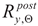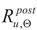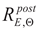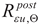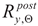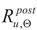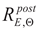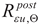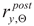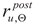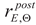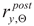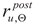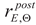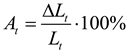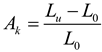1. Introduction—Standard duplex versus lean duplex stainless steels used in construction
Duplex steels have a special place in modern construction industry, where stainless steels are used in wide range of applications. Their intentionally designed and properly balanced two-phase microstructure, comprising of face-centered austenite and body-centered ferrite in approximately equal ratio and crystallizing in a cubic system, determines relatively high strength accompanied by manufacturer warranted ductility, as expected by the user [
1]. The basic difference in the chemical composition of these steels, when compared against the chemical composition typical for conventional stainless steels exhibiting austenitic structure, is substantially higher chromium content by weight (usually between 20-28%) and increased molybdenum content (up to 5%) [
2]. At the same time nickel content is by a rule decreased to 9% while nitrogen content remains at 0.05-0.50% [
3]. Due to the very high corrosion resistance, in particular to the pitting corrosion initiated in the chlorine rich environments, these steels find wide application among others in petrochemical industry, for instance in pipeline construction or construction of pressurized storage tanks [
4].
The chemical composition of duplex steels is usually driven by the requirement to obtain thermodynamic stability of their most substantial components, i.e. austenite and ferrite, and, independently, nitrogen limit solubility. On the one hand, when the combined chromium and molybdenum content by weight in the chemical composition does not exceed 20% one has to take into account the risk of martensitic transformation of austenite. This, by a rule, results in hardening of the material and as a consequence significant deterioration in ductility. Transition of this type is usually related to high susceptibility to brittle failure, occurring in an abrupt fashion, without any forewarning of gradually increasing failure risk. On the other hand, when the chromium and molybdenum content by weight in the designed steel exceeds 35%, the δ-ferrite instability may occur, accompanied at sufficiently high temperature by secondary precipitates, deleterious to its mechanical properties. High pressure of nitrogen dissolved under these conditions in the structure of such steel may constitute an additional source of instabilities generated between individual phases [
5].
As is widely known, the stainless steels of duplex type, depending on the intentionally selected chemical composition may be divided into five basic qualitative groups. These are as follows:
Lean Duplex Stainless Steels - LDSS,
Standard Duplex Stainless Steels (with 22% Cr content) - DSS 22% Cr,
High Alloyed Standard Duplex Stainless Steels (with 25% Cr content) - DSS 25% Cr,
Super Duplex Stainless Steels – SDSS [
6,
7],
Hyper Duplex Stainless Steels - HDSS.
The stainless steels belonging to the LDSS group, when compared against stainless steels belonging to the DSS 22%Cr group, are characterized by the significantly lowered nickel and molybdenum content in their chemical composition. Reduction in the content of these elements, applied to stabilize austenite, requires an addition of manganese. This addition increases solubility of nitrogen in the solution, and as a consequence increases the resistance of these steel grades to pitting corrosion [
8]. However, in the case of LDSS steels this resistance is significantly lower than resistance exhibited by the steels belonging to the DSS 22% Cr group. The LDSS steels have been designed out of necessity as a cheaper substitute of the DSS 22% Cr steels, and have been introduced on the market driven by wide fluctuations in the price of hardly available nickel.
2. Steel grades selected for detailed analysis
The research presented in this paper deals with two, subjectively selected and juxtaposed for comparative purposes, stainless steel grades exhibiting two-phase austenitic-ferritic structure of duplex type. The first of these grades is
X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 stainless steel belonging to the standard duplex group (DSS 22% Cr). Following its classification, this is a high-alloy, chromium-nickel-molybdenum steel. In the commercial nomenclature this steel is denoted as 1.4462 (Werkstoffnummer). The second grade is
X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 stainless steel, also a chromium-nickel-molybdenum one, but counted among the lean duplex steels (LDSS). In the commercial nomenclature this steel is denoted as 1.4162 (Werkstoffnummer). The properties of both these steels are listed in detail in the code EN 10088-1 [
9]. Their chemical composition is listed in the
Table 1.
One may easily note, that the LDSS steel selected for analysis, when compared against the DSS 22% Cr steel, is characterized by significantly decreased nickel and molybdenum content. At the same time it is characterized by substantially increased manganese content.
Both stainless steel grades considered in this paper exhibit comparable mechanical properties when analyzed at room temperature. This in particular refers to the R0.2 yield limit and ultimate strength Rm. These are R0.2 >500 MPa and Rm=660-950 MPa in the case of DSS 22% Cr steel as well as R0.2>480 MPa and Rm=650-850 MPa in the case of LDSS steel, respectively.
3. The purpose and scope of conducted research
Our research was oriented on testing the post-fire mechanical properties exhibited by the compared steel grades. It is widely known, that every steel grade subjected to the action of fire, after cooling does not revert to its initial internal structure, and therefore its properties differ substantially from those exhibited prior to the fire incident. Behavior of stainless steels subjected to the simulated fire tests usually differs from the behavior exhibited by common structural steels, and in particular low-carbon steel grades [
10,
11]. The peculiarity of this behavior is determined by permanent changes occurring in the microstructure of tested material when subjected to the action of high temperature and remaining after cooling [
12]. However, the way these changes occur, and in particular their intensity and probability of initiation depend to a high degree on the characteristics of fire affecting considered steel. The key here is not only the temperature to which the steel has been heated or the heating speed [
13], but also the time during which the material was subjected to the action of constant high temperature [
14]. The situation changes diametrically, if only under those circumstances the steel reached a temperature sufficient for unrestrained initiation of austenitic transformation, accompanied by all more or less important repercussions resulting from the transformation of this type. The tests conducted so far indicated strong dependence of post-fire material properties of considered steels on the cooling mode applied at the end of tests [
15]. When rapid cooling was applied, by voluminous application of water spray to simulate a fire extinguishing action, the cooled material, due to local hardening, may prove to be very susceptible to brittle failure.
The first stage of testing conducted was oriented on identification of such fire scenarios, which could, after application to duplex steel grades selected for detailed analysis, result in unacceptable brittleness of the material [
16]. To this purpose a wide program of experimental tests has been conducted, based on series of instrumented Charpy impact tests planned and adjusted to post-fire conditions. These tests have been conforming to European [
17,
18] and to US [
19,
20] standards. The results of these tests have been in part published and were presented at first in [
21,
22], relating to the credibility of the testing method itself and the conclusions drawn after application of the selected testing methodology, and later on in [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27], taking into account various aspects of final rating.
During research conducted so far the heating level of tested samples has been selected intentionally so as to enable the initiation of deleterious phase changes in the structure of considered material, resulting in decreased ductility. The research was oriented on discerning the sensitivity of tested duplex steels to various types of precipitations related to these changes. The results presented in [
28] have been applied for this purpose. In particular, a more or less extended time of passing through two temperature ranges was of particular interest here:
a 475oC brittleness zone – related to partial change of δ-ferrite into spinoidal secondary α’-ferrite, and precipitation of π, ε and G brittle phases (in the steels tested here this phenomenon occurs in the temperature range of 300-550oC),
a 800oC brittleness zone – induced by precipitation from the solid solution (mostly δ-ferrite) of carbides M7C3 and M23C6, nitrides Cr2N as well as secondary phases σ, χ, R and γ2 (in the steels tested here this phenomenon occurs in the temperature range of 600-1050oC).
The decreased molybdenum content by weight, characteristic for LDSS steels (with respect to analogous content typical for steels belonging to the DSS 22% Cr group), should result in this context in [
29]:
increased upper threshold initiation temperature limit for 475oC brittleness phenomenon,
decreased lower threshold initiation temperature limit for 800oC brittleness phenomenon.
The second part of these tests completing the abovementioned tests dealing with verification of post-fire brittleness, dealt with determination of post-fire mechanical properties of analyzed steels, in particular the yield limit and the tensile strength. The detailed results obtained are presented in the following part of this paper. These results seem to confirm the peculiar behavior of these steels, exhibiting two-phase austenitic-ferritic structure of duplex type, determined in fire conditions. In this context it qualitatively differs from the one exhibited by stainless steels of purely austenitic structure [
11] as well as from the one which seems to be typical of analogous steels exhibiting purely ferritic structure [
30].
Tested samples in the case of both tested steel grades have been taken from hot rolled steel plates. Thus qualitative interpretation of numerical results obtained here should be restricted to the material subjected to this type of plastic processing. Therefore the alternative scenario of testing post-fire mechanical properties of steels subjected to cold forming is not being dealt with here. It is well known, that the plastic processing method, determining the mechanical properties of steel prior to a fire episode affects its properties determined post-fire and after cooling as well. This is discussed, among others, in papers [
31,
32].
