Submitted:
11 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
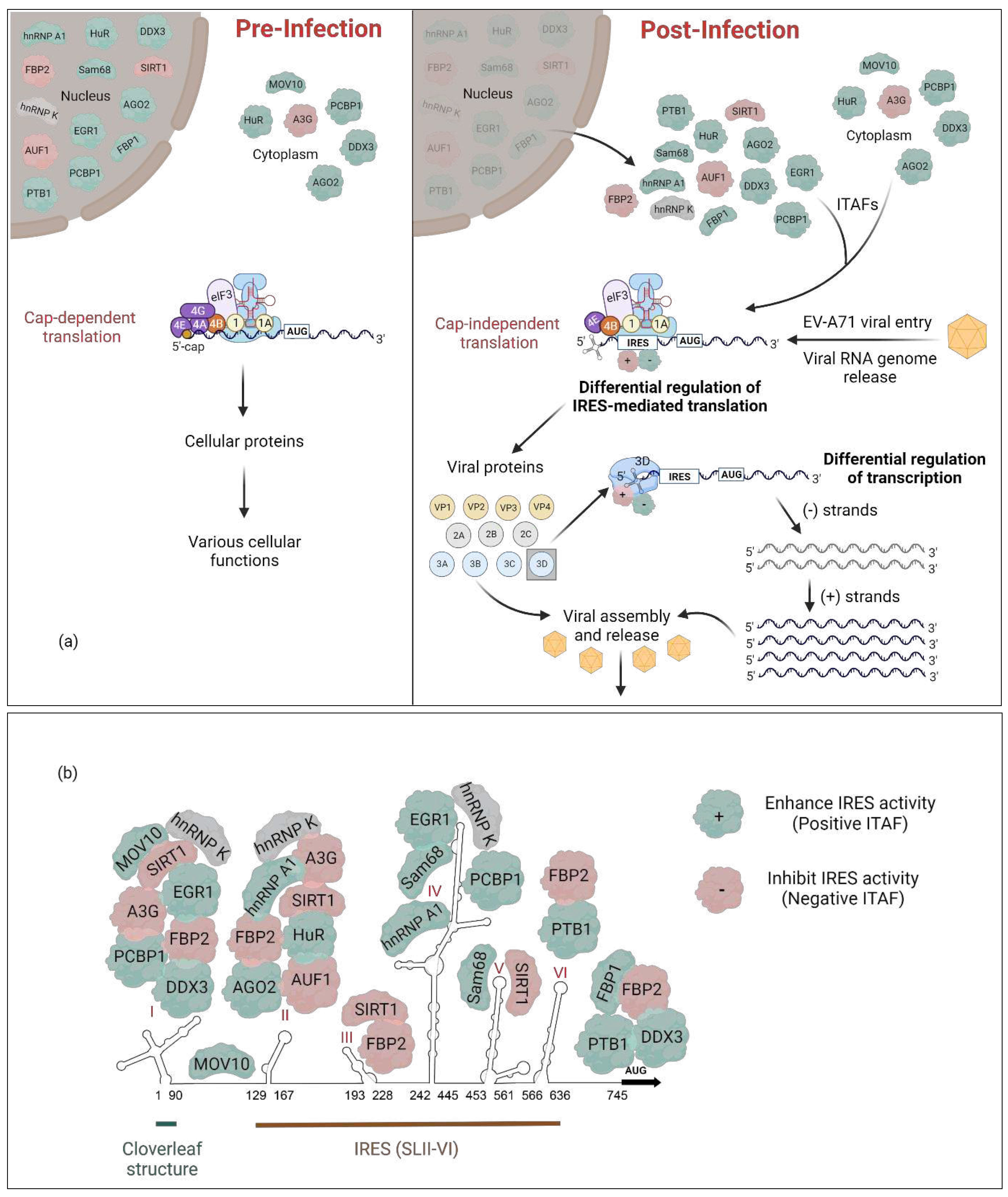
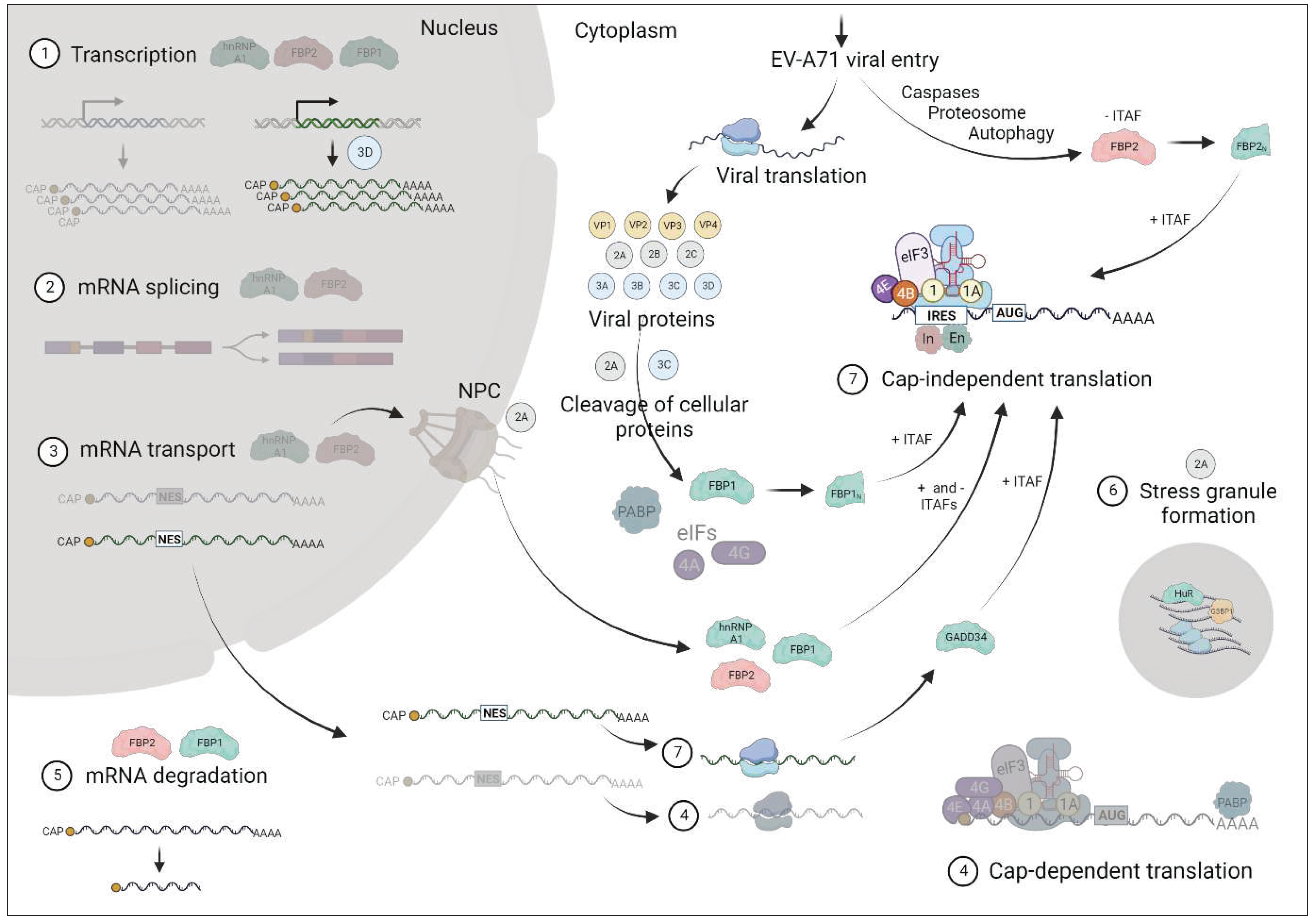
2. Cellular IRES trans-acting factors (ITAFs) that regulate EV-A71 translation
2.1. hnRNP A1
2.2. AUF1 (hnRNP D)
2.3. hnRNP K
2.4. PCBP1 (hnRNP E1)
2.5. PTB (hnRNP I)
2.6. FBP2
- N- and C-terminus cleaved FBP2
2.7. FBP1
- C-terminus cleaved FBP1
2.8. Ago2
2.9. HuR
- Additive effects of Ago2 and HuR
2.10. MOV10
2.11. SIRT1
2.12. Sam68
2.13. FUBP3
2.14. GADD34
2.15. DDX3
2.16. APOBEC3G
2.17. Staufen1
2.18. hnRNP H and hnRNP F
2.19. EGR1
2.20. TIA-1 and TIAR
2.21. Additional cellular proteins
3. Discussion
4. Future perspectives
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nayak, G.; Bhuyan, S. K.; Bhuyan, R.; Sahu, A.; Kar, D.; Kuanar, A. Global Emergence of Enterovirus 71: A Systematic Review. Beni Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 2022, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-M.; Wang, E.-T.; Kuo, H.-W.; Shih, W.-L.; Fang, C.-T.; Liu, D.-P.; Chang, L.-Y. The Secular Trend of Enterovirus A71 after the Implementation of Preventive Measures in Taiwan. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enterovirus 71. https://www.who.int/teams/health-product-policy-and-standards/standards-and-specifications/vaccine-standardization/enterovirus-71 (accessed 2023-11-08).
