Submitted:
11 December 2023
Posted:
11 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Tissue Sample Collection
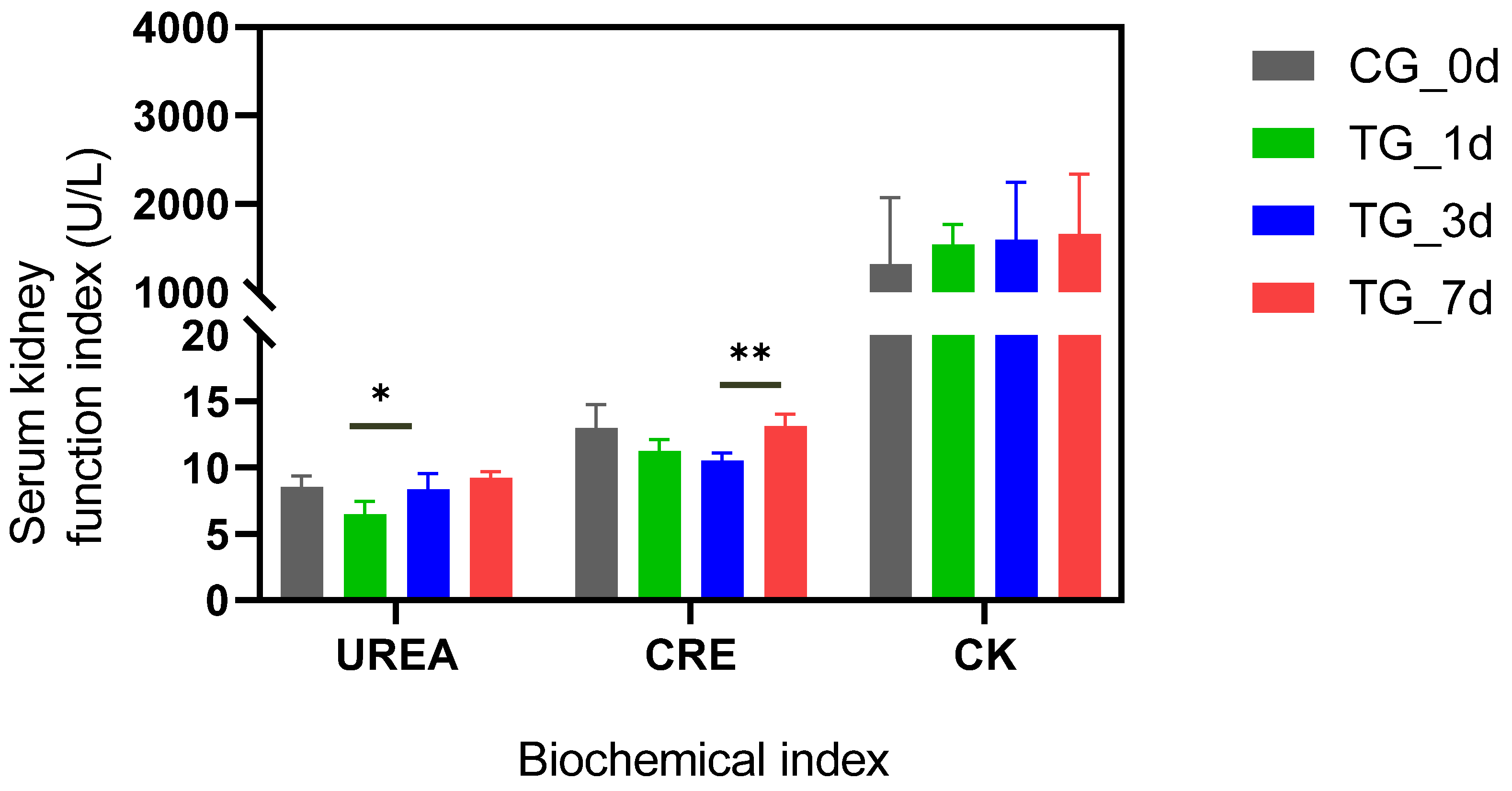
2.4. Biochemical Assay
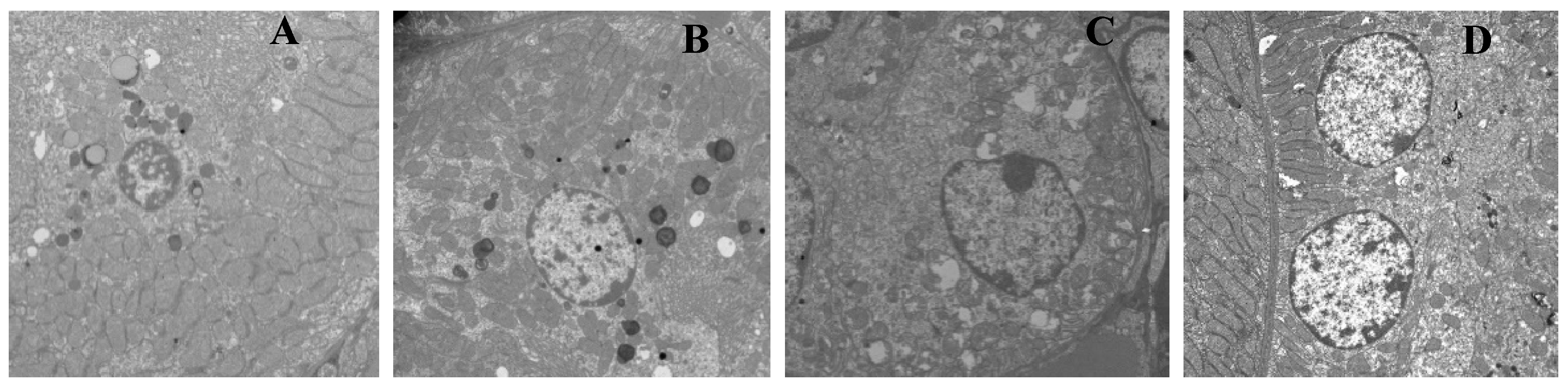
2.5. Ultrastructural Analysis of Kidney
2.6. RNA-Seq
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
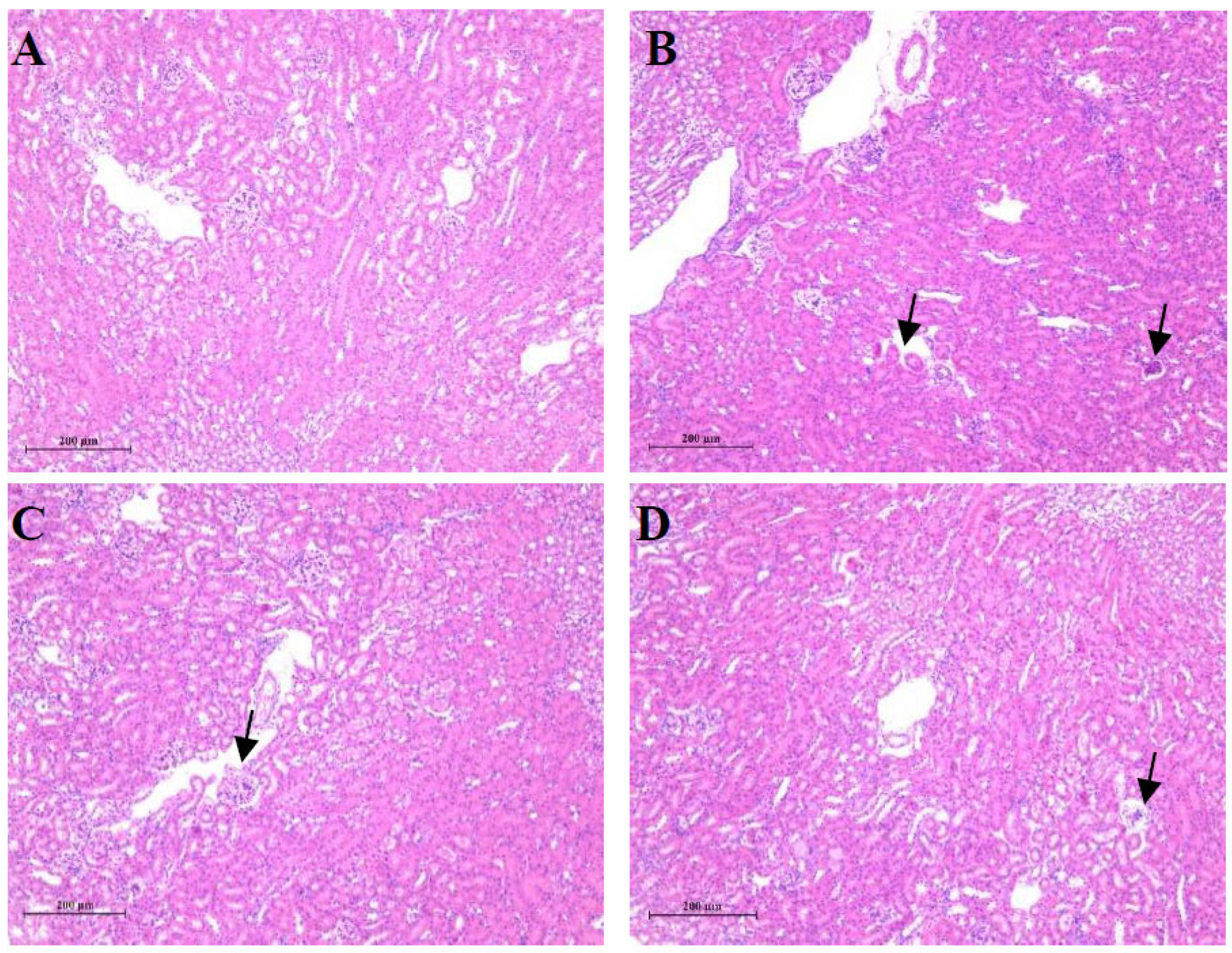
3.1. T-2 Toxin Induced Kidney Damages
3.2. T-2 Toxin-Induced Kidney Ultrastructural Changes
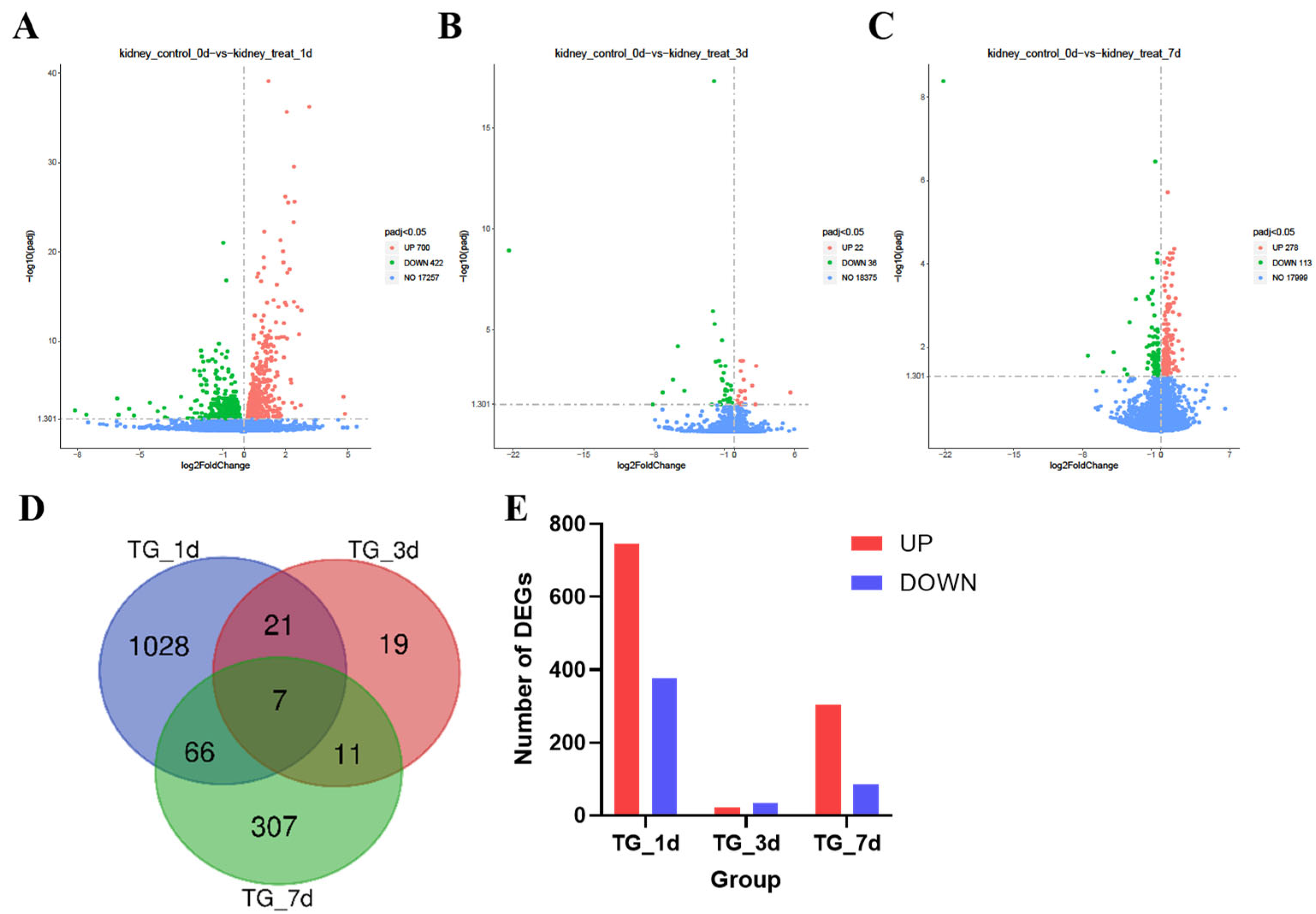
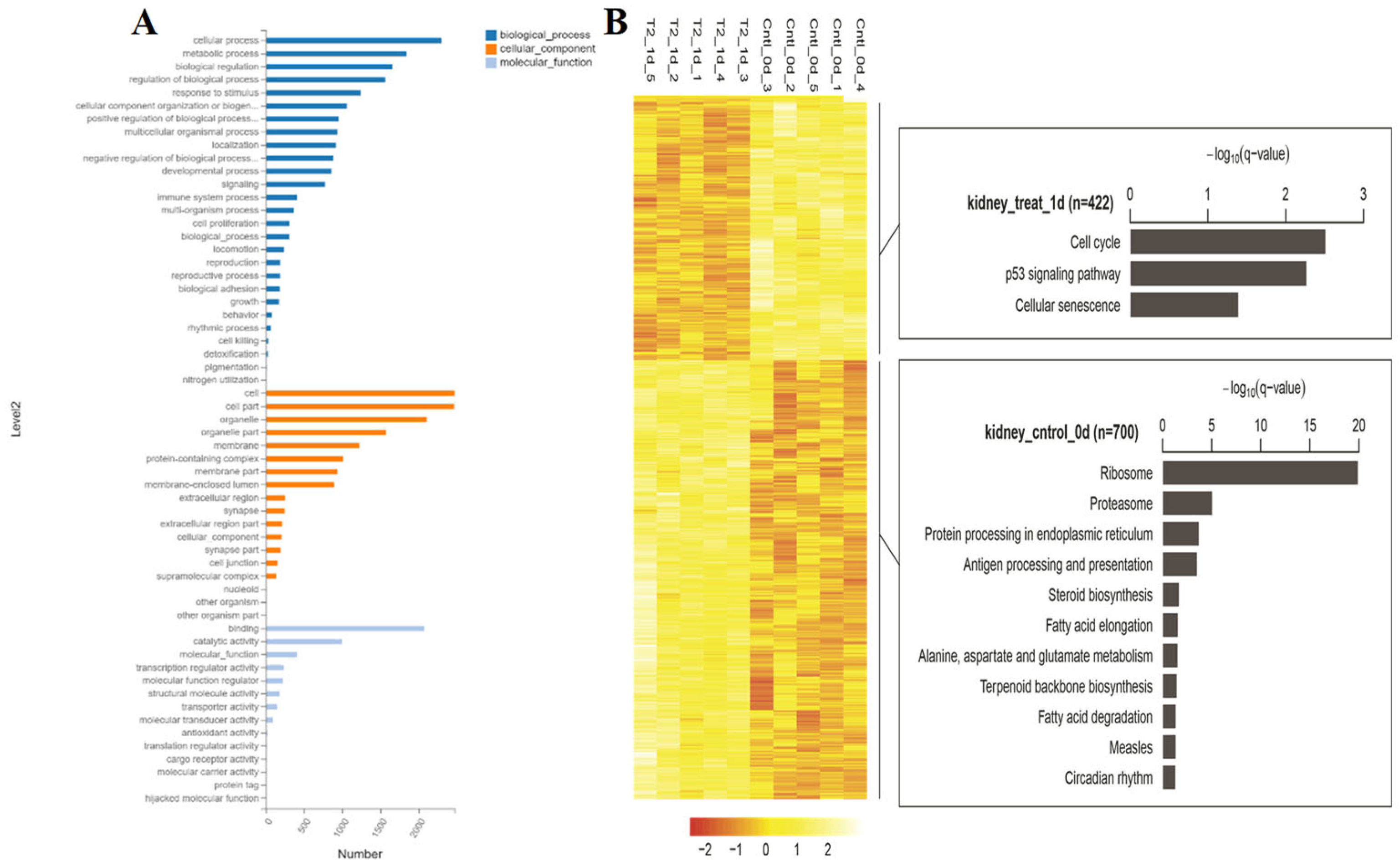
3.3. Transcriptome Analysis of Kidney Injury Induced by T-2 Toxin
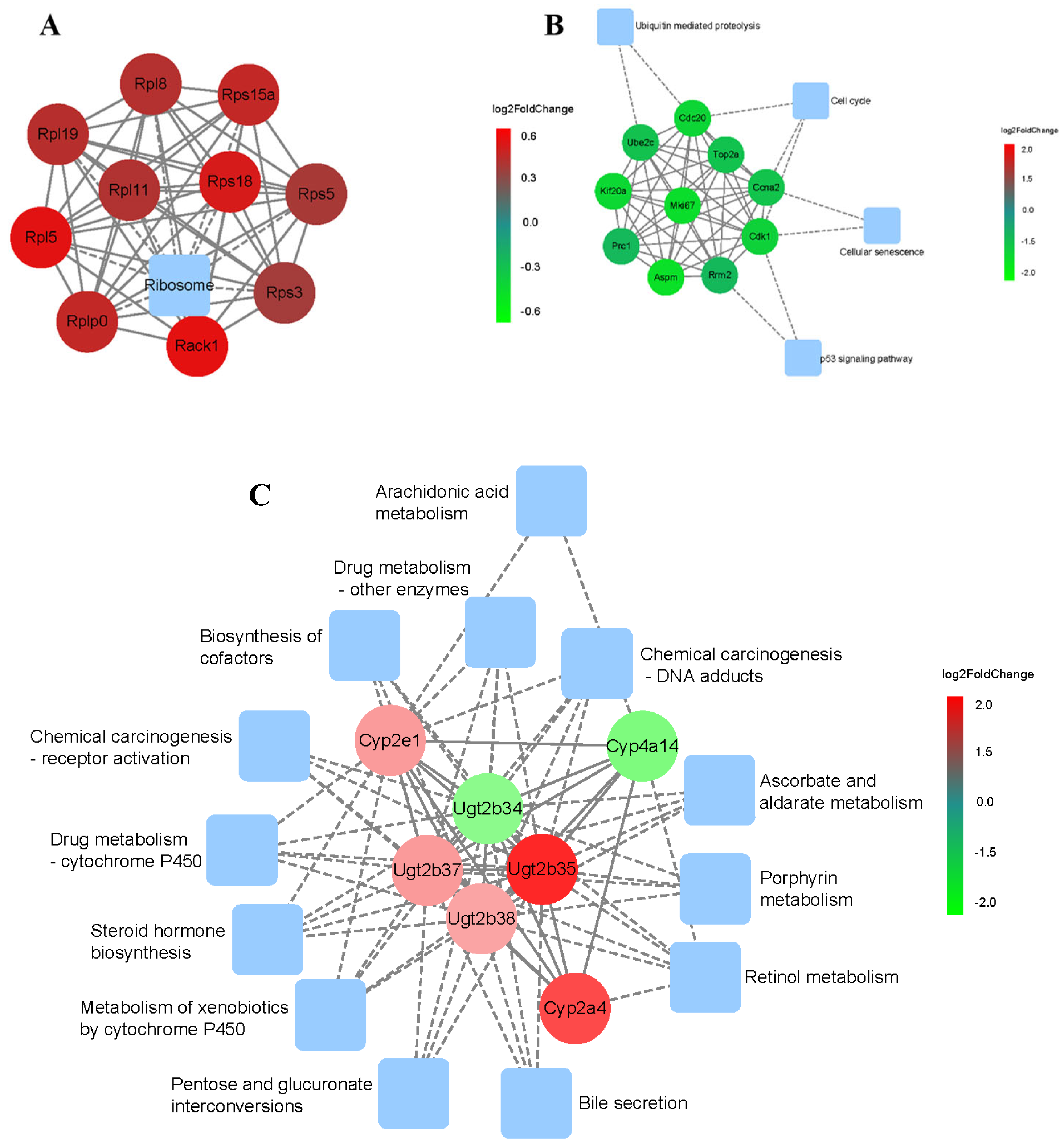
3.4. Temporal Pattern and Network Analysis of Transcriptional Regulators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Beier, R.C.; Shen, J.; De Smet, D.; De Saeger, S.; Zhang, S. T-2 toxin, a trichothecene mycotoxin: review of toxicity, metabolism, and analytical methods. J Agric Food Chem 2011, 59, 3441-3453. [CrossRef]
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 2013, 60, 218-237. [CrossRef]