4. Sample preparation method and conduct of tests
Experimental verification of the yield limit
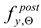
and ultimate strength limit
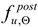
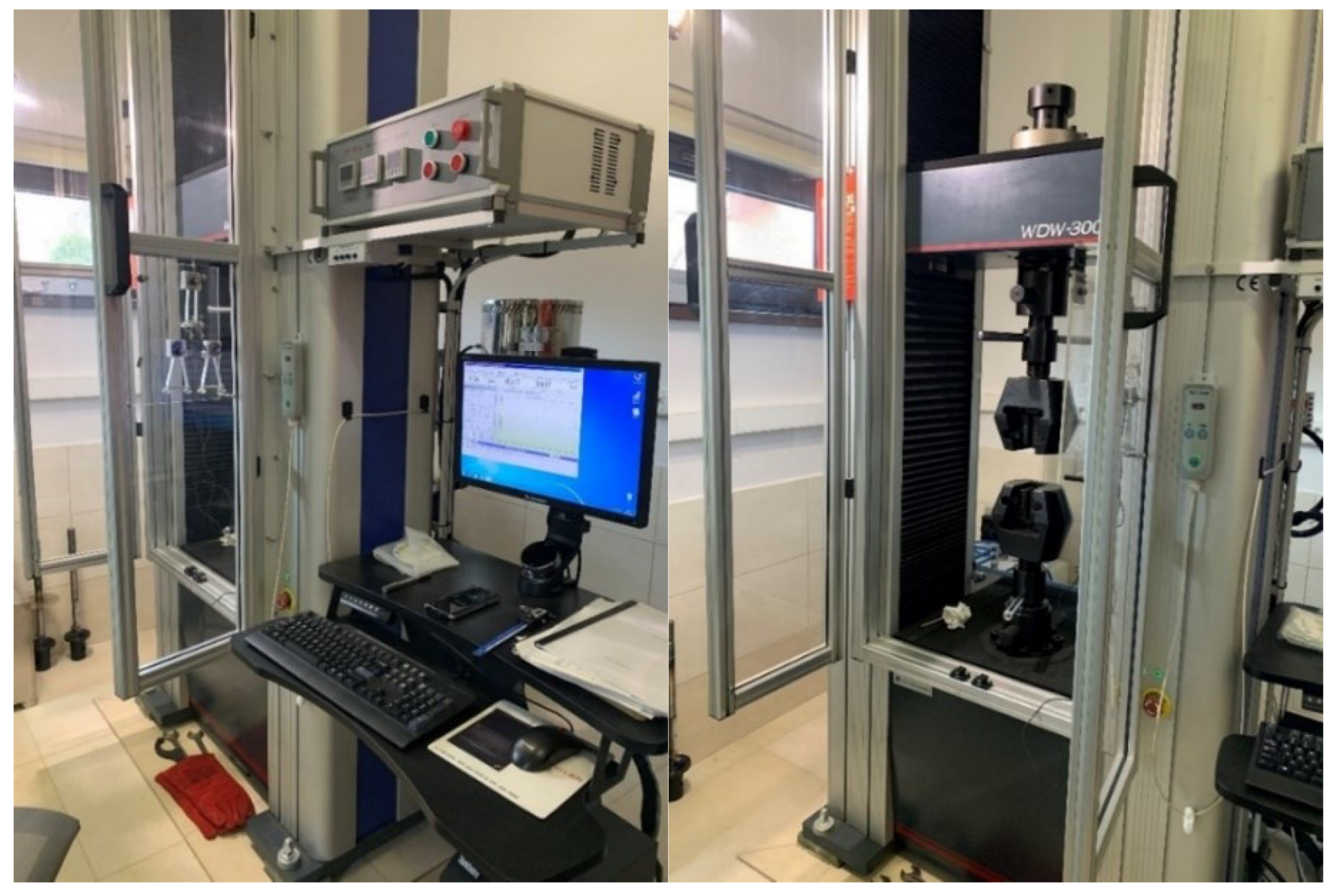
exhibited by duplex steels after simulated fire incident and selected for detailed analysis has been conducted on the strength testing machine WDW-300E, capable of generating maximum tensile force of 300 kN (
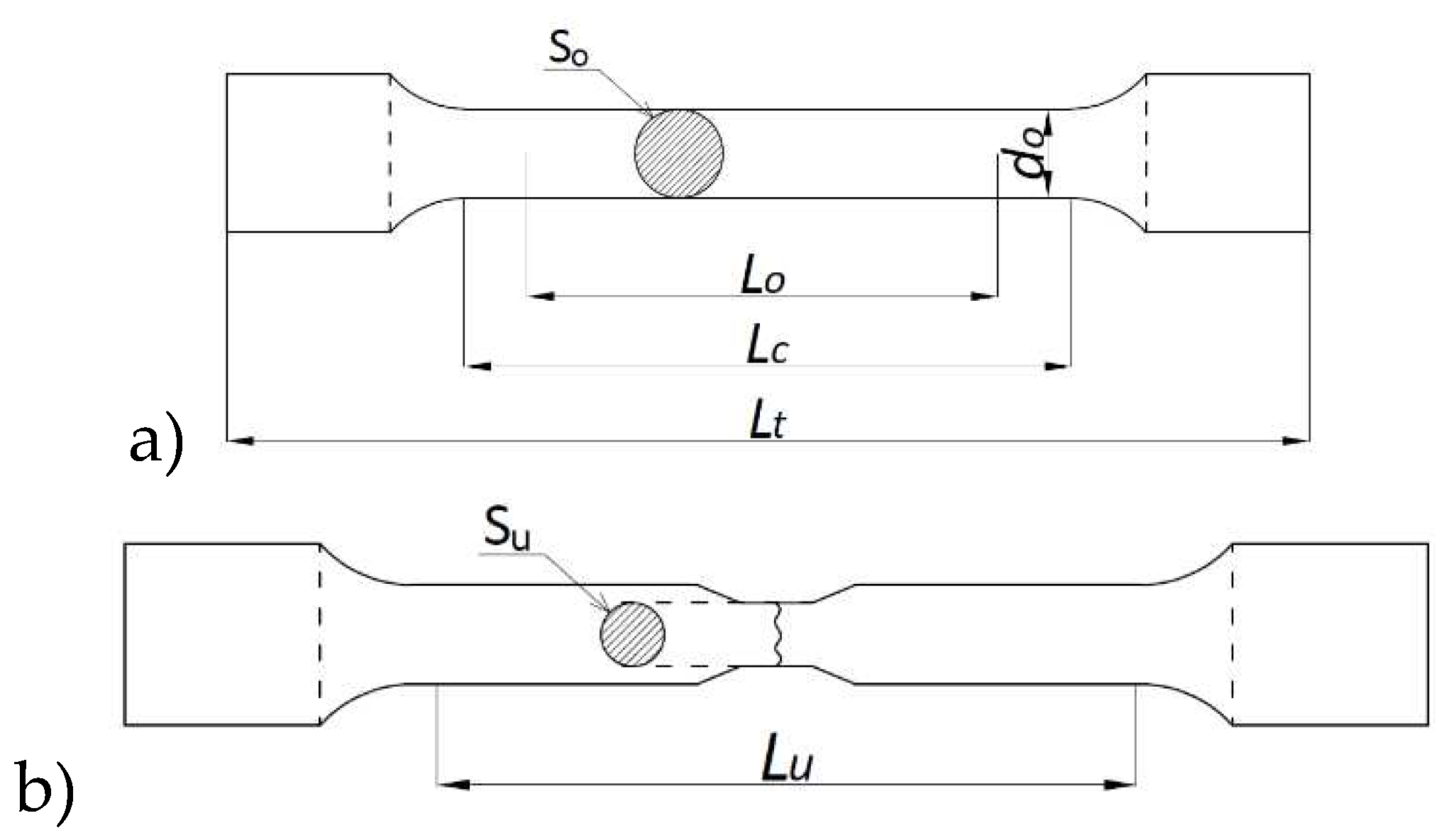
Figure 1). The lower index Θ denotes here an earlier action of fire temperature on the tested specimen, while the upper index denotes that indicated quantity has been determined on the sample effectively cooled after surviving a simulated fire incident. The tested “fivefold" samples of normalized shape and dimensions [
33] (
Figure 2), have been cut from hot rolled steel plates.
Software included with the strength testing machine is capable of registering relations of various types, and in particular those displaying the load – time, extension - time, load - extension, load – displacement or stress – relative displacement relations. Prior to each test an initial base length
L0 equal to 40 mm has been marked on each sample with a scribing device with intermediate points placed every 5 mm (
Figure 3). An extensometer with base length of 25 mm, mounted on the sample as shown in
Figure 5, had been used to measure the elongation. This extensometer has been removed from the sample at the initiation of plastic deformation. After conclusion of test (i.e. after breaking the sample) the final length
Lu (
Figure 2) has been measured with an electronic caliper (
Figure 5).
Figure 3.
Marking of the initial (base) measurement length on a sample.
Figure 3.
Marking of the initial (base) measurement length on a sample.
