1. Introduction
Forests are the crucial ecosystems that play important roles in determining carbon storage, climate and ecological functionalities. Monitoring the spatial and temporal characteristics of the forest structure contributes to interpreting the global carbon cycle and environmental changes [1,2]. Remote sensing technologies have been proved to be highly effective to acquire the forest structure at region and global scales. Passive optical sensor and active radar system can mainly obtain the canopy height and stem volume, but the vertical forest structure information is still missing due to poor penetration [3,4]. Lidar is an active remote sensing technique that can overcome such problem and provide accurate vertical forest structure and underlying topography.
The full-waveform satellite lidar can implement the global forest inventory dependent on the amplitude of the received laser pulse signal reflected from the illuminated target surface. The received waveform provides an excellently resolved measurement of the vertical distribution of the vegetation and ground within laser footprint [5]. As one of the significant indicator parameters for characterizing forest structure, the height percentiles are usually derived from the cumulative distributions of the received waveform [6,7]. Many studies have been carried out to predict the forest characteristics using the height percentiles. For example, the height percentiles were used to develop a prediction system to calculate the stem volume [8–10]. Chen chose the 98% percentile height to represent the highest canopy height and Pang et al. proved that the 75% percentile height has the best correlation with actual canopy height [11,12]. Wang et al. employed canopy height percentiles to estimate the above ground biomass with a determination coefficient of 0.90 [13].
The key point to calculate the canopy percentile heights is how to determine the ground elevation and signal start elevation from the received waveforms. Until now, there are two most common algorithms to derive the canopy height percentiles. The first algorithm attempted to decompose the received waveform into multiple Gaussian components by using Gaussian decomposition method [11,14,15]. The signal start elevation was identified as the first location where the waveform amplitude exceeds a threshold level. The ground elevation was assumed to be last Gaussian component peak location. Thus, the height percentiles can be estimated from the cumulative distributions of the received waveform by their vertical distances relative to the ground elevation. The Gaussian decomposition method can be applicable for the received waveforms over the vegetated area with the flat ground. However, as for mountain areas with steep terrain, the ground return would be broadened and aliased with the vegetation return, which makes it difficult to extract ground component [16]. The second algorithm eliminated such deficiency by fitting the ground Gaussian component based on the ground surface slope calculated from Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) data [13]. Meanwhile, the canopy height percentiles were redefined as the difference between height percentiles of the received waveform and height percentiles of the fitted ground component. This algorithm may have better adaptability compared to the Gaussian decomposition algorithm over the rugged mountain area, but it relies on accurate surface slope derived from a priori knowledge about the underlying topographic relief.
In fact, the received waveform can be regarded as the convolution of the lidar system response and target response within a laser footprint [17,18]. The target response waveform (TRW) over the vegetated region can accurately represent the distributions of the vegetation and ground within the laser footprint of a satellite lidar. The lidar system response represents the convolution of the transmitted laser pulse and lidar receiver impulse response, which can introduce smoothing and broadening effect for the received waveform. As a result, the received waveform shape is different from the actual TRW and cannot completely characterize the transmission property of a laser pulse. Meantime, the broadening received waveform may have some overlapping components leading to false identification of ground component. Hence, the conventional algorithms to derive the canopy height percentiles over rugged mountain area have non-negligible shortcomings: (1) the derived height percentiles deviate from the actual values due to the difference between the received waveform and the TRW; (2) the derived height percentiles may have some offsets due to the inaccurate ground elevation introduced by false extraction of ground peak or low-precision characterization of the Gaussian ground component from SRTM data.
To overcome such shortcomings, this research aims to propose a novel algorithm to derive the height percentiles based on the resolved TRW from the received waveform without the priori topographic relief. The detailed objectives of the research are to (1) extract the TRW from the received waveform by using a Richardson–Lucy deconvolution algorithm; (2) derive the height percentiles based on the shape distribution of the TRW and ground elevation extracted from the TRW; (3) compare the derived height percentiles with those from the conventional algorithms. The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 describes the study site and datasets,
Section 3 illustrates the proposed algorithm,
Section 4 gives the results and discussions, and
Section 5 gives the conclusions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
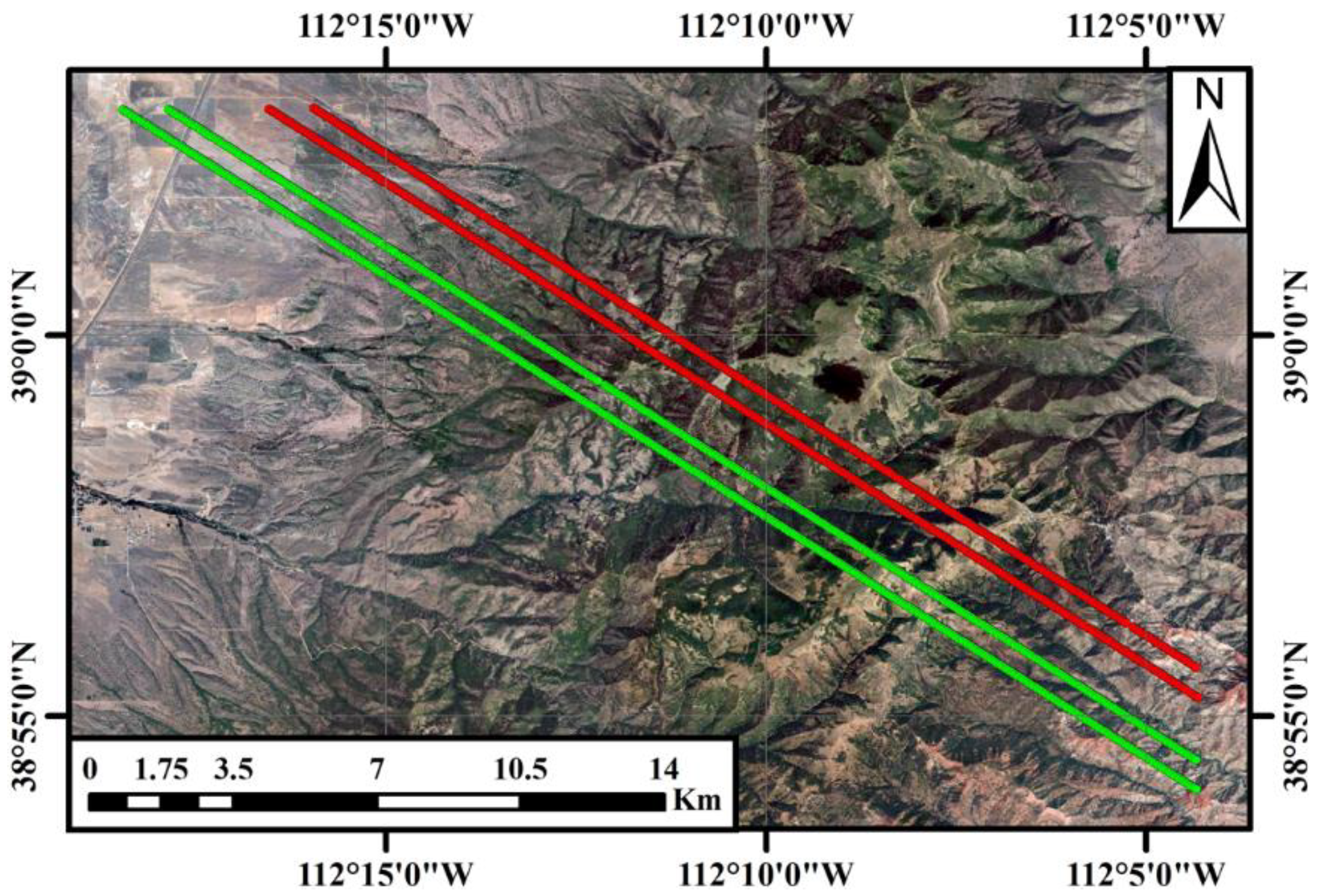
In this study, we employ the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) spaceborne lidar data over a steep mountainous vegetated area to validate the proposed method. The study site is located in the Pahvant Mountains of central Utah, USA, with the geolocation center at 38°56′55″ N112°10′53″ W. The location of the study site and four selected tracks of the GEDI lidar are presented in
Figure 1. The ground tracks of the GEDI lidar are marked by red and green points. Each ground track has an along-track length of round 18 km. The ground track information is listed in
Table 1.
