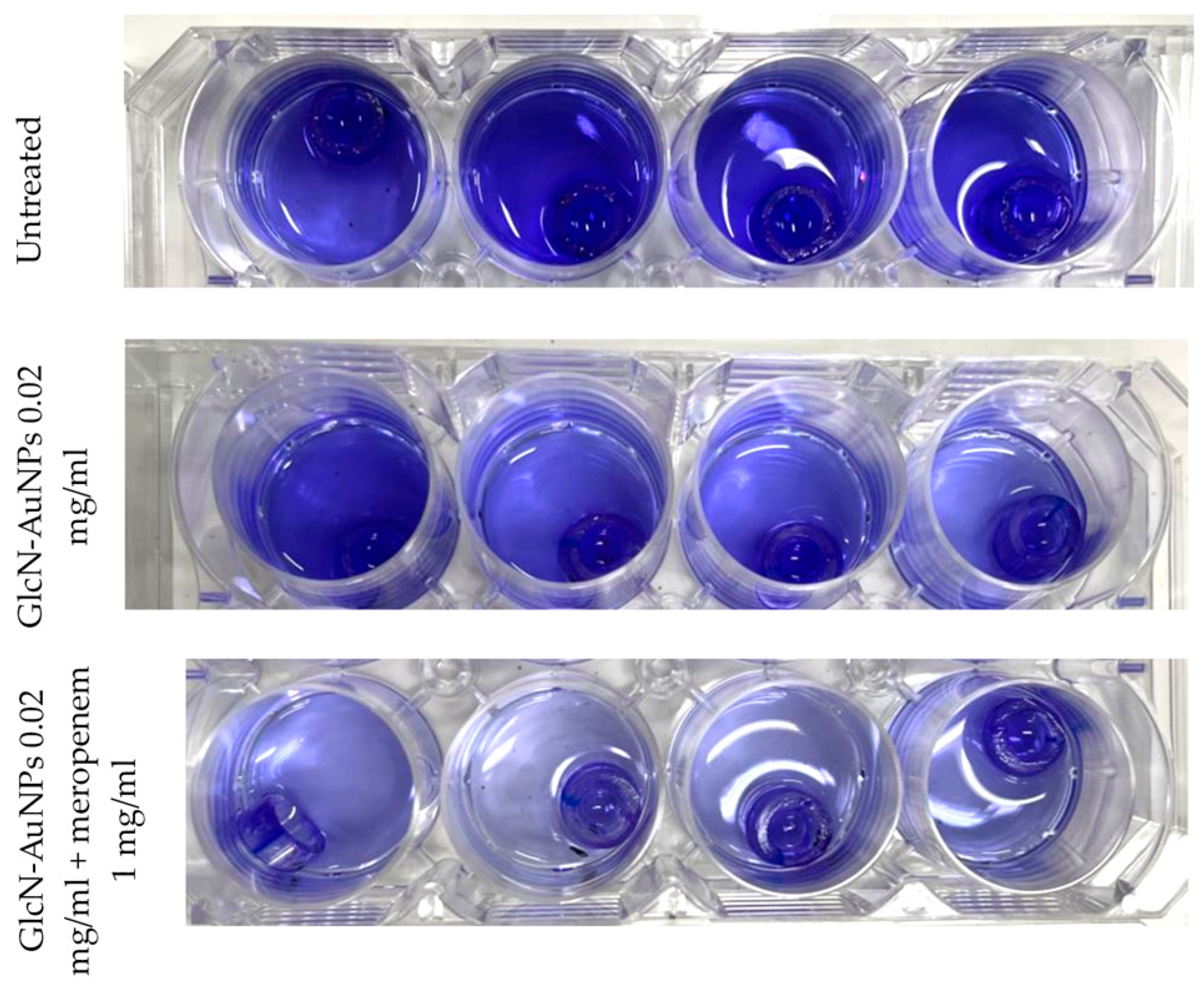
The detection of biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 on endotracheal tube pieces using tissue culture plate method shows different intensities among treatment groups (
Figure 3). In concordance with the interpretation of optical density results presented in
Table 3, the untreated group (first row) showing high intensity indicates strong biofilm production. After exposure to GlcN-AuNPs alone and in combination with meropenem (second and third row), the intensity of biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 was lower, exhibiting moderate biofilm production.
