Submitted:
04 December 2023
Posted:
05 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
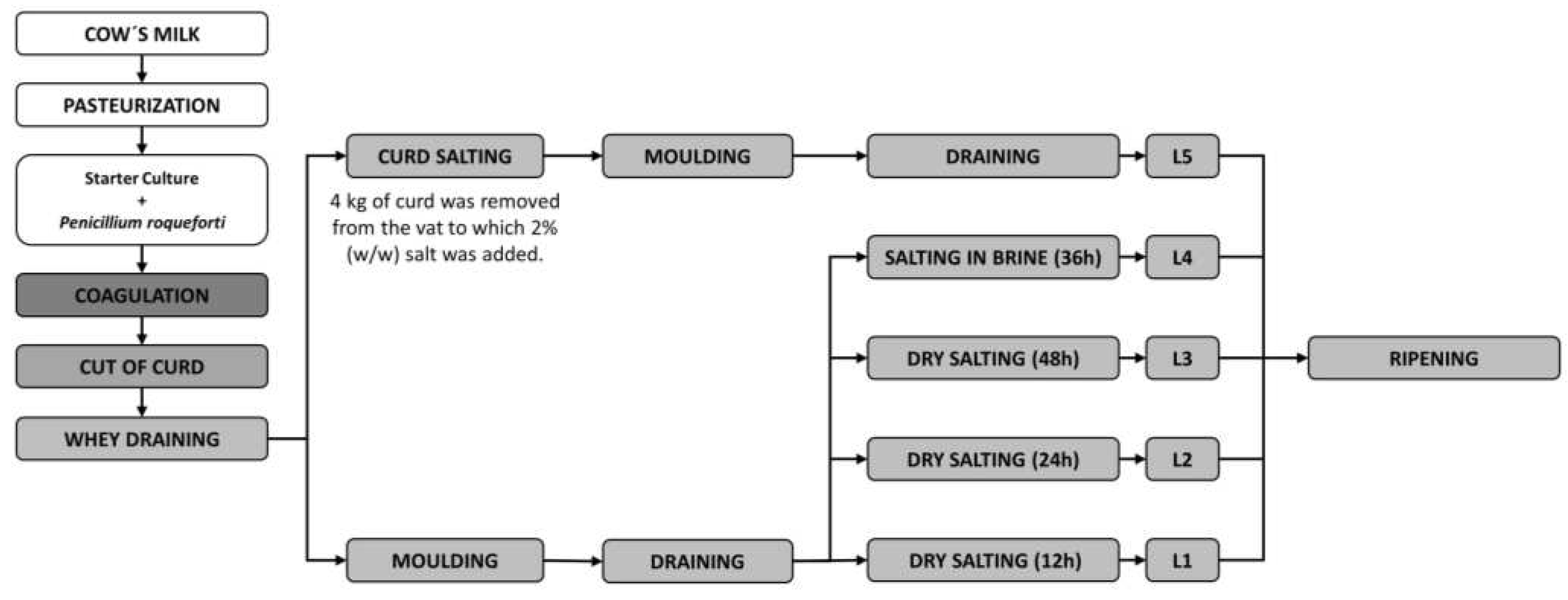
2.1. Cheese production
2.2. Chemical and physico-chemical analysis
2.3. Measurement of the colour of cheeses
2.4. Texture profile analysis
2.5. Sensory analysis
2.6. Statistical analysis
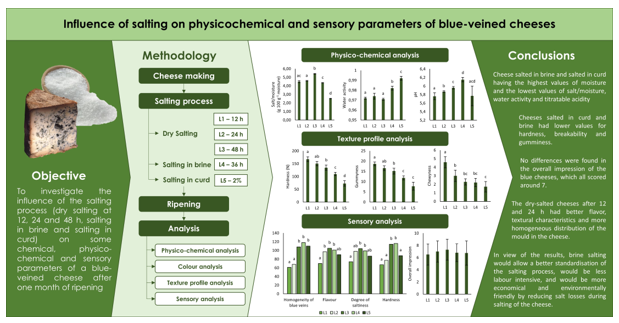
3. Results
3.1. Chemical and physico-chemical parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guinee, T.P.; Fox, F.P. Salt in cheese: physical, chemical and biological aspects. In Cheese: chemistry, physics and microbiology, Fox, P.F; Guinee, T.P., Eds. Elsevier Academic Press, London, 2004, pp. 207-259. [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F. Uniacke-Lowe, T., McSweeney, P.L.H., O'Mahony, J.A. Chemistry and biochemistry of cheese. In Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; Fox, P.F., Uniacke-Lowe, T., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; O’Mahony, J.A., Cham: Springer, 2015; pp. 499–546. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, A.E.; Johnson, E.A.; Nelson, J.H. Survival of Listeria monocytogenes in commercial cheese brines. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 199982, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugampoza, D.; Gkatzionis, K.; Linforth, R. S. T.; Dodd, C. E. R. Acid production, growth kinetics and aroma profiles of Lactobacillus flora from Stilton cheese. Food Chem. 2019, 28, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Díaz, T.M.; Alegría, Á.; Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; Combarros-Fuertes, P.; Fresno, J.M.; Santos, J.A.; Flórez, A.B.; Mayo, B. Blue Cheeses: Microbiology and Its Role in the Sensory Characteristics. Dairy 2023, 4, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, B.; Franco, I.; Fresno, J.M.; Bernardo, A.; Carballo, J. Picón Bejes-Tresviso blue cheese: an overall biochemical survey throughout the ripening process. Int. Dairy J. 2000, 10, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González de Llano, D.; Ramos, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Montilla, A.; Juárez, M. Microbiological and physicochemical characteristics of Gamonedo blue cheese during ripening. Int. Dairy J. 1992, 2, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diezhandino, I.; Fernández, D.; González, L.; McSweeney, P. L. H.; Fresno, J. M. Microbiological, physico-chemical and proteolytic changes in a Spanish blue cheese during ripening (Valdeón cheese). Food Chem. 2015, 168, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Diaz, T. M.; Santos, J. A.; Gonzalez, C. J.; Moreno, B.; Garcia, M. L. Bacteriological quality of a traditional Spanish blue cheese. Milchwirtschaft 1995, 50, 503–505. [Google Scholar]
