1. Introduction
Calcretes are near-surface terrestrial calcium carbonate deposits [
1]. They develop as dust, semi consolidated aragonite or calcite and secondary calcium carbonate formations in loose material such as gravel, sand, silt and soil [
2]. There is no soil called calcrete, but they exist within soil profiles. Calcretes are generally considered indicative of arid and/or semi-arid climates [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7].
Calcretes may include uranium, thorium and vanadium elements and magnesite, sepiolite, dolomite and huntite minerals [
8].
The calcretes provide important clues about the environmental conditions of the older sediments [
9,
10,
11,
12]. The younger calcretes are used to obtain data for the climate changes and active tectonism of an area [
13,
14].
Geochemical data obtained from calcretes, may provide paleo-climatic signs on a regional scale as well as records of rainy and dry periods on a local and regional scale [
15,
16]. It has been stated that there is an enrichment of Ca, Mg and Si oxides in the soil during evaporation periods and a depletion during rainy periods. Additionally, the reddish to yellowish brown coloration, high calcification in paleosols and the preservation of rhizoliths and lime nodules were interpreted as being formed under arid to semi-arid climatic conditions. [
1,
14,
65]. Therefore, it is possible to reveal the paleo-tectonic history of an area by defining the stratigraphic position and characteristics (cyclicity characters) of calcretes sequences controlled by active tectonic [
15].
Calcretes and related sediments have been studied on many regions in Turkey to elucidate the tectonic and paleoclimatic history of a region [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30]. Geochemical and isotopic data obtained from calcretes studied in Turkey and other countries have been used in revealing meteoric environmental conditions on a local/regional scale. These data especially may give important clues about the geochemical properties of surface-groundwater and surrounding rocks in the region.
Konya Fault Zone consists of several normal dip-slip faults passing through the Konya settlement and has the potential of producing an earthquake having a magnitude of 6. Many calcretes formations developed in different fault steps within the fault zone are observed. Dating data obtained from the faults of the Konya Fault Zone may give important clues about the paleo-seismic history of the region and the evolution of the Konya Closed Basin. Therefore, when performing calcrete sampling, care was taken to collect samples from places related to fault lines and where the relative ages of the faults could be determined.
The dating results obtained by the Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) method are stratigraphically compatible. Therefore, this dating method can be used confidently for highly contaminated calcrete sediments [
30,
31,
34].
2. Geological Setting
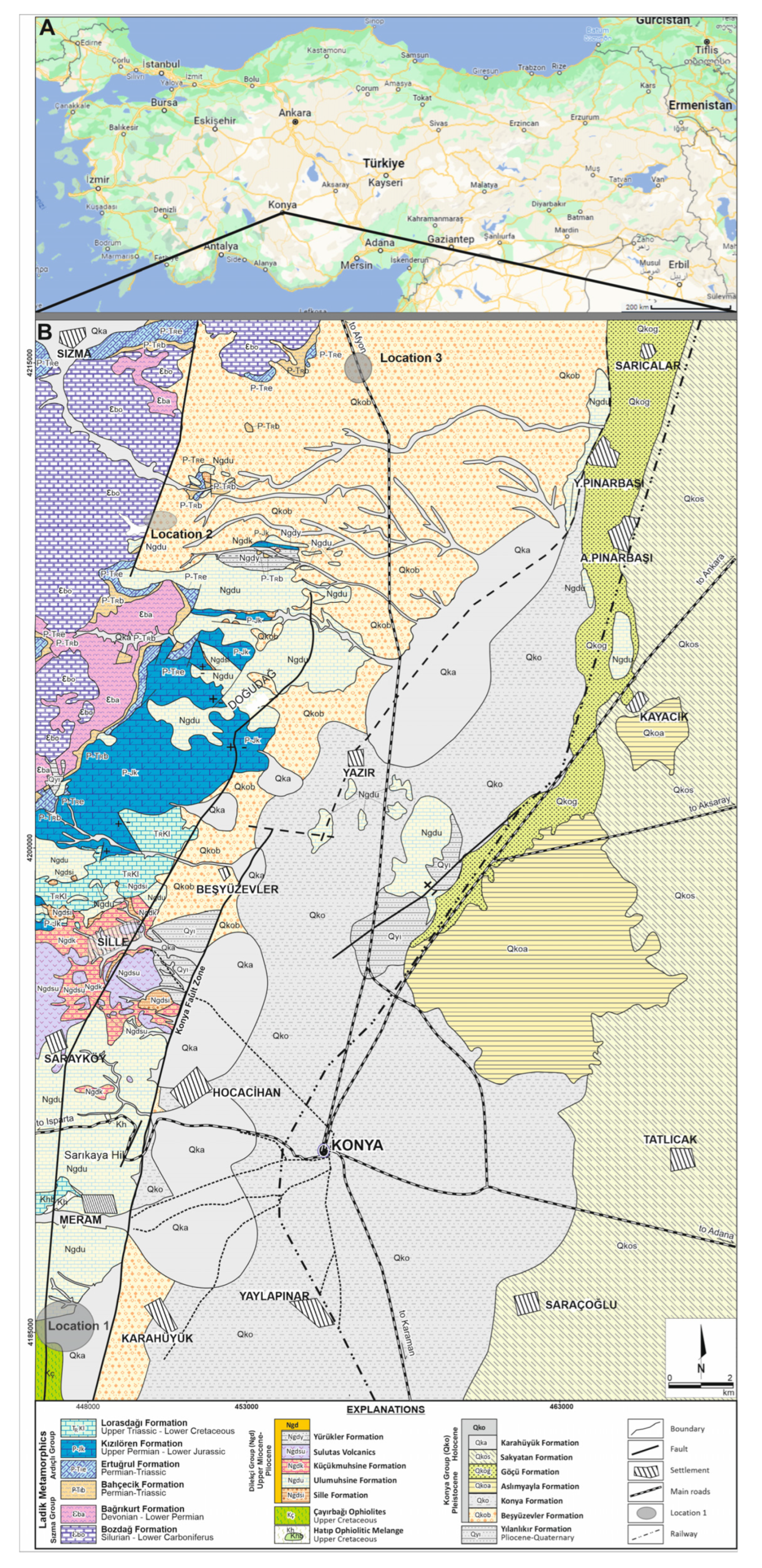
In the Konya region located within the Taurids tectonic union at the northern foothills of the Central Taurus Mountains [
35], units ranging from Silurian-early Carboniferous to Present in age crop out. The oldest unit is the Bozdağ formation which comprises marbles dating from Silurian to early Carboniferous. Bağrıkurt formation consisting of meta-clastic rocks conformably overlies the Bozdağ formation. Permian-early Cretaceous aged Ardıçlı group [
36,
37] conformably overlies metamorphic rocks. In Konya region, Late Cretaceous aged Hatip Ophiolite mélange and Çayırbağı ophiolite overlie the Ardıçlı group with tectonic contact. Hundreds of meter thick Neogene İnsuyu formation, which is characterized by lacustrine mudstone, clayey limestone and limestone, unconformably overlie the Paleozoic and Mesozoic aged rocks In the study area, Neogene volcanic rocks (Dacite-Andesite and volcanoclastic) [
36] cut all rocks with a hot contact (
Figure 1). Quaternary sediments (Konya group) [
32] comprising alluvial fan deposits and young lacustrine sediments cover all old rocks with an angular unconformity. Calcretes generally occur in the red colored pebble-sand-mud type terrestrial sediments (Karahüyük formation). The Karahüyük formation is Quaternary in age and constitutes the upper sedimentary unit of the Konya Group. Karahüyük formation consists of red-burgundy colored mud-supported lenticular conglomerate, pebbly sandstone, sandstone and mudstone, which were deposited in medial-distal fan environments. The thickness of the formation, which is controlled by the active tectonism in the region, varies between 5 to 25 meters [
38].
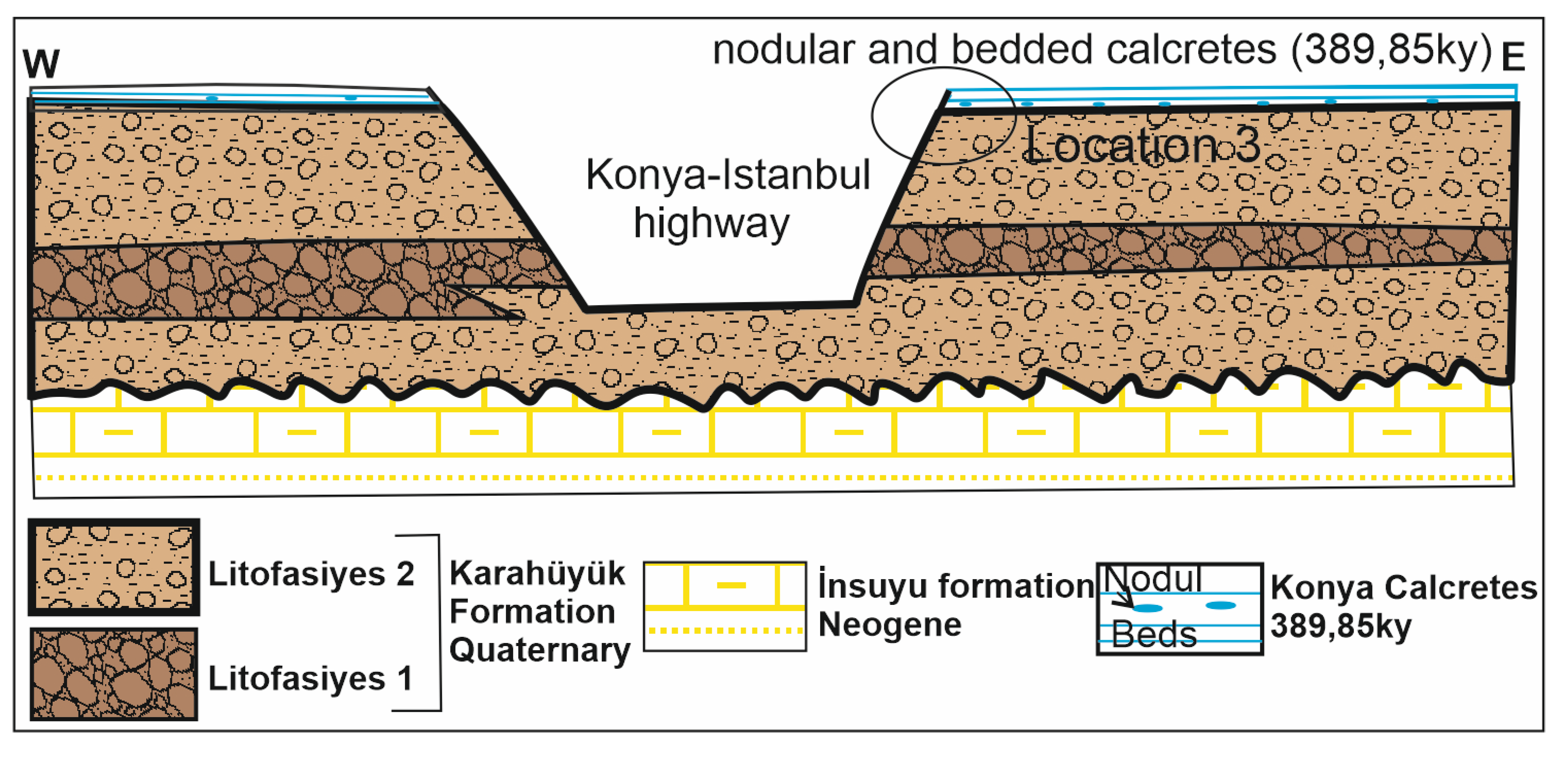
Four different litofacies have been identified in the Karahüyük Formation at the study area. These are;
Ungraded, clast-supported conglomerate facies: This facies comprises poorly sorted, clast supported, granule-boulder conglomerate. A muddy sand matrix surrounds the clasts supported framework. Gravels were mainly derived from ophiolitic rocks. Deposits of this facies are unstratified and lack clast imbrication. This facies grades vertically and laterally into pebbly-sandy mudstone facies. It is product of active tectonic periods. Gravel coating calcrete deposited by the water circulating through the gravels
Pebbly-sandy mud facies: This facies is composed of unbedded red mudstone bearing dispersed well rounded ophiolitic pebbles and sand grains. It grades conformably into gravelly facies below and muddy facies above. It represents deposition in a middle fan during a nonseicmic period. Calcretes in this facies are nodular and gravel coating forms.