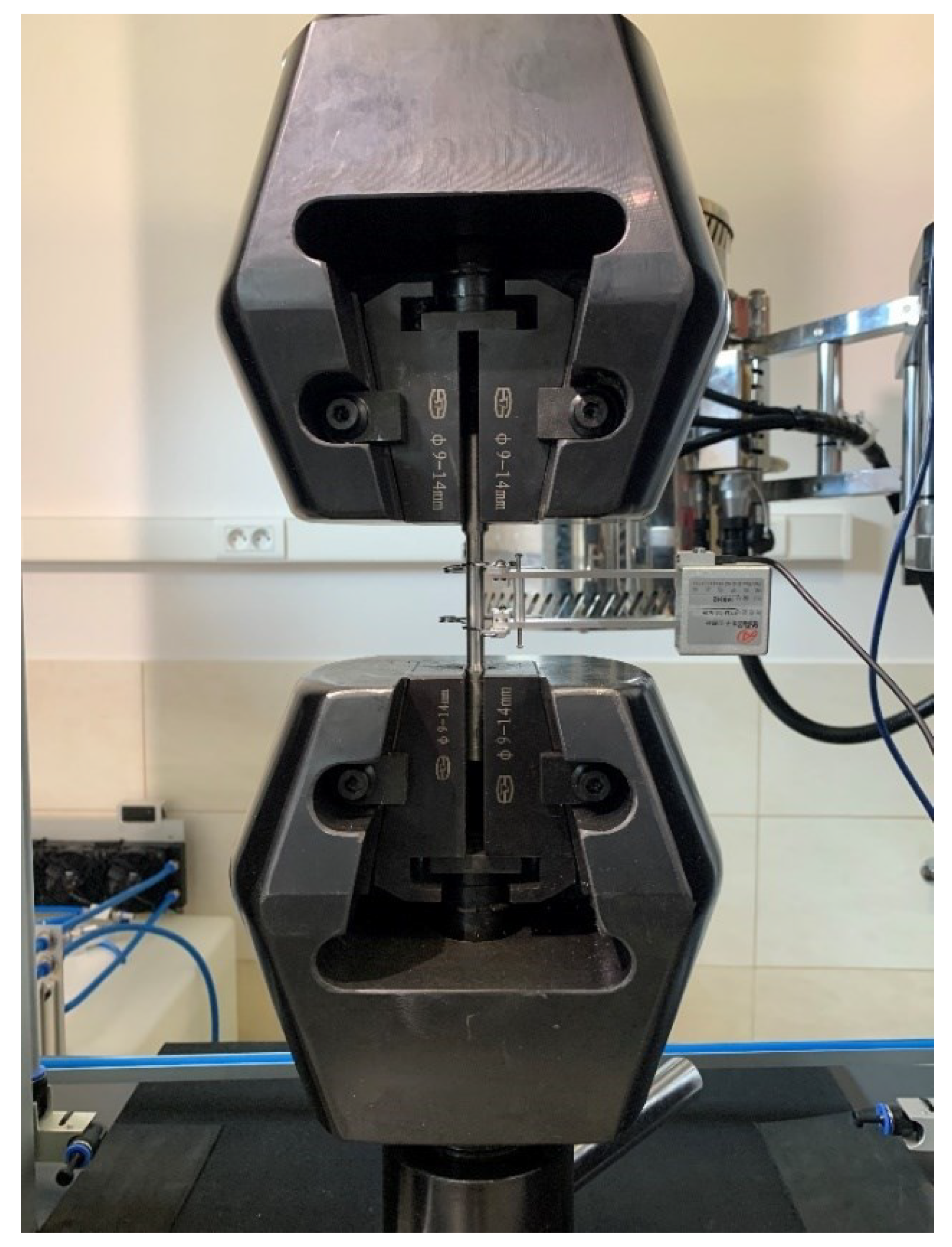
Figure 4.
A sample in the grips of the strength testing machine. Extensometer mounting is visible.
Figure 4.
A sample in the grips of the strength testing machine. Extensometer mounting is visible.
Figure 5.
Equipment used to determine relative elongation on a broken sample.
Figure 5.
Equipment used to determine relative elongation on a broken sample.
As indicated above, the tested samples have bee cooled after prior action of a simulated fire incident (
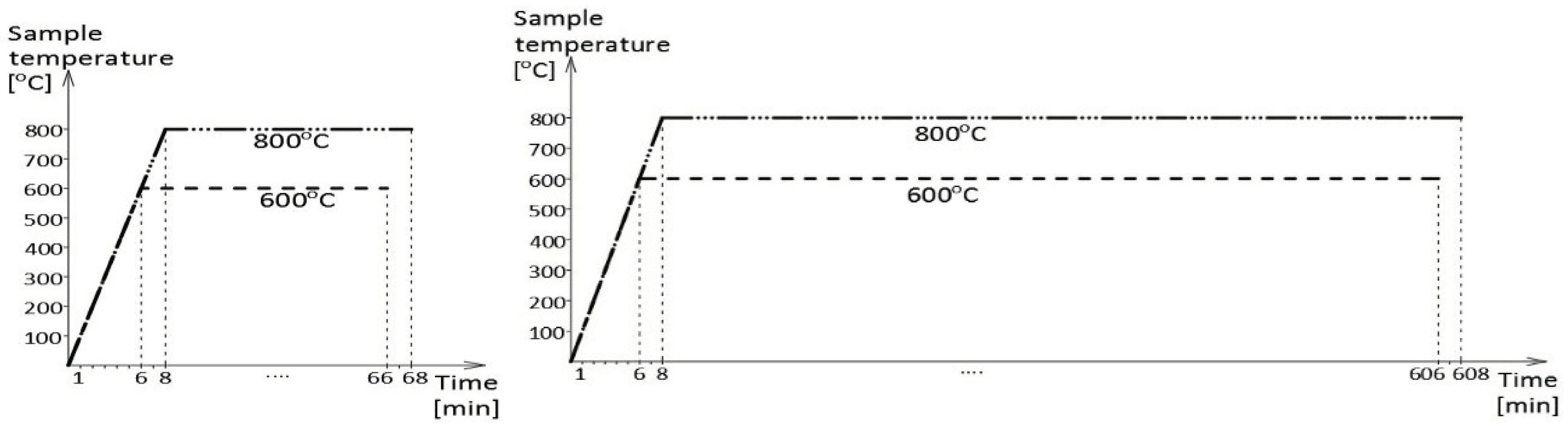
Figure 6). Within the scope of this simulation several fire scenarios have been considered, each time modeled following the isothermal testing mode (the so called
steady-state heating regime). In particular, the following scenarios have been used: a “short” fire with the sample kept for one hour at the fire temperature, and a “long” fire, where the time spent by the sample at the fire temperature has been extended to ten hours. The tested samples have been heated up to the predetermined testing temperature, equal to 600
oC in the first series of tests and 800
oC in the second series with constant speed of 100
oC/min (
Figure 7). These heating levels have been selected intentionally, as the first of these levels is believed to be too low while the second is considered to be sufficiently high to induce during the tests conducted on samples made of mild carbon steel thermally generated permanent structural changes, determining their post-fire strength [
12]. It has been decided to preserve those temperature levels during the tests conducted on samples made of stainless steels of the duplex type for the comparability reasons, to preserve the capability to compare the results obtained during research reported here with the results of other tests.
Different sample cooling modes have been applied during the tests as well. In one group of tests the samples were cooled slowly inside the laboratory furnace, to simulate the self-extinguishing of fire, while in the other group the samples have been cooled rapidly, in water mist, to simulate the fire extinguishing action conducted by fire fighters.
Therefore 18 samples have been subjected to tensile strength testing (2 steel grades times 2 fire simulation scenarios times 2 cooling modes applied plus for each steel grade one so called reference sample made of the material not subjected to the action of simulated fire temperature) [
34].
Chemical composition of samples analyzed here, made of duplex stainless steel as described above, has been positively verified against the composition listed in the code and presented in the
Table 1, using the
Foundry-Master optical emission spectrometer made by Worldwide Analytical Systems, Uedem, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany.
5. The results obtained and their interpretation
5.1. Sample description mode applied
The results obtained during the tests are presented here on the stress – strain graphs prepared separately for each tested steel grade.
The following four character key comprising of digits and letters has been used to describe particular samples tested:
first character (digit 1 or 2) – denotes steel grade tested (1 – X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel, 2 – X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel, respectively),
second character (digit 6 or 8) – denotes sample heating level (6 – 600oC or 8 – 800oC, respectively),
third character (letter F or W) – denotes sample cooling mode after simulated fire incident (F – slow cooling inside the laboratory furnace or W – rapid cooling in water mist, respectively),
fourth character (letter X or Y) – denotes fire simulation scenario applied (X – “long” fire duration or Y – “short” fire duration, respectively).
The σ–ε curve denoted with single digit instead of four letter code refers to the sample made of X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel when marked with 1, while curve denoted with 2 refers to the sample made of X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel and is a typical reference curve, since it has been determined while testing a sample made of an as delivered material, i.e. not subjected to thermal action simulating a fire incident. Since such sample did not undergo heat treatment it was not subjected to cooling.