- Flórez, A.B.; Mayo, B. Microbial diversity and succession during the manufacture and ripening of traditional, Spanish, blue-veined Cabrales cheese, as determined by PCR-DGGE. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006a, 110, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez, A.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Alonso, L.; Mayo, B. Microbial, chemical and sensorial variables of the Spanish traditional blue-veined Cabrales cheese, as affected by inoculation with comercial Penicillium roqueforti spores. Eur. Food Res Technol. 2006b, 222, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresford, T.; Williams, A. The microbiology of cheese ripening 2004. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology Fox, P.F.¸McSweeney, P.L.H..; Cogan, T.M.; Guinee, T.P. Eds. Elsevier, London, 2004; pp. 287-317.
- Guinee, T. P. Salting and the role of salt in cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2004, 57, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroukhi, I.; Bord, C.; Lavigne, R.; Chassard, Ch.; Mardon, J. Exploring alternative salting methods to reduce sodium content in blue-veined cheeses. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 138, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO (2004). ISO 5534:244: Cheese and processed cheese: Determination of the total solids content. Geneva: International Organization for Standarization.
- AOAC (2000). AOAC 935:43. Salt determination. Washington: Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, USA.
- AOAC (1980a) AOAC 140:22. Hydrogen-ion activity (Ph). Washington: Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, USA.
- AOAC (1980b). AOAC 162:47. Acidity in cheese. Washington: Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, USA.
- Diezhandino, I.; Fernández, D.; Sacristán, N.; Combarros-Fuertes, P.; Prieto, B.; Fresno, J.M. Rheological, textural, colour and sensory characteristics of a Spanish blue cheese (Valdeón cheese). Food Sci.Technol. 2016, 65, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, M.C. Food texture and viscosity: concept and measurement. In Science & Technology books, 2nd ed. 2002; Elsevier; https://doi.org/10.4337/9781781956046.00004. [Google Scholar]
- ISO (2006). ISO 8587. Sensorial analysis. Geneva: International Organization for Standarization.
- Breene W., M; Olson N., F.; Price W., V. Salt absorption by Cheddar cheese curd. J. Dairy Sci. 1965, 48, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, F.P.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Salting of Cheese Curd. In Fundamentals of Cheese Science, 2nd ed; Fox, F.P.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; MacSweeney, P.L.H., Eds. Springer, New York, 2017a, pp. 251-277.