Red mudstone facies: This facies is characterized by red colored mudstone with very little gravel and sand. It has conformable boundary with the underlying sandy mud facies and erosional boundary with the overlying mud supported boulder conglomerate. Both nodular and powdery calcrete are present in this facies.
Angular pebbly sandy mudstone facies: This facies is composed of mud including angular ophiolite and limestone block. It is poorly stratified and poorly graded. Having angular blocks points that the sediments of this facies were derived from nearby. It represents relatively active tectonic period.
The deposition of this thick alluvial fan sediments were controlled by tectonic activities of the faults in the area. Having an erosional basal boundaries indicate dense erosion and transportation. Litofacies-1 is interpreted as deposit of middle fan, litofacies-2 and 3 as deposits of distal fan.
Figure 1.
A. Map of Turkey showing the location of Konya; B. Geological map of the study area (modified from) [
38].
Figure 1.
A. Map of Turkey showing the location of Konya; B. Geological map of the study area (modified from) [
38].
3. Materials and Methods
Calcretes were classified based on their micromorphological and chemical characteristics [
1,
2].
The stratigraphic positions and geological features of the calcretes, which are intensely observed in active fault zones and in their close vicinity, were determined during the field studies. In order to elucidate the ages, geochemical properties and evolution of the calcretes, four sections from different localities were measured and 40 samples were collected. Samples were subjected to C and O stable isotope analysis, geochemical analysis, thin section studies and ESR (electron spin resonance) dating.
Since the collected samples were loosely packed, 30 samples were hardened by using polyester and hardening chemicals, then thin sections were prepared from these materials.
Major oxides and trace element, including REEs, contents of 20 samples were obtained by means of Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission Spectrometry (ICP-ES; major elements) and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) by using about 0.2 g of powdered samples at the Acme Analytical Laboratory (Vancouver, Canada). Samples first subjected to lithium borate fusion, then, precision and accuracy were checked by parallel analysis of international reference standards. The minimum detection limit for major and minor elements is 0.01% while for trace element is 0.01 to 1 ppm.
The XRD and SEM analysis of the samples were conducted at ILTEK laboratory in Selçuk University in Turkey.
Carbonate-rich samples were dated by Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) dating method which is based on measurements of the number of paramagnetic centers produced by natural radiation in a material [
39,
40,
41]. Equivalent doses (DE) representing the accumulated natural radiation doses were obtained by means of the additive dose method. Annual dose rates (D) were determined using the natural radioactive element (238U, 232Th, 40K) concentrations, cosmic dose rate contribution, grain sizes of powders, and moisture effect. ESR ages of calcrete samples were calculated taking into account of uranium uptake history of shells using ROSY program [
42]. ESR spectra of the samples were recorded at room temperature by JEOL JESFa-300 X-band ESR spectrometer located at Selçuk University Advanced Technology Research & Application Center, Turkey. The isotopic (δ
18O and δ
13C) analysis of the 18 samples of section A was carried out in by UC Davis Stable Isotope Laboratories of California University, USA by means of MAT 251 Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer.
4. Results
4.1. Konya Calcretes (217.47-389,85 ky)
4.1.1. Description
Calcrete occurrences within and on the Quaternary sediments (Karahüyük formation) in the Konya region were described in detail for the first time in this study (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). In the study area, calcrete deposits in rocks ranging from Neogene to the present at different locations in the study area are closely related to and concentrated around faults. Sampling was realized at three different locations in the Konya fault zone (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). Special care was taken to collect samples from the same fault zone.
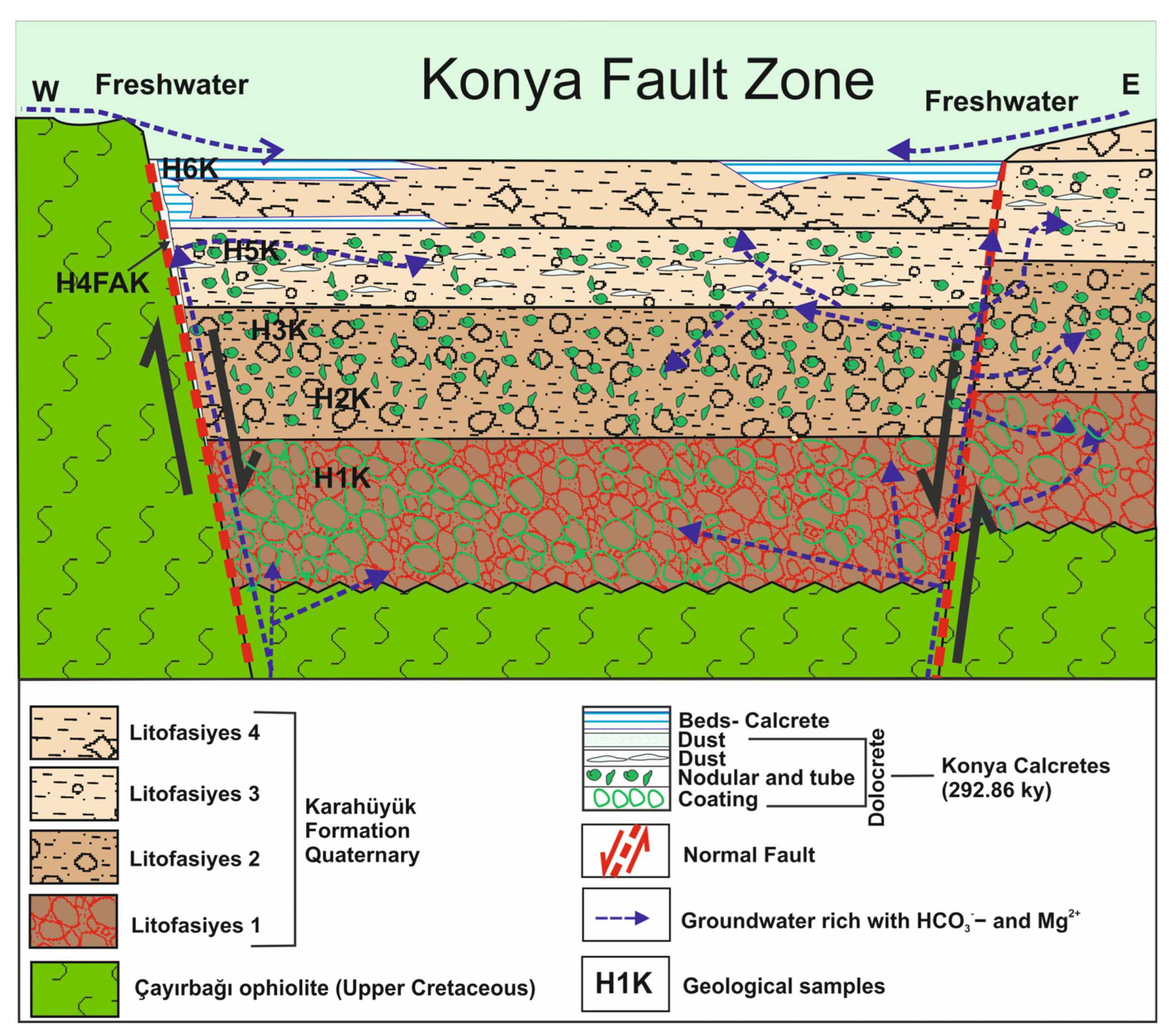
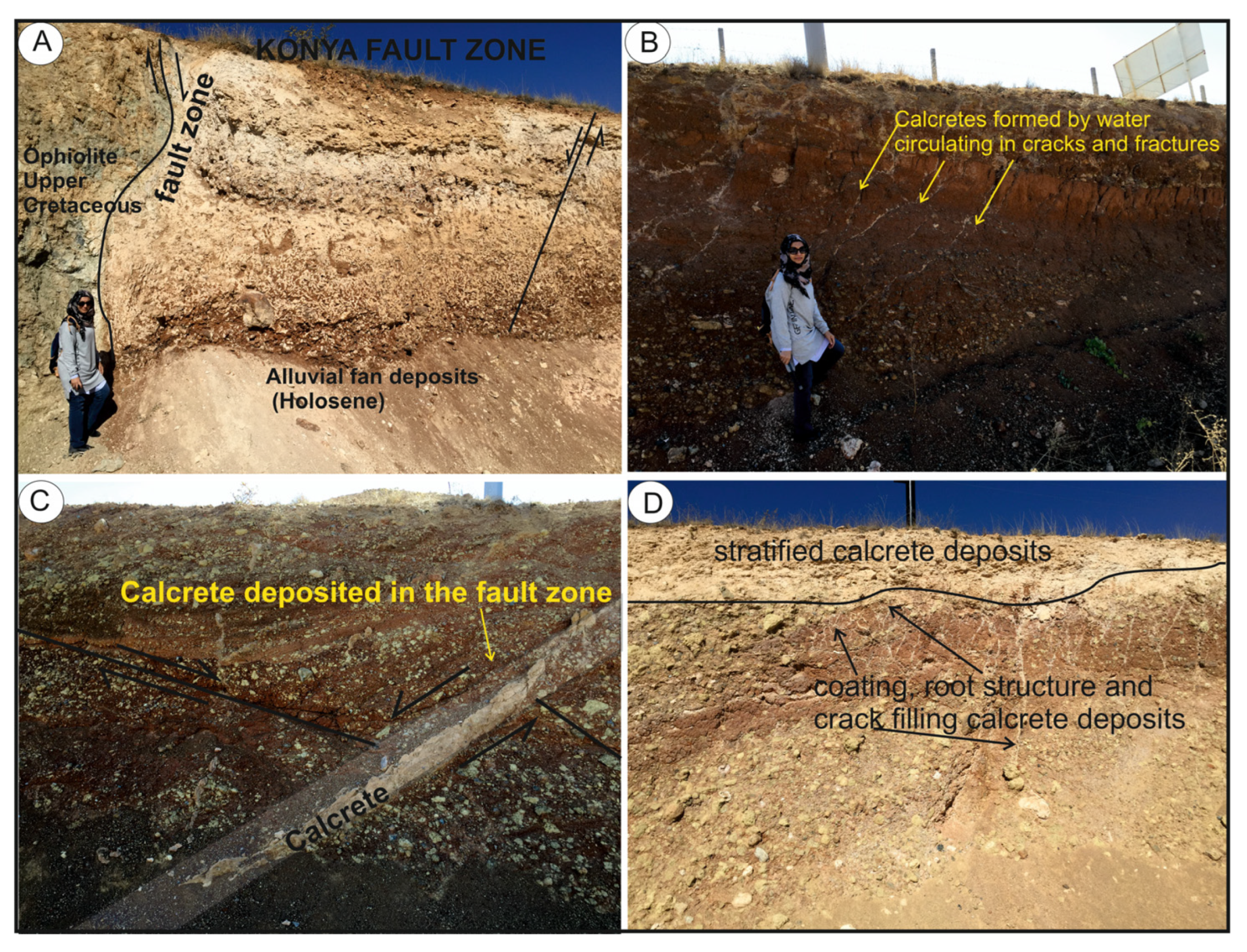
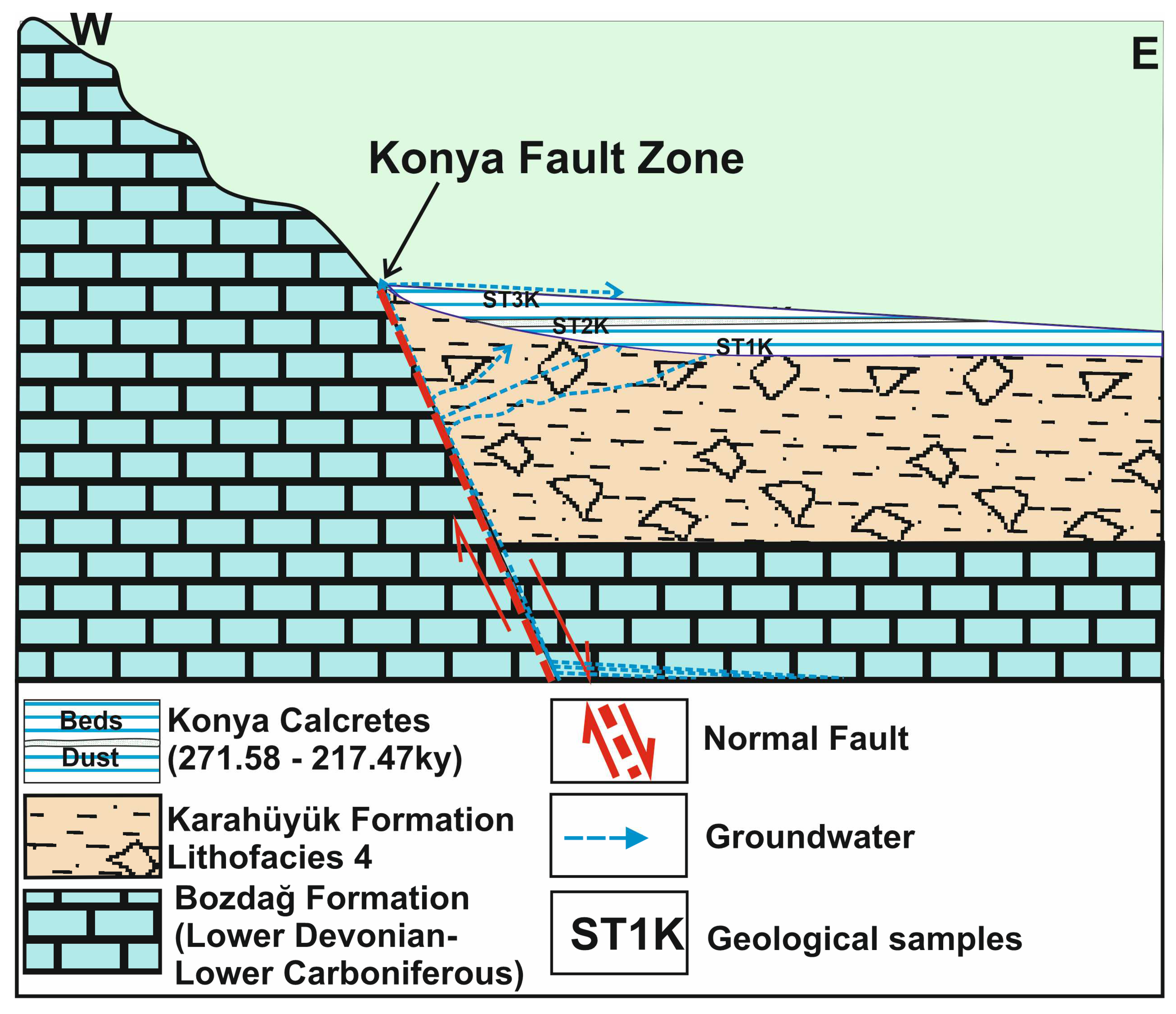
Location 1: Quaternary red alluvial fan deposits unconformably overlying the ophiolitic rocks crop out on a road cut of the Konya-Seydişehir highway. At this location, the first step of the dip-slip normal fault forming the Konya graben is present. The dip-slip fault brings together (
Figure 3) the Late Cretaceous Çayırbağı ophiolite and Holocene aged alluvial fan deposits.
