Submitted:
29 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
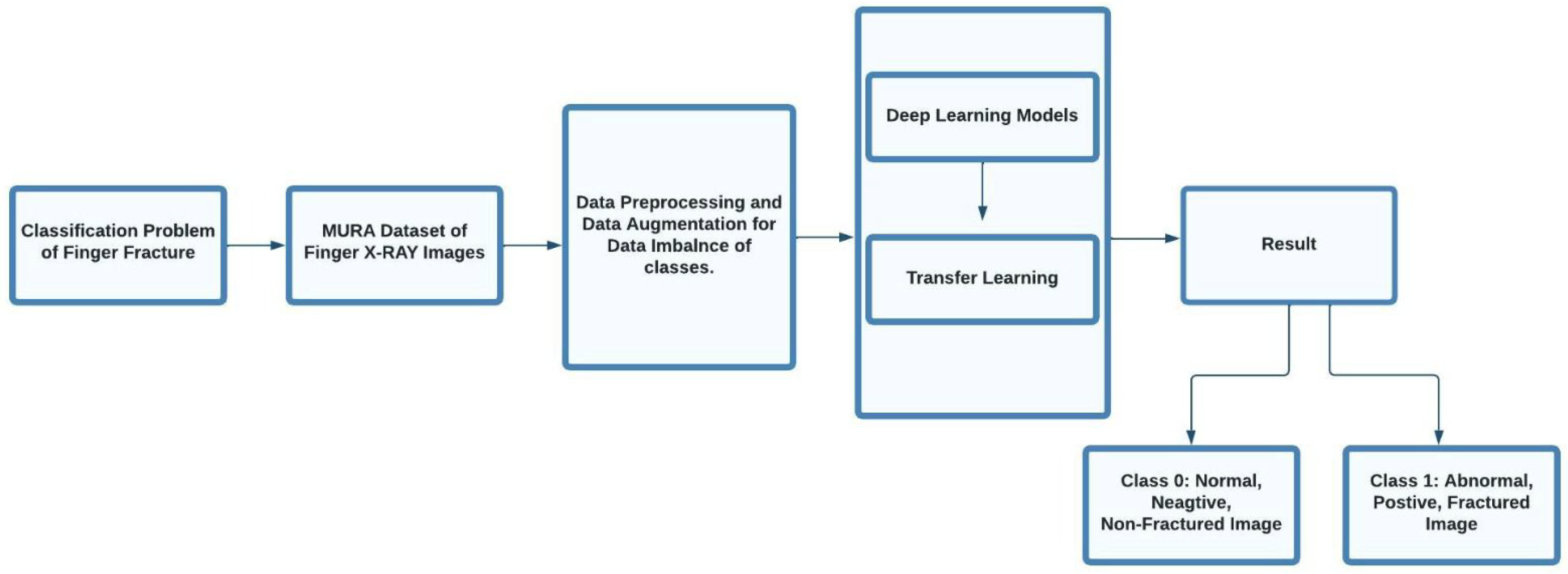
1. Introduction
- Automated Fracture Diagnosis: The research introduces an automated approach to diagnose fractured fingers from images, mitigating risks associated with manual examination.
- Advanced Deep Learning Models: The study employs cutting-edge models, including ResNet34, ResNet50, ResNet101, ResNet152, VGG-16, and VGG-19, showcasing a commitment to leveraging state-of-the-art technologies for medical image analysis.
- Comprehensive Evaluation Metrics: The research pioneers the use of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score as thorough evaluation metrics, contributing to the methodology of assessing deep learning models in the medical domain.
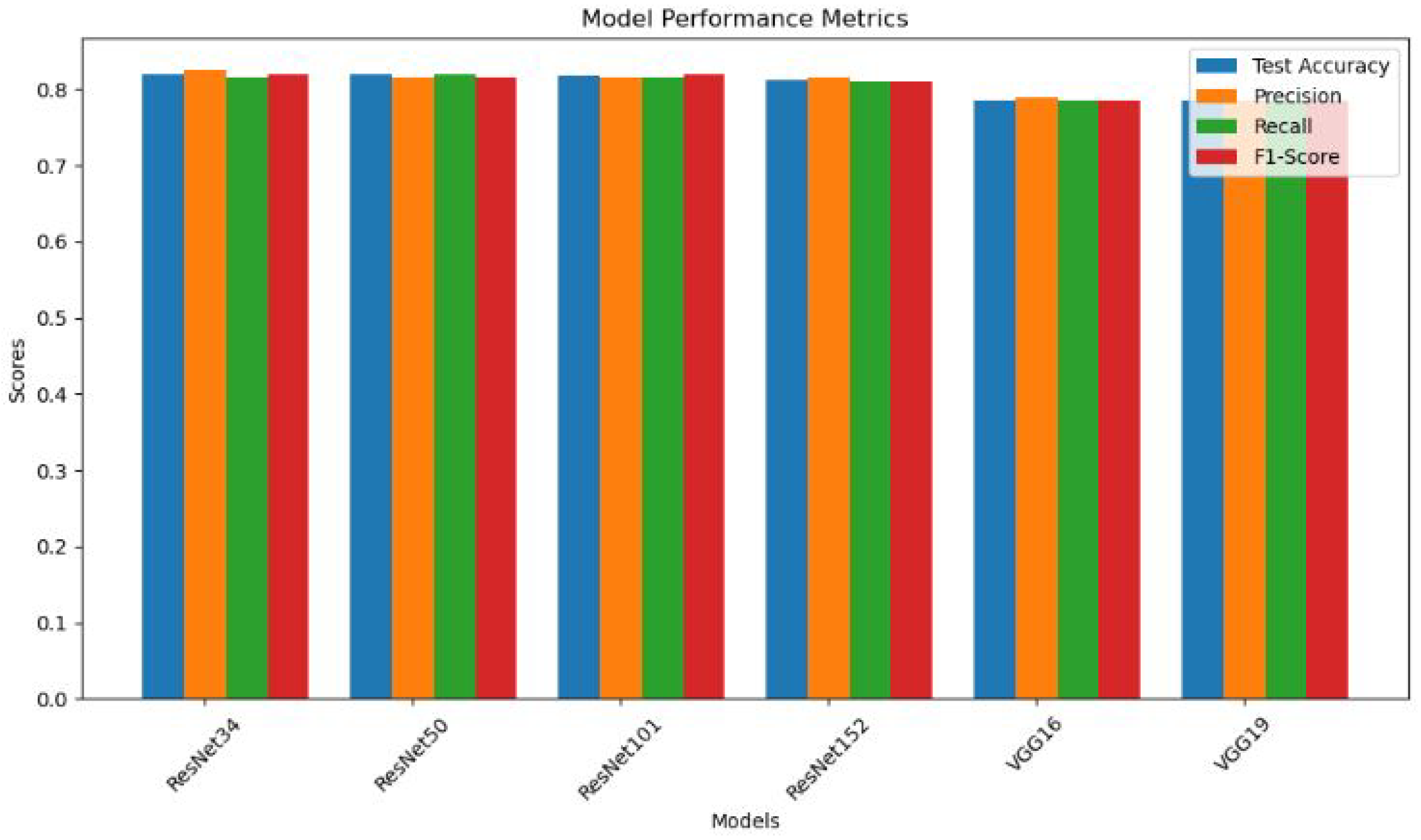
- Performance Comparison: The findings reveal the consistent and robust performance of ResNet models, with a commendable test accuracy of up to 81.9%, surpassing VGG models (78.5%) in the context of finger fracture classification.
