Submitted:
08 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
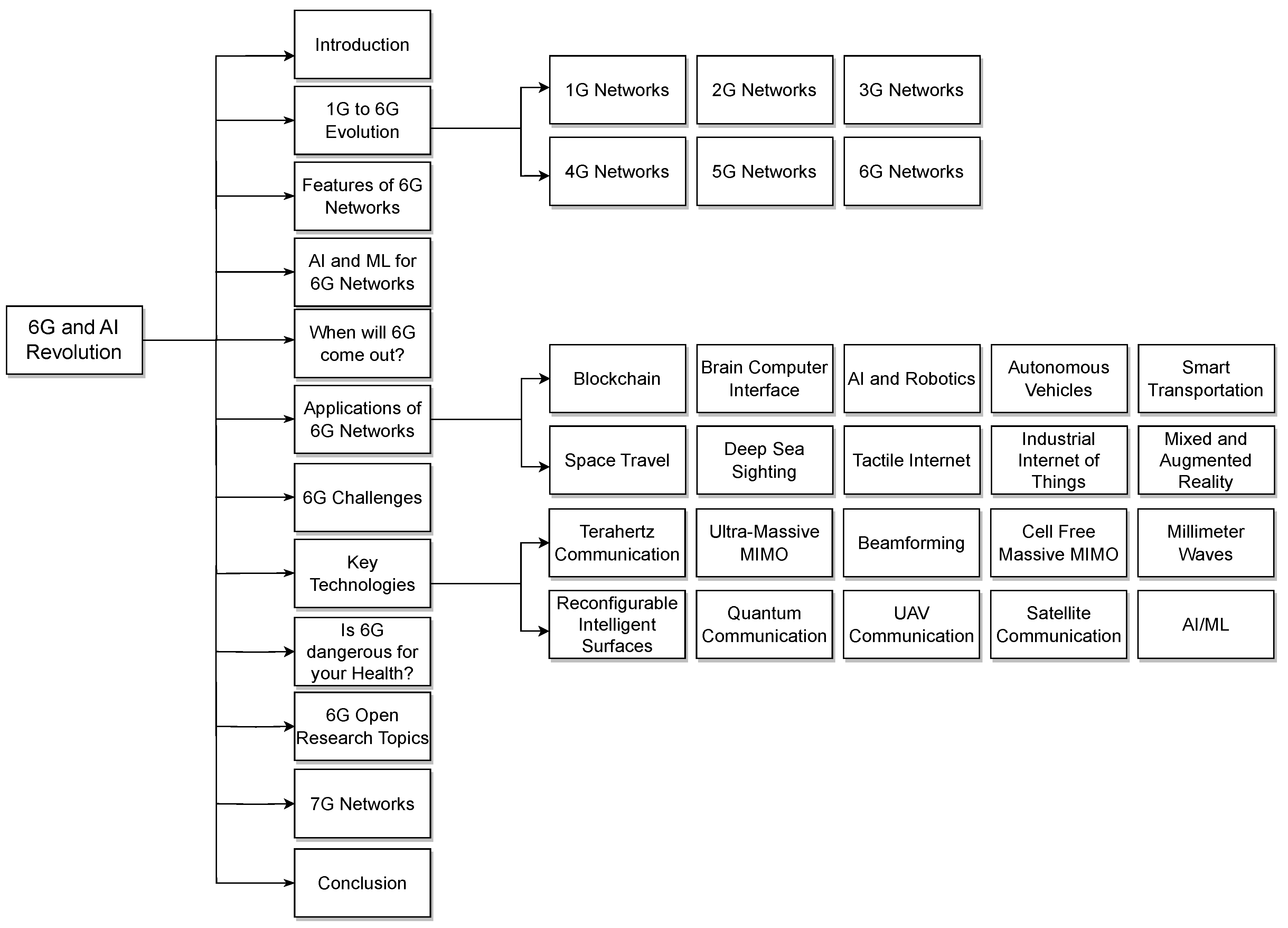
2. Evolution from 1G to 6G Networks
2.1. 1G
2.2. 2G
2.3. 3G
2.4. 4G
2.5. 5G
2.6. 6G

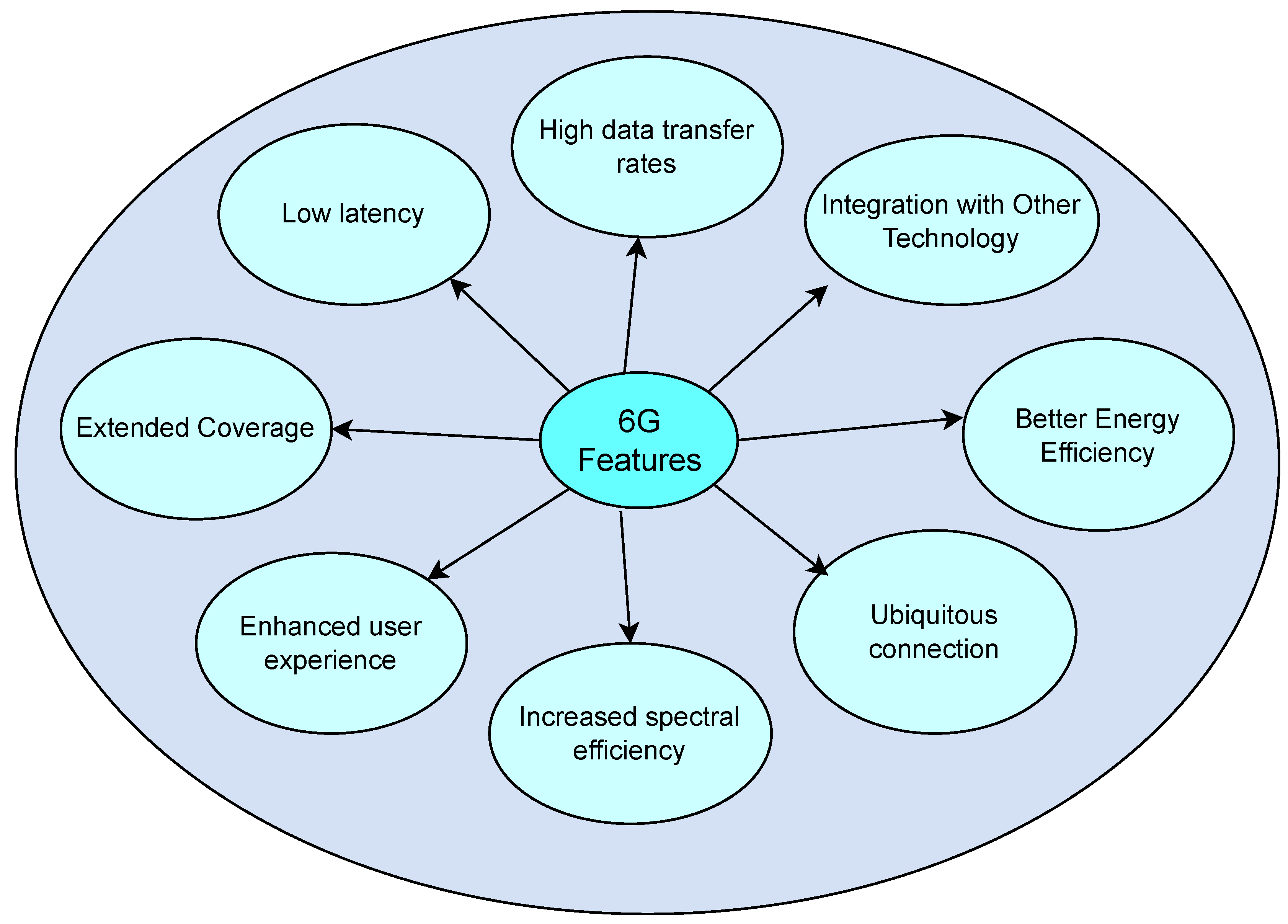
3. Features of 6G
- High data transfer rates: 6G networks are expected to bring tremendous advancements in terms of data transfer speeds, with the potential to reach up to 10 Tbps. This represents a significant increase when compared to the current data transfer speed set for 5G networks, which is 10 Gbps [36].