The calcretes and dolocretes were developed both on the fault plane and within the mud supported alluvial fan deposits in the hanging block at this location (
Figure 3). Five different calcrete and dolocretes levels were observed in the outcrop, which is approximately 6 m thick (
Figure 3 and 4A); these are from the bottom up;
- 5.
- 6.
inclined tube-shaped nodular calcretes developed obliquely to the surface in gravelly-sandy mud (
Figure 4B).
- 7.
nodular and powdery calcretes and dolocretes within mud.
- 8.
- 9.
thick bedded calcretes in muddy level near the surface (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4C).,
Pebble coating type of dolocretes are generally common in Litofacies-1. Shallow groundwater circulating among pebble causes the calcrete formation in the form of coatings on pebbles. Nodular dolocretes occur mainly in the lithofacies-2 and 3. Powdery calcretes were common in lithofacies 3. Almost all of the nodular and powdery dolocretes were deposited in fine-grained clastic sediments. Layered calcretes were observed at two different levels within lithofacies-4 (
Figure 1). Powdery calcrete was also identified at the level between these layered calcretes. Layered calcretes including pebble and blocks are interpreted as being deposited as a result of rapid evaporation of carbonate-rich surface waters under atmospheric conditions.
The thickness of the five different types of calcrete and dolocretes decreases with distance from the fault. The upward movement of groundwater along the systematically formed cracks resulted in the formation of veins dolocretes in the cracks and layered calcretes at the surface (
Figure 4B–D).
Pisolitic structures were often observed in thin sections of calcretes (sections were made by means of polyester) and SEM analyzes (
Figure 5). At this location, dolocrete formations were determined in a 4-5 m thick section from the base (
Figure 5 A–F), and calcretes formations were present only at the uppermost layered section. Dolocretes are represented by disc-shaped dolomite minerals stacked on top of each other (
Figure 5A–D).
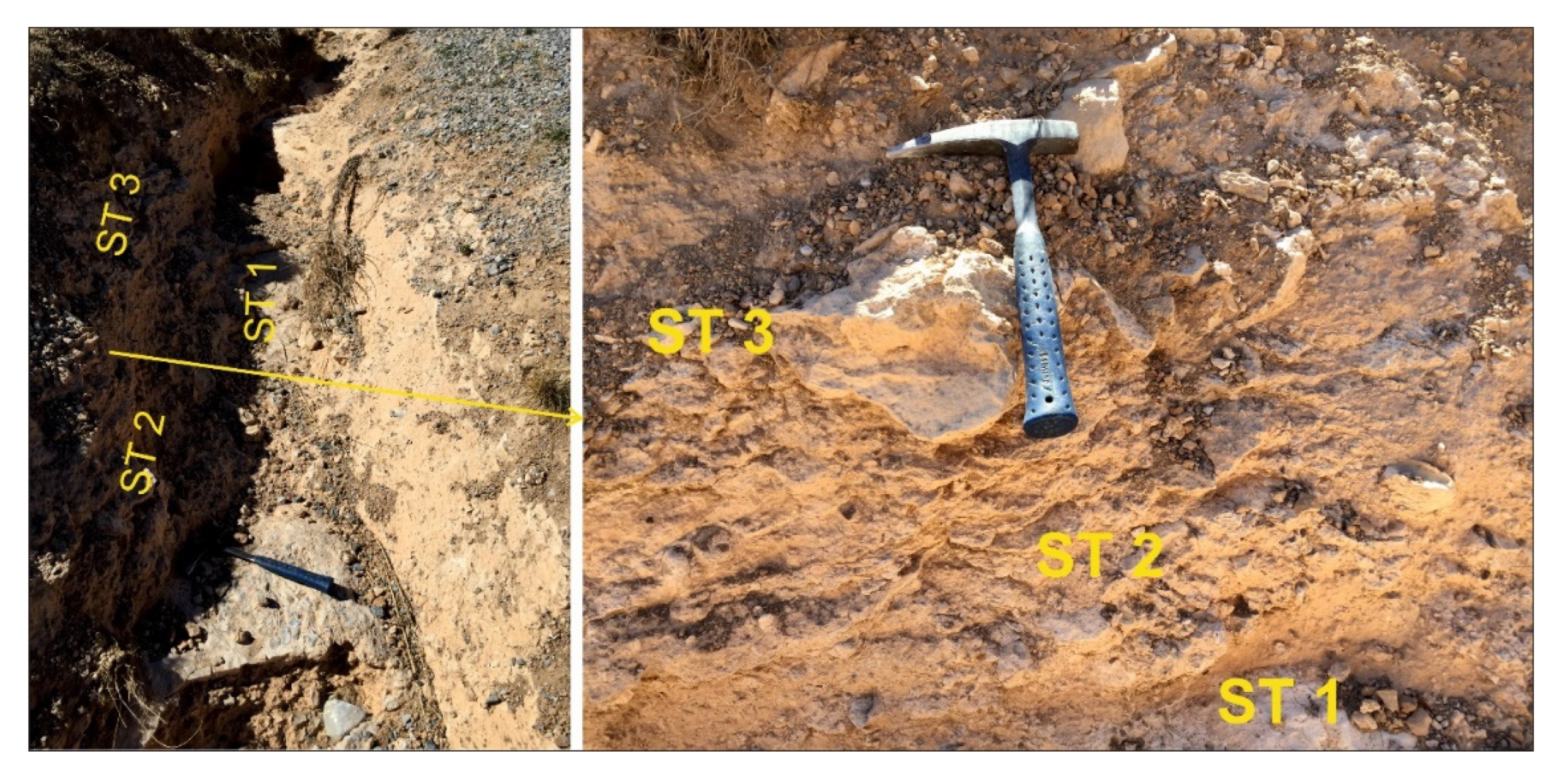
Location 2: In this location at just North of the Selçuk University campus, calcretes were deposited close to the first faults forming KCB as in the location 1. Alluvial fan deposits (Karahüyük formation) lay on Neogene aged lacustrine carbonate rocks overlying the Paleozoic marble with an angular unconformity. The dip-slip fault to the north brings young alluvial deposits and Paleozoic aged marbles side by side. At this site, the Karahüyük formation was deposited close to the fault line under the fault activities and, comprises Lithofacies-4 (Angular pebbly, sandy mud lithofacies) In relation to this fault, layered, and powdery calcretes depositions took place in a 1 m thick zone inclined towards the basin. Calcretes are quite hard and robust in this area and, is observed together with clastic sediments (
Figure 6 and
Figure 7). There are plenty of silt and sand-sized sediments in the calcretes. In the thin section, beside the oolitic and pisolitic grains, pellets were also observed. Stromatolitic structures contributing to caliche precipitation are present around the calcite crystals (
Figure 5 G–H). Calcrete formations in the region occur generally as layered calcretes in areas close to the faults, and as iron-coated nodules within the soil away from the faults.
