Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
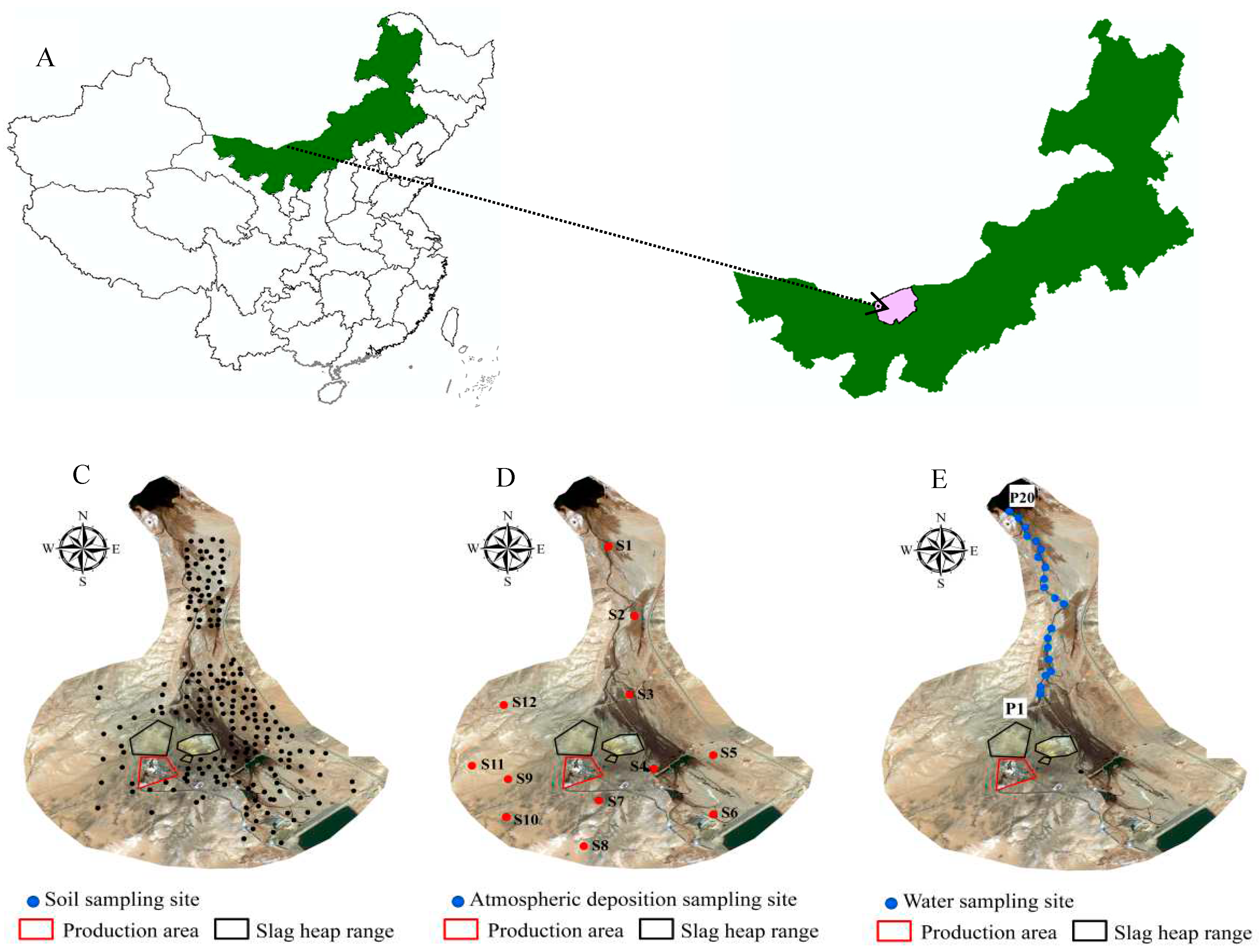
2.1. Studied Area
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.2.1. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.2.2. Atmospheric Deposition Sampling and Analysis
2.2.3. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