The primary land covers of the study site are the rugged mountains and the wildwoods including the pine, cypress, other cold-resistant tree species, and some shrubs. The local airborne lidar data are available in the study site, which indicate that the selected topography has a high relief with the elevations ranging from 1785 m to 2829 m and the surface slopes varying from 1° to 63°. The topographic information within laser footprint and laser shots for four ground tracks are shown in
Table 1. The complicated topography and biological diversity make the selected site suitable for evaluating the performance of the proposed algorithms of height percentiles.
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. GEDI Lidar Dataset
The GEDI lidar onboard the international space station is designed to investigate the vertical forest structure for better understanding of the role of forests in the global carbon cycle. The GEDI lidar comprises three lasers with a 16 ns pulsewidth and 242 Hz repetition frequency at a wavelength of 1064 nm [19,20]. The beams from two full-power laser beams numbered from BEAM 0101 to BEAM 1011 produce four parallel ground tracks, and the splitting beams from one coverage laser numbered from BEAM 0000 to BEAM 0011 also produce four parallel ground tracks. The selected four ground tracks in this study root from two full-power laser beams and two splitting beams, which are marked with green and red points as illustrated in
Figure 1, respectively. Adjacent laser footprints for the selected tracks have the intervals of 60 m in the along-track direction and 600 m in the across-track direction.
The GEDI L1B standard data product provides the precise geographical coordinates for all laser footprints, the geolocated received waveforms and corrected transmitted waveforms with a temporal resolution of 1 ns [21]. In this study, the selected GEDI lidar dataset for about 1200 laser footprints were acquired from L1B Version 2 Data on October 26, 2020.
2.2.2. Airborne Lidar Dataset
The airborne lidar dataset used in this study were mainly gathered with the Optech Galaxy PRIME lidar sensor by the Aerial Department of the Aero-Graphics on August 4, 2020. It is the closet temporal window to the selected GEDI data for maintaining the phenology consistency. The airborne lidar was mounted onboard the Bell helicopter and provided a scan line with a full scanning angle of 46°. The instrument can operate at a laser pulse repetition frequency of 300 kHz and a scanning frequency of 55.6 Hz. As for a flight altitude of 1.6 km, the absolute horizontal and elevation errors of the footprint on the ground are less than 0.16 m and 0.25 m, respectively. The minimum interval distance of the discrete points is less than 0.7 m and the average point density is round 3.3 pulse per square meter. The high-density airborne lidar data can accurately represent three dimensional structures of the targets over the study site and provide a reference for simulating the actual target response.
2.3. Methods
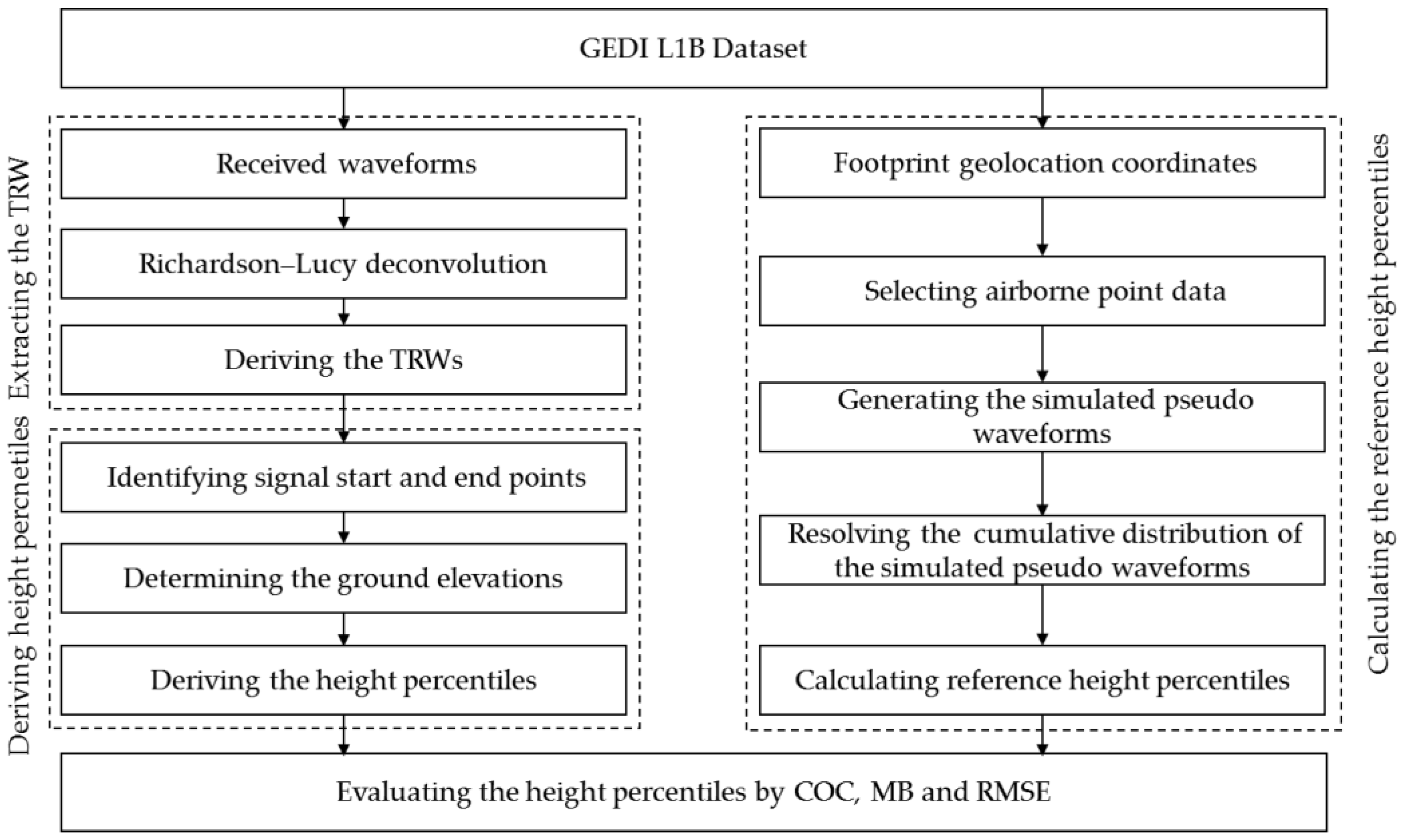
In this study, we propose to extract the TRW from the received waveform and utilize the cumulative distribution of the TRW to derive the height percentiles. Meanwhile, the reference height percentiles calculated from the airborne lidar data are introduced to evaluate the accuracy of the derived height percentiles from the TRW. The detailed flowchart of the proposed method is illustrated in
Figure 2. The methodology comprises four processing steps which are described as the following
Section 2.3.1,
Section 2.3.2,
Section 2.3.3 and
Section 2.3.4.
2.3.1. Extracting the TRW from the Received Waveform
When the transmitted laser pulse projected into the forest, both the vertical canopy structures including foliage, stems, branches trunks and the underlying ground would definitely reflect the laser energy back to the satellite lidar receiver. The strength of the received waveform at a given depth of the canopy depends on the amount of laser illumination penetrating into that depth and the reflectivity of the intercepted surface. Due to the pulse broadening and smoothing effects of lidar system response, the received waveform over the rugged mountain area would be a mixture of the overlapping vegetation and ground components. In addition, each component may deviate from the conventional Gaussian distribution and present asymmetrical shape. It is very difficult to exactly extract all waveform components from the received waveform by the waveform decomposition method.
Owing to the convolution relationship between the TRW and lidar system response, we can utilize the deconvolution algorithm to eliminate the influence of lidar system response on the received waveform. The Richardson–Lucy deconvolution algorithm based on Bayes’ theorem has proved to be an effective time-domain iterative algorithm [23]. The iterative formation can be given by
where
mi(
t) is the resolved TRW after
i iterations,
R(
t) is the denoising received waveform using Gaussian filter [24],
h(
t) represents the lidar system response that can be expressed by the convolution of the transmitted laser pulse and the receiver impulse response. In general, the lidar system response can be replaced by the received waveform returned from the flat ground surface in a clear sky [25].