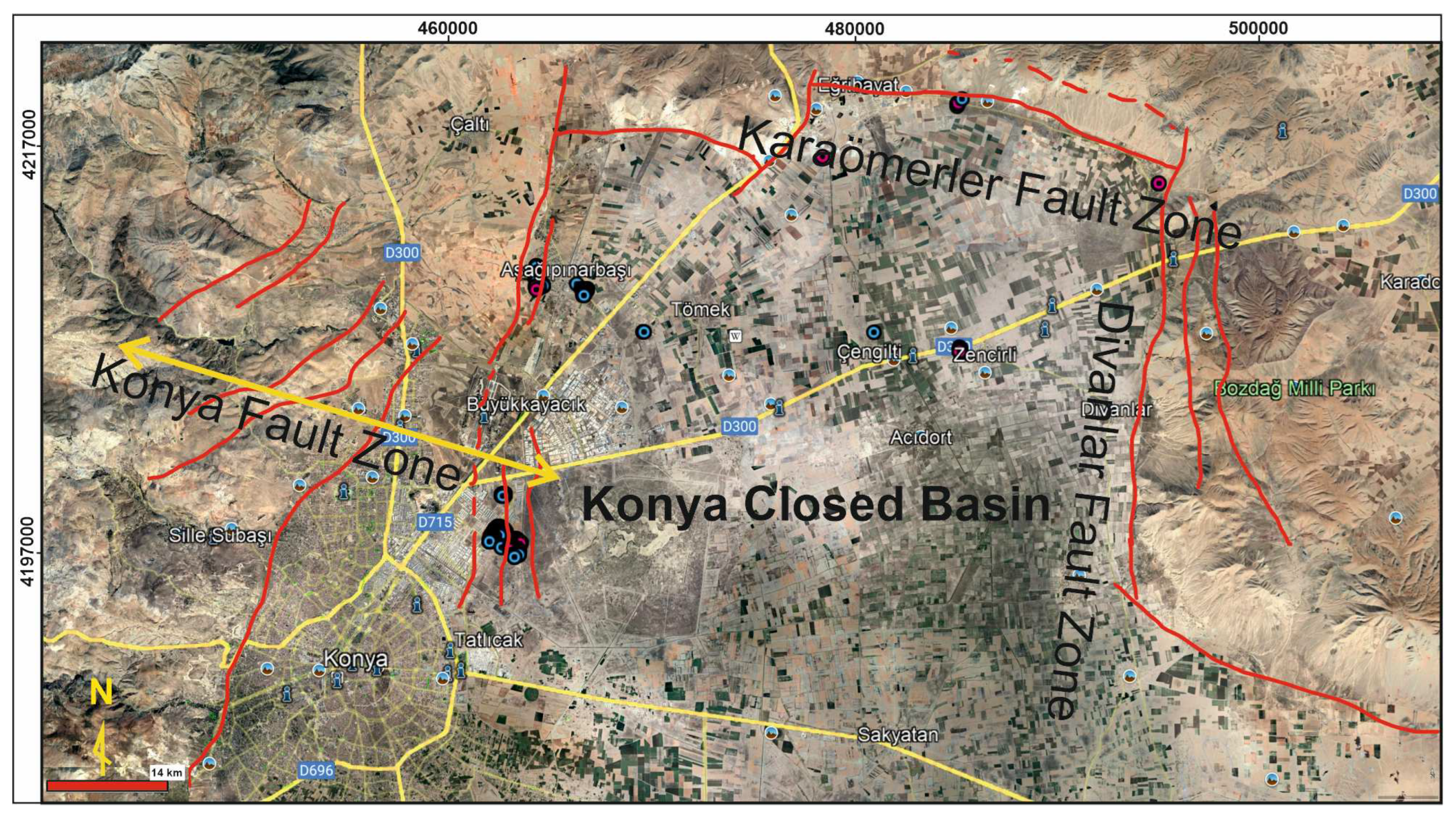
Figure 2.
Active fault systems forming Konya closed basin (Konya fault zone in the west, Karaömerler fault zone in the north and Divanlar fault zone in the east.).
Figure 2.
Active fault systems forming Konya closed basin (Konya fault zone in the west, Karaömerler fault zone in the north and Divanlar fault zone in the east.).
Figure 3.
Geological section of Locaton-1 and calcrete and dolocrete formation model.
Figure 3.
Geological section of Locaton-1 and calcrete and dolocrete formation model.
Figure 4.
Field photos from Location-1. A. Calcretes-and dolocretes deposits at different levels on the oldest fault plane in the Konya fault zone and alluvial fan deposits; B, C and D. Dolocretes precipitated into cracks and fractures, coating and root structure; stratified calcrete deposits.
Figure 4.
Field photos from Location-1. A. Calcretes-and dolocretes deposits at different levels on the oldest fault plane in the Konya fault zone and alluvial fan deposits; B, C and D. Dolocretes precipitated into cracks and fractures, coating and root structure; stratified calcrete deposits.
Figure 5.
A-F; thin section and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) photographs of calcrete samples from H2, H4, H6 at Location 1) and A-D; dolomite minerals observed in H2 and H4 pisolitic calcrete (thin-section and SEM images). E and F; H6 pisolitic calcrete, G and H; SEM image of clay minerals (palygorskite), ST1 (Location 2) clay minerals (palygorskite), algae filaments and calcite minerals (H2…H6 and ST 1 geological sample codes).
Figure 5.
A-F; thin section and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) photographs of calcrete samples from H2, H4, H6 at Location 1) and A-D; dolomite minerals observed in H2 and H4 pisolitic calcrete (thin-section and SEM images). E and F; H6 pisolitic calcrete, G and H; SEM image of clay minerals (palygorskite), ST1 (Location 2) clay minerals (palygorskite), algae filaments and calcite minerals (H2…H6 and ST 1 geological sample codes).
Figure 6.
Geological cross section of Location 2 and model for the formation of calcrete, (ST1K: sample code).
Figure 6.
Geological cross section of Location 2 and model for the formation of calcrete, (ST1K: sample code).
Figure 7.
Field photos from location 2. Calcretes developed at different levels within alluvial fan deposits (ST1....3 geological sample codes).
Figure 7.
Field photos from location 2. Calcretes developed at different levels within alluvial fan deposits (ST1....3 geological sample codes).
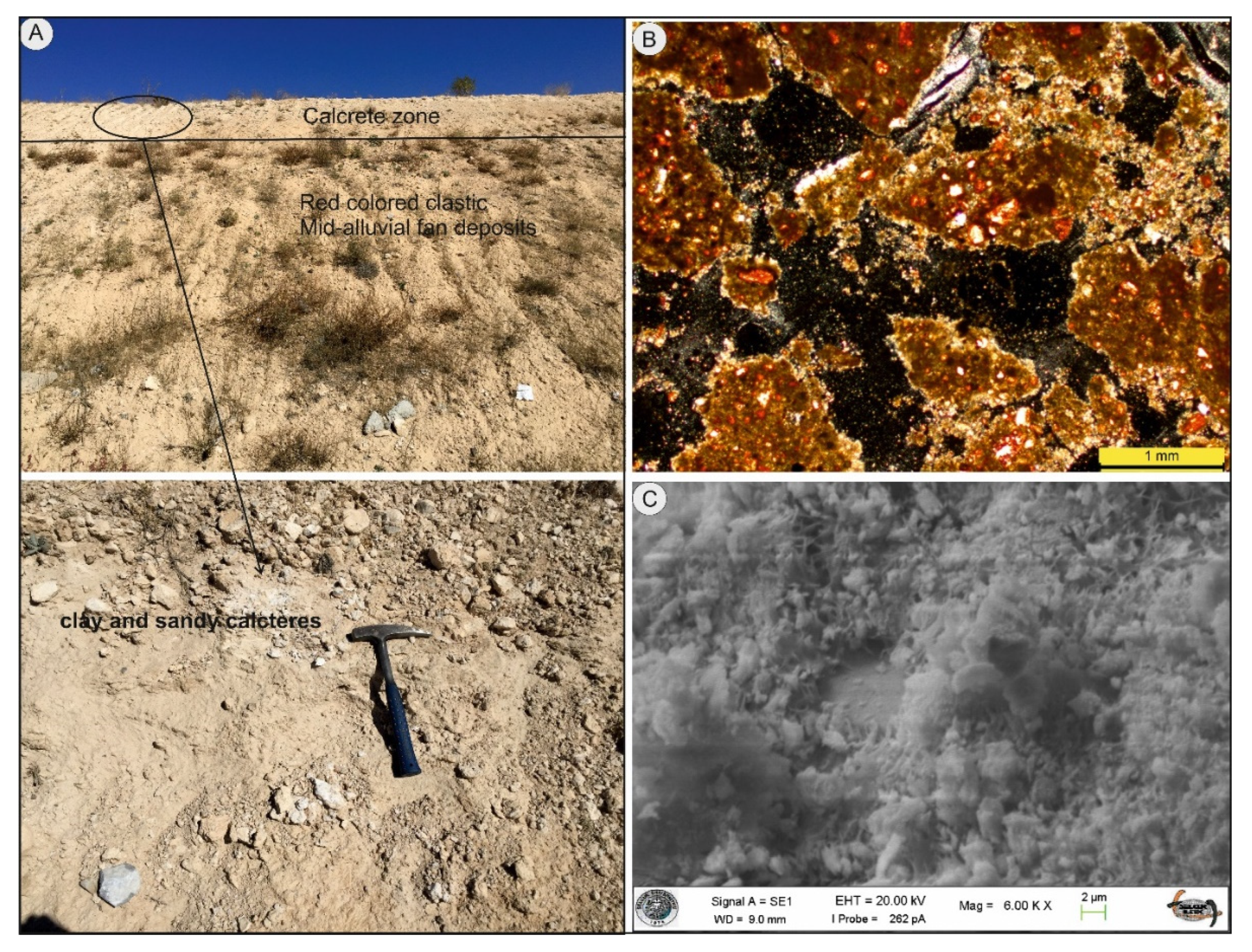
Location 3: This location, which is on the road cut of the Konya-Istanbul highway, is located in the rising block of the dip-slip fault. Calcretes were deposited as nodules and beds in and on the intermediate alluvial fan deposits of the Karahüyük formation overlying the Insuyu formation (
Figure 8). At location-3 , Karahüyük formation is mainly represented by Litofacies-1 and 2. Calcretes are only present in the upper 96 cm part of 15 m thick road cut (
Figure 9A). Silt, sand and fine gravel grains are observed in layered calcretes (
Figure 9A,B).
4.1.2. Sedimentary Structure of Calcretes
The carbonate-rich waters discharging from the fault surface into the alluvial fan and paleosol deposits (Karahüyük formation) caused the precipitation of the calcretes in the form of dust, nodules, root structure (rhizoliths), tubes, beds and fracture and crack infillings. The calcretes are mostly observed as pisolites and tubes. Both stratified and pisolithic forms are found only in calcretes at location 2. Calcretes are occasionally observed as crust rich in Fe+2 around the pebbles (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4-b).
4.1.3. Mineralogy and Petrography
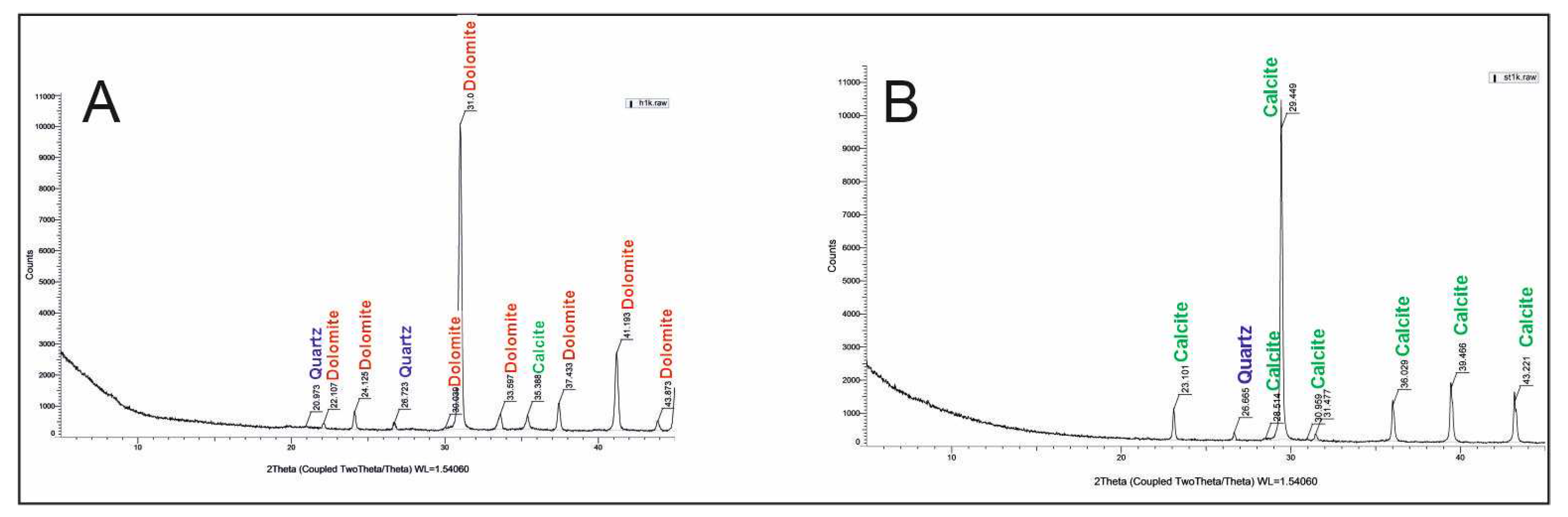
XRD, SEM and thin section studies were carried out to determine mineralogical properties. Dolomites were observed in the calcretes generally associated with ophiolite-rich rocks in and around the study area. Dolomite was not observed in calcretes associated with dolomitic limestone and limestone. Calcite, dolomite, quartz, smectite and palygorskite minerals were encountered in the calcretes. While some levels are rich in carbonate, in the same outcrop, the calcretes also contain clay and quartz minerals. Layered calcrete is observed especially in those associated with faults. Although calcretes have a layered and massive appearance, oolitic and pisolitic formations were also generally observed during petrographic studies. Calcite and dolomite minerals are clear under SEM and XRD (Figures 4,5,9 and 10). Bacterial filaments accompanying carbonate minerals are also present (Figures 5f and 9c).
