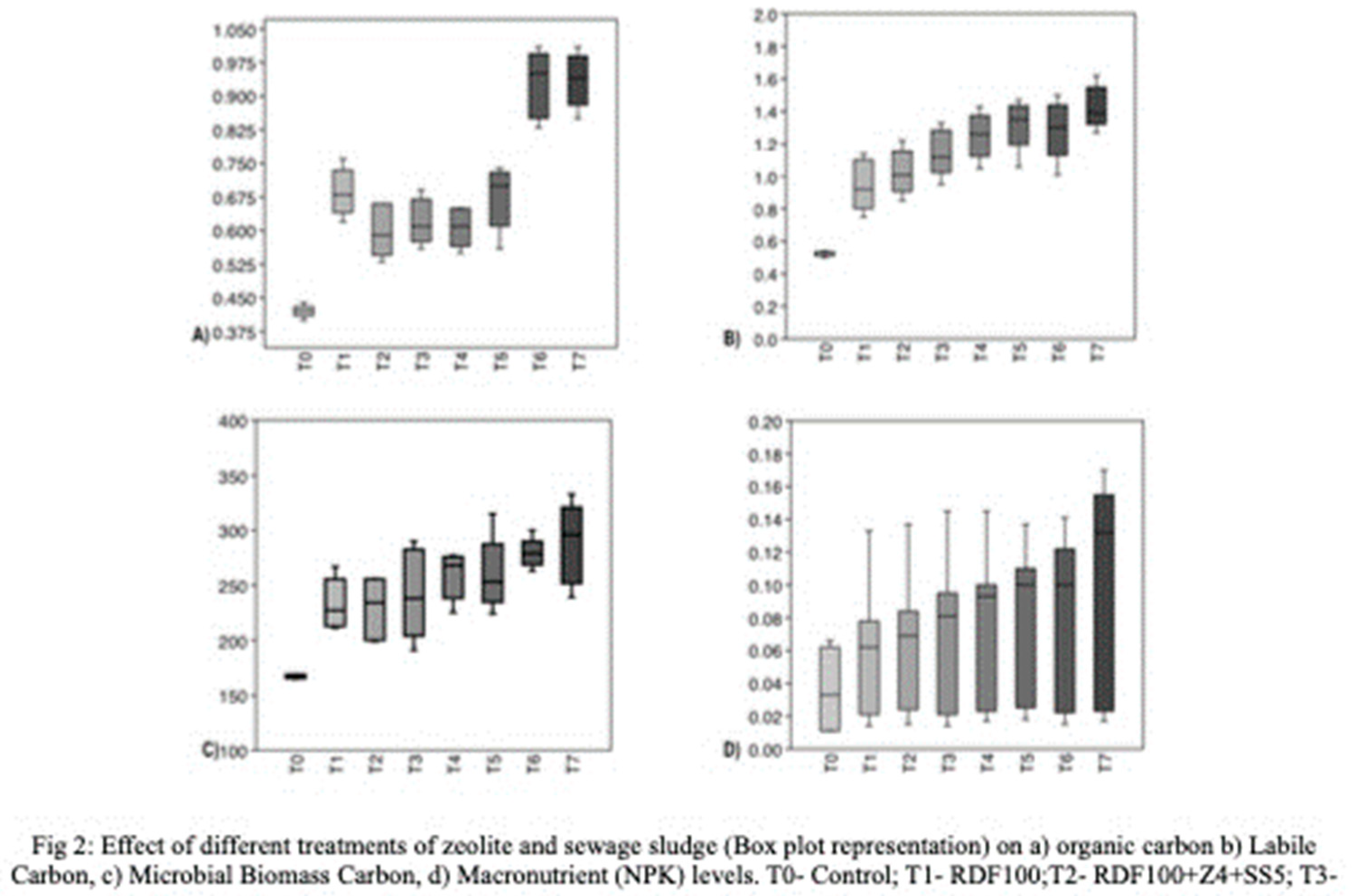
To investigate soil carbon pools, labile carbon was determined at different intervals in the pot soils (
Table 2). At 25 DAT, treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 exhibited significantly higher labile carbon content (1.27 mg/kg). At 40 DAT, treatment RDF75+Z6+SS10 recorded higher labile carbon values (1.4 mg/kg), while at 55 DAT, RDF50+Z6+SS10 showed the highest labile carbon values (1.39 mg/kg), followed by RDF75+Z6+SS10 (1.33 mg/kg) and RDF50+Z4+SS5 (1.30 mg/kg). At 70 DAT, labile carbon was again found to be higher in treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 (1.48 mg/ kg), followed by RDF50+Z4+SS5 (1.38 mg/kg). Zeolite-treated pots exhibited a 156% improvement in labile carbon compared to pots treated with the recommended dose of fertilizer alone, indicating the nutrient and carbon retention properties of zeolite. The application of sewage sludge in combination with microporous nanomaterials like zeolite enhanced the soil's reactive surface area and consequently increased labile carbon levels. Long-term studies [
25] have shown significantly higher carbon management levels in soils treated with sewage sludge. Soil organic carbon levels were significantly correlated with soil labile carbon, highlighting the precise role of zeolite in amplifying soil reaction rates. The enhancement of surface area improves soil microbial functions and protects soil organic matter, leading to a greater accumulation of labile carbon [
12]. Treatment RDF50+Z4+SS5 and RDF50+Z6+SS10 exhibited significantly higher microbial biomass carbon compared to the other treatments (
Table 3). The microbial biomass carbon was positively correlated with soil organic carbon and labile carbon, indicating that the combination of clinoptilolite zeolite and sewage sludge enhances microbial population and, consequently, microbial biomass carbon. A study conducted by Aminiyan and Akhgar [
26] yielded similar findings, demonstrating the positive impact of zeolite on the soil carbon fractions through the promotion of microbial growth.