The resolved TRW is heavily dependent on the iterative times. The excessive iterative time can promote the accuracy of the deconvoluted TRW, but increase the running time of the algorithm. Therefore, an adaptive criterion is proposed to determine the iterative time in this study as
where
Wi(
t) represents the received waveform after
i iterations:
,
M is the waveform sampling length,
A is the maximal amplitude of the received waveform
R(
t), and
δth is the predefined threshold for determining the optimal iterative time. In this study, the threshold
δth is set to be 1%.
2.3.2. Deriving the Height Percentile Based on the TRW
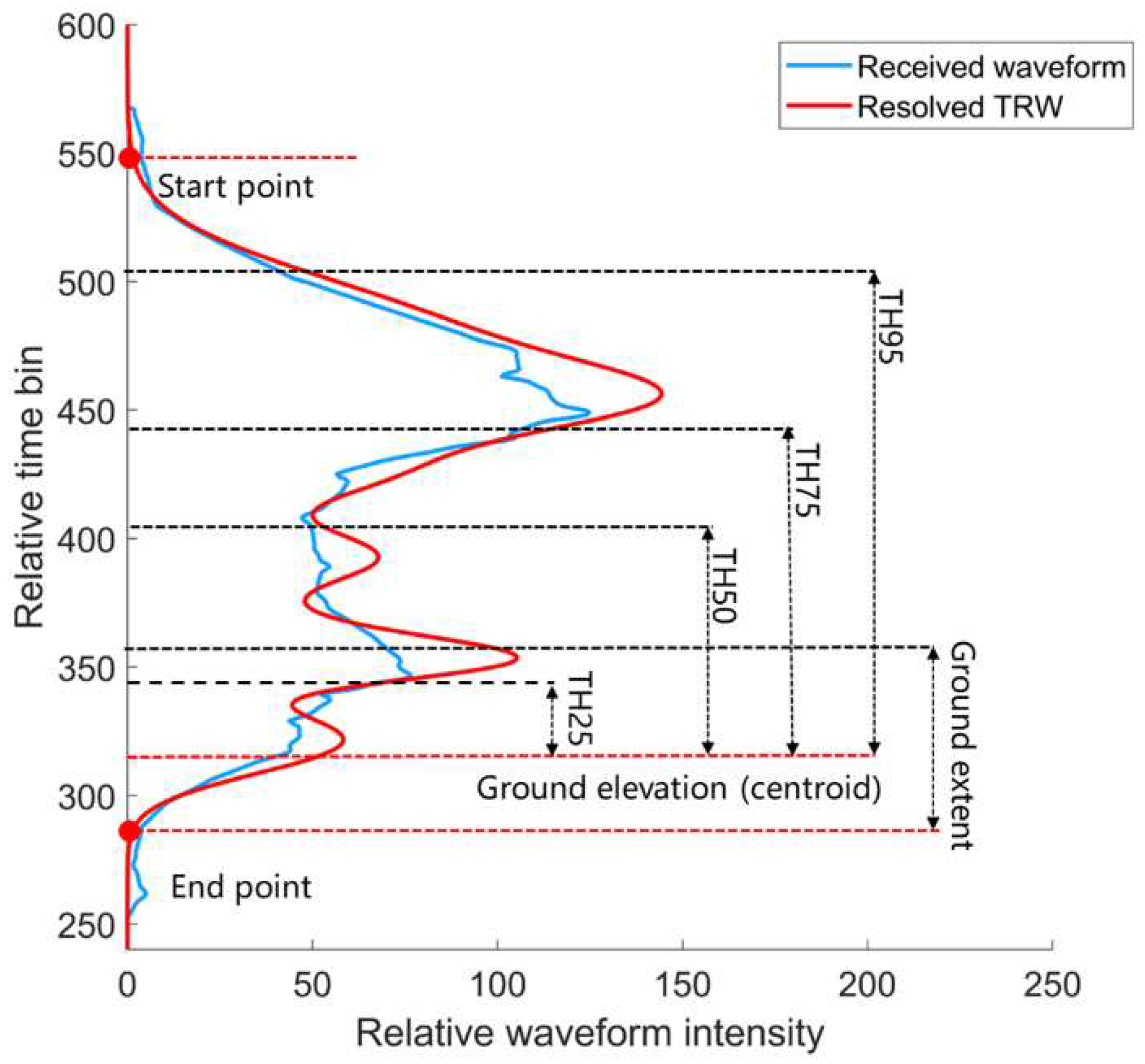
An illustration of the received waveform and the corresponding TRW is presented in
Figure 3. The blue curve is the received waveform over the vegetated area and the red curve is the resolved TRW. It is apparent that both the shape and signal duration of the received waveform are different from those of the TRW, which may result in the difference of height percentiles derived from these two waveforms.
The calculation of the height percentile based on the TRW requires the elevations of the TRW signal start and end points and the ground elevation. The elevations of the TRW signal start and end points are identified by directly seeking the highest and lowest locations where the TRW amplitudes are greater than one percent of the maximums of the TRW, respectively. Based on a minimum height threshold of 4.6 m from the US Forest Service's definition of a tree [26], we predefine that the ground signal duration is the 4.6 m elevation extent above the end point. Hence, the ground elevation can be obtained by calculating the centroid of the TRW components within ground signal duration.
The cumulative distribution of the normalized TRW energy between the start and end points is employed to estimate the height percentiles. The height metrics of the energy percentiles of 25%, 50%, 75% and 95% for the cumulative TRW distribution are defined as TH25, TH50, TH75 and TH95 by their vertical distances relative to the ground elevation. Here, the energy percentiles represent the laser pulse energy levels distributed in different strata of the vegetation within a laser footprint.
2.3.3. Calculating the Reference Height Percentiles
The simulated pseudo-waveform is the indicative of the vertical distribution of reflecting surfaces in the forest canopy and ground. Therefore, it is expected to resemble closely the actual target response. The simulated pseudo-waveform can be generated from the airborne lidar points and spatial energy distribution of the outgoing laser pulse on the ground. In our simulation, only the airborne lidar points within the satellite lidar field of view (FOV) are effectively acceptable. If the spatial energy distribution within satellite lidar laser footprint is assumed to be a Gaussian function, the simulated pseudo-waveform can be described as [27,28]
Ii is the intensity of each airborne lidar point, (
xi,
yi,
zi) are the coordinates of each airborne lidar point, (
x0,
y0) denote the satellite lidar footprint center,
r is the satellite lidar footprint radius (defined as half of e
−1/2 of the maximum),
Δt is the temporal resolution of the received waveform,
c is light speed in vacuum.
Just like deriving the height percentiles from the TRW, the reference height percentiles can be calculated by the cumulative distribution of the normalized pseudo-waveform energy. But the key difference is that the reference ground elevation is the weighted mean elevation of airborne lidar points within laser footprint [27]. We define the height metrics of the energy percentiles of 25%, 50%, 75% and 95% for the cumulative pseudo-waveform distribution as RH25, RH50, RH75 and RH95.
