Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
01 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles anchored carbon (ZnO-C)
2.3. Optimization of adsorptive removal of Zn(II), Cd(II), Co(II) and Mn(II) for wastewater purification
3. Results and discussion
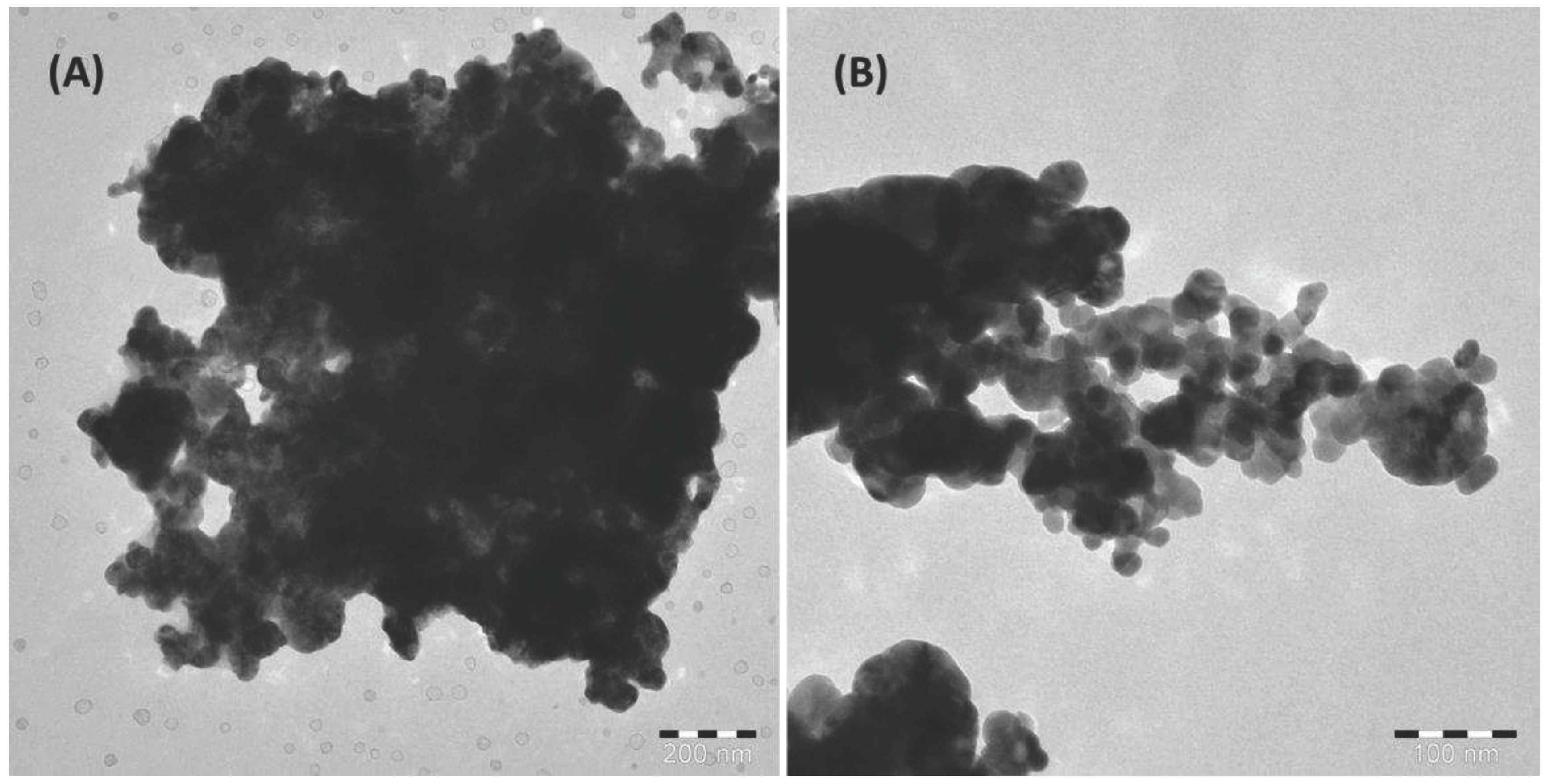
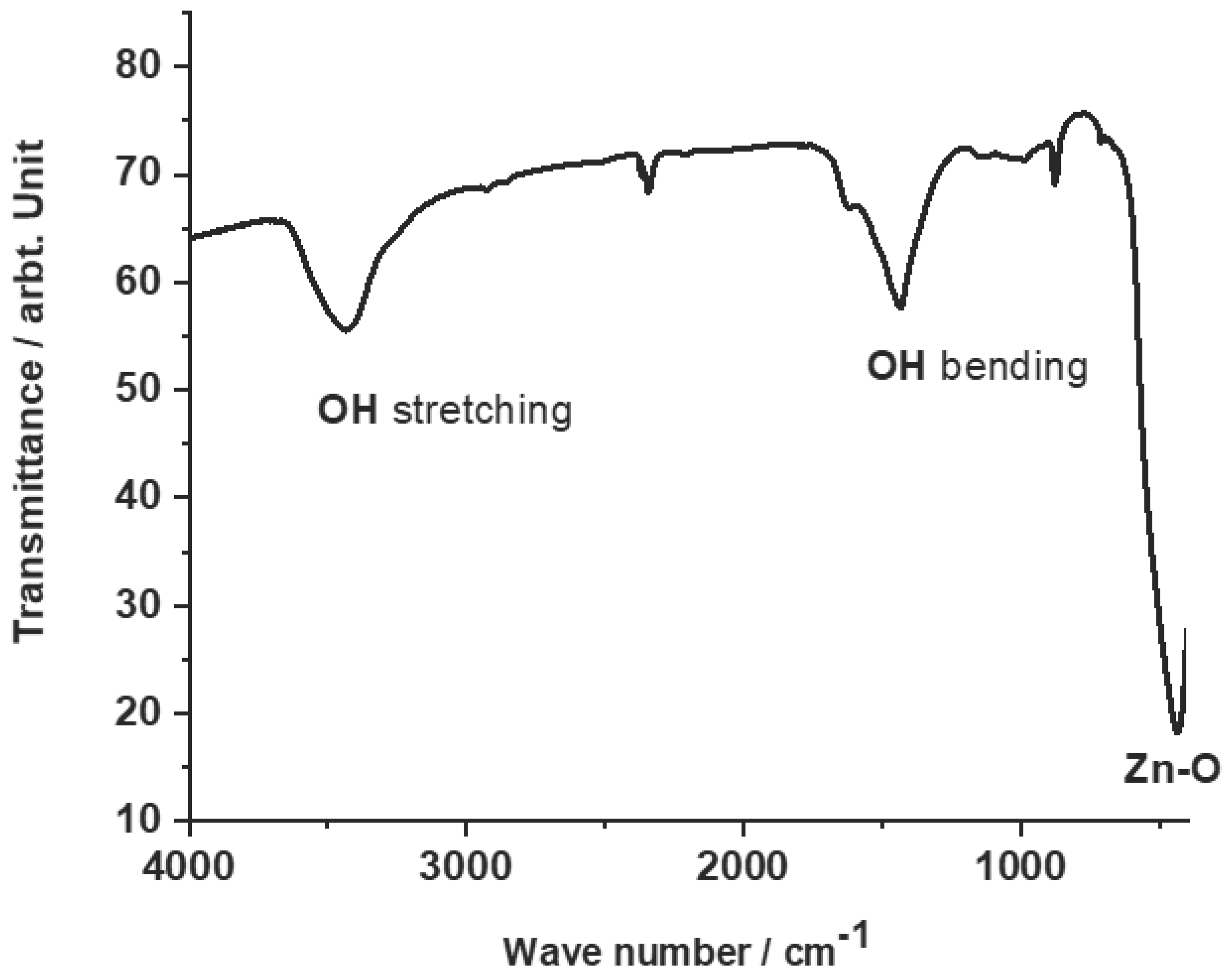
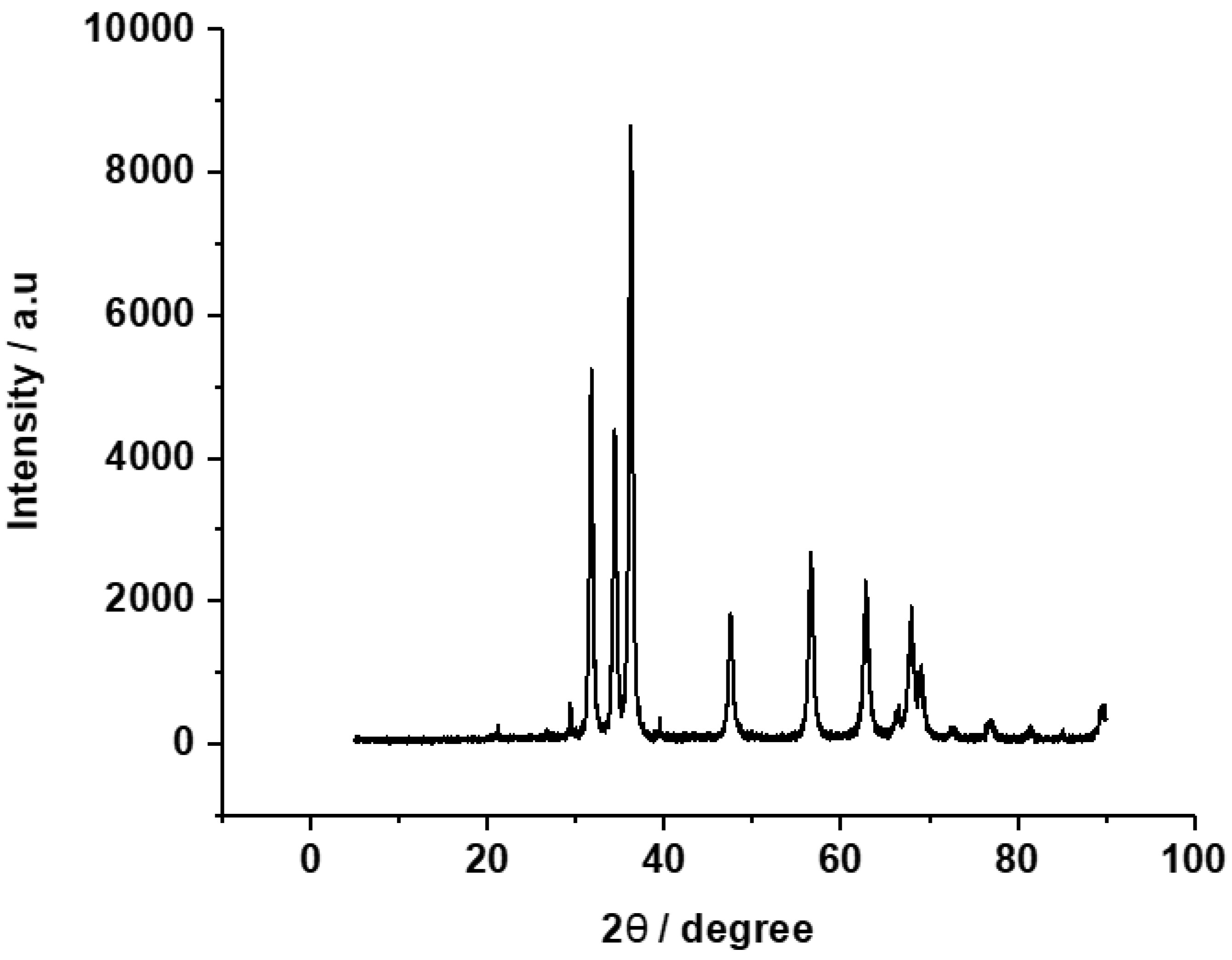
3.1. Characteristics of the developed ZnO-C hybrid adsorbent materials
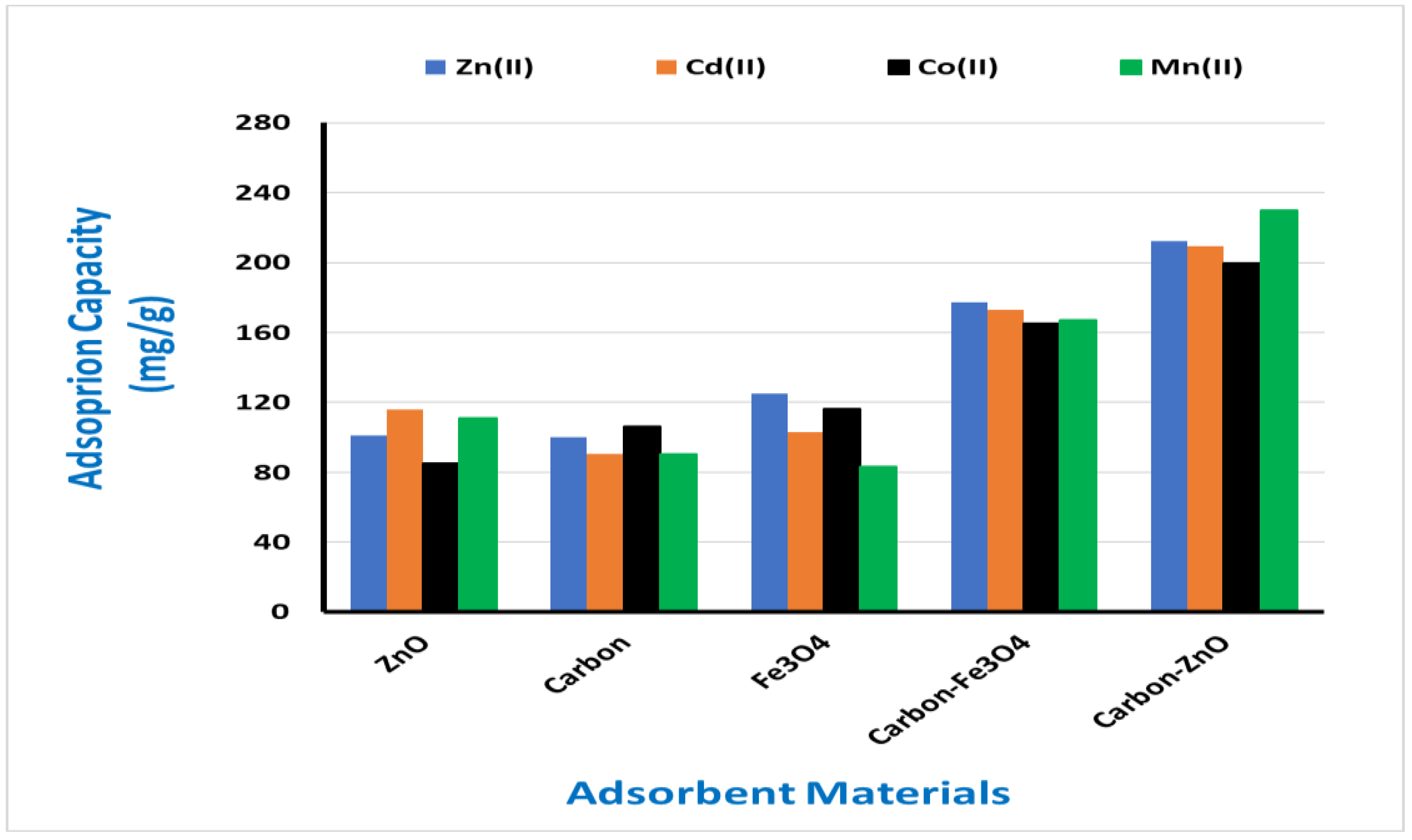
3.2. Utilization of developed hybrid materials for adsoprion application
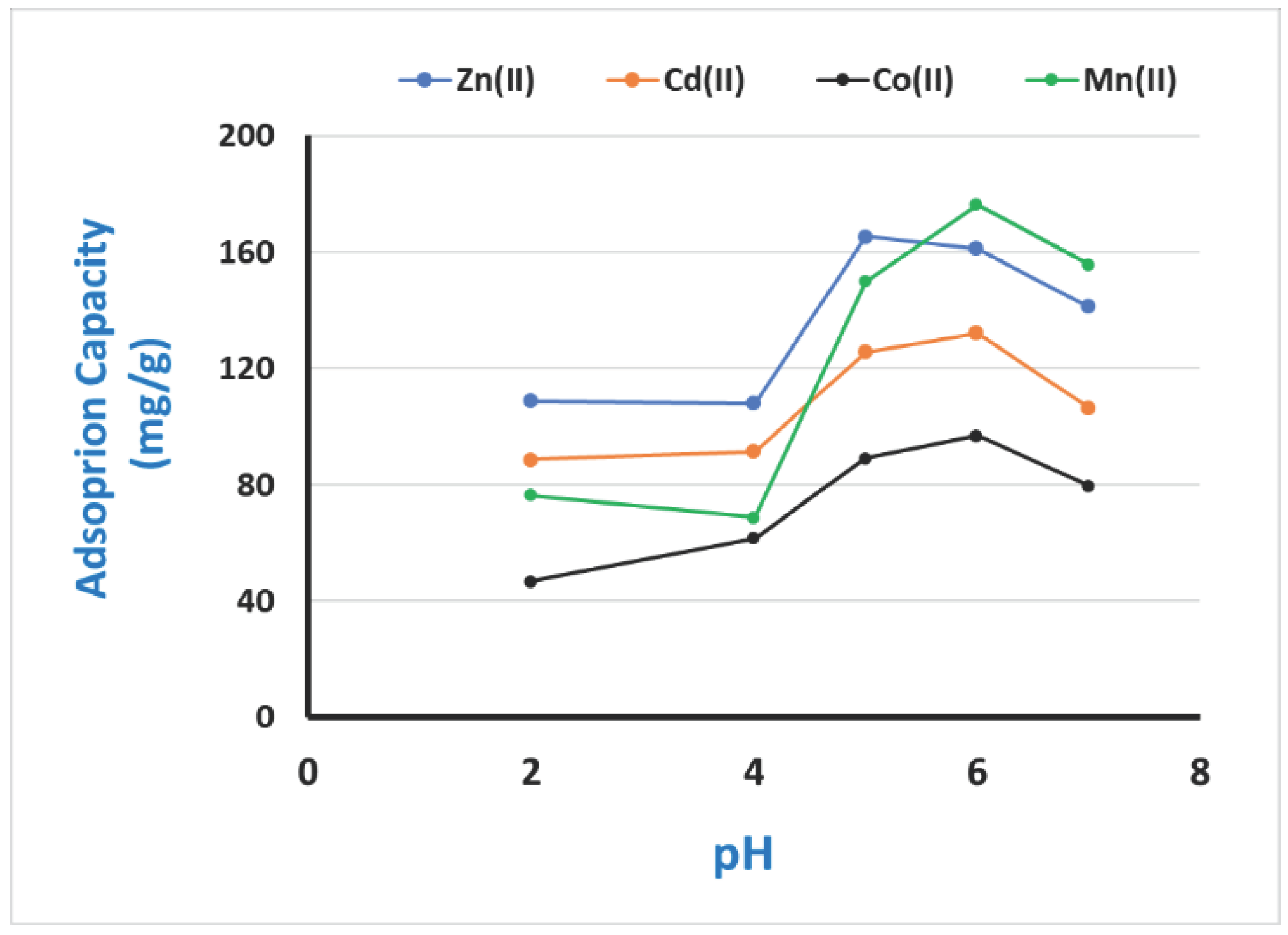
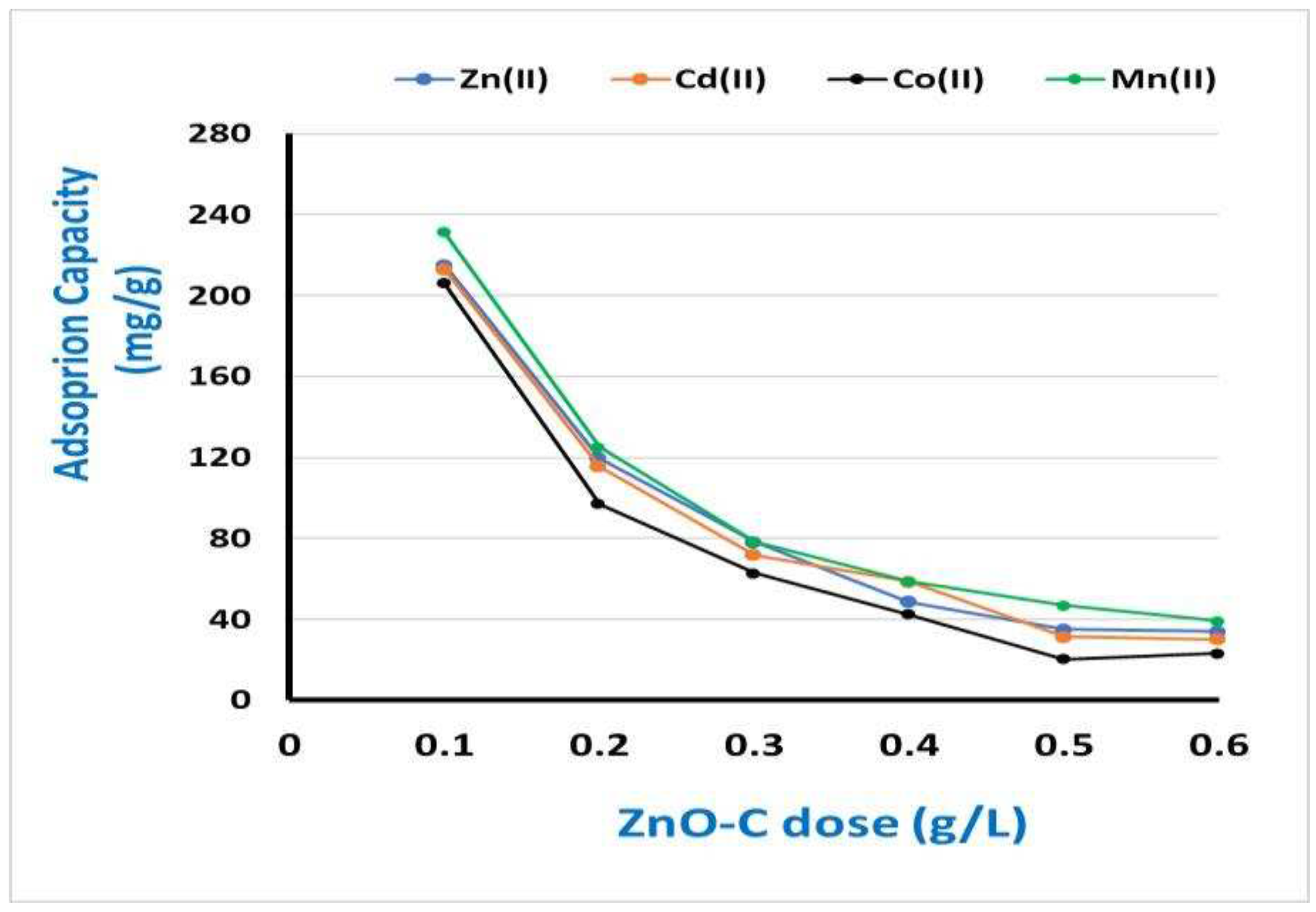
3.3. Optimizing the most influencing factors
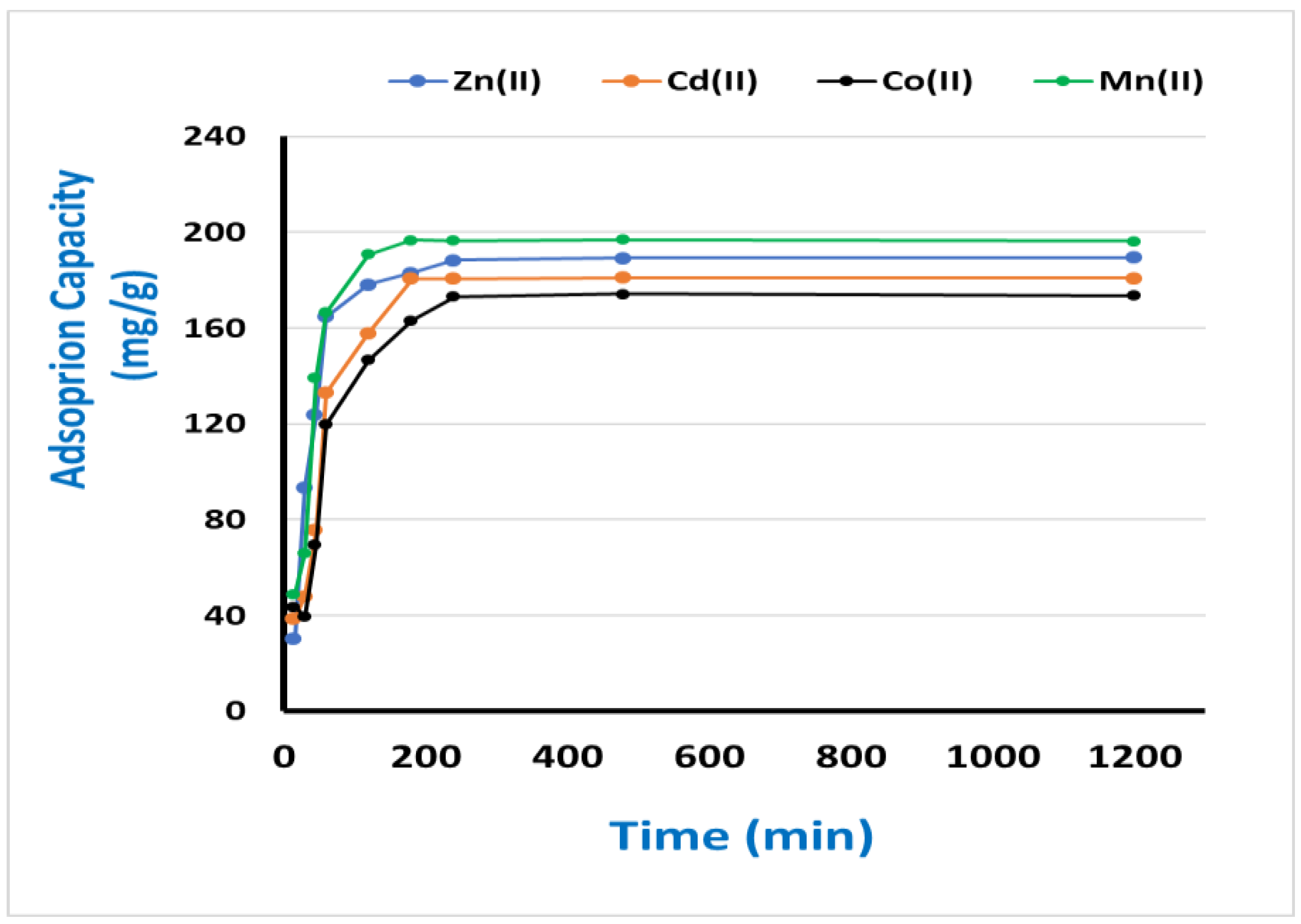
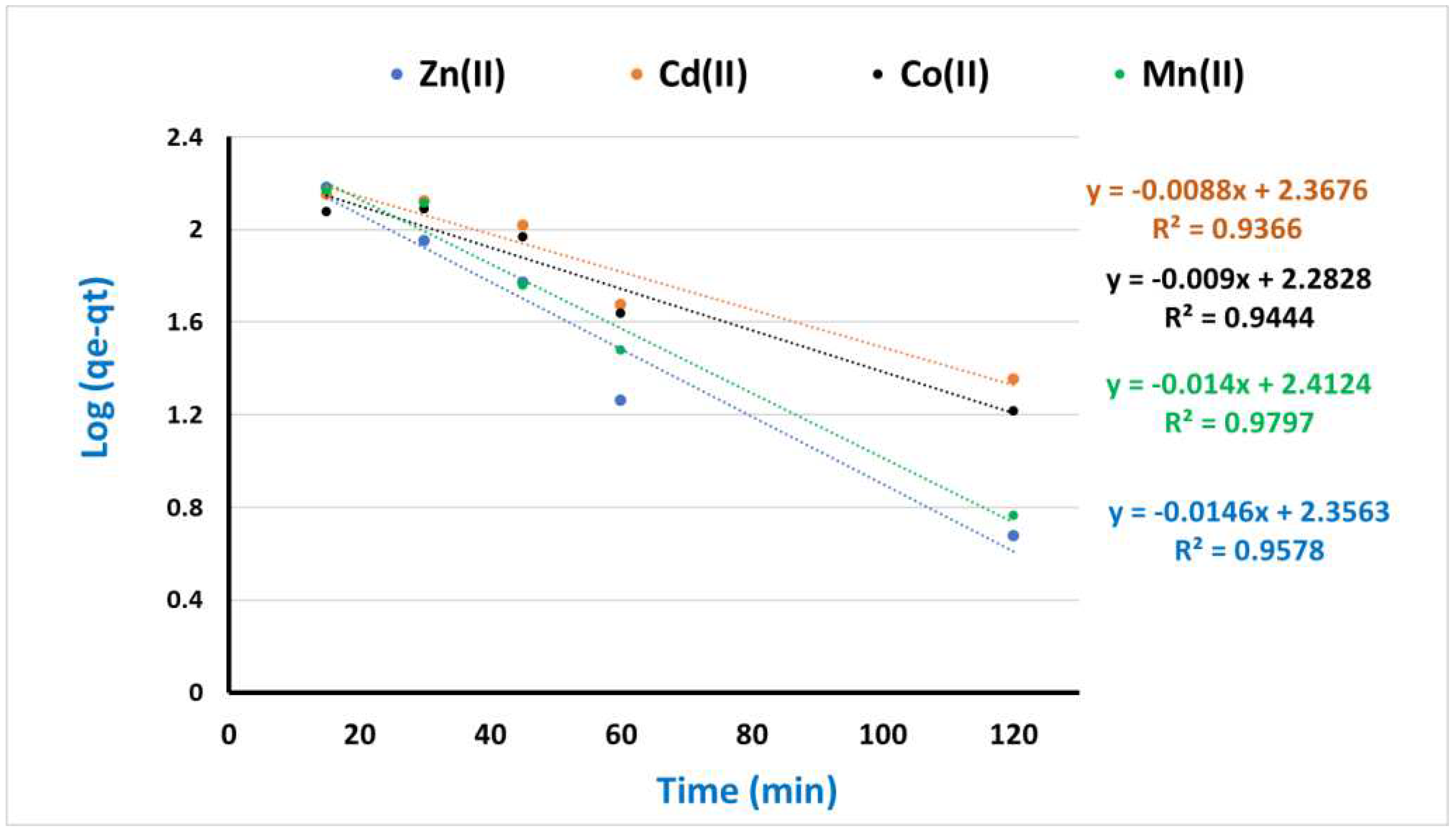
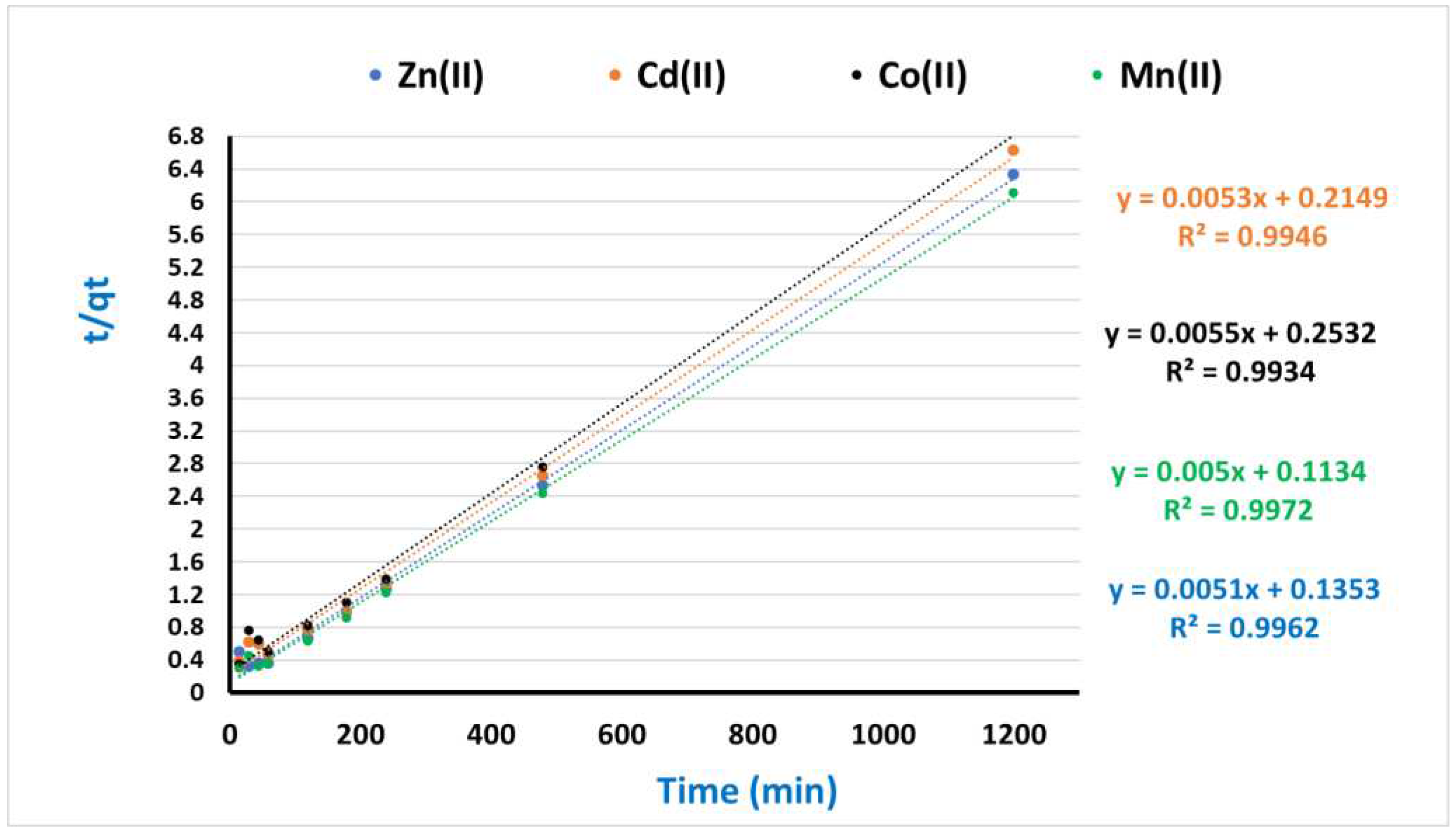
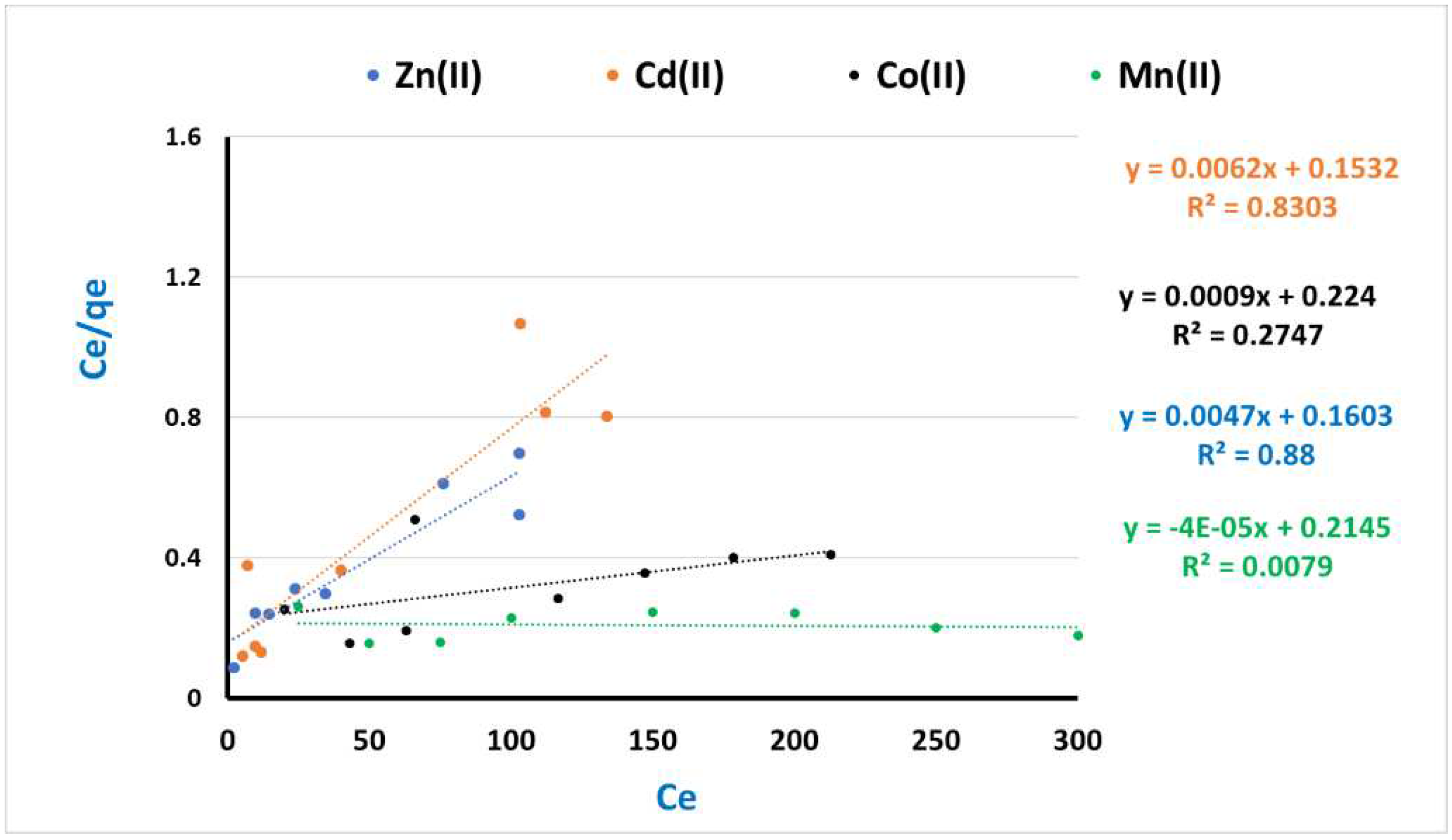
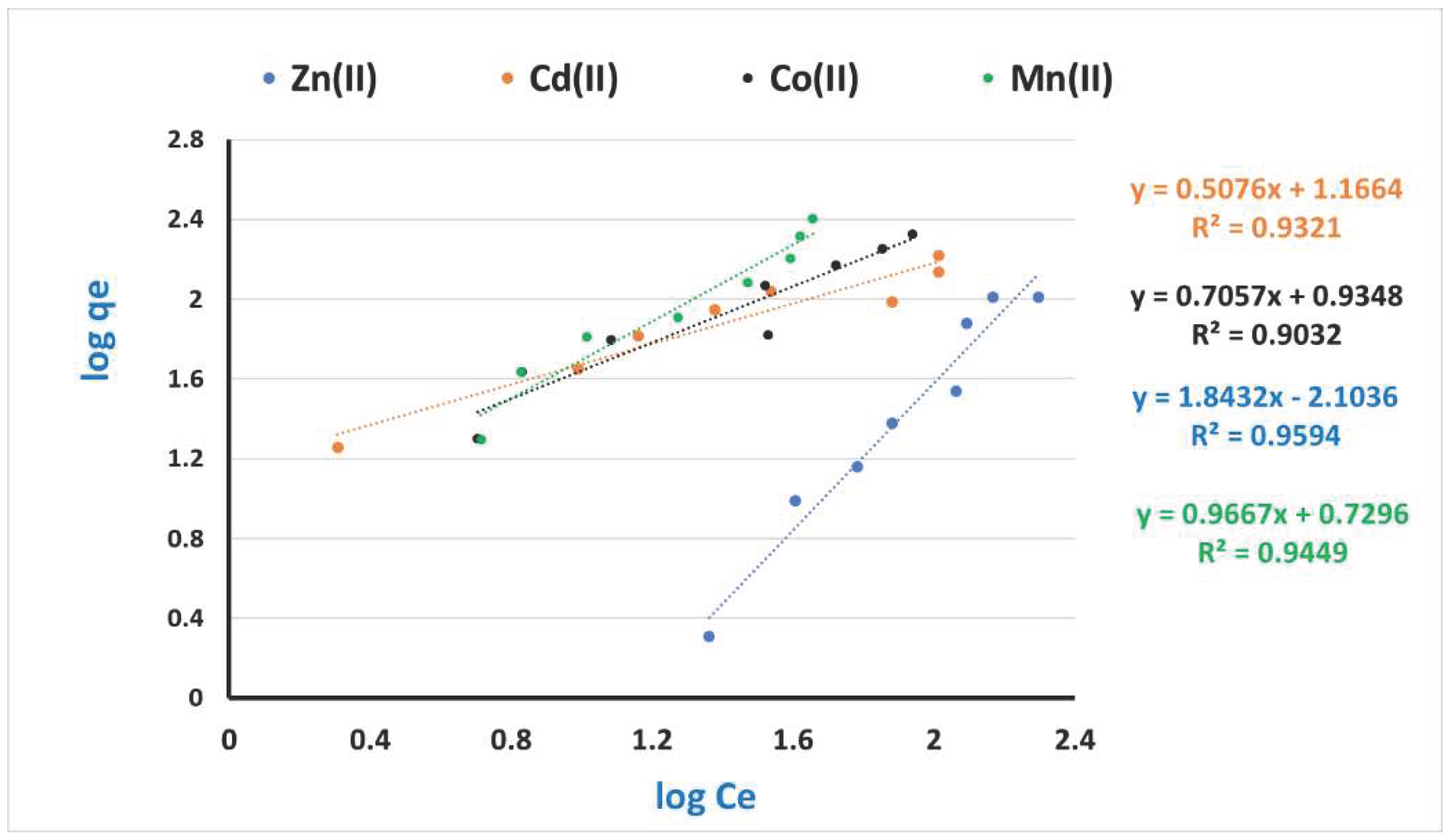
3.4. Kinetic and Equilibrium modeling
3.5. Purification of wastewater using the deviled hybrid adsorbent materials
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Khalafi, T.; Buazar, F.; Ghanemi, K. Phycosynthesis and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Toward Organosulfur Pollutants. Sci Rep 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengaraj, S.; Yeon, K.H.; Moon, S.H. Removal of Chromium from Water and Wastewater by Ion Exchange Resins. J Hazard Mater 2001, 87, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.Y.S.; Lo, W.; Babel, S. Comparisons of Low-Cost Adsorbents for Treating Wastewaters Laden with Heavy Metals. Science of the total environment 2006, 366, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherley, L.R.; Miladinovic, N.D. Comparison of the Ion Exchange Uptake of Ammonium Ion onto New Zealand Clinoptilolite and Mordenite. Water Res 2004, 38, 4305–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, K.; Vahter, M. Time to Re-Evaluate the Guideline Value for Manganese in Drinking Water? Environ Health Perspect 2007, 115, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agusa, T.; Kunito, T.; Fujihara, J.; Kubota, R.; Minh, T.B.; Kim Trang, P.T.; Iwata, H.; Subramanian, A.; Viet, P.H.; Tanabe, S. Contamination by Arsenic and Other Trace Elements in Tube-Well Water and Its Risk Assessment to Humans in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environmental Pollution 2006, 139, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, A.E. Significance and Removal of Manganese in Water Supplies. J Am Water Works Assoc 1960, 52, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhla, M.S.; Kumar, R.; Prasad, L. Zinc Impurity in Drinking Water and Its Toxic Effect on Human Health. Indian Internet Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology 2019, 17, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhla, M.S.; Kumar, R. Contaminant of Heavy Metals in Groundwater & Its Toxic Effects on Human Health & Environment. International Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources 2019, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porea, T.J.; Belmont, J.W.; Maboney, D.H. Zinc-Induced Anemia and Neutropenia in an Adolescent. Journal of Pediatrics 2000, 136, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogawa, K.; Kobayashi, E.; Okubo, Y.; Suwazono, Y. Environmental Cadmium Exposure, Adverse Effects and Preventive Measures in Japan. BioMetals 2004, 17, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, P. Environmental Protection and Regulations in India: Role of the Central Pollution Control Board. Indian Journal of Public Administration 2018, 64, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Gupta, M.; Sharma, S. Process Development for the Removal of Lead and Chromium from Aqueous Solutions Using Red Mud - An Aluminium Industry Waste. Water Res 2001, 35, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, A.; Shiwani, S. Adsorption of Lead Using a New Green Material Obtained from Portulaca Plant. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2012, 9, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L. Hazards of Heavy Metal Contamination. Br Med Bull 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esalah, J.O.; Weber, M.E.; Vera, J.H. Removal of Lead, Cadmium and Zinc from Aqueous Solutions by Precipitation with Sodium Di-(n-Octyl) Phosphinate. Can J Chem Eng 2000, 78, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Cao, X. Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution by Biochars Derived from Anaerobically Digested Biomass. Bioresour Technol 2012, 110, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, A.; Jung, W.; Min, B.; Lee, M.; Choi, U.; Timmes, T.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, C.U.; Kumar, R.; Jeon, B.H. Concurrent Removal of Cadmium and Benzene from Aqueous Solution by Powdered Activated Carbon Impregnated Alginate Beads. Catena (Amst) 2017, 148, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, P.; Chen, M.; Lai, X.; Ahmed, Z.; Zhu, N.; Dang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Liu, T. Preparation and Characterization of the Eco-Friendly Chitosan/Vermiculite Biocomposite with Excellent Removal Capacity for Cadmium and Lead. Appl Clay Sci 2018, 159, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhafez, S.E.A.; Hamad, H.A.; Zaatout, A.A.; Malash, G.F. Management of Agricultural Waste for Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution: Adsorption Behaviors, Adsorption Mechanisms, Environmental Protection, and Techno-Economic Analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2017, 24, 1397–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhamed, F.; Elouear, Z.; Bouzid, J.; Ouddane, B. Multi-Component Adsorption of Copper, Nickel and Zinc from Aqueous Solutions onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Date Stones. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2016, 23, 15801–15806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J. COMMENTARY. 2007, 447, 10–11.
