1. Introduction
Audio classification or sound classification can be referred to as the process of analyzing audio recordings. Audio classification involves the application of machine learning algorithms to raw audio data to categorize the type of audio present. Typically, this process relies on data that has been annotated and classified into target categories by human listeners in various applications.
There is a wide range of different applications for audio classification. Extensive research has been conducted in the field of speech recognition, leading to the advancement of speech-to-text systems. Similarly, audio classification technology has found applications in automating music categorization and powering recommendation engines for music. Classification of environmental sounds has been proposed for the identification of specific species of birds and whales. Additionally, monitoring of environmental sounds in urban environments has been proposed to aid in law enforcement through the identification of sounds that may be associated with crime (i.e., gunshots) or unauthorized construction (i.e. jackhammers). Pioneering efforts are directed toward developing a small, versatile, efficient deep network for acoustic recognition on resource-limited edge devices. Besides, a key component of many intelligent Internet of Things (IoT) applications, including predictive maintenance [
1,
2], surveillance [
3,
4], and ecosystem monitoring [
5,
6], is audio classification. With several possible applications, including audio surveillance[
7] and smart room monitoring[
8], environmental sound categorization (ESC) is a significant study topic in human-computer interaction. Designing suitable features for environmental sound categorization is a practical task because acoustic settings are dynamic and unstructured. A classifier is trained with the features in many existing ESC approaches to determine the category likelihood of each environmental sound wave. The features are frequently generated based on prior knowledge of acoustic settings. One of the effective tools in the field of problem diagnosis is intelligent fault diagnosis[
9,
10]. It is possible to replace diagnosticians by using artificial intelligence techniques like neural networks to quickly evaluate these signals and automatically identify mechanical health issues based on the massively monitored signals of the machines [
11,
12,
13]. Therefore, intelligent problem identification is vital in contemporary enterprises, particularly when there are abundant vibration signals. Edge computing is the concept of performing computations at the edge of the network rather than in the cloud. Edge computing has advantages in terms of decreased latency, increased integrity, and lessened network load. The application of machine learning techniques to edge computing is known as edge AI[
14]. Edge devices can play a crucial role in numerous ways, such as Data Collection, Latency reduction, Cost reduction, Improved security, and Increased reliability. Edge devices are used to collect and process data at the source, reducing the amount of data transmitted to the cloud or data center. By processing data locally, edge devices can reduce the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, reducing the costs associated with data transmission. Edge devices can provide a secure processing environment for sensitive data, reducing the risk of data breaches. It can provide redundancy and failover capabilities, increasing the reliability of systems.
Audio classification or sound classification can be referred to as the process of analyzing audio recordings. Audio classification encompasses the systematic application of machine learning algorithms to analyze unprocessed audio data to identify distinct audio types. This methodology predominantly employs data that has been meticulously annotated and categorized into predefined classes, these classifications being determined by expert human auditors. This approach is widely adopted in numerous applications to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of audio analysis. There is a wide range of different applications for audio classification. A great deal of research has been completed for speech recognition and the development of speech-to-text systems. Additionally, audio classification technology has found its use in the automation of music categorization and the development of music recommendation systems. Classification of environmental sounds has been proposed for the identification of specific species of birds and whales. Additionally, monitoring of environmental sounds in urban environments has been proposed to aid in law enforcement through the identification of sounds that may be associated with crime (i.e., gunshots) or unauthorized construction (i.e. jackhammers). Pioneering efforts are directed toward developing a small, versatile, efficient deep network for acoustic recognition on resource-limited edge devices. Edge devices can perform real-time audio classification, enabling immediate response to audio events. Also, by performing classification locally, edge devices can reduce the latency of the audio classification process, improving the responsiveness of systems. Edge devices can perform audio classification without transmitting sensitive audio data to the cloud, protecting privacy. Edge devices can also help in cost reduction. By reducing the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, edge devices can reduce the costs associated with audio classification.
Deep learning models have shown tremendous success in audio classification tasks. There are several limitations of these models when we want to implement them in any edge device. In general, data collected at the edge of the network from different sensors are sent to the cloud for processing and decision-making. It will create latency for transmitting a massive amount of data, and struggle with privacy concerns. For these reasons, it will be difficult to use edge devices for real-time analytics. If the analysis and recognition occur directly in edge devices, it can overcome the latency. For this, we need to rely on the computation power of the edge devices.