2.3.4. Evaluating the Height Percentiles by Different Methods
The performance of the derived height percentiles based on the TRW in this paper is compared with the extracted the height percentiles by the conventional Gaussian decomposition (GD) method and the slope-adaptive waveform metrics (SWM) [11,13]. We introduce the evaluation metrics including coefficient of correlation (COC), the mean bias (MB) and the root mean square error (RMSE) to assess the differences between the above height percentiles and the reference height percentiles. The COC, MB and RMSE are given by
n denotes the number of the selected footprints, TH
i and RH
i denote the derived height percentile and the reference height percentile for ith laser footprint, THM and RHM are the means of all derived height percentiles and reference height percentiles, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Calculation and Analysis on the TRW
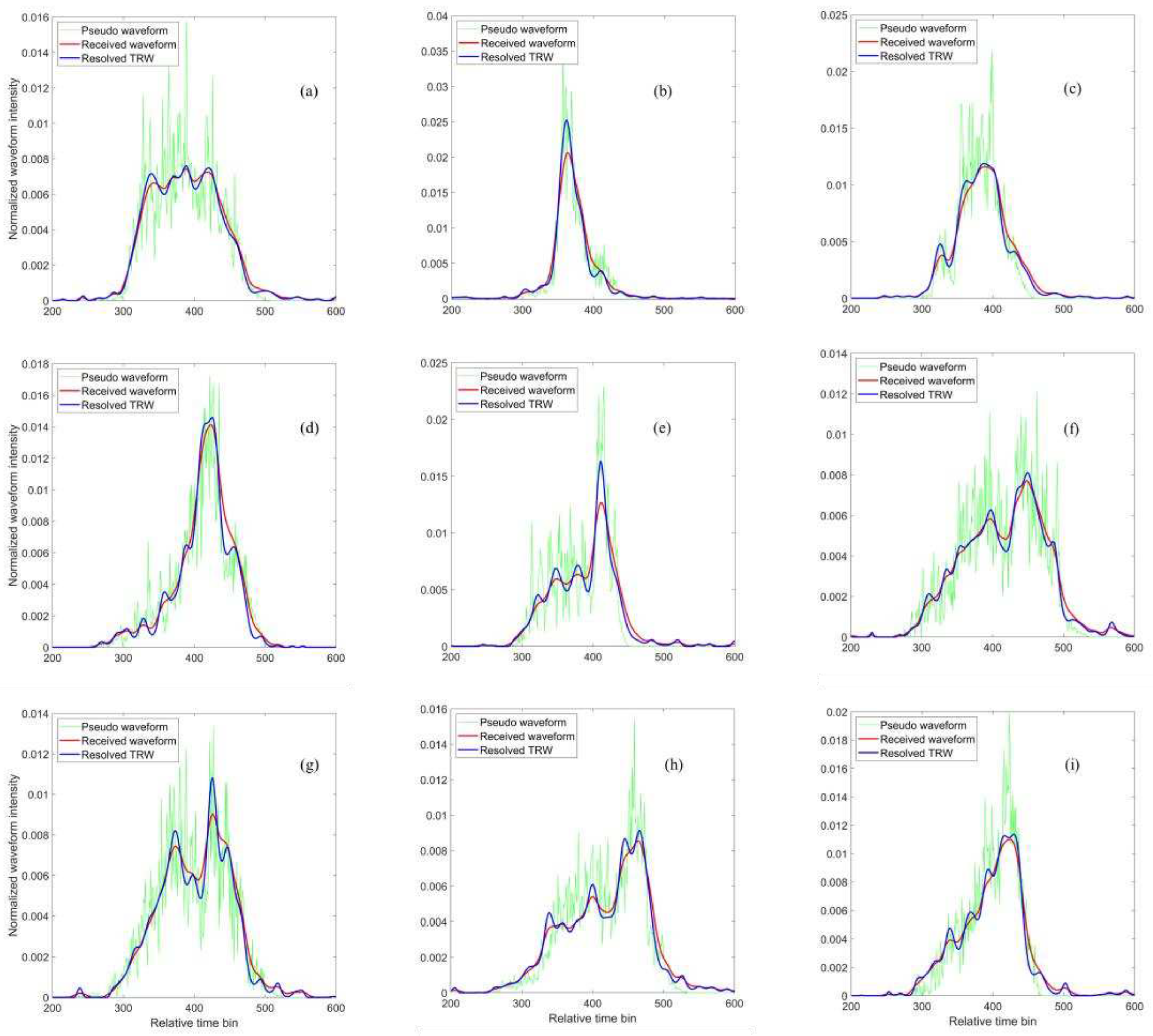
The GEDI laser footprint geolocations in the GEDI L1B data product may deviate from the actual positions due to the laser pointing errors of the GEDI lidar. Hence, in this study, the horizontal geolocations of all GEDI laser footprints are corrected by the waveform matching method [20]. We randomly choose nine laser footprints at the BEAM 0110 ground track and simulate the pseudo waveforms by using the airborne lidar data within the corrected footprints. Furthermore, nine groups of the TRWs are extracted from the corresponding received waveforms based on the proposed method in
Section 2.3.1. We provide the visual comparisons of the received waveforms, the pseudo waveforms and the resolved TRWs for nine laser footprints as presented in
Figure 4.
As shown in
Figure 4, the received waveform shapes present multimodal distributions with multiple waveform components due to the complexity of vertical forest structures. Each waveform component is no longer described by the traditional Gaussian pattern. Meantime, the resolved TRWs are different from the received waveforms and much closer to the pseudo waveforms. It suggests that the resolved TRW can exactly represent the laser transmission property into the forest. Furthermore, the ground components of the resolved TRW can be easily separated from the overlapping components of the received waveforms in
Figure 4h,i, which is favorable to identify the ground returns. The statistical metrics including the COCs and total biases between the resolved TRW, received waveform and the pseudo waveform are calculated and listed in
Table 2.
The average COC between the resolved TRWs and the pseudo waveforms in
Table 2 approximates to 0.95. It reveals that the resolved TRWs have very strong correlations with the pseudo waveforms. In addition, the maximum of total bias is no more than 0.1042. Meanwhile, it is noticed that the received waveforms correlate very well with the pseudo waveforms with the average COC of round 0.90. However, the total biases between the received waveforms and the pseudo waveforms are obviously promoted, which are almost 3.5 times the total biases between the TRWs and the pseudo waveforms. Such slight discrepancy between the TRWs and the pseudo waveforms demonstrates that the resolved TRWs resemble more closely to the pseudo waveforms than the received waveforms. To thoroughly expound the relationship between the resolved TRWs and the pseudo waveforms in the study site, we provide their histograms of the COC, total bias and RMSE for all selected footprints as presented in
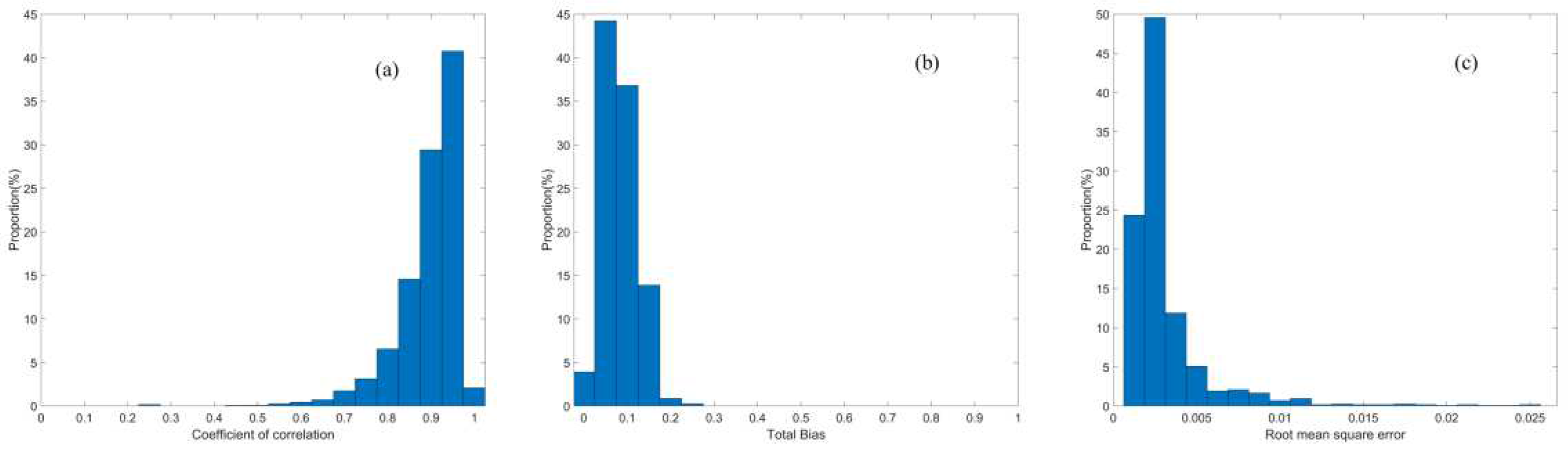
Figure 5.