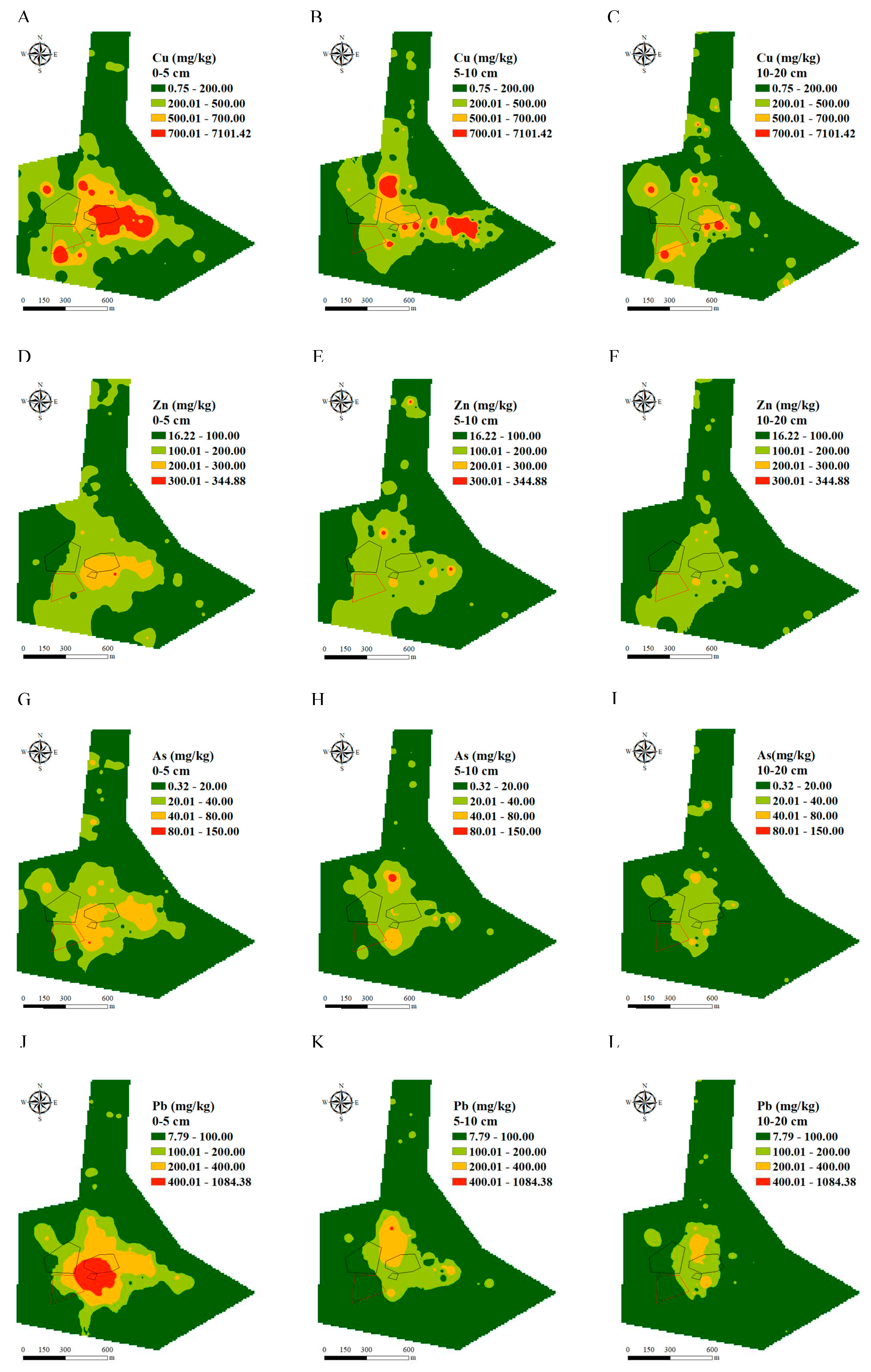
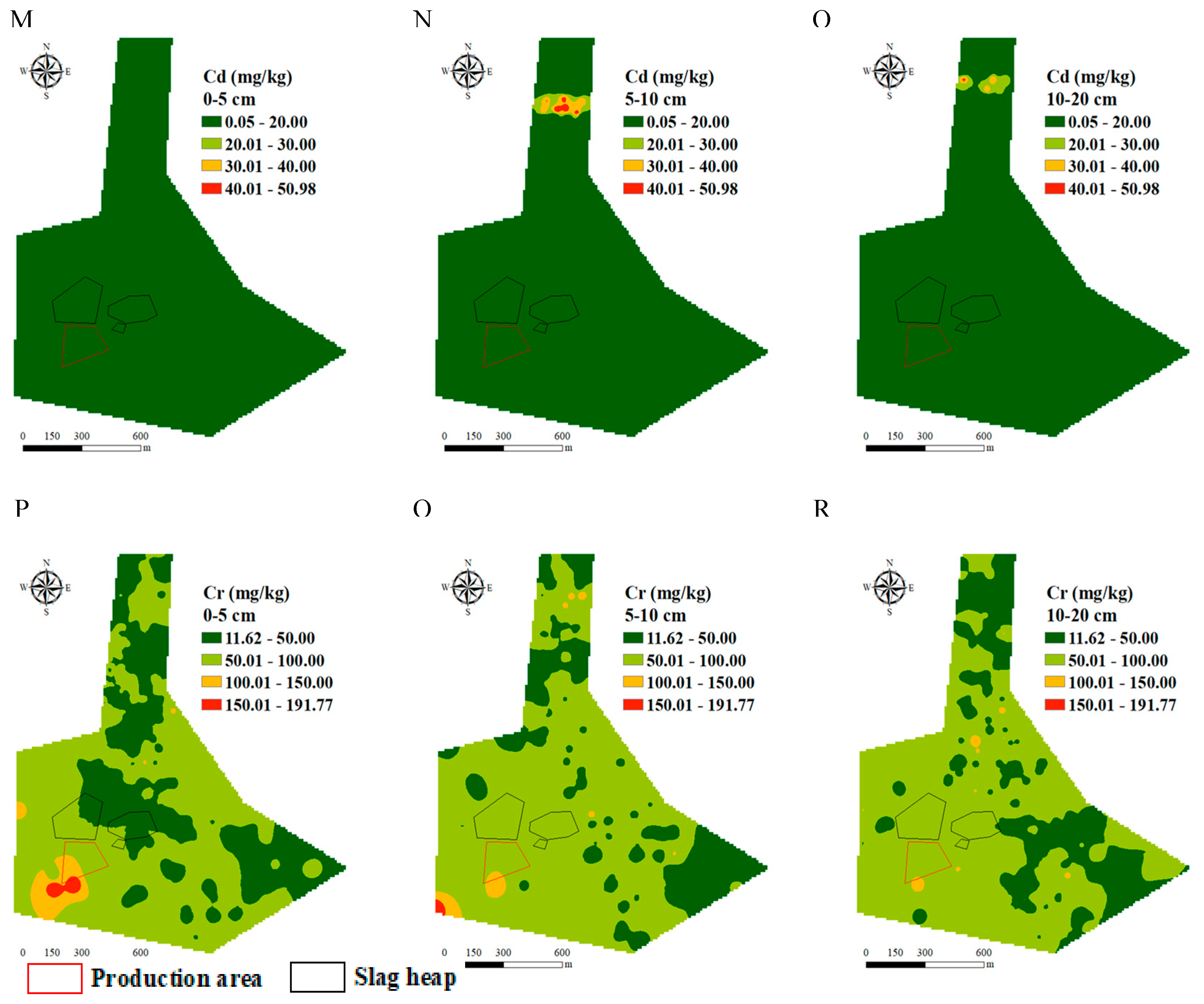
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals
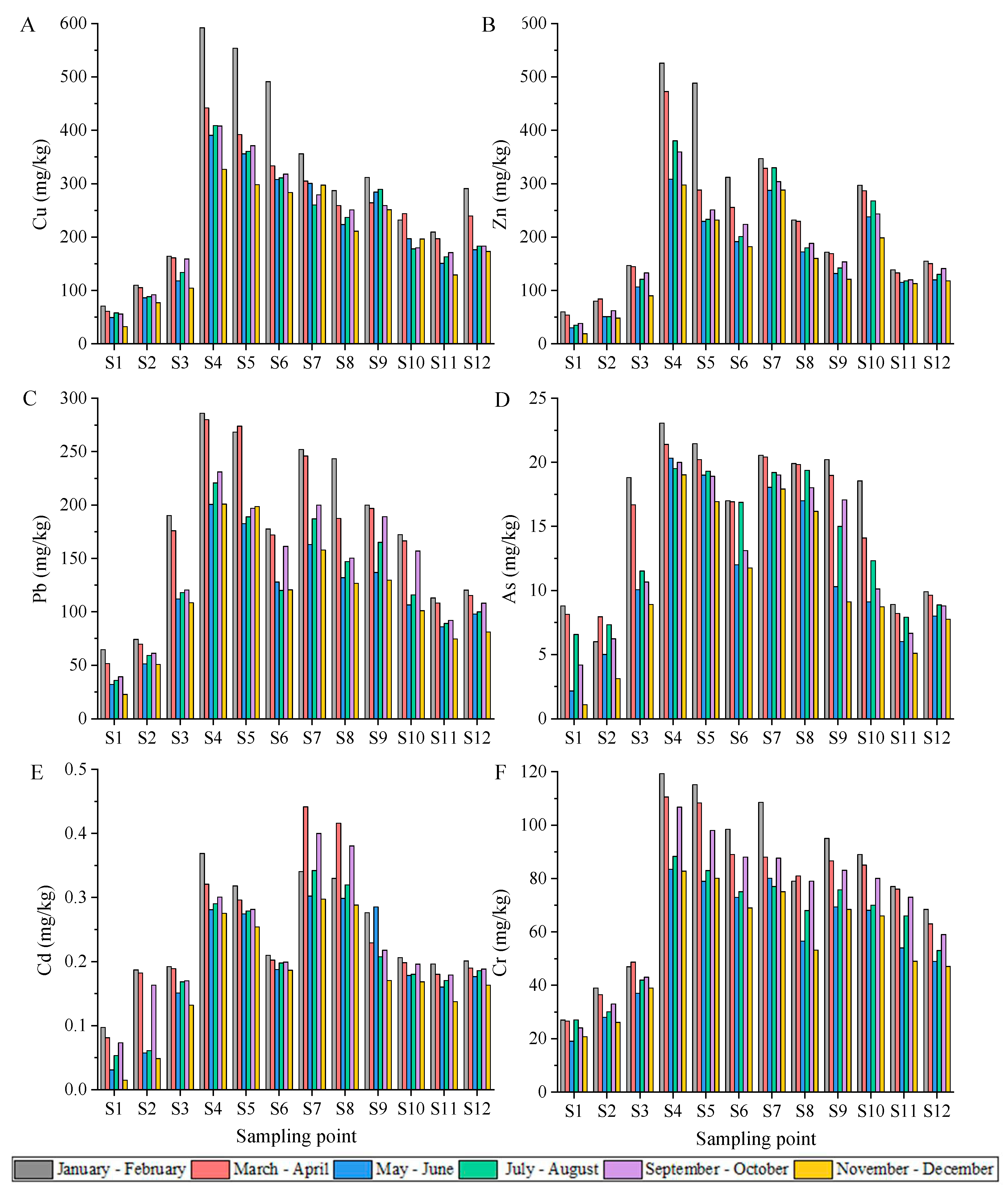
3.2. Atmospheric Deposition of Heavy Metals
3.2.1. Concentration of Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Deposition
3.2.2. Heavy Metal Fluxes in Atmospheric Deposition
3.3. Heavy Metals in River
3.4. Principal Component Analysis of Heavy Metals
4. Discussion
4.1. Heavy Metals Distribution Pattern
4.2. Contribution of Atmospheric Deposition to Heavy Metals Distribution
4.3. Contribution of Surface Runoff Transport to Heavy Metals Distribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Danek, T.; Cheng, X.; Huang, Q. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in soils of Gejiu Tin ore and other metal deposits of Yunnan Province. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2017, 95, 042078.