Deep learning models require a ampule amount of data, extended training time, and large-trained models. So, it is challenging to run deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks on edge devices that have low processing power, no GPU, and low memory [
15,
16]. Krizhevsky et al .[
17] show they used 60 million parameters and 650,000 neurons for five convolutional layers and 1000-way SoftMax. ImageNet dataset consists of 15 million labeled high-resolution images of 22,000 categories. Another popular face recognition method, Deep Face trained about 120 million parameters for more than four million facial images[
18].
In [
19], proposed a large deep convolutional network for audio classification using raw data and then compressed the model for resource-improvised edge devices which produces above state-of-the-art accuracy on ESC-10 (96.65 %), ESC-50 (87.10%), Urban- Sound8K (84.45 %) and AudioEvent (92.57%), we describe the compression pipeline and show that it allows us to achieve 97.22% size reduction and 97.28% FLOP reduction. audio classification on microcontrollers using XNOR-Net for end-to-end raw audio classification was explored, comparing it with pruning-and-quantization methods. It finds that XNOR-Net is efficient for small class numbers, offering significant memory and computation savings. Still, its performance drops with larger class sets where pruning-and-quantization methods are more effective. In [
20], a knowledge distillation method enhances on-device audio classification by transferring temporal knowledge from large models to smaller, on-device models. This method focuses on incorporating the temporal information embedded in attention weights of large transformer-based models into various on-device architectures, including CNNs and RNNs. In [
21], a real-time audio enhancement system is proposed that uses convolutional neural networks for precise audio scene classification, optimizing sound quality with minimal latency. This system efficiently enhances audio frame-by-frame audio, overcoming the limitations of traditional scene-rendering methods in audio devices. A sequential self-teaching approach [
22] for sound event recognition is especially effective in challenging scenarios like weakly labeled or noisy data. It proposes a multi-stage learning process that enhances the generalization ability of sound models, demonstrated by up to 9% improved performance on the large-scale Audioset dataset. Additionally, this method shows enhanced transferability of knowledge, boosting generalization in transfer learning tasks. In [
23], LEAN, a lightweight, efficient deep-learning model for audio classification on resource-limited devices is introduced. It combines a trainable wave encoder with Pretrained YAMNet and cross-attention-based realignment, achieving high performance with a low 4.5MB memory footprint, and improving mean average precision on the FSD50K dataset by 22%. Another approach [
24] is a sequential self-teaching approach for sound event recognition, especially effective in challenging scenarios like weakly labeled or noisy data. It proposes a multi-stage learning process that enhances the generalization ability of sound models, demonstrated by up to 9% improved performance on the large-scale Audioset dataset.
This study aims to perform model compression and acceleration in deep neural networks without significantly decreasing the model performance. The current state of the art for deep learning model compression and acceleration includes pruning and quantization. Analyzing deep learning algorithms with different model compression techniques that can classify audio data with better accuracy in edge devices. I used environmental sound datasets such as UrbanSound8K, ESC 50, and Audio Set datasets for the experiments. There are many different uses for audio classification and edge devices. Their capacity for real-time audio analysis and categorization gives up a wide range of opportunities for enhancing functionality, security, and convenience across numerous fields and spheres of life.
This research provides the following contributions:
Compare different DL models for audio classification for raw audio and Mel Spectrograms.
Apply different model compression techniques to the Neural Network and propose hybrid pruning techniques.
Deploy DL models for audio classification in Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson Nano.
The following layout entails this research. Chapter 2, introduces in detail the algorithm of the proposed method along with the theoretical and technical parts. In Chapter 3, Experimental details and Results are discussed in chapter 4. Conclusions and future works are then drawn in Chapter 5.
