Submitted:
27 December 2023
Posted:
28 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Dialysis prescription and equipment
2.4. Outcomes
2.4.1. Adverse events
2.4.2. Dialysis recovery time
- i.
- Answers given in minutes were recorded directly.
- i.
- Answers in hours were multiplied by 60.
- i.
- Variants of “half a day,” including the “next day,” were given a value of 720 min.
- i.
- Variants of “one day” were given a value of 1440 min.
- i.
- Variants of “more than a day” were given a value of 2160 min (36 h).
2.4.3. Hemodynamic monitoring
2.4.4. Hydration state
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of patients
3.2. Dialysis parameters
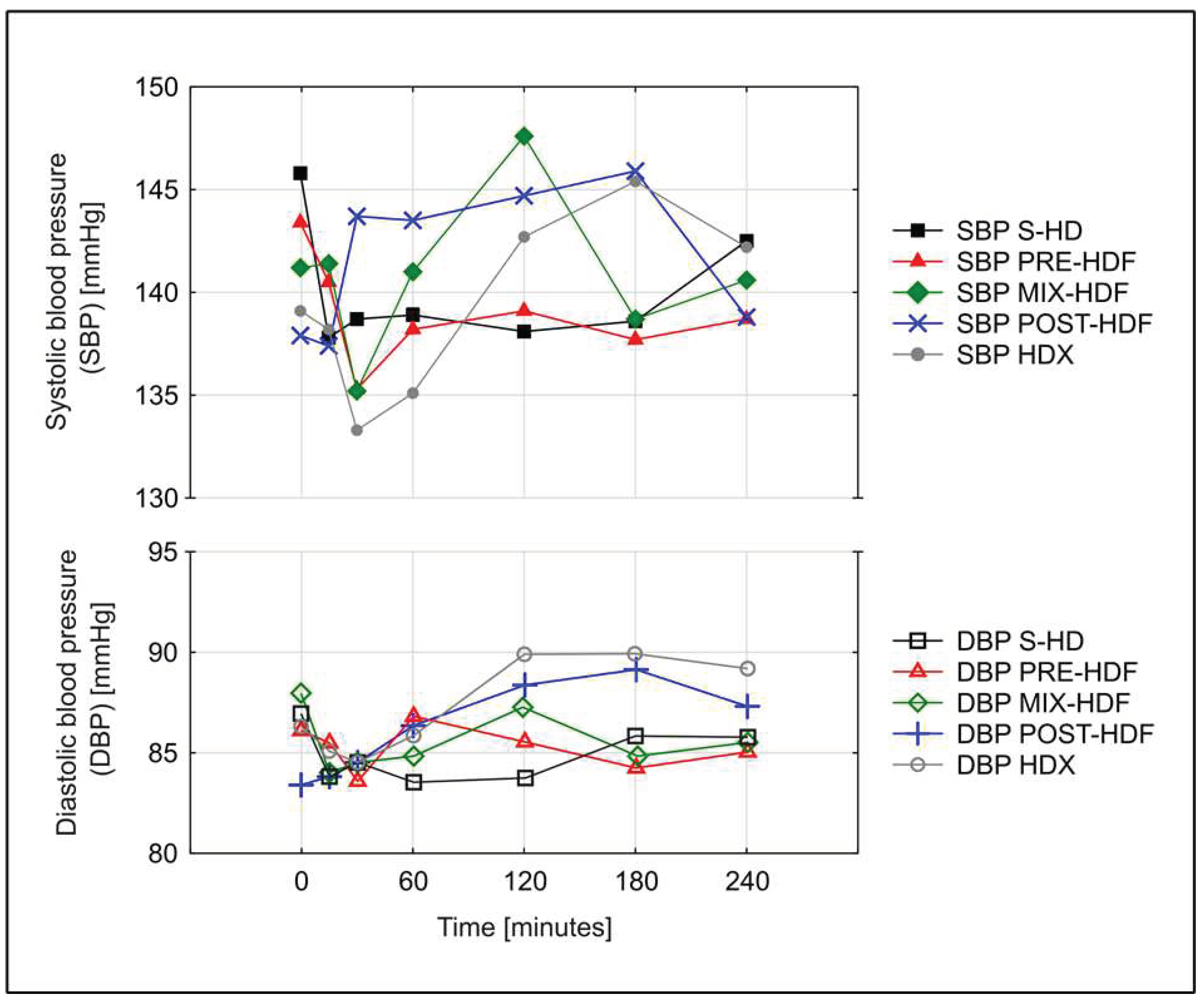
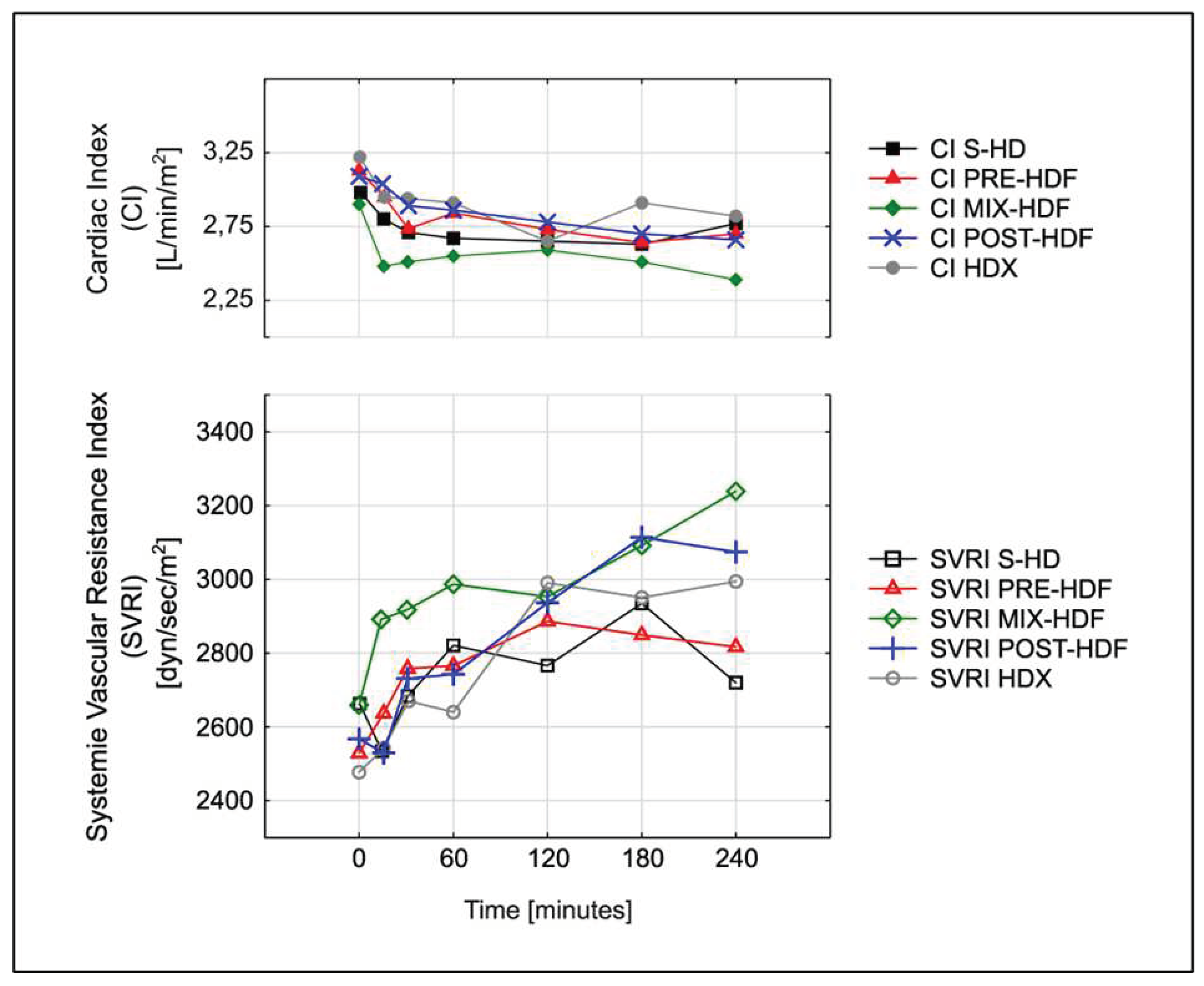
3.3. Hemodynamic parameters.
3.4. Adverse events and dialysis recovery time
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, T., A. M. Zawada, L. Theis, J. Braun, B. Ottillinger, P. Kopperschmidt, A. Gagel, P. Kotanko, M. Stauss-Grabo, J. P. Kennedy, et al. "Hemodiafiltration: Technical and medical insights." Bioengineering (Basel) 10 (2023). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36829639. [CrossRef]
- Pedreros-Rosales, C., A. Jara, E. Lorca, S. Mezzano, R. Pecoits-Filho and P. Herrera. "Unveiling the clinical benefits of high-volume hemodiafiltration: Optimizing the removal of medium-weight uremic toxins and beyond." Toxins (Basel) 15 (2023). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37755957. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., T. Yang, Y. Li, J. Li, Q. Yang, L. Wang, L. Jiang and B. Su. "Effects of expanded hemodialysis with medium cut-off membranes on maintenance hemodialysis patients: A review." Membranes (Basel) 12 (2022). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35323729. [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A., S. A. Peters, M. L. Bots, B. Canaud, M. P. Grooteman, G. Asci, F. Locatelli, F. Maduell, M. Morena, M. J. Nube, et al. "Higher convection volume exchange with online hemodiafiltration is associated with survival advantage for dialysis patients: The effect of adjustment for body size." Kidney Int 89 (2016): 193-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26352299. [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K., T. Hamano, A. Wada, S. Nakai and I. Masakane. "Predilution online hemodiafiltration is associated with improved survival compared with hemodialysis." Kidney Int 95 (2019): 929-38. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30782421. [CrossRef]
- Blankestijn, P. J., R. W. M. Vernooij, C. Hockham, G. F. M. Strippoli, B. Canaud, J. Hegbrant, C. Barth, A. Covic, K. Cromm, A. Cucui, et al. "Effect of hemodiafiltration or hemodialysis on mortality in kidney failure." N Engl J Med 389 (2023): 700-09. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37326323. [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, G. B., L. Nielsen, L. Gendrot, A. Fois, E. Cataldo and G. Cabiddu. "Prescribing hemodialysis or hemodiafiltration: When one size does not fit all the proposal of a personalized approach based on comorbidity and nutritional status." J Clin Med 7 (2018). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30297628. [CrossRef]