- Insights for Future Research: The study provides valuable insights for future research in the field of medical image analysis, particularly in optimizing deep learning models for enhanced accuracy and efficiency in diagnosing finger fractures.
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Date Set
3.2. Data Augmentation
3.3. Data Preprocessing
- 1.
- Detection of the Corresponding Area: A significant portion of the X-ray images in the dataset lacked sufficient size-related semantic information. To address this issue, a series of preprocessing steps were implemented. Initially, the images were converted to grayscale and then double thresholded. Using Otsu’s thresholding value approach, an adaptive threshold value was found, aiming to rectify this inadequacy. This involved assessing within-class variance for the foreground and background color classes in the grayscale pictures. The threshold value chosen was the one that minimized this variance, utilizing Otsu’s thresholding value method. Following this, the thresholded image underwent edge detection techniques to identify and highlight its edges. After this, the original images underwent a cropping process to fine-tune and boost their overall quality.
- 2.
- CLAHE Transformation: In this step, the transformation was achieved by employing contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) with the OpenCV library. The input image was divided into segments, each having its own histogram. Users defined limits for histogram cropping, and based on these specifications, adjustments were applied to the histogram of each segment, resulting in the creation of CLAHE-enhanced versions of the images.
- 3.
- Normalization and Standardization: In this final phase, ImageNet values were employed for the normalization and standardization of the images.
3.4. Models
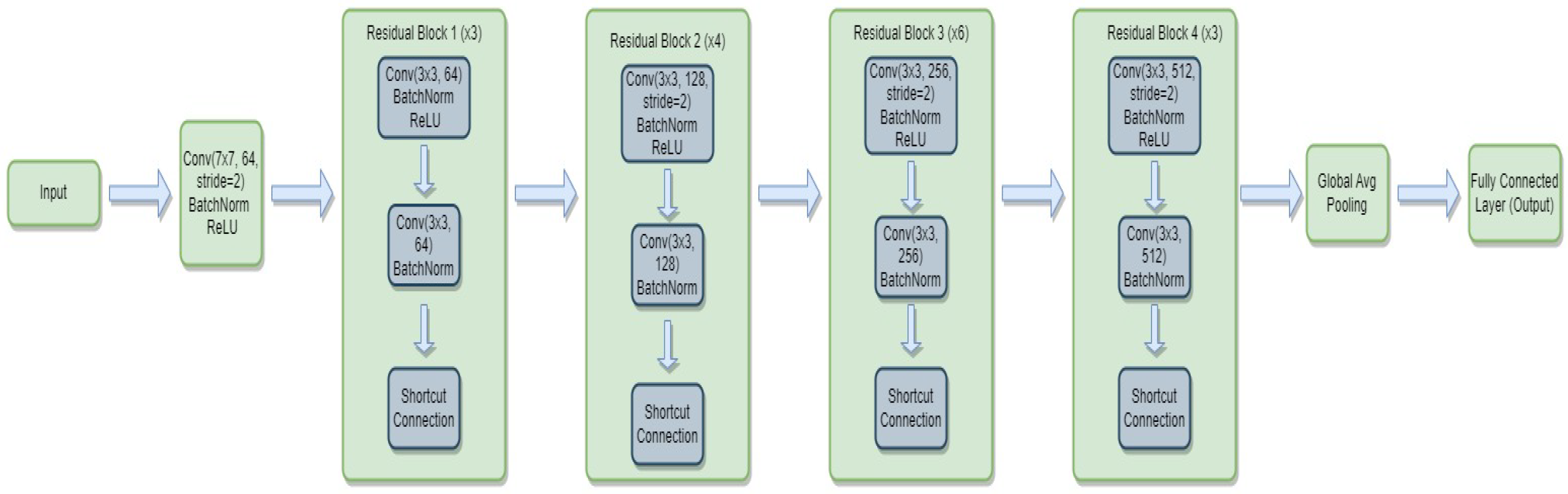
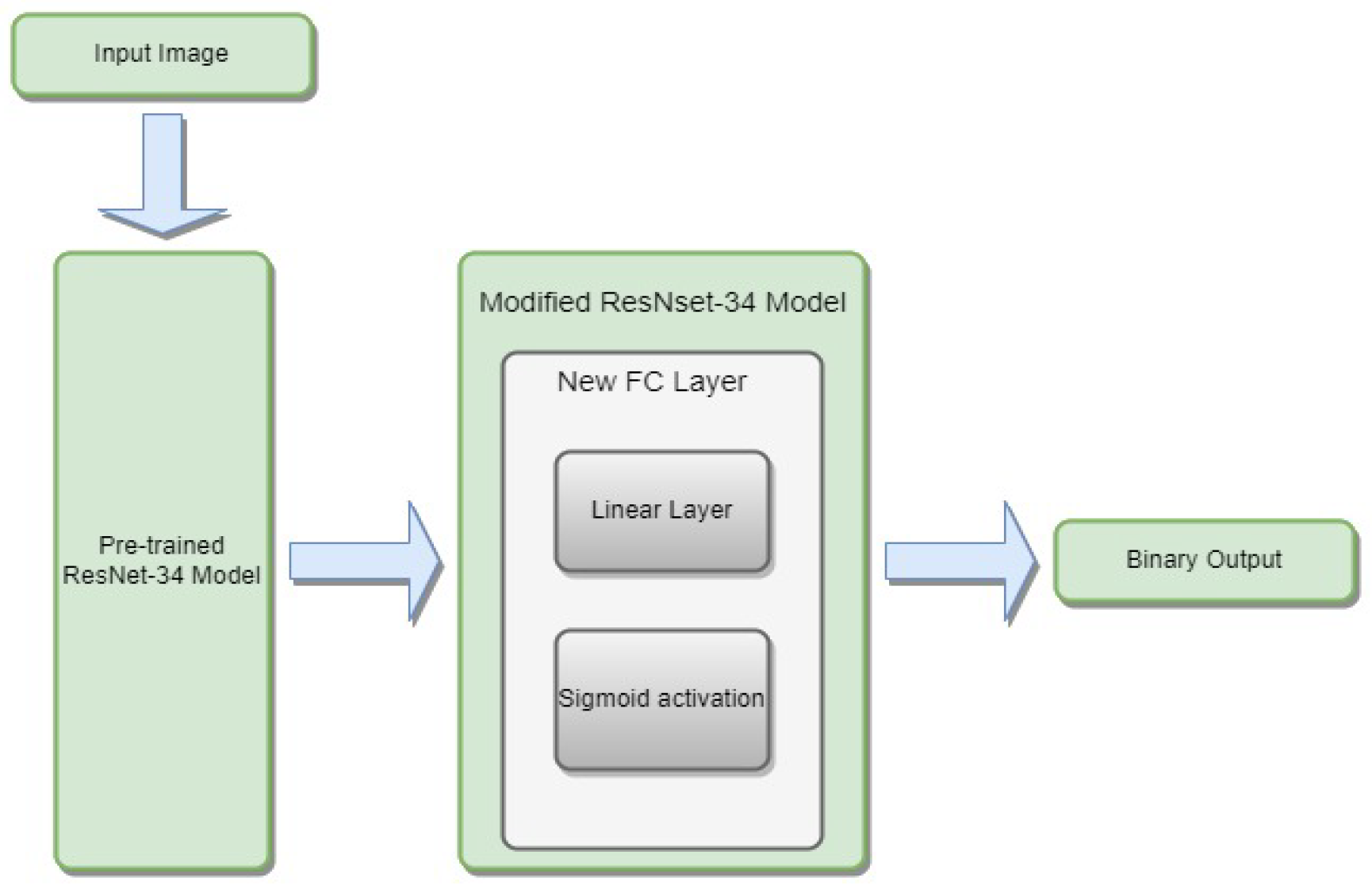
3.4.1. ResNet-34
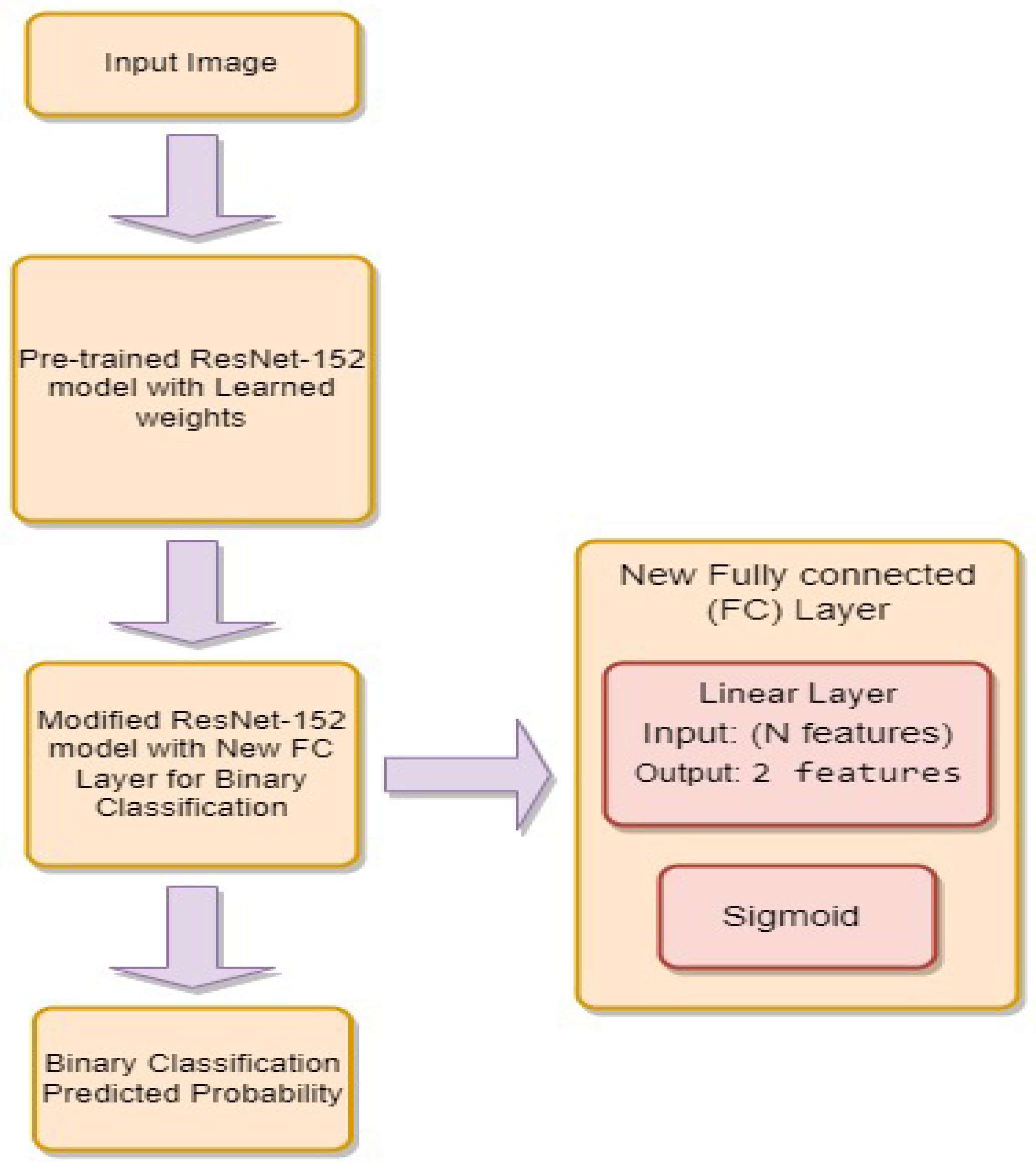
- is the weight matrix for the new linear layer.