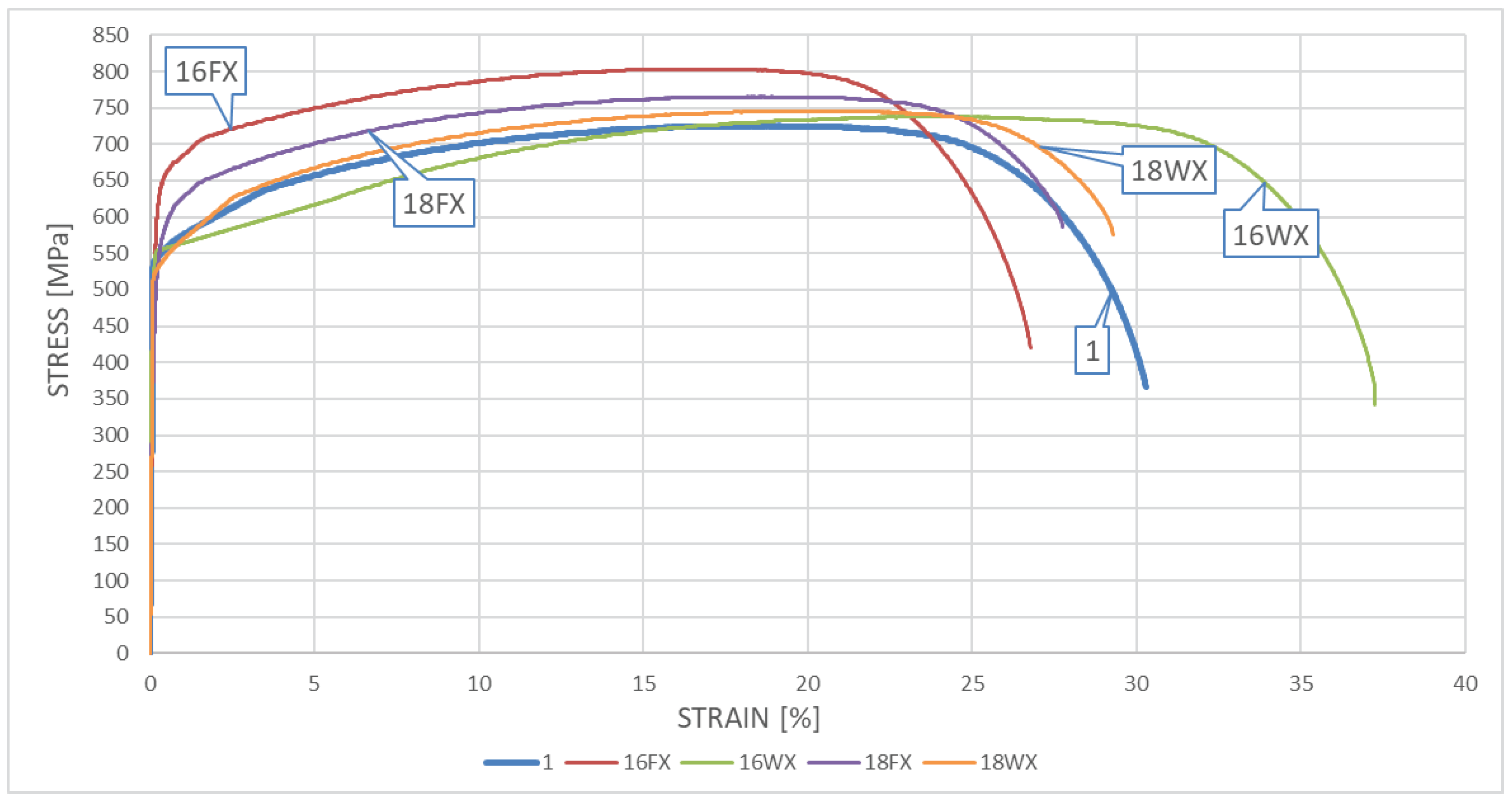
5.2. Results obtained for the DSS 22% Cr X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel
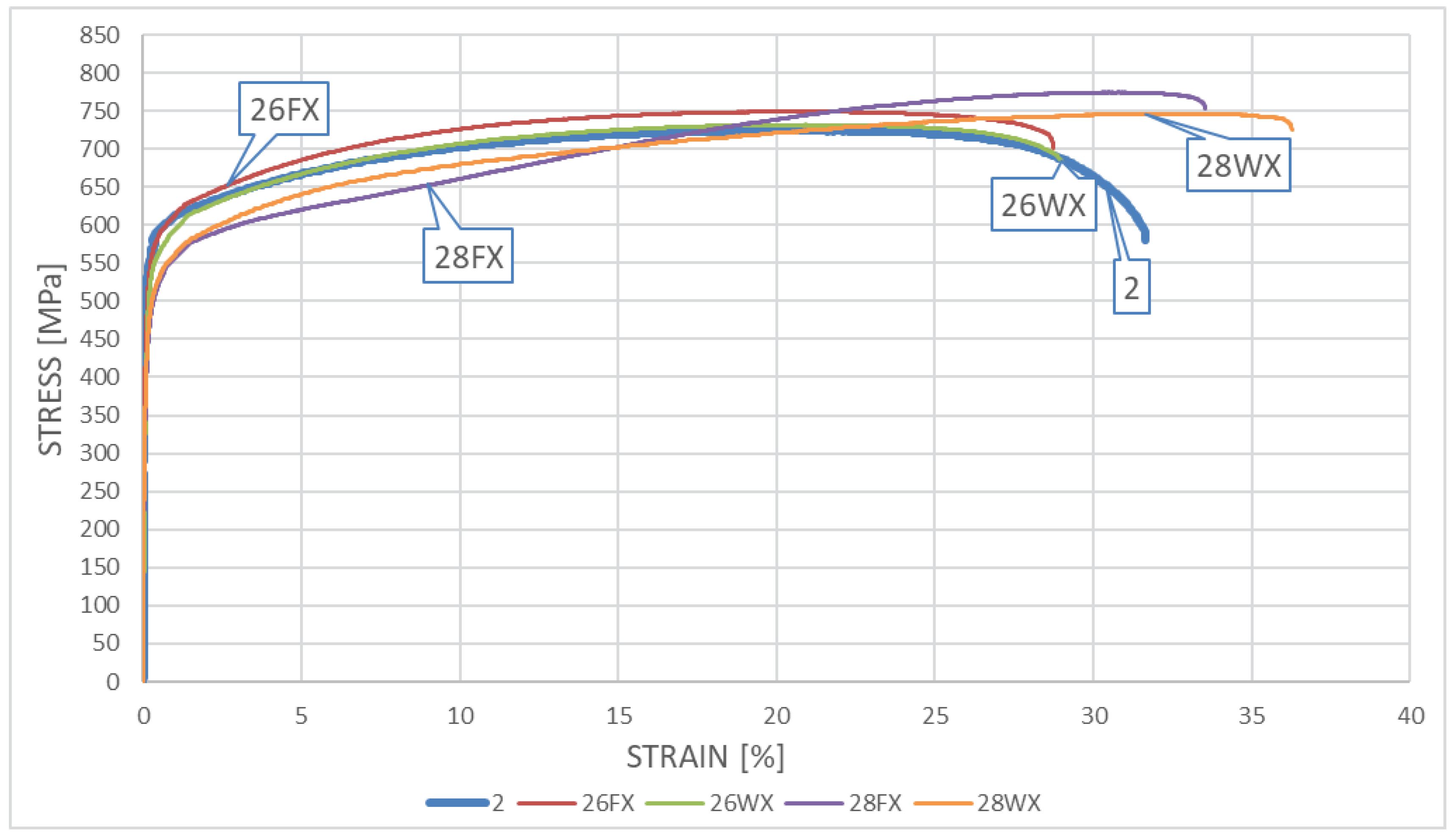
The resultant
σ–
ε curves obtained on samples made of
X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel cooled down after surviving a simulated fire incident are depicted in
Figure 8 – for samples subjected to the simulated “short” fire and in
Figure 9 – for samples subjected to the simulated “long” fire.
One may easily observe on presented graphs, that after surviving a “short” fire the X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel cooled slowly in the furnace exhibits significant strengthening. This phenomenon may be particularly visible on the samples subjected to heating at the temperature of 600oC (the sample 16FX). It has to be noted however, that this strengthening of material, related to partial hardening, is accompanied by simultaneous and quite significant reduction in ductility. This ductility proved to be substantially higher when the sample heated following the same heating program has been cooled down rapidly in water mist (the sample testing scenario denoted as 16WX). On one hand, the sample heating was to low to initiate in the material precipitation of the deleterious phases related to the 800oC brittleness zone, while on the other hand, at sufficiently high speed of cooling, the transition time through the 475oC brittleness zone was relatively short. Therefore, under those conditions, high ductility was not accompanied by simultaneous strengthening of the material, as it cooled down too fast to harden. One may observe here even slight post-fire weakening of the material, if this conclusion is related to lower values of tensile stresses and relatively low magnitude of strains (sample 16WX).
Figure 8.
The σ-ε relationship obtained on samples made of X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel – a “short” fire scenario.
Figure 8.
The σ-ε relationship obtained on samples made of X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel – a “short” fire scenario.
The testing scenario related to heating the steel at 800oC yielded qualitatively different results. Under this scenario the material cooling method selected seemed to have significantly smaller effect. One may compare here the graphs identified as 18FX and 18WX. Ductility of tested steel determined after fire in general remained the same as before. The material strengthening observed post-fire proved to be quantitatively insignificant as well. It seems, that the qualitative differences observed here with respect to the same steel heated for the same “short” time, but at a lower temperature (only 600oC), may be attributed to the hot material entering in this testing scenario the area of influence of 800oC brittleness zone. However, due to the fact that the material remained at this temperature for a relatively “short” time, this influence, albeit important, did not leave any meaningful traces of permanent character.
Figure 9.
The σ-ε relationship obtained on samples made of X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel – a “long” fire scenario.
Figure 9.
The σ-ε relationship obtained on samples made of X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel – a “long” fire scenario.