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Research on Characteristics and Sustainable Development of mineral resources in China. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2019, 300, 022155.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Report on the national general survey of soil contamination. China Environmental Protection Industry 2014, 36, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Xie, C.; Hou, Z. Ecological evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the soil of Pb-Zn mines. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.R.; Susan, T.B. Water contamination with heavy metals and trace elements from Kilembe copper mine and tailing sites in western Uganda; implications for domestic water quality. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffan, J.J.; Brevik, E.C.; Burgess, L.C.; Cerdà, A. The effect of soil on human health: an overview. European Journal of Soil Science 2018, 69, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ren, B.; Song, L. Pollution characteristics and spatial distribution of heavy metals in coal-bearing sandstone soil: a case study of coal mine area in Southwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, X.; Lei, J.; Ran, Q.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, J. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in a typical Pb/Zn smelter in an arid area of northwest China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment 2019, 25, 1661–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, G. The spatial distribution and accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in steppe soils around three mining areas in Xilinhot in Inner Mongolia, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2017, 24, 25416–25430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, K.; Zhu, X. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of soil heavy metals over a typical nonferrous metal mine area in Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 2018, 77, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Lei, C.; Yan, B.; Li, L.L.; Xu, D.M.; Ying, G.G. Spatial distribution and environmental implications of heavy metals in typical lead (Pb)-zinc (Zn) mine tailings impoundments in Guangdong province, South China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2018, 25, 36702–36711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H. Spatial distribution, risk assessment, and source identification of pollutants around gold tailings ponds: a case study in Pinggu District, Beijing, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2021, 193, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, H.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y. The influence of gold mining wastes on the migration-transformation behavior and health risks of arsenic in the surrounding soil of mined-area. Frontiers in Earth Science 2023, 10, 1068763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, C.; An, C.; Mi, Z. Spatial distribution, source identification, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soils from a mining region: a case study of Bayan Obo in northwestern China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment 2020, 27, 1276–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lin, C.; Cheng, H.; Duan, X. Contamination and health risks of soil heavy metals around a lead/zinc smelter in southwestern China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2015, 113, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaman, R.; Peng, C.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, X. Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 823, 153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Gui, H.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Jiang, Y. Characteristics and source identification of heavy metals in abandoned coal-mining soil: a case study of Zhuxianzhuang coal mine in Huaibei coalfield (Anhui, China). Human and Ecological Risk Assessment 2021, 27, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Zhou, Y. Trace metal pollution in topsoil surrounding the Xiangtan manganese mine area (South-Central China): source identification, spatial distribution and assessment of potential ecological risks. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2018, 15, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Gu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Ding, J.; Lun, Z.; Tian, W. Spatial analysis, source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in a coal mining area in Henan, central China. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation 2018, 128, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Feng, C.; Zeng, G.; Gao, X.; Zhong, M.; Li, X.; Fang, Y. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environmental Pollution 2017, 225, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Jiao, W.B.; Qiu, H.Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.X.; Kang, B. Origin and spatial distribution of heavy metals and carcinogenic risk assessment in mining areas at You'xi county southeast China. Geoderma 2018, 310, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrebi, M.; Noori, R.; Bhattarai, R.; Mundher Yaseen, Z.; Tang, Q.; Al-Ansari, N.; Madani, K. Iran's agriculture in the Anthropocene Earth's Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001547.
