Submitted:
08 December 2023
Posted:
08 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
Animal Modeling Data
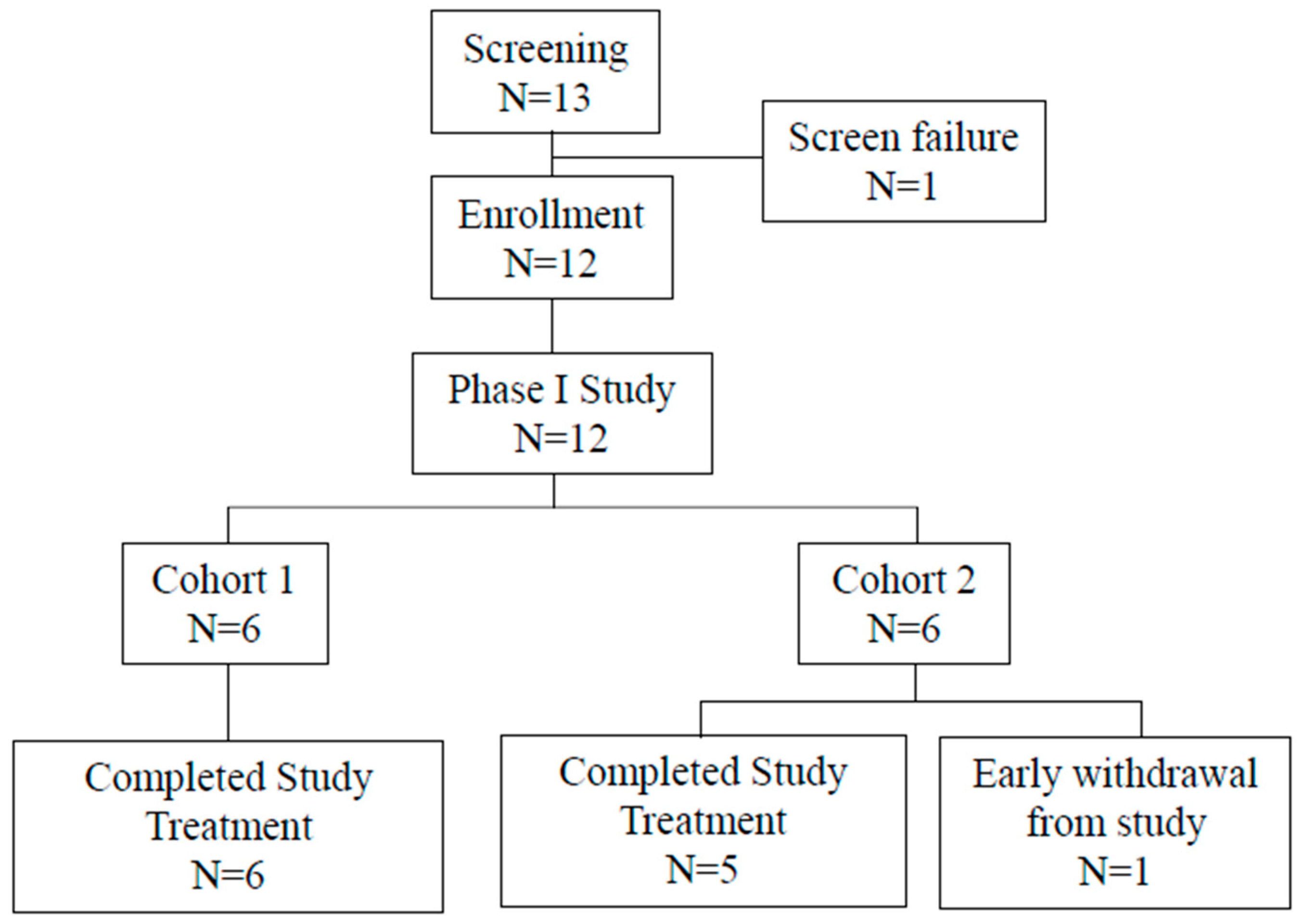
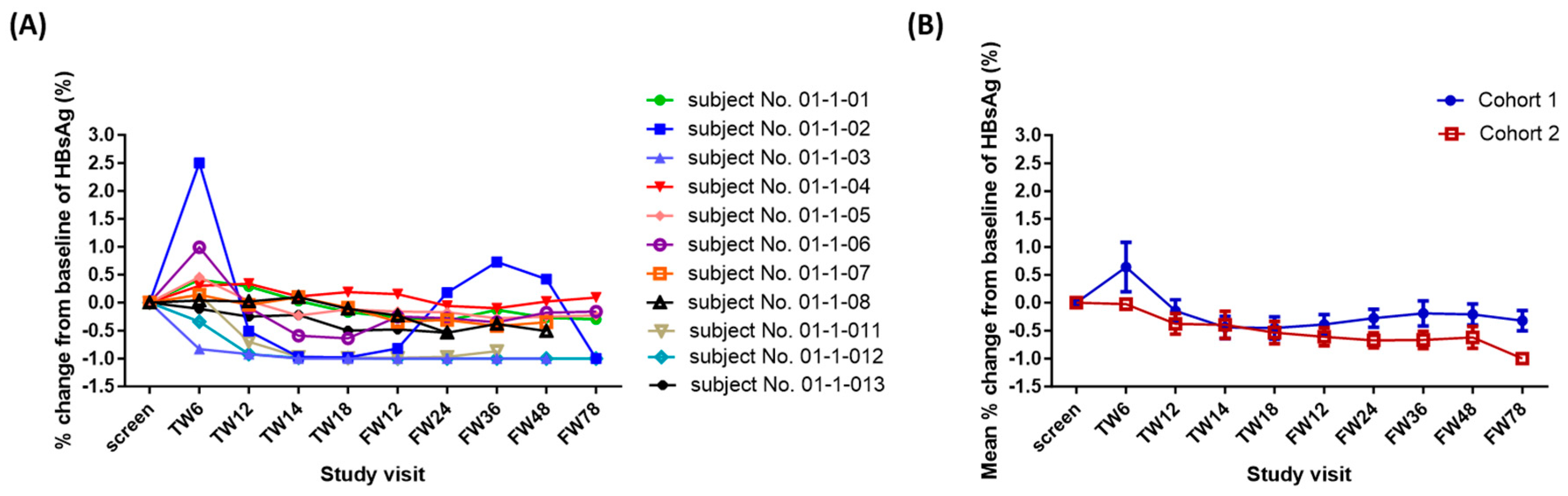
Phase I Clinical Study
3. Discussion
4. Methods
HBV-HDI Mouse Model:
Preclinical Materials:
Treatment of HBV-Carrying CBA/CaJ Mice:
Clinical Materials:
Study Design:
Patients:
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, HB. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2019, 156, 477–491.e1. [CrossRef]
- Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration; Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y. et al., The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683-1691. [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021, 7, 6. [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [CrossRef]
- Vilarinho, S.; Calvisi, D.F. New advances in precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence prediction and treatment. Hepatology. 2014, 60, 1812–1814. [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Kudo, M. Adjuvant therapy after radical surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma: still an unmet need. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019, 8, 414–416. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X.; Ning, Q.Q.; Yang, P.X.; Guan, Y.Y.; Liu, P.X.; Liu, M.L.; Qiao, L.X.; Guo, X.H.; Yang, T.W.; Chen, D.X.; Recent advances in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. World J Hepatol. 2023,15, 460-476. [CrossRef]
- Agata, Y.; Kawasaki, A.; Nishimura, H.; Ishida, Y.; Tsubata, T.; Yagita, H.; Honjo, T. Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 1996, 8, 765-72. [CrossRef]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008, 26, 677-704. [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, K.; Anagnostou, T.; Boussiotis, V.A. The PD1:PD-L1/2 Pathway from Discovery to Clinical Implementation. Front Immunol. 2016, 7, 550. [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1 (PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012, 24, 207–212. [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.; Verdon, D.J.; Brooks, A.E.; Gaggar, A.; Nguyen, A.H.; Subramanian, G.M.; Schwabe, C.; Dunbar, P.R. Anti-PD-1 blockade with nivolumab with and without therapeutic vaccination for virally suppressed chronic hepatitis B: A pilot study. J Hepatol. 2019, 71, 900–907. [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Du, S.; Yang, H. HBsAg seroclearance reduces the risk of late recurrence in HBV-related HCC. J Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1469–1470. [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.; He, Q.; Luo, P.; Xu, Z.; Yang, X. Research Status and Outlook of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020, 14, 3625–3649. [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, J.; Page, D.B.; Li, B.T.; Connell, L.C.; Schindler, K.; Lacouture, M.E.; Postow, M.A.; Wolchok, J.D. Toxicities of the anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Ann Oncol. 2015, 26, 2375-2391. [CrossRef]