2. Methodology
In the realm of image categorization, deep learning demonstrates exceptional proficiency, producing transformative outcomes in diverse domains. This advanced computational approach also exhibits significant potential in auditory classification tasks, including the categorization of musical genres and environmental soundscapes. The research methodology proposed for this study is outlined as follows:
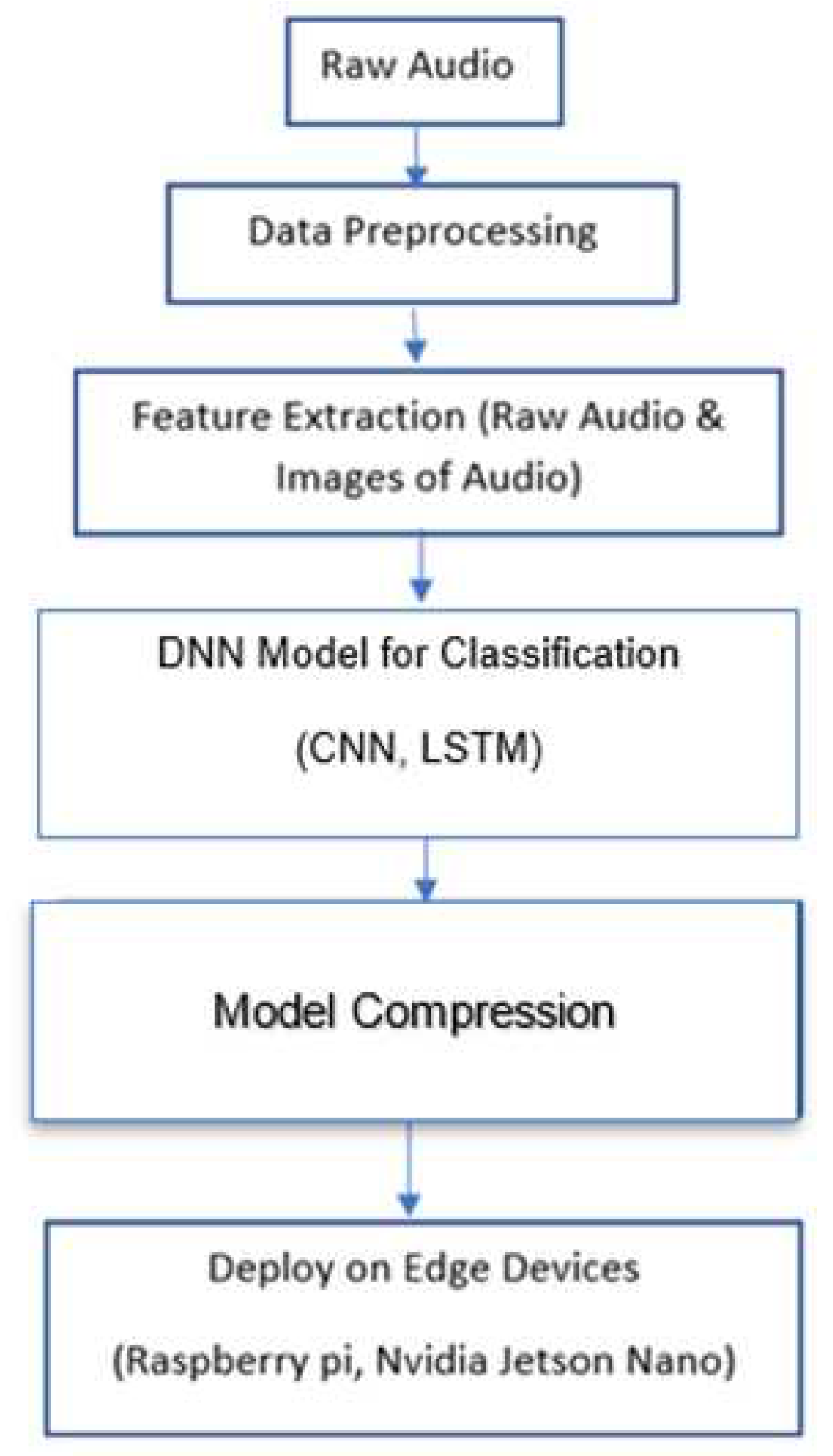
Figure 1.
PipeLine of the Proposed Method.
Figure 1.
PipeLine of the Proposed Method.
2.1. Feature Selection
Sound is an auditory experience created by variations in air pressure. These variations can be graphically represented over time, showing the intensity and pattern of sound waves. A sound wave’s amplitude, visible as the height of the wave, indicates the sound’s intensity. The wave’s periodic nature, where each cycle repeats regularly, is crucial in understanding sound patterns. The period of a sound wave is the duration it takes to complete one full cycle, while the frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), is the number of complete cycles per second. The frequency is inversely proportional to the period. Real-world sounds, such as musical instruments or human voices, are typically more complex than simple periodic waves. They are composed of multiple frequencies, each contributing to the overall sound. The quality or ’timbre’ of a sound is what allows the human ear to differentiate between different sounds, even if they have the same pitch and loudness. To utilize sound in digital formats, such as for deep learning models, it must be converted into a series of numerical values. This process is achieved through sampling, where the sound wave’s amplitude is measured at fixed time intervals. The sample rate, or the number of samples taken per second, is a critical factor in capturing the sound’s characteristics. A common sample rate in audio applications is 44,100 samples per second.
