1. Introduction
The increasing challenge of age-associated cognitive decline has become a prominent global concern as the population ages. Modifiable lifestyle factors such as nutritional status and physical activity have been recognized as protective factors against cognitive decline. Extensive literature has underscored the link between nutritional status and cognitive decline. Cross-sectional studies from various populations including Canadian, Greek, Singaporean, and Chinese [
1,
2,
3,
4] consistently reported correlation between malnutrition or nutritional risks and higher level of cognitive decline, whereas dietary intake of nutrient-rich foods including tea [
5], egg [
6], fruits, milk, and yogurt [
7,
8], is associated with reduced risks of cognitive decline. Furthermore, intervention studies, implementing diverse dietary patterns, have demonstrated efficacy in attenuating the progression of cognitive deterioration [
9,
10,
11]. Adequate nutrition is proposed to be fundamental for sustaining optimal brain function [
12,
13], whereas deficiencies in essential nutrients contributed to cognitive impairment through affecting essential metabolic activities including enzymatic reactions and neurotrophic factor expressions [
14,
15].
Similarly, physical activity emerges as another pivotal factor significantly impacting cognitive function. Evidence suggests that regular physical exercise corresponds to observable improvements in cognitive function [
11,
16,
17], while physical inactivity is associated with cognitive deficits [
18,
19]. Intervention studies employing physical exercises of various types including aerobic exercises, mind-body exercise, and culturally tailored exercise, have also proven to be effective [
20,
21,
22,
23]. Multifaceted explanations, encompassing improved blood flow, neurogenesis, and the release of neurotrophic factors, have been proposed to underlie this protective effect [
24].
While both nutritional status and physical activity have consistently shown associations with cognitive function, intervention studies examining the impact of both diet and physical activity on cognitive decline has yielded mixed and sometimes inconclusive results [
11,
25,
26]. These outcomes underscore the complexity of the relationship between lifestyle factors and cognitive health and the need to consider the potential modification effects of psycho-social variables. Happiness is increasingly recognized as a crucial factor for health conditions and has been shown to be associated with cognitive function [
27,
28]. Furthermore, demographic factors such as age also showed influences on various aspects of older adult lifestyles [
29,
30].
Importantly, questions also remain regarding the underlying connections of nutrition, physical activity, and cognition. Mounting evidence has indicated a significant positive association between happiness and both physical activity [
31,
32,
33] and cognitive function. However, few studies have explored its associations with nutritional status, while little evidence has shown its potential mediating effects on the link between physical activity and cognition.
Given the previous identified associations among nutritional status, physical activity, happiness [
34], the current study aims to further validate these associations in the context of cognitive function in older adults. Additionally, we seek to explore potential modification effects of happiness and demographic variables such as age, and mediation effects of happiness, in a sample of Chinese community-dwelling older adults.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Settings
The current study is part of a cross-sectional study on Chinese community-dwelling older adults. The cohort recruited a sample of 755 Chinese older adults (44.5% males and 55.5% females) aged over 60 years from multiple communities in Shanghai metropolitan city during 2017. A comprehensive survey covering demographics, happiness, cognition, lifestyle, sleep, nutrition, and social connections was delivered. A total of 150 interviewers, comprising of 40 nursing supervisors from Shanghai Longhua Hospital and 110 interns from Shanghai Shuguang Hospital assisted with interview procedures. For older adults who were not capable of completing the survey independently, the interviewers verbally guided them through each item and recorded their results. The survey was completed by 709 participants, with 699 left in the present study after excluding 10 individuals who had no OASR record. Informed consent was obtained from all participants and institutional review board approval was obtained from the ethics committees for research at both Shanghai Shuguang Hospital and Shanghai Longhua Hospital. All research was performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Nutritional Status
Nutritional status was evaluated using the Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA®), a screening tool to assess nutritional status in older adults [
35]. The instrument is composed of 18 questions, which is grouped into 4 sub-domains: anthropometric measurements, global assessment, dietary questionnaire, and subjective assessment [
36]. The sum of the instrument score ranges from 0 to 30, with lower score indicating risks of malnutrition. For linear regression analysis, the score was categorized into 3 groups using recommended thresholds: 1 = malnutrition (MNA < 17); 2 = at risk of malnutrition (17 ≤ MNA < 23.5); 3 = normal nutritional status (MNA ≥ 24). MNA was reported to show an internal consistency of 0.83, and a test–retest reliability of 0.89 [
37]. Reliability of the Chinese version of the MNA was 0.698 [
38]. In the present study, the reliability α was 0.633.
2.2.2. Physical Activity
Physical activity was measured by the General Information Survey through the following question: “Do you often participate in physical exercise (such as Tai chi, jogging, walking, public square dancing, ball sports, biking, etc.)? 1 = no, 2 = yes.”