- Low latency: 6G networks are expected to provide ultra-low latency, potentially reaching as low as 0.1 ms, which is a significant improvement over the latency of 5G networks with latency requirement of 1 ms [37].
- Extended coverage: 6G networks are expected to have an extended coverage range, potentially reaching deep-sea, space, and underground areas. This would enable the use of new applications such as deep-sea sightseeing, space travel, and industrial internet [38].
- Enhanced user experience: 6G networks are projected to enhance the user experience by amplifying the capabilities of extended reality, augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence [39].
- Increased spectral efficiency: 6G networks are expected to offer spectral and network efficiency ten times greater than that of 5G networks [40].
- Ubiquitous connection: 6G networks are expected to provide enormous broadcasting data and support more than 1 million connections, which is a hundred times more than current 5G networks [41].
- Better energy efficiency: 6G networks are expected to have an optimized energy consumption, resulting in longer battery life, making it more sustainable and efficient to use [42].
- Integration with other technology: Anticipated integration of 6G networks involves seamless incorporation with other technologies such as the likes of IoT, cloud computing, and big data analytics, ensuring efficient connections across various systems [43].
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for 6G Networks
5. When Will 6G Come Out?
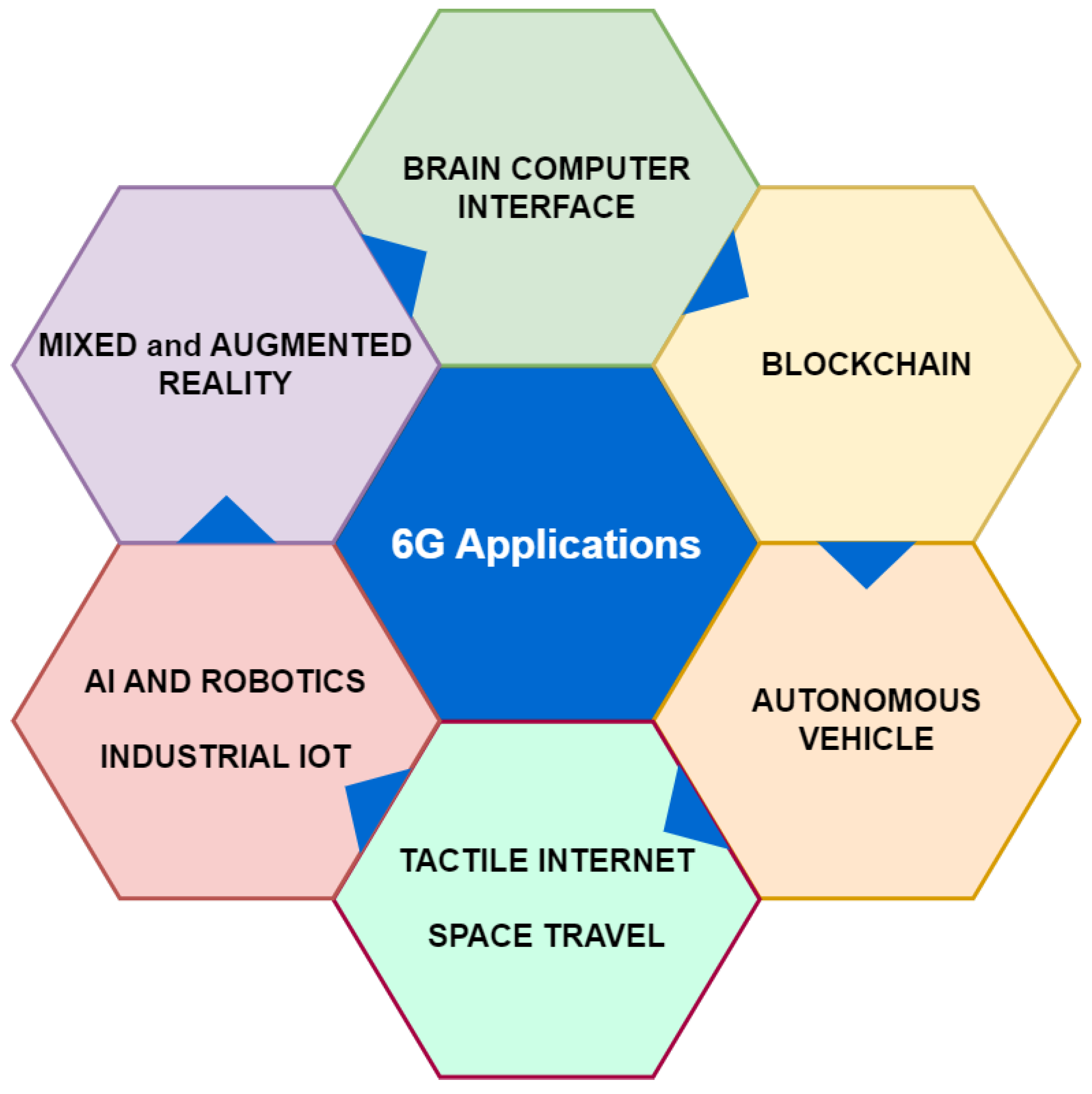
6. Applications of 6G Network
6.1. Brain-Computer Interfaces
6.2. Blockchain
6.3. Space Travel
6.4. Deep Sea Sightseeing
6.5. Tactile Internet
6.6. Industrial Internet of Thing
6.7. Mixed and Augmented Reality
6.8. Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
6.9. Autonomous Vehicles and Smart Transportation Systems
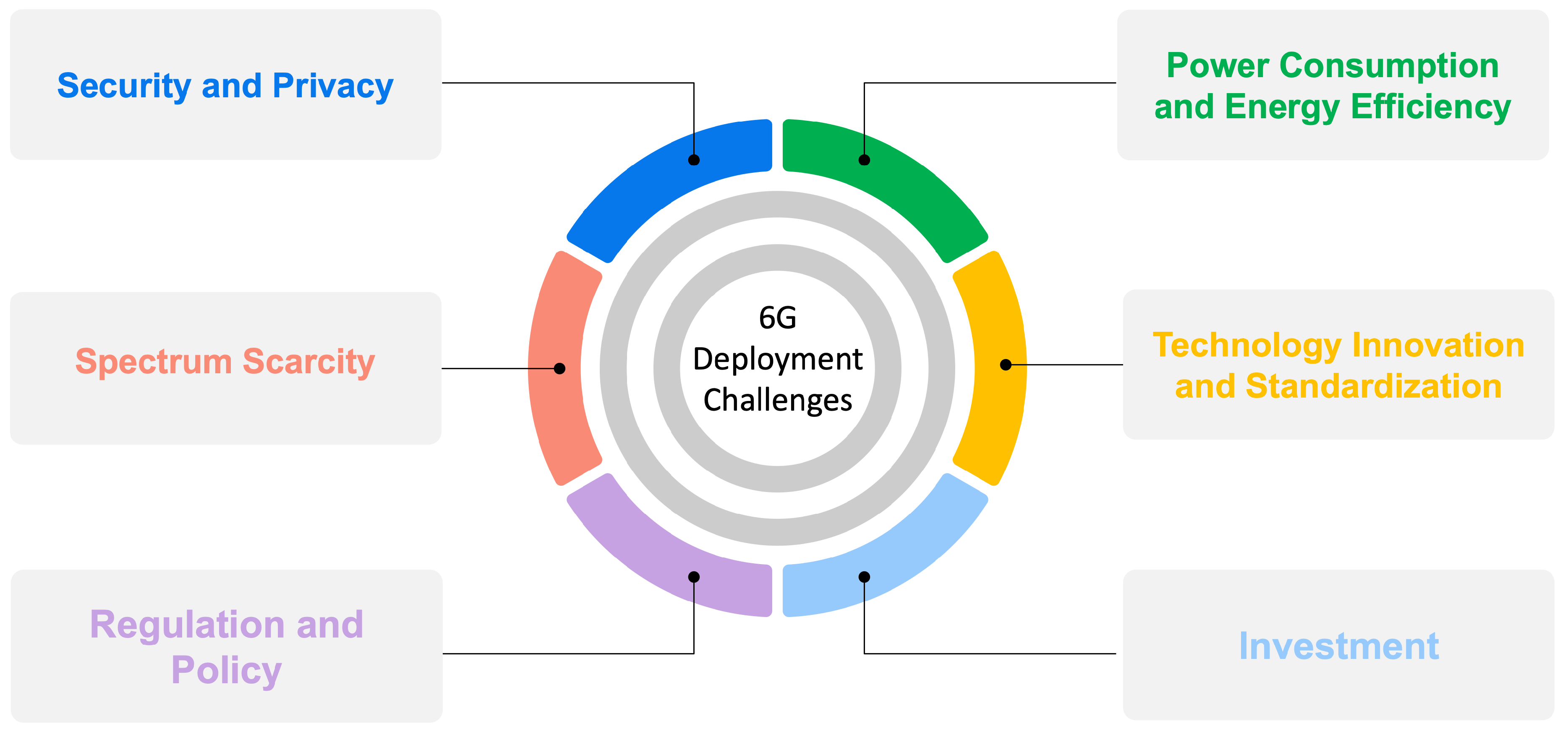
7. Challenges for 6G Deployment
- Technology Innovation and Standardization Technical difficulties in implementing new enabling technologies like millimeter- and terahertz-wave communication, massive and ultra-massive MIMO, artificial intelligence, machine learning, quantum communication, and ultra-reliable low-latency communication [75].
