Submitted:
05 December 2023
Posted:
06 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bibliometric data collection and analysis
2.2. Patent data collection
3. Results and discussion
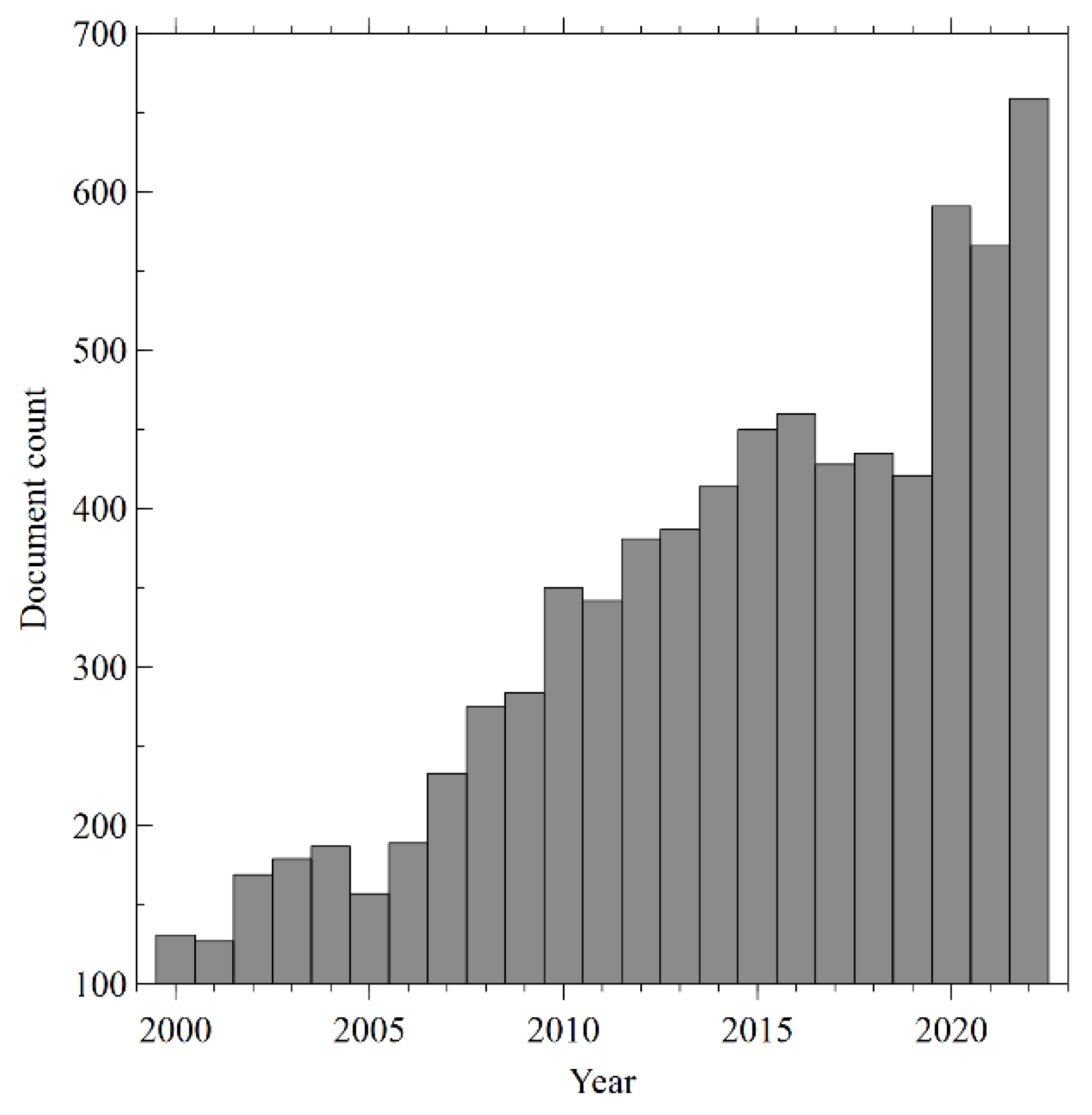
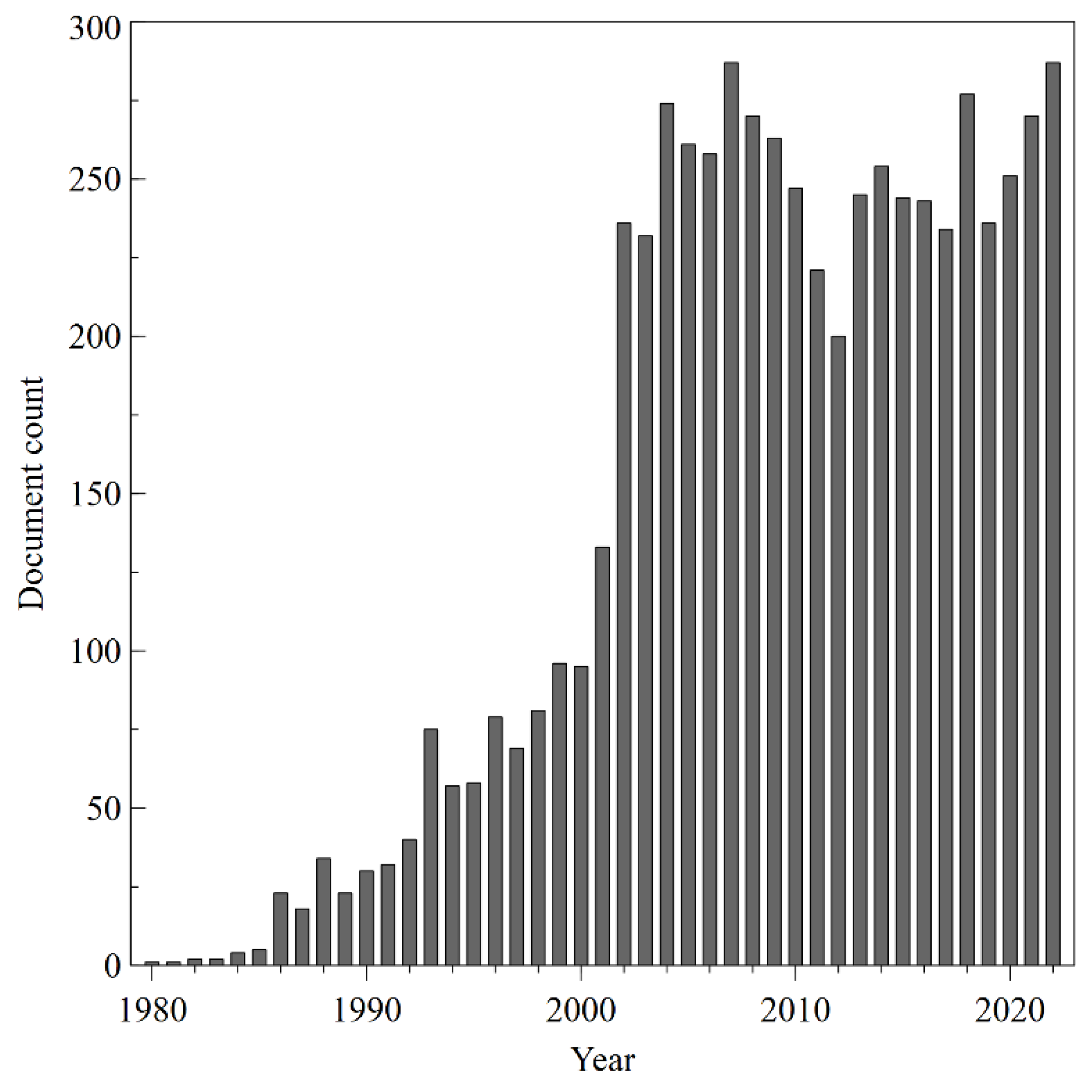
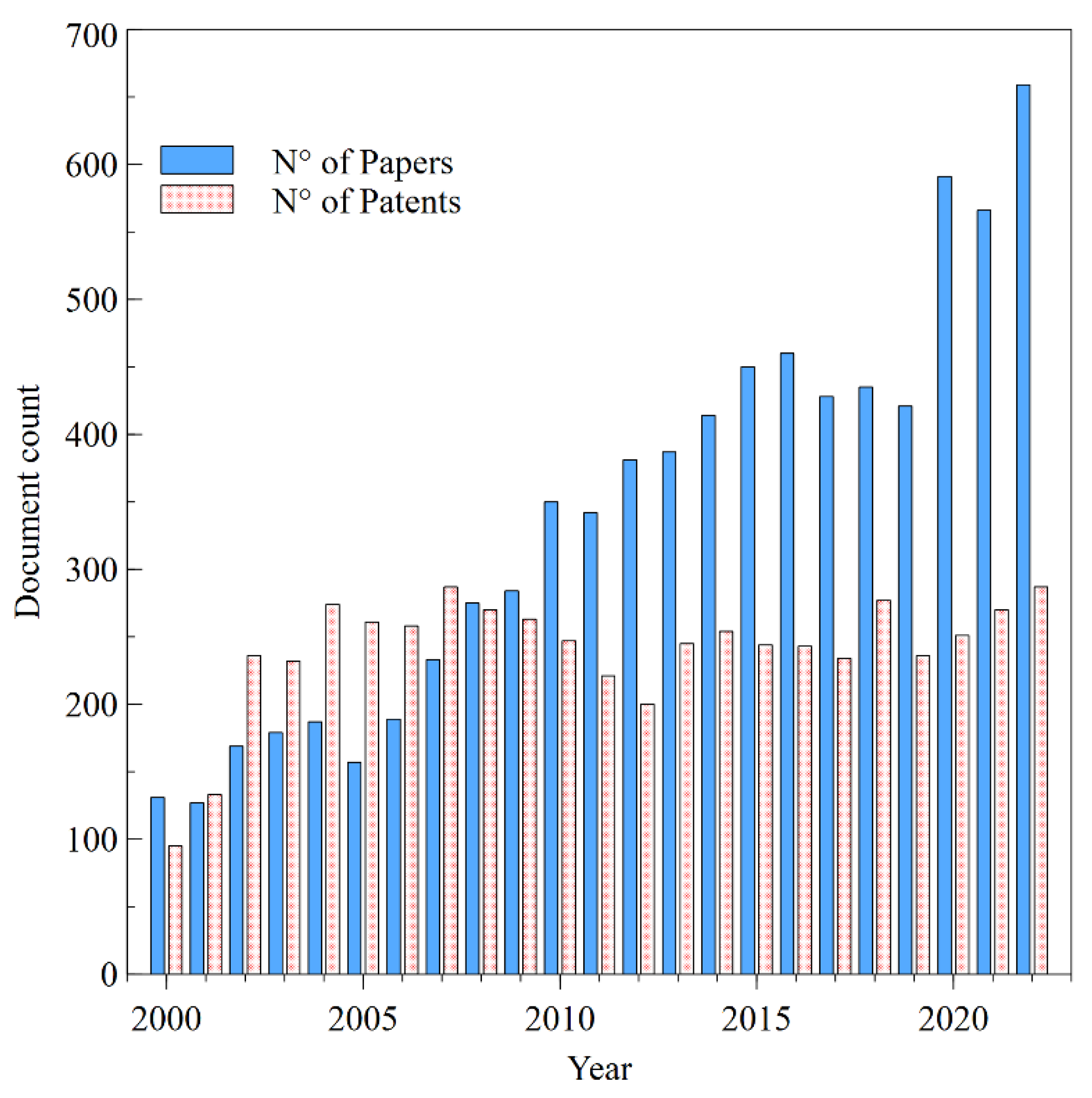
3.1. Annual global publication on transdermal drug delivery
3.2. Top 10 Journals and cited articles
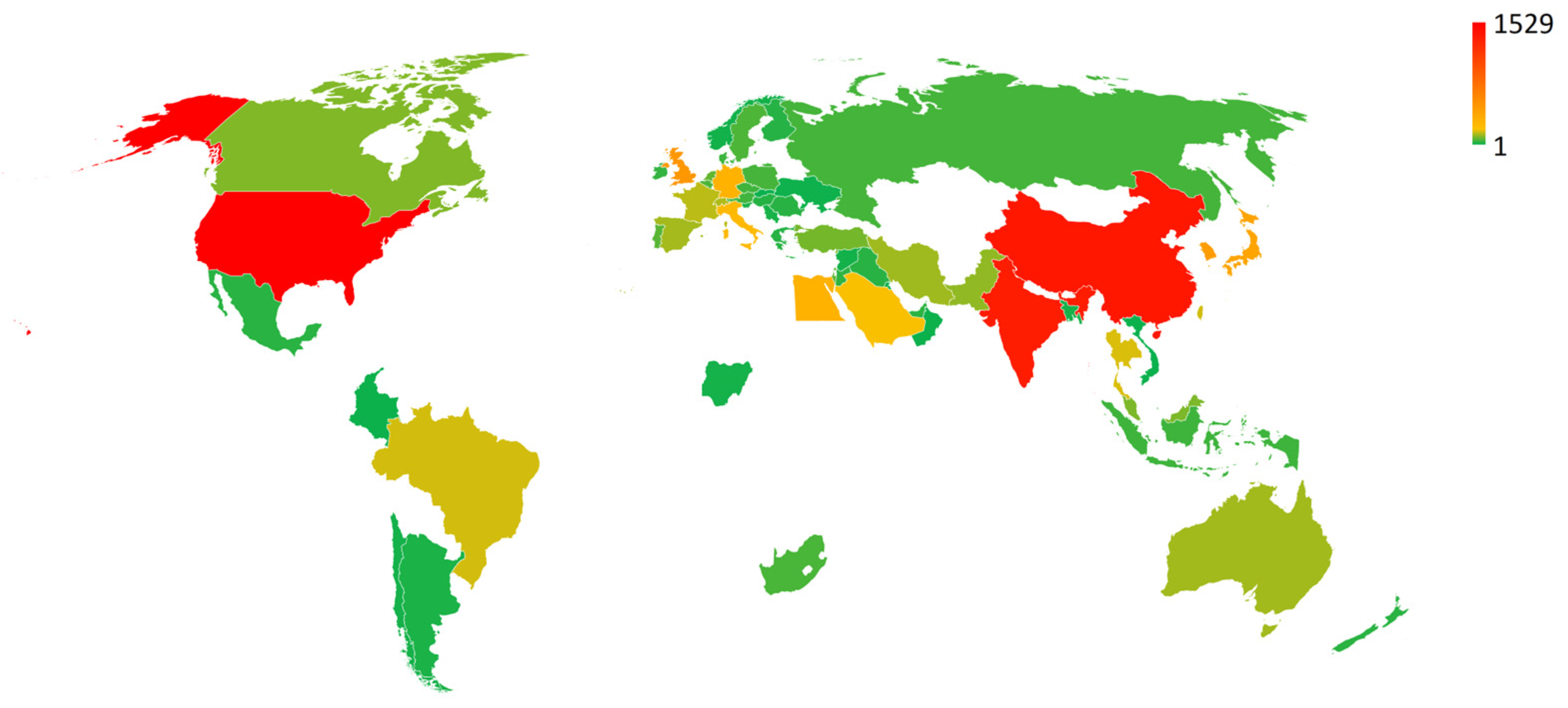
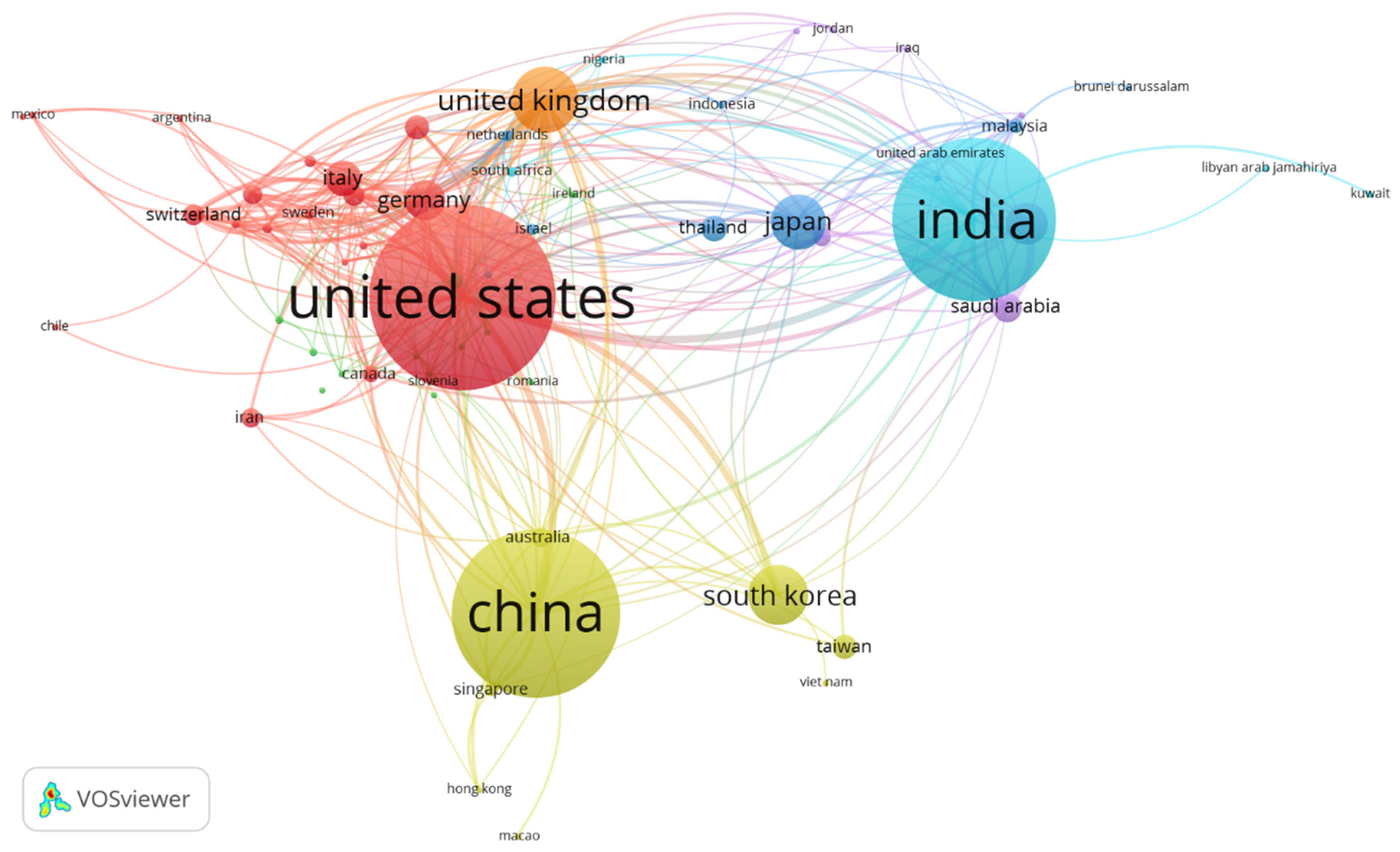
3.3. Co-authorship of countries
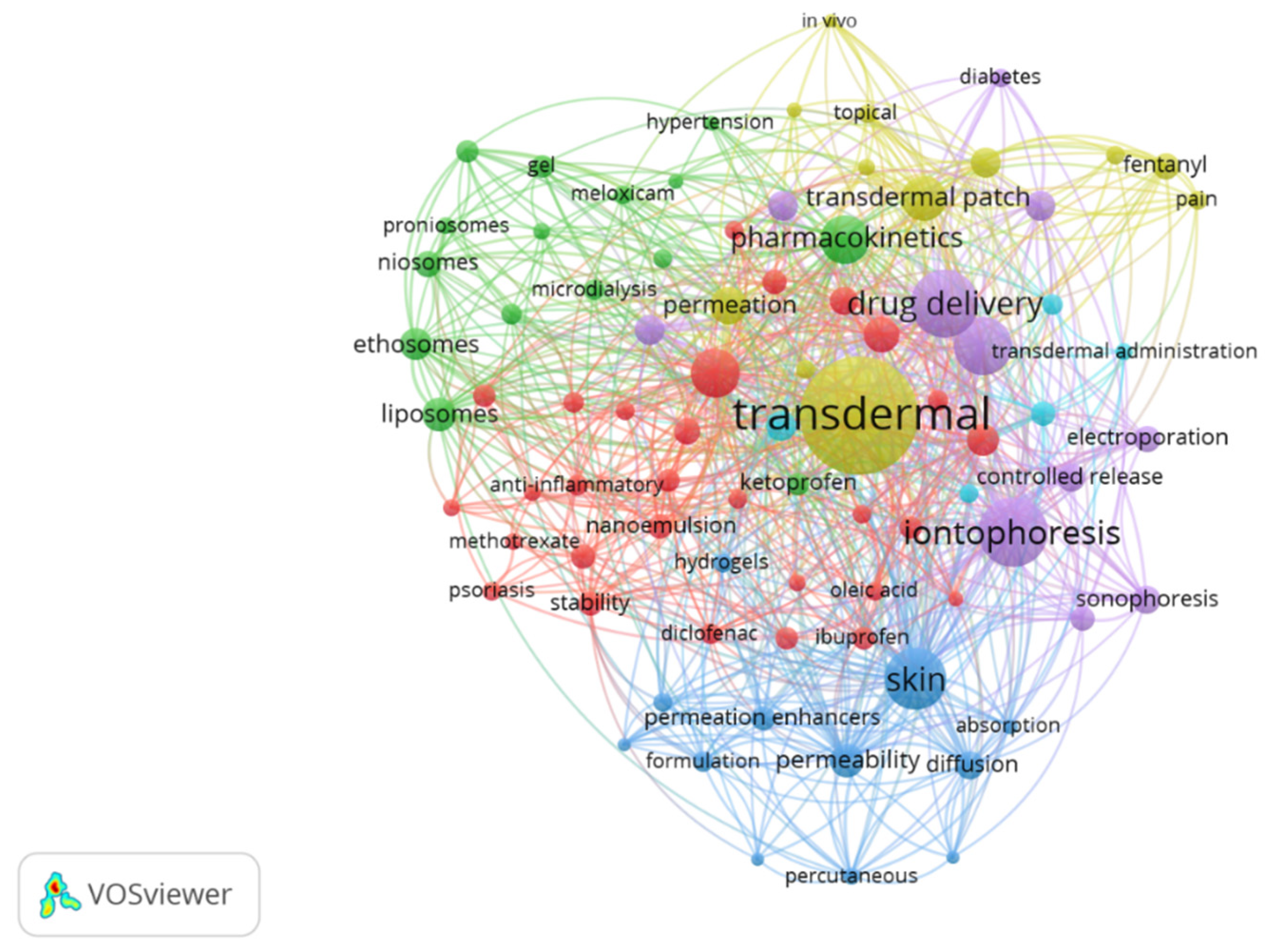
3.4. The co-occurrence analysis of the top keywords
3.5. Patent database analysis