- Miyachi, N.; Zagrijtschuk, O.; Kang, L.; Yonezu, K.; Qin, A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ropeginterferon alfa-2b in healthy Japanese and Caucasian Subjects After Single Subcutaneous Administration. Clin Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 391–404. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Qin, A.; Fang, J.; Wang, T.F.; Tsai, C.W.; Lin, K.C.; Teng, C.L.; Larouche, R. Novel long-acting ropeginterferon alfa-2b: Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety in a phase 1 clinical trial. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 2396–2407. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Tsai, C.Y.; Tsai, C.W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Qin, A.; Teng, C.; Song, B.; Wang, MX. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of novel long acting ropeginterferon alfa-2b in healthy Chinese subjects. Adv Ther. 2021, 38, 4756–4770. [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves Treatment for Rare Blood Disease: Treatment is First FDA-Approved Option Patients Can Take Regardless of Previous Therapies [Press release; date: Nov 12, 2021]. available on: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-treatment-rare-blood-disease#:~:text=Rare%20Blood%20Disease-,FDA%20NEWS%20RELEASE,-FDA%20Approves%20Treatment. Accessed 7 Sept 2023.
- European Medicines Agency. Besremi: EPAR-Medicine Overview. 2019; available on: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/besremi. Accessed 7 Sept 2023.
- Verstovsek, S.; Komatsu, N.; Gill, H.; Jin. J.; Lee, S.E.; Hou, H.A.; Sato, T.; Qin, A.; Urbanski, R.; Shih, W. SURPASS-ET: phase III study of ropeginterferon alfa-2b versus anagrelide as second-line therapy in essential thrombocythemia. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 2999–3009. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Qin, A.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chen, P.J. Novel Pegylated Interferon for the Treatment of Chronic Viral Hepatitis. Viruses. 2022, 14, 1128. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Chuang, W.L.; Qin, A.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhu, L.Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Chen, J.J.; Lo, C.C.; Zhou, X.; Mao, X. et al. A phase 3 clinical trial validating the potency and safety of an innovative, extra-long-acting interferon in chronic hepatitis C. JGH Open. 2022, 6, 782–791. [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Urbansky, R.W.; Yu, L.; Ahmed, T.; Mascrenhas, J. An Alternative Dosing Strategy for Ropeginterferon alfa-2b may Help Improve Outcomes in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: An Overview of Previous and Ongoing studies with Perspectives on the Future. Front Oncol. 2023, 13, 1109866. [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, L.; Qin, A.; Wu, D.; Shao, Z.; Bai, J.; Chen, S.; Duan, M.; Zhou, H.; Xu, N.; et al. A new dosing regimen of ropeginterferon alfa-2b is highly effective and tolerable: findings from a phase 2 study in Chinese patients with polycythemia vera. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023,12, 55. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Hsu, C.W.; Lu, S.N.; Yu, M.L.; Su, C.W.; Su, W.W.; Chien, R.N.; Hsu, C.S.; Hsu, S.J.; Lai, H.C. et al. Ropeginterferon alfa-2b every 2 weeks as a novel pegylated interferon for patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol Int. 2020, 14, 997-1008. [CrossRef]
- Huang, LR.; Wu, HL.; Chen, PJ.; Chen DS. An immunocompetent mouse model for the tolerance of human chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006, 103, 17862-17867. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1258-1266. [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Cao, L.J.; Song, H.F.; Xu, P.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.C.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, X.F. Expression of PD-L1 on CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells of Patients with Chronic HBV Infection and Its Correlation with Clinical Parameters. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 418–24. [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lan, P.; Han, Q. Huang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, G.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J. et al. Oncofetal gene SALL4 reactivation by hepatitis B virus counteracts miR-200c in PD-L1-induced T cell exhaustion. Nat Commun. 2018, 9, 1241. [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.F.; Li, T.C.; Wang, T.; Wu, T.H.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.C.; Shyu, W.C.; Su, I.J.; Jeng, L.B. Increased Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Pre-S2 Mutant. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2020, 7, 385-401. [CrossRef]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.Y.; Choo, S.P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H. R.d.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 2017, 389, 2492-2502. [CrossRef]