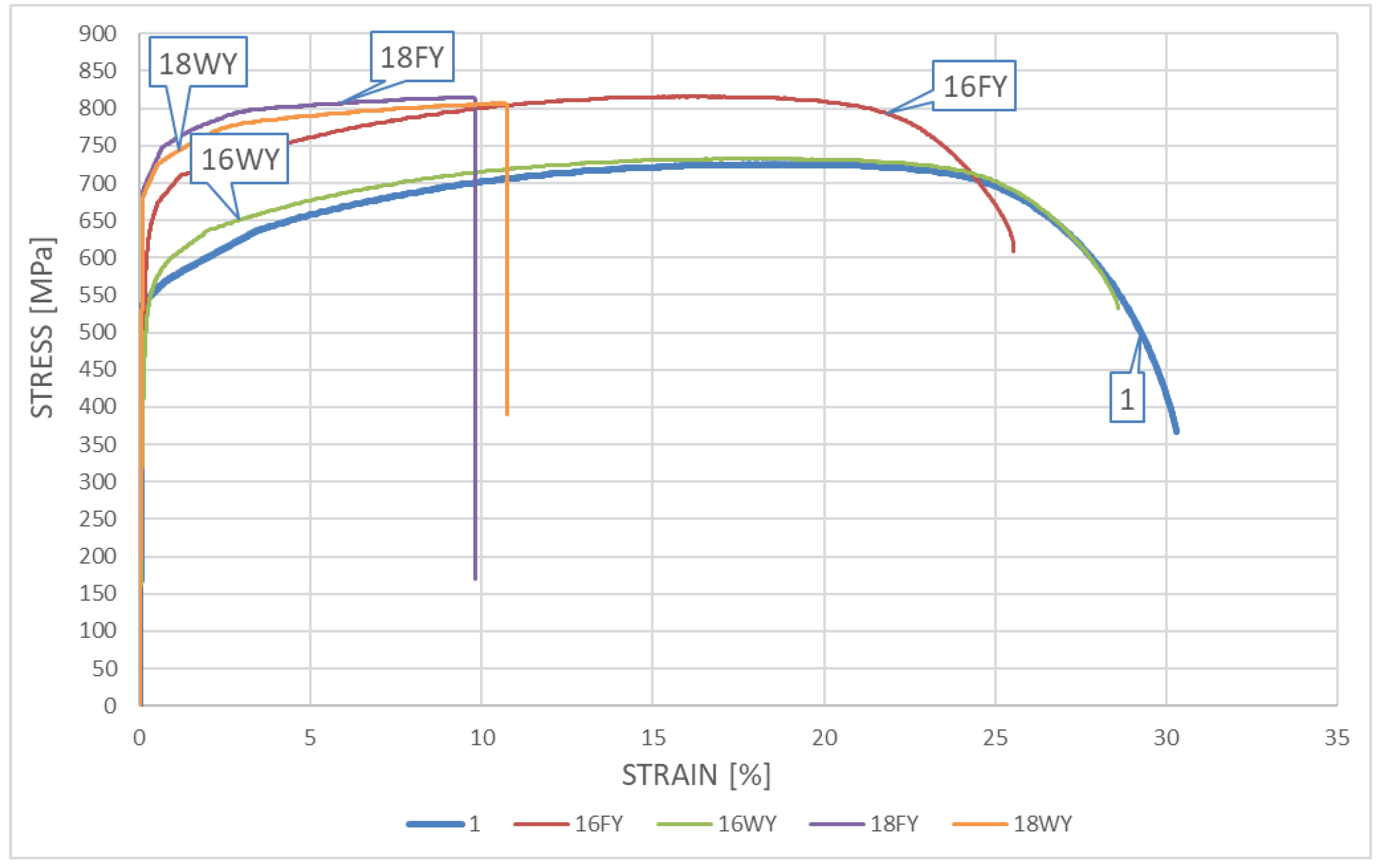
The relationships obtained during testing the influence of “long” fire on this steel grade are of similar character. Under each of the scenarios considered in detail here the tested steel hardened substantially. The hardening was significantly more pronounced, than the one observed on samples subjected to “short” fire. So long heating time proved to be the key quantitative difference, as it resulted in heavily expressed 800oC brittleness phenomenon. This phenomenon resulted in significant hardening of tested steel but at the same time disqualified it from extended service after surviving a fire incident. This is visible on graphs identified as 18FY and 18WY. This type of threat was not revealed during the simulation of “short” fire, as the one hour long heating time was too short to realize precipitation of deleterious precipitates related to the 800oC brittleness zone in amounts capable of affecting the properties of tested material. The higher post-fire ductility observed on samples tested following the 16WY scenario with respect to analogous ductility observed on samples tested following the 16FY scenario, associated with less pronounced hardening of tested material may be attributed to faster transition of the cooled sample through the 475oC brittleness zone.
Detailed juxtaposition of experimentally determined material parameters describing post-fire mechanical properties of
X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel is listed in the
Table 2, where:
- -
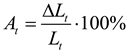
- denotes relative elongation of the sample, measured with respect to its total length
Lt (
Figure 2),
- -
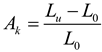
- denotes relative elongation of the initial measurement base, measured on the broken sample (
Figure 2).
Table 2.
Post-fire mechanical properties of the X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel determined during static tensile test.
Table 2.
Post-fire mechanical properties of the X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel determined during static tensile test.
| Sample identification |
R0.2 [MPa] |
Rm [MPa] |
At [%] |
Ak [%] |
| 1 |
537 |
726 |
30.3 |
34.1 |
| 16FX |
607 |
803 |
26.8 |
32.8 |
| 16WX |
533 |
737 |
37.3 |
37.8 |
| 18FX |
506 |
766 |
27.8 |
30.6 |
| 18WX |
520 |
746 |
29.3 |
32.8 |
| 16FY |
604 |
816 |
25.6 |
29.3 |
| 16WY |
521 |
735 |
28.6 |
34.3 |
| 18FY |
689 |
815 |
9.8 |
5.3 |
| 18WY |
681 |
805 |
10.8 |
5.6 |
Due to the destruction mode of samples made of this steel grade, the cross-sectional area after breaking (Su) could not be measured, and therefore it was impossible to determine the reduction in the area of cross-section Z [%].
5.3. Results obtained for the LDSS X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel
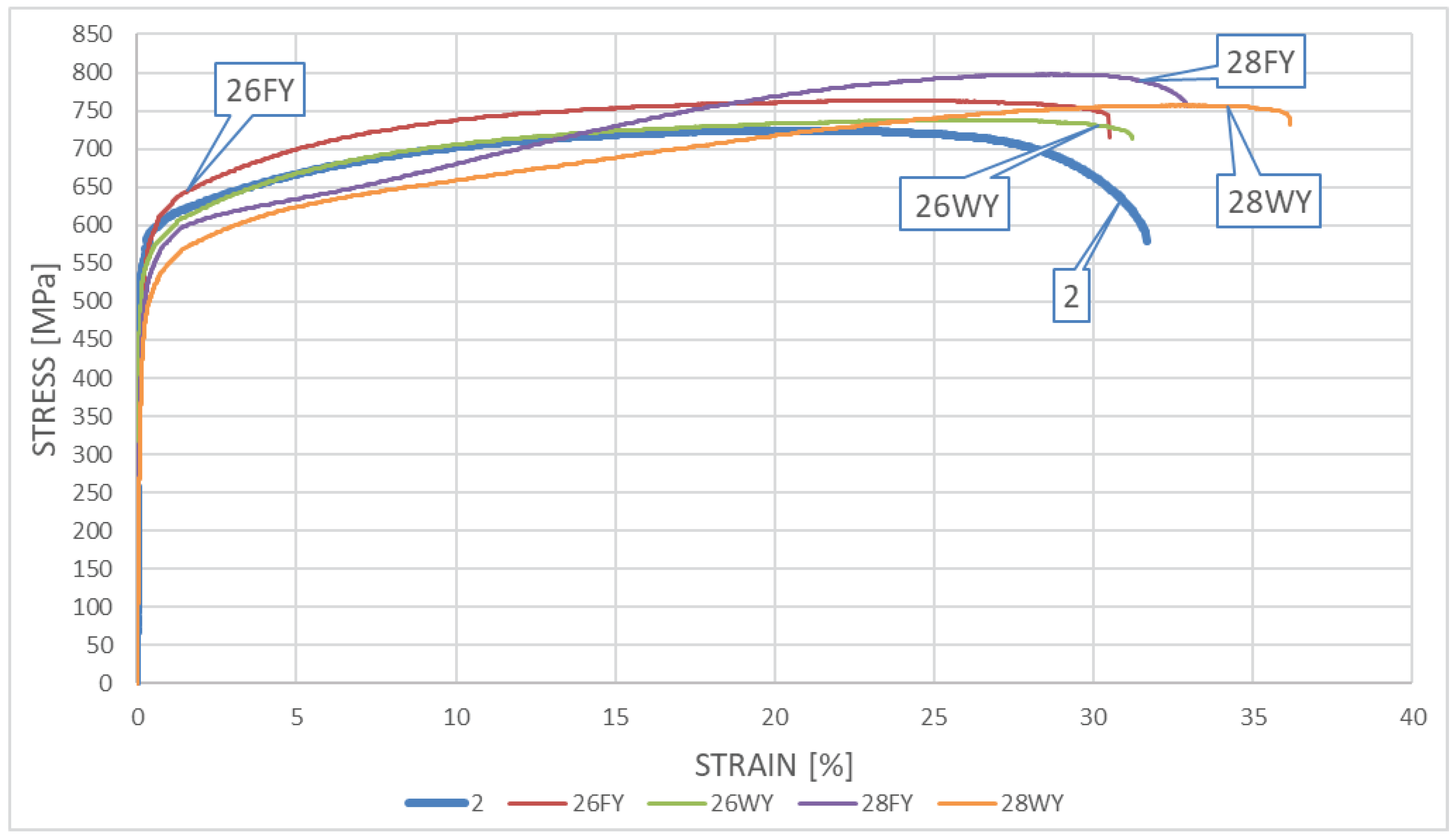
Appropriate
σ–ε relationships, obtained during the tests on samples subjected to heating followed by cooling and made of
X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel are depicted in
Figure 10 – relating to the “short” fire scenario and in
Figure 11 – relating to the “long” fire scenario.