- Bandwidth Scarcity Identifying and allocating sufficient spectrum in the Terahertz (THz) frequency range for 6G is a significant challenge. THz frequencies offer the potential for high data rates but come with propagation challenges and require new regulatory frameworks [76].
- Interoperability with Existing Networks: Ensuring interoperability between different technologies across various industries and use cases is a complex challenge as many other networks use different standards and protocols [77].
- Investment Cost The deployment of 6G infrastructure is expected to be cost-intensive, requiring substantial investments in advanced technologies, equipment, and infrastructure. This might pose a financial challenge for network operators and end-users. This financial burden could hinder the broad adoption of 6G, especially in less economically developed regions and remote rural areas [78].
- Regulation and Policy Regulatory issues may arise due to new spectrum, and technologies used, necessitating developing and implementing new policies and regulations [79].
- Power consumption Power consumption is another concern, as the increased data rates and the number of devices connected to the network will result in higher power usage. Sharing spectrum and infrastructure, implementing cell-free massive MIMO, and integrating communication and sensing are all pivotal aspects. Yet, the paramount transformation with 6G lies in the shift to higher frequencies, surpassing the 100 GHz threshold [80].
- International Collaboration and Harmonization The competitive landscape, with multiple companies and countries vying to be the first to launch and deploy 6G. Promoting collaboration and harmonization of 6G standards and regulations on a global scale is crucial to ensure the success and widespread adoption of 6G technology will be challenging.
- Security and Privacy There will be new security concerns as the network will transmit large amounts of sensitive data. Besides increasing connectivity and integrating various devices and systems, security and privacy will be a significant challenge [81].
- Environmental Concerns The production of 6G infrastructure requires various raw materials, including rare earth metals and minerals. The extraction processes can have environmental and social impacts, contributing to habitat destruction, pollution, and resource depletion [82].