- Huang, P.-N.; Shih, S.-R. Update on Enterovirus 71 Infection. Curr Opin Virol 2014, 5, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Yan, B.; Xu, C.; Yin, Q.; Yang, D. Global Spatiotemporal Transmission Patterns of Human Enterovirus 71 from 1963 to 2019. Virus Evolution 2021, 7, veab071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wörner, N.; Rodrigo-García, R.; Antón, A.; Castellarnau, E.; Delgado, I.; Vazquez, È.; González, S.; Mayol, L.; Méndez, M.; Solé, E.; Rosal, J.; Andrés, C.; Casquero, A.; Lera, E.; Sancosmed, M.; Campins, M.; Pumarola, T.; Rodrigo, C. Enterovirus-A71 Rhombencephalitis Outbreak in Catalonia: Characteristics, Management and Outcome. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2021, 40, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Gou, F.; Yang, X.; Cheng, Y.; McClymont, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, W. Prototypes Virus of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease Infections and Severe Cases in Gansu, China: A Spatial and Temporal Analysis. BMC Infectious Diseases 2022, 22, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messacar, K.; Burakoff, A.; Nix, W. A.; Rogers, S.; Oberste, M. S.; Gerber, S. I.; Spence-Davizon, E.; Herlihy, R.; Dominguez, S. R. Notes from the Field: Enterovirus A71 Neurologic Disease in Children - Colorado, 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2018, 67, 1017–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhan, L. N. T.; Hong, N. T. T.; Nhu, L. N. T.; Nguyet, L. A.; Ny, N. T. H.; Thanh, T. T.; Han, D. D. K.; Van, H. M. T.; Thwaites, C. L.; Hien, T. T.; Qui, P. T.; Quang, P. V.; Minh, N. N. Q.; van Doorn, H. R.; Khanh, T. H.; Chau, N. V. V.; Thwaites, G.; Hung, N. T.; Tan, L. V. Severe Enterovirus A71 Associated Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease, Vietnam, 2018: Preliminary Report of an Impending Outbreak. Euro Surveill 2018, 23, 1800590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIAID Emerging Infectious Diseases/Pathogens | NIH: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. https://www.niaid.nih.gov/research/emerging-infectious-diseases-pathogens (accessed 2023-11-08).
- Li, M.-L.; Shih, S.-R.; Tolbert, B. S.; Brewer, G. Enterovirus A71 Vaccines. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, E.-J.; Shin, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, T.-G.; Chang, S.-Y. Enterovirus 71 Infection and Vaccines. Clin Exp Vaccine Res 2017, 6, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-F.; Sam, I.-C.; AbuBakar, S. Phylogenetic Designation of Enterovirus 71 Genotypes and Subgenotypes Using Complete Genome Sequences. Infect Genet Evol 2010, 10, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B. A.; Pallansch, M. A. Complete Nucleotide Sequence of Enterovirus 71 Is Distinct from Poliovirus. Virus Res 1995, 39, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolbert, M.; Morgan, C. E.; Pollum, M.; Crespo-Hernández, C. E.; Li, M.-L.; Brewer, G.; Tolbert, B. S. HnRNP A1 Alters the Structure of a Conserved Enterovirus IRES Domain to Stimulate Viral Translation. J Mol Biol 2017, 429, 2841–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Xu, P.; Wang, R. Y. L. Translation Control of Enterovirus A71 Gene Expression. J Biomed Sci 2020, 27, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Chen, S.; Cheng, A.; Wang, M. Roles of the Picornaviral 3C Proteinase in the Viral Life Cycle and Host Cells. Viruses 2016, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, K.-F.; Li, M.-L.; Hung, C.-T.; Shih, S.-R. Enterovirus 71 3C Protease Cleaves a Novel Target CstF-64 and Inhibits Cellular Polyadenylation. PLoS Pathog 2009, 5, e1000593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Xiao, X.; Xue, Q.; Jin, Q.; He, B.; Wang, J. Cleavage of Interferon Regulatory Factor 7 by Enterovirus 71 3C Suppresses Cellular Responses. J Virol 2013, 87, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Han, N.; Xiao, X.; Jin, Q.; He, B.; Wang, J. Enterovirus 71 3C Inhibits Cytokine Expression through Cleavage of the TAK1/TAB1/TAB2/TAB3 Complex. J Virol 2014, 88, 9830–9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-L.; Lin, J.-Y.; Chen, B.-S.; Weng, K.-F.; Shih, S.-R.; Calderon, J. D.; Tolbert, B. S.; Brewer, G. EV71 3C Protease Induces Apoptosis by Cleavage of hnRNP A1 to Promote Apaf-1 Translation. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0221048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, S.; Ou, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, J.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Jia, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, M. Multiple Functions of Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins in the Positive Single-Stranded RNA Virus Life Cycle. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 989298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeda, A.; Krainer, A. R. Regulation of Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing by hnRNP A1 and Splicing Factor SF2. Cell 1992, 68, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean-Philippe, J.; Paz, S.; Caputi, M. hnRNP A1: The Swiss Army Knife of Gene Expression. Int J Mol Sci 2013, 14, 18999–19024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, W. M.; Choi, M.; Dreyfuss, G. A Nuclear Export Signal in hnRNP A1: A Signal-Mediated, Temperature-Dependent Nuclear Protein Export Pathway. Cell 1995, 83, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henics, T.; Sanfridson, A.; Hamilton, B. J.; Nagy, E.; Rigby, W. F. Enhanced Stability of Interleukin-2 mRNA in MLA 144 Cells. Possible Role of Cytoplasmic AU-Rich Sequence-Binding Proteins. J Biol Chem 1994, 269, 5377–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B. J.; Burns, C. M.; Nichols, R. C.; Rigby, W. F. Modulation of AUUUA Response Element Binding by Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1 in Human T Lymphocytes. The Roles of Cytoplasmic Location, Transcription, and Phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 1997, 272, 28732–28741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-S.; Manche, L.; Xu, R.