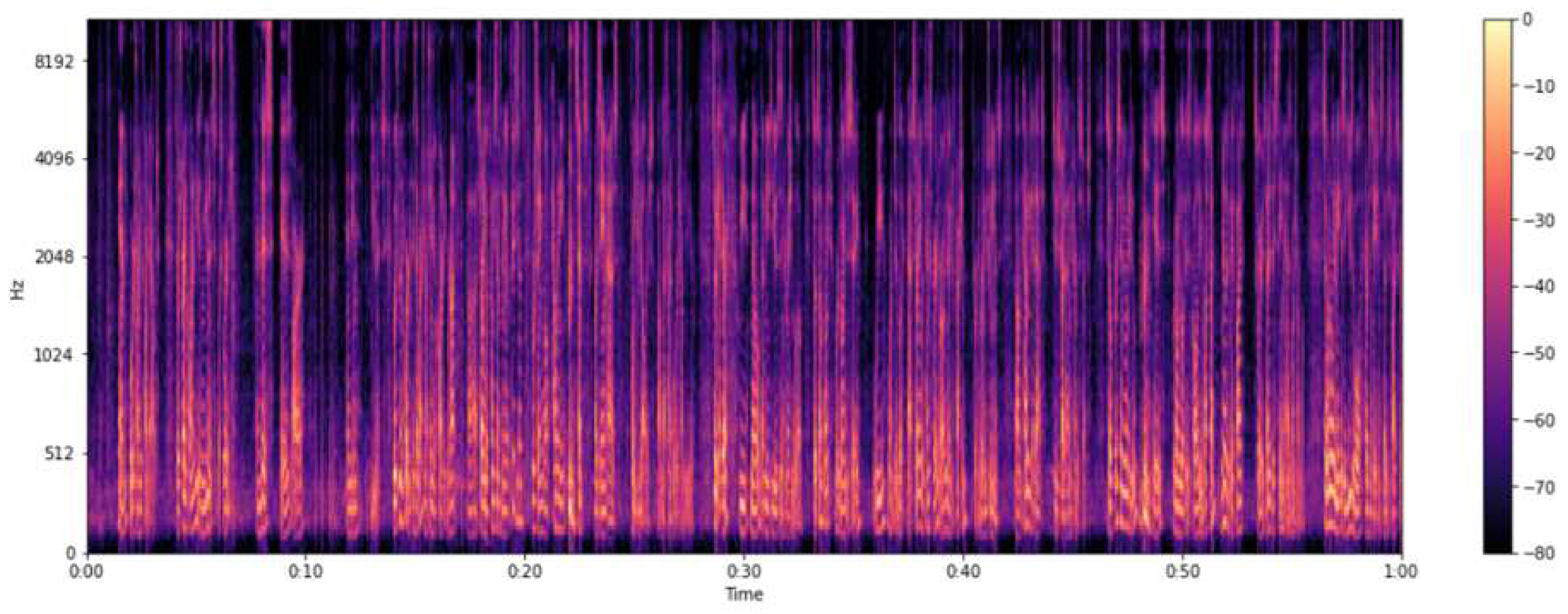
In the era before deep learning, audio processing in machine learning relied heavily on digital signal processing techniques and required extensive domain-specific knowledge.With the advent of deep learning, the need for such specialized techniques has diminished. Deep learning models can process audio data more directly, reducing the need for manual feature extraction. A significant advancement in deep learning for audio is the conversion of audio data into image formats. These ’images’ of sound are then processed using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures, a common approach in deep learning.
Figure 2.
Mel Spectrograms
Figure 2.