- is the bias vector for the new linear layer.
- x is the input.
- is the sigmoid activation function.
- represents the feature extraction process of the ResNet-34 model.
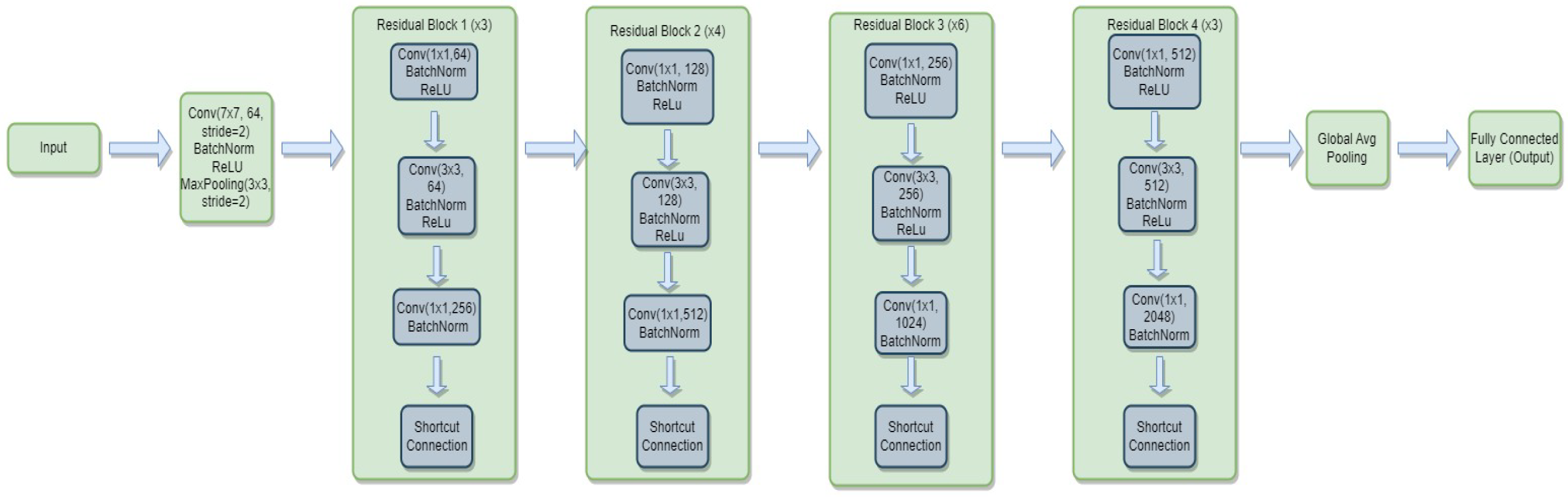
3.4.2. ResNet-50
- is the weight matrix for the new linear layer.
- is the bias vector for the new linear layer.
- x is the input.
- is the sigmoid activation function.
- represents the feature extraction process of the ResNet-50 model.