Figure 10.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) diffractogram of calcretes, A. location 1. H1: dolocrete; B. location 2. ST1: calcrete.
Figure 10.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) diffractogram of calcretes, A. location 1. H1: dolocrete; B. location 2. ST1: calcrete.
4.1.4. Geochemistry
The results of chemical analyzes of calcrete samples are given in
Table 1. The MgCO
3 ratio of the calcrete in the location-1 varies between 16.67 and 43.94%. The CaO ratio is between 8.44% and 37.13%. EDX analyzes also support chemical analyzes. At location-1, six levels of calcrete have been observed. Of these level, only calcrete in H6 level is calcitic in composition, others are dominantly dolomitic. The SiO
2 content of calcrete from level H3 is higher than the other levels. At location-2, the MgCO
3 content varies between 0.98-2.07%, CaO content between 45.05-51.26% and SiO
2 content between 3.22-8.24%. There are pronounced differences in MgCO
3, CaO and SiO
2 contents of calcretes in Location-1 and Location-2.
At location-3, the MgCO3 content of the calcrete varies between 8.07% and 9.06%, the CaO content between 34.94% and 40.16% and SiO2 between 14.38-20.59%. Although MgCO3, CaO and SiO2 contents of calcretes at location-3 are similar to those from location-2, there is a distinct difference in MgCO3 and SiO2 contents.
4.1.5. Stable Isotope Geochemistry
Stable isotope ratios of carbon (δ
13C) and oxygen (δ
18O) of calcretes vary from -3.62 to -7.45 and from -3.74to -9.69 respectfully (
Table 2). Stable isotope ratios of carbon (δ
13C) in dolocretes are between -4.02 and -7.45 and stable oxygen isotope (δ
18O) values between -3.74 and -4.78. Stable isotope ratios of carbon (δ
13C) in calcretes are between -3.62 and -7.62 and stable oxygen isotope (δ
18O) values between -3.74 and -9.62 (
Table 2).
Table 1.
Major oxide contents of Konya calcretes based on ICP-MS analysis.
Table 1.
Major oxide contents of Konya calcretes based on ICP-MS analysis.
| |
SiO2
|
Al2O3
|
Fe2O3
|
MgO |
Mg |
MgCO3
|
CaO |
Na2O |
K2O |
TiO2
|
P2O5
|
MnO |
Cr2O3
|
LOI |
| SAMPLES |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
| H1K |
4.08 |
0.56 |
0.9 |
19.73 |
11.90 |
41.27 |
29.57 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
0.03 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
0.053 |
44.9 |
| H1S |
20.12 |
2.85 |
5.29 |
16.2 |
9.77 |
33.88 |
18.61 |
0.05 |
0.21 |
0.13 |
0.01 |
0.1 |
0.339 |
35.8 |
| H2K |
10.37 |
1.53 |
2.54 |
18.67 |
11.26 |
39.05 |
24.81 |
0.02 |
0.07 |
0.07 |
0.01 |
0.03 |
0.15 |
41.5 |
| H2S |
12.35 |
1.85 |
2.83 |
18.07 |
10.90 |
37.79 |
23.59 |
0.04 |
0.13 |
0.08 |
0.03 |
0.05 |
0.154 |
40.6 |
| H3K |
49.17 |
1.04 |
10.09 |
11.94 |
7.20 |
24.97 |
8.44 |
0.01 |
0.07 |
0.04 |
0.04 |
0.07 |
0.354 |
18.4 |
| H3S |
41.59 |
4.24 |
7.45 |
11.65 |
7.03 |
24.37 |
10.32 |
0.11 |
0.35 |
0.19 |
0.05 |
0.11 |
0.376 |
23.2 |
| H4FAK |
5.97 |
0.84 |
0.75 |
20.82 |
12.56 |
43.54 |
27.61 |
0.01 |
0.05 |
0.07 |
0.01 |
0.1 |
0.011 |
43.8 |
| H4FAS |
16.89 |
2.61 |
2.19 |
21.01 |
12.67 |
43.94 |
20.05 |
0.01 |
0.25 |
0.18 |
0.02 |
0.03 |
0.032 |
36.5 |
| H5K |
14.97 |
1.36 |
1.91 |
18.01 |
10.86 |
37.67 |
23.9 |
0.03 |
0.07 |
0.07 |
0.02 |
0.02 |
0.081 |
39.4 |
| H5S |
11.25 |
1.82 |
2.07 |
18.4 |
11.10 |
38.48 |
24.92 |
0.03 |
0.09 |
0.1 |
0.01 |
0.03 |
0.089 |
41 |
| H6K |
13.53 |
1.05 |
1.15 |
7.97 |
4.81 |
16.67 |
37.13 |
0.04 |
0.09 |
0.06 |
0.02 |
0.01 |
0.085 |
38.6 |
| H6S |
15.31 |
1.28 |
1.33 |
8.59 |
5.18 |
17.97 |
34.71 |
0.05 |
0.1 |
0.07 |
0.03 |
0.01 |
0.098 |
38.1 |
| DB1K |
14.38 |
1.69 |
0.81 |
4.33 |
2.61 |
9.06 |
40.16 |
0.1 |
0.22 |
0.12 |
0.03 |
0.01 |
0.003 |
38 |
| DB1S |
20.59 |
3.83 |
1.69 |
3.86 |
2.33 |
8.07 |
34.94 |
0.19 |
0.53 |
0.26 |
0.05 |
0.02 |
0.007 |
33.8 |
| ST1K |
3.22 |
0.93 |
0.47 |
0.47 |
0.28 |
0.98 |
51.26 |
0.04 |
0.13 |
0.05 |
0.06 |
0.01 |
0.003 |
43.3 |
| ST1S |
5.57 |
1.77 |
0.73 |
0.68 |
0.41 |
1.42 |
48.69 |
0.06 |
0.22 |
0.09 |
0.06 |
0.01 |
0.008 |
42 |
| ST2K |
3.64 |
1.06 |
0.44 |
0.49 |
0.30 |
1.02 |
50.71 |
0.05 |
0.14 |
0.06 |
0.05 |
0.01 |
0.003 |
43.3 |
| ST2S |
5.76 |
1.79 |
0.72 |
0.63 |
0.38 |
1.32 |
48.5 |
0.08 |
0.23 |
0.09 |
0.06 |
0.01 |
0.003 |
42.1 |
| ST3K |
4.42 |
1.3 |
0.53 |
0.62 |
0.37 |
1.30 |
50.02 |
0.07 |
0.19 |
0.07 |
0.04 |
0.01 |
0.002 |
42.6 |
| ST3S |
8.74 |
2.55 |
1.11 |
0.99 |
0.60 |
2.07 |
45.5 |
0.11 |
0.38 |
0.14 |
0.06 |
0.02 |
0.005 |
40.3 |
Table 2.
δ13C and δ18O stable isotope ratios of Konya calcretes.
Table 2.
δ13C and δ18O stable isotope ratios of Konya calcretes.
| SAMPLE |
Calcrete Type |
δ13C (VPDB) |
δ18O (VPDB) |
SAMPLE |
Calcrete Type |
δ13C (VPDB) |
δ18O (VPDB) |
| H1S |
Dolocrete |
-5.37 |
-4.78 |
H5K |
Dolocrete |
-4.08 |
-3.74 |
| H2S |
Dolocrete |
-5.08 |
-4.53 |
H6K |
Calcrete |
-6.38 |
-7.28 |
| H3S |
Dolocrete |
-4.99 |
-4.51 |
ST1D |
Calcrete |
-7.32 |
-9.33 |
| H4FAS |
Dolocrete |
-7.45 |
-3.87 |
ST1S |
Calcrete |
-7.02 |
-9.18 |
| H4FAD |
Dolocrete |
-6.20 |
-4.10 |
ST1KD |
Calcrete |
-7.03 |
-9.69 |
| H5S |
Dolocrete |
-4.46 |
-4.07 |
ST1K |
Calcrete |
-6.96 |
-9.43 |
| H6S |
Calcrete |
-6.41 |
-7.62 |
ST2S |
Calcrete |
-6.11 |
-8.66 |
| H1K |
Dolocrete |
-5.03 |
-4.36 |
ST2K |
Calcrete |
-6.28 |
-8.30 |
| H2K |
Dolocrete |
-5.03 |
-4.54 |
ST3K |
Calcrete |
-7.41 |
-9.48 |
| H3K |
Dolocrete |
-4.02 |
-3.91 |
ST3S |
Calcrete |
-7.01 |
-8.53 |
| H4F |
Dolocrete |
-6.08 |
-4.51 |
DB1K |
Calcrete |
-5.74 |
-7.61 |
| H5KD |
Dolocrete |
-4.05 |
-3.74 |
DB1S |
Calcrete |
-3.62 |
-7.12 |
4.1.6. Age of Calcretes by ESR Method
In this study, samples were dated by means of ESR method. The ESR ages of the samples were calculated by using the ESR age equations in the [
33] and by considering the Uranium is in equilibrium. Equivalent dose (DE), annual dose (D) and ESR age (TESR) values of calcrete samples are listed in
Table 3 and
Table 4. Samples starting with code H, S and D were compiled from three different locations and dated. Of these samples, H4FAK were taken from the fault surface.
5. Discussion
Konya fault zone is an important active fault zone that directly threatens the city of Konya and has faults longer than 15 km. There are more than 7 normal fault lines extending along parallel lines within the Konya fault zone, located in the western part of Konya Close Basin. The faults shown in
Figure 2 shape the Konya Closed Basin. Dating these faults will provide data about the history of the basin and the cyclicity of paleo-earthquakes. The faults have not been dated while conducting paleo-seismological analyzes in the region. The seismic history of the region, without knowing the ages of the faults, will be incomplete. Ages and geochemical properties of calcretes provided data for elucidating the tectonic history, paleo-hydrogeological and paleoclimatic features of the region.
In terms of calcrete types and the facies in which they formed in the region, the pebble coating type of calcretes are generally common in the ungraded, clast-supported conglomerate facies (Litofacies-1). Nodular and powdery calcretes were mainly observed in the Pebbly-sandy mud facies (Litofacies 2) and the red mudstone facies (Litofacies 3) Layered calcretes were formed near and/or at the surface of the angular pebbly sandy mudstone facies (Litofacies 4). The presence of sand-gravel-block sized clastic sediments within the calcretes at levels close to the surface points that the formation is open to atmospheric conditions.
Although the calcretes formed within the soil zone receive material from the surrounding rocks, there is no transported sediment content.
Calcrete formations were observed on fault lines adjacent to Quaternary sediments (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). For this reason, the ages of calcretes from three locations in the study area vary (
Table 4). Konya calcretes, which are associated with faults, also shed light on the seismic history of the region. In particular, Location 1 is located in the first fault zone that forms the western slope of the KCB. The H4FAK sample taken from calcretes deposited on the fault plane was dated as 292.86 ky. This date marks the first faulting period in the region. The reliability of the ESR method was tested by comparing the age of the ESR dating method with the age of C-14 and Uranium/Thorium dating methods used previously in dating the carbonate sediments [30,43-45]. Therefore, the obtained dates are considered to be reliable.
Two different characteristics of Konya calcretes emerge as considering the data obtained. The first one is predominantly dolocretes formations in location 1. Dolomitization is explained in many studies as being secondary formation in association with Mg-rich clayey sediments. However, SEM, XRD and ICP-MS analyzes show that dolocretes in this location were primarily precipitated. If the source of Mg was clayey sediments rich in Mg, different mineral formations should be also observed in the diagenetic process. As seen in
Figure 5B,D, any secondary clay mineral developments were not observed among the disc-shaped dolomite accumulations [
21,
46,
47,
49,
50].