- Zawierucha, J., J. Małyszko, A. Dębska-Ślizień, M. Durlik, M. Krajewska, G. Chmiel, K. Ciechanowski, M. Klinger, J. Małyszko, M. Nowicki, et al. "Expert panel position statement on indication for hemodiafiltration (hdf) therapy in end stage renal disease patients." NEFROL. DIAL. POL. 22 (2018): 9-12.
- Schiffl, H. "Online hemodiafiltration and mortality risk in end-stage renal disease patients: A critical appraisal of current evidence." Kidney Res Clin Pract 38 (2019): 159-68. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31137926. [CrossRef]
- Marcelli, D., C. Scholz, P. Ponce, T. Sousa, P. Kopperschmidt, A. Grassmann, B. Pinto and B. Canaud. "High-volume postdilution hemodiafiltration is a feasible option in routine clinical practice." Artif Organs 39 (2015): 142-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25277688. [CrossRef]
- Smith, J. R., N. Zimmer, E. Bell, B. G. Francq, A. McConnachie and R. Mactier. "A randomized, single-blind, crossover trial of recovery time in high-flux hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration." Am J Kidney Dis 69 (2017): 762-70. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28024931. [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R. M., P. A. Heidenheim, G. Nesrallah, A. X. Garg, R. Suri and C. Daily Hemodialysis Study Group London Health Sciences. "Minutes to recovery after a hemodialysis session: A simple health-related quality of life question that is reliable, valid, and sensitive to change." Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1 (2006): 952-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17699312. [CrossRef]
- Scherhag, A., J. J. Kaden, E. Kentschke, T. Sueselbeck and M. Borggrefe. "Comparison of impedance cardiography and thermodilution-derived measurements of stroke volume and cardiac output at rest and during exercise testing." Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 19 (2005): 141-7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16025233. [CrossRef]
- Moissl, U. M., P. Wabel, P. W. Chamney, I. Bosaeus, N. W. Levin, A. Bosy-Westphal, O. Korth, M. J. Muller, L. Ellegard, V. Malmros, et al. "Body fluid volume determination via body composition spectroscopy in health and disease." Physiol Meas 27 (2006): 921-33. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16868355. [CrossRef]
- Shroff, R., C. Basile, F. van der Sande, S. Mitra and A. EuDial Working Group* of the European Renal. "Haemodiafiltration for all: Are we convinced?" Nephrol Dial Transplant (2023). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37391380. [CrossRef]