In addition, endotracheal tube pieces exposed to untreated Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 demonstrated biofilm production, with the biofilm manifesting as confluent sheets of cells within a dense extracellular matrix observed by scanning electron microscope (
Figure 4A). In contrast, the negative control tube containing Tripticase Soy Broth media showed no evidence of biofilm formation upon scanning electron microscopy examination (
Figure 4D).
Figure 4B displays the distribution of intact planktonic cells not covered by an extracellular matrix, indicating the inhibition of biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 after exposure to GlcN-AuNPs 0.02 mg/ml alone. The combination of GlcN-AuNPs 0.02 mg/ml and meropenem 1 mg/ml applied to the ETT pieces resulted in a simultaneous effect. The SEM image shows damage to planktonic cells, and the extracellular matrix sheet is absent (
Figure 4C).
3.3. Biofilm Inhibition Activities of GlcN-AuN, Both Alone and in Combination with Meropenem, against Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 on the Endotracheal Tube
The results demonstrated a decrease in biofilm production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 9027 on the endotrachael tube after exposure to either GlcN-AuNPs alone or in combination with meropenem (
Figure 4). The percentage of biofilm inhibition was 26% and 71% after exposure to GlcN-AuNPs alone and in combination with meropenem, respectively. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 exhibited the lowest level of biofilm formation, significantly decrease after exposure to the combination of GlcN-AuNPs and meropenem (p=0.001). The Tukey post hoc test revealed a significant decrease in the biofilm formation level of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 9027 when treated with the combination of GlcN-AuNPs and meropenem, compared to both the untreated group and those treated with GlcN-AuNPs alone (
Table 3).
Table 3.
Biofilm activity assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 treated with GlcN-AuNPs.
Table 3.
Biofilm activity assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 treated with GlcN-AuNPs.
| Group |
Replication |
OD |
Mean +SD |
Interpretation |
| Untreated |
1 |
1.863 |
2.466 +0.406a
|
Strong biofilm formation |
| 2 |
2.724 |
| 3 |
2.584 |
| 4 |
2.695 |
| GlcN-AuNPs 0.02 mg/ml |
1 |
2.618 |
1.832 +0.601a
|
Moderate biofilm formation |
| 2 |
1.887 |
| 3 |
1.648 |
| 4 |
1.176 |
| GlcN-AuNPs 0.02 mg/ml + meropenem 1 mg/ml |
1 |
0.908 |
0.720 +0.173b
|
Moderate biofilm formation |
| 2 |
0.533 |
| 3 |
0.620 |
| 4 |
0.819 |
Figure 4.
Biofilm forming activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027. The assessment of biofilm formation was conducted using the microtiter plate technique and staining with crystal violet. The graph displays the average + standard deviation of biofilm formation derived from three groups. Group 1=untreated; group 2=GlcN-AuNP 0.02 mg/ml; group 3=GlcN-AuNPs 0.02 mg/ml + meropenem 1 mg/ml.
Figure 4.
Biofilm forming activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027. The assessment of biofilm formation was conducted using the microtiter plate technique and staining with crystal violet. The graph displays the average + standard deviation of biofilm formation derived from three groups. Group 1=untreated; group 2=GlcN-AuNP 0.02 mg/ml; group 3=GlcN-AuNPs 0.02 mg/ml + meropenem 1 mg/ml.
4. Discussion
Ventilator-associated pneumonia is defined as pneumonia that develops after 48 hours patient undergoes mechanical ventilation via an ETT while in the hospital. The formation of a biofilm on the ETT significantly contributes to the occurrence of VAP [
9]. This type of pneumonia manifests in 25%-56% of all mechanically ventilated patients [
26].
Ventilator-associated pneumonia primarily arises from multidrug-resistant and extremely drug-resistant strains of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, resulting in heightened rates of treatment failure. Additionally, the effectiveness of antibiotics such as aminoglycosides, quinolones, and β-lactams are limited by the rapid formation of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms on the endotracheal tube surface. These microbial communities represent a crucial virulence factor of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa [
27,
28]. Biofilms created by
Pseudomonas aeruginosa establish conditions more conducive to bacterial persistence, as embedded bacteria pose greater challenges for elimination compared to their planktonic counterparts [
25].