8. Key Technologies for 6G Deployment
8.1. Terahertz Communication
8.2. Ultra-Massive MIMO
8.3. Beamforming
8.4. Cell-Free Massive MIMO
8.5. Millimeter Waves:
8.6. Re-Configurable Intelligent Surfaces
8.7. Quantum Communication
8.8. UAV/Satellite Communication
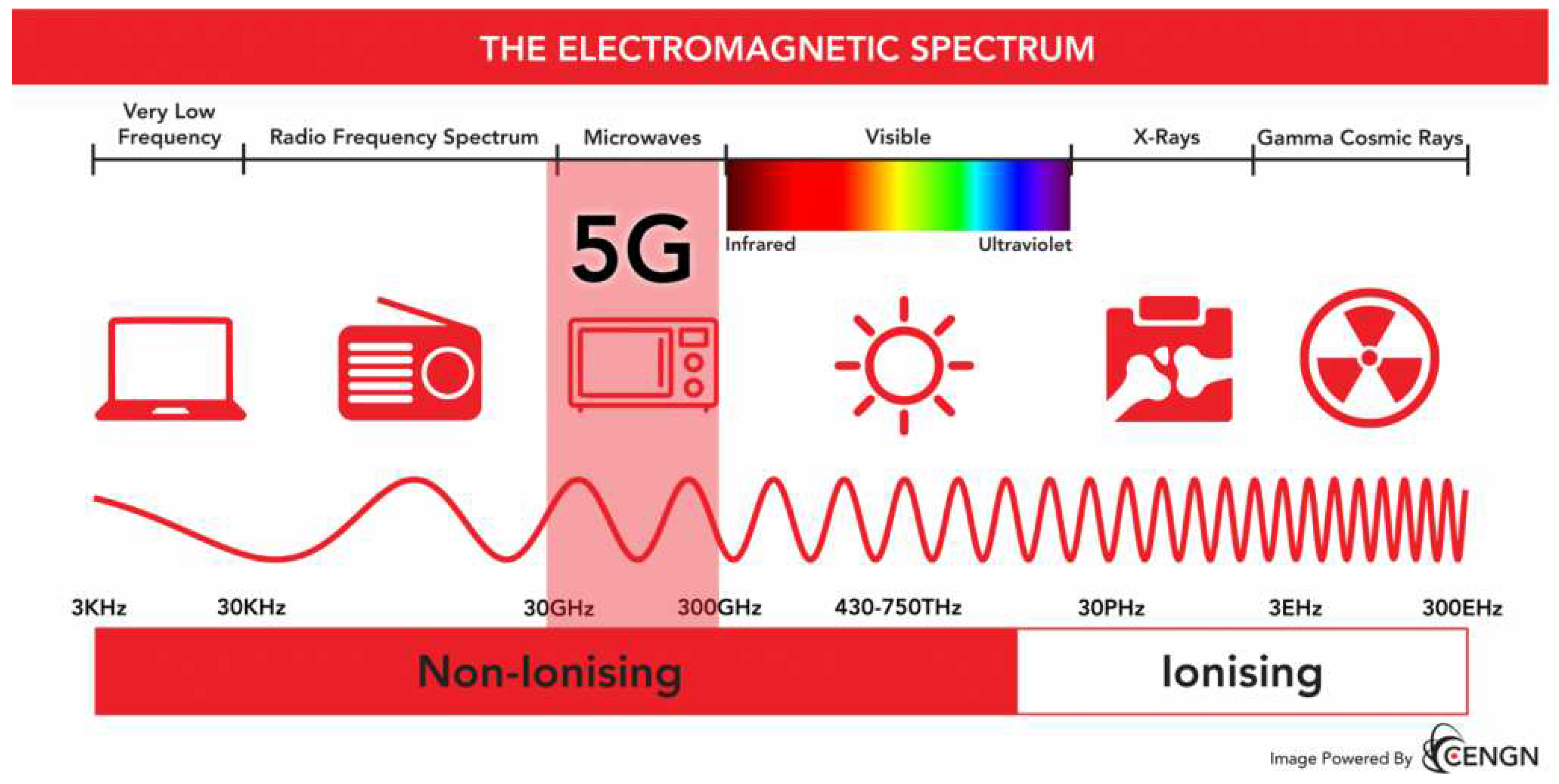
9. Is 6G Dangerous for Your Health?
10. Open Research Topics
- (1)
- Investigation into Advanced Modulation and Coding Schemes: Research is needed on new schemes adapted for the high frequency bands and extensive bandwidths of 6G. This includes studying techniques for enhanced spectrum utilization and improved data throughput, critical for reliable communication in various environments.
- (2)
- Seamless Integration of Satellite and Terrestrial Networks: There is a significant opportunity for research in the integration of satellite and terrestrial networks. This requires the development of new protocols and architectures to facilitate efficient network handover and connectivity, especially in remote areas.
- (3)
- Application of Artificial Intelligence in Network Performance:There is a wide scope for using AI to optimize 6G network operations. Research areas include predictive analytics, congestion management, and adaptive resource allocation based on real-time network conditions.
- (4)
- Development of Energy-Efficient Solutions in 6G Networks: As the number of connected devices grows, research into energy-efficient technologies for 6G networks becomes imperative. This involves creating low-power hardware solutions and sustainable network operation methods.
- (5)
- Enhancing Security and Privacy in 6G Networks: There is a pressing need for research into advanced security and privacy measures. This includes the development of new encryption techniques, secure communication protocols, and methods to ensure data privacy in an interconnected environment.
- (6)
- Exploration of Quantum Communication in 6G: Research into the application of quantum communication within 6G networks offers potential for secure and efficient data transmission. This includes studies on quantum key distribution, entanglement, and integration with existing telecommunications infrastructure.
- (7)
- Identifying and Developing New Applications and Services: There is a need for research into applications that exploit the capabilities of 6G, such as advanced virtual/augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and smart city infrastructure, to unlock new possibilities and services.
- (8)
- Research on Network Slicing and Customization: Investigating network slicing as a method for providing tailored network services is a promising research area. This includes studies on resource allocation, network functionality customization, and quality of service optimization for different applications.
- (9)
- Achieving Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication: Focusing on URLLC in 6G is crucial for supporting critical applications like remote healthcare and industrial automation. Research is needed to minimize latency, enhance reliability, and ensure consistent service quality.
11. 7G Networks
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
| AMPS | Advanced Mobile Phone System |
| TACS | Total Access Communication System |
| NMT | Nordic Mobile Telephone |
| SMS | Short Message Service |
| PDC | Personal Digital Cellular |
| WCDMA | Wideband Code Division Multiple Access |
| MMS | Multimedia Message Support |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| RIS | Re-configurable Intelligent Surfaces |
References
- Bangerter, B.; Talwar, S.; Arefi, R.; Stewart, K. Networks and Devices for the 5G Era. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU). IMT Traffic Estimates for the Years 2020 to 2030. Available online: https://www.itu.int/pub/r-rep-m.2370. (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Sinclair, M.; Maadi, S.; Zhao, Q.; Hong, J.; Ghermandi, A.; Bailey, N. Assessing the Socio-Demographic Representativeness of Mobile Phone Application Data. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 158, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, P.; Dürr, F.; Rothermel, K. TOMP: Opportunistic Traffic Offloading Using Movement Predictions. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Clearwater Beach, FL, USA; 2012; pp. 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseien, G.F.; Shah, K.W. A Review on 5G Technology for Smart Energy Management and Smart Buildings in Singapore. Energy AI 2022, 7, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, A.; Nencioni, G. The Role of 5G Technologies in a Smart City: The Case for Intelligent Transportation System. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataria, H.; Shafi, M.; Molisch, A.F.; Dohler, M.; Sjöland, H.; Tufvesson, F. 6G Wireless Systems: Vision, Requirements, Challenges, Insights, and Opportunities. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1166–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murroni, M.; Anedda, M.; Fadda, M.; Ruiu, P.; Popescu, V.; Zaharia, C.; Giusto, D. 6G—Enabling the New Smart City: A Survey. Sensors 2023, 23, 7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banafaa, M.; Shayea, I.; Din, J.; Hadri Azmi, M.; Alashbi, A.; Ibrahim Daradkeh, Y.; Alhammadi, A. 6G Mobile Communication Technology: Requirements, Targets, Applications, Challenges, Advantages, and Opportunities. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 64, 245–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M.T.R. Insights. AI-Powered 6G Networks Will Reshape Digital Interactions. Available online: https://www.technologyreview.com/2023/10/26/1082028/ai-powered-6g-networks-will-reshape-digital-interactions/ (accessed on 29 October 2023).