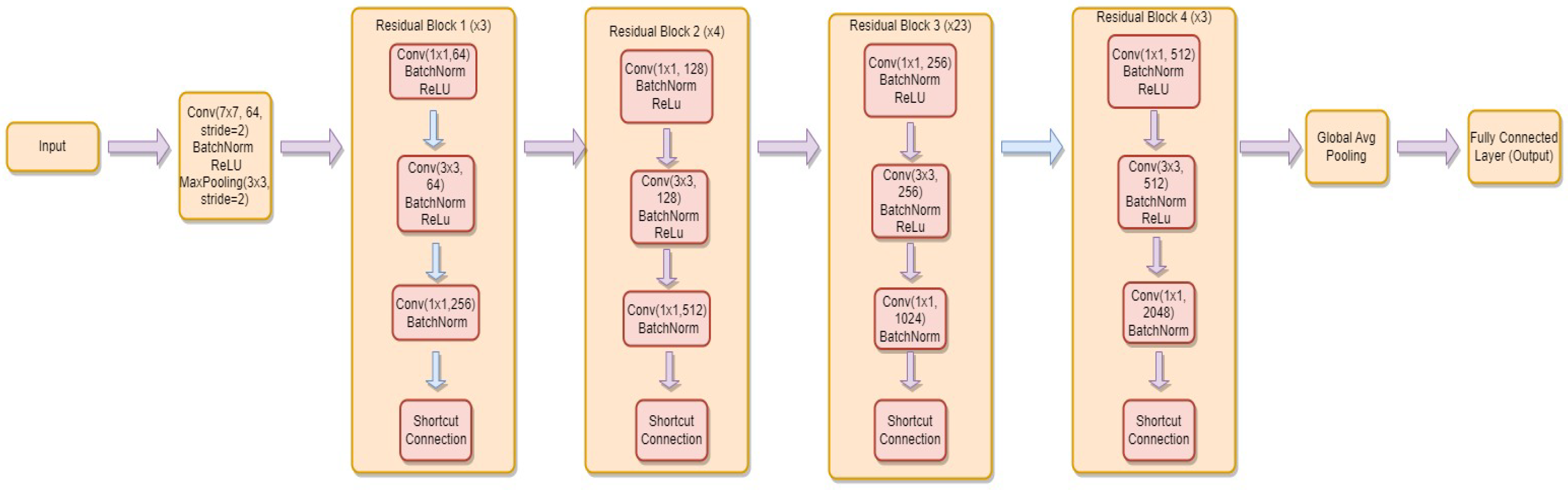
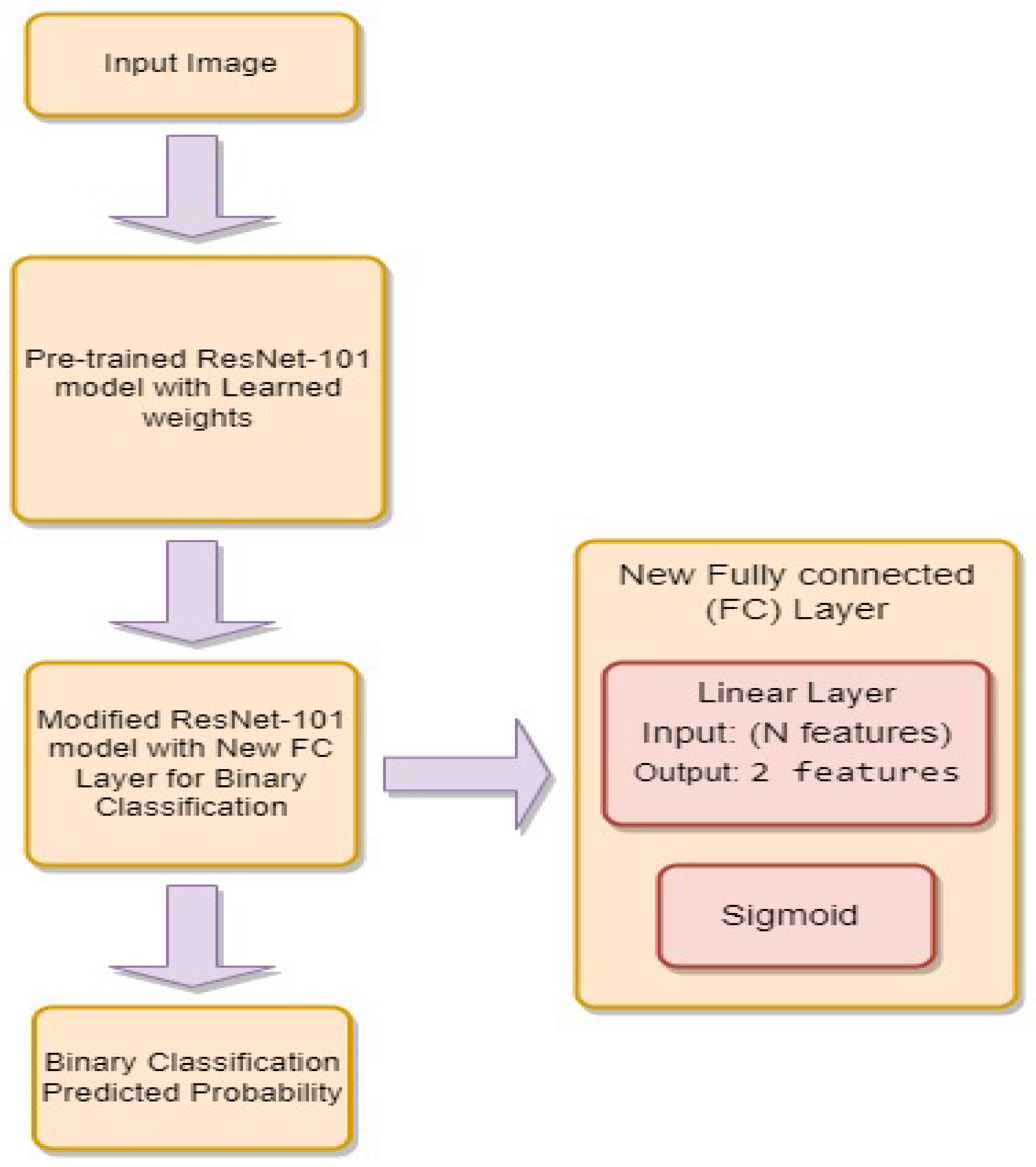
3.4.3. ResNet-101
- is the weight matrix for the new linear layer.
- is the bias vector for the new linear layer.
- x is the input.
- is the sigmoid activation function.
- represents the feature extraction process of the ResNet-101 model.
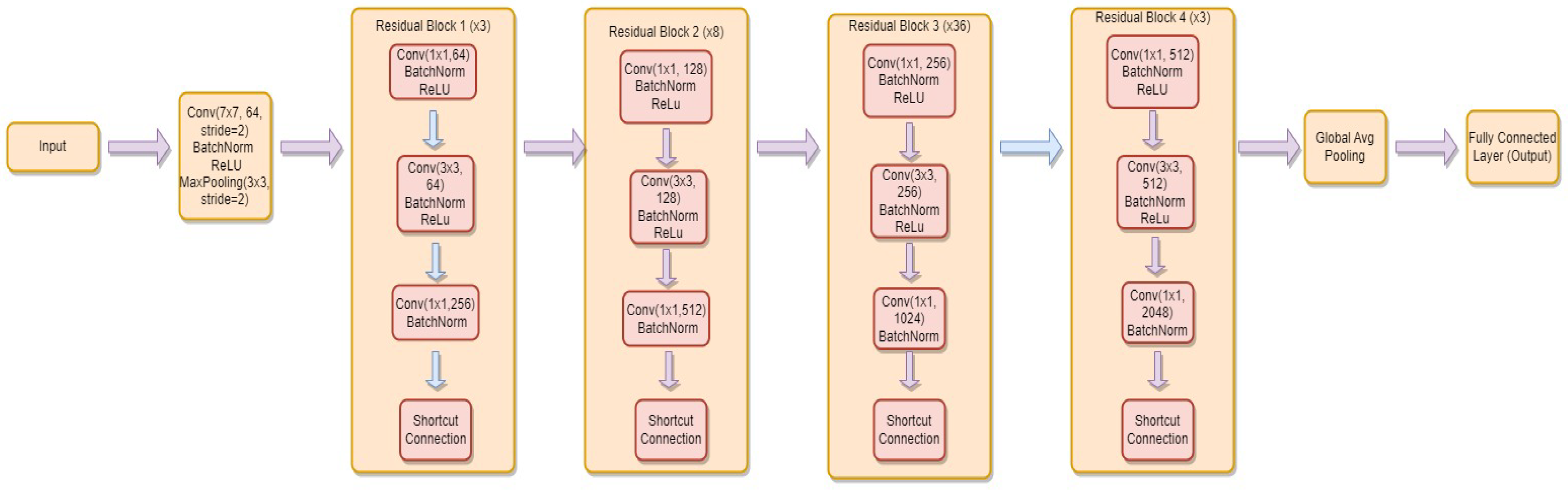
3.4.4. ResNet-152
- is the weight matrix for the new linear layer.