- Merkus, M. P., K. J. Jager, F. W. Dekker, E. W. Boeschoten, P. Stevens and R. T. Krediet. "Quality of life in patients on chronic dialysis: Self-assessment 3 months after the start of treatment. The necosad study group." Am J Kidney Dis 29 (1997): 584-92. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9100049. [CrossRef]
- Bello, A. K., I. G. Okpechi, M. A. Osman, Y. Cho, H. Htay, V. Jha, M. Wainstein and D. W. Johnson. "Epidemiology of haemodialysis outcomes." Nat Rev Nephrol 18 (2022): 378-95. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35194215. [CrossRef]
- Puchalska-Reglińska, E., A. Debska-Slizien, B. Biedunkiewicz, P. Tylicki, K. Polewska, B. Rutkowski, R. Gellert and L. Tylicki. "Extremely high mortality in covid-19 hemodialyzed patients before the anti-sars-cov-2 vaccination era. Large database from the north of poland." Pol Arch Intern Med 131 (2021): 643-48. https://www.mp.pl/paim/issue/article/16028/. [CrossRef]
- Monardo, P., A. Lacquaniti, S. Campo, M. Bucca, T. Casuscelli di Tocco, S. Rovito, A. Ragusa and A. Santoro. "Updates on hemodialysis techniques with a common denominator: The personalization of the dialytic therapy." Semin Dial 34 (2021): 183-95. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33592133. [CrossRef]
- Flythe, J. E., A. Dorough, J. H. Narendra, D. Forfang, L. Hartwell and E. Abdel-Rahman. "Perspectives on symptom experiences and symptom reporting among individuals on hemodialysis." Nephrol Dial Transplant 33 (2018): 1842-52. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29672712. [CrossRef]
- Caplin, B., H. Alston and A. Davenport. "Does online haemodiafiltration reduce intra-dialytic patient symptoms?" Nephron Clin Pract 124 (2013): 184-90. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24401696. [CrossRef]
- Jhamb, M., C. Argyropoulos, J. L. Steel, L. Plantinga, A. W. Wu, N. E. Fink, N. R. Powe, K. B. Meyer, M. L. Unruh and S. Choices for Healthy Outcomes in Caring for End-Stage Renal Disease. "Correlates and outcomes of fatigue among incident dialysis patients." Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4 (2009): 1779-86. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19808226. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, L., D. Brown, D. Hu, G. M. Chertow, J. A. Vassalotti and S. Prichard. "Intradialytic symptoms and recovery time in patients on thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis: A cross-sectional online survey." Kidney Med 2 (2020): 125-30. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32734233. [CrossRef]
- Rayner, H. C., L. Zepel, D. S. Fuller, H. Morgenstern, A. Karaboyas, B. F. Culleton, D. L. Mapes, A. A. Lopes, B. W. Gillespie, T. Hasegawa, et al. "Recovery time, quality of life, and mortality in hemodialysis patients: The dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study (dopps)." Am J Kidney Dis 64 (2014): 86-94. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24529994. [CrossRef]