2.2.3. Cognitive Function
We assessed cognitive decline using the memory/cognition problems syndrome scale of the self-report Older Adult Self-Report (OASR) [
39]. The OASR is a self-administered instrument examining various domains of older adults including adaptive functioning, personal strengths, behavioral, emotional, and social problems [
39]. OASR has been proven to be valid for Chinese-speaking older adults [
40,
41], with the cognitive subscale being previously reported in the same population [
42]. The cognitive decline scale was derived from 9 items, asking about cognitive issues including “cannot concentrate” and “forget names”. All items were rated on a three-point scale (0 = not true, 1 = sometimes true, and 2 = often true). The total score was calculated by summing 9 items and normalizing under the T-score format (mean = 50, SD = 10). Higher scores indicated a greater degree of cognitive decline.
2.2.4. Happiness
Happiness was evaluated by the Subjective Happiness Scale (SHS) [
43]. SHS is a 4-item instrument for the measurement of global subjective happiness [
43]. The items ask if the respondent considered himself a happy person, happier than peers, generally very happy, and generally not very happy. Each question is scored from 1 to 7, which sums to a total score of 4 to 28. Higher scores represent greater happiness. SHS was reported to show a good reliability (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.79 to 0.94) [
43], and has been validated in Chinese population [
44]. In this study, a threshold of 20 was set to dichotomize participants into unhappy (SHS < 20), and happy (SHS >= 20) sub-groups.
2.2.5. Covariates
Sociodemographic and other relevant information including age, gender, income, education, and marital status was used as covariates in the current study. Income was categorized into three groups: low income, middle income, and high income (i.e., < 1000 RMB, 1000 – 3000 RMB, > 3000 RMB, 1 RMB ≈ 0.15 USD in 2017). Education was grouped into below high school degree, high school degree, and college degree or above. Marital status was coded as living with spouses (married or cohabiting with spouses/partners), and others (unmarried, divorced, separated, or widowed).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Basic demographic characteristics were summarized using descriptive statistics including mean, standard deviation (SD), and percentages as appropriate. To assess the marginal associations between nutritional status (indicated as nutrition below), physical activity (indicated as exercise below), and cognitive decline, Pearson’s correlation coefficients in-between and with continuous demographic variables were first calculated. The associations were then assessed using linear regression models, adjusted for age, gender, income, education, and marital status. Separate models were constructed for nutrition and exercise, respectively, with age, gender, income, education, and marital status adjusted. The interaction effect of nutrition and exercise was also examined. Due to the positive skewness of cognitive decline score, log-transformation was applied as a sensitivity analysis. To examine the interactions with happiness and age, we added their cross-product with nutrition or exercise respectively. If the interaction was significant, we conducted stratified analyses in dichotomized sub-groups. Specifically, in unhappy (happiness < 20) and happy (happiness >= 20) groups for the dissection of happiness interactions and in young-old (age < 74) and old-old (age >= 74) groups for that of age. Mediation analyses were then implemented using a two-step causal medication model if happiness mediated the association between the original nutrition score, exercise, and cognitive decline. A 1000 bootstrapping estimation was used, and 95% confidence intervals were reported. All analyses were performed using RStudio Version 4.3; p-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
The basic characteristics of the older adults are presented in
Table 1. Of the 699 included participants, 312 (44.84%) were males, while the average age was 69.58 (SD = 7.46) years. 428 (62.12%) older adults reported having below high school degrees; 182 reported having high school degrees (26.42%), and the rest 79 (11.47%) of older adults had obtained college degrees or higher. For marital status, 499 (71.70%) reported living with their spouses. As for nutritional status (indicated as nutrition below), 25 (3.78%) reported having protein-calorie undernutrition, 271 (40.94%) reported being at risk of malnutrition, and 366 (55.29%) reported having normal nutrition. With respect to physical activity (indicted as exercise below), 477 (71.70%) participants reported doing exercise. The raw average score of cognitive decline was 3.02 ± 3.15. The average score for happiness was 17.77 (SD = 3.13, range 4 to 28).
Bivariate correlations between nutrition, exercise, cognitive decline, and happiness are summarized in
Table S1. Both nutrition (r = -0.25, p <0.001) and exercise (r = -0.13, p <0.001) were significantly associated with cognitive decline. Happiness significantly correlated with nutrition (r = 0.21, p <0.001), exercise (r = 0.15, p<0.001), and cognitive decline (r = -0.17, p <0.001). In addition, higher ages corresponded to lower levels of nutrition (r = -0.13, p <0.001), but not exercise and happiness (p >0.05).