| Applicant Name | % documents | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Noven Pharma | 4.3 | USA |
| Alza Corp | 3.1 | USA |
| 3M Innovative Properties Co | 2.0 | USA |
| Univ California | 1.0 | USA |
| Acrux Dds Pty LTD | 1.0 | Australia |
| Mylan Technologies INC | 0.9 | USA |
| Kimberly Clark Co | 0.9 | USA |
| Corium Int INC | 0.8 | USA |
| Chrono Therapeutics INC | 0.8 | USA |
| Koninkl Philips Electronics Nv | 0.7 | Holland |
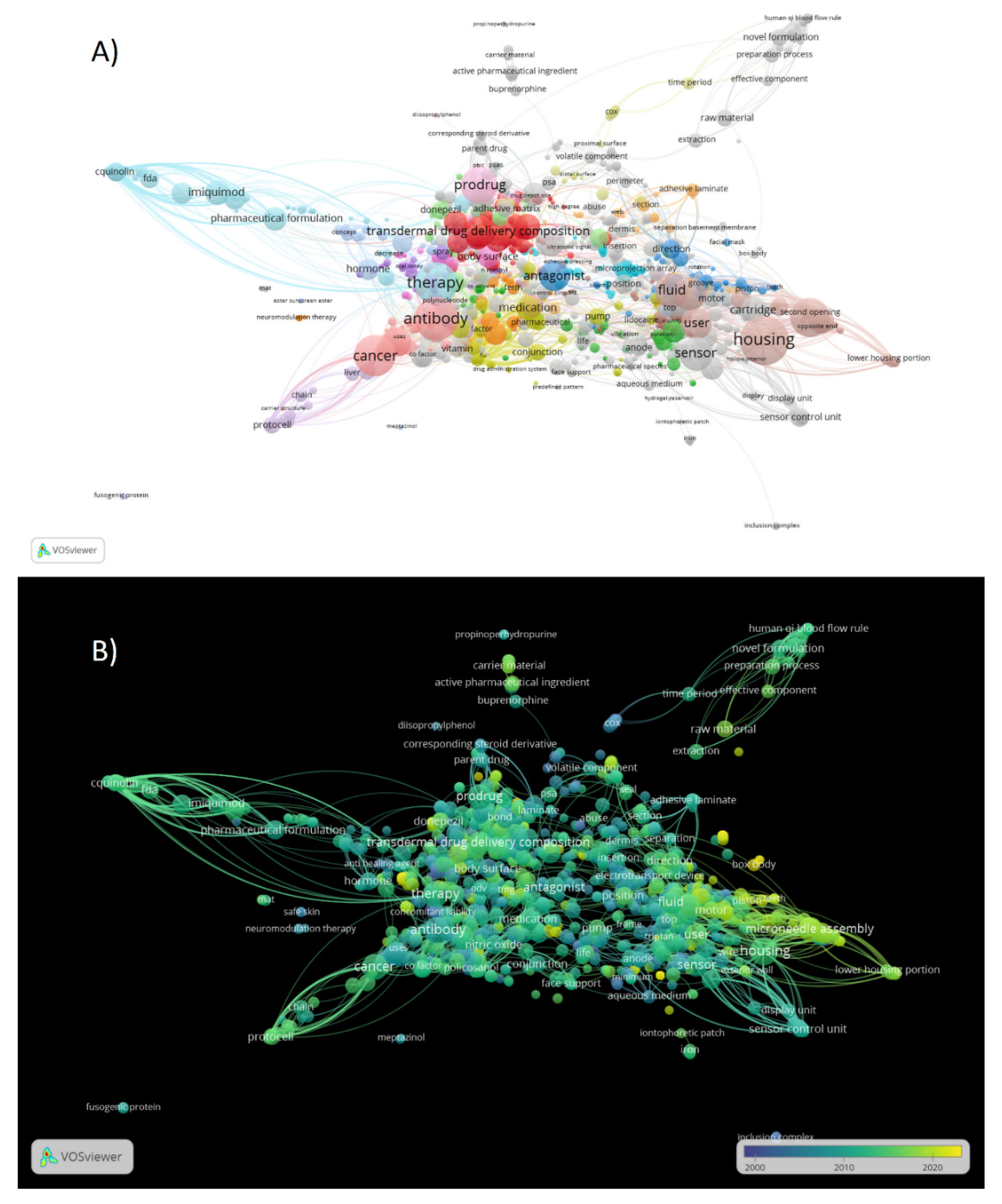
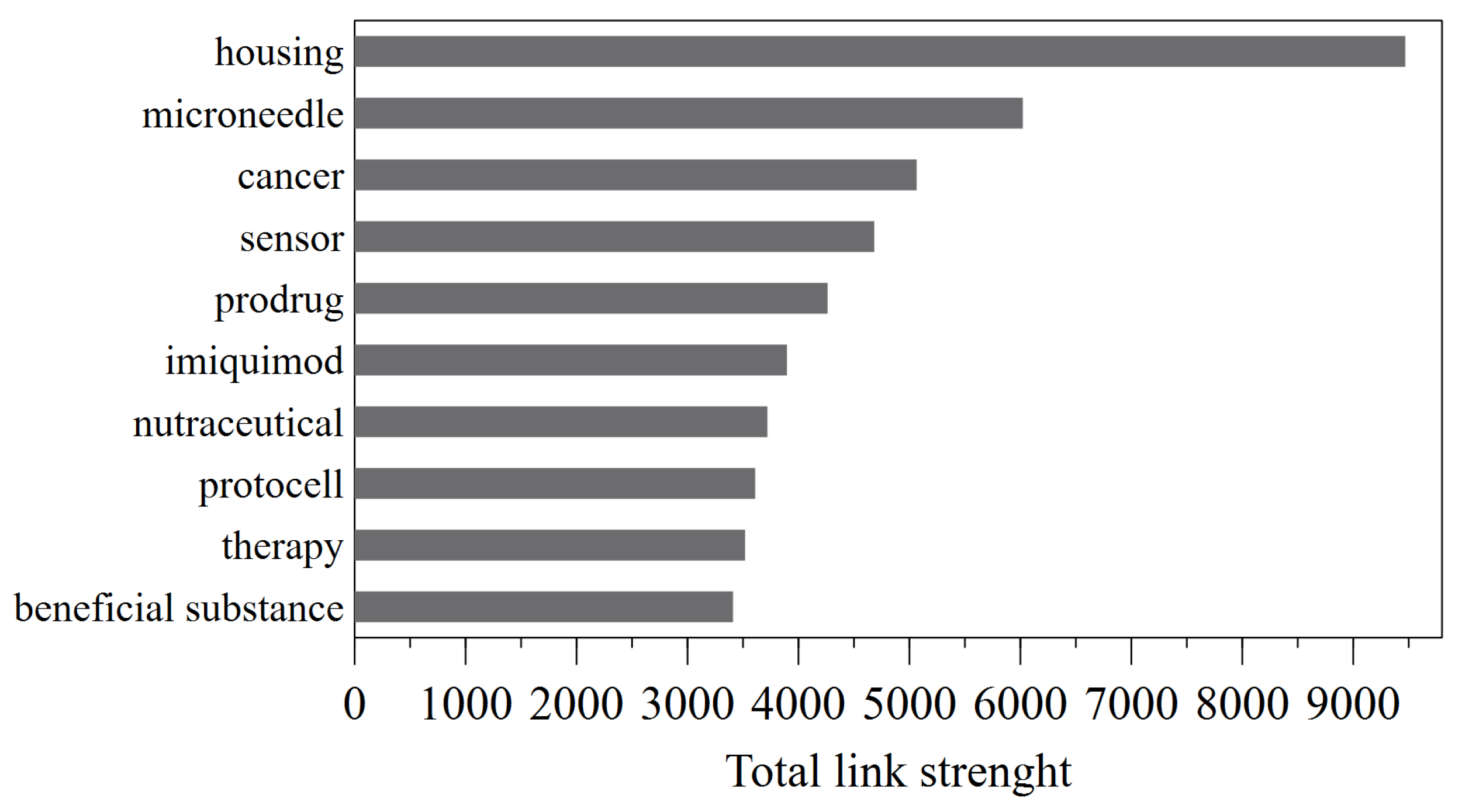
3.6. The co-occurrence analysis of the top keywords of recovered patents
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Transdermal Drug Delivery; Guy, Richard H.; Hadgraft, J., Ed.; 2nd ed.; New York - Basel, 2003; ISBN 082470861X.
- Williams, A. Transdermal and Topical Drug Delivery from Theory to Clinical Practice; Pharmaceutical Press, 2003; ISBN 9780853694892.
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S.; Langer, R. Current Status and Future Potential of Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 115–124. [CrossRef]
- Percutaneous Absorption; Bronaugh, R. L.; Maibach, H.I., Ed.; 2005; Vol. 155; ISBN 9780429186493.
- Miller, M.A.; Pisani, E. The Cost of Unsafe Injections. Bull. World Health Organ. 1999, 77, 808–811.
- Pammolli, F.; Magazzini, L.; Riccaboni, M. The Productivity Crisis in Pharmaceutical R&D. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 428–438. [CrossRef]
- Novel Drug Delivery Technologies Innovative Strategies for Drug Re-Positioning; Misra, A.; Shahiwala, A., Ed.; 2019; ISBN 978-981-13-3641-6.
- Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538.
- Newman, M.E.J. Coauthorship Networks and Patterns of Scientific Collaboration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004, 101, 5200–5205. [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-Based Clustering of Publications Using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070.