- Saung, M.T.; Pelosof, L.; Casak, S.; Donoghue, M.; Lemery, S.; Yuan, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Schotland, P.; Chuk, M.; Davis, G.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab for the Treatment of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Previously Treated with Sorafenib. Oncologist. 2021, 26, 797-806. [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Yin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, L.; Cai, L.; Zhou, Q. Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with HBV/HCV infection and advanced-stage cancer: A systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020, 99, e19013.
- Burns, E.A.; Muhsen, I.N.; Anand, K.; Xu, J.; Umoru, G.; Arain, A.N.; Abdelrahim, M. Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Cancer Patients Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J Immunother. 2021, 44, 132-139. [CrossRef]
- Féray, C.; López-Labrador, F.X. Is PD-1 blockade a potential therapy for HBV? JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 142–144. [CrossRef]
- Stark, G.R.; Kerr, I.M.; Williams, B.R.; Silverman, R.H.; Schreiber, R.D. How cells respond to Interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998, 67, 227–264. [CrossRef]
- Mazewsky, C.; Perez, R.E.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. Type I interferon (IFN)-regulated activation of canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 606456. [CrossRef]
- Theofilopoulos, A.N.; Baccala, R.; Beutler, B.; Kono, D.H. Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005, 23, 307–336. [CrossRef]
- Piehler, J.; Thomas, C.; Garcia, K.C.; Schreiber, G. Structural and dynamic determinants of type I interferon receptor assembly and their functional interpretation. Immunol Rev. 2012, 250, 317-334. [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.S.; Rautela, J.; Hertzog, P.J. Antitumour actions of interferons: implications for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2016,16,131–144. [CrossRef]
- Voest,; E.E.; Kenyon, B.M.; O’Reilly, M.S.; Truitt, G.; D’Amato, R.J.; Folkman, J. Inhibition of angiogenesis in vivo by interleukin 12. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 581–586. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Gutman, M.; Bucana, C.D., Sanchez, R.; Llansa, N.; Fidler, IJ. Interferons alpha and beta down-regulate the expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in human carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995, 92, 4562–4566. [CrossRef]
- Roos, G.; Leandersson, T.; Lundgren, E. Interferon-induced cell cycle changes in human hemapoietic cell lines and fresh leukemic cells. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 5358–5362.