- El-Toni, A.M.; Habila, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Labis, J.P.; ALOthman, Z.A. Simple and Facile Synthesis of Amino Functionalized Hollow Core-Mesoporous Shell Silica Spheres Using Anionic Surfactant for Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) Adsorption and Recovery. Chemical Engineering Journal 2014, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habila, M.A.; Alothman, Z.A.; El-Toni, A.M.; Al-Tamrah, S.A.; Soylak, M.; Labis, J.P. Carbon-Coated Fe<inf>3</Inf>O<inf>4</Inf> Nanoparticles with Surface Amido Groups for Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction of Cr(III), Co(II), Cd(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) Prior to Their Quantitation by ICP-MS. Microchimica Acta 2017, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, P.; Fu, J.; Wallen, S.L. Completely “Green” Synthesis and Stabilization of Metal Nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 2003, 125, 13940–13941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, D.M.; Silva, R.; Hechenleitner, A.A.W.; Radovanovic, E.; Melo, M.A.C.; Pineda, E.A.G. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO, CuO and a Mixed Zn and Cu Oxide. Mater Chem Phys 2009, 115, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc Oxide-from Synthesis to Application: A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buazar, F.; Bavi, M.; Kroushawi, F.; Halvani, M.; Khaledi-Nasab, A.; Hossieni, S.A. Potato Extract as Reducing Agent and Stabiliser in a Facile Green One-Step Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles. J Exp Nanosci 2016, 11, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmus, Z.; Kurt, B.Z.; Durmus, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Graphene Oxide/Zinc Oxide (GO/ZnO) Nanocomposite and Its Utilization for Photocatalytic Degradation of Basic Fuchsin Dye. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.L. ZnO Thin-Film Transistors. Zinc Oxide Bulk, Thin Films and Nanostructures: Processing, Properties, and Applications, 2006; 415–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc Oxide-from Synthesis to Application: A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buazar, F.; Alipouryan, S.; Kroushawi, F.; Hossieni, S.A. Photodegradation of Odorous 2-Mercaptobenzoxazole through Zinc Oxide/Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite. Applied Nanoscience (Switzerland) 2015, 5, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arularasu, M. V.; Sendhil, M.; Rajendran, T. V.; Mani, G.; Aljuwayid, A.M.; Habila, M.A. Recent Advantages of Zinc Oxide/Carbon Nanotubes/Reduced Graphene Oxide Based Nanocomposite for the Visible Light Photodegradation. Inorg Chem Commun 2022, 139, 109332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arularasu, M. V.; Sendhil, M.; Rajendran, T. V.; Mani, G.; Aljuwayid, A.M.; Habila, M.A. Recent Advantages of Zinc Oxide/Carbon Nanotubes/Reduced Graphene Oxide Based Nanocomposite for the Visible Light Photodegradation. Inorg Chem Commun 2022, 139, 109332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawashdeh, N.A.F.; Allabadi, O.; Aljarrah, M.T. Photocatalytic