Mel Spectrograms
A spectrum represents the range of different frequencies that make up a sound signal. The fundamental frequency is the lowest frequency in a signal, and its multiples are known as harmonics. A spectrogram is a visual representation of how a sound signal’s spectrum changes over time. It plots frequency against time, using colors to indicate the amplitude or strength of each frequency at each point in time. Spectrograms provide a detailed view of the distribution of a signal’s strength across its frequencies, offering valuable insights for audio processing in deep learning. MEL spectrograms are a crucial tool in audio classification due to their alignment with human auditory perception, particularly emphasizing frequencies below 1000 Hz which are vital in understanding speech and music. They aid in reducing the dimensionality of audio data, converting complex audio signals into a more manageable form without losing essential features. This aspect is particularly beneficial in making the data processing more computationally efficient. Additionally, MEL spectrograms offer robustness against noise by focusing on perceptually significant sound components, thus enhancing the quality of audio analysis. They also provide an improved feature representation, leading to better classification results in various audio-related tasks such as speech recognition and music genre classification. Furthermore, their compatibility with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) makes them an excellent choice for extracting hierarchical features, an essential aspect of modern audio classification systems. These characteristics make MEL spectrograms a preferred choice in the field of audio signal processing.
2.2. Model Architecture
The model consists of several types of layers, including Convolutional layers (Conv2d), Batch Normalization layers (BatchNorm2d), Rectified Linear Unit layers (ReLu), Max Pooling layers (MaxPool2d), a Permutation layer (Permute), Average Pooling layer (AvgPool2d), a Flatten layer, a Linear layer, and a Softmax layer. Convolutional Layers: These are the primary layers for feature extraction in the model. They have varying input and output shapes, indicating different kernel sizes and feature map dimensions. For instance, the first Conv2d layer takes an input of shape (1, 1, 30225) and produces an output of shape (8, 1, 15109). Batch Normalization and ReLU Layers: These are used following convolutional layers for normalization and applying the ReLU activation function, respectively.
Pooling Layers: MaxPool2d and AvgPool2d are used for downsampling the feature maps. Permute Layer: Changes the dimension order of the tensor. Flatten Layer: Converts multi-dimensional feature maps into a one-dimensional vector. Linear Layer: A fully connected layer that maps the flattened features to a space of dimension (1, n ). Softmax Layer: Used for classification, outputs probability distribution across n classes. The model has a total of 4,735,378 parameters, indicating its complexity and capacity. The model performs approximately 544,422,040 floating-point operations. FLOPs are a measure of computational complexity, indicating how many operations are required to make a forward pass through the network. In LSTM, we employ the bidirectional unit and dense layer at the model’s conclusion. Adam is employed as the optimizer in all models. We used the following hyperparameters to extract the features from the Mel spectrograms: 128 Mels, n _fft of 512, window size of 400, 16 kHz sample rate, and hop length of 160. To create the Mel spectrograms, we combine STFT and the Hann window.
2.3. Model Compression
For deploying audio classification models on resource-constrained devices like Raspberry Pi 4 and NVIDIA Jetson Nano, selecting the right model compression techniques is crucial to balance performance and efficiency.
2.3.1. Pruning
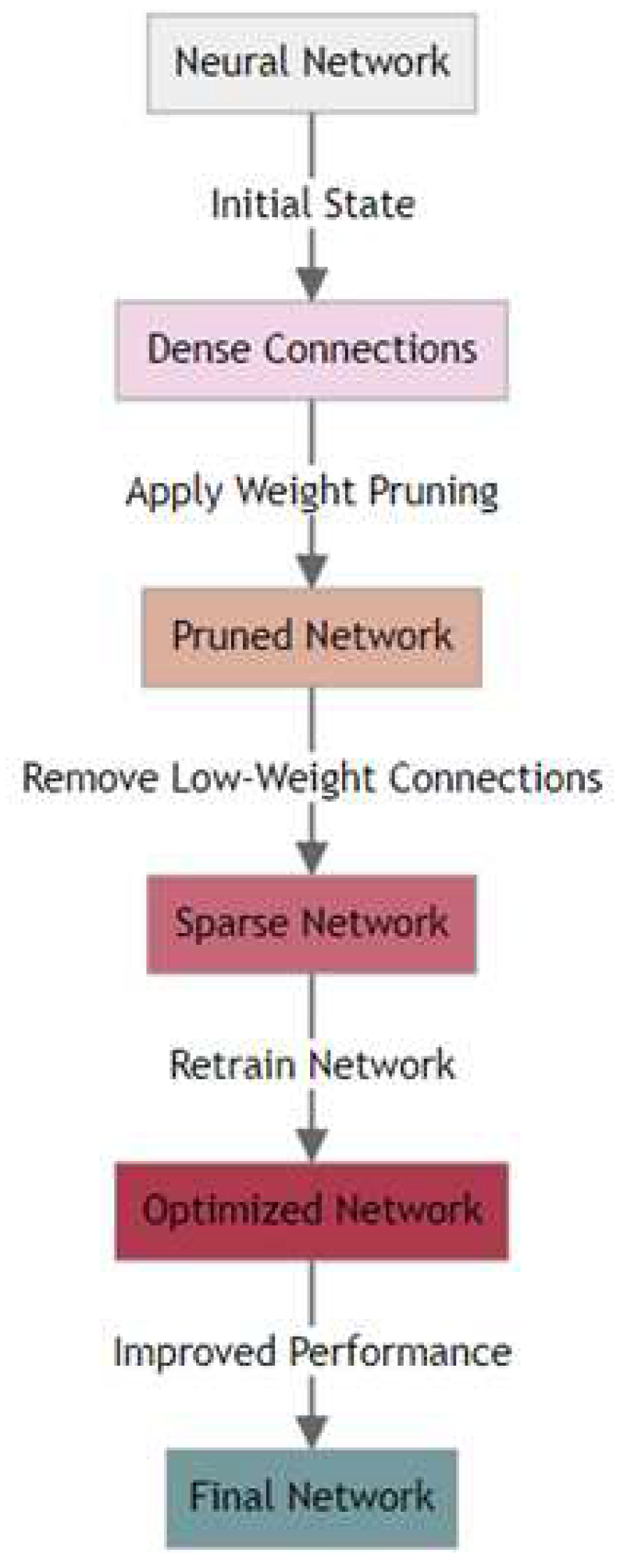