- Zhan, J.X. GVC Transformation and a New Investment Landscape in the 2020s: Driving Forces, Directions, and a Forward-Looking Research and Policy Agenda. J. Int. Bus. Policy 2021, 4, 206–220. [CrossRef]
- Naqeeb Ur Rehman, E.H.; Mao, X. Does Public R\&D Complement or Crowd-out Private R\&D in Pre and Post Economic Crisis of 2008? J. Appl. Econ. 2020, 23, 349–371. [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [CrossRef]
- Bird, D.; Ravindra, N.M. Transdermal Drug Delivery and Patches—An Overview. Med. DEVICES \& SENSORS 2020, 3, e10069. [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Singla, A.; Lee, Y. Biomedical Applications of Collagen. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 221, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration Enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 128–137. [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 581–587. [CrossRef]
- Touitou, E.; Dayan, N.; Bergelson, L.; Godin, B.; Eliaz, M. Ethosomes — Novel Vesicular Carriers for Enhanced Delivery: Characterization and Skin Penetration Properties. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 403–418. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Biodegradable Polymer Microneedles: Fabrication, Mechanics and Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 51–66. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, M.; Cho, H.R.; Kang, T.; Shin, K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Wearable/Disposable Sweat-Based Glucose Monitoring Device with Multistage Transdermal Drug Delivery Module. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601314. [CrossRef]
- McAllister, D. V; Wang, P.M.; Davis, S.P.; Park, J.-H.; Canatella, P.J.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated Needles for Transdermal Delivery of Macromolecules and Nanoparticles: Fabrication Methods and Transport Studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 13755–13760. [CrossRef]
- Kalia, Y.N.; Naik, A.; Garrison, J.; Guy, R.H. Iontophoretic Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 619–658. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, J.-H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2113–2124. [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G. Lipid Vesicles and Other Colloids as Drug Carriers on the Skin. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 675–711. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, X.; Cen, Y.; Xiao, D. Research Hotspot and Trend of Microneedles in Biomedical Field: A Bibliometric Analysis from 2011 to 2020. Burns 2022, 48, 959–972. [CrossRef]
- Rasool, B.K.A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.F.; Fahmy, S.A.; Saad, H.S.; Khan, S.A. Development and Evaluation of Ibuprofen Transdermal Gel Formulations. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 9, 355–363. [CrossRef]
- Pradal, J. Comparison of Skin Permeation and Putative Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Commercially Available Topical Products Containing Ibuprofen and Diclofenac. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 2805–2814. [CrossRef]
- Benbow, T.; Campbell, J. Microemulsions as Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems for Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): A Literature Review. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1849–1855. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Verma, S.; Singh, M.; Chalotra, T.; Utreja, P. Advanced Drug Delivery Systems for Transdermal Delivery of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: A Review. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1087–1099. [CrossRef]
- Panpan Xie Wei Xue, W.Q.Y.L.L.Y.Z.Y.; Shi, A. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Ibuprofenamine Hydrochloride Spray (NSAIDs), a New Drug for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis, in Healthy Chinese Subjects. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 629–638. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Gupta, N.V.; Sastri, K.T.; M, S.; Chand, P.; Kumar, H.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Gowda, D. V; Jain, V. Current Progressions in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems for Management of Rheumatoid and Osteoarthritis: A Comprehensive Review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 73, 103476. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Joshi, N.K. Formulation, Development and Evaluation of Ketoprofen Loaded Transethosomes Gel. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2022, 12, 86–90. [CrossRef]
- Alany, R. Topical and Transdermal Formulation and Drug Delivery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 457. [CrossRef]
- Sriaandhal Sabalingam; Malitha Aravinda Siriwardhene A Review on Emerging Applications of Emulgel as Topical Drug Delivery System. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2022, 13, 452–463. [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, S.; Whiteman, A.; Brandner, B. Transdermal Drug Delivery in Pain Management. Contin. Educ. Anaesthesia, Crit. Care Pain 2011, 11, 39–43. [CrossRef]
- Skaer, T.L. Dosing Considerations with Transdermal Formulations of Fentanyl and Buprenorphine for the Treatment of Cancer Pain. J. Pain Res. 2014, 7, 495–503. [CrossRef]
- Margetts, L.; Sawyer, R. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Principles and Opioid Therapy. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2007, 7, 171–176. [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Bian, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, J. Pain Management with Transdermal Drug Administration: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 618, 121696. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Manda, P.; Pavurala, N.; Khan, M.A.; Krishnaiah, Y.S.R. Development and Validation of in Vitro–in Vivo Correlation (IVIVC) for Estradiol Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems. J. Control. Release 2015, 210, 58–66. [CrossRef]
- Somayaji, M.R.; Das, D.; Garimella, H.T.; German, C.L.; Przekwas, A.J.; Simon, L. An Integrated Biophysical Model for Predicting the Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Transdermally Delivered Compounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 167, 105924. [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S. Modeling Skin Permeability to Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Solutes Based on Four Permeation Pathways. J. Control. Release 2003, 86, 69–92. [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.P.; Murthy, N.; Prausnitz, M.R. Minimally Invasive Protein Delivery with Rapidly Dissolving Polymer Microneedles. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 933–938. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Cheng, C.-M. Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems for Fighting Common Viral Infectious Diseases. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1498–1508. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hanning, S.; Falconer, J.; Locke, M.; Wen, J. Recent Advances in Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes): Fabrication, Characterization, Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 18–39. [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Chávez, J.J.; Bonilla-Martínez, D.; Angélica, M.; Villegas-González; Molina-Trinidad, E.; Casas-Alancaster, N.; Revilla-Vázquez, A.L. Microneedles: A Valuable Physical Enhancer to Increase Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 51, 964–977. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, R. Mechanism and Application of Chitosan and Its Derivatives in Promoting Permeation in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15. [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Mishra, A.; Nayak, S.; Soni, V. Transdermal Delivery of Antihypertensive Agents: A Tabular Update. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 2011, 3. [CrossRef]
- Alhodieb, F.S.; Barkat, M.A.; Barkat, H.A.; Ab Hadi, H.; Khan, M.I.; Ashfaq, F.; Rahman, M.A.; Hassan, M.Z.; Alanezi, A.A. Chitosan-Modified Nanocarriers as Carriers for Anticancer Drug Delivery: Promises and Hurdles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 457–469. [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Badran, M.; Elmowafy, M.; Soliman, G.M. Spironolactone-Loaded LeciPlexes as Potential Topical Delivery Systems for Female Acne: In Vitro Appraisal and Ex Vivo Skin Permeability Studies. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Dhote, V.; Bhatnagar, P.; Mishra, P.K.; Mahajan, S.C.; Mishra, D.K. Iontophoresis: A Potential Emergence of a Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Park, H.; Seo, J.; Lee, S. Sonophoresis in Transdermal Drug Deliverys. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 56–65. [CrossRef]
- A Charoo, N.; Rahman, Z.; A Repka, M.; N Murthy, S. Electroporation: An Avenue for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 125–136.
- Lavon, I.; Kost, J. Ultrasound and Transdermal Drug Delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 670–676. [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.C.; Gupta, M. Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems in Diabetes Management: A Review. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 13–25. [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.; Narasimhan, B.; Wang, Q. Biocompatible Nanoparticles and Vesicular Systems in Transdermal Drug Delivery for Various Skin Diseases. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 555, 49–62. [CrossRef]
- Kateh Shamshiri, M.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Khodabandeh Shahraky, M.; Rahimi, F. Lecithin Soybean Phospholipid Nano-transfersomes as Potential Carriers for Transdermal Delivery of the Human Growth Hormone. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9023–9033.
- Barone, A.; Cristiano, M.C.; Cilurzo, F.; Locatelli, M.; Iannotta, D.; Di Marzio, L.; Celia, C.; Paolino, D. Ammonium Glycyrrhizate Skin Delivery from Ultradeformable Liposomes: A Novel Use as an Anti-Inflammatory Agent in Topical Drug Delivery. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111152. [CrossRef]
- Serpico, L.; Dello Iacono, S.; De Stefano, L.; De Martino, S.; Battisti, M.; Dardano, P.; Pedatella, S.; De Nisco, M. PH-Sensitive Release of Antioxidant Se-Glycoconjugates through a Flexible Polymeric Patch. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 178, 111486. [CrossRef]
- Tsioris, K.; Raja, W.K.; Pritchard, E.M.; Panilaitis, B.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Fabrication of Silk Microneedles for Controlled-Release Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 330–335. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pu, X.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, L. A Semi-Interpenetrating Network-Based Microneedle for Rapid Local Anesthesia. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 78, 103984. [CrossRef]
- Tombs, E.L.; Nikolaou, V.; Nurumbetov, G.; Haddleton, D.M. Transdermal Delivery of Ibuprofen Utilizing a Novel Solvent-Free Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive (PSA): TEPI® Technology. J. Pharm. Innov. 2018, 13, 48–57. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, F.; Ziyadi, H.; Baghali, M.; Luo, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Pvp/Pva Nanofiber Mat as a Novel Potential Transdermal Drug-Delivery System for Buprenorphine: A Solution Needed for Pain Management. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Ita, K.; Simon, L. Modelling of Dissolving Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Theoretical and Experimental Aspects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 68, 137–143. [CrossRef]
- Electrospinning and Crosslinking of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Composite Nanofiber for Transdermal Drug Delivery - Cui - 2018 - Advances in Polymer Technology - Wiley Online Library.