- is the bias vector for the new linear layer.
- x is the input.
- is the sigmoid activation function.
- represents the feature extraction process of the ResNet-152 model.
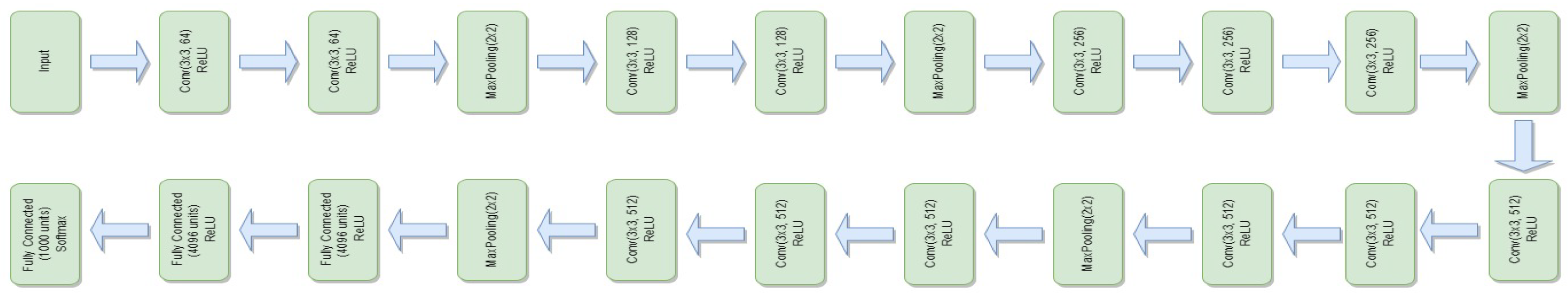
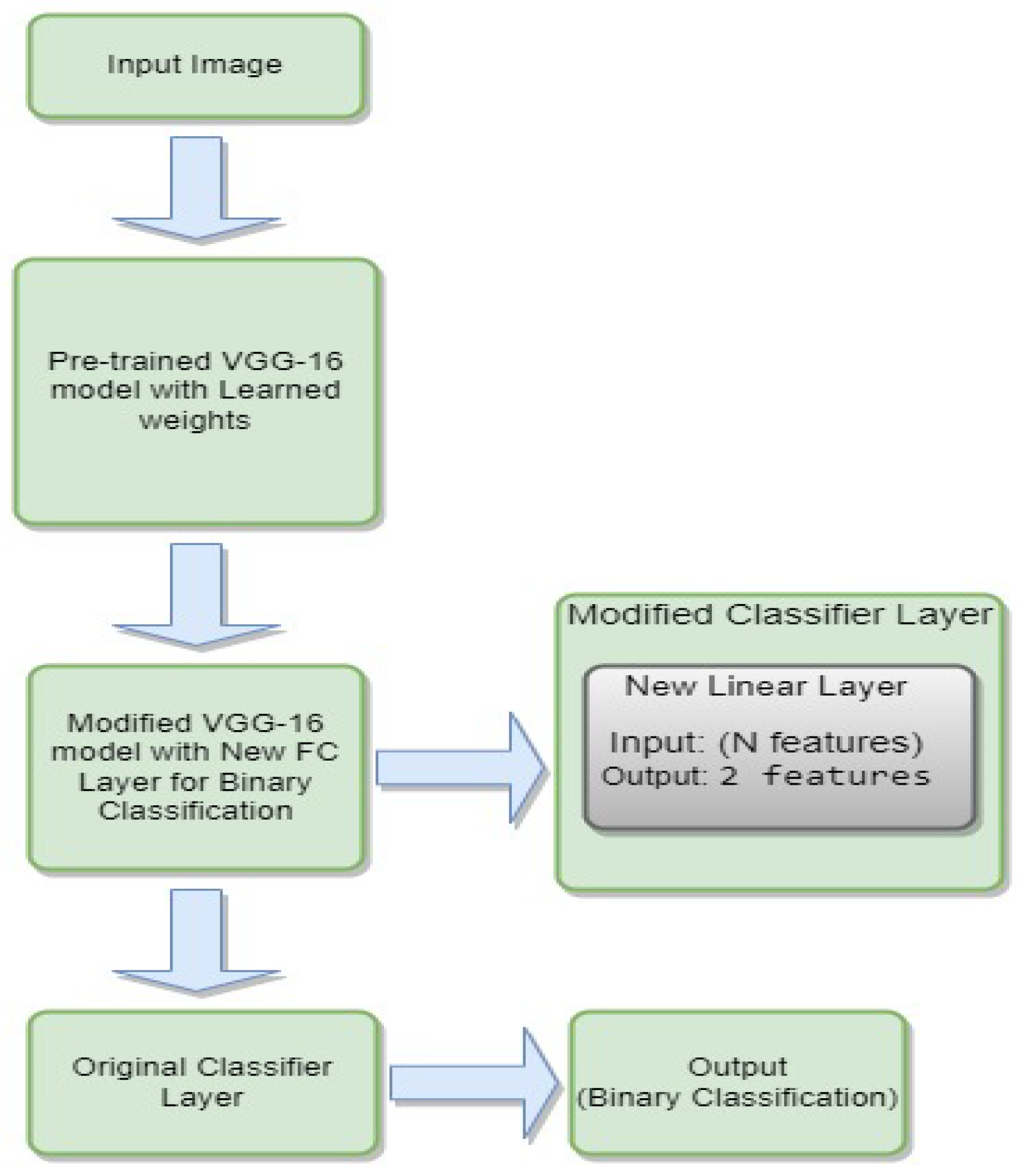
3.4.5. VGG-16
- is the weight matrix for the new linear layer.