- Qiao, P.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhang, Z. Process, influencing factors, and simulation of the lateral transport of heavy metals in surface runoff in a mining area driven by rainfall: a review. Science of the Total Environment 2023, 857, 159119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Jahanara, I.; Jolly, Y.N. Assessment of physicochemical properties of water and their seasonal variation in an urban river in Bangladesh. Water Science and Engineering 2021, 14, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderschueren, R.; Doevenspeck, J.; Helsen, F.; Mounicou, S.; Santner, J.; Delcour, J.A.; Smolders, E. Cadmium migration from nib to testa during cacao fermentation is driven by nib acidification. LWT-Food Science and Technology 2022, 157, 113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Beiyuan, J.; Wei, X.; Qi, J.; Wang, L.; Xiao, T. Thallium and potentially toxic elements distribution in pine needles, tree rings and soils around a pyrite mine and indication for environmental pollution. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 828, 154346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cai, J.; Gao, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M. Pollution level, ecological risk assessment and vertical distribution pattern analysis of heavy metals in the tailings dam of an abandon Lead–Zinc mine. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hong, C.; Xing, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Feng, L.; Ma, S. Spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in natural pasture soil around copper-molybdenum mine in northeast China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2018, 154, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.B.; Luo, M.; Xiang, L.; Zha, L.S.; Yang, H.L. Analysis on the Distribution Characteristics and Influence Mechanism of Migration and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Mining Wasteland. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 2023, 44, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Wu, C.; Bi, X.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, H.; Ye, J.; Yu, Q. Soil pH change induced by smelting activities affects secondary carbonate production and long-term Cd activity in subsoils. Applied Geochemistry 2023, 152, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A.; Shi, X. Effects of mining activities on the distribution, controlling factors, and sources of metals in soils from the Xikuangshan South Mine, Hunan Province. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management 2022, 18, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, G.; Zhao, H.; Wu, D. Partitioning, leachability, and speciation of chromium in the size-fractions of soil contaminated by chromate production. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Gu, C.; Ying, H.; Feng, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Fraction distribution of heavy metals and its relationship with iron in polluted farmland soils around distinct mining areas. Applied Geochemistry 2021, 130, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Heavy metal | Sampling point | |||||||||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | |
| Cu | 17.04 | 31.99 | 52.31 | 221.59 | 193.91 | 163.45 | 135.30 | 101.42 | 120.21 | 83.32 | 66.36 | 85.67 |
| Zn | 12.33 | 21.59 | 46.20 | 202.49 | 143.97 | 109.07 | 141.45 | 80.31 | 64.41 | 103.79 | 47.86 | 55.73 |
| As | 1.62 | 2.04 | 4.78 | 10.56 | 9.56 | 6.96 | 8.64 | 7.61 | 6.58 | 4.94 | 2.78 | 3.62 |
| Pb | 12.81 | 20.96 | 51.39 | 122.08 | 108.41 | 69.97 | 90.74 | 68.45 | 73.67 | 55.59 | 36.58 | 42.65 |
| Cd | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| Cr | 7.50 | 11.03 | 15.94 | 50.83 | 46.68 | 39.14 | 38.85 | 28.82 | 34.64 | 31.08 | 25.69 | 23.27 |