-M.; Krainer, A. R. hnRNP A1 Associates with Telomere Ends and Stimulates Telomerase Activity. RNA 2006, 12, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guil, S.; Cáceres, J. F. The Multifunctional RNA-Binding Protein hnRNP A1 Is Required for Processing of miR-18a. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2007, 14, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mili, S.; Shu, H. J.; Zhao, Y.; Piñol-Roma, S. Distinct RNP Complexes of Shuttling hnRNP Proteins with Pre-mRNA and mRNA: Candidate Intermediates in Formation and Export of mRNA. Mol Cell Biol 2001, 21, 7307–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñol-Roma, S.; Dreyfuss, G. Shuttling of Pre-mRNA Binding Proteins between Nucleus and Cytoplasm. Nature 1992, 355, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jd, L.; Bs, T. Idiosyncrasies of hnRNP A1-RNA Recognition: Can Binding Mode Influence Function. Seminars in cell & developmental biology 2019, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Shih, S.-R.; Pan, M.; Li, C.; Lue, C.-F.; Stollar, V.; Li, M.-L. hnRNP A1 Interacts with the 5’ Untranslated Regions of Enterovirus 71 and Sindbis Virus RNA and Is Required for Viral Replication. J Virol 2009, 83, 6106–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levengood, J. D.; Tolbert, M.; Li, M.-L.; Tolbert, B. S. High-Affinity Interaction of hnRNP A1 with Conserved RNA Structural Elements Is Required for Translation and Replication of Enterovirus 71. RNA Biol 2013, 10, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Li, M.-L.; Huang, P.-N.; Chien, K.-Y.; Horng, J.-T.; Shih, S.-R. Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonuclear Protein K Interacts with the Enterovirus 71 5’ Untranslated Region and Participates in Virus Replication. J Gen Virol 2008, 89 Pt 10, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Li, M.-L.; Shih, S.-R. Far Upstream Element Binding Protein 2 Interacts with Enterovirus 71 Internal Ribosomal Entry Site and Negatively Regulates Viral Translation. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila-Calderon, J.; Li, M.-L.; Penumutchu, S. R.; Haddad, C.; Malcolm, L.; Hargrove, A. E.; Brewer, G.; Tolbert, B. S. Enterovirus Evolution Reveals the Mechanism of an RNA-Targeted Antiviral and Determinants of Viral Replication. bioRxiv February 20, 2023, p 2023.02.20.529064. [CrossRef]
- Fialcowitz, E. J.; Brewer, B. Y.; Keenan, B. P.; Wilson, G. M. A Hairpin-like Structure within an AU-Rich mRNA-Destabilizing Element Regulates Trans-Factor Binding Selectivity and mRNA Decay Kinetics. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 22406–22417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geuens, T.; Bouhy, D.; Timmerman, V. The hnRNP Family: Insights into Their Role in Health and Disease. Hum Genet 2016, 135, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Brewer, G. The Regulation of mRNA Stability in Mammalian Cells: 2.0. Gene 2012, 500, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pont, A. R.; Sadri, N.; Hsiao, S. J.; Smith, S.; Schneider, R. J. mRNA Decay Factor AUF1 Maintains Normal Aging, Telomere Maintenance, and Suppression of Senescence by Activation of Telomerase Transcription. Mol Cell 2012, 47, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroia, G.; Cuesta, R.; Brewer, G.; Schneider, R. J. Control of mRNA Decay by Heat Shock-Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway. Science 1999, 284, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-Y.; Bergman, N.; Sadri, N.; Schneider, R. J. Assembly of AUF1 with eIF4G–Poly(A) Binding Protein Complex Suggests a Translation Function in AU-Rich mRNA Decay. RNA 2006, 12, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsimer, K. S.; Gratacós, F. M.; Knapinska, A. M.; Lu, J.; Krause, C. D.; Wierzbowski, A. V.; Maher, L. R.; Scrudato, S.; Rivera, Y. M.; Gupta, S.; Turrin, D. K.; De La Cruz, M. P.; Pestka, S.; Brewer, G. Chaperone Hsp27, a Novel Subunit of AUF1 Protein Complexes, Functions in AU-Rich Element-Mediated mRNA Decay. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28, 5223–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila-Calderon, J.; Patwardhan, N. N.; Chiu, L.-Y.; Sugarman, A.; Cai, Z.; Penutmutchu, S. R.; Li, M.-L.; Brewer, G.; Hargrove, A. E.; Tolbert, B. S. IRES-Targeting Small Molecule Inhibits Enterovirus 71 Replication via Allosteric Stabilization of a Ternary Complex. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Li, M.-L.; Brewer, G. mRNA Decay Factor AUF1 Binds the Internal Ribosomal Entry Site of Enterovirus 71 and Inhibits Virus Replication. PLoS One 2014, 9, e103827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathcart, A. L.; Rozovics, J. M.; Semler, B. L. Cellular mRNA Decay Protein AUF1 Negatively Regulates Enterovirus and Human Rhinovirus Infections. J Virol 2013, 87, 10423–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Brewer, G.; Li, M.-L. HuR and Ago2 Bind the Internal Ribosome Entry Site of Enterovirus 71 and Promote Virus Translation and Replication. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0140291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stains, J. P.; Lecanda, F.; Towler, D. A.; Civitelli, R. Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein K Represses Transcription from a Cytosine/Thymidine-Rich Element in the Osteocalcin Promoter. Biochem J 2005, 385 Pt 2, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Razanau, A.; Feng, D.; Lobo, V. G.; Xie, J. Control of Alternative Splicing by Forskolin through hnRNP K during Neuronal Differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 8059–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Xiong, H.; Wei, J.; Gao, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; He, Q.-Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, L. Cytoplasmic hnRNPK Interacts with GSK3β and Is Essential for the Osteoclast Differentiation. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 17732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Naiki, T.; Saito, M.; Irie, K. hnRNP K Interacts with RNA Binding Motif Protein 42 and Functions in the Maintenance of Cellular ATP Level during Stress Conditions. Genes Cells 2009, 14, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habelhah, H.; Shah, K.; Huang, L.; Ostareck-Lederer, A.; Burlingame, A. L.; Shokat, K. M.; Hentze, M. W.; Ronai, Z. ERK Phosphorylation Drives Cytoplasmic Accumulation of hnRNP-K and Inhibition of mRNA Translation. Nat Cell Biol 2001, 3, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomsztyk, K.; Denisenko, O.; Ostrowski, J. hnRNP K: One Protein Multiple Processes. Bioessays 2004, 26, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffers, H.; Dejgaard, K.; Celis, J. E. Characterisation of Two Major Cellular Poly(rC)-Binding Human Proteins, Each Containing Three K-Homologous (KH) Domains. Eur J Biochem 1995, 230, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Dong, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Kim, C.; Song, Y.; Kang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Wu, J. PolyC-Binding Protein 1 Interacts with 5′-Untranslated Region of Enterovirus 71 RNA in Membrane-Associated Complex to Facilitate Viral Replication. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e87491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyagarajan, A.; Szaro, B. G. Phylogenetically Conserved Binding of Specific K Homology Domain Proteins to the 3’-Untranslated Region of the Vertebrate Middle Neurofilament mRNA. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 49680–49688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Rayala, S. K.; Gururaj, A. E.; Talukder, A. H.; O’Malley, B. W.; Kumar, R. Signaling-Dependent and Coordinated Regulation of Transcription, Splicing, and Translation Resides in a Single Coregulator, PCBP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 5866–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.-X.; Yin, R.-H.; Kong, X.-Z.; Zhang, T.; Huang, X.-H.; Zheng, W.-W.; Yang, Y.; Zhan, Y.-Q.; Xu, W.-X.; Yu, M.; Ge, C.-H.; Guo, J.-T.; Li, C.-Y.; Yang, X.-M. THAP11, a Novel Binding Protein of PCBP1, Negatively Regulates CD44 Alternative Splicing and Cell Invasion in a Human Hepatoma Cell Line. FEBS Lett 2012, 586, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Huang, X.-H.; Dong, L.; Hu, D.; Ge, C.; Zhan, Y.-Q.; Xu, W.-X.; Yu, M.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Tang, L.; Li, C.-Y.; Yang, X.-M. PCBP-1 Regulates Alternative Splicing of the CD44 Gene and Inhibits Invasion in Human Hepatoma Cell Line HepG2 Cells. Mol Cancer 2010, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A. K.; Flock, K. E.; Godavarthi, C. L.; Loh, H. H.; Ko, J. L. Molecular Basis Underlying the Poly C Binding Protein 1 as a Regulator of the Proximal Promoter of Mouse Mu-Opioid Receptor Gene. Brain Res 2006, 1112, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S. P.; Tang, Y. H.; Smith, R. Functional Diversity of the hnRNPs: Past, Present and Perspectives. Biochem J 2010, 430, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, J. G.; Mayer, S. A.; Tempst, P.; Nadal-Ginard, B. Characterization and Molecular Cloning of Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein: A Component of a Complex Necessary for Pre-mRNA Splicing. Genes Dev 1991, 5, 1237–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, F. M.; Makeyev, E. V. Regulation of mRNA Abundance by Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein-Controlled Alternate 5’ Splice Site Choice. PLoS Genet 2014, 10, e1004771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M. A.; Masuda, A.; Ohe, K.; Ito, M.; Hutchinson, D. O.; Mayeda, A.; Engel, A. G.; Ohno, K. HnRNP L and hnRNP LL Antagonistically Modulate PTB-Mediated Splicing Suppression of CHRNA1 Pre-mRNA. Sci Rep 2013, 3, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderberg, M.; Raffalli-Mathieu, F.; Lang, M. A. Identification of a Regulatory Cis-Element within the 3’-Untranslated Region of the Murine Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) mRNA; Interaction with Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins I and L and Role in the iNOS Gene Expression. Mol Immunol 2007, 44, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, M.; Yaman, I.; Gaccioli, F.; Zeenko, V. V.; Wang, C.; Caprara, M. G.; Venema, R. C.; Komar, A. A.; Snider, M. D.; Hatzoglou, M. The hnRNA-Binding Proteins hnRNP L and PTB Are Required for Efficient Translation of the Cat-1 Arginine/Lysine Transporter mRNA during Amino Acid Starvation. Mol Cell Biol 2009, 29, 2899–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarifar, F.; Yao, P.; Eswarappa, S. M.; Fox, P. L. Repression of VEGFA by CA-Rich Element-Binding microRNAs Is Modulated by hnRNP L. EMBO J 2011, 30, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Ye, F.; Wang, G.; Han, W.; Wei, Z.; Yin, B.; Yuan, J.; Qiang, B.; Peng, X. Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein Regulates Enterovirus 71 Translation Through Interaction with the Internal Ribosomal Entry Site. Virol Sin 2019, 34, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, H.; Turck, C. W.; Nikolic, J. M.; Black, D. L. A New Regulatory Protein, KSRP, Mediates Exon Inclusion through an Intronic Splicing Enhancer. Genes Dev 1997, 11, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis-Smyth, T.; Duncan, R. C.; Zheng, T.; Michelotti, G.; Levens, D. The Far Upstream Element-Binding Proteins Comprise an Ancient Family of Single-Strand DNA-Binding Transactivators *. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1996, 271, 31679–31687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lellek, H.; Kirsten, R.; Diehl, I.; Apostel, F.; Buck, F.; Greeve, J. Purification and Molecular Cloning of a Novel Essential Component of the Apolipoprotein B mRNA Editing Enzyme-Complex. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 19848–19856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherzi, R.; Chen, C.-Y.; Trabucchi, M.; Ramos, A.; Briata, P. The Role of KSRP in mRNA Decay and microRNA Precursor Maturation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2010, 1, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabucchi, M.; Briata, P.; Filipowicz, W.; Rosenfeld, M. G.; Ramos, A.; Gherzi, R. How to Control miRNA Maturation? RNA Biol 2009, 6, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briata, P.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ramos, A.; Gherzi, R. Functional and Molecular Insights into KSRP Function in mRNA Decay. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013, 1829, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L.; Kung, Y.-A.; Weng, K.-F.; Lin, J.-Y.; Horng, J.-T.; Shih, S.-R. Enterovirus 71 Infection Cleaves a Negative Regulator for Viral Internal Ribosomal Entry Site-Driven Translation. J Virol 2013, 87, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Q. M. Far Upstream Element Binding Protein 1: A Commander of Transcription, Translation and Beyond. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.; Bazar, L.; Michelotti, G.; Tomonaga, T.; Krutzsch, H.; Avigan, M.; Levens, D. A Sequence-Specific, Single-Strand Binding Protein Activates the Far Upstream Element of c-Myc and Defines a New DNA-Binding Motif. Genes Dev 1994, 8, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanich, M. E.; Moss, B. L.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Townsend, R. R.; Weber, J. D. Identification of FUSE-Binding Protein 1 as a Regulatory mRNA-Binding Protein That Represses Nucleophosmin Translation. Oncogene 2011, 30, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Harris, D.; Pandey, V. N. The FUSE Binding Protein Is a Cellular Factor Required for Efficient Replication of Hepatitis C Virus. J Virol 2008, 82, 5761–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.-L.; Liao, C.-L.; Lin, Y.-L. FUSE Binding Protein 1 Interacts with Untranslated Regions of Japanese Encephalitis Virus RNA and Negatively Regulates Viral Replication ▿. J Virol 2011, 85, 4698–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-N.; Lin, J.-Y.; Locker, N.; Kung, Y.-A.; Hung, C.-T.; Lin, J.-Y.; Huang, H.-I.; Li, M.-L.; Shih, S.-R. Far Upstream Element Binding Protein 1 Binds the Internal Ribosomal Entry Site of Enterovirus 71 and Enhances Viral Translation and Viral Growth. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, 9633–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-T.; Kung, Y.-A.; Li, M.-L.; Brewer, G.; Lee, K.-M.; Liu, S.-T.; Shih, S.-R. Additive Promotion of Viral Internal Ribosome Entry Site-Mediated Translation by Far Upstream Element-Binding Protein 1 and an Enterovirus 71-Induced Cleavage Product. PLoS Pathog 2016, 12, e1005959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höck, J.; Meister, G. The Argonaute Protein Family. Genome Biol 2008, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirle, N. T.; MacRae, I. J. The Crystal Structure of Human Argonaute2. Science 2012, 336, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazopoulou, V. I.; Delis, A. D.; Georgiou, S.; Pagakis, S. N.; Filippa, V.; Dragona, E.; Kloukina, I.; Chatzitheodoridis, E.; Trebicka, J.; Velentzas, A. D.; Thiele, M.; Gagos, S.; Thanos, D.; Tseleni-Balafouta, S.; Stravopodis, D. J.; Anastasiadou, E. AGO2 Localizes to Cytokinetic Protrusions in a P38-Dependent Manner and Is Needed for Accurate Cell Division. Commun Biol 2021, 4, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, S.; Steitz, J. A. AU-Rich-Element-Mediated Upregulation of Translation by FXR1 and Argonaute 2. Cell 2007, 128, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C. M.; Steitz*, J. A. HuR and mRNA Stability. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedeva, S.; Jens, M.; Theil, K.; Schwanhäusser, B.; Selbach, M.; Landthaler, M.; Rajewsky, N. Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of Regulatory Interactions of the RNA-Binding Protein HuR. Molecular Cell 2011, 43, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X. C.; Steitz, J. A. Overexpression of HuR, a Nuclear-Cytoplasmic Shuttling Protein, Increases the in Vivo Stability of ARE-Containing mRNAs. EMBO J 1998, 17, 3448–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uren, P. J.; Burns, S. C.; Ruan, J.; Singh, K. K.; Smith, A. D.; Penalva, L. O. F. Genomic Analyses of the RNA-Binding Protein Hu Antigen R (HuR) Identify a Complex Network of Target Genes and Novel Characteristics of Its Binding Sites. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 37063–37066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, D.; Shen, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, R. Silencing of HuR Inhibits Osteosarcoma Cell Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via AGO2 in Association With Long Non-Coding RNA XIST. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Z. Enterovirus 71 Induces Anti-Viral Stress Granule-like Structures in RD Cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 476, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chang, L.; Wang, X.; Su, A.; Feng, C.; Fu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zheng, N.; Wu, Z. MOV10 Interacts with Enterovirus 71 Genomic 5’UTR and Modulates Viral Replication. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 479, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregersen, L. H.; Schueler, M.; Munschauer, M.; Mastrobuoni, G.; Chen, W.; Kempa, S.; Dieterich, C.; Landthaler, M. MOV10 Is a 5’ to 3’ RNA Helicase Contributing to UPF1 mRNA Target Degradation by Translocation along 3’ UTRs. Mol Cell 2014, 54, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, G.; Landthaler, M.; Peters, L.; Chen, P. Y.; Urlaub, H.; Lührmann, R.; Tuschl, T. Identification of Novel Argonaute-Associated Proteins. Curr Biol 2005, 15, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abudu, A.; Wang, X.; Dang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Xiang, S.-H.; Zheng, Y.-H. Identification of Molecular Determinants from Moloney Leukemia Virus 10 Homolog (MOV10) Protein for Virion Packaging and Anti-HIV-1 Activity*. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2012, 287, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Islam, R. Mammalian Sirt1: Insights on Its Biological Functions. Cell Commun Signal 2011, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Schoonjans, K.; Auwerx, J. Sirtuin Functions in Health and Disease. Molecular Endocrinology 2007, 21, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-S.; Ott, M. The Ups and Downs of SIRT1. Trends Biochem Sci 2008, 33, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagans, S.; Pedal, A.; North, B. J.; Kaehlcke, K.; Marshall, B. L.; Dorr, A.; Hetzer-Egger, C.; Henklein, P.; Frye, R.; McBurney, M. W.; Hruby, H.; Jung, M.; Verdin, E.; Ott, M. SIRT1 Regulates HIV Transcription via Tat Deacetylation. PLoS Biol 2005, 3, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.