3.2. Nutrition, Exercise, and Cognitive Decline
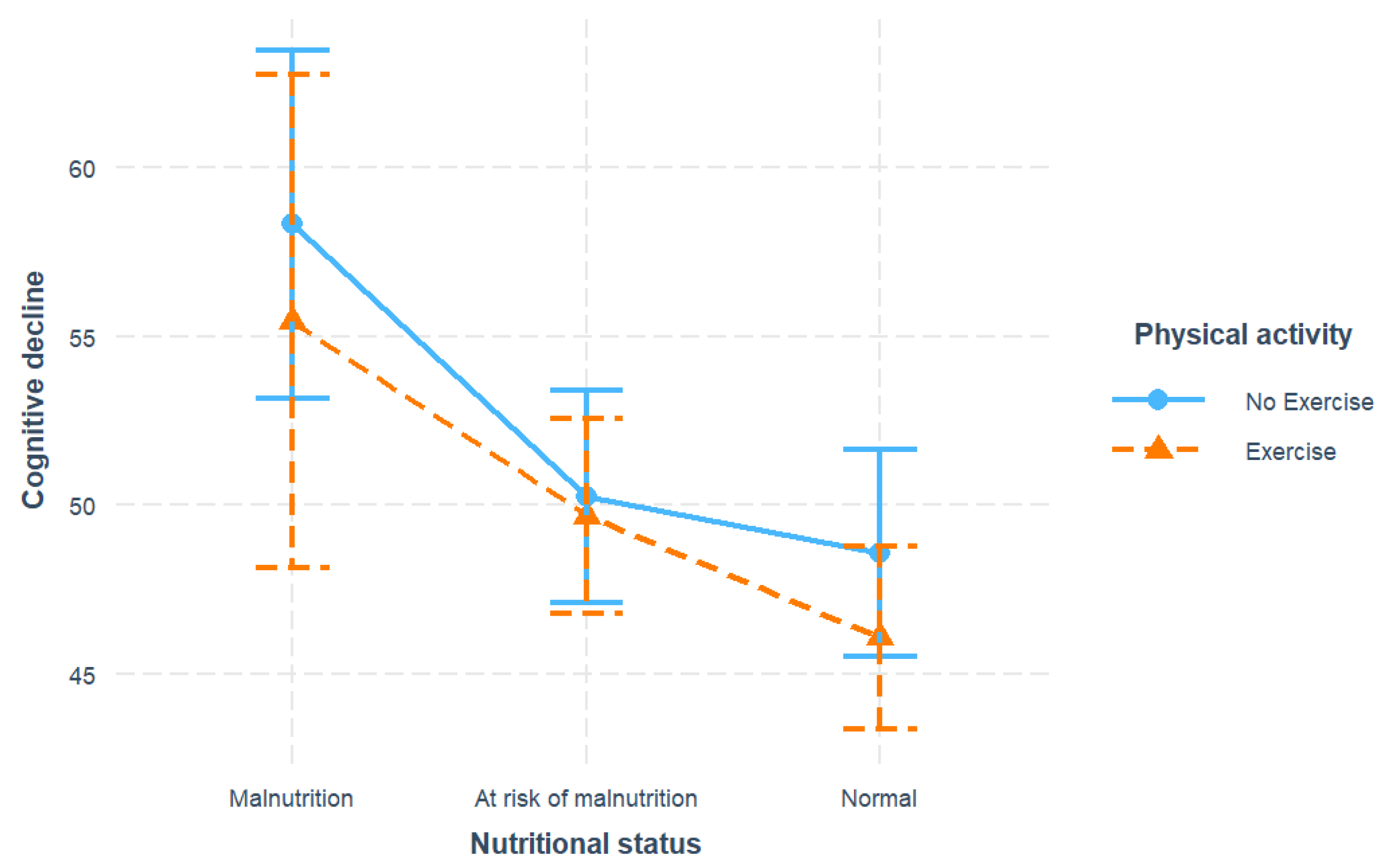
We first examined the associations between nutrition, exercise, and cognitive decline, with results summarized in
Figure 1 and
Table 2. For nutritional status, both the malnutrition (β = 10.63, SE = 2.09, p <0.001) and the at-risk levels (β = 3.10, SE = 0.78, p <0.001) significantly predicted elevated cognitive decline compared to normal nutrition, after adjusting for covariates. For physical activity, exercise was associated with decreased cognitive decline with respect to non-exercise (β = -2.13, SE = 0.81, p = 0.009). However, the interaction of malnutrition and exercise showed no significance.