- Morena, M., A. Jaussent, L. Chalabi, H. Leray-Moragues, L. Chenine, A. Debure, D. Thibaudin, L. Azzouz, L. Patrier, F. Maurice, et al. "Treatment tolerance and patient-reported outcomes favor online hemodiafiltration compared to high-flux hemodialysis in the elderly." Kidney Int 91 (2017): 1495-509. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28318624. [CrossRef]
- Schiffl, H. "High-volume online haemodiafiltration treatment and outcome of end-stage renal disease patients: More than one mode." Int Urol Nephrol 52 (2020): 1501-06. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32488753. [CrossRef]
- Maduell, F., F. Moreso, M. Pons, R. Ramos, J. Mora-Macia, J. Carreras, J. Soler, F. Torres, J. M. Campistol, A. Martinez-Castelao, et al. "High-efficiency postdilution online hemodiafiltration reduces all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients." J Am Soc Nephrol 24 (2013): 487-97. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23411788. [CrossRef]
- Ethier, I., I. Nevis and R. S. Suri. "Quality of life and hemodynamic effects of switching from hemodialysis to hemodiafiltration: A canadian controlled cohort study." Can J Kidney Health Dis 8 (2021): 20543581211057717. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34804556. [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F., F. Mastrangelo, B. Redaelli, C. Ronco, D. Marcelli, G. La Greca and G. Orlandini. "Effects of different membranes and dialysis technologies on patient treatment tolerance and nutritional parameters. The italian cooperative dialysis study group." Kidney Int 50 (1996): 1293-302. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8887291. [CrossRef]
- Park, H. C. and Y. K. Lee. "Who is the winner, pre-, post-, or mixed-dilution hemodiafiltration?" Kidney Res Clin Pract 40 (2021): 332-34. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34510854. [CrossRef]
- Donauer, J., C. Schweiger, B. Rumberger, B. Krumme and J. Bohler. "Reduction of hypotensive side effects during online-haemodiafiltration and low temperature haemodialysis." Nephrol Dial Transplant 18 (2003): 1616-22. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12897103. [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F., P. Altieri, S. Andrulli, P. Bolasco, G. Sau, L. A. Pedrini, C. Basile, S. David, M. Feriani, G. Montagna, et al. "Hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration reduce intradialytic hypotension in esrd." J Am Soc Nephrol 21 (2010): 1798-807. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20813866. [CrossRef]