- Zavareh, H.S.; Pourmadadi, M.; Moradi, A.; Yazdian, F.; Omidi, M. Chitosan/Carbon Quantum Dot/Aptamer Complex as a Potential Anticancer Drug Delivery System towards the Release of 5-Fluorouracil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1422–1430. [CrossRef]
- Qindeel, M.; Ahmed, N.; Sabir, F.; Khan, S.; Ur-Rehman, A. Development of Novel PH-Sensitive Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 629–641. [CrossRef]
- Auda, S.H.; Fathalla, D.; Fetih, G.; El-Badry, M.; Shakeel, F. Niosomes as Transdermal Drug Delivery System for Celecoxib: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 1229–1245. [CrossRef]
- Say, J.; Tomasco, M.F..; Heller, A.; Gal, Y.; Aria, B.; Heller, E.; Plante, P.J.; Vreeke, M.S.; Friedman, K.A..; Colman, F.C. US 8 617 071 B2 - Analyte Monitoring Device and Method of Use 2013.
- Porter, A.L. Forecasting and Management of Technology; John Wiley & Sons, 1991; Vol. 18; ISBN 0471512230.
- Speziali, M.G.; Livio, D.F.; Tarabal, V.S.; Granjeiro, P.A. Technology Landscape and a Short Patentometric Review for Antibiofilm Technologies. World Pat. Inf. 2023, 72, 102158. [CrossRef]
- Schild, I. Patent or Perish. On the Nature and Role of Patenting amongst Linkoping University Researchers; Working paper, Umea University, Dept of Sociology, 2004.
- Ingrole, R.S.J.; Azizoglu, E.; Dul, M.; Birchall, J.C.; Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Trends of Microneedle Technology in the Scientific Literature, Patents, Clinical Trials and Internet Activity. Biomaterials 2021, 267, 120491. [CrossRef]
- Azmana, M.; Mahmood, S.; Hilles, A.R.; Mandal, U.K.; Al-Japairai, K.A.S.; Raman, S. Transdermal Drug Delivery System through Polymeric Microneedle: A Recent Update. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101877. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Linh C.;Nguyen, An-Dien;Allen Le, K. US 10 303 851 B2 - Physician-Centric Health Care Delivery Platform 2019.
- Castel, J.C. US 8 523 791 B2 - Multi-Modal Drug Delivery System 2013.
- Searle, Gary; Knapp, Keith N ; Tunkel, Roman; Skutnik, Peter Vedrine, L. US 9 375 529 B2 - Extended Use Medical Device 2016.
- Huang, Zhili Joseph; DiPierro, G. US 8 372 040 B2 - Portable Drug Delivery Device Including Detachable and Replaceable Administration or Dosing Element 2013.
- Dipierro, G.G.S.A. US 8 252 321 B2 - Biosynchronoustrandermal Drug Delivery for Longevity. Anti-Agin Fatigue Management, Obesity, Weight Loss, Weight Management, Delivery of Nutraceuticals, and the Treatment of Hyperglicemia, Alzheimer’s Disease, Sleep Disorders, Parkinsons 2012.
- Yuzhakov, V. V US 7 658 728 B2 - Microneedle Array, Patch, and Applicator for Transdermal Drug Delivery 2010.
- de Fougerolles, Antonin; Elbashir, S.M. US 9 186 372 B2 - Split Dose Administration 2008, 2.
- Gorman, William; Garibotto, John T.; Flaherthy, J. Christopher; CAI, Amy W.; Dragosits, Thomas, J. WO 2004/060436 A2 - Skin Attachment Apparatus and Method for Patient Infusion Device 2004.
- King, G.W.. US 7 206 632 B2 - Patient Sensory Response. Evaluation for Neuromodulation Efficacy Rating 2007.
- Bookbinder, Louis H.; Kundu, A.; Frost, G.I. US 7 871 607 B2 - Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases and Methods of Preparing and Using Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases. Syst. methods Robot. gutter Clean. along an axis Rotat. 2011.
- Giles-Komar, J.; Knight, D.; Peritt, D.; Mohit, T. WO 2004/39826 A1 - Anti-Il-6 Antibodies, Compositions, Methods and Uses 2004.
- Kaplan, L.M..; Ahmad, N.N..; Harris, J.L.; Felder, K.D..; Pastorelli, A. US 11 154 559 B2 - Methods and Compositions of Bile Acids 2021.
- Heavner, G.A..; Knight, D.; Ghrayeb, J.; Scallon, B.J..; Nesspor, T.C..; Kutoloski, K.A. WO 2004/002417 A2 - Mammalian CH1 Delected Mimetibodies, Compositions, Mwthods and Uses 2004.
- Tomalia, D.A..; Swanson, D.R..; Huang, B.; Pulgam, V.R.; Heinzelmann, R., J.; Svenson, S.; Reyna, L.A..; Chauhan, A.S.; DeMattei, C.R. US 7 985 424 B2 - Dendritic Polymers with Enhanced Amplificatiob and Interior Functionality 2011.
- Heavner, G.; Knight, D.M..; Scallon, B.; Ghrayeb, J.; Nesspor, T.C..; Huang, C. WO 2005/032460 A2 - Human Epo Mimetic Hinge Core Mimetibodies, Compositions, Methods and Uses 2005.
- Tamarkin, D.; Fried-Man, D.; Meir, E. WO 2004/037225 A2 - Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Foam 2004.
- Xu, B. US 7 591 806 B2 - High-Aspect-Ratio Microdevices and Methods for Transdermal Delivery and Sampling of Active Substances 2009.
- Heather, D.L..; McCluskie, M.J. WO 01/95935 A1 - Immunostimulatory Nucleic Acids for Inducing a Th2 Immune Response 2001.
- Khan, Arifulla; Reinhard, J.F. jr WO2012118562A1 - Compositions and Methods for Treating Depression, Adhd and Other Central Nervous System Disorders Employing Novel Bupropion Compounds, and Methods for Production and Use of Novel Bupropion Compounds and Formulations.
- Schøller, J.; Pedersen, H.; Brix, L. US 10 369 204 B2 - Molecular Vaccines for Infectious Disease 2019.
- Tamarkin, Dov; Friedman, D.E.M. WO 2005/018530 A2 - Penetrating Pharmaceutical Foam 2005.
- Perricone, V.N.; Sayed, Y.A. US 8 668 937 B2 - Topical Nitric Oxide Systems and Methods of Use Thereof 2014.
- Ashley, C.E.; Brinker, C.J.; Carnes, E.C.; Fekrazad, M.H.; Felton, L.A.; Negrete, O.; Padilla, D.P.; Wilkinson, B.S.; Wilkinson, D.C.; Willman, C.L. US 2017 / 0232115 A1 - Porous Nanoparticle-Supported Lipid Bilayers (Protocells) for Targeted Delivery Including Transdermal Delivery of Cargo and Methods Thereof 2017.