- Singh, P.R.; Singh, V.K.; Yadav, R.; Chaurasia, S.N. 6G Networks for Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Smart Cities Applications: A Scoping Review. Telemat. Informatics Rep. 2023, 9, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Alsabah et al. 6G Wireless Communications Networks: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 148191–148243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quy, V.K.; Chehri, A.; Quy, N.M.; Han, N.D.; Ban, N.T. Innovative Trends in the 6G Era: A Comprehensive Survey of Architecture, Applications, Technologies, and Challenges. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 39824–39844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. F. M. Shahen Shah, "A Survey From 1G to 5G Including the Advent of 6G: Architectures, Multiple Access Techniques, and Emerging Technologies," 2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2022; pp. 1117-1123. [CrossRef]
- Chataut, R.; Akl, R. Massive MIMO Systems for 5G and Beyond Networks—Overview, Recent Trends, Challenges, and Future Research Direction. Sensors 2020, 20, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serôdio, C.; Cunha, J.; Candela, G.; Rodriguez, S.; Sousa, X.R.; Branco, F. The 6G Ecosystem as Support for IOE and Private Networks: Vision, Requirements, and Challenges. Future Internet 2023, 15, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbank, J.L.; Andrusenko, J.; Everett, J.S.; Kasch, W.T. M. Second-Generation (2G) Cellular Communications. In Wireless Networking: Understanding Internetworking Challenges; IEEE: 2013; pp. 250-365. [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.K.; Halpern, S.; Smolik, K.F. Third Generation (3G) Mobile Communications Systems. In 1999 IEEE International Conference on Personal Wireless Communications (Cat. No.99TH8366); Jaipur, India, 1999; pp. 39-43. [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; From 1G to 5G: The Evolution of Mobile Communications. Mpirical, 11 August 2023. Available online: https://www.mpirical.com/blog/the-evolution-of-mobile-communication. (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Central Intelligence Agency. Central Intelligence Agency. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/telecommunication-systems. (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Vergados, D.D.; Panoutsakopoulos, A.; Douligeris, C. Group Registration with Distributed Databases for Location Tracking in 3G Wireless Networks. Comput. Networks 2008, 52, 1521–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlman, E.; Parkvall, S.; Sköld, J. Introduction. In 4G, LTE Evolution and the Road to 5G, 2016, pp. 1–5. Available online. [CrossRef]
- Lopa, V. Evolution of Mobile Generation Technology: 1G to 5G and Review of Upcoming Wireless Technology 5G. Int. J. Mod. Trends Eng. Res. 2015, 2, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Deepender, Manoj; Shrivastava, U.; Verma, J.K. A Study on 5G Technology and Its Applications in Telecommunications. In 2021 International Conference on Computational Performance Evaluation (ComPE); Shillong, India, 2021; pp. 365-371. [CrossRef]
- Guevara, L.; Auat Cheein, F. The Role of 5G Technologies: Challenges in Smart Cities and Intelligent Transportation Systems. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasralla, M.M.; Khattak, S.B.; Ur Rehman, I.; Iqbal, M. Exploring the Role of 6G Technology in Enhancing Quality of Experience for M-Health Multimedia Applications: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2023, 23, 5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Lin, X.; Di, B.; Zhang, H.; Hernando, F.J.; Tan, A.S.; Mumtaz, S.; Demir, Ö.T.; Chen-Hu, K. Technology Trends for Massive MIMO towards 6G. Sensors 2023, 23, 6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y. A Comprehensive Study of 5G and 6G Networks. In 2021 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Smart Grid (ICWCSG); Hangzhou, China, 2021; pp. 321-326. [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.H.; Nordin, R. Evolution towards Fifth Generation (5G) Wireless Networks: Current Trends and Challenges in the Deployment of Millimetre Wave, Massive MIMO, and Small Cells. Telecommun. Syst. 2016, 64, 617–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.N.; Ahmad, A.R.; Qassim, Q.S.; Natiq, H.; Subhi, M.A.; Mahmoud, M. From 5G to 6G Technology: Meets Energy, Internet-of-Things, and Machine Learning: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman Yarali. "Networks of the Future." In From 5G to 6G: Technologies, Architecture, AI, and Security; IEEE: 2023, pp. 21-52. [CrossRef]
- Kommadi, B. (2023). AI and ML Applications: 5G and 6G. 5G and 6G Enhanced Broadband Communications [Working Title]. [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.S.; 5G 90% More Energy Efficient than 4G, Nokia and Telefónica Find. Smart Energy International, 5 May 2021. Available online: https://www.smart-energy.com/digitalisation/5g-90-more-energy-efficient-than-4g-nokia-and-telefonica-find/ (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Kshirsagar, P.R.; Reddy, D.H.; Dhingra, M.; Dhabliya, D.; Gupta, A. A Review on Comparative Study of 4G, 5G, and 6G Networks. In 2022 5th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I); Uttar Pradesh, India, 2022; pp. 1830-1833. [CrossRef]
- Rekkas, V.P.; Sotiroudis, S.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Wan, S.; Karagiannidis, G.K.; Goudos, S.K. Machine Learning in Beyond 5G/6G Networks—State-of-the-Art and Future Trends. Electronics 2021, 10, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimachia, K.; Staff, T.; Clarke, M.; McQuarrie, K.; Millares, L.; Azhar, A.; Abbott, B. 5G vs 6G: What’s the Difference? TechRepublic, 23 February 2023. Available online: https://www.techrepublic.com/article/5g-vs-6g/ (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Adhikari, M.; Hazra, A. 6G-Enabled Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication in Edge Networks. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2022, 6, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokazono, Y.; Kohara, H.; Kishiyama, Y.; Asai, T. Extreme Coverage Extension in 6G: Cooperative Non-terrestrial Network Architecture Integrating Terrestrial Networks. In 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC); Austin, TX, USA, 2022; pp. 138-143. [CrossRef]
- Insights, M.T. R.; (2023a, October 26). AI-powered 6G networks will reshape digital interactions. Available online: https://www.technologyreview.com/2023/10/26/1082028/ai-powered-6g-networks-will-reshape-digital-interactions/ (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Jain, P.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, N.; Guizani, M. Dynamic and Efficient Spectrum Utilization for 6G With THz, mmWave, and RF Band. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 3264–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 6G Flagship. Key Drivers and Research Challenges for 6G Ubiquitous Wireless Intelligence. Available online: https://www.6gflagship.com/key-drivers-and-research-challenges-for-6g-ubiquitous-wireless-intelligence/ (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Ansere, J.A.; Kamal, M.; Khan, I.A.; Aman, M.N. Dynamic Resource Optimization for Energy-Efficient 6G-IoT Ecosystems. Sensors 2023, 23, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Du, Q.; Lu, L.; Zhang, S. Overview of the Integration of Communications, Sensing, Computing, and Storage as Enabling Technologies for the Metaverse over 6G Networks. Electronics 2023, 12, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5G/6G Wireless Networks. 5G/6G | Homeland Security. Available online: https://www.dhs.gov/science-and-technology/5g6g (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Ubiquitous 6G: China already head start? INTEGRAL Website (EN). Available online: https://www.integralnewenergy.com/?p=31920 (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Huawei started research on 6G ‘A long time ago’, CEO says. Available online: https://www.rcrwireless.com/20190930/5g/huawei-started-research-6g-long-time-ago-ceo-says (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Times, G.; China Ramping up Research into 6G. Global Times. Available online: https://www.globaltimes.cn/content/1188617.shtml (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Tomás, J.P.; LG to Focus on 6G Research with Partnership with Keysight Technologies. RCR Wireless News, 8 April 2021. Available online: https://www.rcrwireless.com/20210408/business/lg-to-focus-on-6g-research-with-partnership-with-keysight-technologies (accessed on November 2, 2023).