3.3. Interaction Effects of Happiness and Age
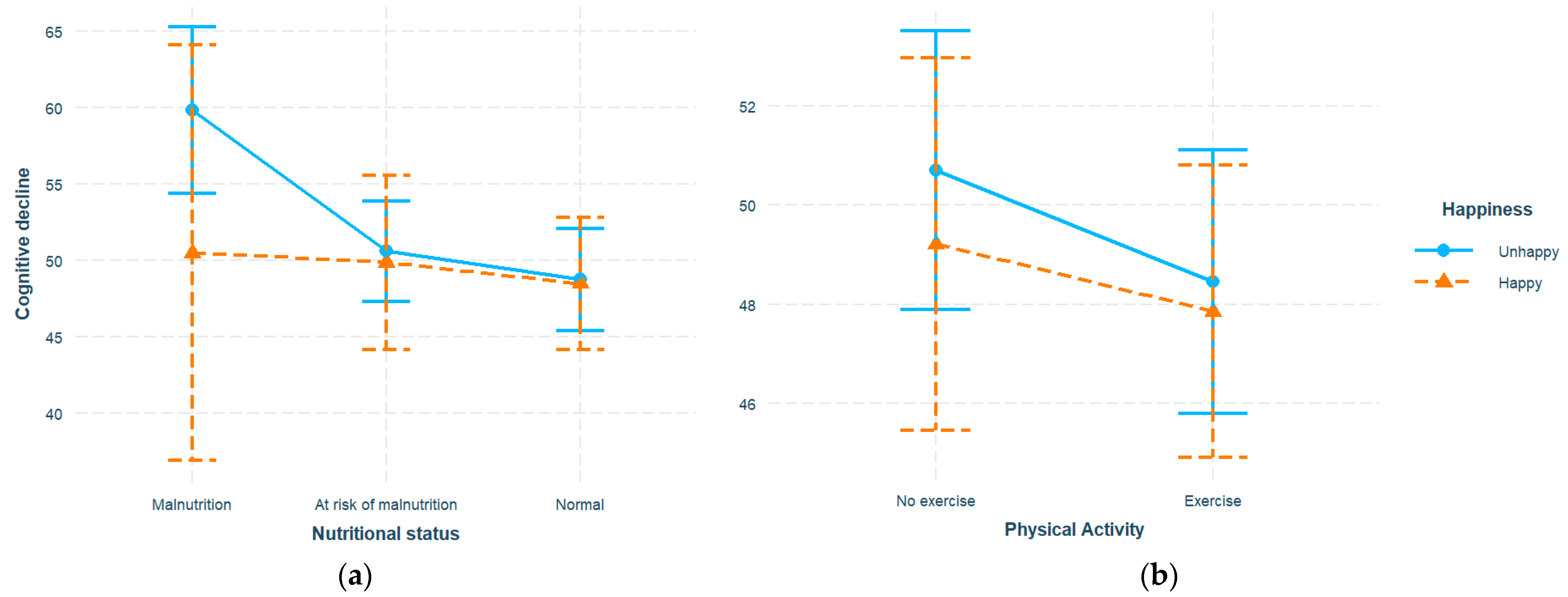
We then investigated whether the identified associations varied across different subpopulations. The interaction terms with happiness were added to previous models. Malnutrition corresponded to higher cognitive decline score (β = 36.37, SE = 9.47, p <0.001), while higher happiness score predicted improved cognition (β = -0.43, SE = 0.16, p = 0.010). In addition, a significant interaction between happiness and malnutrition was observed (β = -1.79, SE = 0.60, p = 0.003). Similarly, exercise (β = -11.78, SE = 4.44, p = 0.008) and happiness (β = -0.86, SE = 0.19, p <0.001) exhibited a significant negative association with cognitive decline, with their interaction also being significant (β = 0.58, SE = 0.25, p = 0.020). No three-way interaction between nutrition, exercise, and happiness were identified. In sensitivity analysis, no significant changes were identified with log-transformation applied. To explore the identified interaction, participants were dichotomized into happy (happiness >= 20, n = 202) and unhappy (happiness < 20, n = 480) sub-groups (
Table 2) where the analyses were replicated. Nutrition and exercise still significantly predicted elevated cognitive decline level in the unhappy group (
Figure 2). Malnutrition and at-risk levels exhibited an increase of 11.10 points (β = 11.10, SE = 2.30, p <0.001) and 2.96 points (β = 2.96, SE = 0.95, p = 0.002) with reference to the normal level, respectively, while exercise corresponded to a decrease of 2.35 points (β = -2.35, SE = 0.96, p = 0.015). However, the associations in the happy group did not show a statistical significance. The interactions with various demographic variables including age, gender, and education level were also explored, with significant interactions only observed with age (β = -0.71, SE = 0.25, p = 0.006), and significant malnutrition-cognition association particularly in the young-old (age < 74) but not the old-old (age >= 74) sub-population (
Table S2, Figure S1).