The second is the calcretes deposited at the top level of Location 1 and the CaCO
3-rich calcretes formations precipitated in Locations 2 and 3. The lack of dolomitization in the parts close to the surface at Location 1 is interpreted as the fact that the calcretes here developed as hard-layered and nodular calcretes as a result of evaporation of fresh surface waters on the surface and in the parts close to the surface before reaching the depths due to the paleoclimatic conditions, For this reason, calcretes deposited in H6 and locations 2 and 3 have richer δ
18O values [
6,
15,
21] (
Table 1;
Figure 12,
Figure 13 and
Figure 14). These differences are clearly observed in SEM, main oxide and C and O Stable isotopic analyses. Therefore, CaMg(CO
3)
2 and CaCO
3-rich calcretes have different formation histories [
46,
47,
48,
49].
Dolocrete was formed as a result of dolomite precipitation by the Mg+2 enriched waters circulating within the ophiolitic rocks and then discharging into the soil zone with the capillary system. At location 1, six differing calcretes levels were determined. Of these levels, dolomite mineral was clearly observed, from bottom to top, in H1, H2, H3, H4 FAK, H5 levels, but no dolomite mineral was detected at the top level.
In Turkey, similar formations have been observed at the Ankara provincial border in the northeast of Konya, and in Çanakkale and Mersin regions [
6,
49,
50,
51]. In addition, dolomitization is also observed in calcretes in Turkey and some other countries [
51], especially in calcrete formations occurring in Mg-rich clayey sediments. In these muddy levels, dolocretes formations can occur as a result of chemical reactions taken place in Mg-rich pore waters and alteration of clays [
6,
49,
50,
51].
Table 5.
Table showing the geological characteristics of Konya Calcretes and Dolocretes [
1].
Table 5.
Table showing the geological characteristics of Konya Calcretes and Dolocretes [
1].
| Location |
Calcrete Type |
Sedimentary Structure |
Diagenetic Enviroment |
Origin |
ESR Dating (ky) |
| 1 |
Calcrete |
Lamina |
Top Meteoric Conditions,
Freshwater limestone |
Carbonates and Ultramafics |
292,86 |
| Dolocrete |
Dust, nodules, root structure (rhizoliths), tubes |
Meteoric conditions that influence groundwater |
Carbonates |
| 2 |
Calcrete |
Lamina, dust, nodules, |
Top Meteoric Conditions |
Marble and Carbonates |
217.47
259.99
271.58 |
| 3 |
Calcrete |
Lamina, dust, nodules, |
Top Meteoric Conditions |
Carbonates |
389.85 |
In addition, calcretes at Location-1 fall in the ultramafic rock area while calcretes at Location-2 fall in the carbonate (limestone and dolomitic limestone) rocks area on the diagram used in determining the origin of the tufa and travertines (
Figure 12). This situation reported by [
52] points out that the diagram developed for determining the origin of tufa and travertines can also be applied for calcretes in a similar way. It is also seen in this diagram that the origin of the dolomites in Location 1 is ophiolitic rocks. The calcretes in the other two locations are associated with carbonate rocks and their CaO amounts are close to each other. In addition, in
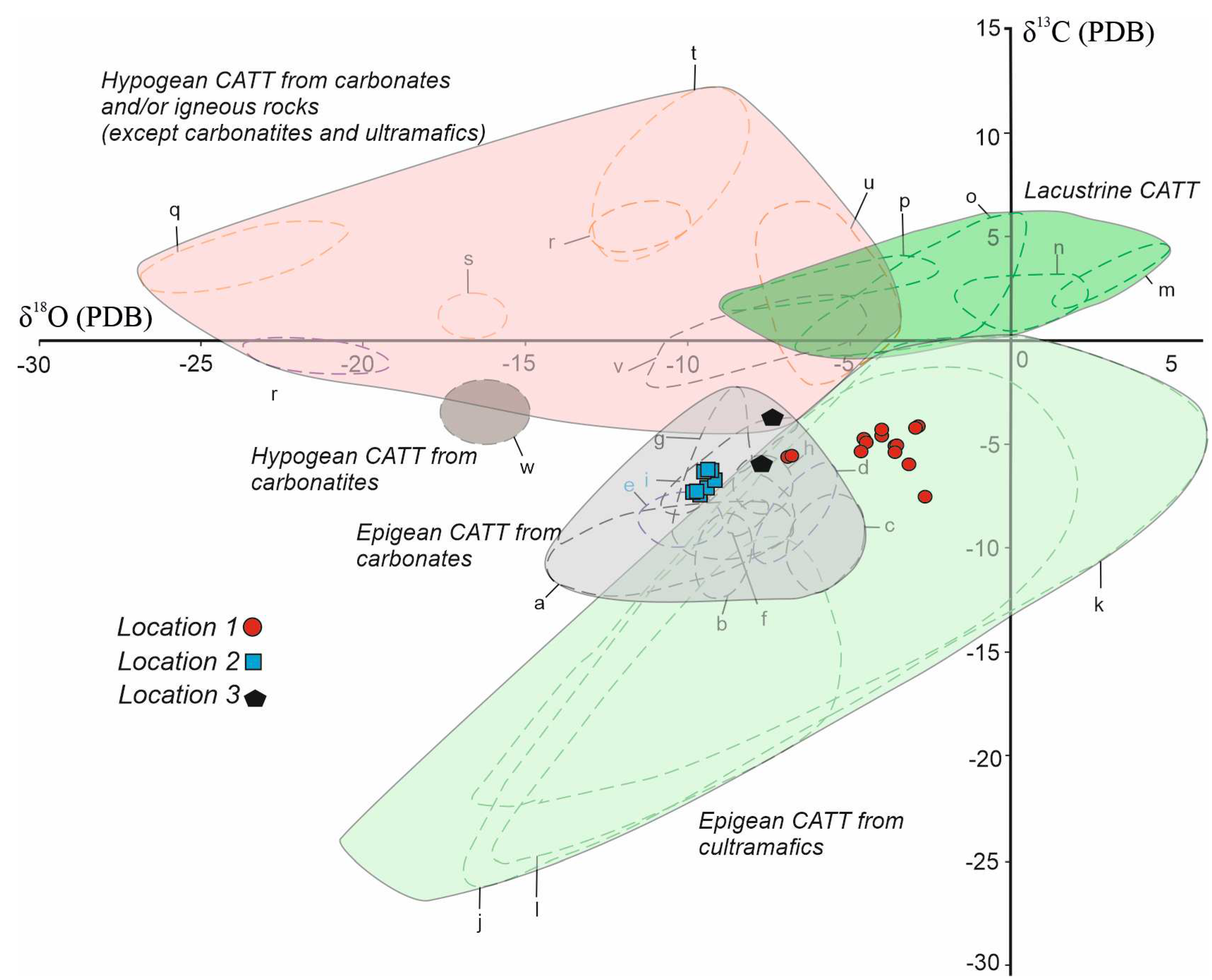
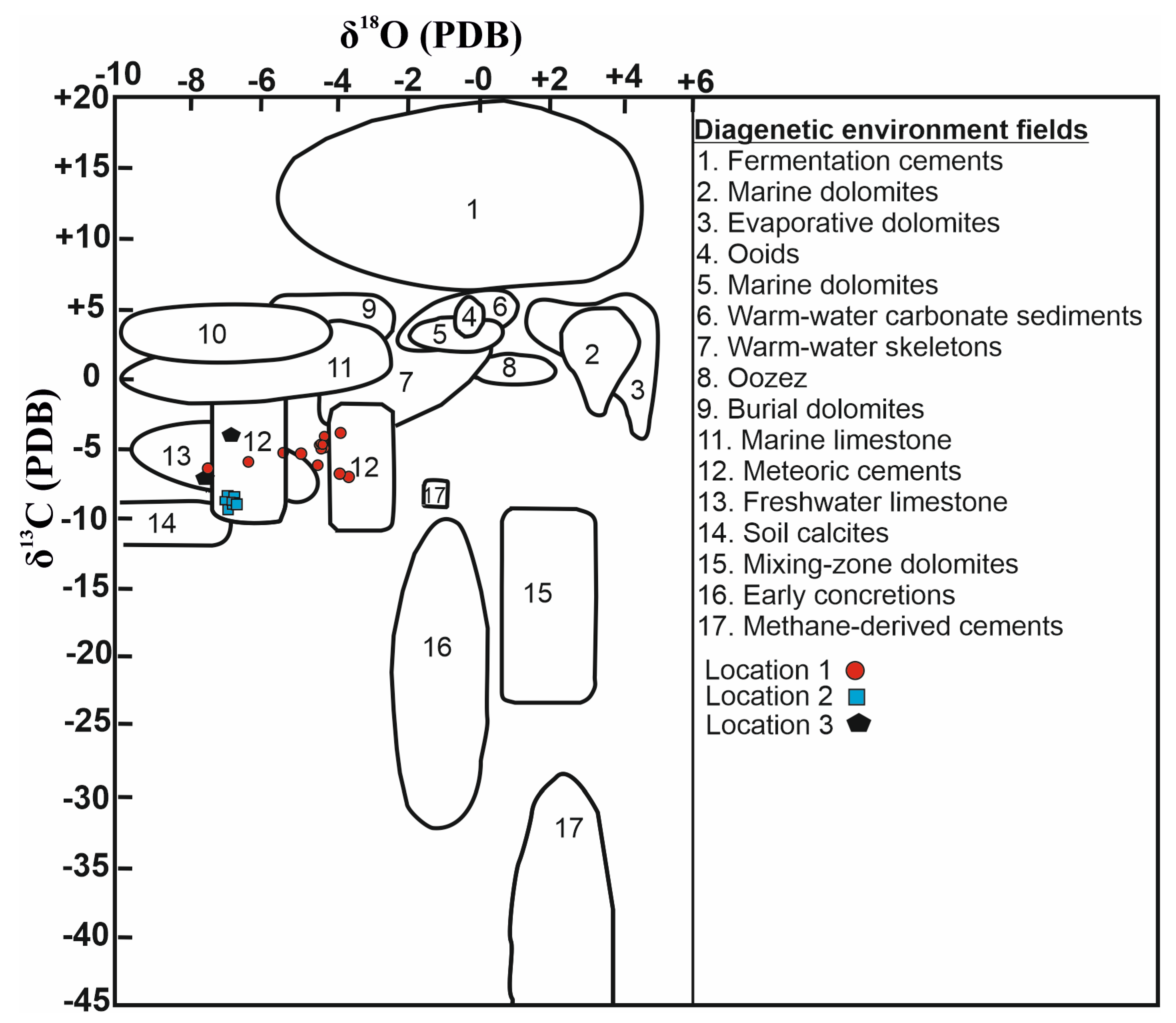
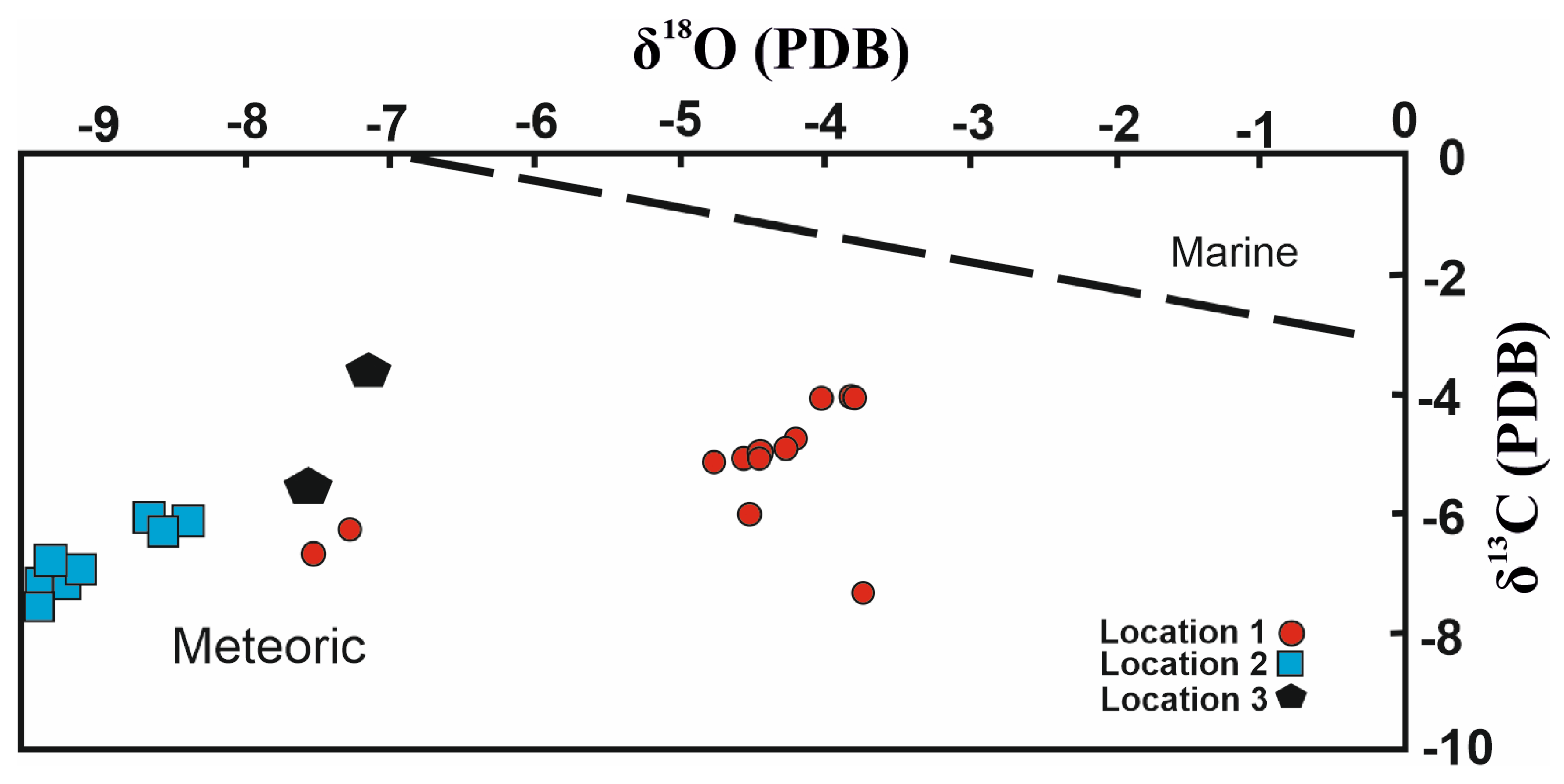
Figure 12, the origin of the samples appears as being epigenetic carbonate rock (Neogene and Mesozoic carbonate rocks). Besides, on the diagrams constructed by using C and O stable isotope values, data from calcretes diagenetic environments falls in meteoric environments (
Figure 13 and
Figure 14) [
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59], Also, the measured C and O stable isotope values of the calcretes is close to the typical isotope values of soil carbonates, which are mostly composed of CO
2 produced by C4 type vegetation and supports a pedogenic or shallow groundwater origin [
52,
60].