- Park, K. S., E. W. Kang, T. I. Chang, W. Jo, J. T. Park, T. H. Yoo, S. W. Kang and S. H. Han. "Mixed- versus predilution hemodiafiltration effects on convection volume and small and middle molecule clearance in hemodialysis patients: A prospective randomized controlled trial." Kidney Res Clin Pract 40 (2021): 445-56. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34370930. [CrossRef]
- Bolton, S., R. Gair, L. G. Nilsson, M. Matthews, L. Stewart and N. McCullagh. "Clinical assessment of dialysis recovery time and symptom burden: Impact of switching hemodialysis therapy mode." Patient Relat Outcome Meas 12 (2021): 315-21. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34764715. [CrossRef]
- Pongsittisak, W., P. Satpanich, S. Jaturapisanukul, R. Keawvichit, S. Prommool, T. Trakranvanich, T. Ngamvichukorn and S. Kurathong. "Medium cut-off versus low-flux dialyzers in hemodialysis patients with covid-19: Clinical outcomes and reduction in interleukin-6." Blood Purif 52 (2023): 591-99. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37231799. [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, J. C., A. Bunch, F. Ardila, E. Zuniga, J. I. Vesga, A. Rivera, R. Sanchez, R. M. Sanabria and I. Colombian Registry of Expanded Hemodialysis. "Impact of medium cut-off dialyzers on patient-reported outcomes: Corexh registry." Blood Purif 50 (2021): 110-18. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33176299. [CrossRef]
- Penny, J. D., F. R. Salerno, A. Akbari and C. W. McIntyre. "Pruritus: Is there a grain of salty truth?" Hemodial Int 25 (2021): E10-E14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32996258. [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, M., G. Cobo, B. Lindholm and P. Stenvinkel. "Inflammation and protein-energy wasting in the uremic milieu." Contrib Nephrol 191 (2017): 58-71. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28910791. [CrossRef]
- Hadad-Arrascue, F., L. G. Nilsson, A. S. Rivera, A. A. Bernardo and J. B. Cabezuelo Romero. "Expanded hemodialysis as effective alternative to on-line hemodiafiltration: A randomized mid-term clinical trial." Ther Apher Dial 26 (2022): 37-44. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34125503. [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y., K. Maeda, M. Moriishi, H. Kawanishi and T. Masaki. "Comparison of the pre-dilution and post-dilution methods for online hemodiafiltration." J Artif Organs (2023). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37010653. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y., M. J. Jang, J. Jeon, J. E. Lee, W. Huh, B. S. Choi, C. W. Park, H. J. Chin, C. L. Kang, D. K. Kim, et al. "Cardiovascular risk comparison between expanded hemodialysis using theranova and online hemodiafiltration (cartoon): A multicenter randomized controlled trial." Sci Rep 11 (2021): 10807. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34031503. [CrossRef]