3.1.
The initial available nitrogen content in the soil was 0.098 g/kg, which significantly increased after soil treatment. At 25 DAT, treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 displayed significantly higher available nitrogen values (0.30 g/kg), and similar trends were observed at 40 DAT (
Table 4). The period between 25 and 40 DAT was crucial, as it coincided with the peak activity of plant roots, which absorb nitrogen for vegetative growth. At 55 DAT, treatment RDF75+Z6+SS10 exhibited significantly higher available nitrogen values (0.23) compared to the other treatments. Treatments RDF50+Z4+SS5 and RDF50+Z6+SS10 showed a tendency to enhance soil available nitrogen, particularly during the early stages of crop growth, and later stabilized nutrient mobilization. This could be attributed to the efficient nutrient absorption and reduced leaching characteristics of zeolite. Studies have shown that zeolite, when combined with organic manures, prevents ammonia leaching by providing a structural matrix-like framework, thereby improving soil nutrient retention [
27]. The initial available phosphorus content, which is crucial for plant functions, was recorded at 0.015 g/kg. Treatment RDF75+Z6+SS10 consistently showed higher significant values of available phosphorus throughout the cultivation period (
Table 5). This suggests that zeolite, along with organic matter, creates a reactive matrix that efficiently holds and stabilizes available nutrients, even at higher concentrations of mineral fertilizers. According to research by Omogbohu and Akinkunmi [
28], an appropriate concentration of phosphorus is required to satisfy soil sorption sites, enabling phosphorus to be made available to plants. Zeolite-like nanomaterials provide the framework to hold such crucial soil nutrients throughout cultivation [
8]. Soil-available potassium, another crucial element for plant biochemical reactions, was initially reported at 0.075 g/gm and significantly increased among the treatments at later stages (25 DAT). Treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 exhibited significantly higher available potash values.
The utilization of zeolite has a tendency to improve the availability of potassium in the soil [
29] due to its slow nutrient release characteristics and increased surface area for oxidation (
Table 6). Treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10, despite receiving only 50% of the recommended fertilizer dose, benefits from the organic carbon provided by sewage sludge and the enhanced soil reactions facilitated by zeolite, leading to more stable nutrient mineralization and availability [
8]. To compare soil carbon with soil available macronutrients (NPK), box plots were constructed using data from soil carbon pools and macronutrient measurements taken at 25, 40, 55, 70, and 85 DAT (
Figure 2). It is evident that treatments RDF50+Z4+SS5 and RDF50+Z6+SS10, which received 50% RDF, 4-6% zeolite, and 5-10% sewage sludge, significantly influenced soil carbon pools (SOM, LB, MBC). The levels of soil carbon also have an impact on the availability of soil macronutrients (NPK).
The box plots depicting macronutrients (NPK) demonstrate that the soil treated solely with mineral fertilizer exhibits substantial variation in nutrient availability throughout the cultivation period. However, treatments incorporating a higher percentage of zeolite and sewage sludge ensure nutrient availability and stability during the cultivation period.
Treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 exhibited significantly higher levels of Zinc (0.0046 g/kg). The concentration of soil iron during the initial stages was measured at 0.0072 g/kg, and later on, significantly higher levels were observed in treatment T6 (Data not shown). The incorporation of zeolite and sewage sludge in the treatments improved the concentration of copper and manganese in the soil. Zeolite, with its enhanced cation exchange properties, facilitated the mobilization of micronutrients in the soil, thereby increasing their concentration [
30]. Additionally, the use of organic matter such as sewage sludge may contribute to the stabilization of the ability to absorb positively charged ions. Principal component analysis of soil micronutrients segregated the treatments into two groups: those with combinations of zeolite and sewage sludge (RDF 100 +Z 6 +SS 10, RDF 75 +Z 6 +SS 10, RDF 50 +Z 4 +SS 5, and RDF50+Z6+SS10), and those without zeolite and sewage sludge (Control and RDF100). This further confirms the role of zeolite in retaining micronutrients in the soil. The count of leaves per plant was conducted at 25, 40, 55, 70, and 85 days after transplanting. The treatment RDF100 exhibited the maximum number of leaves, with 65 recorded, indicating that the addition of zeolite and sewage sludge enhances soil nitrate availability, leading to an increase in leaf numbers [
31]. At 40 days after transplanting, the leaf count was significantly higher in treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10, suggesting a proportional reduction in RDF combined with the use of nanomaterials that enhance soil nutrient availability [
32]. The incorporation of zeolite, RDF, and sewage sludge in all treatments at 40 days after transplanting resulted in a 137% higher leaf count compared to the control. Such an increase in leaf number is crucial during the vegetative growth stage of plants[
33]. The number of tillers indicates the efficiency of plant nutrient uptake, and the observations from the experiment revealed that the number of tillers was significantly higher in treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10, with a count of 18.33 at 25 days after transplanting. Similar trends were observed at 40 and 85 days after transplanting. At 55 days after transplanting, treatment T7 exhibited the highest number of tillers (35.33), followed by RDF50+Z4+SS5 (32). The results at 70 and 85 days after transplanting also showed significantly higher numbers of tillers in the pots treated with RDF50+Z6+SS10, with values of 36.66 and 38, respectively. All pots treated with zeolite and sewage sludge demonstrated a positive impact compared to treatments without fertilizer or only RDF without zeolite and sewage sludge.
At 25 days after transplanting (DAT), the plant height was significantly higher in treatment RDF75+Z6+SS10 (56.33) and RDF100+Z4+SS5 (56.75). However, in later stages of growth, the plant height was significantly higher in treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10, possibly due to the slow nutrient release activity of sewage sludge, which stabilizes the nutrient flow during the later stages of plant growth. Another study by Rabai et al [
34] also suggests that zeolite amendments improve plant height in later stages. The culm length was significantly higher in treatment RDF100+Z4+SS5 (18.67) and lowest in the control (12.37). At 40 days after transplanting, the culm length was significantly higher in treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 (21.04), probably due to the impact of sewage sludge and RDF provided during the earlier stages of plant growth. The highest significant value for culm length was found in treatment RDF50+Z4+SS5 (23.33) at 55 DAT and 70 DAT (28.66). After 25 DAT, there was no significant growth in culm length for the next two crop stages; however, after 70 DAT, the culm length steeply increased.
This study highlights the role of organic matter in stabilizing the soil nutrient flow and enhancing culm length during the later stages of cultivation. At the initial stages of crop growth, leaf length was high in treatment RDF100+Z4+SS5, RDF75+Z6+SS10, and RDF50+Z6+SS10 (25 DAT); however, at later stages, treatment RDF75+Z6+SS10 consistently showed higher positive impacts and enhanced leaf length. The vegetation growth period (40 and 50 DAT) of the crop was most crucial in determining yield. In the control pot, leaf length was significantly lower (43.7 and 48.4 cm) respectively. Leaf length was comparatively good in RDF75+Z6+SS10 at 25, 40, and 50 DAT. There was not much difference between the highest two treatments (RDF100+Z4+SS5 and RDF50+Z6+SS10) compared to treatment RDF75+Z6+SS10 (Data not shown). The reason why RDF75+Z6+SS10 showed the maximum significantly higher values may be attributed to the absorption of nutrients by the zeolite in earlier stages and their release at later stages for the plant. Zeolite application promotes leaf area and overall plant height [
35]. Stem girth was recorded significantly higher in treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10, measuring 49.06 mm at 25 DAT, compared to the control, which had significantly lower values. It is evident that an increased number of tillers enhance stem girth and nutrient availability. Zeolite mediates continuous nutrient availability and improves stem girth [
36].