- Jiang, W.; Han, B.; Habibi, M.A.; Schotten, H.D. The Road towards 6G: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 2, 334–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, J.F.; Ekin, S.; Choi, W.; Song, I. A Perspective on Terahertz Next-Generation Wireless Communications. Technologies 2019, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Writer, S.; Japan Readies $2bn to Support Industry Research on 6G Tech. Nikkei Asia, 21 November 2019. Available online: https://asia.nikkei.com/Business/Technology/Japan-readies-2bn-to-support-industry-research-on-6G-tech (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- 6G on the Horizon: A Global Overview of the Latest Developments in Wireless Technology: Market Research Blog. Market Research Reports® Inc., 5 April 2023. Available online: https://www.marketresearchreports.com/blog/2023/04/05/6g-horizon-global-overview-latest-developments-wireless-technology (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Alraih, S.; Shayea, I.; Behjati, M.; Nordin, R.; Abdullah, N.F.; Abu-Samah, A.; Nandi, D. Revolution or Evolution? Technical Requirements and Considerations towards 6G Mobile Communications. Sensors 2022, 22, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Chen, X.; Jiang, T. Guest Editorial: Brain-Computer-Interface Inspired Communications. China Commun. 2022, 19, iii–v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; (2023, March 16). Wireless Brain-Computer Interactions (BCI) and 6G Connectivity. Telecom Trainer. Available online: https://www.telecomtrainer.com/wireless-brain-computer-interactions-bci/ (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Pajooh, H.H.; Demidenko, S.; Aslam, S.; Harris, M. Blockchain and 6G-Enabled IoT. Inventions 2022, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewa, T.; Gür, G.; Kalla, A.; Ylianttila, M.; Bracken, A.; Liyanage, M. The Role of Blockchain in 6G: Challenges, Opportunities and Research Directions. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd 6G Wireless Summit (6G SUMMIT), Levi, Finland; 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.N.; Ahmad, A.R.; Qassim, Q.S.; Natiq, H.; Subhi, M.A.; Mahmoud, M. From 5G to 6G Technology: Meets Energy, Internet-of-Things and Machine Learning: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicandia, F.A.; Fonseca, N.J.G.; Bacco, M.; Mugnaini, S.; Genovesi, S. Space-Air-Ground Integrated 6G Wireless Communication Networks: A Review of Antenna Technologies and Application Scenarios. Sensors 2022, 22, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.P. A Review on 6G for Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network: Key Enablers, Open Challenges, and Future Direction. J. King Saud Univ. - Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 6949–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwis, C.D.; Kalla, A.; Pham, Q.-V.; Kumar, P.; Dev, K.; Hwang, W.-J.; Liyanage, M. Survey on 6G Frontiers: Trends, Applications, Requirements, Technologies and Future Research. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 2, 836–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiki Abir, Md. A.; Chowdhury, M.Z.; Jang, Y.M. Software-Defined UAV Networks for 6G Systems: Requirements, Opportunities, Emerging Techniques, Challenges, and Research Directions. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2023, 4, 2487–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; She, C.; Li, Y.; Niyato, D.; Dohler, M.; Vucetic, B. Intelligent Communications for Tactile Internet in 6G: Requirements, Technologies, and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2021, 59, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banafaa, M.; Shayea, I.; Din, J.; Hadri Azmi, M.; Alashbi, A.; Ibrahim Daradkeh, Y.; Alhammadi, A. 6G Mobile Communication Technology: Requirements, Targets, Applications, Challenges, Advantages, and Opportunities. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 64, 245–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Wang, C.-X.; Huang, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Sheng, B.; Wang, D.; Pan, Z.; Zhu, P.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Tao, X.; Liang, Y.-C. Towards 6G Wireless Communication Networks: Vision, Enabling Technologies, and New Paradigm Shifts. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, P.K.; Charrua-Santos, F. 6G Enabled Industrial Internet of Everything: Towards a Theoretical Framework. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, Z.; Le, K.N.; Saeed, N.; Munawar, H.S. Towards 6G Internet of Things: Recent Advances, Use Cases, and Open Challenges. ICT Express 2023, 9, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, K. Deep Learning-Based Offloading for Mobile Augmented Reality Application in 6G. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 95, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admin. The Impact of 6G on Virtual and Augmented Reality. isp.page. 2023. Available online: https://isp.page/news/the-impact-of-6g-on-virtual-and-augmented-reality/ (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Qiao, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Serikawa, S.; Guizani, M.; Lv, Z. A Survey on 5G/6G, AI, and Robotics. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 95, 107372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, L.; Buyya, R. Artificial Intelligence Applications and Self-Learning 6G Networks for Smart Cities Digital Ecosystems: Taxonomy, Challenges, and Future Directions. Sensors 2022, 22, 5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wang, L.; Gui, J.; Jiang, P.; Chen, X.; Zeng, F.; Wan, S. A Review of 6G Autonomous Intelligent Transportation Systems: Mechanisms, Applications and Challenges. J. Syst. Archit. 2023, 142, 102929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Madrid, J.; Sanchez-Iborra, R.; Ortiz, J.; Santa, J. The Role of Vehicular Applications in the Design of Future 6G Infrastructures. ICT Express 2023, 9, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- "How 6G Networking Will Solve Your City’s Traffic Problems." n.d.-a. Available online: https://www.avnet.com/wps/portal/us/resources/article/how-6g-networking-will-solve-traffic-problems/ (accessed on 4 November 2023).
- Tataria, H.; Shafi, M.; Dohler, M.; Sun, S. Six Critical Challenges for 6G Wireless Systems: A Summary and Some Solutions. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2022, 17, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaona, W.; Kenta, U.; Janne, L.; Nizar, Z. Device-to-device Communications at the Terahertz Band: Open Challenges for Realistic Implementation. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2023, 7, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharche, S.; Dere, P. Interoperability Issues and Challenges in 6G Networks. Journal of Mobile Multimedia 2022. [CrossRef]
- Electronics Sourcing. 2023, April 13. "6G is happening, and here’s what you need to know." [Online]. Available: https://electronics-sourcing.com/2023/04/13/6g-is-happening-and-heres-what-you-need-to-know/ (Accessed on ). 8 November.
- Sri, A. ; Muhammad Suryanegara. "Visible Light Communication (VLC) for 6G Technology: The Potency and Research Challenges." In 2020 Fourth World Conference on Smart Trends in Systems, Security and Sustainability (WorldS4), 2020, pp. 490-493. [CrossRef]
- imec. 6G Energy Efficiency. Available online: https://www.imec-int.com/en/articles/boost-6g-energy-efficiency-we-need-models-can-handle-its-complexities. 8 November 2023.
- Wang, M.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S.; Zhou, W. Security and Privacy in 6G Networks: New Areas and New Challenges. Digit. Commun. Networks 2020, 6, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Ravi Kumar, R.; Garg, N.; Joshi, K.; Pillai, B.G.; Joshi, U. Analysis of Potential Health and Environmental Risks Associated with 6G Wireless Communication Networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE); 2023; pp. 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Pados, D.A.; Batalama, S.N.; Einarsson, E.; Bird, J.P.; Jornet, J.M. The Teranova Platform: An Integrated Testbed for Ultra-Broadband Wireless Communications at True Terahertz Frequencies. Comput. Netw. 2020, 179, 107370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ng, C.; Huo, Y.; Hu, R.Q.; Wang, N.; Chen, C.-M.; Vasudevan, K.; Yang, J.; Montlouis, W.; Ayanda, D.; Mishra, K.V.; Tekbıyık, K.; Hussain, N.; Sahoo, H.K.; Miao, Y. Massive MIMO. 2022 IEEE Future Networks World Forum (FNWF) 2022, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokia. Spectrum for 6G Explained. Available online: https://www.nokia.com/about-us/newsroom/articles/spectrum-for-6G-explained/. Accessed on , 2023. 28 November.