To compress the model for audio classification we used magnitude pruning and Taylor pruning. Using magnitude pruning and Taylor pruning for model compression offers several benefits, particularly when deploying models on resource-constrained devices like the Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson Nano. These benefits stem from the ability of these techniques to reduce model size and computational complexity while maintaining acceptable levels of accuracy. Magnitude pruning significantly reduces the number of parameters in a neural network by eliminating weights with the smallest magnitudes. This leads to a smaller model size, making it more suitable for devices with limited storage, like the Raspberry Pi. With fewer weights to process, the computational load during inference is reduced. This can lead to faster response times, which is crucial for real-time audio classification applications on both Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson Nano. Smaller and less complex models require less power to run, which is beneficial for battery-powered or energy-sensitive applications, a common scenario for Raspberry Pi-based projects. The reduced model size offers more flexibility in deploying complex models on the Raspberry Pi, which might otherwise be infeasible due to memory constraints.
Taylor pruning considers the impact of each weight on the loss function, allowing for a more informed decision about which weights to prune. This often results in better preservation of model accuracy compared to magnitude pruning. By focusing on the removal of weights that have the least effect on model output, Taylor pruning ensures that the computational resources of the NVIDIA Jetson Nano are used more efficiently, focusing on weights that contribute most to the model’s performance. Taylor pruning can be applied to a variety of neural network architectures, making it a versatile choice for different types of audio classification models that might be deployed on these devices. For the NVIDIA Jetson Nano, which has more computational power than the Raspberry Pi, Taylor pruning can effectively balance model complexity and performance, optimizing the use of its GPU capabilities.
A hybrid pruning approach leveraging both magnitude and Taylor pruning techniques can provide a more effective and adaptable solution for model compression. It allows for a nuanced balance between model size, computational efficiency, and accuracy, which is particularly beneficial in resource-constrained environments or in applications where both speed and accuracy are crucial. Magnitude pruning effectively reduces the model size by eliminating weights with the smallest magnitudes, which are often deemed less important. However, this approach doesn’t always consider the overall impact of each weight on the model’s output. Taylor pruning, on the other hand, evaluates the impact of weights on the loss function, providing a more nuanced view of each weight’s importance. By combining these two methods, a hybrid approach can prune the model more aggressively than magnitude pruning alone (thus reducing the size and computational load) while still maintaining a higher level of accuracy, as it considers the impact of pruning on model performance like Taylor pruning. Different layers of a neural network might have varying levels of sensitivity to pruning. A hybrid approach allows for a more tailored pruning strategy, where magnitude pruning can be applied more aggressively in layers that are less sensitive, and Taylor pruning can be used in layers where accuracy is more critical. Different neural network architectures may respond differently to pruning. A hybrid approach provides the flexibility to adjust the pruning strategy according to the specific architecture, whether it’s a convolutional neural network for image processing or a recurrent neural network for sequence modeling like audio classification. On devices like the Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson Nano, the reduced model size from magnitude pruning leads to faster inference times and lower power consumption. The careful pruning from the Taylor method ensures that this efficiency does not come at the cost of a significant drop in accuracy. A hybrid approach needs to be implemented iteratively, starting with magnitude pruning to quickly reduce size and then refining with Taylor pruning to fine-tune the model. This iterative process leads to a more optimized balance between size, speed, and accuracy. A comparison of the performance of the different pruning techniques is shown in
Table 3.