- Doenyas-Barak, K., M. de Abreu, L. E. Borges, H. A. Tavares Filho, F. Yunlin, Z. Yurong, N. W. Levin, A. M. Kaufman, S. Efrati, D. Pereg, et al. "Non-invasive hemodynamic profiling of patients undergoing hemodialysis - a multicenter observational cohort study." BMC Nephrol 20 (2019): 347. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31481031. [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M. M., M. M. Zeid, O. M. R. Hamza and N. M. Elkholy. "Dialysis recovery time: Associated factors and its association with quality of life of hemodialysis patients." BMC Nephrol 23 (2022): 298. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36050656. [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A., A. Guirguis, M. Almond, C. Day, J. Chilcot, M. Da Silva Gane, N. Fineberg, K. Friedl, B. Spencer, D. Wellsted, et al. "Postdialysis recovery time is extended in patients with greater self-reported depression screening questionnaire scores." Hemodial Int 22 (2018): 369-76. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29461016. [CrossRef]
- Bossola, M., E. Di Stasio, S. Giungi, F. Rosa and L. Tazza. "Fatigue is associated with serum interleukin-6 levels and symptoms of depression in patients on chronic hemodialysis." J Pain Symptom Manage 49 (2015): 578-85. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25135658. [CrossRef]
- Yoowannakul, S., S. Vongsanim, K. Tangvoraphonkchai and A. Davenport. "Do patients dialysing with higher ultrafiltration rates report more intradialytic symptoms and longer postdialysis recovery times?" Artif Organs (2023). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37916538. [CrossRef]
- Vinson, A. J., D. Collister, S. Ahmed and K. Tennankore. "Underrepresentation of women in recent landmark kidney trials: The gender gap prevails." Kidney Int Rep 7 (2022): 2526-29. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36531883. [CrossRef]
| Gender (Men/Women) | 11/1 |
| Causes of ESRD (n/%) | |
| Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease | 4 / 33.4 |
| Glomerulonephritis (primary or secondary) | 3 / 25.0 |
| Hypertensive nephropathy | 2 / 16.7 |
| Renal malformation | 1 / 8.3 |
| Interstitial nephropathy Other |
1 / 8.3 1/ 8.3 |
| Age (years) | 52.5 (15.5) |
| AACI (points) | 4.5 (2.2) |
| Dialysis vintage (months) | 42.5 (31.04) |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) Weight (kg) spKt/Vurea Hemoglobin (g/dl) Albumin (g/l) |
23.8 (3.6) 73.7 (14.2) 1.5 (0.3) 10.9 (0.9) 33.1 (4.9) |
| S-HD | HDX | PRE-HDF | MIX-HDF | POST-HDF | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time min | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 | NA |
| Blood flow ml/min | 350 | 350 | 350 | 350 | 350 | NA |
| Dialysate flow ml/min | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | NA |
| Ultrafiltration ml | 2.12 (0.74) | 2.33 (0.62) | 2.45 (0.8) | 2.29 (0.74) | 2.19 (0.52) | p=0.6 |
| Ultrafiltration/ dry weight % | 0.028 | 0.032 | 0.034 | 0.031 | 0.029 | p=0.56 |
| Total convection l | NA | NA | 61.5 (7.2) | 47.1 (11.4) | 25.6 (3.8) | NA |