- is the bias vector for the new linear layer.
- x is the input.
- is the sigmoid activation function.
- represents the feature extraction process of the VGG-16 model.
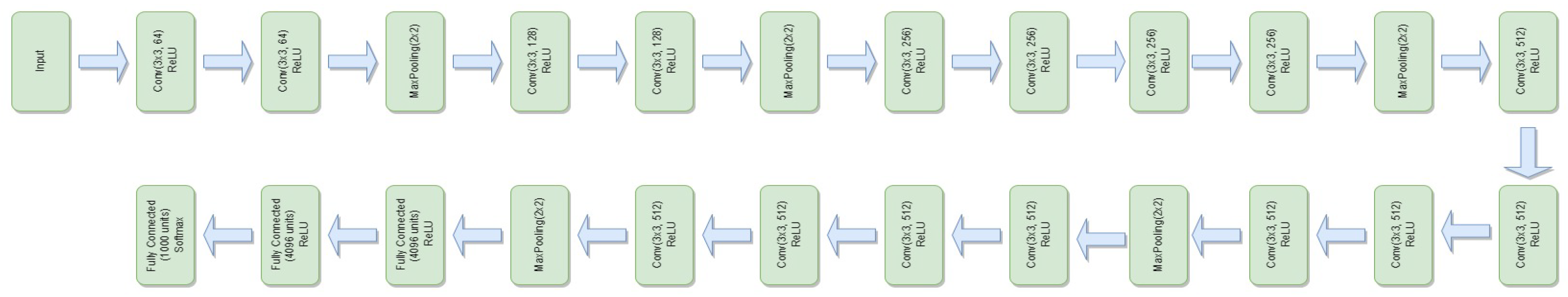
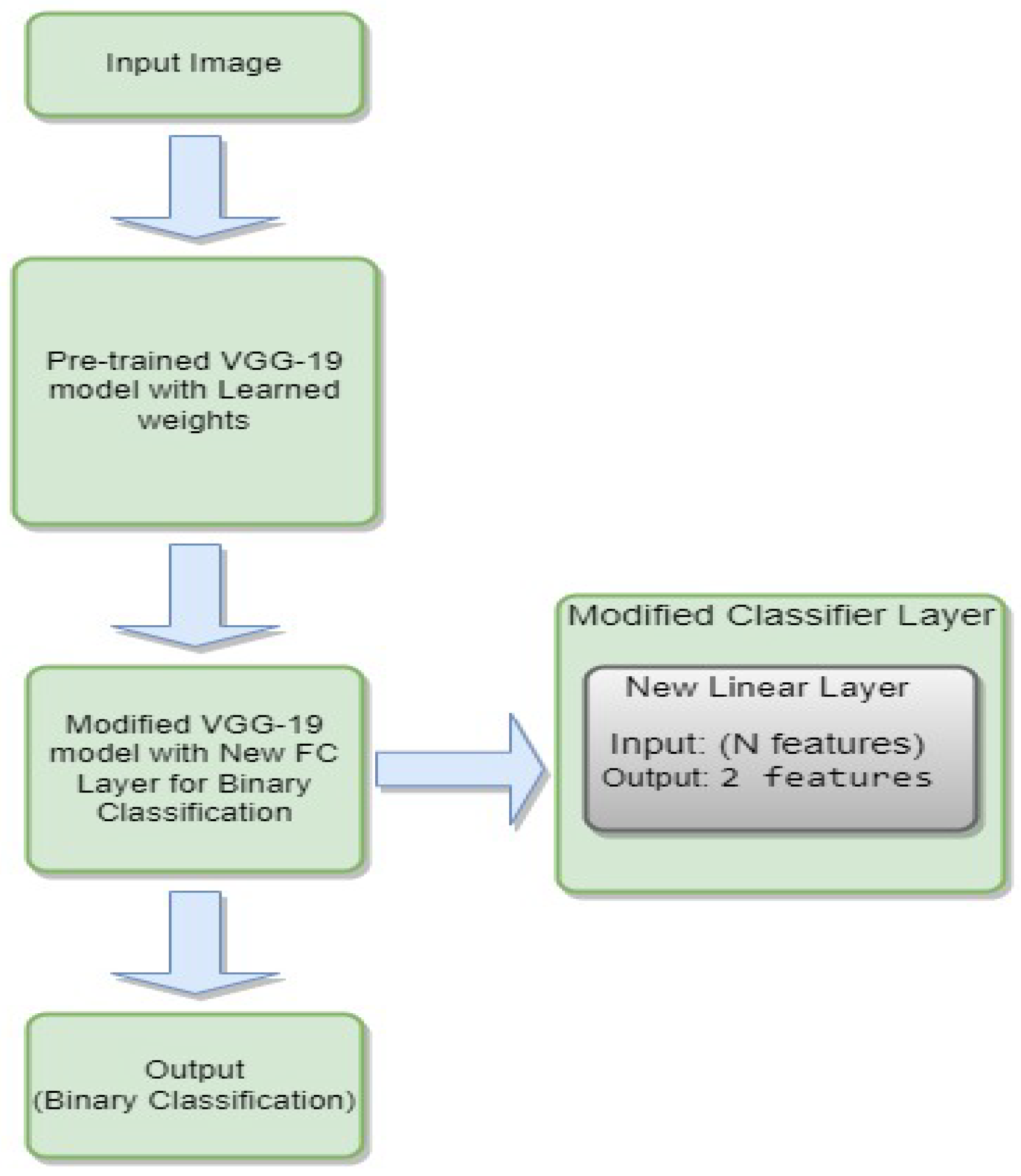
3.4.6. VGG-19
- is the weight matrix for the new linear layer.
- is the bias vector for the new linear layer.
- x is the input.
- is the sigmoid activation function.
- represents the feature extraction process of the VGG-19 model.
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
- 1.
- Training/Testing Accuracy:
- 2.
- Precision:
- 3.
- Recall (Sensitivity or True Positive Rate):
- 4.
- F1-score:
4.2. Classification Results of Our Models
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusion and Future Work
- ResNet Model Consistency: ResNet models (ResNet34, ResNet50, ResNet101, ResNet152) exhibit consistent and robust performance across all evaluation metrics. The minimal variation in results indicates the reliability of ResNet architectures for the specific task of finger fracture classification.