Detailed analysis of both these graphs indicates relatively small influence of the simulated fire action on mechanical properties of the tested material determined experimentally post-fire. Both material strength and ductility in general seem to remain unaffected by the fire action regardless of fire duration applied (“short” fire versus “long” one). The quantitative differences observed seem to be negligible from the point of view of a potential designer striving to keep the analysed material in service after a fire incident, as these changes do not affect the capability of the material to safely resist the loads applied to it. It does not seem to be important, how the sample was cooled after surviving a fire incident, the temperature at which the sample has been kept, or for how long it has been kept at such temperature. One may even dare to say, that under several of the testing scenarios followed, the post-fire mechanical properties of the tested material slightly improved when compared against the same properties determined on the samples in “as manufactured” condition, i.e. not affected by the simulated fire action.
In general, the weak influence of fire incident duration and intensity on the registered post-fire strength and ductility clearly distinguishes the LDSS steel from the DSS 22% Cr steel described above. This is a consequence of a shift to the right on the TTT (Time – Temperature – Transformation) graph of the temperature range related to the 800oC brittleness. Thus, from the practical point of view, application of the LDSS steel seems to be safer when compared against the SDSS steel, if only the risk of prior exposure to fire should be considered.
Detailed juxtaposition of experimentally determined material parameters describing post-fire mechanical properties of
X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel is listed in the
Table 3. The sample destruction mode, analogous to the one observed on samples made of
X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel, precluded the measurement of cross-section area after breaking. As a result the value of parameter
Z [%], identifying the degree of sample necking, could not be determined.
6. Quantification of post-fire recovery coefficients observed on strength and ductility of tested steels
The coefficients quantifying permanent change in given quantity determined on the cooled material after a fire episode when compared against its initial value characterizing considered material before a simulated fire exposure will constitute an a posteriori recovery measure of strength and ductility observed on stainless steels tested here. Therefore the following quotients, in the professional bibliography identified as
retention factors referring to, respectively:
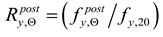
– the yield limit,
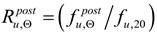
– the ultimate tensile strength,
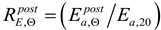
– the linear modulus of elasticity and
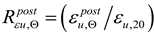
– the limit strain of tested steel sample resulting in fracture will be used here. Detailed values of these factors obtained during the tests reported here are listed in
Table 4 and
Table 5, separately for each steel grade tested. These results are also shown in
Figure 12a–d for the
X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel and below in
Figure 13a–d for the
X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel, with each testing result attributed to testing scenario indicated by a symbol explained in detail in the chapter 5.1 of this paper. The graphs mentioned here depict retention factors obtained experimentally in our research, related to their values recommended for practical application, juxtaposed in papers [
35,
36] for steels of duplex two-phase internal structure as a result of research by Molkens and his team. For
X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel, belonging to the LDSS group, this data, presented in
Figure 13a-13d has been completed by alternative recommendations originating in [
29], as these recommendations have been calibrated taking into account the specificity of this material. It has to be underlined, however, that all these values mentioned above and recommended for practical application are interpreted as appropriate quantiles of material properties interpreted as random variables. Thus the probability of their actual underestimation, accepted by the user of a given building that is to be used after a fire, is set at an intentionally low level.
The yield limit of steel
fy is understood on these graphs as a conventional value, listed at the
R0.2 stress level. The value of limit strain
εu has been determined based on the measured elongation
At listed in detail in
Table 2 and
Table 3, to preserve the compliance with scale used on horizontal axis in Figure 8-11.
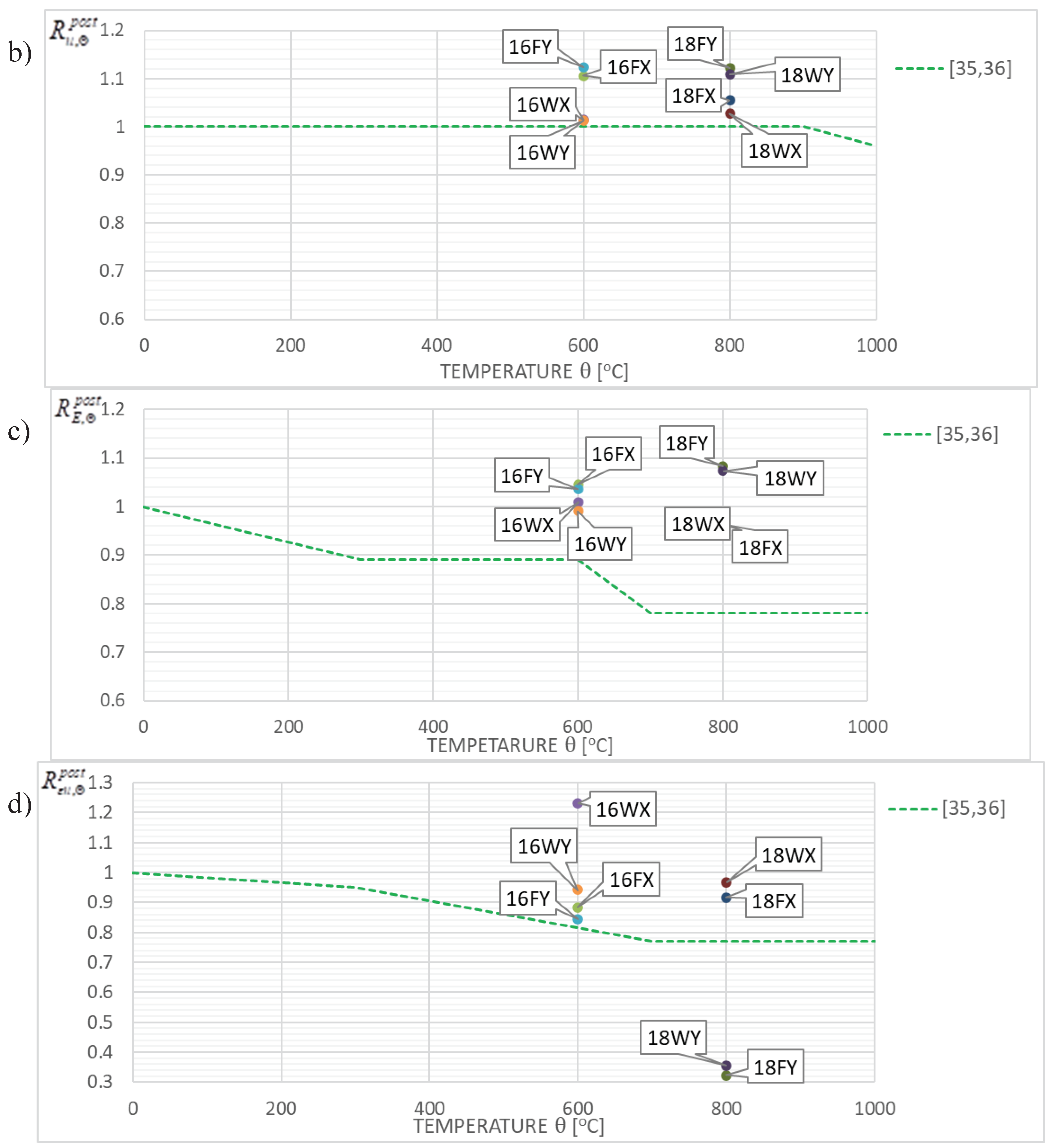
Figure 12.
Post-fire strength and ductility retention factors obtained during tests on
X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 stainless steel grade juxtaposed with their values recommended in [
35,
36].
Figure 12.
Post-fire strength and ductility retention factors obtained during tests on
X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 stainless steel grade juxtaposed with their values recommended in [
35,
36].
Figure 13.
Post fire strength and ductility retention factors obtained during tests on
X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 stainless steel grade juxtaposed with their values recommended in [
29] as well as in [
35,
36].
Figure 13.
Post fire strength and ductility retention factors obtained during tests on
X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 stainless steel grade juxtaposed with their values recommended in [
29] as well as in [
35,
36].
The results of research reported here seem, to a large extent, positively conform to the recommendations contained in papers [
35,
36], as they are located in general on safe side when compared against the bottom limit values contained therein. This remark pertains not only to the post-fire strength of tested steel but also to its post-fire ductility. A significantly reduced capacity for plastic strain exhibited by a sample previously heated for a sufficiently long time at the temperature of 800
oC, regardless of the cooling mode applied (as shown for samples denoted as 18FY and 18WY in
Figure 12d, and, independently, in
Figure 9) seems to be a notable exception here. Such behavior, due to the inherent risk of brittle failure unequivocally excludes the capacity for extended use of this steel grade and in particular for safe load-bearing service after a fire. It is clearly visible, that in many fire development scenarios, which may occur in real life, the tested steel does not fully recover its strength after surviving a fire incident followed by effective cooling. However, in many other scenarios mechanical properties of this steel visibly improve, and this may justify the absence of recommendation to apply an appropriate reduction in limit tensile strength value and an assumption of
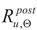
as depicted in
Figure 12b and 13b. In this context the recommendation contained in [
35,
36] pertaining to the reduction in the value of linear elasticity coefficient (
Figure 12c and 13c) seems to be very safe as well.
However, our research reported here did not confirm so clear improvement in the post-fire ductility exhibited by the
X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel belonging to the LDSS group and effectively cooled after a simulated fire exposure at 800
oC, as the authors of paper [
29] (
Figure 13c) would like to see.