Meropenem, belonging to the β-lactam antibiotics class, is regarded as one of the most effective therapeutic choices for addressing multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa [
25]. Nevertheless, there is a global trend of elevated carbapenem resistance observed among these organisms [
29].
Nanomaterials exhibiting heightened antimicrobial properties show potential as viable substitutes for conventional antibiotics. They offer a distinct advantage by circumventing prevalent antibiotic resistance strategies, as the mechanisms underlying most antibiotic resistance are not aligned with the pathways through which nanomaterials exert their effects [
30]. As mentioned earlier, the impact of nanomaterials in inhibiting biofilm formation encompasses various mechanisms such as physical disruption, surface modification, antimicrobial release, interference with quorum sensing, electrostatic interactions, mechanical stress, photothermal effects, and enzymatic degradation [
13,
14]. In addition, there have been reports on the synergistic effect of combining nano materials with antibiotics to prevent the biofilm formation [
20]. A prior study documented the benefit of antimicrobial and antibiofilm effect of meropenem and ZnO nanoparticles to protect the cornea rat model from pseudomonas-induced keratitis [
25].
To our knowledge, this study is the first to experiment with synthesizing glucosamine phosphate with gold nanoparticles (GlcN-AuNPs) and applying it simultaneously with meropenem to inhibit biofilm formation on the endotracheal tube. Gold nanoparticles are widely recognized for their significant potential in various biomedical applications such as drug delivery, imaging, and diagnostics. Specifically, AuNPs have been extensively studied and investigated for their versatility in these fields including their ease of preparation, surface reactivity, and unique optical properties [
31]. Gold is acknowledged as a non-toxic nanomaterial; however, the substances employed in its preparation and modification may have toxic properties. This toxicity tends to become apparent when the concentration of gold nanoparticles is elevated. Despite this, AuNPs exhibit notable antibacterial effects. At specific concentrations, these nanoparticles do not display toxic effects on normal cells [
16]. In addition, the small size of AuNPs, along with their biocompatibility, minimal toxicity, and the potential for the simultaneous assembly of various molecular functionalities, renders them appealing for biomedical applications in therapy and sensing [
31].
In this study, we observed the biofilm inhibition effect of AuNPs conjugated with glucosamine phosphate against
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 on the endotracheal tube. This finding is consistent with a previous study that highlighted the effectiveness of AuNPs in combating biofilm-related infections caused by
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 [
32]. Simultaneously, all experimental indications suggest a crucial role played by the glucose subunit found in glucosamine phosphate [
33]. This sugar stimulates the generation of intracellular NAG-6-P that would inactivate the regulator NagC causing a decrease in biofilm formation [
34].
Moreover, this study illustrated the synergistic impact of GlcN-NPs and meropenem in restraining the formation of biofilm by
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 on the endotracheal tube. The biofilm inhibition rate was nearly threefold greater when exposed to the combination of GlcN-NPs and meropenem compared to GlcN-NPs alone. The collaboration between nanomaterials and antibiotics could potentially contribute to enhancing the activity of biofilm inhibition against
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 [
25]. Nevertheless, additional research is warranted to explore the influence of GlcN-NPs in conjunction with meropenem on clinical
Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates, particularly those derived from lower respiratory specimens of mechanically ventilated patients.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our study highlights the potential for employing combination therapies involving nanomaterials and antibiotics, as opposed to relying solely on antibiotics. This approach aims to mitigate the risk of increased resistance, thereby reducing the likelihood of elevated morbidity and mortality resulting from treatment failures. Our findings underscore the enhanced antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy achieved with the combination of GlcN-NPs and meropenem, presenting a successful strategy to counter the emerging resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to carbapenems.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, D.S. and A.B.; methodology, D.S. and A.B; formal analysis, D.S.; investigation, R.F.P., Y.M., S.P., L.D., H.A., and Y.L.N; resources, D.S. and A.B.; data curation, D.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.S. and Y.M; writing—review and editing, D.S., A.B., R.F.P., Y.M.; supervision, D.S. and A.B,; project administration, D.S.; funding acquisition, D.S. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research and the APC was funded by PROGRAM PENELITIAN KOLABORASI INDONESIA - 21 PTNBH TAHUN ANGGARAN 2023 (Brawijaya University, grant number 801.12/UN10.C10/TU/2023).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were not applicable due to not involving humans or animals.