- Grandér, D.; Sangfelt, O.; Erickson, S. How does interferon exert its cell growth inhibitory effect? Eur J Haematol. 1997, 59, 129–135. [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Q.; Tao, N., Dergay, A.; Moy, P.; Fawell, S., Davis, A.; Wilson, J.M.; Barsoum, J. Interferon-beta gene therapy inhibits tumor formation and causes regression of established tumors in immune-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998, 95, 14411–14416. [CrossRef]
- Qin, A. An anti-cancer surveillance by the interplay between interferon-beta and retinoblastoma protein RB1. Front Oncol. 2023, 13, 1173467. [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Q.; Beckham, C.; Brown, J.L.; Lukashev, M.; Barsoum, J. Human and mouse IFN-β gene therapy exhibits different anti-tumor mechanisms in mouse models. Mol Therapy. 2001, 4, 356-64. [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.L.; Barsoum, J.; Qin, X.Q. CD4+ T helper cell-independent anti-tumor response mediated by murine IFN-beta gene delivery in immunocompetent mice. J Interferon cytokine Res. 2002, 22, 719-28. [CrossRef]
- Cooksley, W.G.; Piratvisuth, T.; Lee, S.D.; Mahachai, V.; Chao.; Y.C.; Tanwandee, T.; Chutaputti, A., Chang, W.Y.; Zahm, F.E.; Pluck, N. Peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kDa): an advance in the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 2003, 10, 298-305. [CrossRef]
- Marcellin, P.; Lau, G.K.; Bonino, F.; Farci, P.; Hadziyannis, S.; Jin, R.; Lu, Z.M.; Piratvisuth, T.; Germanidis, G.; Yurdaydin, C.; et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a alone, lamivudine alone, and the two in combination in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2004, 351, 1206-1217. [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; Zonneveld, M.V.; Senturk, H.; Zeuzem, S.; Akarca, U.S.; Cakaloglu, Y.; Simon, C.; So, T.M.K.; Gerken, G.; de Man, R.A.; et al. Pegylated interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive hepatitis B: a randomized trial. The Lancet.2005, 365, 123-129. [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.H.; Hsu, C.W.; Chang, M.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Lai, M.W.; Yeh, C.T. Peginterferon is superior to nucleos(t)ide analogues for prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B. J Infect Dis. 2016, 213, 966-974. [CrossRef]