An alternative approach to describe the dependence of post-fire steel mechanical properties reduction factor on the maximum temperature at which the steel had been heated has been proposed in paper [
36]. The reduction of
i-th property in this approach is still measured by the retention coefficient
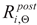
, but this time it is interpreted as a product of the code reduction coefficient
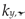
,
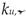
and
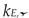
respectively, determined as for the fire conditions based on the Appendix C to the code [
37], and a corresponding recovery factor
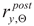
,
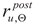
and
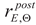
, specified for post-fire conditions. The recovery factors
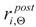
in this method are determined as a quotient of
i-th value determined on a sample cooled after fire and appropriately reduced value of the same property determined at given heating time under assumption of fire scenario. Therefore, for example
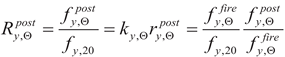
. Juxtaposition of recovery factors obtained during research presented here accompanied by the information on sample heating and cooling scenarios followed during the tests is presented in
Table 6 and
Table 7.
7. Concluding remarks
The research conducted by us has shown quite significant differences in post-fire mechanical properties exhibited by the stainless steel grades compared. In spite of the fact, that the X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel, belonging to the LDSS class due to its intentionally selected chemical composition, is usually treated as a cheaper substitute of the X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel belonging to the DSS 22% Cr class, it proved to be more resistant in the context of post-fire brittleness phenomenon. A risk of this type is, for stainless steels exhibiting two-phase austenitic-ferritic microstructure of duplex type, particularly important. This is usually associated with the potential capacity to reveal harmful precipitates in the structure of the material, negatively affecting its strength and ductility. This precipitation process usually intensifies in two temperature ranges, at high temperature – the so called 800oC brittleness, and at lower temperature – the so called 475oC brittleness, respectively. The extent to which passing through both these ranges would permanently weaken given steel grade during cooling process and persist after the steel attained the ambient temperature depends mostly on the time spent passing through both these ranges. Therefore rapid cooling of tested samples in water mist, significantly speeding up the cooling process, usually proves to be more advantageous, when compared against traditional slow cooling in the muffle furnace, modeling self-extinguishing of the fire. However, overly rapid cooling may result in local hardening of the material. This will result in strengthening, but at the expense of substantial increase in susceptibility to brittle failure.
It has to be underlined, that during the research reported here the 800oC brittleness zone was reached only when following the scenarios, where the tested samples were heated at the temperature enabling austenitic transformation. When following the “short” fire scenario the samples were kept at this temperature for a time too short to fully reveal the deleterious phenomena related to the 800oC brittleness. Only after this time has been extended to 10 hours, as in the “long” fire scenario, it was possible to observe full scale results of the coincidence of both phenomena described above.
Of all testing scenarios applied during our research, only those denoted as 18FY and 18WY resulted in material state after simulated fire excluding its capacity to safely resist the loads applied. Let us note, however, that under those scenarios the cooling mode applied proved to be unimportant. The full scale brittleness revealed itself in those cases as a direct result of heating to sufficiently high temperature, initiating austenitic transformation in its internal structure, followed by keeping the hot material at this temperature for a time long enough to fully reveal the deleterious results of 800oC brittleness phenomenon.
Both the retention factor values
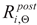
, listed in this paper in the
Table 4 and
Table 5, as well as the correlated values of recovery factors
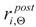
, listed here in the
Table 6 and
Table 7 allow the potential designer, deciding whether to further use a given steel grade to safely support the loads applied to it after fire, the opportunity to assess to what extent this steel grade retained its initial strength and ductility under those circumstances. Of course, the values assigned to recovery factors in this approach are substantially higher than those assigned to retention factors, as the former refer to material properties significantly deteriorated in fire temperature, instead of those characterizing it prior to fire incident and thus not subject to reduction.
Detailed analysis of these factors determined during our experiments leads to the conclusion, that for both steel grades tested the ultimate strength
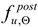
determined after simulated fire, in each of tested simulated fire scenario episodes was not only fully preserved, but even slightly increased. This conclusion does not hold in the case of conventional yield limit
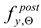
, but the relative reduction of this value, as determined during the experiment, does not seem to be computationally relevant. Let us note, however, that when this evaluation criterion is applied, the degree to which it is permanently reduced, determined on the material cooled after surviving an a priori fire incident, seems to be more pronounced when a steel grade belonging to the LDSS is considered.
In general, the
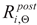
retention factor values close to 1.0 obtained during our experiments on both steel grades indicate that the possible further use of these steel grades after fire is restricted by a qualitative understanding of the possible risk of full scale brittleness effects being revealed in the material, as the risk of brittle failure seems to constitute the critical factor here. As shown above, such critical scenario has been identified and discussed. The value of
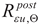
related to this scenario, indicates that only 32-36% of the initial material ductility has been recovered (
Table 4). Interestingly, as mentioned earlier, this type of threat was not identified for steel classified as LDSS (
Table 5) in the fire scenarios analyzed.
Figure 12 and
Figure 13 included in this paper confirm, that the recommendations presented in papers [
35,
36] and interpreted as appropriate quantiles of particular values treated as random variables have been calibrated generally in a safe way, though, in certain cases in a somewhat risky manner. The proposals for such calibrations found in [
29] seem not to be confirmed in the view of our research. This is visible in particular in
Figure 13d.
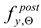 and ultimate strength limit
and ultimate strength limit 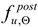 exhibited by duplex steels after simulated fire incident and selected for detailed analysis has been conducted on the strength testing machine WDW-300E, capable of generating maximum tensile force of 300 kN (Figure 1). The lower index Θ denotes here an earlier action of fire temperature on the tested specimen, while the upper index denotes that indicated quantity has been determined on the sample effectively cooled after surviving a simulated fire incident. The tested “fivefold" samples of normalized shape and dimensions [33] (Figure 2), have been cut from hot rolled steel plates.
exhibited by duplex steels after simulated fire incident and selected for detailed analysis has been conducted on the strength testing machine WDW-300E, capable of generating maximum tensile force of 300 kN (Figure 1). The lower index Θ denotes here an earlier action of fire temperature on the tested specimen, while the upper index denotes that indicated quantity has been determined on the sample effectively cooled after surviving a simulated fire incident. The tested “fivefold" samples of normalized shape and dimensions [33] (Figure 2), have been cut from hot rolled steel plates.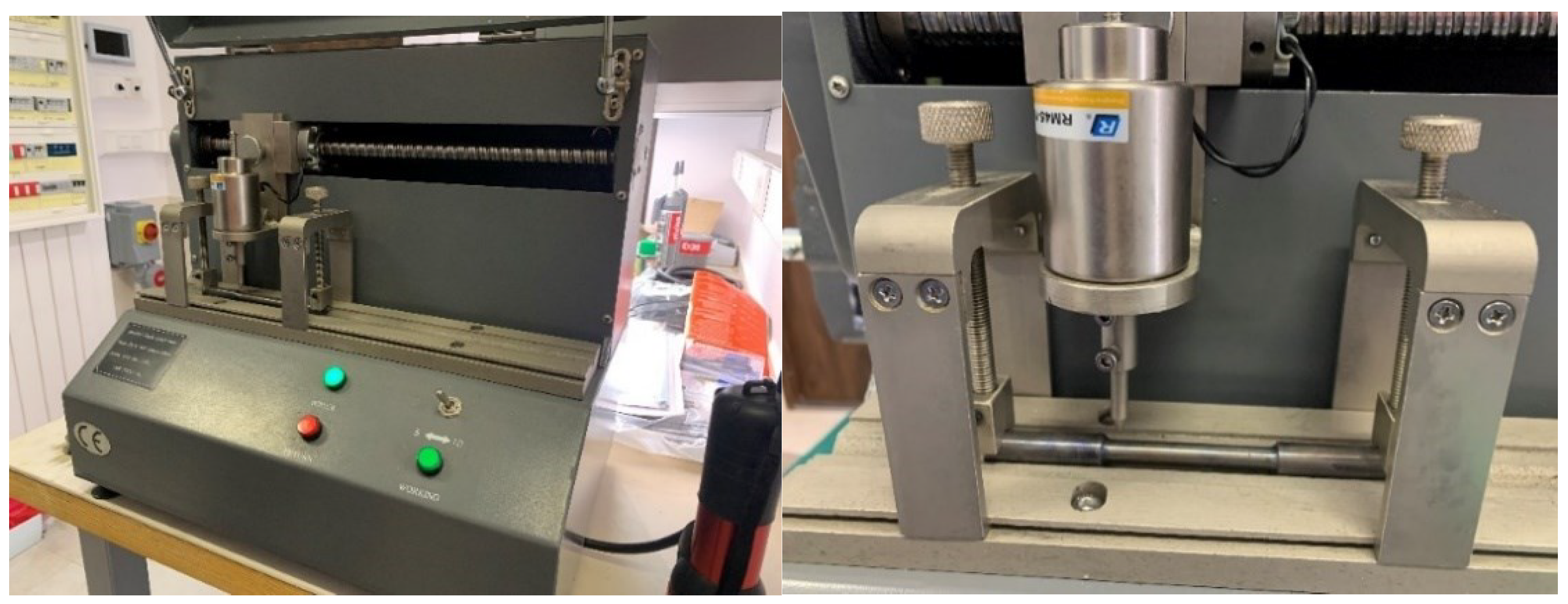

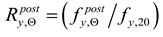 – the yield limit,
– the yield limit, 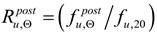 – the ultimate tensile strength,
– the ultimate tensile strength, 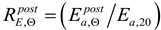 – the linear modulus of elasticity and
– the linear modulus of elasticity and 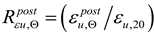 – the limit strain of tested steel sample resulting in fracture will be used here. Detailed values of these factors obtained during the tests reported here are listed in Table 4 and Table 5, separately for each steel grade tested. These results are also shown in Figure 12a–d for the X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel and below in Figure 13a–d for the X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel, with each testing result attributed to testing scenario indicated by a symbol explained in detail in the chapter 5.1 of this paper. The graphs mentioned here depict retention factors obtained experimentally in our research, related to their values recommended for practical application, juxtaposed in papers [35,36] for steels of duplex two-phase internal structure as a result of research by Molkens and his team. For X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel, belonging to the LDSS group, this data, presented in Figure 13a-13d has been completed by alternative recommendations originating in [29], as these recommendations have been calibrated taking into account the specificity of this material. It has to be underlined, however, that all these values mentioned above and recommended for practical application are interpreted as appropriate quantiles of material properties interpreted as random variables. Thus the probability of their actual underestimation, accepted by the user of a given building that is to be used after a fire, is set at an intentionally low level.