-H.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Chen, W.-X.; Cai, X.-F.; Chen, K.; Ko, B. C. B.; Song, C.-L.; Ran, L.-K.; Li, W.-Y.; Huang, A.-L.; Chen, J. Sirtuin 1 Regulates Hepatitis B Virus Transcription and Replication by Targeting Transcription Factor AP-1. J Virol 2014, 88, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, L.; Cui, J.; Song, Y.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, F.; Ho, W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Wu, J. SIRT1 Inhibits EV71 Genome Replication and RNA Translation by Interfering with the Viral Polymerase and 5′UTR RNA. J Cell Sci 2016, 129, 4534–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, N.; Herrlich, P.; König, H. Signal-Dependent Regulation of Splicing via Phosphorylation of Sam68. Nature 2002, 420, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paronetto, M. P.; Cappellari, M.; Busà, R.; Pedrotti, S.; Vitali, R.; Comstock, C.; Hyslop, T.; Knudsen, K. E.; Sette, C. Alternative Splicing of the Cyclin D1 Proto-Oncogene Is Regulated by the RNA-Binding Protein Sam68. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of Sam68 in Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation. Int J Mol Sci 2013, 14, 23402–23419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, S.; Totty, N. F.; Hsuan, J. J.; Courtneidge, S. A. A Target for Src in Mitosis. Nature 1994, 368, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, M. J.; Wiesner, S.; Sudol, M. WW and SH3 Domains, Two Different Scaffolds to Recognize Proline-Rich Ligands. FEBS Lett 2002, 513, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galarneau, A.; Richard, S. The STAR RNA Binding Proteins GLD-1, QKI, SAM68 and SLM-2 Bind Bipartite RNA Motifs. BMC Molecular Biology 2009, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Taylor, S. J.; Shalloway, D. Specificity and Determinants of Sam68 RNA Binding: IMPLICATIONS FOR THE BIOLOGICAL FUNCTION OF K HOMOLOGY DOMAINS *. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1997, 272, 27274–27280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, P.; Schafer, E. A.; Rieder, E. The Nuclear Protein Sam68 Is Cleaved by the FMDV 3C Protease Redistributing Sam68 to the Cytoplasm during FMDV Infection of Host Cells. Virology 2012, 425, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, A. E.; Schlegel, A.; Kirkegaard, K. Human Protein Sam68 Relocalization and Interaction with Poliovirus RNA Polymerase in Infected Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Cong, H.; Tien, P. Nuclear Protein Sam68 Interacts with the Enterovirus 71 Internal Ribosome Entry Site and Positively Regulates Viral Protein Translation. J Virol 2015, 89, 10031–10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Tong, W.; Chen, Y.-M. FUSE Binding Protein FUBP3 Is a Potent Regulator in Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection. Virology Journal 2021, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Anandram, S.; Ross, C.; Srivastava, S. FUBP3 Regulates Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Progression through PRC2 Complex Regulated PAK1-ERK Signalling. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 2023, 27, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, F.-J.; Lin, C.-W.; Lai, C.-C.; Lan, Y.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Hsueh, K.-C.; Lin, T.-H.; Chang, H. C.; Wan, L.; Sheu, J. J.-C.; Lin, Y.-J. Kaempferol Inhibits Enterovirus 71 Replication and Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES) Activity through FUBP and HNRP Proteins. Food Chemistry 2011, 128, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-I.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Lin, J.-Y.; Kuo, R.-L.; Liu, H.-P.; Shih, S.-R.; Wu, C.-C. Interactome Analysis of the EV71 5′ Untranslated Region in Differentiated Neuronal Cells SH-SY5Y and Regulatory Role of FBP3 in Viral Replication. PROTEOMICS 2016, 16, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brush, M. H.; Weiser, D. C.; Shenolikar, S. Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-Inducible Protein GADD34 Targets Protein Phosphatase 1α to the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Promotes Dephosphorylation of the α Subunit of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 2. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Jiang, X.; Xin, H.; Zheng, X.; Xue, X.; Chen, J.-L.; Qi, B. GADD34-Mediated Dephosphorylation of eIF2α Facilitates Pseudorabies Virus Replication by Maintaining de Novo Protein Synthesis. Veterinary Research 2021, 52, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakos-Zebrucka, K.; Koryga, I.; Mnich, K.; Ljujic, M.; Samali, A.; Gorman, A. M. The Integrated Stress Response. EMBO Rep 2016, 17, 1374–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalet, A.; Argüello, R. J.; Combes, A.; Spinelli, L.; Jaeger, S.; Fallet, M.; Vu Manh, T.-P.; Mendes, A.; Perego, J.; Reverendo, M.; Camosseto, V.; Dalod, M.; Weil, T.; Santos, M. A.; Gatti, E.; Pierre, P. Protein Synthesis Inhibition and GADD34 Control IFN-β Heterogeneous Expression in Response to dsRNA. EMBO J 2017, 36, 761–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavarino, G.; Cláudio, N.; Couderc, T.; Dalet, A.; Judith, D.; Camosseto, V.; Schmidt, E. K.; Wenger, T.; Lecuit, M.; Gatti, E.; Pierre, P. Induction of GADD34 Is Necessary for dsRNA-Dependent Interferon-β Production and Participates in the Control of Chikungunya Virus Infection. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1002708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, K.; Tambe, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Isono, T.; Haneda, M.; Isobe, K.