- Bin-Umer, M.A.; McLaughlin, J.E.; Butterly, M.S.; McCormick, S.; Tumer, N.E. Elimination of damaged mitochondria through mitophagy reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress and increases tolerance to trichothecenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 11798-11803. [CrossRef]
- Polak-Sliwinska, M.; Paszczyk, B. Trichothecenes in Food and Feed, Relevance to Human and Animal Health and Methods of Detection: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2021, 26. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.S.; Zhang, H.; Cui, J.G.; Li, J.L. Heme-oxygenase-1 as a target for phthalate-induced cardiomyocytes ferroptosis. Environ Pollut 2023, 317, 120717. [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Kang, P.; Yang, J.; Shen, B.; Zhou, Z.; Duan, L.; Deng, J.; Huang, H.; Pei, F.X. The effect of Kashin-Beck disease-affected feed and T-2 toxin on the bone development of Wistar rats. Int J Rheum Dis 2010, 13, 266-272. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Wang, G.; Huo, H.; Li, W. Identification of HIF-1alpha/VEGFA signaling pathway and transcription factors in Kashin-Beck disease by integrated bioinformatics analysis. Exp Ther Med 2021, 22, 1115. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Qin, Z.; Kuca, K.; You, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, A.; Musilek, K.; Chrienova, Z.; Nepovimova, E.; Oleksak, P., et al. An update on T-2 toxin and its modified forms: metabolism, immunotoxicity mechanism, and human exposure assessment. Arch Toxicol 2020, 94, 3645-3669. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Shao, B.; Li, Y. The nephrotoxicity of T-2 toxin in mice caused by oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis is related to Nrf2 pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 2021, 149, 112027. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Huo, S.; Du, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y. T-2 Toxin Induces Kidney Fibrosis via the mtROS-NLRP3-Wnt/beta-Catenin Axis. J Agric Food Chem 2022, 70, 13765-13777. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, J.; Li, B.; Huo, S.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Y.; Song, M.; Shao, B.; Li, Y. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy mitigates T-2 toxin-induced nephrotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 2022, 164, 113078. [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, C.; Fan, L.; Hu, H.; Yin, S. The combination of T-2 toxin and acrylamide synergistically induces hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity via the activation of oxidative stress and the mitochondrial pathway. Toxicon 2021, 189, 65-72. [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Xiao, X.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hoyer, D.; Shen, J.; Tang, S.; Velkov, T. T-2 toxin neurotoxicity: role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Arch Toxicol 2019, 93, 3041-3056. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.; Rao, P.V. Brain oxidative stress after dermal and subcutaneous exposure of T-2 toxin in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 2010, 48, 3436-3442. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, J.; Jin, H.; Xiao, H.; Peng, S.; Xie, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J. T-2 toxin induces cardiotoxicity by activating ferroptosis and inhibiting heme oxygenase-1. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 140087. [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Das Gupta, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Velkov, T.; Shen, J. T-2 toxin and its cardiotoxicity: New insights on the molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Food Chem Toxicol 2022, 167, 113262. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Spermatogenesis disorder caused by T-2 toxin is associated with germ cell apoptosis mediated by oxidative stress. Environ Pollut 2019, 251, 372-379. [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y.; Park, H.J. T-2 mycotoxin Induces male germ cell apoptosis by ROS-mediated JNK/p38 MAPK pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2023, 262, 115323. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, P.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, B.; Liu, M.; Song, M.; Huang, W.; Li, Y. Review of the Reproductive Toxicity of T-2 Toxin. J Agric Food Chem 2020, 68, 727-734. [CrossRef]
- Jacevic, V.; Wu, Q.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K. Efficacy of methylprednisolone on T-2 toxin-induced cardiotoxicity in vivo: A pathohistological study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2019, 71, 103221. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, G.; Li, X.; Giri, S.S., et al. Dietary T-2 toxin induces transcriptomic changes in hepatopancreas of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) via nutrition metabolism and apoptosis-related pathways. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2023, 249, 114397. [CrossRef]
- Middlebrook, J.L.; Leatherman, D.L. Binding of T-2 toxin to eukaryotic cell ribosomes.