- Sutherland B, J. Control of salt absorption and whey drainage in Cheddar cheese manufacture. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1974, 29, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, P.; Kelly, A.L.; Sheehan, J.J. Structure-function relationships in cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2692–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, A.; Farahat, S.; Farag, A. Ripening changes and quality of recombined milk blue cheese as affected by mould strain and salting method. Food Chem. 1988, 29, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisig, W. The importance of salt in the manufacturing and ripening of cheese. IDF Factsheet, 001/2017-03.
- Van den Tempel, T.; Nielsen, M. Effects of atmospheric conditions, NaCl and pH on growth and interactions between moulds and yeasts related to blue cheese production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 57, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bodega, M.; Mauriz, E.; Gómez, A.; Martín, J. F. Proteolytic activity, mycotoxins and andrastin A in Penicilium roqueforti strains isolated from Cabrales, Valdeón and Bejes-Tresviso local varieties of blue-veined cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 163, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coton, E.; Coton, M.; Hymery, N.; Mounier, J.; Jany, J. L. Penicillium roqueforti: an overview of its genetics, physiology, metabolism and biotechnological applications. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2020, 34, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, T. , Le Piver, M., Perón, A.C., Lieben, P., Lavigne, R., Brunel, S., Rouyere, D., Place, M., Bonnarme, P, Giraud, T., Branca, A., Landaud, S.; Chassard, C. Strong effect of Penicillium roqueforti populations on volatile and metabolic compounds responsable for aromas, flavor and texture in blue cheeses. Int. J. Food Microbiol, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, F.P.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H. (2017b). Biochemistry of cheese ripening. In Fundamentals of Cheese Science, 2nd ed; Fox, F.P.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; MacSweeney, P.L.H., Eds. Springer, New York, 2017b, pp. 391-443.
- Alonso, L.; Juarez, M.; Ramos, M.; Martin-Alvarez, P.J. Effects of changes during ripening and frozen storage on the physicochemical and sensory characteristics of Cabrales cheeses. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1987, 22, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, R.; Burzigotti, M.; Smacchi, E.; Corsetti, A. ; De Angelis, Microbiology and biochemistry of gorgonzola cheese during ripening. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, A.; Ciocia, F.; Beck, T.K.; Lillevang, S.K. , McSweeney, P.L.H. Proteolysis in Danish blue cheese during ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 97, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarmpoutis, I. V. .; McSweeney, P. L. H.; Fox, P. F. Proteolysis in blue veined cheese: An intervarietal study. Irish J. Agric Food Res, 1997; 36, 219–229. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/25562306.
- Saurel, R.; Pajonk, A.; Andrieu, J. Modelling of French Emmental cheese water activity during salting and ripening periods. J. Food Eng. 2004, 63, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, D.K.; Guinee. T.P.; Hou, J.; Wilkinson, M.G. Effects of variation in cheese composition and maturation on water activity in Cheedar cheese during ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 30, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanachkina, P.; MacCarty, C.; Guinee, T. Effect of variying the salt and fat content in Cheedar cheese on aspects of the performance of a comercial starter culture preparation during ripening. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 224, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, M.M. Principais problemas dos queijos. Causas e prevençao. 3nd ed. Setembro Editora Sao Paulo, Brasil, 2017.
- Kneifel, W.; Ulberth, F.; Schaffer, E. Tristimulus color reflectance measurement of milk and dairy products. Lait 1992, 72, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudy, S.; Bilska, A.; Kowalski, R.; Teichert, J. Colour of milk and milk products in CIE Lab space. Med. Weter. 2020, 76, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, B.; Djekic, I.; Miocinovic, J.; Djordjevic, V.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Mörlein, D.; Tomasevic, I. What Is the Color of Milk and Dairy Products and How Is It Measured? Foods 2020, 9, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavia, M.; Guamis, B.; Trujillo, A.; Capellas, M.; Ferragut, V. Changes in microestructural, textural and color characteristics during ripening of Manchego-type cheese by brine vacuum impregnation. Int. Dairy J. 1999, 9, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J. A.; Johnson, M. E.; Horne, D. S. Invited review: Perspectives on the basis of the rheology and texture properties of cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2725–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, L.; Gómez, R.; Fernández-Salguero, J. Sensory characterisctics of ewe milk made with three types of coagulant: Calf rennet, powdered vegetable coagulant and crude aqueous extract from Cyanara cardunculus. J. Food Qual. 2007, 30, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, A. J.; Hansen, C. L.; McMahon, D. J. Effect of salt on structure-function relationships of cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, V.; Mishra, S. Reduced-sodium cheeses: Implications of reducing sodium chloride on cheese quality and safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 733–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, S.; Fresno, M. Effect of the ripening period and intravarietal comparison on chemical, textural and sensorial characteristics of palmero (PDO) goat cheese. Animals, 2021; 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, F.P.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Cheese: Structure, Rheology, and texture. In Fundamentals of Cheese Science, 2nd ed; Fox, F.P.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; MacSweeney, P.L.H., Eds. Springer, New York, 2017c, pp. 475-532.