3.4. Mediation Effects of Happiness
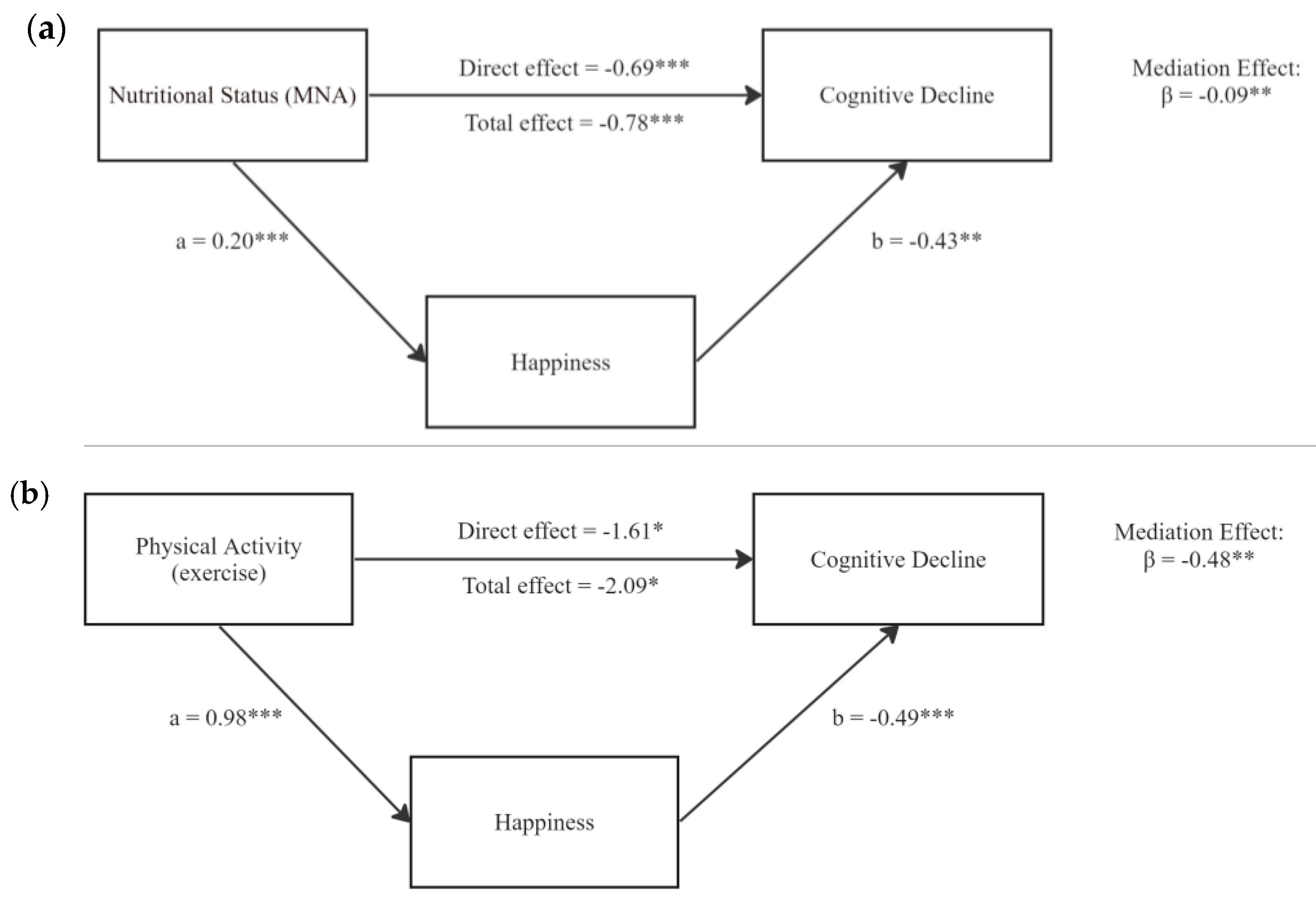
Given the significant associations between nutrition, exercise, happiness, and cognitive decline, we further investigated potential mediating roles of happiness (
Table 3). As shown in
Figure 3, with nutrition exerting a negative total effect on cognitive decline (β = -0.78, p < 0.001), happiness partially mediated this association (indirect effect: β = -0.09, p = 0.006; direct effect: β = -0.69, p < 0.001), accounting for 11.54% of the total effect. Happiness also significantly mediated the association between exercise and cognitive decline (indirect effect: β = -0.48, p = 0.016, 22.97%). The direct effect of exercise on cognitive decline remained significant (β = -1.61, p = 0.050) and accounted for 77.03% of the total effect.
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
As the global population skews towards an older demographic, it has become increasingly important to explore and implement interventions that target lifestyle choices as a method of preserving the healthy aging process---particularly, nutrition and exercise are two implementable factors that are associated with cognitive decline. This cross-sectional study involving community-dwelling, older adults in Shanghai, China yielded several key findings. First, decreased nutrition is associated with higher cognitive decline and increased exercise is associated with lower cognitive decline. Second, happiness, specifically a lack of happiness, moderates the association between nutrition and cognitive decline and exercise and cognitive decline. Finally, and most importantly, happiness serves as a mediator between the associations of nutrition and exercise with cognitive decline. These results are crucial to informing feasible interventions for older adults to preserve their mental acuity in the aging process.
4.2. Association between Nutrition, Exercise, and Cognitive Decline
Our results indicated that both nutrition and physical activity are individually associated with enhanced cognitive function. This is consistent with the current literature: dietary interventions have been effective at slowing cognitive decline and sufficient nutrition is essential for prime brain function [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. It is possible that inadequate nutrition, particularly low levels of vitamin B, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids, prevents the necessary metabolic activity for the expression of beneficial neurotrophic factors, as these vitamins are preferentially taken up by brain tissue [
14]. Proper supplementation of these nutrients can preserve ideal levels of brain activity and serve as a protector against cognitive decline. In addition, regular physical exercise and interventions involving exercise improve cognitive function [
11,
15,
16,
19,
20,
21,
22]. Specifically, the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex gray matter are targets of aerobic exercise, and improved blood flow to these regions enhances memory and executive decision-making, both of which can protect cognitive function [
23]. However, the interactive effect between nutrition and physical activity on cognitive decline was insignificant. Current literature is mixed on this synergistic effect---Nijholt et al. found that only a healthy diet, and not exercise, is positively associated with good cognitive function [
43]. Meanwhile, other intervention studies have shown mixed results among all three variables [
11,
24,
25]. Our study’s findings contribute additional input to clarifying the relationship between these variables; nutrition and exercise may individually be important targets for improving the outlook on cognitive decline, but their coupled influence may be minimal.