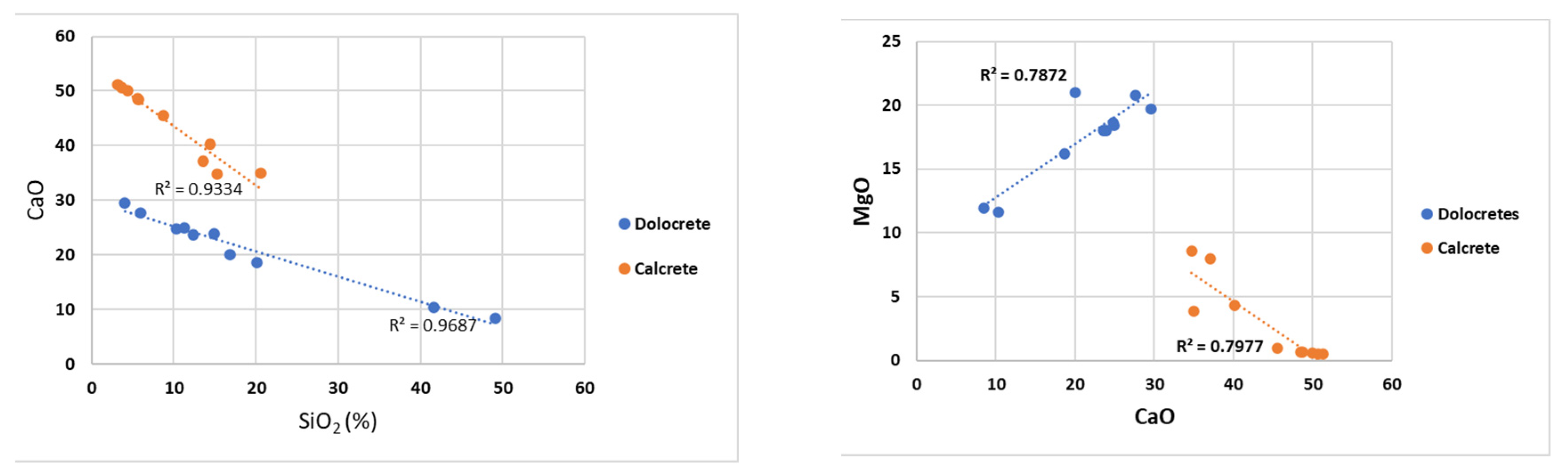
The MgO, CaO and SiO
2 contents of the calcretes and dolocretes in these locations differ significantly (
Figure 11). The expected inverse proportion between CaO and SiO
2 is observed. As it is known, the probability of carbonate precipitation decreases in depositional areas where siliceous clastics are dense [
61,
62]. Moreover, while there is a linear relationship between MgO-CaO in dolocretes, there is an inverse relationship between MgO-CaO in calcretes. This clearly shows that CaO and MgO act together from the same source, especially in the formation of dolocretes [
63,
64,
65]. Calcretes receive ions from different sources. Another important point emerges while making comparisons between CaO-SiO
2 and MgO-CaO, dolocretes and calcretes cluster in different regions on the diagrams [
65] This situation, observed not only in the main oxide values but also in SEM, XRD and C and O stable isotope studies, clearly indicates the consistency between the analyses.
Figure 11.
Diagrams showing the relationship between % CaO-SiO2 and MgO-CaO of dolocretes and calcretes in the Konya region.
Figure 11.
Diagrams showing the relationship between % CaO-SiO2 and MgO-CaO of dolocretes and calcretes in the Konya region.
Figure 12.
The distribution of δ
18O and δ
13C values of the studied samples on the combined δ
18O (‰PDB) and δ
13C (‰PDB) plot for recent to modern calcitic or dolomitic calcretes [
66].
Figure 12.
The distribution of δ
18O and δ
13C values of the studied samples on the combined δ
18O (‰PDB) and δ
13C (‰PDB) plot for recent to modern calcitic or dolomitic calcretes [
66].
Figure 13.
Diagenetic environment plot of δ
13C and δ
18O of Konya calcretes [
63,
67].
Figure 13.
Diagenetic environment plot of δ
13C and δ
18O of Konya calcretes [
63,
67].
Figure 14.
Diagenetic environment diagram of δ
13C and δ
18O at K
onya Calcretes [
67,
68].
Figure 14.
Diagenetic environment diagram of δ
13C and δ
18O at K
onya Calcretes [
67,
68].
6. Conclusions
The Konya calcretes were named for the first time in this study, and their origin and geological features were determined. In the Konya region, two terrestrial carbonates, calcretes and dolocretes, have been interpreted as being deposited under different meteoric environmental conditions (
Table 5). Calcretes have developed in the form of powder, tube and coatings. It has been determined that the calcretes in the region are related to the faults and the waters freely circulating in the discontinuity planes precipitated the calcretes. Calcretes at three different locations were investigated within the same fault zone. At the location 1, epigean calcrete is dominant. The source of Mg
+2 was interpreted as being derived from underlying ultramafic rocks. At the locations-2 and 3, calcretes were developed in the units overlying carbonate rocks. Both geochemical and isotopic data revealed that these calcretes are epigean and that source of ions is carbonate rocks.
The calcrete samples taken from the fault surface were dated by using ESR method and a relative age of 239 ky for faulting was found. This study revealed, for the first time, important data about the formation age of KCB. The age of the calcretes formed in the Konya fault zone and closely related to the faults varies between 218 and 293 ky. Having different ages for calcretes are interpreted as being resulted form faulting developed at different time.
Dating the active faults in the Konya region will supply important data about what kind of seismic activity will affect the residential area with a population of approximately 2 million in the future and the cyclicality of earthquakes that will occur.
Funding
This study was supported by Selçuk University Scientific Research Projects (BAP) Coordinatorship (Project No: 7201156).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank very much to Prof. Dr. Hükmü ORHAN, Prof.Dr. Ülkü Sayın and Prof. Dr. Ayhan ÖZMEN for their contributions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wright, V.P.; Tucker, M.E. Calcretes. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. 1991, 1-351. [CrossRef]
- Klappa, C. F. Calcified filaments in Quaternary calcretes: organo-mineral interactions in the subaerial vadose environment, Journal of Sedimentary Research. 1979, 49 (3). [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.R.; Phang, C.; Wildman, J.E.; Lintern, M.J. Genesis of some calcretes in the southern Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: implications for mineral exploration. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences. 1997, 44: 87-103. [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Zarza, A. M.; Wright, V. Calcretes. Developments in Sedimentology. 2010, 61, 225-267. [CrossRef]
- Achyuthan, H.; Shankar, N.; Braida, M.; Ahmad, S.M. Geochemistry of calcretes (calcic palaeosols and hardpan), Coimbatore, Southern India: formation and paleoenvironment. Quaternary International. 2012, 265: 155-169.7. [CrossRef]
- Eren, M.; Kaplan, M.Y.; Kadir, S.; Kapur, S. Comparison of stable isotope values of Quaternary calcretes from Adana and Mersin provinces: implications on controlling factors. Turkish J Earth Sci. 2019, 28: 706-718. [CrossRef]
- Herranz, J.E.; Pozo, M. Sepiolite and Other Authigenic Mg-Clay Minerals Formation in Different Palustrine Environments (Madrid Basin, Spain). Minerals. 2022, 12, 987. [CrossRef]
- Atabey E., Atabey N.; Kara H. Sedimentology of caliche (calcrete) occurrences of the Kırşehir region. Bull. Miner. Res. Explor. 1998, 120, 69—80.
- James, N.P. Holocene and Pleistocene calcareous crust (caliche) profiles: Criteria for subaerial exposure. J. Sed. Petrology. 1972, 42, 817—836. [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S.; Duricrusts in tropical landscapes. Clarendon Press, Oxford. 1973, 1—174.
- Goudie, A.S. Calcrete. In: Goudie A.S. & Pye K. (Eds.): Chemical sediments and geomorphology. Academic Press, London. 1983, 93—131.
- Tucker, M.E. Sedimentary petrology: An introduction to the origin of sedimentary rocks. Blackwell Science, Oxford. 1991, p. 260.
- Buol, S.W.; Hole, F.D.; McCracken, R.J.; Southard R.J. Soil genesis and classification. Iowa State University Press, Mes-Ames, IA. 1997, 1—527.
- Tabor, N.J. Paleoclimate isotopic proxies derived from Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic Paleosols and modern soils. University of California, PhD Thesis, Davis, California, 2002, 1-213.
- Gallala, W.; Gaied, M. E.; Essefi, E.; Montacer, M. Pleistocene calcretes from eastern Tunisia: The stratigraphy, the microstructure and the environmental significance. Journal of African Earth Sciences. 2010, 58(3), 445–456. [CrossRef]
- Venu, U.A.; Velmayil, P.; Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Sial, A. Geochemical and stable isotope (δ13C & δ18O) signatures of Calcrete in and around Pandalgudi, Southern Tamilnadu, India and its implications on Palaeoclimate. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 2022, 15-913. [CrossRef]
- Kapur, S.; Çavuşgil, V.S.; Fitzpatrick, E.A. Soil-calcrete (caliche) relationship on a Quaternary surface of the Çukurova Region, Adana (Turkey). In: Federoff N., Bresson L.M. & Courty M.A. (Eds.): Soil micromorphology. Assoc. Francaise pour L’Etude du sol, Paris. 1987, 597—603.