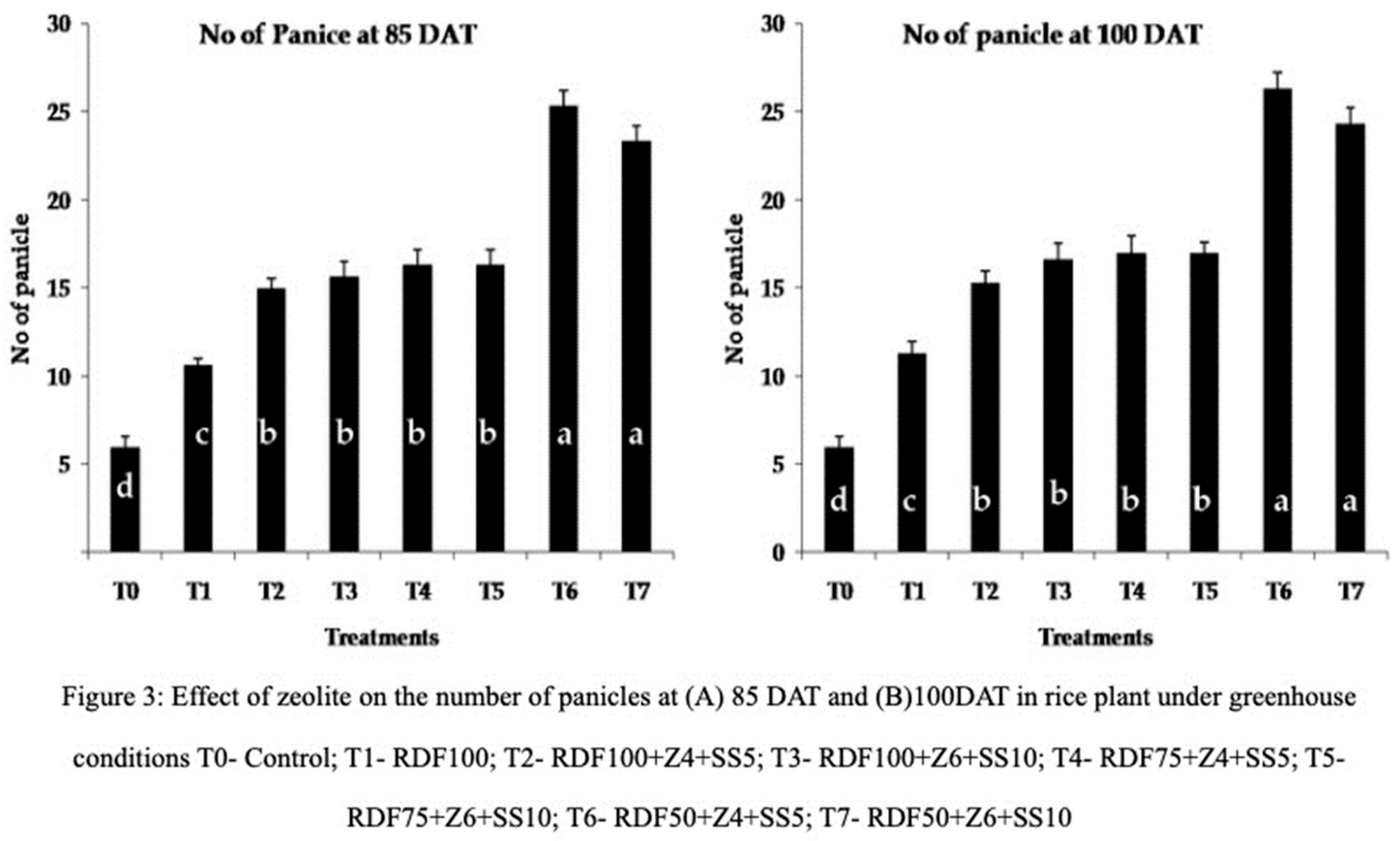
The count of panicles, which represents a fraction of yield, was conducted at 85 and 100 days after transplanting (DAT). The highest numbers of panicles were observed in treatment RDF50+Z4+SS5 (25.33 and 26.33) and treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 (25.33 and 24.33) at 85 and 100 DAT, respectively (
Figure 3). These results indicate that both RDF50+Z4+SS5 and RDF50+Z6+SS10 had a significant impact on panicle development. In both treatments, the recommended dose of fertilizer was reduced while additional zeolite and sewage sludge were provided, which may have enhanced soil nutrient mineralization. Zheng et al [
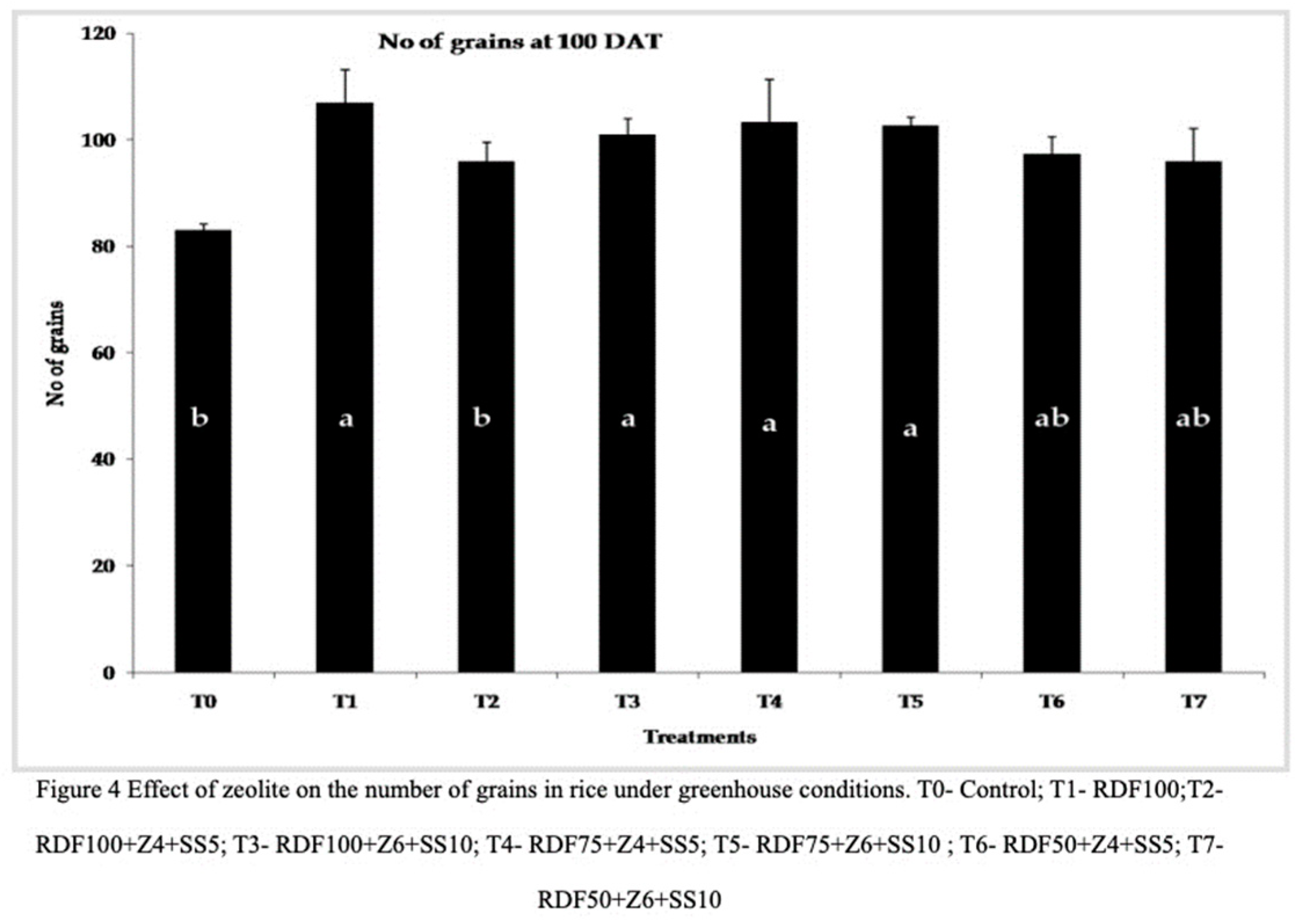
37] explained the role of zeolite in promoting the number of panicles and overall rice yield. Treatment RDF100+Z6+SS10 (101), RDF75+Z4+SS5 (103.33), and RDF75+Z6+SS10 (102.66) significantly influenced the number of grains at 100 DAT, while the control treatment (83) and RDF100+Z4+SS5 (96) had the lowest effect. Zeolite and sewage sludge amended pots showed an average increase of fourteen percent compared to the control treatment and RDF100 (
Figure 4). The application of zeolite may contribute to the controlled release of nutrients throughout the various stages of crop growth, thereby enhancing yield parameters [
38].
Treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 (330.33) exhibited the highest grain yield, followed by RDF50+Z4+SS5 (309.5). The increase in the number of panicles positively influenced the grain yield (Figure 5). The zeolite-treated pot showed a significantly higher grain yield compared to the control, which aligns with the findings of Zheng et al. [
37]. According to Sepaskhah and Barzegar [