-I.; Kobayashi, T.; Hino, O.; Okabe, H.; Chano, T.; Inoue, H. Suppression of Viral Replication by Stress-Inducible GADD34 Protein via the Mammalian Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase mTOR Pathway. J Virol 2007, 81, 11106–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liao, Y.; Yap, P. L.; Png, K. J.; Tam, J. P.; Liu, D. X. Inhibition of Protein Kinase R Activation and Upregulation of GADD34 Expression Play a Synergistic Role in Facilitating Coronavirus Replication by Maintaining De Novo Protein Synthesis in Virus-Infected Cells. J Virol 2009, 83, 12462–12472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Marshall, H.; Natarajan, V. GADD34 Attenuates HIV-1 Replication by Viral 5’-UTR TAR RNA-Mediated Translational Inhibition. Virology 2020, 540, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brush, M. H.; Shenolikar, S. Control of Cellular GADD34 Levels by the 26S Proteasome. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28, 6989–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K. S.; Xiang, W.; Alexander, L.; Lane, W. S.; Paul, A. V.; Wimmer, E. Interaction of Poliovirus Polypeptide 3CDpro with the 5’ and 3’ Termini of the Poliovirus Genome. Identification of Viral and Cellular Cofactors Needed for Efficient Binding. J Biol Chem 1994, 269, 27004–27014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, M.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.; Tan, J.; Qiao, W. Enterovirus 71 Activates GADD34 via Precursor 3CD to Promote IRES-Mediated Viral Translation. Microbiol Spectr 10 (1), e01388-21. [CrossRef]
- Venkataramanan, S.; Gadek, M.; Calviello, L.; Wilkins, K.; Floor, S. N. DDX3X and DDX3Y Are Redundant in Protein Synthesis. RNA 2021, 27, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, M. Human DEAD-Box Protein 3 Has Multiple Functions in Gene Regulation and Cell Cycle Control and Is a Prime Target for Viral Manipulation. Biochem Pharmacol 2010, 79, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rifo, R.; Rubilar, P. S.; Limousin, T.; de Breyne, S.; Décimo, D.; Ohlmann, T. DEAD-Box Protein DDX3 Associates with eIF4F to Promote Translation of Selected mRNAs. EMBO J 2012, 31, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-S.; Tsai, A.-H.; Ho, Y.-F.; Huang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Hwang, L.-H. Stimulation of the Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES)-Dependent Translation of Enterovirus 71 by DDX3X RNA Helicase and Viral 2A and 3C Proteases. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Choudhry, H.; Cao, W. Apolipoprotein B mRNA Editing Enzyme Catalytic Polypeptide-like Family Genes Activation and Regulation during Tumorigenesis. Cancer Sci 2018, 109, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, M.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Wu, S.; Guo, T.; Cen, S.; Jiang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. APOBEC3G Is a Restriction Factor of EV71 and Mediator of IMB-Z Antiviral Activity. Antiviral Research 2019, 165, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrholz, M.; Kendl, S.; Prifert, C.; Weissbrich, B.; Lemon, K.; Rennick, L.; Duprex, P. W.; Rima, B. K.; Koning, F. A.; Holmes, R. K.; Malim, M. H.; Schneider-Schaulies, J. The Innate Antiviral Factor APOBEC3G Targets Replication of Measles, Mumps and Respiratory Syncytial Viruses. Journal of General Virology 2012, 93, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D. H.; Hu, J. Reverse Transcriptase- and RNA Packaging Signal-Dependent Incorporation of APOBEC3G into Hepatitis B Virus Nucleocapsids. Journal of Virology 2008, 82, 6852–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, A.; Iwatani, Y. APOBEC3G-Mediated G-to-A Hypermutation of the HIV-1 Genome: The Missing Link in Antiviral Molecular Mechanisms. Front Microbiol 2016, 7, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ning, S.; Su, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, B.; Yu, X.-F.; Zhang, W. Enterovirus 71 Antagonizes the Inhibition of the Host Intrinsic Antiviral Factor A3G. Nucleic Acids Research 2018, 46, 11514–11527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, L.; Duchaîne, T.; Luo, M.; Nabi, I. R.; DesGroseillers, L. Mammalian Staufen Is a Double-Stranded-RNA- and Tubulin-Binding Protein Which Localizes to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. Mol Cell Biol 1999, 19, 2220–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y. K.; Furic, L.; Desgroseillers, L.; Maquat, L. E. Mammalian Staufen1 Recruits Upf1 to Specific mRNA 3’UTRs so as to Elicit mRNA Decay. Cell 2005, 120, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, S. W.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Sun, S. Advances and Breakthroughs in IRES-Directed Translation and Replication of Picornaviruses. mBio 2023, 14, e0035823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furic, L.; Maher-Laporte, M.; DesGroseillers, L. A Genome-Wide Approach Identifies Distinct but Overlapping Subsets of Cellular mRNAs Associated with Staufen1- and Staufen2-Containing Ribonucleoprotein Complexes. RNA 2008, 14, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Ou, B.-T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chan, H.-H.; Chen, C.-J.; Wang, R. Y. Staufen1 Protein Participates Positively in the Viral RNA Replication of Enterovirus 71. Viruses 2019, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackham, S. L.; McGarvey, M. J. A Host Cell RNA-Binding Protein, Staufen1, Has a Role in Hepatitis C Virus Replication before Virus Assembly. J Gen Virol 2013, 94 Pt 11, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamyan, L. G.; Chatel-Chaix, L.; Ajamian, L.; Milev, M. P.; Monette, A.; Clément, J.-F.; Song, R.; Lehmann, M.; DesGroseillers, L.; Laughrea, M.; Boccaccio, G.; Mouland, A. J. Novel Staufen1 Ribonucleoproteins Prevent Formation of Stress Granules but Favour Encapsidation of HIV-1 Genomic RNA. J Cell Sci 2010, 123 Pt 3, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lucas, S.; Peredo, J.; Marión, R. M.; Sánchez, C.; Ortín, J. Human Staufen1 Protein Interacts with Influenza Virus Ribonucleoproteins and Is Required for Efficient Virus Multiplication. J Virol 2010, 84, 7603–7612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauger, D. M.; Lin, C.; Garcia-Blanco, M. A. hnRNP H and hnRNP F Complex with Fox2 To Silence Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 Exon IIIc. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2008, 28, 5403–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Xie, N.; Su, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liu, D.; Jia, S.; Xing, X.; Han, L.; Li, G.; Tong, T.; Chen, J. HnRNP F/H Associate with hTERC and Telomerase Holoenzyme to Modulate Telomerase Function and Promote Cell Proliferation. Cell Death Differ 2020, 27, 1998–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, G.; Cibelli, G. Regulation of Life and Death by the Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Egr-1. Journal of Cellular Physiology 2002, 193, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, B.-C.; Yu, S.-L.; Chen, J. J. W.; Chang, S.-Y.; Yan, B.-S.; Hong, Q.-S.; Singh, S.; Kao, C.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Su, K.-Y.; Li, K.-C.; Cheng, C.-L.; Cheng, H.-W.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, C.-N.; Yang, P.-C. Enterovirus-Induced miR-141 Contributes to Shutoff of Host Protein Translation by Targeting the Translation Initiation Factor eIF4E. Cell Host & Microbe 2011, 9, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, X.; Zhao, R.; Wang, P.; Han, Y.; Luo, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Wu, J. Early Growth Response-1 Facilitates Enterovirus 71 Replication by Direct Binding to the Viral Genome RNA. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 2015, 62, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedersha, N. L.; Gupta, M.; Li, W.; Miller, I.; Anderson, P. RNA-Binding Proteins TIA-1 and TIAR Link the Phosphorylation of eIF-2 Alpha to the Assembly of Mammalian Stress Granules. J Cell Biol 1999, 147, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschald, O. R.; Malec, V.; Krasteva, G.; Hasan, D.; Kamlah, F.; Herold, S.; Rose, F.; Seeger, W.; Hänze, J. TIAR and TIA-1 mRNA-Binding Proteins Co-Aggregate under Conditions of Rapid Oxygen Decline and Extreme Hypoxia and Suppress the HIF-1α Pathway. J Mol Cell Biol 2010, 2, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J. P.; Lloyd, R. E. Poliovirus Unlinks TIA1 Aggregation and mRNA Stress Granule Formation. Journal of Virology 2011, 85, 12442–12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Si, X.; Wang, T.; Zhong, X.; Tong, L.; Luan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhong, Z. Protease 2A Induces Stress Granule Formation during Coxsackievirus B3 and Enterovirus 71 Infections. Virol J 2014, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Chu, Y.; Su, A.; Wu, Z. TIA-1 and TIAR Interact with 5′-UTR of Enterovirus 71 Genome and Facilitate Viral Replication. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2015, 466, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
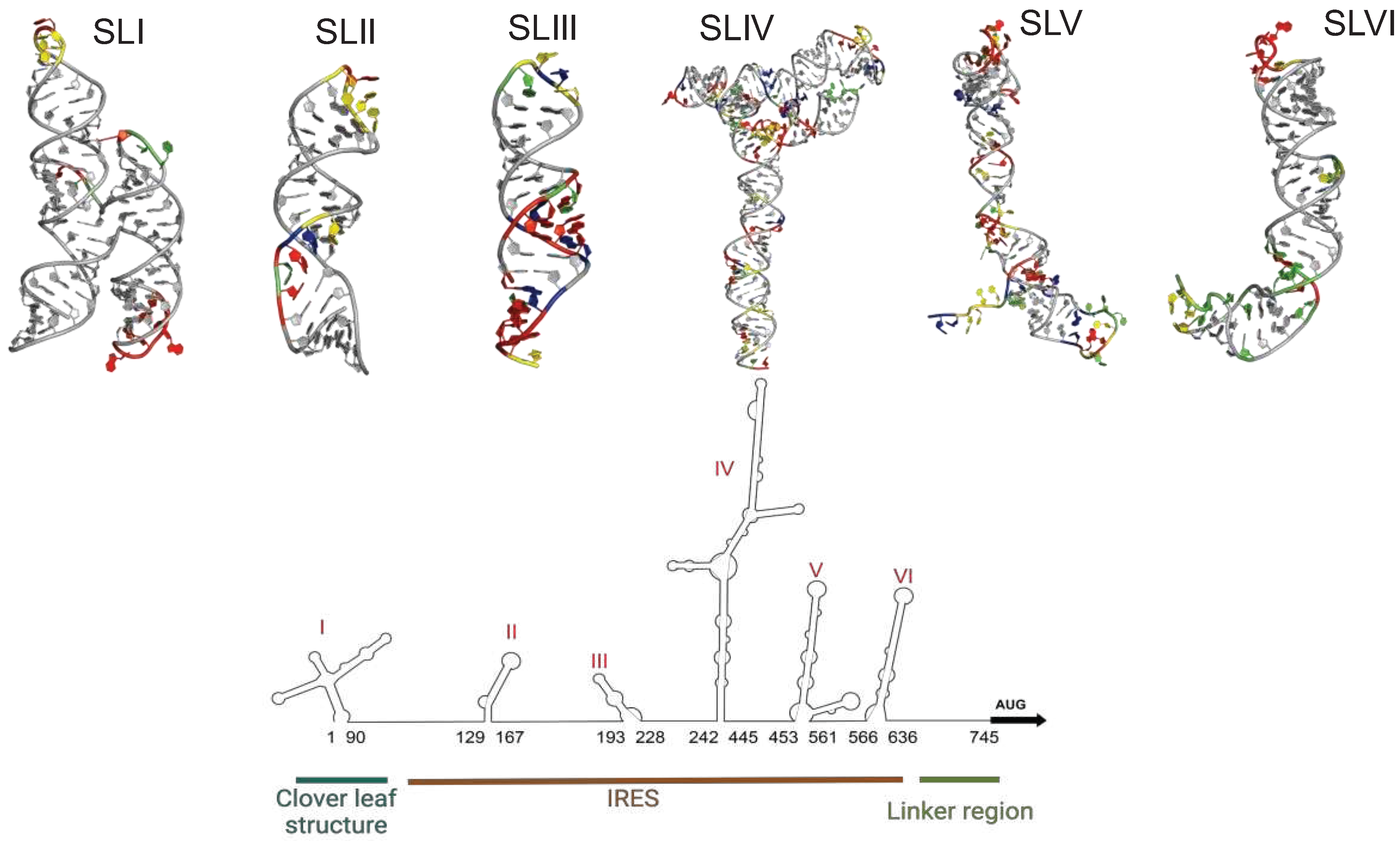
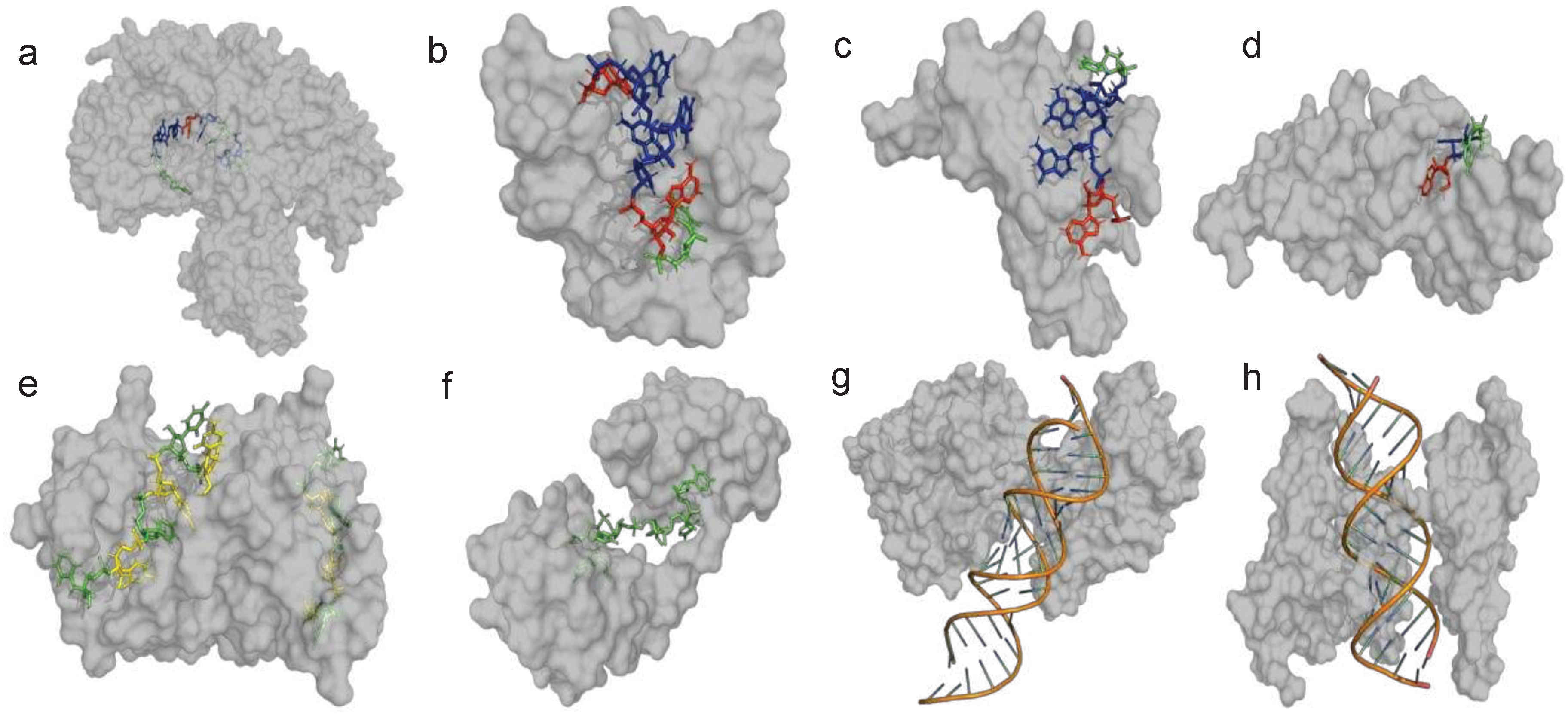
| ITAF | Other Names | Cellular distribution | Regulatory Site | IRES activity | Reference(s) | PDB ID(s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-infection | Post-infection | ||||||
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 | hnRNP A1 | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | SLII and IV | Enhancement | [34] |
4YOE: 1.92 Å 5MPL: NMR 5MPG: NMR |
| AU-rich element RNA-binding protein 1 | AUF1, hnRNP D |
Nucleus | Cytoplasm | SLII | Inhibition | [45], [46] | 1WTB: NMR 1X0F: NMR |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K | hnRNP K | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | SLI, II, and IV | - | [35] | 1J5K: NMR 1ZZI: 1.80Å 1ZZJ: 2.30 Å 7CRE: 3.00 Å |
| Poly(c)-binding protein 1 | PCBP1, hnRNP E1 |
Nucleus, Cytoplasm |
Cytoplasm | SLI and IV | Enhancement | [56] | 1ZTG: 3 Å 3VKE: 1.77 Å |
| Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 | PTB, PTB1 PTBP1 hnRNP I |
Nucleus | Cytoplasm | SLVI + linker (564 - 742 nt) | Enhancement | [69] |
2N3O: NMR 2AD9: NMR 2ADB: NMR 2ADC: NMR |
| Far upstream binding protein 2 | FBP2, FUBP2 KSRP, KHSRP |
Nucleus | Cytoplasm | SLI-SLII (1-167) SLII-SLIII (91-228) SLVI + linker (566-745) | Inhibition | [36] | 4B8T: NMR |
| C-terminus cleaved FBP2 | FBP21–503 | - | - | 5’-UTR | Enhancement | [76] | |
| N-terminus cleaved FBP2 | FBP2190 –711 | - | - | 5’-UTR | Inhibition | [76] | |
| Far upstream binding protein 1 | FBP1 FUBP1 |
Nucleus | Cytoplasm | Linker (686-714 nt) | Enhancement | [82] | 1J4W: NMR |
| Cleaved FBP1 | FBP11-371 | - | - | Linker (656-674 nt) | Enhancement | [83] | |
| Argonaute 2 | Ago2 | Nucleus, Cytoplasm (P-bodies) |
- | SLII | Enhancement | [48] | 5KI6: 2.15 Å |
| Human Antigen R | HuR, ELAVL11 |
Nucleus, shuttles to Cytoplasm2 |
Cytoplasm3 | SLII | Enhancement | [48] | 4ED5: 2.00 Å 6G2K: 2.00 Å 6GC5: 1.90 Å 6GD2: 1.90 Å |
|
Moloney leukemia virus 10 (C-terminus domain) |
MOV10 | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm (P-bodies & aggregates perinuclear) |
SLI and IRES (Excluding the linker region) |
Enhancement | [98] | |
| Silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 | SIRT1 | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | SLI, II, III and V |
Inhibition | [107] | |
| 68-kDa Src-associated protein in mitosis | Sam68, KHDRBS1 |
Nucleus | Cytoplasm | SLIV and V | Enhancement | [117] | |
| Far upstream element-binding protein 3 | FUBP3 | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | 5’-UTR | Enhancement | [120,121] | |
| growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 34 | GADD34, PPP1R15A |
ER membrane Mitochondial membrane |
- | 5’-UTR | Enhancement | [131,132] | |
| DEAD-box protein 3 | DDX3 | Nucleus Cytoplasm |
- | Full 5’-UTR | Enhancement | [136] | 6O5F: 2.5 Å |
| apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3G | APOBEC3G, A3G |
Cytoplasm (mainly) Nucleus P-bodies |
Cytoplasm Virions |
SLI and II | Inhibition | [56], [142] | 5ZVA: 2.30 Å 5ZVB: 2.00 Å 6BUX: 1.86 Å 7UXD: 1.50 Å |
| Staufen homolog 1 | Staufen1 | Rough ER Cytoplasm |
- | 5’-UTR | Enhancement | [147] | 6HTU: 2.89 Å |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H | HNRNP H | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | 5’-UTR | Enhancement | [120] | |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein F | HNRNP F | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | 5’-UTR | Enhancement | [120] |
2KFY: NMR 2KG0: NMR 2KG1: NMR |
| Early growth response-1 | EGR1 | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | SLI and IV | Enhancement | [155] | 4R2A: 1.59 Å |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