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Nepovimova, E.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. Toxic mechanisms of the trichothecenes T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol on protein synthesis. Food Chem Toxicol 2022, 164, 113044. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Shao, B.; Han, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y. The Protective Effect of Selenium on T-2-Induced Nephrotoxicity Is Related to the Inhibition of ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Mice Kidney. Biol Trace Elem Res 2022, 200, 206-216. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, S.P.; Liu, C.W.; Cai, Y.Q. The protection of selenium on ROS mediated-apoptosis by mitochondria dysfunction in cadmium-induced LLC-PK(1) cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2009, 23, 288-294. [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 2012, 7, 562-578. [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 550. [CrossRef]
- Meneely, J.; Greer, B.; Kolawole, O.; Elliott, C. T-2 and HT-2 Toxins: Toxicity, Occurrence and Analysis: A Review. Toxins (Basel) 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Herwig, R.; Hardt, C.; Lienhard, M.; Kamburov, A. Analyzing and interpreting genome data at the network level with ConsensusPathDB. Nat Protoc 2016, 11, 1889-1907. [CrossRef]
- Mclaughlin, J.E.; Bin-Umer, M.A.; Tortora, A.; Mendez, N.; McCormick, S.; Tumer, N.E. A genome-wide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals a critical role for the mitochondria in the toxicity of a trichothecene mycotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 21883-21888.
- Bin-Umer, M.A.; McLaughlin, J.E.; Basu, D.; McCormick, S.; Tumer, N.E. Trichothecene mycotoxins inhibit mitochondrial translation--implication for the mechanism of toxicity. Toxins (Basel) 2011, 3, 1484-1501. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.H.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Nüssler, A.K.; Xiong, L.Y.; Kuča, K.; Dohnal, V.; Zhang, X.J.; Yuan, Z.H. Oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity and metabolism of T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol in animals and humans: an update. Arch Toxicol 2014, 88, 1309-26. [CrossRef]
- Cundliffe, E.; Cannon, M.; Davies, J. Mechanism of inhibition of eukaryotic protein synthesis by trichothecene fungal toxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1974, 71, 30-34.
- Charitou, P.; Burgering, B.M. Forkhead box(O) in control of reactive oxygen species and genomic stability to ensure healthy lifespan. Antioxid Redox Signal 2013,19, 1400-1419. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Guo, X. Expression Profiles of Selenium-Related Genes in Human Chondrocytes Exposed to T-2 Toxin and Deoxynivalenol. Biol Trace Elem Res 2019, 190, 295-302. [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, H.; Lu, W.; Yuan, J. MEHP-induced oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in HepG2 cells correlates with p53-mediated mitochondria-dependent signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 2012, 50, 2424-2431. [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.F.; Yu, S.Y.; Sun, L.; Zuo, J.; Luo, K.T.; Wang, M.; Fu, X.L.; Zhang, F.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G.Y., et al. T-2 toxin induces mitochondrial dysfunction in chondrocytes via the p53-cyclophilin D pathway. J Hazard Mater 2023, 465, 133090. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