2.3.2. Quantization
8-bit quantization is a highly effective technique for optimizing deep learning models for deployment on devices like the Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson Nano. It addresses the key challenges of limited computational resources, storage capacity, and power constraints, making it a popular choice for edge computing applications. Quantization reduces the precision of the weights and activations in a neural network from 32-bit floating-point to 8-bit integers. This reduction in bit-width leads to a significant decrease in model size, which is crucial for devices with limited storage capacity like the Raspberry Pi. 8-bit integers are computationally less expensive to process than 32-bit floating-point numbers. This results in faster computation during model inference, which is particularly beneficial for real-time applications like audio or video processing. With smaller data sizes, the memory bandwidth requirement is reduced. This means that data can be transferred more quickly between the memory and the processor, further speeding up the inference process. Most deep learning frameworks support 8-bit quantization, making it a widely accessible technique for optimizing models for edge deployment. We can see the performance of quantization on Table 6. While quantization can lead to a slight decrease in model accuracy, 8-bit quantization often strikes a good balance between maintaining acceptable accuracy levels and achieving significant efficiency gains.
3. Experimental Details
All the experiments will be conducted using Python and for hardware, Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson Nano were used. The Convolutional Neural Network is implemented in PyTorch version 2.1.0 and the Wavio audio library is used to process the audio files.
3.1. Datasets
The UrbanSound8K dataset was created in 2013 by Salamon, J., Jacoby, C., & Bello, J. P. as part of their research in audio event classification. The dataset is designed to be a resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of audio processing and machine learning. The audio files were recorded in various urban environments, including streets, parks, and residential areas, with a focus on capturing the sounds of everyday life in cities. The UrbanSound8K dataset is a collection of 8,000 audio files recorded in various urban environments. Each file is labeled with one of 10 different classes, including "air conditioning," "car horn," "children playing," "dog bark," "drilling," "engine idling," "gunshot," "jackhammer," "siren," and "street music." Each of the 8,000 audio files in the dataset is 4 seconds long and is labeled with one of the 10 classes mentioned earlier. The dataset was created to provide a challenging and diverse set of audio events that can be used to evaluate and compare the performance of different audio classification algorithms [8]. The ESC-50 dataset is a collection of 2,000 environmental sound recordings organized into 50 different classes. The classes include various types of natural sounds, such as water sounds, animal sounds, and weather sounds, as well as man-made sounds, such as vehicle sounds, alarm sounds, and musical instrument sounds. Each sound recording is 5 seconds long and is annotated with the corresponding class label. AudioSet is a large-scale dataset of audio events and scenes created by Google. The dataset contains over 2 million 10-second audio clips, representing a diverse range of sounds, including human speech, music, animal sounds, and environmental sounds. Each audio clip is annotated with one or more labels from a hierarchical ontology of over 632 sound event classes, including fine-grained classes such as "saxophone" and "dog bark" as well as broader classes such as "music" and "animal."
3.2. Data Preprocessing
The ESC-50 dataset comprises a total of 2,000 audio samples, each with a duration of five seconds. These samples are recorded at two distinct sampling rates: 16kHz and 44.1kHz. The dataset is meticulously organized into 50 distinct and balanced classes, with each class containing 40 individual audio samples. Additionally, the ESC-50 dataset is partitioned into five separate splits, a structure that facilitates the implementation of 5-fold cross-validation, thereby aiding researchers in obtaining unbiased and comparable experimental results. In contrast, the UrbanSound8K (US8K) dataset encompasses 8,732 labeled audio clips. Each clip, featuring urban soundscapes, has a maximum duration of four seconds and is recorded at a sampling rate of 22.05kHz. This dataset is categorized into 10 classes. Notably, the US8K dataset is pre-arranged into 10 folds, specifically designed to support 10-fold cross-validation. This arrangement is instrumental in ensuring that the research outcomes are unbiased and comparable, adhering to rigorous academic standards. The network in question is configured to process audio data sampled at 20kHz, with each input corresponding to a length of 30,225 data points. This length equates to approximately 1.51 seconds of audio. The decision to downsample the data to 20kHz was driven by the objective to minimize the input size, reduce the overall model size, and decreasing power consumption. It is noteworthy that, based on empirical observations, the performance of the network remains consistent and unaffected when handling audio that has been resampled at this lower rate. This indicates that the reduction in sampling rate to 20kHz does not detrimentally impact the network’s ability to process and analyze audio data effectively.