4.3. Modification Effect of Happiness
In this study, happiness and age were found to be moderators for the associations between nutrition, exercise, and cognitive decline. Specifically, the nutritional status and physical activity of older adults who were unhappy significantly predicted cognitive decline. This is consistent with the increasing evidence that happiness is positively associated with both physical activity and cognitive function [
29,
30,
31]. Physical activity has been shown to increase life satisfaction and happiness in older adults, suggesting that happier older adults may be more willing to engage in exercise and thus reap its mental benefits that both continues the feeling of satisfaction and protects against cognitive decline [
44]. To our knowledge, there is few research regarding the moderating effect of happiness on nutrition and cognitive decline, so this result provides an additional outlet that can be explored in terms of developing personalized and feasible interventions for protecting the cognitive health of older adults. Age also served as a moderator between nutrition and cognition. Current literature has explored the modification effect of age on physical activity and cognitive health; for instance, Zhu et al. highlighted age as a significant moderator in a meta-analysis of combined cognitive and physical intervention effects [45]. Since our results expand the impact of age on cognition, this underscores the necessity of an in-depth assessment of age-specific dynamics within these associations.
4.4. Mediation Effect of Happiness
Importantly, our results show that happiness serves as a mediating factor of both nutrition and physical activity on cognitive decline. Previous research has shown positive associations between happiness with physical activity and cognitive function, but few have explored the relationship between happiness and nutrition [
29,
30,
31]. Shi et al. found that depression and physical activity mediated the positive correlation between happiness and cognitive function; our results expand upon these findings to show that happiness is exchangeable as a mediator between physical activity and cognitive function [46].
While few current studies have examined the mediating effect that happiness has on the relationship between nutrition and cognitive health in older adults, possible mechanisms for this impact can be inferred from the current literature. Specifically, the gut microbiome has emerged as a key link between diet and mood, and poor microbiome health, which is indicative of a poor diet, has been shown to be associated with psychiatric disorders [47]. The metabolites produced by gut bacteria as a result of one’s diet, such as short chain fatty acids, are directly conferred to the brain and impact neurological health [47]. This supports how happiness operates as a mediating variable: detrimental changes to gut health via a poor diet can cause short-term changes in happiness and mood, which may eventually manifest as long-term cognitive deficits. Our study’s findings are significant in expanding the role that happiness plays in older adults’ mental acuity and highlights the mechanisms by which nutrition and physical activity can impact cognitive health, showing the importance of developing interventions in these areas.
4.5. Limitations, Implications, and Conclusions
These findings should be interpreted considering the limitations of the study. First, the collected nutrition status data may not be fully comprehensive of each individual’s nutritional habits because this data was based on a self-report instrument rather than a 24-hour dietary record. This extends to the data collection on physical activity as well---there was a lack of systematic data collection on physical activity, and the self-report may not have captured all nuances in the adults’ exercise habits. In addition, due to the cross-sectional nature of this study, a causal relationship between the discussed variables may not be able to be established. Finally, since this research was conducted in community-dwelling adults from a major metropolitan city, these results may not be fully generalizable to the whole Chinese population.