The correlation coefficients in
Figure 5a are variable for each measurement due to the diverse forest structure within each laser footprint. We partition correlation coefficients into five segments with a range from 0 to 1 and an interval of 0.2 based on the definition of the correlation strength. When the correlation strengths vary from very weak to very strong, we discover that the COC proportions rapidly increase and take values of 0.00%, 0.18%, 0.26%, 2.53% and 97.03%. It indicates that 99.56% of the resolved TRWs correlate very well with the pseudo waveforms. Meanwhile, the total biases in
Figure 5b are distributed within a narrow range and 94.86% of total bias is less than 0.15. The RMSE in
Figure 5c presents analogous distribution and 97.99% of RMSE is less than 0.005. The detailed statistical results of the COC, total bias and RMSE for all footprints in the study site are enumerated in
Table 3.
The mean values of the COC, total bias and RMSE in
Table 3 are equal to 0.92, 0.0813 and 0.0016, respectively. The greater COC and smaller bias and RMSE reveal that the resolved TRWs have strong similarities with the pseudo waveforms. Combing with the histograms in
Figure 5, we can conclude that the resolved TRWs are more applicable for the extraction of the height percentiles than the received waveforms.
3.2. Extraction and Analysis on Height Percentiles
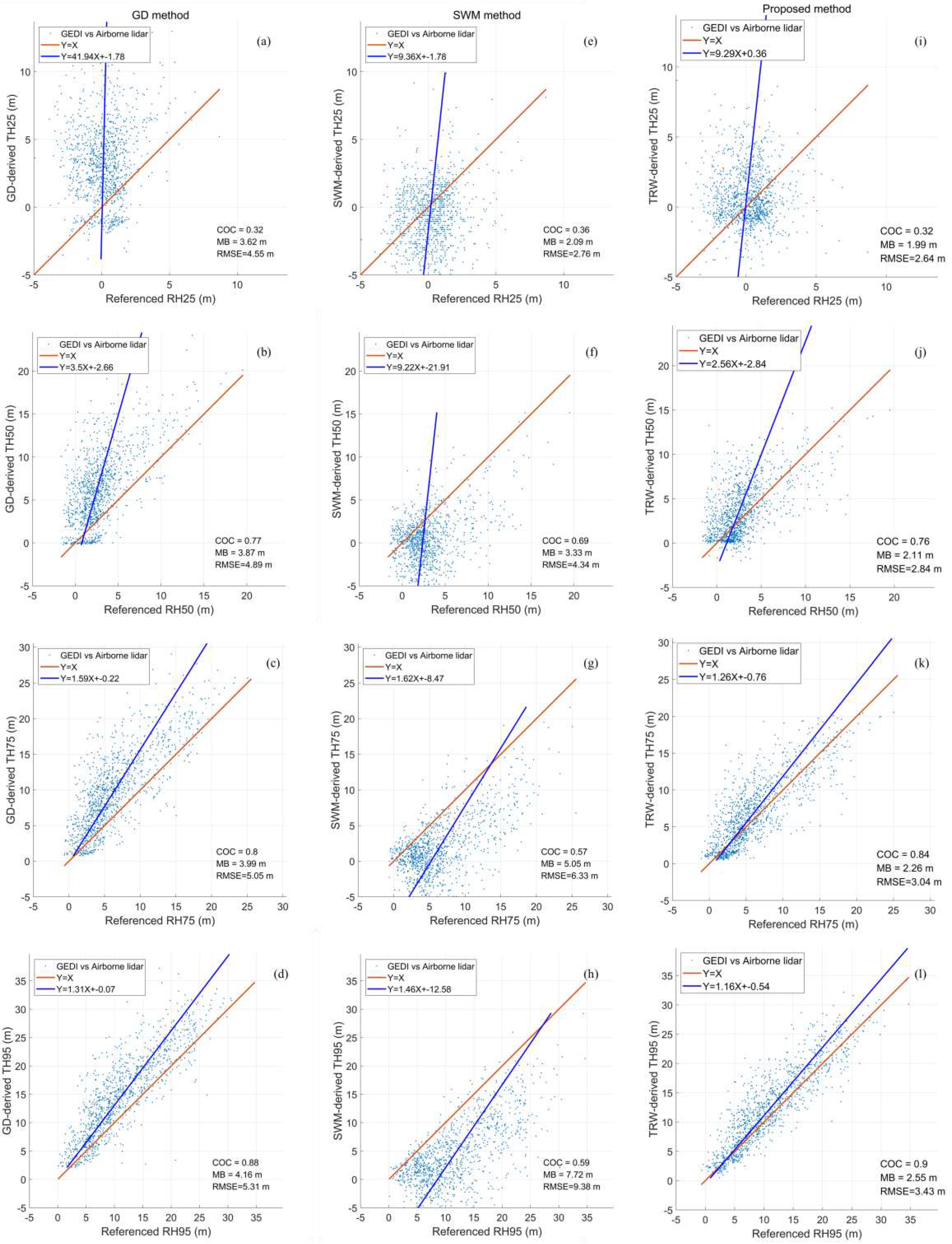
Based on the accumulative distributions of the resolved TRWs and the received waveforms, we extract the height percentiles by the proposed algorithm, Gaussian decomposition method (GD method) and the SWM method. These derived height percentiles are directly compared with the reference height percentiles from airborne lidar data to evaluate their differences. The scatter plots of reference height percentiles of RH25, RH50, RH75 and RH95 versus derived height percentiles of TH25, TH50, TH75 and TH95 from different algorithms are illustrated in
Figure 6.
The results in
Figure 6 indicate that the derived height percentiles from three abovementioned algorithms present some differences with the reference height percentiles. When the energy percentiles vary from 25% to 95%, the gradients of the best fitting lines rapidly decline and nearly approach to 1, and the COC values increase gradually. It suggests that the derived height percentiles may trend to the reference values with the increasing of the energy percentiles. Meanwhile, the derived height percentiles from the GD method and our proposed algorithm have stronger correlations with the reference height percentiles than the SWM method. In addition, the accuracies of the derived height percentiles from our proposed algorithm have been significantly improved compared with the GD and SWM methods. The MB values decrease by 1.61~1.76 m and 0.10~5.17 m, and the RMSE values decrease by 1.88~2.05 m and 0.12~5.95 m, respectively. There are two principal reasons leading to the inferior derived height percentiles for the GD and SWM methods. The first reason is that the received waveform should not be modelled by the multiple Gaussian functions, especially for ground components over the rugged mountain area. The second reason is that the ground elevation should not be determined by the last ground component peak from GD method and end point of the fitted ground component from SWM method.