- Alliance. 6G Technologies. Available online: https://www.nextgalliance.org/wp-content/uploads/dlm_uploads/2022/07/TWG-report-6G-technologies.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Fayad, A.; Cinkler, T.; Rak, J.; Jha, M. Design of Cost-Efficient Optical Fronthaul for 5G/6G Networks: An Optimization Perspective. Sensors 2022, 22, 9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spectrum Options and Allocations for 6G: A Regulatory and Standardization Review. Available online: https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/202287/1/Spectrum_Options_and_Allocations_for_6G_A_Regulatory_and_Standardization_Review.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Taneja, A.; Saluja, N.; Taneja, N.; Alqahtani, A.; Elmagzoub, M.A.; Shaikh, A.; Koundal, D. Power Optimization Model for Energy Sustainability in 6G Wireless Networks. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- City, S.; (2021, December 29). 6G: Global standards vs. fragmented ecosystems. Available online: https://www.thesmartcityjournal.com/en/articles/6g-global-standards-vs-fragmented-ecosystems (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Hexa-X and Data Protection Evolution in 6G - Ericsson. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2023/10/hexa-x-and-data-protection-evolution-in-6g (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Morra, J.; Engineers Look to Adopt a More Sustainable Approach to Electronic Design. Electronic Design, 10 November 2023. Available online: https://www.electronicdesign.com/resources/industry-insights/article/21275020/electronic-design-engineers-look-to-adopt-a-more-sustainable-approach-to-electronic-design (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Basic Information About Electronics Stewardship | US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/smm-electronics/basic-information-about-electronics-stewardship (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Techopedia. (n.d.-d). When 6G met AI: How next-gen mobile networks will work. Available online: https://www.techopedia.com/6g-and-ai-next-gen-mobile-networks-will-change-the-world (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Ashwin, M.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Mubarakali, A.; Sivakumar, B. (2023a). Efficient Resource Management in 6G Communication Networks Using Hybrid Quantum Deep Learning Model. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, L.; Buyya, R. Artificial Intelligence Applications and Self-Learning 6G Networks for Smart Cities Digital Ecosystems: Taxonomy, Challenges, and Future Directions. Sensors 2022, 22, 5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloudait. (2023, August 1). Ai-enabled self-healing networks: A crucial pillar of 6G reliability. AI Tools Practical Handbook. Available online: https://www.cloudaitech.net/ai-enabled-self-healing-networks-a-crucial-pillar-of-6g-reliability/ (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Rekkas, V.P.; Sotiroudis, S.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Wan, S.; Karagiannidis, G.K.; Goudos, S.K. Machine Learning in Beyond 5G/6G Networks—State-of-the-Art and Future Trends. Electronics 2021, 10, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.M.; Saeed, R.A.; Abdelhaq, M.; Alsaqour, R.; Hasan, M.K.; Mokhtar, R.A. Anomaly Detection in 6G Networks Using Machine Learning Methods. Electronics 2023, 12, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspitasari, A.A.; An, T.T.; Alsharif, M.H.; Lee, B.M. Emerging Technologies for 6G Communication Networks: Machine Learning Approaches. Sensors 2023, 23, 7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dulaimi, O.; Al-Dulaimi, M.; Al-Dulaimi, A.; Alexandra, M.O. Cognitive Radio Network Technology for IoT-Enabled Devices. Eng. Proc. 2023, 41, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Hui, N.; Cui, X.; Wu, J.; Peng, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xing, C. Service-aware 6G: An Intelligent and Open Network Based on the Convergence of Communication, Computing, and Caching. Digit. Commun. Networks 2020, 6, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Tham, M.-L.; Wong, Y.J.; Al-Habashna, A.; Wainer, G.; Zhu, Y.X.; Dagiuklas, T. Empowering Non-Terrestrial Networks with Artificial Intelligence: A Survey. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 100986–101006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murroni, M.; Anedda, M.; Fadda, M.; Ruiu, P.; Popescu, V.; Zaharia, C.; Giusto, D. 6G—Enabling the New Smart City: A Survey. Sensors 2023, 23, 7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, A.; Jha, R.K.; Jha, K.R. Reinforcement Learning (RL) for Optimal Power Allocation in 6G Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 OPJU International Technology Conference on Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Development (OTCON), Raigarh, Chhattisgarh, India; 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswat, S.K.; Deolia, V.K.; Shukla, A. Allocation of Power in NOMA-Based 6G-Enabled Internet of Things Using Multi-Objective Based Genetic Algorithm. J. Elect. Eng. 2023, 74, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, L.; Ni, W.; Liu, Y. Efficiency-Optimized 6G: A Virtual Network Resource Orchestration Strategy by Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization. Digital Commun. Networks 2023. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dai, J.; Pang, S.; Wang, C. Deep Learning in the Ubiquitous Human–Computer Interactive 6G Era: Applications, Principles and Prospects. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Rosa, E.; Yu, W. Data-Driven Fuzzy Modeling Using Restricted Boltzmann Machines and Probability Theory. in IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, vol. 50, no. 7, pp. 2316-2326, 20. 20 July. [CrossRef]
- Moubayed, A.; Shami, A.; Al-Dulaimi, A. On End-to-End Intelligent Automation of 6G Networks. Future Internet 2022, 14, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Deng, J.; Tang, Q.; Liu, G. Optimization of Quality of AI Service in 6G Native AI Wireless Networks. Electronics 2023, 12, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X, S.; An Innovative Technology for 6G Communication Networks. Tech Xplore - Technology and Engineering News. 2022. Available online: https://techxplore.com/news/2022-02-technology-6g-networks.html (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J. From Terahertz Imaging to Terahertz Wireless Communications. Engineering 2023, 22, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Q.; He, J.; Habibi, M.A.; Melnyk, S.; El-Absi, M.; Han, B.; Renzo, M.D.; Schotten, H.D.; Luo, F.-L.; El-Bawab, T.S.; Juntti, M.; Debbah, M.; Leung, V.C. Terahertz Communications and Sensing for 6G and Beyond: A Comprehensive View. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Aslam, T.; Ahmed, I.; Ali, S.; Aslam, M.I. Terahertz Communication and Associated Challenges in 6G Cellular Networks. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computing and Information Sciences (ICCIS); pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Lin, X.; Di, B.; Zhang, H.; Hernando, F.J.L.; Tan, A.S.; Mumtaz, S.; Demir, Ö.T.; Chen-Hu, K. Technology Trends for Massive MIMO towards 6G. Sensors 2023, 23, 6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.; (2021, January 26). 5G and gan: Understanding sub-6ghz massive mimo infrastructure. Embedded.com. Available online: https://www.embedded.com/5g-and-gan-understanding-sub-6ghz-massive-mimo-infrastructure/ (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Dala Pegorara Souto, V.; Dester, P.S.; Soares Pereira Facina, M.; Gomes Silva, D.; de Figueiredo, F.A.P.; Rodrigues de Lima Tejerina, G.; Silveira Santos Filho, J.C.; Silveira Ferreira, J.; Mendes, L.L.; Souza, R.D.; et al. Emerging MIMO Technologies for 6G Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Tian, Z.; Mei, W.; Chen, Z.; Han, C.; Li, S.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, R. Beamforming Technologies for Ultra-Massive MIMO in Terahertz Communications. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2023, 4, 614–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.Z.; Shahjalal, Md.; Ahmed, S.; Jang, Y.M. 6G Wireless Communication Systems: Applications, Requirements, Technologies, Challenges, and Research Directions. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2020, 1, 957–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Santacruz, J.; Meyer, E.; Budé, R.X. F.; Stan, C.; Jurado-Navas, A.; Johannsen, U.; Tafur Monroy, I.; Rommel, S.; Outdoor MM-wave 5G/6G Transmission with Adaptive Analog Beamforming and IFOF Fronthaul. Nature News 2023, 25. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-40112-w (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- Kassam, J.; Castanheira, D.; Silva, A.; Dinis, R.; Gameiro, A. A Review on Cell-Free Massive MIMO Systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, S.; Letaief, K.B. Cell-Free Massive MIMO for 6G Wireless Communication Networks. J. Commun. Inf. Netw. 2021, 6, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Du, J.; Liao, Y. Multi-User Scheduling for 6G V2X Ultra-Massive MIMO System. Sensors 2021, 21, 6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmal, M.; Siddiqa, A.; Jeong, B.; Seo, J.; Kim, D. Cell-Free Massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Challenges and Opportunities: A Survey. ICT Express 2023. [CrossRef]