39], the application of nitrogen with zeolite facilitated the slow release of fertilizer, leading to improved rice crop yield. The straw yield in the zeolite-treated pot was 103 percent higher, indicating that the application of zeolite along with sewage sludge enhanced plant biomass and dry weight. Previous research by Aainaa et al [
36] supports the positive impact of zeolite application on yield parameters, and incorporating organic matter may provide a standardized approach for further investigation of the precise impact of nano-materials.
There is a significant correlation between soil nutrients, organic carbon, labile carbon, microbial biomass carbon, and plant growth and yield parameters (
Table 7). Total organic carbon exhibited a significant correlation with available nitrogen (0.76**), available phosphorus (0.60**), and available potassium (0.64**). Similarly, labile carbon showed a significant impact on available nitrogen (0.527**), available phosphorus (0.78**), and available potassium (0.81**). The organic carbon fraction displayed a strong correlation with leaf number (0.6**), tiller number (0.71**), plant height (0.8*), clum length (0.51*), and stem girth (0.76**). Soil carbon fractions (labile carbon, organic carbon, and microbial biomass carbon) exhibited a strong correlation with growth and yield parameters, indicating that the use of nanomaterials may improve rice growth and yield. Bybordi and Ebrahimian [
40] suggested that zeolite application significantly affected macronutrients (NPK) and micronutrients such as Zn and Fe. Long-term experiments conducted by Brock et al [
41] demonstrated a positive correlation between soil organic matter and yield in organic farming, with potential variations in correlations under conventional farming systems.