4. Results
In this study, the extraction of low-level features from raw audio data is a critical step, with a particular focus on the Zero Crossing Rate (ZCR). ZCR, a key measure in the analysis of audio signals, quantifies the frequency at which the audio waveform crosses the zero amplitude axis, thereby providing insights into the frequency content of the signal. This metric is integral to various digital signal processing applications, including speech and music analysis, as well as broader audio classification tasks. The utility of ZCR lies in its ability to effectively differentiate between tonal sounds, which exhibit a lower ZCR, and more noisy or percussive elements, characterized by a higher ZCR.
A notable challenge arises when the audio contains significant ’dead spots’ or segments of minimal amplitude, as these can obscure the distinctive features of the audio, leading to difficulties in classification. To mitigate this issue, the initial step involves the cleansing of audio data by removing dead space, utilizing a technique that involves the application of a signal envelope. The signal envelope, a conceptual curve outlining the extremes of the audio waveform, provides a framework for identifying and excising sections of the audio below a threshold of 20 dB.
For uniformity and computational efficiency, the audio clips are standardized to a fixed frame size. To facilitate real-time GPU-based extraction of audio features from Mel spectrograms, the study employs Keras Audio Preprocessors (Kapre). Kapre’s capabilities extend to the optimization of signal parameters in real-time, significantly simplifying and enhancing the reliability of model deployment. In
Table 1, the comparison between the audio classification using raw audio and Mel Spectrograms is shown. Mel Spectrograms achieve the highest accuracy of 95%.
Table 1.
Audio classification comparison between feature extractions by raw audio and Mel Spectrogram.
Table 1.
Audio classification comparison between feature extractions by raw audio and Mel Spectrogram.
| Datasets |
Raw Audio |
Mel Spectrograms |
| ESC-50 |
91% |
92.7% |
| UrbanSound8k |
79% |
84% |
| AudioSet |
90% |
95% |
We have also shown that with the proposed methodology, the experimental result also performs better than many existing models.
Table 2.
Comparison our result with the existing result of Mel Spectrogram.
Table 2.
Comparison our result with the existing result of Mel Spectrogram.
| Networks |
ESC50 |
US8k |
| Pizak-CNN [25] |
64.50% |
73.70% |
| Multi-CNN[26] |
89.50% |
- |
| GoogLENet [27] |
73% |
93% |
| Proposed |
92.7% |
84% |
Hybrid pruning, combining magnitude and Taylor pruning, offers superior model optimization by balancing the efficient size reduction of magnitude pruning with the precision of Taylor pruning. In
Table 3, we can see that hybrid pruning gets better accuracy than individual pruning methods. This approach enhances network performance and generalization while maintaining an optimal level of complexity. It strikes a fine balance between computational efficiency and the retention of crucial network features.
Table 3.
Comparision Between Different Pruning Methods.
Table 3.
Comparision Between Different Pruning Methods.
| Pruning Methods |
Accuracy |
| Weight |
88% |
| Taylor |
88.75% |
| Hybrid |
89.25% |
Though we got better accuracy for audio classification using pruning techniques, the model size and execution time were less using quantization techniques. A comparison between accuracy and model size is shown in
Table 4.
Table 4.
Comparison Between Pruning and Quantization.
Table 4.
Comparison Between Pruning and Quantization.
| Model Compression |
Accuracy |
Model Size |
| Original Model |
92% |
18.18 MB |
| Pruning |
89.25% |
528KB |
| Quantization |
85.25% |
157KB |
Later, the audio classification model was deployed in Raspberry Pi4 and NVIDIA Jetson Nano to check performance.
Table 5 shows the results of the accuracy, inference time, and power consumption in the devices.
Table 5.
Performance of audio classification on Edge Devices.
Table 5.
Performance of audio classification on Edge Devices.
| Device |
Accuracy |
Inference Time |
Power Consumption |
| Raspberry pi4 |
85% |
3.89 sec/it |
7 watts |
| NVIDIA Jetson Nano |
88% |
2.12 sec/it |
10 watts |