- Dala Pegorara Souto, V.; Dester, P.S.; Soares Pereira Facina, M.; Gomes Silva, D.; de Figueiredo, F.A.P.; Rodrigues de Lima Tejerina, G.; Silveira Santos Filho, J.C.; Silveira Ferreira, J.; Mendes, L.L.; Souza, R.D.; et al. Emerging MIMO Technologies for 6G Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moltchanov, D.; Sopin, E.; Begishev, V.; Samuylov, A.; Koucheryavy, Y.; Samouylov, K. A Tutorial on Mathematical Modeling of 5G/6G Millimeter Wave and Terahertz Cellular Systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tuts. 2022, 24, 1072–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethw. Millimeter Waves. 12 April 2017. Available online: https://ethw.org/Millimeter_Waves.
- Qu, K.; Chen, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, N.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, T.; Feng, Y. An Electromechanically Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface for Enhancing Sub-6G Wireless Communication Signal. J. Inf. Intell. 2023, 1, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Chehri, A.; Fortier, P. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for 5G and beyond Wireless Communications: A Comprehensive Survey. Energies 2021, 14, 8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique, P.S.; Prasad, R. 6G Networks Orientation by Quantum Mechanics. J. ICT Standardization. 2022. Available online. [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.J.; Sharma, S.K.; Wyne, S.; Patwary, M.N.; Asaduzzaman, M. Quantum Machine Learning for 6G Communication Networks: State-of-the-Art and Vision for the Future. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 46317–46350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.P. A Review on 6G for Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network: Key Enablers, Open Challenges, and Future Direction. J. King Saud Univ. - Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 6949–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukliński, S.; Szczypiorski, K.; Chemouil, P. UAV Support for Mission Critical Services. Energies 2022, 15, 5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telli, K.; Kraa, O.; Himeur, Y.; Ouamane, A.; Boumehraz, M.; Atalla, S.; Mansoor, W. A Comprehensive Review of Recent Research Trends on Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Systems 2023, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M. 30 August 2019. Risks to Human Health: High-Frequency Radio Waves. Available online: https://www.myfanwywebb.com/5g-6g-risks-to-human-health-high-frequency-radio-waves/ (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- US EPA. Electric and Magnetic Fields from Power Lines. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/radtown/electric-and-magnetic-fields-power-lines (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- ITU. 5G, Human Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (EMF) and Health. Available online: https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/backgrounders/Pages/5G-EMF-health.aspx (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- Simkó, M.; Mattsson, M.-O. 5G Wireless Communication and Health Effects—A Pragmatic Review Based on Available Studies Regarding 6 to 100 GHz. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Devices and Radiological Health. Cell Phones. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/radiation-emitting-products/home-business-and-entertainment-products/cell-phones (accessed on 25 November 2023).

| Performance Indicator | 4G | 5G | 6G |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Data Transfer Rate | 100 Mbps | 10 Gbps | Up to 10 Tbps |
| Minimum Latency | 10 ms | 1 ms | Up to 0.1 ms |
| Maximum Device Density per sq km | 0.1 million devices | 1 million devices | 10 million devices |
| Energy Efficiency | 1x | 100x more efficient than 4G | 100x more efficient than 5G |
| Spectral Efficiency | 1x | 100x more efficient than 4G | 100x more efficient than 5G |
| Available Spectrum | Up to 6 GHz | Up to 300 GHz | Up to 3 THz |
| Maximum Mobility | 200 km/h | 300 km/h | 600 km/h |
| Artificial Intelligence Integration | None | Partial | Full |
| Challenges | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Technology innovation and standardization | Establish testbeds to validate the performance of millimeter- and terahertz-wave communication in different environments. This includes testing for signal propagation, interference, and device compatibility. Invest in the research and development of signal processing algorithms that can efficiently handle the massive number of antennas involved in MIMO systems. This includes beamforming, channel estimation, and interference management [83,84]. |
| Scarcity of high-frequency spectrum for bandwidth allocation |
Collaborate with regulatory bodies to identify and allocate specific frequency bands for 6G, with a focus on millimeter and terahertz bands. This involves conducting spectrum studies to identify underutilized or unallocated frequency ranges [85]. |
| Interoperability between current and 6G networks | The technologies should be built to interoperate with the existing network and devices [86]. |
| Investment cost | Implement a phased approach to 6G deployment, focusing on specific geographic areas, use cases, or network functionalities. This approach minimizes heavy upfront costs [87]. |
| Regulatory and Policy Challenges | Establish international agreements and collaborate with regulatory bodies to harmonize spectrum allocation for 6G. Encourage the development of dynamic spectrum sharing technologies to optimize spectrum utilization [88]. |
| Power consumption | A model for optimizing power has been introduced for a 6G-enabled massive IoT network. The primary objective is to enhance overall system performance, providing energy-saving features. Through efficient power resource management, the model minimizes power overhead attributed to the extensive number of connected devices. The assessment of the proposed network includes an analysis of the maximum allocated power and spectral efficiency under various network operations and distinct precoding schemes [89]. |
| International collaboration and harmonization | Encourage international collaboration in standardization bodies to develop unified standards for 6G technologies. Harmonize spectrum allocation, protocols, and interfaces to ensure interoperability and a consistent user experience [90]. |
| Security and Privacy | While robust security mechanisms are in place for safeguarding data during transit, there is a pressing need to prioritize the protection of data in processing and storage for comprehensive end-to-end security in 6G. Techniques such as oblivious computing, confidential computing, homomorphic encryption, and privacy-centric identifiers can be employed across both 6G network services and components [91]. |
| Environmental concerns | Design devices and infrastructure for longevity and ease of recycling. Establish collection and recycling programs for end-of-life electronic components. Encourage manufacturers to adopt sustainable product life cycles [92,93]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