| Rank | Source | IF (2022) | Total publications (Percentage) |
Total Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | International Journal of Pharmaceutics | 6.270 | 525 (6.7 %) | 23,596 |
| 2 | Journal Of Controlled Release | 11.467 | 262 (3.4 %) | 19,315 |
| 3 | Journal Of Pharmaceutical Sciences | 3.534 | 226 (2.9 %) | 6,606 |
| 4 | Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy | 3.225 | 178 (2.3 %) | 4,365 |
| 5 | AAPS Pharmscitech | 3.246 | 158 (2.0 %) | 4,451 |
| 6 | Journal Of Drug Delivery Science and Technology | 3.981 | 155 (2.0 %) | 1,837 |
| 7 | Pharmaceutical Research | 4.580 | 153 (2.0 %) | 7,893 |
| 8 | Pharmaceutics | 6.072 | 135 (1.7 %) | 1,724 |
| 9 | European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics | 5.589 | 126 (1.6 %) | 6,486 |
| 10 | Drug Delivery | 6.420 | 122 (1.6 %) | 2,462 |
| Title | PY | Journal | Citations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomedical applications of collagen | 2001 | International Journal of Pharmaceutics | 1,516 | [16] |
| Penetration enhancers | 2012 | Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews | 1,509 | [17] |
| Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery | 2004 | Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews | 1,102 | [18] |
| Ethosomes - Novel vesicular carriers for enhanced delivery: Characterization and skin penetration properties | 2000 | Journal of Controlled Release | 1,044 | [19] |
| Biodegradable polymer microneedles: Fabrication, mechanics, and transdermal drug delivery | 2005 | Journal of Controlled Release | 693 | [20] |
| Wearable/disposable sweat-based glucose monitoring device with multistage transdermal drug delivery module | 2017 | Science Advances | 679 | [21] |
| Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: Fabrication methods and transport studies | 2003 | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | 658 | [22] |
| Iontophoretic drug delivery | 2004 | Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews | 641 | [23] |
| Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery | 2008 | Biomaterials | 639 | [24] |
| Lipid vesicles and other colloids as drug carriers on the skin | 2004 | Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews | 573 | [25] |
| Author Name | Country | Affiliation | Documents count |
|---|---|---|---|
| Banga, A.K. | United States | University of Atlanta | 78 |
| Donnelly, R.F. | Ireland | Queen’s University Belfast | 75 |
| Prausnitz, M.R. | United States | Georgia Institute of Technology | 69 |
| Kalia, Y.N. | Suisse | Université de Genève | 61 |
| Fang, L. | China | Shenyang Pharmaceutical University | 58 |
| Mitragotri, S. | United States | Georgia Institute of Technology | 50 |
| Aqil, M. | Saudi Arabia | King Saud University | 49 |
| Stinchcomb, A.L. | United States | University of Maryland School of Pharmacy | 46 |
| Opanasopit, P. | Thailand | Silpakorn University | 38 |
| Shin, S.C. | South Korea | Chonnam National University | 38 |
| Funding Sponsor | Country | Documents count |
|---|---|---|
| National Natural Science Foundation | China | 469 |
| National Institutes of Health | United States | 237 |
| National Research Foundation | Korea | 117 |
| National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering | United States | 79 |
| Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities | China | 74 |
| Japan Society for the Promotion of Science | Japan | 72 |
| Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico | Brasil | 70 |
| Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior | Brasil | 70 |
| National Science Foundation | United States | 70 |
| Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology | Japan | 64 |
| Subject Area | Documents count |
|---|---|
| Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics | 4,778 |
| Medicine | 1,790 |
| Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology | 1,553 |
| Chemistry | 1,337 |
| Materials Science | 1,132 |
| Engineering | 852 |
| Chemical Engineering | 791 |
| Physics | 509 |
| Immunology and Microbiology | 134 |
| Multidisciplinary | 124 |
| Keywords | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | Cluster 4 | Cluster 5 | Cluster 6 | |
| anti-inflammatory curcumin diclofenac sodium dissolving MNs ethosome hyaluronic acid hydrogel ibuprofen in vitro release indomethacin ketoprofen liposome meloxicam methotrexate microemulsion nanoemulsion nanoparticle |
nanostructured lipid carriers oleic acid penetration enhancer percutaneous absorption psoriasis rheumatoid arthritis skin irritation skin penetration skin permeability skin permeation solid lipid nanoparticles stability stratum corneum sustained release topical delivery transdermal absorption transdermal permeation |
bioavailability buprenorphine enhancer estradiol fentanyl human skin lidocaine microdialysis pain patch pharmacodynamics pharmacokinetic transdermal administration transdermal delivery system transdermal patch |
absorption controlled release diclofenac diffusion drug delivery systems formulation hydrogels mathematical model percutaneous permeability protein delivery skin solubility surfactants |
chitosan drug release flux hypertension in vitro in vivo nanoparticles permeation permeation enhancer release topical transdermal transdermal patches |
diabetes drug delivery electroporation insulin iontophoresis microneedles sonophoresis ultrasound |
ethosomes factorial design gel liposomes niosomes optimization proniosomes transfersomes |
| Drug/prodrug/NPs Released | Methods of Preparation and Formulation Details | System Operation | Inference | Cluster | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium glycyrrhizinate (A.G.) | Ammonium glycyrrhizinate - ultra-deformable liposomes (A.G.-ULs) were obtained by dissolving the drug in the lipid components during the synthesis of ULs (thin-layer evaporation technique) | High dimensional stable ULs pass intact through the skin and deliver AG in specific tissues in a controlled manner | Anti-inflammatory effect | 6 | [58] |
| Resveratrol/ caffeic acid containing glycoconjugates | Imbibition of PEGDA/HEMA films in water solution containing the glycoconjugates | pH-dependent release of synthetic selenium-containing glycoconjugates | Antioxidant effect, potential wound healing acceleration | 3 | [59] |
| Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) enzyme | Silk MNs obtained by aqueous-based micro-molding and simultaneous loading with HRP | The degradation rate of silk fibroin and the diffusion rate of the entrained molecules can be controlled by adjusting post-processing conditions | Tunable release kinetics | 5 | [60] |
| Lidocaine hydrochloride (LIDH) | UV crosslinked methacrylated chondroitin sulfate (CS-MA) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) K29/32MNs loaded with LIDH | At body temperature PVP K29/32 rapidly dissolve, with subsequent release of LIDH | Local anesthesia | 5 | [61] |
| Ibuprofenamine hydrochloride (2-(Diethylamino) ethyl 2-(4-isobutylphenyl) propionate hydrochloride | Clinical trial research, in which spray Ibuprofenamine hydrochloride penetrates the skin and biological barrier into the lesion tissue after administration | Spray Ibuprofenamine hydrochloride (prodrug of ibuprofen) penetrates the skin and is quickly converted into therapeutic ibuprofen | Anti-inflammatory effect | 1 | [31] |
| Ibuprofen | Hot-melt poly(ether-urethane)-silicone crosslinked pressure-sensitive adhesive (HMPSAs) drug reservoir formation | Adhesive matrix releases ibuprofen that penetrates the skin. The presence of chemical enhancers, di(ethylene) glycol monoethyl ether (DEGEE), facilitates the API penetration | Anaesthetic in case of moderate pain | 1 | [62]x |
| Buprenorphine hydrochloride (Bup) | Electrospinning of poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) and a blend of 50/50 W/W of buprenorphine-loaded poly(vinyl alcohol (PVA) and PVP polymer solutions in water, used as a drug carrier for buprenorphine (Bup): (Bup/PVP) and(Bup/PVP/PVA) | Bup-loaded crosslinked nanofibers improve carrier retention and provide a controlled release of Bup | Controlled release | 2 | [63] |
| Fentanyl citrate | Sucrose based MN model are made from a water-soluble matrix, premixed with fentanyl citrate | Dissolving MNs are submerged in a rectangular compartment. The top and the bottom of the compartment represent the SC and the bloodstream, respectively. Once an MN patch is applied to the skin, the needles penetrate the dermis and begin to dissolve. | Controlled release | 2 | [64] |
| Ampicillin sodium | Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/ chitosan (CS) composite nanofibers are fabricated by electrospinning, and then crosslinked through glulataraldehyde (GA) | Crosslinked PVA/CS composite nanofibers have a lower drug release rate and a smaller amount of drug burst release than that of PVA/CS, showing potential as TDD system | Controlled release of drugs | 4 | [65] |
| 5-FU anti-cancer drug | 5-fluorouracil-chitosan-carbon quantum dot-aptamer (5-FU-CS-CQD-Apt) nanoparticle is synthesized owing to W/O emulsification method | 5-FU-CS-CQD-Apt shows a pH-sensitive and sustained drug release profile | Release of the drug in a controlled manner | 4 | [66] |
| Piroxicam | Nanoprecipitation technique is used for preparation of drug loaded Eudragit S100 (ES100)/NPs. | ES100 as a nanocarrier for transdermal delivery of Piroxicam | pH-sensitive permeation | 3 | [67] |