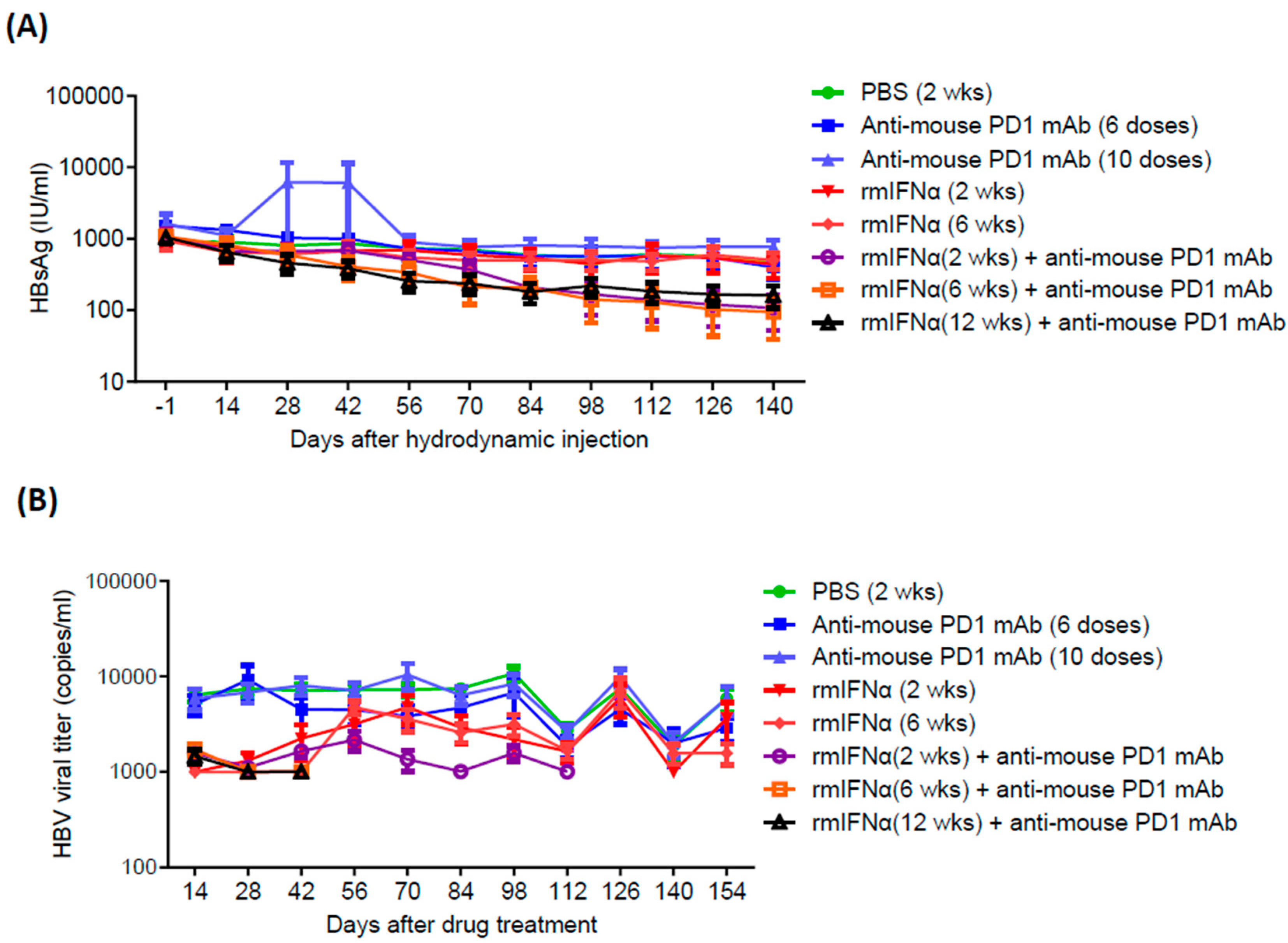
| Treatment Groups | Mean HBsAg (IU/ml) | HBsAg clearance rate |
| PBS | 471.9 | 0% (0/6) |
| Anti-PD1 (6 doses) | 398.6 | 20% (2/10) |
| Anti-PD1 (10 doses) | 769.1 | 10% (1/10) |
| rmIFN-α (2wk) | 441.2 | 0% (0/6) |
| rmIFN-α (6wk) | 504.7 | 0% (0/6) |
| rmIFN-α (2wk) +anti-PD1 (6 doses) | 107.8 (p value = 0.0012) | 20% (2/10) |
| rmIFN-α (6wk) +anti-PD1 (6 doses) | 94.3 (p value = 0.0009) | 44.4% (4/9) |
| rmIFN-α (12wk) +anti-PD1 (6 doses) | 162.1 (p value = 0.0040) | 0% (0/10) |
| Characteristics | P1101 + Anti-PD1 N=12 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort 1 N=6 |
Cohort 2 N=6 |
Total N=12 |
|
| Age, years | |||
| Mean (SD) | 64.2 (6.1) | 59.5 (12.9) | 61.8 (10.3) |
| Range (Min-Max) | 53-72 | 40-75 | 40-75 |
| Gender | |||
| Male, n (%) | 5 (83%) | 4 (67%) | 9 (75%) |
| Female, n (%) | 1 (17%) | 2 (33%) | 3 (25%) |
| Liver Cirrhosis | |||
| Yes | 3 (50%) | 3 (50%) | 6 (50%) |
| No | 3 (50%) | 3 (50%) | 6 (50%) |
| AEs, n (%) | Cohort 1 (N=6) | Cohort 2 (N=6) | Total (N=12) | ||||
| Any AE | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 12 (100.0) | ||||
| Any SAE | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||
| AEs occurring in >10% of patients n (%) | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | |
| Pyrexia | 4 (66.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6 (50.0) |
| ALT increased | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 5 (41.7) |
| AST increased | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 5 (41.7) |
| Fatigue | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (33.3) |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 3 (25.0) |
| Decreased appetite | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | 2 (16.7) |
| Insomnia | 1 (16.7) | 0 | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (16.7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