4. Discussion
Though the derived accuracies of the height percentiles from the resolved TRW have been improved, there are still some differences between the derived height percentiles and the reference height percentiles from the pseudo waveform, as presented in
Figure 6. According to the abovementioned results in
Section 3.1, the resolved TRWs resemble closely to the pseudo waveforms. Hence, we speculate that the deviations of the derived height percentiles probably originate from the inaccurate ground elevation. To investigate the hypothesis, we specially select one of laser footprints where the derived height percentiles have the average differences of 3.70 m for our proposed algorithm and 8.87 m for GD method in
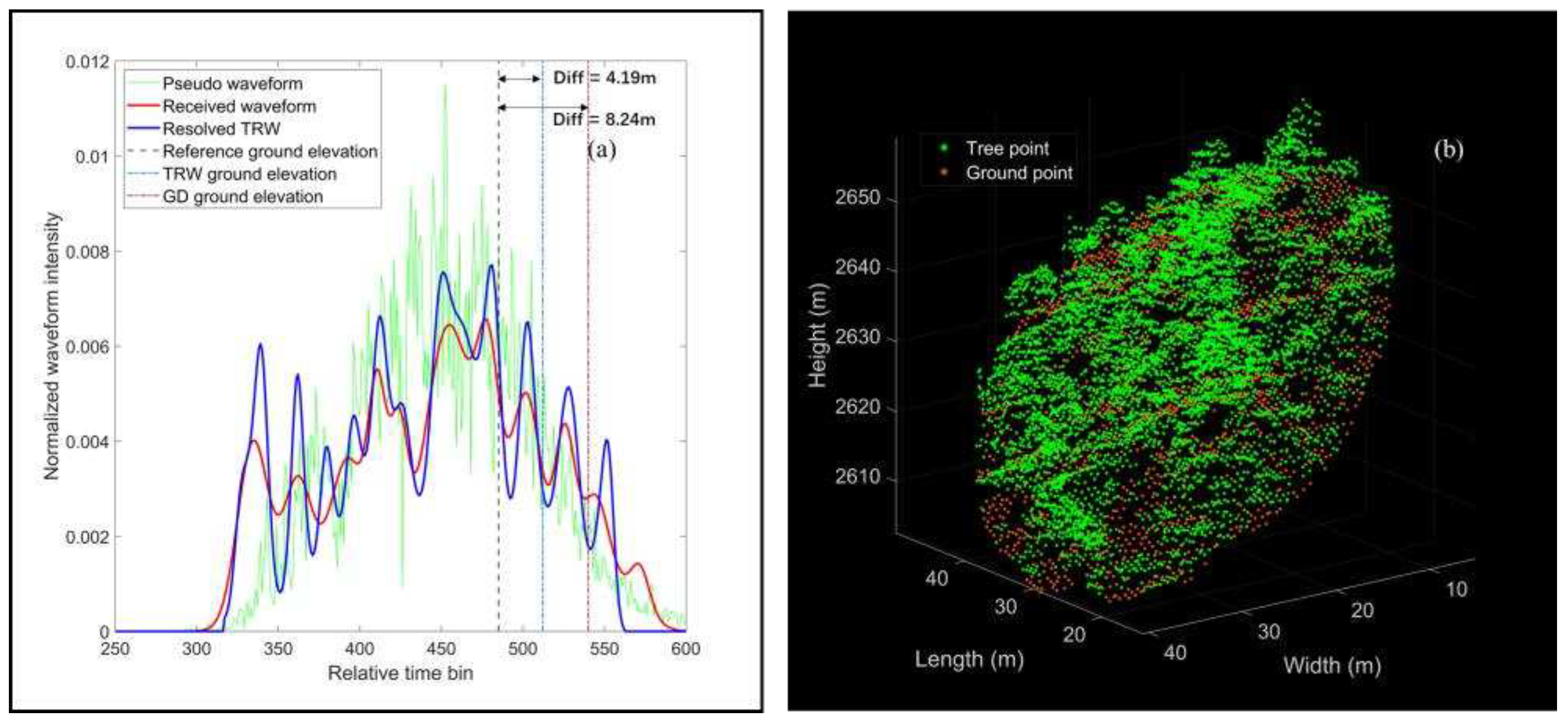
Figure 6. The received waveform, pseudo waveform, the resolved TRW and airborne point cloud within the selected footprint are displayed in
Figure 7.
As shown in
Figure 7, the received waveform comprises several vegetation and ground components due to the complicated forest structure within the selected laser footprint. Especially, there is an apparent inclination of round 53.08° and rugged relief for the ground in
Figure 7b, leading to the multiple components and pulse broadening effect for the ground returns. Even though the resolved TRW and the GD waveform seem to be basically in accordance with the pseudo waveform, it is still impossible to exactly identify all ground components from the resolved TRW and GD waveform. Thus, the resolved ground elevations from the proposed algorithm and GD method would deviate from the reference ground elevation. The locations of the resolved ground elevations are marked by blue and purple dot dashed lines and the reference ground elevation is marked by black dashed line in
Figure 7a, respectively. The differences of ground elevations for our proposed algorithm and GD method approximate to 4.19 m and 8.24 m, which are close to the average deviation (3.70 m and 8.87 m) of the derived height percentiles.
To explore the influence of ground elevation error on the derived height percentiles by our proposed algorithm and GD method, we attempt to replace the resolved ground elevation by the reference ground elevation and recalculate the derived height percentiles. In this study, we define such recalculated height percentiles as the renewed height percentiles. The derived height percentiles, reference height percentiles and renewed height percentiles for the selected footprint are listed in
Table 4.
As seen from
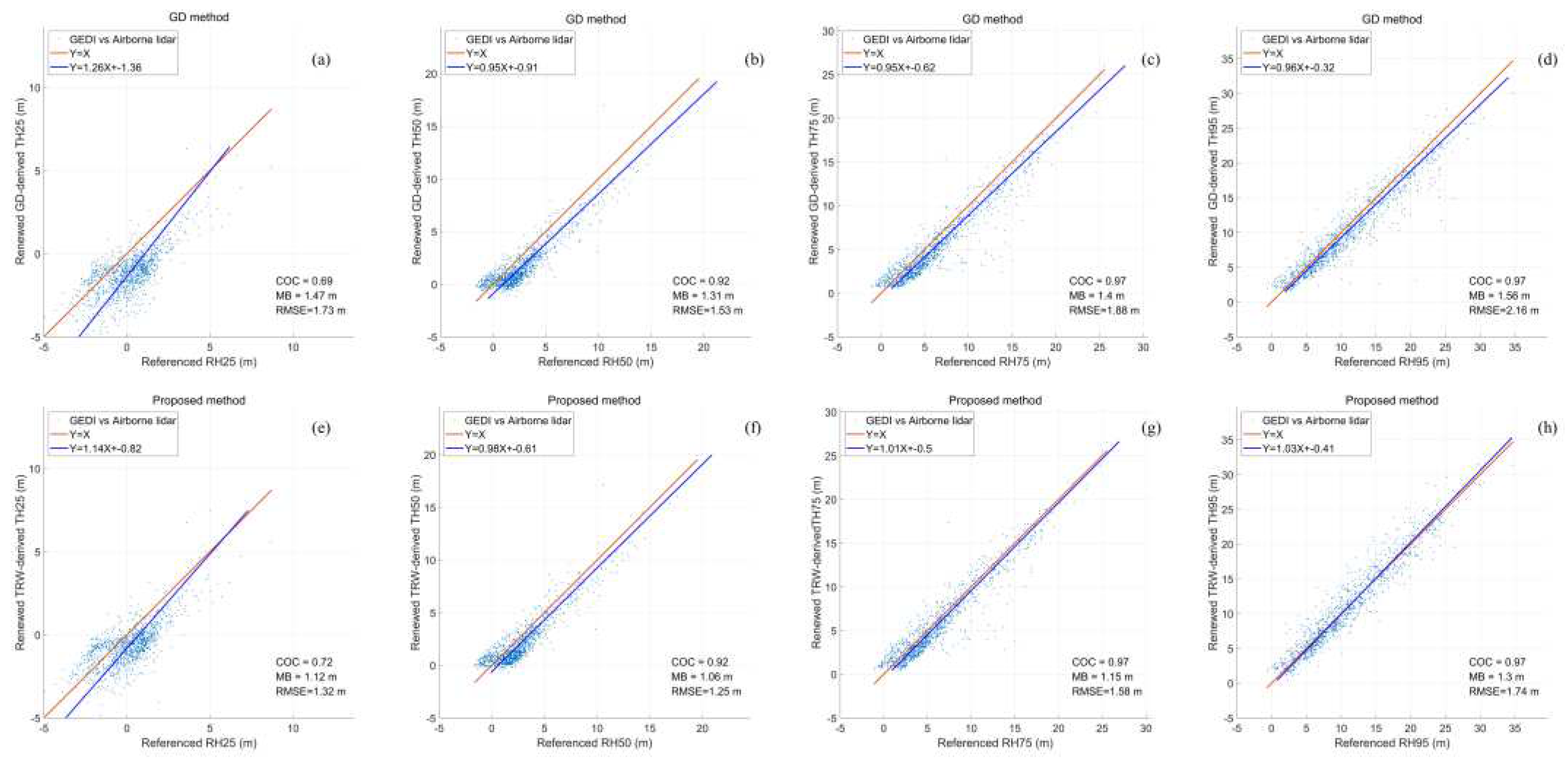
Table 4, the differences between the derived height percentiles by the proposed algorithm and GD method and reference height percentiles, range from 1.64 m to 4.79 m and 6.32 m to 12.02 m. However, the differences between the corresponding renewed height percentiles and reference height percentiles rapidly decrease and only range from -0.06 m to 0.63 m and -0.87 m to 2.82 m. The accuracies of the renewed height percentiles have been greatly improved. To further validate the effect of the reference ground elevations on the height percentiles by the proposed algorithm, we plot the renewed height percentiles for all laser footprints as presented in
Figure 8.