| Celecoxib (CXB) | CXB niosomes by thin film hydration method | The release of CXB from different niosomal gel formulations (Span 60 or Span 40 and cholesterol) depends on the viscosity of the prepared gels | Anti-inflammatory activity of the drug from niosomal gel formulations | 1,6 | [68] |
| Jurisdiction | Documents Count |
|---|---|
| United States | 3,002 |
| China | 793 |
| European Patents | 608 |
| Canada | 268 |
| Korea, Republic of | 222 |
| Australia | 207 |
| Japan | 90 |
| Mexico | 84 |
| Taiwan | 68 |
| United Kingdom | 37 |
| CPC | % |
|---|---|
| A61K9/0014 | 10.6 |
| A61K9/7061 | 8.2 |
| A61P29/00 | 6.0 |
| A61M37/0015 | 5.8 |
| A61K9/7084 | 5.8 |
| A61P35/00 | 5.4 |
| A61K47/10 | 5.3 |
| A61K45/06 | 4.9 |
| A61P43/00 | 4.7 |
| A61P25/00 | 4.5 |
| Application Number | Application Date | Title | Owners | Rif |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US 10 303 851 B2 | 14/03/2014 | Physician-centric health care delivery platform | HANA PATENT TECHNOLOGY LLC | [75] |
| US 8 523 791 B2 | 11/08/2009 | Multi-modal drug delivery system | CAREWEAR CORP | [76] |
| US 9 375 529 B2 | 02/09/2009 | Extended use medical device | BECTON DICKINSON AND COMPANY | [77] |
| US 8 372 040 B2 | 24/05/2006 | Portable drug delivery device including a detachable and replaceble administration or dosing element | CHRONO THERAPEUTICS INC | [78] |
| US 8 617 071 B2 | 31/10/2006 | Analyte monitoring device and methods of use | ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC | [69] |
| US 8 252 321 B2 | 31/10/2007 | Biosynchronous transdermal drug delivery for longevity, anti-aging, fatigue management, obesity, weight loss, weight management, delivery of nutraceuticals, and the treatment of hyperglycemia, alzheimer’s disease, sleep disorders, parkinson’s disease, aids, epilepsy, attention deficit disorder, nicotine addiction, cancer, headache and pain control, asthma, angina, hypertension, depression, cold, flu and the like | CHRONO THERAPEUTICS INC | [79] |
| US 7 658 728 B2 | 10/01/2006 | Microneedle array, patch, and applicator for transdermal drug delivery | YUZHAKOV VADIM V | [80] |
| US 9 186 372 B2 | 21/05/2013 | Split dose administration | MODERNA THERAPEUTICS | [81] |
| WO 2004/060436 A2 | 04/12/2003 | Skin attachament apparatus and method for patient infusion device | INSULET CORP | [82] |
| US 7 206 632 B2 | 30/01/2004 | Patient sensory response evaluation for neuromodulation efficacy rating | MEDTRONIC INC | [83] |
| Application Number | Application Date | Title | Owners | Note on TDD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US 7 871 607 B2 | 23/02/2005 | Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases | HALOZYME INC | Novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture and administration (including TDD) that can be applied to enhance the bioavailability (and potentially improve other pharmacokinetic and / or pharmacodynamic properties) of pharmacologic and other agents that are useful for treating or diagnosing various disease conditions | [84] |
| WO 2004/39826 A1 | 26/10/2002 | Anti-il-6 antibodies, compositions, methods and uses | CENTOCOR INC | Transdermal administration of anti-IL-6 antibody encapsulated in a delivery device such as a liposome or polymeric nanoparticles, microparticle, microcapsule, or microspheres (referred to collectively as microparticles unless otherwise stated) | [85] |
| US 11 154 559 B2 | 28/09/2012 | Methods and compositions of bile acids | GEN HOSPITAL CORP | A carrier that protects the composition against rapid release, such as a controlled release formulation, including implants, transdermal patches, and microencapsulated delivery systems | [86] |
| WO 2004/002417 A2 | 27/06/2003 | Mammalian CH1 deleted mimetibodies, compositions, methods and uses | CENTOCOR INC | CH1-deleted mimetibody or specified portion or variant in either the stable or preserved formulations or solutions described, can be administered via a variety of delivery methods including TDD | [87] |
| US 7 985 424 B2 | 21/12/2005 | Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality | DENDRITIC NANOTECHNOLOGIES INC | Dendritic polymers can have utility in many application (in vivo diagnostic imaging, drug delivery, drug discovery, in vitro diagnostics, coatings for medical devices, anti-biofouling coatings, TDD, chemotherapies, NIR absorbers, magnetic bioreactor, etc. | [88] |
| WO 2005/032460 A2 | 03/09/2004 | Human epo mimetic hinge core mimetibodies, compositions, methods and uses | CENTOCOR INC | Mammalian EPO mimetic hinge core mimetibodies that can be used by contacting or administering by at least one mode comprising TDD | [89] |
| WO 2004/037225 A2 | 24/10/2003 | Cosmetic and pharmaceutical foam | FOAMIX LTD | Alcohol-free, pharmaceutical foam carrier and its use | [90] |
| US 7 591 806 B2 | 18/05/2005 | High-aspect-ratio microdevices and methods for transdermal delivery and sampling of active substances | XU BAI | High-aspect-ratio microdevices (including microneedles) and the method of making and using the same, for TDD | [91] |
| WO 01/95935 A1 | 22/01/2001 | Immunostimulatory nucleic acids for inducing a th2 immune response | OTTAWA HEALTH RESEARCH INST | The compounds can be administered to the skin, e.g., topically in the form of a skin cream, by injection, or any other method of administration where access to the skin cells and/or target APCs by the compounds is obtained | [92] |
| US 8 372 040 B2 | 22/01/2001 | Portable drug delivery device including a detachable and replaceable administration or dosing element | CHRONO THERAPEUTICS INC | A device for TDD and administration of differing dosages at specific times of the day automatically pursuant to a pre-programmed dosage profile | [78] |
| Application Number |
Application Date |
Title | Owners | Note | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US 7 871 607 B2 | 23/02/2005 | Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases | HALOZYME INC | Novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture and administration (including TDD) that can be applied to enhance the bioavailability (and potentially improve other pharmacokinetic and / or pharmacodynamic properties) of pharmacologic and other agents that are useful for treating or diagnosing various disease conditions | [84] |
| US 7 985 424 B2 | 21/12/2005 | Dendritic polymers with enhanced amplification and interior functionality | DENDRITIC NANOTECHNOLOGIES INC | Dendritic polymers can have utility in many application (in vivo diagnostic imaging, drug delivery, drug discovery, in vitro diagnostics, coatings for medical devices, anti-biofouling coatings, TDD, chemotherapies, NIR absorbers, magnetic bioreactor, etc. | [88] |
| WO2012118562A1 | 02/03/2012 | Compositions and methods for treating depression, adhd and other central nervous system disorders employing novel bupropion compounds, and methods for production and use of novel bupropion compounds and formulations | RHINE PHARMACEUTICALS LLC | Compositions and methods are disclosed using a purified (R)(-) enantiomer of bupropion (including prodrug) to treat central nervous system disorders | [93] |
| WO 2004/037225 A2 | 24/10/2003 | cosmetic and pharmaceutical foam | FOAMIX LTD | Alcohol-free, pharmaceutical foam carrier and its use | [90] |
| US 8 523 791 B2 | 11/08/2009 | Multi-modal drug delivery system | CAREWEAR CORP | A device for the transdermal delivery of a therapeutic agent at a treatment site comprising a mechanical vibration element, a light source, and a heating and/or cooling element | [76] |
| WO 01/95935 A1 | 22/01/2001 | Immunostimulatory nucleic acids for inducing a th2 immune response | OTTAWA HEALTH RESEARCH INST | The compounds can be administered to the skin, e.g., topically in the form of a skin cream, by injection, or any other method of administration where access to the skin cells and/or target APCs by the compounds is obtained | [92] |
| US 10 369 204 B2 | 02/10/2009 | Molecular vaccines for infectious disease | AGILENT TECHNOLOGIES INC | Methods for construction of pharmamers, i.e., vaccine components characterized by their multimerization domain and the attached biologically active molecules, and their use in preparation of vaccines that contains the pharmamers alone or in combination with other molecules | [94] |
| WO 2005/018530 A2 | 20/08/2004 | Penetrating pharmaceutical foam | FOAMIX LTD | Alcohol-free cosmetic or pharmaceutical foam composition comprising water, a hydrophobic solvent, a surface-active agent, a gelling agent, an active component selected from the group of urea, hydroxy acid and a therapeutic enhancer and a propellant. The foam further comprises active agents and excipients with therapeutic properties having enhanced skin penetration | [95] |
| US 8 668 937 B2 | 17/03/2012 | Topical nitric oxide systems and methods of use thereof | TRANSDERMAL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC | Compositions for delivery of nitric oxide, transdermally and/or to a mucosal surface | [96] |
| US 2017 / 0232115 A1 | 12/10/2012 | Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof | SANDIA CORP | The protocells enhance SC permeability and enable transdermal delivery of active ingredients including macromolecules | [97] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