Activity of Graphene Oxide/Zinc Oxide Nanocomposites with Embedded Metal Nanoparticles for the Degradation of Organic Dyes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 28046–28055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Hao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, L. The Selective Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Dental Wastewater. Chem Phys 2020, 534, 110750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshhesab, Z.M.; Sarfaraz, M.; Asadabad, M.A. Preparation of ZnO Nanostructures by Chemical Precipitation Method. Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic, Metal-Organic, and Nano-Metal Chemistry 2011, 41, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.; Tapia, C.; Leiva-Aravena, E.; Leiva, E. Graphene Oxide–ZnO Nanocomposites for Removal of Aluminum and Copper Ions from Acid Mine Drainage Wastewater. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadian, M.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Fard, M.M.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Hadadian, M.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Fard, M.M.; Ahmadzadeh, H. Synergistic Effect of Graphene Nanosheets and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Adsorption of Ni (II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions. ApPhA 2018, 124, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, E.; Tapia, C.; Rodríguez, C.; Palet, C.; Bastos-Arrieta, J. Highly Efficient Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Acidic Aqueous Solution Using ZnO Nanoparticles as Nano-Adsorbents. Water 2021, Vol. 13, Page 2960 2021, 13, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habila, M.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Hakami, H.M.; Alanazi, A.G. Influence of Synthesis-Heating Conditions on the Porosity and Performance of a Carbon Nanotube/SDS-Alumina Nanocomposite for Effective Wastewater Treatment: Fabrication, Characterization, and Adsorption Modeling. Ind Eng Chem Res 2023, 62, 12571–12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habila, M.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Hakami, H.M.; ALOthman, M.R.; Sheikh, M. Recyclable Carbon-Based Hybrid Adsorbents Functionalized with Alumina Nanoparticles for Water Remediation. Crystals 2023, Vol. 13, Page 598 2023, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed El-Toni, A.; Habila, M.A.; Abbas Ibrahim, M.; Puzon Labis, J.; ALOthman, Z.A. Simple and Facile Synthesis of Amino Functionalized Hollow Core–mesoporous Shell Silica Spheres Using Anionic Surfactant for Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) Adsorption and Recovery. CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL 2014, 251, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habila, M.; Sheikh Moshab, M.; Mohamed El-Toni, A.; S. Al-Awadi, A.; A. ALOthman, Z. Facile Strategy for Fabricating an Organosilica-Modified Fe3O4 (OS/ Fe3O4) Hetero-Nanocore and OS/ Fe3O4@SiO2 Core–Shell Structure for Wastewater Treatment with Promising Recyclable Efficiency. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 7626–7638. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, N.; Zhao, C.; Sun, X.; Han, R.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Z. High-Efficiency Foam Fractionation of Anthocyanin from Perilla Leaves Using Surfactant-Free Active Al2O3 Nanoparticle as Collector and Frother: Performance and Mechanism. Food Chem 2023, 427, 136708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihsanullah; Al-Khaldi, F.A.; Abusharkh, B.; Khaled, M.; Atieh, M.A.; Nasser, M.S.; Laoui, T.; Saleh, T.A.; Agarwal, S.; Tyagi, I.; et al. Adsorptive Removal of Cadmium(II) Ions from Liquid Phase Using Acid Modified Carbon-Based Adsorbents. J Mol Liq 2015, 204, 255–263. [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, J.; Yuan, X.; Dong, H.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Hua, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. Facile Synthesis of Alumina-Decorated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Simultaneous Adsorption of Cadmium Ion and Trichloroethylene. Chemical Engineering Journal 2015, 273, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M. qin; Jin, X. ying; Lu, X.Q.; Chen, Z. liang Adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) onto Natural Kaolinite Clay. Desalination 2010, 252, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, N.M.; Alicia, R.F.; Abdullah, E.C.; Sahu, J.N.; Haslija, A.B.A.; Tan, J. Statistical Optimization and Kinetic Studies on Removal of Zn2+ Using Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes and Magnetic Biochar. J Environ Chem Eng 2013, 1, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, J.; Shao, D.; Ren, X.; Wang, X. Poly(Acrylic Acid) Grafted Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes by Plasma Techniques for Co(II) Removal from Aqueous Solution. Chemical Engineering Journal 2012, 210, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bosco, S.M.; Jimenez, R.S.; Vignado, C.; Fontana, J.; Geraldo, B.; Figueiredo, F.C.A.; Mandelli, D.; Carvalho, W.A. Removal of Mn(II) and Cd(II) from Wastewaters by Natural and Modified Clays. Adsorption 2006, 12, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoubi, H.; Zidani, O.; Mouflih, M.; Gourai, M.; Sebti, S. Removal of Cadmium from Water Using Natural Phosphate as Adsorbent. In Proceedings of the Procedia Engineering; Elsevier Ltd, 2014; Vol. 83, pp. 386–393. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, M.A.; Imran, M.; Amjad, M.; Abbas, G.; Tahir, M.; Murtaza, B.; Zakir, A.; Shahid, M.; Bulgariu, L.; Ahmad, I. Batch and Column Scale Removal of Cadmium from Water Using Raw and Acid Activated Wheat Straw Biochar. Water (Switzerland) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, T.; Nayaka, Y.A.; Viswanatha, R.; Basavanna, S.; Venkatesha, T.G. Kinetics and Thermodynamics Studies on the Adsorption of Zn(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Powder Technol 2012, 217, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engates, K.E.; Shipley, H.J. Adsorption of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, and Ni to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Effect of Particle Size, Solid Concentration, and Exhaustion. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2011, 18, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adigun, O.A.; Oninla, V.O.; Babarinde, N.A.A.; Oyedotun, K.O.; Manyala, N. Characterization of Sugarcane Leaf-Biomass and Investigation of Its Efficiency in Removing Nickel(II), Chromium(III) and Cobalt(II) Ions from Polluted Water. Surfaces and Interfaces 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Singh, H.; Sharma, S.; Barman, P.; Saini, A.; Verma, G. Synthesis and Characterization of Graphene Oxide-Bovine Serum Albumin Conjugate Membrane for Adsorptive Removal of Cobalt(II) from Water. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2021, 18, 3915–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jlil, S.A. Adsorption of Cobalt Ions from Waste Water on Activated Saudi Clays. Appl Water Sci 2017, 7, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, R.; Ashtiani Moghaddam, Z.; Ghafourian, H. Removal of Cobalt(II) Ion from Water by Adsorption Using Intact and Modified Ficus Carica Leaves as Low-Cost Natural Sorbent. Desalination Water Treat 2016, 57, 19890–19902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qomi, M.H.; Eisazadeh, H.; Hosseini, M.; Namaghi, H.A. Manganese Removal from Aqueous Media Using Polyaniline Nanocomposite Coated on Wood Sawdust. Synth Met 2014, 194, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhou, G.; Tang, Y.; Chu, L.; Liu, C.; Zeng, Z.; Luo, S. New Double Network Hydrogel Adsorbent: Highly Efficient Removal of Cd(II) and Mn(II) Ions in Aqueous Solution. Chemical Engineering Journal 2015, 275, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khobragade, M.U.; Pal, A. Investigation on the Adsorption of Mn(II) on Surfactant-Modified Alumina: Batch and Column Studies. J Environ Chem Eng 2014, 2, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budinova, T.; Savova, D.; B.Tsyntsarski; Ania, C.O.; Cabal, B.; Parra, J.B.; Petrov, N. Biomass Waste-Derived Activated Carbon for the Removal of Arsenic and Manganese Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Appl Surf Sci 2009, 255, 4650–4657. [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Fox, J.T. Synthesis and Appraisal of a Hydroxyapatite/Pectin Hybrid Material for Zinc Removal from Water. RSC Adv 2019, 9, 21095–21105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, M. Removal of Zinc Ions from Aqueous Solution Using Polyaniline Nanocomposite Coated on Rice Husk. Iranica Journal of Energy & Environment 2012, 3, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.M.; Lien, H.L. Dendrimer-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Removal of Zinc (II) from Aqueous Solutions. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 2011, 13, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Hao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, L. The Selective Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Dental Wastewater. Chem Phys 2020, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.Z.N.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Yusof, N.; Mohd Yusop, M.Z.; Hamdan, R.; Awang, N.A.; Ismail, N.H.; Rosman, N.; Sazali, N.; Ismail, A.F. Pb(II) Removal and Its Adsorption from Aqueous Solution Using Zinc Oxide/Graphene Oxide Composite. Chem Eng Commun 2021, 208, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
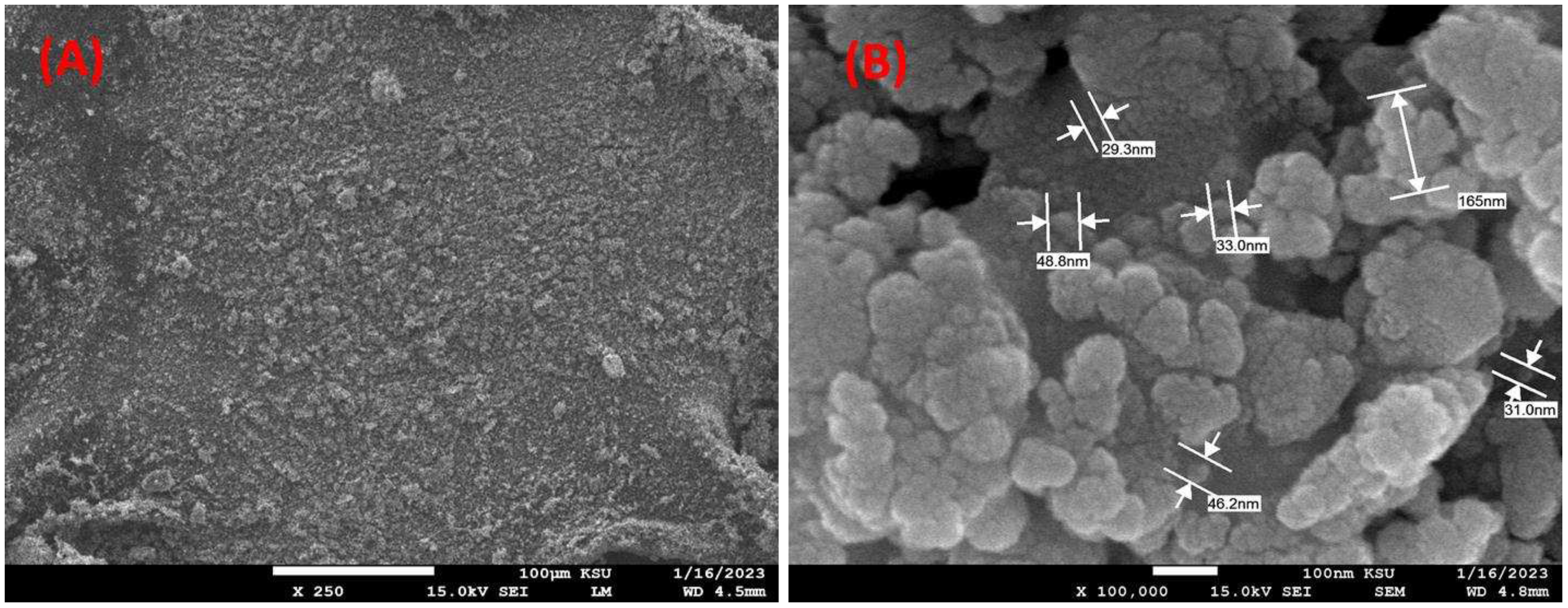

| Model | Equation | Constants |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo 1st order model | k1: the rate constant of the pseudo 1st order (min−1). | |
| Pseudo 2nd order model | K the rate constant of the pseudo 2nd (min−1). | |
| Langmuir isotherms |
Qomax (mg/g): maximum adsorption capacity KL (L/mg): a constant associated with the affinity ZnO-C and adsorbed heavy metals ions |
|
| Freundlich isotherms |
KF (mg/g)/(mg/L)n: Freundlich constant;. n (dimensionless) is the Freundlich intensity parameter. |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,exp (mg/g) | K1(min−1) | qe,cal(mg/g) | R2 | k2(g/mg.min) | qe,cal(mg/g) | R2 | |
| Cd(II) | 183.0 | 0.000192 | 196.1 | 0.957 | 0.00634 | 227.1 | 0.996 |
| Ni(II) | 180.0 | 0.000131 | 188.7 | 0.936 | 0.003821 | 233.1 | 0.994 |
| Mn(II) | 163.0 | 0.000119 | 181.8 | 0.944 | 0.000391 | 191.7 | 0.993 |
| Pb(II) | 196.0 | 0.00022 | 200.0 | 0.979 | 0.006079 | 258.4 | 0.997 |
| Adsorbate (heavy metals ions) | Langmuir constants | Freundlich constants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Q max. | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| Zn(II) | 0.029 | 212.77 | 0.88 | 3.21 | 0.54 | 0.95 |
| Cd(II) | 0.040 | 161.29 | 0.83 | 2.55 | 1.97 | 0.93 |
| Co(II) | 0.004 | 1111.11 | 0.27 | 2.55 | 1.42 | 0.90 |
| Mn(II) | - | - | - | 2.07 | 1.03 | 0.94 |
| Adsorbent | Wastewater | Initial concentration before treatment (mg/L) | Detected concentration After treatment (mg/L) | Removal Efficiency % | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Co | Cd | Zn | Mn | Co | Cd | Zn | Mn | Co | Cd | Zn | ||
| Carbon- Fe3O4 | Vally Water | 3.56 | 5.85 | 4.16 | 8.81 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 96 | 98 | 95 | 98 |
| Industrial Wastewater | 15.64 | 21.04 | 17.04 | 11.81 | 0.43 | 1.40 | 1.14 | 0.79 | 97 | 93 | 93 | 93 | |
| Rain Wastewater | 1.50 | 2.51 | 1.91 | 3.43 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 96 | 100 | 96 | 91 | |
| Cabon-ZnO | Vally Water | 3.56 | 5.85 | 4.16 | 8.81 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 99 | 97 | 98 | 98 |
| Industrial Wastewater | 15.64 | 21.04 | 17.04 | 11.81 | 1.05 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 1.07 | 93 | 100 | 99 | 91 | |
| Rain Wastewater | 1.50 | 2.51 | 1.91 | 3.43 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 96 | 98 | 99 | 97 | |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Optimum | Qe | Rf |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid modified carbon-based adsorbents | Cd(II) ion | pH = 7 contact time=120min |