– the limit strain of tested steel sample resulting in fracture will be used here. Detailed values of these factors obtained during the tests reported here are listed in Table 4 and Table 5, separately for each steel grade tested. These results are also shown in Figure 12a–d for the X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 steel and below in Figure 13a–d for the X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel, with each testing result attributed to testing scenario indicated by a symbol explained in detail in the chapter 5.1 of this paper. The graphs mentioned here depict retention factors obtained experimentally in our research, related to their values recommended for practical application, juxtaposed in papers [35,36] for steels of duplex two-phase internal structure as a result of research by Molkens and his team. For X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 steel, belonging to the LDSS group, this data, presented in Figure 13a-13d has been completed by alternative recommendations originating in [29], as these recommendations have been calibrated taking into account the specificity of this material. It has to be underlined, however, that all these values mentioned above and recommended for practical application are interpreted as appropriate quantiles of material properties interpreted as random variables. Thus the probability of their actual underestimation, accepted by the user of a given building that is to be used after a fire, is set at an intentionally low level.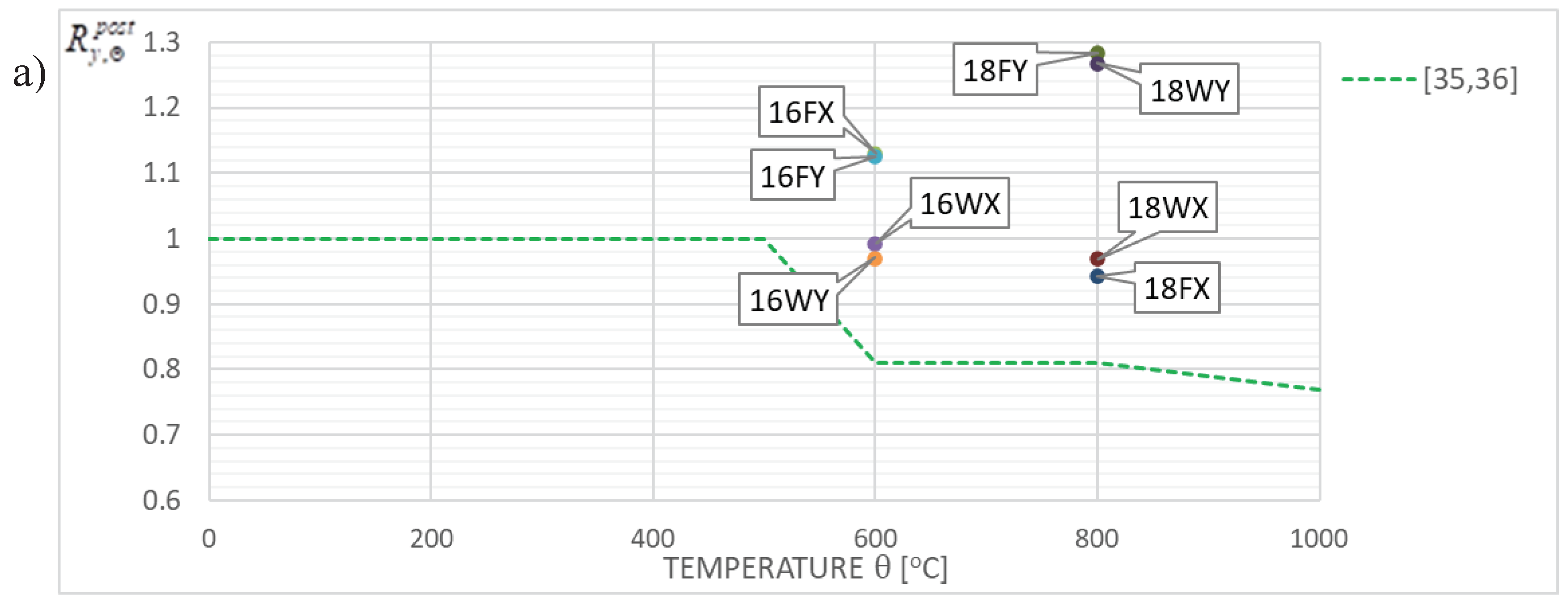


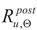 as depicted in Figure 12b and 13b. In this context the recommendation contained in [35,36] pertaining to the reduction in the value of linear elasticity coefficient (Figure 12c and 13c) seems to be very safe as well.
as depicted in Figure 12b and 13b. In this context the recommendation contained in [35,36] pertaining to the reduction in the value of linear elasticity coefficient (Figure 12c and 13c) seems to be very safe as well.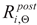 , but this time it is interpreted as a product of the code reduction coefficient
, but this time it is interpreted as a product of the code reduction coefficient 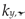 ,
, 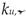 and
and 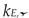 respectively, determined as for the fire conditions based on the Appendix C to the code [37], and a corresponding recovery factor
respectively, determined as for the fire conditions based on the Appendix C to the code [37], and a corresponding recovery factor 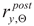 ,
, 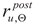 and
and 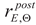 , specified for post-fire conditions. The recovery factors
, specified for post-fire conditions. The recovery factors 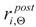 in this method are determined as a quotient of i-th value determined on a sample cooled after fire and appropriately reduced value of the same property determined at given heating time under assumption of fire scenario. Therefore, for example
in this method are determined as a quotient of i-th value determined on a sample cooled after fire and appropriately reduced value of the same property determined at given heating time under assumption of fire scenario. Therefore, for example 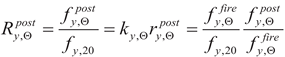 . Juxtaposition of recovery factors obtained during research presented here accompanied by the information on sample heating and cooling scenarios followed during the tests is presented in Table 6 and Table 7.
. Juxtaposition of recovery factors obtained during research presented here accompanied by the information on sample heating and cooling scenarios followed during the tests is presented in Table 6 and Table 7.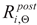 , listed in this paper in the Table 4 and Table 5, as well as the correlated values of recovery factors
, listed in this paper in the Table 4 and Table 5, as well as the correlated values of recovery factors 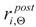 , listed here in the Table 6 and Table 7 allow the potential designer, deciding whether to further use a given steel grade to safely support the loads applied to it after fire, the opportunity to assess to what extent this steel grade retained its initial strength and ductility under those circumstances. Of course, the values assigned to recovery factors in this approach are substantially higher than those assigned to retention factors, as the former refer to material properties significantly deteriorated in fire temperature, instead of those characterizing it prior to fire incident and thus not subject to reduction.
, listed here in the Table 6 and Table 7 allow the potential designer, deciding whether to further use a given steel grade to safely support the loads applied to it after fire, the opportunity to assess to what extent this steel grade retained its initial strength and ductility under those circumstances. Of course, the values assigned to recovery factors in this approach are substantially higher than those assigned to retention factors, as the former refer to material properties significantly deteriorated in fire temperature, instead of those characterizing it prior to fire incident and thus not subject to reduction.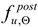 determined after simulated fire, in each of tested simulated fire scenario episodes was not only fully preserved, but even slightly increased. This conclusion does not hold in the case of conventional yield limit
determined after simulated fire, in each of tested simulated fire scenario episodes was not only fully preserved, but even slightly increased. This conclusion does not hold in the case of conventional yield limit 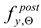 , but the relative reduction of this value, as determined during the experiment, does not seem to be computationally relevant. Let us note, however, that when this evaluation criterion is applied, the degree to which it is permanently reduced, determined on the material cooled after surviving an a priori fire incident, seems to be more pronounced when a steel grade belonging to the LDSS is considered.
, but the relative reduction of this value, as determined during the experiment, does not seem to be computationally relevant. Let us note, however, that when this evaluation criterion is applied, the degree to which it is permanently reduced, determined on the material cooled after surviving an a priori fire incident, seems to be more pronounced when a steel grade belonging to the LDSS is considered.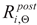 retention factor values close to 1.0 obtained during our experiments on both steel grades indicate that the possible further use of these steel grades after fire is restricted by a qualitative understanding of the possible risk of full scale brittleness effects being revealed in the material, as the risk of brittle failure seems to constitute the critical factor here. As shown above, such critical scenario has been identified and discussed. The value of
retention factor values close to 1.0 obtained during our experiments on both steel grades indicate that the possible further use of these steel grades after fire is restricted by a qualitative understanding of the possible risk of full scale brittleness effects being revealed in the material, as the risk of brittle failure seems to constitute the critical factor here. As shown above, such critical scenario has been identified and discussed. The value of 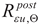 related to this scenario, indicates that only 32-36% of the initial material ductility has been recovered (Table 4). Interestingly, as mentioned earlier, this type of threat was not identified for steel classified as LDSS (Table 5) in the fire scenarios analyzed.
related to this scenario, indicates that only 32-36% of the initial material ductility has been recovered (Table 4). Interestingly, as mentioned earlier, this type of threat was not identified for steel classified as LDSS (Table 5) in the fire scenarios analyzed.