- Kapur, S.; Yaman, S.; Gökçen, S.L.; Yetiş, C. Soil stratigraphy and Quaternary caliche in the Misis area of the Adana Basin, southern Turkey. Catena. 1993, 20, 431—445. [CrossRef]
- Kapur, S.; Çavuşçugil, V.; Şenol, M.; Gürel, N.; Fitzpatrick, E.A. Geomorphology and pedogenetic evolution of Quaternary calcretes in the northern Adana Basin of southern Turkey. Z. Geomorphology. 1990, 34, 1, 49—59. [CrossRef]
- Kapur S.; Saydam C.; Akça E.; Çavuşçugil, V.S.; Karaman, C.; Atalay, I.; Özsoy T. Carbonate pools in soil of the Mediterranean: a case study from Anatolia. In: Lal R., Klmble J.M., Eswaran H., Stewart B.A. (Eds.): Global climate change and pedogenic carbonates. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida. 2000, 187—212.
- Kaplan, M.Y.; Eren, M.; Kadir, S.; Kapur, S. Mineralogical, geochemical and isotopic characteristics of Quaternary calcretes in the Adana region, southern Turkey: Implications on their origin. Catena. 2013, 101, 164-177. [CrossRef]
- Eren, M. Genesis of tepees in the Quaternary hardpan calcretes, Mersin, S Turkey. Carbonates And Evaporites. 2007, 22, 123-134. [CrossRef]
- Eren, M.; Kadir, S.; Hatipoğlu, Z.; Gül, M. Quaternary calcrete development in the Mersin area, southern Turkey. Turkish J. Earth Sci. 2008, 17, 763—784.
- Kadir, S.; Eren, M. The occurrence and genesis of clay minerals associated with Quaternary caliches in the Mersin area, southern Turkey. Clays Clay Miner. 2008, 56: 244-258. [CrossRef]
- Eren, M.; Kadir, S.; Hatipoğlu, Z.; Gül, M. Quaternary calcrete development in the Mersin area, southern Turkey, Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences. 2008, 17 (4), 763-784.
- Eren, M. Stable isotope geochemistry of Quaternary calcretes in the Mersin area, southern Turkey—A comparison and implications for their origin. Chemie der Erde. 2011, 71, 31—37. [CrossRef]
- Gürel, A.; Kadir, S. Geology, mineralogy and origin of clay minerals of the Pliocene Fluvial-Lacustrine deposits in the Cappadocian Volcanic Province, Central Anatolia, Turkey. Clays and Clay Miner. 2006, 54, 555—570. [CrossRef]
- Gürel, A.; Kadir, S. Geology and mineralogy of Late Miocene clayey sediments in the southeastern part of the Central Anatolian Volcanic Province, Turkey. Clays and Clay Minerals. 2008, 56, 307-321. [CrossRef]
- Küçükuysal, C. Palaeoclimatological approach to Plio-Quaternary paleosol-calcrete sequences in Bala and Gölbaşı (Ankara) by using mineralogical and geochemical proxies. METU PhD Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey, 2011, 1—246.
- Küçükuysal, C.; Engin, B.; Türkmenoğlu, A.G.; Aydaş, C. ESR dating of calcrete nodules from Bala, Ankara (Turkey): Preliminary results, Applied radiation and isotopes. 2011, 69 (2), 492-499. [CrossRef]
- Özer, A.M.; Wieser, A.; Göksu, H.Y.; Müller, P.; Regulla, D.F.; Erol, O. ESR and TL age determination of caliche nodules. Int. J. Radiation Applications and Instrument. Part A-Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 1989, 40, 1159-1989. [CrossRef]
- Atalay, I. Palaeosols as indicators of the climatic changes during Quaternary period in S Anatolia. J. Arid Environments. 1996, 32, 23—35. [CrossRef]
- Kadir, S.; Eren, M.; Külah, T.; Erkoyun, H. l.; Huggett, J.; Önalgil, N. Genesis of palygorskite and calcretes in Pliocene Eskişehir Basin, west central Anatolia, Turkey, Catena. 2017, 168, 62-78. [CrossRef]
- Coskun, A.; Horasan, B. Y.; Ozturk, A. Heavy metal distribution in stream sediments and potential ecological risk assessment in Konya Northeast region. Environmental Earth Sciences. 2021, 80(5). [CrossRef]
- Özgül, N. Toroslar’ın bazı temel jeoloji özellikleri. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Turkey. 1976, 19, 65–78.
- Eren, Y., The geology of the Eldeş-Derbent-Tepeköy-Söğütözü (Konya) region (in Turkish with English abstract). Unpublished PhD. thesis, Selçuk University, Konya. 1993. 224 pp.
- Göğer, E.; Kıral, K. Geology of Kızılören region (in Turkish). Mineral Research and Exploration Report. 1973, R.Num. 5204. [CrossRef]
- Horosan, B. Y. Konya çevresindeki toprakların jeokimyası / Geochemistry of the soils in the vicinity of Konya. Selçuk Üniversitesi (Phd thesis), 2014, 258p.
- Ikeya, M. New applications of electron spin resonance: dating, dosimetry and microscopy. World Scientific. 1993, p.500.
- Grün, R. Electron spin resonance (ESR) dating. Quaternary international. 1989, 1, 65-109. [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, B.A.; Skinner, A. R.; Blickstein, J. I.; Montoya, A. C.; Florentin, J. A.; Baboumian, S. M.; Ahmed, I. J.; Deely, A. E. ESR in the 21st century: From buried valleys and deserts to the deep ocean and tectonic uplift, Earth-Science Reviews. 2016, 158, 125-159. [CrossRef]
- Brennan B.J; Rink, W.J.; Rule E.M; Schwarcz H.P.; Prestwich W.V. The ROSY ESR dating program. Ancient TL 17, 1999, (2): 45-53. [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Yi, C.; Yang, H.; Xu, X.; Hu, G. The ESR Signals in Different Minerals and the Bleaching of Feldspar. Minerals. 2023, 13, 1108. [CrossRef]
- Kailath, A. J.; Rao, T. K. G.; Dhir, R. P.; Nambi, K. S. V.; Gogte, V. D.; Singhvi, A. K. Electron spin resonance characterization of calcretes from Thar desert for dating applications. Radiation Measurements. 2000, 32(4), 371–383. [CrossRef]
- Engin, B.; Kapan-Yeşilyurt, S.; Taner, G.; Demirtaş, H.; Eken, M. ESR dating of Soma (Manisa, West Anatolia – Turkey) fossil gastropoda shells. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms. 2006, 243(2), 397–406. [CrossRef]
- Gürel, A.; Özcan, S. Paleosol and dolocrete associated claymineral occurrences in siliciclastic red sediments of the Late Miocene Kömişini Formation of the Tuzgölü basin in central Turkey. Catena. 2016, 143, 102–113. [CrossRef]
- Kadir, S.; Eren, M.; Atabey, E. Dolocretes and associated palygorskite occurrences in siliciclastic red mudstones of the Sariyer formation (Middle Miocene), southeastern side of the Çanakkale strait, Turkey. Clays and Clay Minerals. 2010, 58: 205-219. [CrossRef]
- Küçükuysal, C. Late Pleistocene calcretes from Central Anatolia (Lakes Eymir and Mogan, Gölbaşı Basin): Comparison to quaternary calcretes from Turkey. Journal of Earth Science. 2016, 27(5), 874–882. [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, F.I. Occurrences and genesis of calcrete and dolocrete in the Mio-Pleistocene fluviatile sequence in Kuwait, northeast Arabian Peninsula. Sedimentary Geology. 2007, 199, 129_139. [CrossRef]
- Küçükuysal, C; Kapur, S. Mineralogical, geochemical and micromorphological evaluation of the Plio-Quaternary paleosols and calcretes from Karahamzalı, Ankara (Central Turkey). Geologica Carpathica. 2014, 65, 3, 241—253. [CrossRef]
- Arakel, A. Genesis of calcrete in Quaternary soil profiles, Hutt and Leeman lagoons, Western Australia. Journal of Sedimentary Research. 1982, 52 (1). [CrossRef]
- Bajnóczi, B.; Horváth, Z.; Demény, A.; Mindszenty A. Stable isotope geochemistry of calcrete nodules and septarian concretions in a Quaternary ‘red clay’ paleovertisol from Hungary. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies. 2006, 42, 335—350. [CrossRef]
- Moore, C. H.; Wade, W. J. Meteoric Diagenetic Environment. Carbonate Reservoirs-Porosity and Diagenesis in a Sequence Stratigraphic Framework. 2013, 165–206.
- Paquet, H.; Ruellan, A. Calcareous Epigenetic Replacement in Soils and Calcrete Formation. In Soils and Sediments, Eds: Springer. 1997. p. 21-42.
- Esteban, M.; Klappa, C.F. Subaerial exposure environments: Carbonate Depositional Environments (Eds. by P.A. Scholle, D. G. Bebout ve C. H. Moore). AAPG. Mem. 1983, 33, 2-54.
- Nash, D. J.; Smith, R. F. Multiple calcrete profiles in the Tabernas Basin, southeast Spain: their origins and geomorphic implications. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. 1998, 23 (11), 1009-1029.
- Cerling, T.E. The stable isotope composition of modern soil carbonate and its relationship to climate. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 71, 229—240. [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Keppens, E.; Paepe R. The use of oxygen and carbon isotope composition of pedogenic carbonates from Pleistocene palaeosols in NW Bangladesh, as palaeoclimatic indicators. Quarter. Sci. Rev. 1997, 16, 161—168. [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.E.; Singhvi, A.K.; Kailath, A.J.; Kuhn, R., Dennis, P.F.; Tandon, S.K.; Dhir, R.P. Do stable isotope data from calcrete record late Pleistocene monsoonal climate variation in the Thar Desert of India? Quaternary Research. 1998, 50 (3), 240-251. [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, T. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of the unsaturated zone: an important control of groundwater hardness in limestones. Journal of Hydrology. 1977, 35 (1-2), 111-123. [CrossRef]
- Flügel, E. Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks, Analysis, Interpretation and Application. Springer Berlin. 2004, 976 p.
- Tucker, M. E.; Wright, V. P. Carbonate Sedimentology. Blackwell science. 1990, 487 p.
- Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Madhavaraju, J.; Sial, A.N. Petrography and stable isotope geochemistry of the cretaceous El Abra Limestones (Actopan), Mexico: implication on diagenesis. J Geol Soc India. 2011, 77:349–359. [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, V.; Khodabakhsh, S.; Halverson, G.; Bahramabadi, B.; Bui, T.H. Quaternary calcretes of Qazvin Plain (N Iran) based on multi-story geochemical and petrographic signatures. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 2023, 16:513. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A. K.; Bansod, M. N.; Singh, A.; Sharma, N. Geochemistry of paleosols and calcretes from Quaternary sediments of Purna alluvial basin, central India: An emphasis on paleoclimate. Rhizosphere. 2019, 11, 100162. [CrossRef]
- Teboul, P.A.; Durlet, C.; Gaucher E.C.; Virgone, A.; Girard, J.P.; Curie, J.; Lopez, B. Origins of elements building travertine and tufa: New perspectives provided by isotopic and geochemical tracers, Sedimentary Geology. 2016, 334, 97-114. [CrossRef]
- Venu, U.A.; Velmayil, P.; Armstrong-Altrin, J.S. Calcrete profiles in Puthukulam quarry section, Sathankulam region, Southern Tamilnadu, India: implications on palaeoclimate significance. Journal of Sedimentary Environments. 2020, 5:493–503. [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, M. Carbonate diagenesis in the Kallankurichchi Formation, Ariyalur Group, South India and its implications on petroleum prospects. J Earth Syst Sci. 2008, 71:407–418.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).