M-CNTs= 2.02 mg/g M-AC= 1.98 mg/g M-CNFs= 1.58 mg/g M-FA= 1.22 mg/g |
[46] |
| Alumina-decorated multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) | Cd (II) ion trichloroethylene (TCE) |
pH = 7 contact time=240min |
Cd (II) ion= 27.21 mg/g TCE = 19.84 mg/g |
[47] |
| Natural kaolinite clay | Pb(II), Cd (II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) | pH = 5.5-7 contact time= 30 min |
Pb=2.35 mg/g Cd= 0.88 mg/g Ni= 0.90 mg/g Cu= 1.22 mg/g |
[48] |
| Functionalized carbon nanotubes and magnetic biochar | Zn(II) | pH = 10 contact time= 120 min |
functionalized CNT= 1.05 mg/g magnetic biochar= 1.18 mg/g |
[49] |
| Poly(acrylic acid) multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT-g-PAA) | Co(II) | pH = 6 contact time= 300 min |
3.55×10−4molg−1 | [50] |
| Natural and modified clay |
Mn(II) Cd(II) |
pH =1-6 contact time= 60 min |
NT-25/Cd(II)= 11.2 mg/g NT-25/Mn(II)= 6.0 mg/g |
[51] |
| Natural phosphate(NP) | Cd(II) | pH = 5 |
26mg/g | [52] |
| straw biochar (WSB)and acid treated wheat straw biochar (AWSB) | Cd(II) | pH = 6 contact time (5–180 min) |
WSB= 31.65 mg/g AWSB= 74.63 mg/g |
[53] |
| ZnO nanoparticles | Zn(II) Cd(II) Hg(II) |
pH = 5.5 |
357 mg/g for Zn(II) 387 mg/g for Cd(II) 714 mg/g for Hg(II) |
[54] |
| TiO2 nanoparticles | Pb, Cd, Cu, Ni, Zn | pH = 8 |
- | [55] |
| Sugarcane leaves (SCL) | Ni2+ Cr3+ Co2+ |
pH = 8 for Cr3+ |
51.3 mg/g for Ni2+ 62.5 mg/g for Cr3+ 66.7 mg/g for Co2+ |
[56] |
| graphene oxide-bovine serum Albumin(GO-BSA) |
Co(II) | pH = 6 |
184 mg/g | [57] |
| activated Saudi clays |
Co(II) | - | 12.9 mg/g for treated Tabbuk clay 12.55 mg/g for treated Bahhah clay |
[58] |
| intact and modified Ficus carica leaves (FCLs) |
Co(II) | pH = 6 |
33.9 mg/g | [59] |
| Polyaniline/sawdust composite | Mn(II) |
pH = 10 contact time= 30 min |
58.824 mg/g | [60] |
| Poly (sodium acrylate)- graphene oxide (PSA-GO) double network hydrogel | Mn(II) Cd(II) |
pH = 6 |
Mn(II) : 165.5 mg/g Cd(II): 238.3mg/g |
[61] |
| Surfactant Modified Alumina (SMA) | Mn(II) |
pH = 4.04-8.05 Contact time= 30 min |
2.04 mg/g | [62] |
| Activated carbon from bean pods waste | Mn(II) As (III) |
pH = 5-6 Contact time: 30 min |
Mn(II) =23.4 mg/g As (III)=1.01 mg/g |
[63] |
| hydroxyapatite/pectin hybrid material | Zn(II) |
pH = 5 |
330.4 mg/g | [64] |
| Polyaniline Nanocomposite Coated on Rice Husk(PAn/RH) | Zn(II) |
pH = 3 Contact time: 20 min |
24.3 mg/g | [65] |
| Dendrimer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles | Zn(II) |
pH= 7 | 24.3 mg/g | [66] |
| Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) |
Cr3+ | pH = 3-7 Contact time:20 min |
88.547 mg/g | [67] |
| Zinc oxide/ graphene oxide composite (ZnO/GO) | Pb(II) | pH = 5 Contact time:160 min |
909.09 mg/g | [68] |
| ZnO-C | Zn(II), Cd(II), Co(II), Mn(II) | pH=2 Contact time: 180 min |
This work | |
| Fe3O4-C | Zn(II), Cd(II), Co(II), Mn(II) | pH=2 Contact time: 180 min |
This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