Compared with the derived height percentiles by the proposed algorithm in
Figure 6, the renewed height percentiles in
Figure 8 present stronger correlation strength with the reference height percentiles. The MB and RMSE of the GD method decrease by mean values of 63.24% and 63.20%. And the MB and RMSE of the proposed method decrease by mean values of 47.90% and 50.82%. It suggests that the renewed height percentiles by the GD method have preferable promotion than those by our proposed algorithm. But the accuracies of the renewed height percentiles by the proposed algorithm are still higher than GD method. The average MB and RMSE are decreased by 0.28 m and 0.35 m. The comparisons demonstrate that accurate ground elevation plays a significant role in determining the derived height percentiles by these two methods. Nevertheless, the derived height percentiles by the GD method are more susceptible to the ground elevation. Therefore, it is worthwhile to carry out the research on the extraction of ground elevation by using the resolved TRW or received waveform over the rugged mountainous area.
5. Conclusions
We propose a novel algorithm to derive the height percentiles by using the TRW extracted from the received waveform with the Richardson–Lucy deconvolution algorithm. The TRWs resolved from the GEDI lidar waveforms in the study site have strong correlations and slight deviations with the actual TRWs (pseudo waveforms) simulated by the coincident airborne lidar data. Such resolved TRW can represent laser transmission property into the forest since the influence of lidar system response on the received waveform is eliminated. The derived height percentiles from the proposed algorithm have higher precisions compared with the Gaussian decomposition method and the slope-adaptive waveform metrics method. The MB and RMSE values of the derived height percentiles decrease by the mean values of 1.96 m and 2.72 m, respectively.
The inadequate identification of all ground components from the TRW over the rugged mountain area is the significant factor reducing the accuracies of the derived height percentiles. Our proposed algorithm presents good applicability in the extraction of the height percentiles for the complicated ground returns. In the future research, how to extract higher-precision ground elevation from the resolved TRW should be further explored.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z. and H.S.; methodology, H.S., H.Z., and Q.Z.; software, H.S. and H. W.; validation, H.S., H.Z. and H.W.; formal analysis, H.Z. and H.S.; investigation, H.S.; resources, H.W. and H.S.; data curation, H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z. and H.S.; writing—review and editing, H.Z. and Y.M.; visualization, H.S.; supervision, H.Z. and S.L.; project administration, H.Z.; funding acquisition, H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41971302 and 42371440.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank for the GEDI data products. We would also like to thank the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for providing the high-resolution airborne LiDAR point cloud data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Koetz B, Morsdorf F, Sun G, et al. "Inversion of a lidar waveform model for forest biophysical parameter estimation." IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 3.1 (2006): 49-53. [CrossRef]
- Jonckheere I, Fleck S, Nackaerts K, et al. "Review of methods for in situ leaf area index determination: Part I. Theories, sensors and hemispherical photography." Agricultural and forest meteorology 121.1-2 (2004): 19-35. [CrossRef]
- Wulder M A, Hall R J, Coops N C, et al. "High spatial resolution remotely sensed data for ecosystem characterization." BioScience 54.6 (2004): 511-521. [CrossRef]
- Song C, Dickinson M B. "Extracting forest canopy structure from spatial information of high resolution optical imagery: tree crown size versus leaf area index." International Journal of Remote Sensing 29.19 (2008): 5605-5622. [CrossRef]
- Duncanson L I, Niemann K O, Wulder M A. "Estimating forest canopy height and terrain relief from GLAS waveform metrics." Remote Sensing of Environment 114.1 (2010): 138-154. [CrossRef]
- Harding D J, Dabney P W, Valett S. "Polarimetric, two-color, photon-counting laser altimeter measurements of forest canopy structure." International Symposium on Lidar and Radar Mapping 2011: Technologies and Applications. Vol. 8286. SPIE, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Lee S, Ni-Meister W, Yang W, et al. "Physically based vertical vegetation structure retrieval from ICESat data: Validation using LVIS in White Mountain National Forest, New Hampshire, USA." Remote Sensing of Environment 115.11 (2011): 2776-2785. [CrossRef]
- Maltamo M, Eerikäinen K, Packalén P, et al. "Estimation of stem volume using laser scanning-based canopy height metrics." Forestry 79.2 (2006): 217-229. [CrossRef]
- Naesset E. "Estimating timber volume of forest stands using airborne laser scanner data." Remote sensing of environment 61.2 (1997): 246-253. [CrossRef]
- Næsset E. "Practical large-scale forest stand inventory using a small-footprint airborne scanning laser." Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research 19.2 (2004): 164-179. [CrossRef]
- Chen Q. "Assessment of terrain elevation derived from satellite laser altimetry over mountainous forest areas using airborne lidar data." ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 65.1 (2010): 111-122. [CrossRef]
- Pang Y, Zhao F, Li Z, et al. "Research on Average Tree Height Extraction from Airborne Lidar." Journal of Remote Sensing 2008 (01): 152-158.
- Wang Y, Ni W, Sun G, et al. "Slope-adaptive waveform metrics of large footprint lidar for estimation of forest aboveground biomass." Remote Sensing of Environment 224 (2019): 386-400. [CrossRef]
- Næsset E, Bollandsås O M, Gobakken T, et al. "Model-assisted estimation of change in forest biomass over an 11 year period in a sample survey supported by airborne LiDAR: A case study with post-stratification to provide “activity data”." Remote Sensing of Environment 128 (2013): 299-314. [CrossRef]
- Sun G, Ranson K J, Kimes D S, et al. "Forest vertical structure from GLAS: An evaluation using LVIS and SRTM data." Remote Sensing of Environment 112.1 (2008): 107-117. [CrossRef]
- Dubayah R O, Sheldon S L, Clark D B, et al. "Estimation of tropical forest height and biomass dynamics using lidar remote sensing at La Selva, Costa Rica." Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 115.G2 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Zhang Z, Xie H, Tong X, et al. "A combined deconvolution and Gaussian decomposition approach for overlapped peak position extraction from large-footprint satellite laser altimeter waveforms." IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 13 (2020): 2286-2303. [CrossRef]
- Zhou T, Popescu S C, Krause K, et al. "Gold–A novel deconvolution algorithm with optimization for waveform LiDAR processing." ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 129 (2017): 131-150. [CrossRef]
- Lang N, Kalischek N, Armston J, et al. "Global canopy height regression and uncertainty estimation from GEDI LIDAR waveforms with deep ensembles." Remote Sensing of Environment 268 (2022): 112760. [CrossRef]
- Lee S K, Fatoyinbo T, Marselis S M, et al. "Spaceborne data fusion for large-scale forest parameter estimation: GEDI LiDAR & Tandem-X INSAR missions." IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Xu Y, Ding S, Chen P, et al. "Horizontal Geolocation Error Evaluation and Correction on Full-Waveform LiDAR Footprints via Waveform Matching." Remote Sensing 15.3 (2023): 776. [CrossRef]
- Hofton M, Blair JB, Story S, Yi D. "Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) for GEDI transmit and receive waveform processing for L1 and L2 products. " University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA. 2019: 44.
- Tai, Y. W., Tan, P., & Brown, M. S. "Richardson-lucy deblurring for scenes under a projective motion path." IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 33.8 (2010): 1603-1618. [CrossRef]
- Duong V H. "Processing and application of ICESat large footprint full waveform laser range data." (2010).