- Cantor, M.D.; Van der Tempel, T.; Hansen, T.K.; Ardö, Y. Blue cheese. In Cheese Chemistry, physics and microbiology; Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Cogan T.M., Guinee, T.P. Eds, Elsevier, London, 2004, pp. 178-198.
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Moisture (g 100 g-1 cheese) |
41.42a ± 0.87 | 40.07b ± 0.14 | 39.72b ± 0.30 | 45.16c ± 0.33 | 45.60c ± 0.79 |
|
Salt content* (g 100 g-1 cheese) |
1.86a ± 0.02 | 1.84a ± 0.022 | 2.15b ± 0.01 | 1.97c ± 0.01 | 1.15d ± 0.21 |
|
Salt/moisture (g 100 g-1 moisture) |
4.50ac ± 0.12 | 4.59a ± 0.04 | 5.42b ± 0.04 | 4.35c ± 0.04 | 2.51d ± 0.04 |
| aw | 0.972a ± 0.001 | 0.974a ± 0.003 | 0.971a ± 0.001 | 0.982b ± 0.002 | 0.992c ± 0.002 |
|
Titratable acidity (g 100 g-1 total solids) |
2.36a ± 0.07 | 2.26a ± 0.10 | 2.27a ± 0.20 | 1.42b ± 0.12 | 1.71c ± 0.07 |
| pH | 5.76a ± 0.08 | 5.87b ± 0.02 | 5.96c ± 0.03 | 6.15d ± 0.05 | 5.77acd ± 0.23 |
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | 84.52 ± 3.20 | 83.49 ± 3.38 | 83.08 ± 3.90 | 86.30 ± 2.96 | 85.69 ± 3.64 |
| a* | -0.94a ± 1.12 | -0.54a ± 0.98 | -1.08a ± 1.06 | 0.51b ± 0.68 | -0.03ab ± 0.81 |
| b* | 13.66 ± 1.52 | 13.78 ± 1.90 | 13.27 ± 1.21 | 13.95 ± 1.25 | 12.61 ± 1.47 |
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fracturability (N) | 55.23a± 3.25 | 47.10b ± 4.23 | 43.54b ± 2.92 | 25.32c ± 3.07 | 27.02d ± 1.26 |
| Hardness (N) | 167.63a± 9.44 | 150.22ab ± 8.63 | 134.55b ± 9.97 | 109.66c ± 6.95 | 72.9d ± 10.82 |
| Adhesiveness (N·s) | -4.29 ± 1.18 | -3.49 ± 0.83 | -3.78 ± 0.87 | -3.93 ± 1.36 | -5.28 ± 1.44 |
| Cohesiveness | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.1 | 0.11 ± 0.01 |
| Elasticity | 0.25a ± 0.04 | 0.18b ± 0.03 | 0.15b ± 0.01 | 0.19bc ± 0.03 | 0.22c ± 0.02 |
| Gummyness | 18.66a ± 0.90 | 16.53ab ± 1.14 | 15.13b ± 1.41 | 11.78c ± 0.98 | 7.74c ± 1.92 |
| Chewyness | 4.59a ± 0.65 | 2.99b ± 0.67 | 2.28bc ± 0.36 | 2.21bc ± 0.48 | 1.72c ± 0.61 |
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degree of mould development | 71a | 66a | 116b | 106b | 106b |
| Homogeneity of blue veins | 61a | 68a | 108b | 118b | 110b |
| Odour | 92 | 93 | 95 | 93 | 92 |
| Flavour | 70a | 97b | 105b | 101b | 90ab |
| Degree of saltiness | 74a | 98ab | 104b | 99b | 87ab |
| Hardness | 67a | 77a | 114b | 116b | 88a |
| Overall impression | 6.50 ± 1.72 | 7.00 ± 1.74 | 7.30 ± 1,72 | 6.80 ± 1.45 | 6.75 ± 1.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