- High Accuracy: All ResNet models achieve test accuracies above 81%, showcasing their effectiveness in distinguishing between fractured and non-fractured finger images. This high level of accuracy is crucial for reliable medical diagnoses.
- Balanced Precision and Recall: The ResNet models maintain a balance between precision and recall, with values ranging from 81.0% to 82.5%. This equilibrium shows how well the models can distinguish between positive (fractured) and negative (non-fractured) cases.
-
Comparable VGG Model Performance: VGG16 and VGG19 models demonstrate comparable but slightly lower performance compared to ResNet models. The test accuracy of approximately 78.5% suggests a slightly reduced ability to correctly classify fractured and non-fractured finger images.In future, the focus can be on improving the accuracy of finger fracture classification by fine-tuning ResNet architectures and employing auto-encoders, ensemble learning approaches, data augmentation, transfer learning with pre-trained Models and Continuous Model Monitoring and Updation.
Acknowledgments
References
- Liang, S.; Gu, Y. Towards robust and accurate detection of abnormalities in musculoskeletal radiographs with a multi-network model. Sensors 2020, 20, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, N.; Dhaka, V.S.; Chaudhary, H. Classification of human bones using deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IOP conference series: materials science and engineering; IOP Publishing, 2019; Volume 594, p. 012024. [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi, L.; Audisio, A.; Cirrincione, G.; Aprato, A.; Vezzetti, E. Vision transformer for femur fracture classification. Injury 2022, 53, 2625–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, T.; Roy, S. Bone fracture detection using deep supervised learning from radiological images: A paradigm shift. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, F.; Hardalaç, F.; Peker, O.; Tolunay, T.; Tokgöz, N. Classification of shoulder x-ray images with deep learning ensemble models. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanam, S.R.; Srinivas, Y.; Chakravarty, S. A systematic review on approach and analysis of bone fracture classification. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chea, P.; Mandell, J.C. Current applications and future directions of deep learning in musculoskeletal radiology. Skeletal radiology 2020, 49, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yin, B.; Cao, W.; Feng, C.; Fan, G.; He, S. Diagnostic accuracy of deep learning in orthopaedic fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Radiology 2020, 75, 713–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhoom, A.; Al-Hiealy, M.R.J.; Abu-Naser, S.S. Bone Abnormalities Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning-Vgg16 Algorithm. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 2022, 100, 6173–6184. [Google Scholar]
- Krogue, J.D.; Cheng, K.V.; Hwang, K.M.; Toogood, P.; Meinberg, E.G.; Geiger, E.J.; Zaid, M.; McGill, K.C.; Patel, R.; Sohn, J.H.; et al. Automatic hip fracture identification and functional subclassification with deep learning. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence 2020, 2, e190023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B. An attention-based cascade R-CNN model for sternum fracture detection in X-ray images. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology 2022, 7, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sserubombwe, R. Automatic bone fracture detection in x-ray images using deep learning. PhD thesis, Makerere University, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, B.; Zhang, G.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Arm fracture detection in X-rays based on improved deep convolutional neural network. Computers & Electrical Engineering 2020, 81, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijowski, R.; Liu, F.; Caliva, F.; Pedoia, V. Deep learning for lesion detection, progression, and prediction of musculoskeletal disease. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging 2020, 52, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Samsonov, A.; Blankenbaker, D.; Larison, W.; Kanarek, A.; Lian, K.; Kambhampati, S.; Kijowski, R. Deep learning approach for evaluating knee MR images: achieving high diagnostic performance for cartilage lesion detection. Radiology 2018, 289, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, N.; Naseer, A.; Tamoor, M.; Zafar, K. Alzheimer Disease Classification through Transfer Learning Approach. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, A.; Tamoor, M.; Azhar, A. Computer-aided COVID-19 diagnosis and a comparison of deep learners using augmented CXRs. Journal of X-ray Science and Technology 2022, 30, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, S.; Mehmud, M.; Alamgir, Z.; Shahid, S. Dynamic Spatial Correlation in Graph WaveNet for Road Traffic Prediction. Transportation Research Record 2023, 03611981221151024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, M.A.B.; Alamgir, Z. Improving mortality prediction in Acute Pancreatitis by machine learning and data augmentation. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 150, 106077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.N.K.; Cutsuridis, V. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks with Transfer Learning for Bone Fracture Recognition using Small Exemplar Image Datasets. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Workshops (ICASSPW); IEEE, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Pailla, B.; Tadepalli, K.; Roy, S. Robust MSFM Learning Network for Classification and Weakly Supervised Localization. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023; pp. 2442–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Kandel, I.; Castelli, M.; Popovič, A. Musculoskeletal images classification for detection of fractures using transfer learning. Journal of imaging 2020, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.B.; Kumar, G.; Sultania, G.; Agashe, S.S.; Sinha, P.R.; Kang, C. Deep learning based MURA defect detection. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Cloud Systems 2019, 5, e6–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total Images | Normal | Abnormal |
|---|---|---|
| 2142 | 1389 | 753 |
| Models | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet34 | 0.8190 | 0.8246 | 0.8146 | 0.82 |
| ResNet50 | 0.8188 | 0.8146 | 0.820 | 0.8149 |
| ResNet101 | 0.8171 | 0.8152 | 0.8152 | 0.82 |
| ResNet152 | 0.8117 | 0.815 | 0.81 | 0.81 |
| VGG16 | 0.7851 | 0.79 | 0.7849 | 0.7849 |
| VGG19 | 0.7851 | 0.7849 | 0.7849 | 0.7849 |
| Architecture | Dataset Scope | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| VGG-16 | Whole MURA | 78 |
| ResNet50 | Whole MURA | 78 |
| MSFMR50 | Finger Fracture | 81 |
| VGG-19 | Finger Fracture | 71.4 |
| ResNet | Finger Fracture | 70.1 |
| Naive DL network | Whole MURA | 81 |
| VGG(ours) | Finger Fracture | 78.5 |
| ResNet(ours) | Finger Fracture | 81.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