- Mallet C, Bretar F. "Full-waveform topographic lidar: State-of-the-art." ISPRS Journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing 64.1 (2009): 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Neuenschwander, A., & Pitts, K. "The ATL08 land and vegetation product for the ICESat-2 Mission." Remote sensing of environment 221 (2019): 247-259. [CrossRef]
- Popescu S C, Zhao K, Neuenschwander A, et al. "Satellite lidar vs. small footprint airborne lidar: Comparing the accuracy of aboveground biomass estimates and forest structure metrics at footprint level." Remote Sensing of Environment 115.11 (2011): 2786-2797. [CrossRef]
- Silva C A, Saatchi S, Garcia M, et al. "Comparison of small-and large-footprint lidar characterization of tropical forest aboveground structure and biomass: a case study from Central Gabon." IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 11.10 (2018): 3512-3526. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Location of the study site in the Pahvant Mountains of central Utah, USA, and data trajectories of the GEDI lidar. The green points represent the ground tracks produced by GEDI full-power laser beams and the red points represent the ground tracks produced by GEDI splitting laser beams.
Figure 1.
Location of the study site in the Pahvant Mountains of central Utah, USA, and data trajectories of the GEDI lidar. The green points represent the ground tracks produced by GEDI full-power laser beams and the red points represent the ground tracks produced by GEDI splitting laser beams.
Figure 2.
Detailed flowchart of the proposed algorithm. The procedure includes four processing steps: extracting the TRW from the received waveform, deriving the height percentiles based on the resolved TRW, calculating the reference height percentiles from the simulated pseudo waveform, and evaluating the height percentiles.
Figure 2.
Detailed flowchart of the proposed algorithm. The procedure includes four processing steps: extracting the TRW from the received waveform, deriving the height percentiles based on the resolved TRW, calculating the reference height percentiles from the simulated pseudo waveform, and evaluating the height percentiles.
Figure 3.
An illustration of the received waveform (blue curve) and TRW (red curve) extracted from the received waveform, and the definition of height percentiles from the TRW.
Figure 3.
An illustration of the received waveform (blue curve) and TRW (red curve) extracted from the received waveform, and the definition of height percentiles from the TRW.
Figure 4.
Comparisons of the received waveforms, the pseudo waveforms and the resolved TRWs for nine randomly selected laser footprints. All waveforms are normalized by their own total energies, respectively. The start points of the relative time of all waveforms correspond to the first points of GEDI waveform, and relative time interval for each bin is 1 ns.
Figure 4.
Comparisons of the received waveforms, the pseudo waveforms and the resolved TRWs for nine randomly selected laser footprints. All waveforms are normalized by their own total energies, respectively. The start points of the relative time of all waveforms correspond to the first points of GEDI waveform, and relative time interval for each bin is 1 ns.
Figure 5.
Histograms of the statistical metrics about the relationship between the resolved TRWs and the pseudo waveforms for the selected footrpints in the study site. (a) COC; (b) Total bias; (c) RMSE.
Figure 5.
Histograms of the statistical metrics about the relationship between the resolved TRWs and the pseudo waveforms for the selected footrpints in the study site. (a) COC; (b) Total bias; (c) RMSE.
Figure 6.
Scatter plots of reference height percentiles of RH25, RH50, RH75 and RH95 versus derived height percentiles of TH25, TH50, TH75 and TH95 from different algorithms. (a)-(d) are Gaussian decomposition method; (e)-(h) are slope-adaptive waveform metrics, and (i)-(l) are the proposed method. Red lines and blue lines represent the ‘Y=X’ and the best fitting lines, respectively.
Figure 6.
Scatter plots of reference height percentiles of RH25, RH50, RH75 and RH95 versus derived height percentiles of TH25, TH50, TH75 and TH95 from different algorithms. (a)-(d) are Gaussian decomposition method; (e)-(h) are slope-adaptive waveform metrics, and (i)-(l) are the proposed method. Red lines and blue lines represent the ‘Y=X’ and the best fitting lines, respectively.
Figure 7.
An example illustration of satellite lidar data and airborne lidar data within the selected laser footprint. (a) GD waveform, pseudo waveform and resolved TRW; (b) Airborne point cloud. All waveforms are normalized by the total energy.
Figure 7.
An example illustration of satellite lidar data and airborne lidar data within the selected laser footprint. (a) GD waveform, pseudo waveform and resolved TRW; (b) Airborne point cloud. All waveforms are normalized by the total energy.
Figure 8.
Scatter plot of renewed height percentiles from the GD method and proposed algortihm vs reference height percentile. (a) and (e) Renewed TH25 vs RH25; (b) and (f) Renewed TH50 vs RH50; (c) and (g) Renewed TH75 vs RH75; (d) and (h) Renewed TH95 vs RH95.
Figure 8.
Scatter plot of renewed height percentiles from the GD method and proposed algortihm vs reference height percentile. (a) and (e) Renewed TH25 vs RH25; (b) and (f) Renewed TH50 vs RH50; (c) and (g) Renewed TH75 vs RH75; (d) and (h) Renewed TH95 vs RH95.
Table 1.
Topographic information within laser footprint for the selected ground tracks.
Table 1.
Topographic information within laser footprint for the selected ground tracks.
| Beam type |
Ground track |
Laser shots |
Surface slope (°) |
Elevation (m) |
| Splitting beam |
BEAM 0010 |
286 |
1.59~45.09 |
1785.9~2828.1 |
| Splitting beam |
BEAM 0011 |
291 |
2.28~41.60 |
1844.0~2787.4 |
| Full-power beam |
BEAM 0101 |
279 |
1.37~42.85 |
1918.7~2660.5 |
| Full-power beam |
BEAM 0110 |
296 |
1.36~63.15 |
1842.7~2876.2 |
Table 2.
Statistical metrics between the resolved TRW, received waveform and the pseudo waveform for nine randomly selected laser footprints at the BEAM 0110 ground track.
Table 2.
Statistical metrics between the resolved TRW, received waveform and the pseudo waveform for nine randomly selected laser footprints at the BEAM 0110 ground track.
| Footprint number |
COC |
Total Bias |
TRW vs pseudo
waveform |
Received waveform vs pseudo waveform |
TRW vs pseudo
waveform |
Received waveform vs pseudo waveform |
| 60 |
0.94 |
0.89 |
0.0890 |
0.2623 |
| 70 |
0.97 |
0.94 |
0.0626 |
0.2710 |
| 92 |
0.94 |
0.90 |
0.0668 |
0.3060 |
| 119 |
0.95 |
0.93 |
0.0863 |
0.2512 |
| 123 |
0.94 |
0.82 |
0.0781 |
0.3858 |
| 156 |
0.93 |
0.87 |
0.1005 |
0.2879 |
| 166 |
0.94 |
0.90 |
0.0989 |
0.2704 |
| 180 |
0.94 |
0.91 |
0.1042 |
0.2676 |
| 244 |
0.96 |
0.93 |
0.0644 |
0.2417 |
Table 3.
Statistical results of the COC, total bias and RMSE between the resolved TRW and the pseudo waveform for all footprints in the study site.
Table 3.
Statistical results of the COC, total bias and RMSE between the resolved TRW and the pseudo waveform for all footprints in the study site.
| Metrics |
COC |
Total Bias |
RMSE |
| Maximum |
0.99 |
0.2351 |
0.0310 |
| Mean |
0.92 |
0.0813 |
0.0016 |
| Minimum |
0.29 |
0.0096 |
0.0006 |
Table 4.
Derived height percentiles, reference height percentiles and renewed height percentiles by the GD method and proposed algorithm for the selected footprint.
Table 4.
Derived height percentiles, reference height percentiles and renewed height percentiles by the GD method and proposed algorithm for the selected footprint.
| Energy percentile |
25% |
50% |
75% |
95% |
| Reference height percentile (m) |
-0.68 |
5.01 |
10.87 |
18.37 |
| Difference for derived height percentile (m) |
GD method |
6.32 |
7.53 |
9.62 |
12.02 |
| Difference for renewed height percentile (m) |
-0.87 |
0.67 |
1.42 |
2.82 |
| Difference for derived height percentile (m) |
Proposed algorithm |
1.64 |
2.84 |
5.54 |
4.79 |
| Difference for renewed height percentile (m) |
0.27 |
-0.06 |
0.63 |
0.42 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).