Data Availability Statement
The data from this study are available upon request from the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the Dean of Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Brawijaya, Malang, Indonesia, and the Head of Laboratory of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Brawijaya, Malang, Indonesia who facilitated our study.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no conflict of interest reported by any of the authors in relation to this article.
References
- Mulcahy, L. R.; Isabella, V. M.; Lewis, K. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms in Disease. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmawati, D.; Fahmi, M. Z.; Abdjan, M. I.; Wasito, E. B.; Siswanto, I.; Mazlan, N.; Rohmah, J.; Baktir, A. In Vitro Assessment on Designing Novel Antibiofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Using a Computational Approach. Molecules 2022, 27, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenke, P.; Köves, B.; Nagy, K.; Hultgren, S. J.; Mendling, W.; Wullt, B.; Grabe, M.; Wagenlehner, F. M. E.; Cek, M.; Pickard, R.; Botto, H.; Naber, K. G.; Johansen, T. E. B. Update on Biofilm Infections in the Urinary Tract. World J. Urol. 2012, 30, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, M. T. T.; Wibowo, D.; Rehm, B. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shineh, G.; Mobaraki, M.; Perves Bappy, M. J.; Mills, D. K. Biofilm Formation, and Related Impacts on Healthcare, Food Processing and Packaging, Industrial Manufacturing, Marine Industries, and Sanitation–A Review. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 629–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejnickova, K.; Hola, V.; Ruzicka, F. Catheter-Related Infections Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Virulence Factors Involved and Their Relationships. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 72, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerioli, M.; Batailler, C.; Conrad, A.; Roux, S.; Perpoint, T.; Becker, A.; Triffault-Fillit, C.; Lustig, S.; Fessy, M. H.; Laurent, F.; Valour, F.; Chidiac, C.; Ferry, T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Implant-Associated Bone and Joint Infections: Experience in a Regional Reference Center in France. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotterbeekx, A.; Xavier, B. B.; Bielen, K.; Lammens, C.; Moons, P.; Schepens, T.; Ieven, M.; Jorens, P. G.; Goossens, H.; Kumar-Singh, S.; Malhotra-Kumar, S. The Endotracheal Tube Microbiome Associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, Z.; Hamad, A. A.; Sheikh, A. F.; Khosravi, N. A.; Fard, S. S.; Motahar, M.; Mehr, F. J.; Abbasi, F.; Meghdadi, H.; Bakhtiyariniya, P.; Heydari, R.; Moradi, M.; Dezfuli, A. A. Z. The Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance of Bacterial Profile from Endotracheal Tube of Patients Admitted to Intensive Care Unit in Southwest of Iran. PLoS One. 2022, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S. D.; Schwartz, S. A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganism, 2023; 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanya, D. R. A.; Onésime, D.; Vizzarro, G.; Jacquier, N. Recent Advances in Therapeutic Targets Identification and Development of Treatment Strategies towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital-Lopez, F. G.; Reifman, J.; Wallqvist, A. Biofilm Formation Mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Predicted via Genome-Scale Kinetic Models of Bacterial Metabolism. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H. M.; Tran, H.; Booth, M. A.; Fox, K. E.; Nguyen, T. H.; Tran, N.; Tran, P. A. Nanomaterials for Treating Bacterial Biofilms on Implantable Medical Devices. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pericolini, E.; Colombari, B.; Ferretti, G.; Iseppi, R.; Ardizzoni, A.; Girardis, M.; Sala, A.; Peppoloni, S.; Blasi, E. Real-Time Monitoring of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Formation on Endotracheal Tubes in Vitro. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles: A Novel Nanomaterial for Various Medical Applications and Biological Activities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Huang, K.; Li, H. H.; Lu, Y. G.; Zheng, D. L. Antibacterial Properties of Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles and Their Application in Oral Biology. J. Nanomater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine: Recent Advances and Prospects. Acta Naturae 2011, 3, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiben, V.; Yamada, C. H.; Telles, J. P.; De Andrade, A. P.; Arend, L. N. V. S.; Ribeiro, V. S. T.; Dantas, L. R.; Suss, P. H.; Tuon, F. F. A Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Outbreak Associated with a Polymyxin Shortage during the COVID Pandemic: An in Vitro and Biofilm Analysis of Synergy between Meropenem, Gentamicin and Sulbactam. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşkın Kafa, A. H.; Hasbek, M. Synergistic Efficacy of Meropenem, Ciprofloxacin and Colistin Antibiotics against Planktonic and Biofilm Forms of Myroides odoratimimus Bacterial Isolates. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 40, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Buitimea, A.; Garza-Cárdenas, C. R.; Román-García, M. F.; Ramírez-Díaz, C. A.; Ulloa-Ramírez, M.; Morones-Ramírez, J. R. Nanomaterials-Based Combinatorial Therapy as a Strategy to Combat Antibiotic Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. Adsorbed Tween 80 Is Unique in Its Ability to Improve the Stability of Gold Nanoparticles in Solutions of Biomolecules. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2114–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, S.; Ramasamy, M.; Baskaran, R.; Ahn, S. J.; Yun, K. Ultraviolet Light and Laser Irradiation Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Glucosamine-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harika, K.; Shenoy, V.; Narasimhaswamy, N.; Chawla, K. Detection of Biofilm Production and Its Impact on Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Bacterial Isolates from Chronic Wound Infections. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2020, 12, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedan, S.; Shubair, Z.; Almaaytah, A. Synergism of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptide WLBU2 with Antibacterial Agents against Biofilms of Multi-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Telbany, M.; Mohamed, A. A.; Yahya, G.; Abdelghafar, A.; Abdel-Halim, M. S.; Saber, S.; Alfaleh, M. A.; Mohamed, A. H.; Abdelrahman, F.; Fathey, H. A.; Ali, G. H.; Abdel-Haleem, M. Combination of Meropenem and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles; Antimicrobial Synergism, Exaggerated Antibiofilm Activity, and Efficient Therapeutic Strategy against Bacterial Keratitis. Antibiotics 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ling, X.; Liu, G.; Xiao, J. Antimicrobial Coating: Tracheal Tube Application. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, B.; Fernández-Barat, L.; Di Domenico, E. G.; Marín, M.; Cercenado, E.; Merino, I.; de Pablos, M.; Muñoz, P.; Guembe, M. Characterization of the Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Causing Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B. R.; Lin, T. J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and Alternative Therapeutic Strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çiçek, A. Ç.; Ertürk, A.; Ejder, N.; Rakici, E.; Kostakoğlu, U.; Yıldız, İ. E.; Özyurt, S.; Sönmez, E. Screening of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Epidemiological Features in Hospital and Community-Associated Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The Antimicrobial Activity of Nanoparticles: Present Situation and Prospects for the Future. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gómez, P.; Pérez de la Lastra Aranda, C.; Tosat-Bitrián, C.; Bueso de Barrio, J. A.; Thompson, S.; Sot, B.; Salas, G.; Somoza, Á.; Espinosa, A.; Castellanos, M.; Palomo, V. Nanomedical Research and Development in Spain: Improving the Treatment of Diseases from the Nanoscale. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. G.; Ansari, M. A.; Alzohairy, M. A.; Alomary, M. N.; Alyahya, S.; Jalal, M.; Khan, H. M.; Asiri, S. M. M.; Ahmad, W.; Mahdi, A. A.; El-Sherbeeny, A. M.; El-Meligy, M. A. Biogenic Gold Nanoparticles as Potent Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Nano-Antibiotics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, Á.; Lyu, Y.; Mancin, F.; Scrimin, P. Glucosamine Phosphate Induces AuNPs Aggregation and Fusion into Easily Functionalizable Nanowires. Nanomaterials 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicard, J. F.; Vogeleer, P.; Le Bihan, G.; Rodriguez Olivera, Y.; Beaudry, F.; Jacques, M.; Harel, J. N-Acetyl-Glucosamine Influences the Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).