| SBP predialysis mmHg | 147.7 (27.5) | 144.1 (20.3) | 147.7 (26.6) | 147.3 (20.3) | 144.3 (22.4) | p=0.95 |
| DBP predialysis mmHg | 88.5 (18.8) | 88.3 (16.9) | 89.9 (20.4) | 89.9 (16.4) | 86.1 (18.0) | p=0.93 |
| TBW predialysis l | 39.76 (8.04) | 41.64 (11.65) | 39.05 (6.84) | 40.15 (7.32) | 39.7 (8.4) | p=0.93 |
| TBW postdialysis l | 38.17 (8.03) | 40.46 (12.51) | 37.5 (6.97) | 38.56 (7.29) | 37.44 (8.24) | p=0.85 |
| ECW predialysis l | 19.1 (3.2) | 19.9 (3.3) | 20.1 (3.5) | 19.3 (3.5) | 18.9 (3.2) | p=0.74 |
| ECW postdialysis l | 17.2 (3.1) | 17.43 (3.1) | 17.38 (2.9) | 18.2 (5.7) | 16.7 (2.9) | p=0.77 |
| ICW predialysis l | 21.31 (5.6) | 23.3 (7.5) | 22.2 (5.1) | 20.7 (4.2) | 20.8 (5.4) | p=0.62 |
| ICW postdialysis l | 21.33 (5.7) | 24.5 (8.8) | 24.2 (6.5) | 21.2 (4.7) | 20.7 (5.5) | p=0.17 |
| S-HD | HDX | PRE-HDF | MIX-HDF | POST-HDF | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP 1st minute mmHg | 145.8 (24.6) | 139.1 (17.2) | 143.4 (22.6) | 141.2 (18.0) | 137.9 (21.9) | p=0.75 |
| SBP 240 minute mmHg | 142.5 (35.5) | 142.2 (28.3) | 138.7 (35.7) | 140.6 (35.5) | 138.8 (29.2) | p=0.98 |
| DBP 1st minute mmHg | 87.0 (17.5) | 86.3 (14.3) | 86.1 (16.7) | 87.9 (16.6) | 83.4 (15.8) | p=0.85 |
| DBP 240 minute mmHg | 85.7 (17.1) | 89.1 (21.3) | 84.9 (17.3) | 85.3 (20.5) | 87.3 (18.7) | p=0.91 |
| AUC SBP | 323 816.6 (72 781.6) | 318 930.3 (61 252.4) | 316 602.0 (68 292.8) | 305 190.3 (76 556.9) | 313 049.4 (80 028.1) | p=0.8 |
| AUC DPB | 194 716.4 (37 664.1) | 192 651.0 (53 530.6) | 194 253.7 (33 794.1) | 190 661.9 (44 971.5) | 191 900.7 (44 991.7) | p=0.88 |
| AUC MAP | 237 748.1 (46 888.6) | 230 184.4 (59 405.4) | 235 096.4 (42 932.1) | 231 486.3 (53 996.6) | 234 209.5 (47 871.5) | p=0.23 |
| AUC CI | 6559.2 (1439.5) | 6770.9 (1271.3) | 6512.5 (1256.4) | 6093.9 (1282.4) | 6680.9 (1652.9) | p=0.65 |
| AUC SVRI | 6 176 119.3 (1 325 662.8) |
6 456 193.4 (1 473 702.1) | 6 256 567.9 (999 108.8) |
7 075 464.9 (1 930 210.7) | 6 301 942.5 (1 337 688.1) | p=0.34 |
| S-HD | HDX | PRE-HDF | MIX-HDF | POST-HDF | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic hypotension n | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | p=1.0 |
| AEs potentially related to BP/fluid shifts n | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | p=0.39 |
| AEs potentially not related to BP/fluid shifts n | 7 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 2 | p=0.47 |
| Intradialytic clotting events n | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | p=0.51 |
| All AEs n (%) | 8 (33.3%) | 6 (25%) | 7 (29.2%) | 9 (37.5%) | 10 (41.7%) | p=0.76 |
| Immediate DRT n (%) | 11 (45.8%) | 12 (50%) | 15 (62.5%) | 9 (37.5%) | 10 (41.7%) | p=0.10 |
| Delayed DRT min | 360.0 (180-720) |
180 (120-390) |
60 (30-600) |
360 (180-360) |
390 (60-720) |
p=0.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