Principal component analysis (PCA) has been commonly employed as a multivariate method for classifying treatments, as demonstrated in a study by Ullah et al [
42]. In a recent investigation conducted by Sachin and Isler [
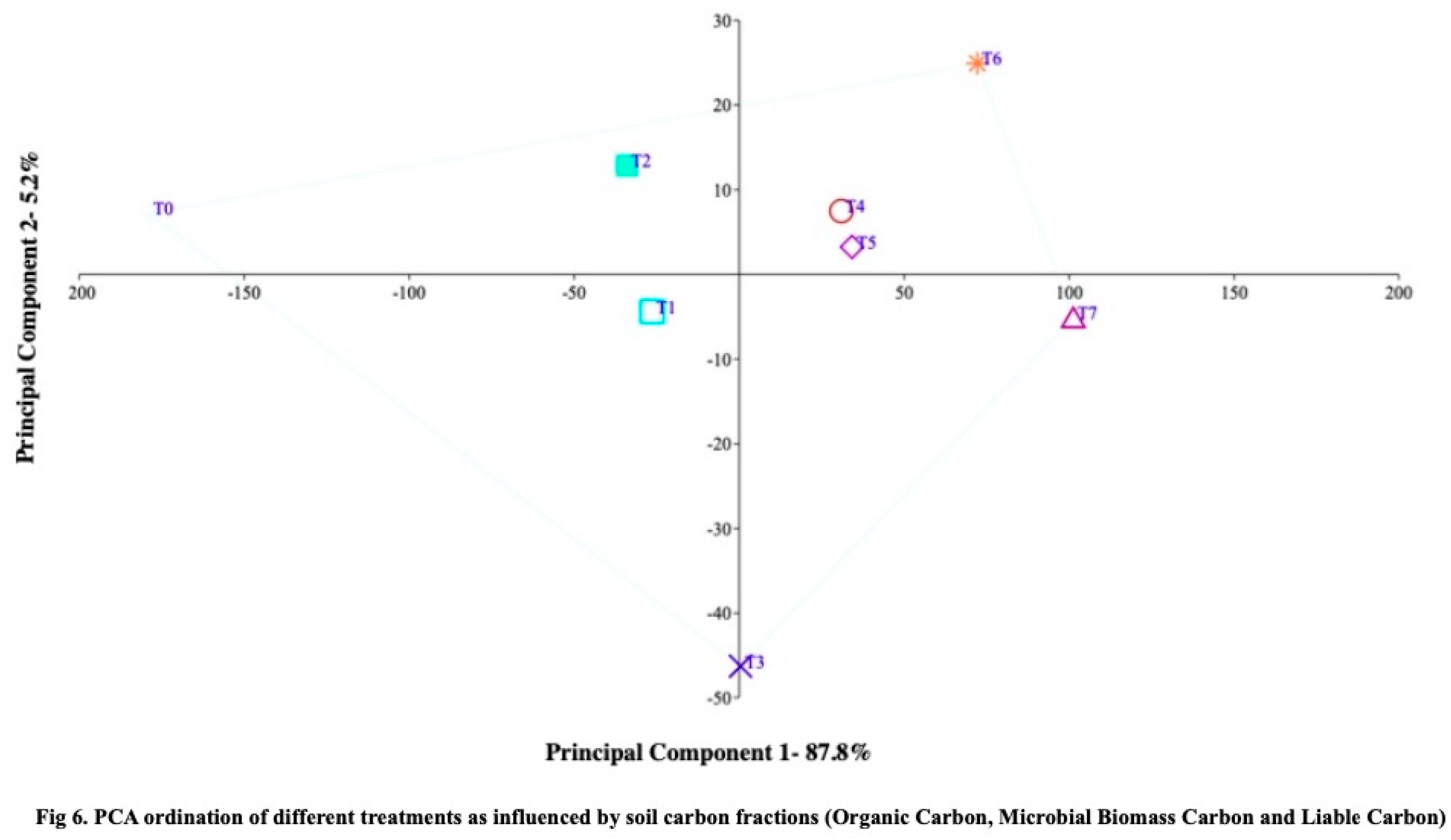
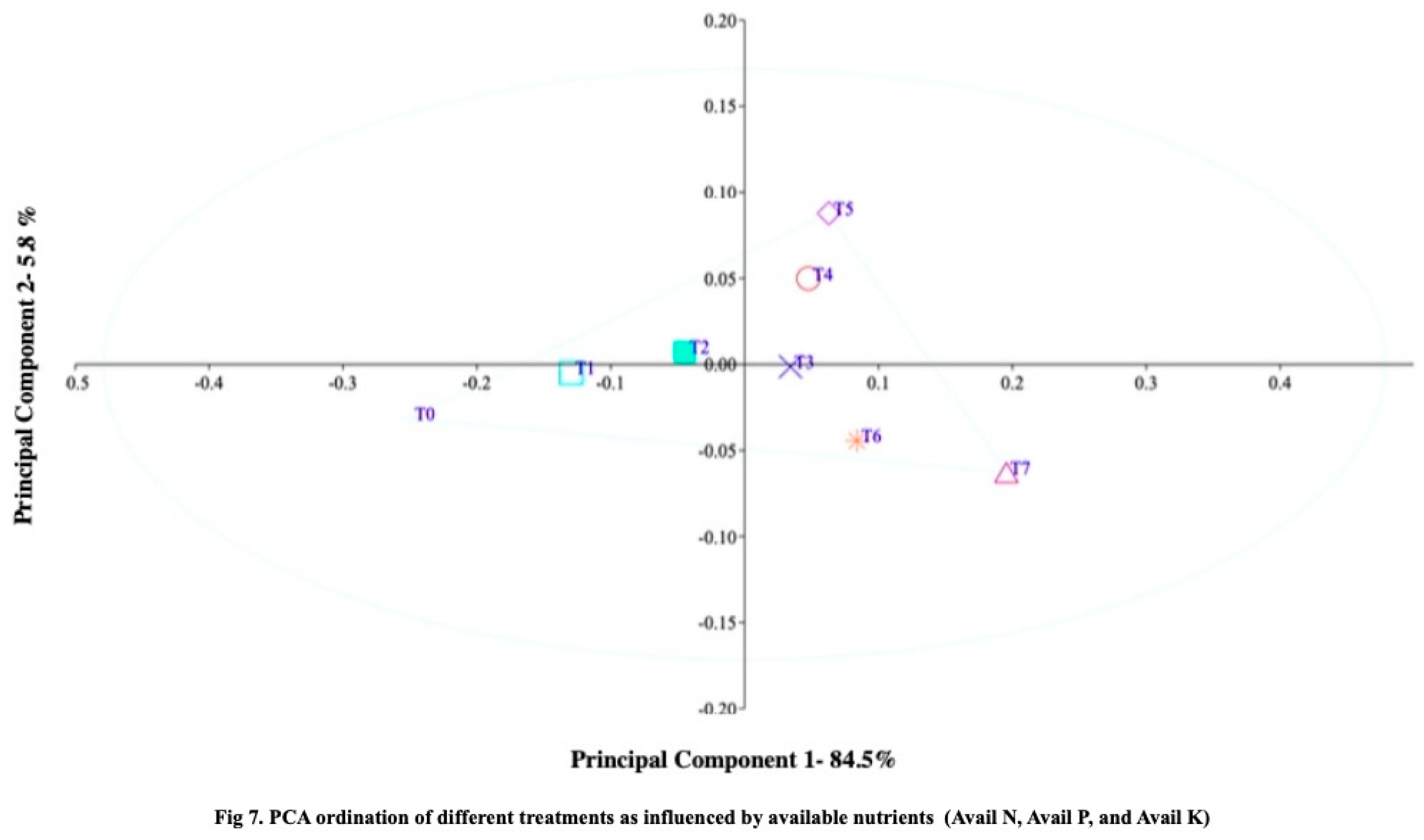
43], PCA was utilized to classify the differences in zinc and iron treatments and their effects on soybean yield components. The results of the research study demonstrate that treatment T7-RDF50+Z6+SS10 exhibited higher values for soil carbon fractions (organic carbon, microbial biomass carbon, and liable carbon) compared to the other treatments (
Figure 6), indicating that zeolite application may enhance soil carbon stability during the cultivation period. The principal component ordination analysis of major macronutrients (available nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) in the soil showed significantly higher values for treatment T7-RDF50+Z6+SS10, suggesting that zeolite application may also improve soil nutrient availability (
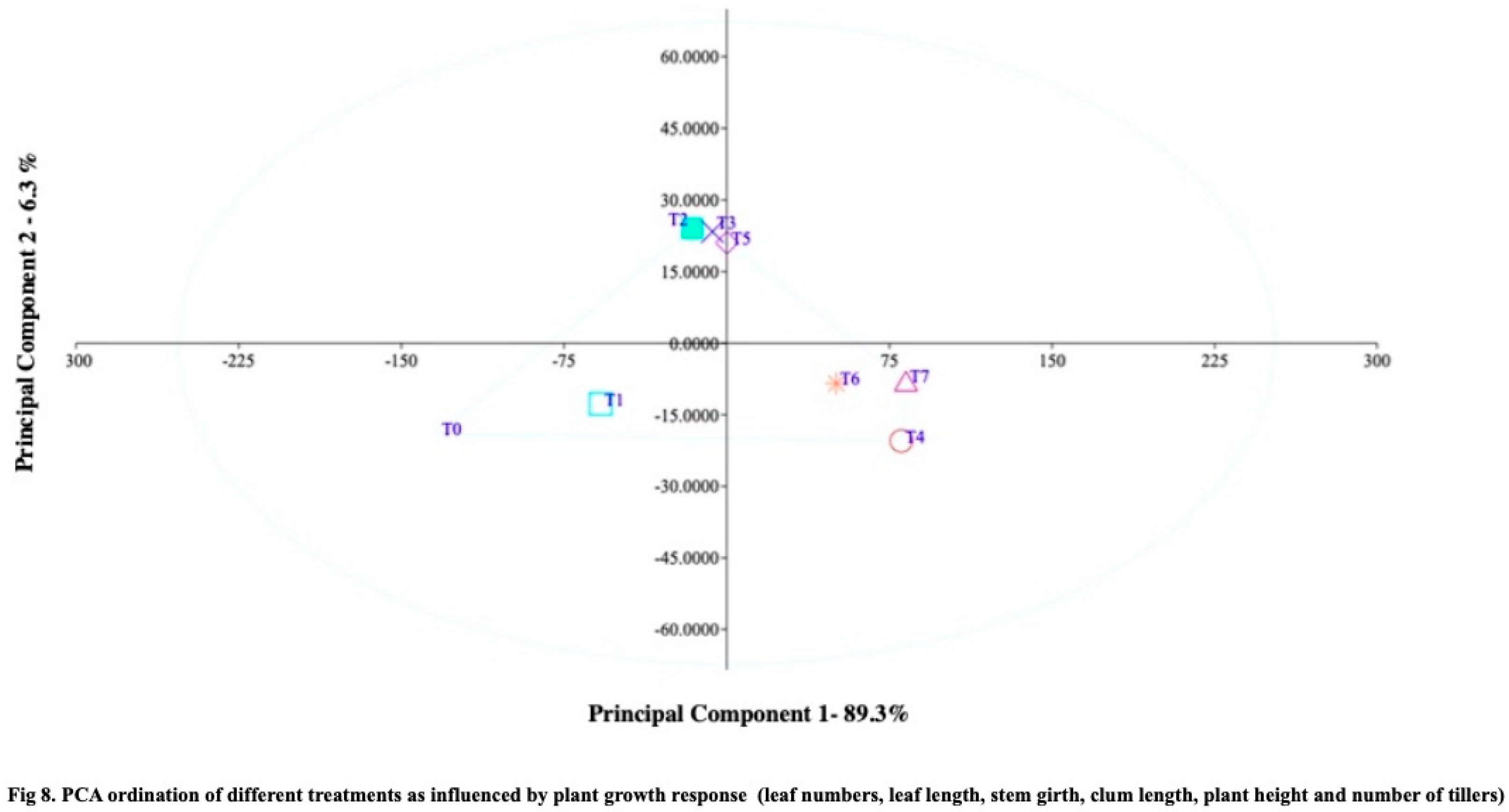