Nevertheless, these results still hold major implications in providing accessible and feasible interventions for older adults. Our study found that happiness serves as a mediator and moderator for the significant associations between nutrition and exercise with cognitive decline, respectively. As the first study to connect happiness with nutrition and exercise in their associations with cognitive decline, these findings may encourage older adults to develop and maintain adequate lifestyle habits focusing on nutritional and physical activity whilst pursuing activities that promote happiness. This research may offer insights to inform future design and implementation of cognitive interventions tailored to promote positive emotional status and demographic sub-groups, ultimately contributing to the development of effective strategies for mitigating cognitive decline in aging populations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Figure S1: Association of nutritional status with cognitive decline at different age sub-groups; Table S1: Bivariate Pearson’s correlation between variables; Table S2: Adjusted association of cognitive decline with nutritional status, stratified by age.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Jianghong Liu; Data curation, Jianghong Liu; Formal analysis, Michael Pan; Investigation, Jianghong Liu; Methodology, Jianghong Liu, Haoer Shi and Rui Feng; Project administration, Jianghong Liu; Resources, Jianghong Liu; Software, Michael Pan; Supervision, Jianghong Liu and Rui Feng; Validation, Jianghong Liu; Visualization, Michael Pan; Writing – original draft, Jianghong Liu, Michael Pan, McKenna Sun and Haoer Shi; Writing – review & editing, Jianghong Liu, McKenna Sun, Haoer Shi and Rui Feng. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the ethics committees for research at both Shanghai Shuguang Hospital and Shanghai Longhua Hospital (identifying number: 2020-GZR-02-053X).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate Qiuzi Sun and Hua Mei who assisted in coordinating the project. We thank the nurses from Shanghai Longhua Hospital and Shuguang Hospital for their help in data collection. We also thank Qianqian Zhang for help initial data organization and suggestion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chye, L.; Wei, K.; Nyunt, M.S.Z.; Gao, Q.; Wee, S.L.; Ng, T.-P. Strong Relationship between Malnutrition and Cognitive Frailty in the Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Studies (SLAS-1 and SLAS-2). The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease 2018, 5, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzorou, M.; Vadikolias, K.; Pavlidou, E.; Serdari, A.; Vasios, G.; Tryfonos, C.; Giaginis, C. Nutritional status is associated with the degree of cognitive impairment and depressive symptoms in a Greek elderly population. Nutritional Neuroscience 2020, 23, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Duan, J.; Deng, Y.; Tu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Lü, Y. Nutritional status of an elderly population in Southwest China: a cross-sectional study based on comprehensive geriatric assessment. The journal of nutrition, health & aging 2015, 19, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Trinca, V.; Anderson, N.D.; Fiocco, A.J.; Ferland, G.; Laurin, D.; Keller, H.H. Nutrition risk and cognitive performance in community-living older adults without cognitive impairment: a cross-sectional analysis of the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukik, L.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z. Tea Consumption Is Associated with Reduced Cognitive Decline and Interacts with Iron Intake: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study on 4,820 Old Adults. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2022, 90, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukik, L.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z. Association between egg consumption and cognitive function among Chinese adults: long-term effect and interaction effect of iron intake. British Journal of Nutrition 2022, 128, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y.; Yun, J.M. Association between diets and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 50 years or older. Nutr Res Pract 2018, 12, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.; Chan, D.; Woo, J. A cross sectional study to examine the association between dietary patterns and cognitive impairment in older Chinese people in Hong Kong. The journal of nutrition, health & aging 2013, 17, 757–765. [Google Scholar]
- McGrattan, A.M.; McEvoy, C.T.; McGuinness, B.; McKinley, M.C.; Woodside, J.V. Effect of dietary interventions in mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review. British Journal of Nutrition 2018, 120, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Sala-Vila, A.; Serra-Mir, M.; Corella, D.; de la Torre, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Fitó, M.; Pérez-Heras, A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Age-Related Cognitive Decline: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Internal Medicine 2015, 175, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Veronese, N.; Vernuccio, L.; Catanese, G.; Inzerillo, F.; Salemi, G.; Barbagallo, M. Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Other Lifestyle Factors in the Prevention of Cognitive Decline and Dementia. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardener, S.L.; Rainey-Smith, S.R. The Role of Nutrition in Cognitive Function and Brain Ageing in the Elderly. Current Nutrition Reports 2018, 7, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, T.M.; Manosso, L.M.; Yau, S.-y.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Brocardo, P.S. In Pursuit of Healthy Aging: Effects of Nutrition on Brain Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.L. Nutrient intake, nutritional status, and cognitive function with aging. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2016, 1367, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Bai, C.; Feng, Q.; Gu, D. Serum Vitamin D3 Concentration, Sleep, and Cognitive Impairment among Older Adults in China. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaertner, B.; Buttery, A.K.; Finger, J.D.; Wolfsgruber, S.; Wagner, M.; Busch, M.A. Physical exercise and cognitive function across the life span: Results of a nationwide population-based study. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2018, 21, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falck, R.S.; Landry, G.J.; Best, J.R.; Davis, J.C.; Chiu, B.K.; Liu-Ambrose, T. Cross-Sectional Relationships of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior With Cognitive Function in Older Adults With Probable Mild Cognitive Impairment. Physical Therapy 2017, 97, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, J.D.; Brown, D.R.; McGuire, L.C.; Taylor, C.A.; Fulton, J.E.; Carlson, S.A. Cross-sectional association between physical activity level and subjective cognitive decline among US adults aged ≥45 years, 2015. Preventive Medicine 2020, 141, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, T.R.S.; Tribess, S.; Sasaki, J.E.; Meneguci, J.; Martins, C.A.; Freitas, I.F.; Romo-Perez, V.; Virtuoso, J.S. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Relationship of Physical Activity with Depression and Cognitive Deficit in Older Adults. Journal of Aging and Physical Activity 2016, 24, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondell, S.J.; Hammersley-Mather, R.; Veerman, J.L. Does physical activity prevent cognitive decline and dementia?: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kowal, I.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Perez, A.; Rao, H.; Group, C.O.A.Q.E. Culturally tailored group Qigong exercise in older Chinese immigrants: A feasibility study. Geriatric Nursing 2023, 51, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joseph Michael, N.; Nicolas, C.; Kate Louise, P.; Disa Jane, S.; Ben, R. Exercise interventions for cognitive function in adults older than 50: a systematic review with meta-analysis. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2018, 52, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasson, L.S.; Nyberg, L.; Kramer, A.F.; Lundquist, A.; Riklund, K.; Boraxbekk, C.-J. Aerobic Exercise Intervention, Cognitive Performance, and Brain Structure: Results from the Physical Influences on Brain in Aging (PHIBRA) Study. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lista, I.; Sorrentino, G. Biological Mechanisms of Physical Activity in Preventing Cognitive Decline. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology 2010, 30, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Séverine, S.; Aline, D.; Jean-François, D.; Jessica, A.; Alexis, E.; Mika, K.; Archana, S.-M. Physical activity, cognitive decline, and risk of dementia: 28 year follow-up of Whitehall II cohort study. BMJ 2017, 357, j2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherbuin, N.; Anstey, K.J. The Mediterranean diet is not related to cognitive change in a large prospective investigation: the PATH Through Life study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2012, 20, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Luchetti, M.; Aschwanden, D.; Sesker, A.A.; Stephan, Y.; Sutin, A.R.; Terracciano, A. The association between happiness and cognitive function in the UK Biobank. Current Psychology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; He, X.; Pan, D.; Qiao, H.; Li, J. Happiness, depression, physical activity and cognition among the middle and old-aged population in China: a conditional process analysis. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlin, Å.; MacDonald, S.W.; de Frias, C.M.; Nilsson, L.-G.; Dixon, R.A. How do health and biological age influence chronological age and sex differences in cognitive aging: moderating, mediating, or both? Psychology and aging 2006, 21, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrenetxea, J.; Pan, A.; Feng, Q.; Koh, W.-P. Factors associated with depression across age groups of older adults: The Singapore Chinese health study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2022, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, C.W.; Yang, H.F.; Huang, W.T.; Fan, S.Y. The Relationships between Physical Activity and Life Satisfaction and Happiness among Young, Middle-Aged, and Older Adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, W. A Systematic Review of the Relationship Between Physical Activity and Happiness. Journal of Happiness Studies 2019, 20, 1305–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.; Jiang, X.; Kelly, P.; Chau, J.; Bauman, A.; Ding, D. Don't worry, be happy: cross-sectional associations between physical activity and happiness in 15 European countries. BMC public health 2015, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Mei, H.; Rao, H. Social Connection and Lifestyle Factors Associated With Happiness in Urban Older Adults in China: A Cross-Sectional Study With a Community Sample. Research in Gerontological Nursing 2023, 16, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B.; Garry, P. Mini Nutritional Assessment: a practical assessment tool for grading the nutritional state of elderly patients. The mini nutritional assessment: MNA. Nutrition in the elderly 1997, 15–60. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.C.; Vincent, J.I. Clinical measurement properties of malnutrition assessment tools for use with patients in hospitals: a systematic review. Nutr J 2020, 19, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleda, M.; Bolibar, I.; Pares, R.; SALVAff, A. RELIABILITY OF THE MINI NUTRITIONAL, ASSESSMENT (MNA). The Journal of Nutrition 2002, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, C.; Sha, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xie, S.; Kwauk, S.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C. Assessing the nutritional status of elderly Chinese lung cancer patients using the Mini-Nutritional Assessment (MNA(®)) tool. Clin Interv Aging 2013, 8, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achenbach, T.M.; Newhouse, P.A.; Rescorla, L.A. Manual for the ASEBA Older Adult Forms & Profiles: For Ages 60-90+: Older Adult Self-report: Older Adult Behavior Checklist: an Integrated System of Multi-informant Assessment; ASEBA: 2004.
- Liu, J.; Lee, C.M.; An, Y.; Sun, Q.; Mei, H.; Shi, S.; Ivanova, M.; Rao, H. Application of the older adult self-report and older adult behavior checklist to Chinese older adults: Syndrome structure and inter-informant agreement. Journal of Gerontological Nursing 2022, 48, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, M.Y.; Achenbach, T.M.; Rescorla, L.A.; Turner, L.V.; Dumas, J.A.; Almeida, V.; Anafarta-Sendag, M.; Bite, I.; Boomsma, D.I.; Caldas, J.C. The generalizability of Older Adult Self-Report (OASR) syndromes of psychopathology across 20 societies. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2020, 35, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, M.A.; Sun, Q.; Mei, H.; Rao, H.; Liu, J. Mental Fatigue Is Associated with Subjective Cognitive Decline among Older Adults. Brain Sciences 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyubomirsky, S.; Lepper, H.S. A measure of subjective happiness: Preliminary reliability and construct validation. Social indicators research 1999, 46, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, H.; Ni, M.Y.; Lee, P.H.; Tam, W.W.; Lam, T.H.; Leung, G.M.; McDowell, I. Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the Subjective Happiness Scale: evidence from the Hong Kong FAMILY Cohort. International journal of behavioral medicine 2014, 21, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).