Figure 7). The Principal Component Analysis (PCA) plot of plant growth response revealed significant differences among the treatments, with Treatment T0 showing more negative scores and Treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 exhibiting higher positive scores. The Principal Component Analysis (PCA) plot effectively differentiated the treatments based on the variations observed in growth and yield data. Principal component 1, representing the plant growth response, accounted for a substantial 89.3% of the overall variation (
Figure 8), highlighting significant distinctions among the treatments. Specifically, the Control and RDF100 treatments stood apart from the other treatments. By comparing the PCA scores of PC1 and PC2, it was evident that treatment T0 exhibited predominantly negative scores, while treatment RDF50+Z6+SS10 demonstrated notably higher positive scores.
Moreover, treatments RDF100+Z4+SS5, RDF100+Z6+SS10, and RDF75+Z6+SS10 clustered together, while treatments RDF75+Z4+SS5, RDF50+Z4+SS5, and RDF50+Z6+SS10 also formed a distinct cluster, exhibiting enhanced positive values of plant growth response. The findings of this study validate the effectiveness of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) in assessing and establishing relationships among treatments, particularly in the context of nano-material soil applications. PCA proves to be an efficient tool for evaluating the impact and effectiveness of nano materials in relation to soil parameters and rice yield. Based on the findings of the present study, it can be concluded that the application of zeolite at a concentration of 6% and sewage sludge at a concentration of 10%, along with a 50% recommended dose of fertilizer, elicit positive responses in rice plant growth. Additionally, the use of zeolite at 4% and sewage sludge at 5% of the recommended dose of fertilizer also results in improved plant growth.
The study highlights the significant role of soil carbon fractions, namely labile carbon, soil organic carbon, and microbial biomass carbon, in influencing the growth and yield characteristics of rice plants. Changes in soil carbon fractions have a direct impact on plant growth, indicating that the utilization of nano-materials in soil has the potential to enhance soil carbon fractions and contribute to more sustainable utilization of natural resources. However, further research focusing on soil molecular studies is necessary to gain a deeper understanding of the changes in soil microbial ecology resulting from the application of zeolite and sewage sludge.