| Heavy metal | Date | Sampling point | |||||||||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | ||
| Cu | 11/2020-12/2020 | 1.60 | 4.24 | 6.02 | 25.54 | 22.48 | 20.52 | 22.25 | 14.00 | 17.55 | 13.40 | 8.03 | 11.34 |
| 01/2021-02/2021 | 3.78 | 6.51 | 10.51 | 55.70 | 50.57 | 43.91 | 28.59 | 20.92 | 24.09 | 15.63 | 13.82 | 21.53 | |
| 03/2021-04/2021 | 3.23 | 6.16 | 10.25 | 38.78 | 32.78 | 26.33 | 23.24 | 18.17 | 18.67 | 16.91 | 13.44 | 16.48 | |
| 05/2021-06/2021 | 2.51 | 4.82 | 7.15 | 32.02 | 28.60 | 23.73 | 22.82 | 14.76 | 20.57 | 13.44 | 9.51 | 11.63 | |
| 07/2021-08/2021 | 3.03 | 4.97 | 8.32 | 34.98 | 29.27 | 24.04 | 18.45 | 16.04 | 21.17 | 11.75 | 10.46 | 12.33 | |
| 09/2021-10/2021 | 2.89 | 5.29 | 10.06 | 34.56 | 30.21 | 24.92 | 19.95 | 17.54 | 18.16 | 12.18 | 11.10 | 12.35 | |
| Zn | 11/2020-12/2020 | 0.94 | 2.65 | 5.20 | 23.25 | 17.48 | 13.17 | 21.55 | 10.60 | 8.45 | 13.53 | 7.02 | 7.72 |
| 01/2021-02/2021 | 3.21 | 4.74 | 9.42 | 49.47 | 44.60 | 27.89 | 27.87 | 16.91 | 13.27 | 20.01 | 9.15 | 11.47 | |
| 03/2021-04/2021 | 2.85 | 4.93 | 9.18 | 41.47 | 24.08 | 20.18 | 25.06 | 16.10 | 11.95 | 19.87 | 9.08 | 10.34 | |
| 05/2021-06/2021 | 1.54 | 2.85 | 6.45 | 25.30 | 18.44 | 14.75 | 21.83 | 11.36 | 9.55 | 16.22 | 7.26 | 7.92 | |
| 07/2021-08/2021 | 1.83 | 2.86 | 7.53 | 32.55 | 18.93 | 15.53 | 23.42 | 12.18 | 10.40 | 17.69 | 7.57 | 8.78 | |
| 09/2021-10/2021 | 1.97 | 3.57 | 8.41 | 30.45 | 20.44 | 17.55 | 21.73 | 13.16 | 10.79 | 16.46 | 7.79 | 9.50 | |
| As | 11/2020-12/2020 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.51 | 1.49 | 1.28 | 0.85 | 1.34 | 1.07 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.32 | 0.51 |
| 01/2021-02/2021 | 0.47 | 0.36 | 1.21 | 2.17 | 1.96 | 1.52 | 1.65 | 1.45 | 1.56 | 1.25 | 0.59 | 0.73 | |
| 03/2021-04/2021 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 1.06 | 1.88 | 1.69 | 1.34 | 1.56 | 1.39 | 1.34 | 0.98 | 0.56 | 0.66 | |
| 05/2021-06/2021 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 1.67 | 1.53 | 0.92 | 1.37 | 1.12 | 0.74 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.53 | |
| 07/2021-08/2021 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.72 | 1.67 | 1.57 | 1.30 | 1.36 | 1.31 | 1.10 | 0.81 | 0.51 | 0.60 | |
| 09/2021-10/2021 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.67 | 1.69 | 1.54 | 1.03 | 1.36 | 1.26 | 1.20 | 0.68 | 0.43 | 0.59 | |
| Heavy metal | Date | Sampling point | |||||||||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | ||
| Pb | 11/2020-12/2020 | 1.12 | 2.79 | 6.27 | 15.70 | 14.97 | 8.72 | 11.81 | 8.40 | 9.06 | 6.90 | 4.64 | 5.32 |
| 01/2021-02/2021 | 3.44 | 4.39 | 12.19 | 26.90 | 24.50 | 15.88 | 20.24 | 17.74 | 15.46 | 11.61 | 7.46 | 8.91 | |
| 03/2021-04/2021 | 2.72 | 4.08 | 11.18 | 24.57 | 22.90 | 13.58 | 18.74 | 13.15 | 13.91 | 11.54 | 7.38 | 7.93 | |
| 05/2021-06/2021 | 1.63 | 2.87 | 6.78 | 16.45 | 14.66 | 9.86 | 12.38 | 8.71 | 9.90 | 7.27 | 5.42 | 6.47 | |
| 07/2021-08/2021 | 1.87 | 3.32 | 7.34 | 18.89 | 15.34 | 9.28 | 13.27 | 9.95 | 12.08 | 7.65 | 5.71 | 6.74 | |
| 09/2021-10/2021 | 2.03 | 3.52 | 7.63 | 19.57 | 16.04 | 12.65 | 14.30 | 10.50 | 13.26 | 10.62 | 5.98 | 7.28 | |
| Cd | 11/2020-12/2020 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 01/2021-02/2021 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 03/2021-04/2021 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 05/2021-06/2021 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 07/2021-08/2021 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 09/2021-10/2021 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Cr | 11/2020-12/2020 | 1.03 | 1.44 | 2.25 | 6.46 | 6.04 | 4.99 | 5.61 | 3.53 | 4.78 | 4.50 | 3.05 | 3.08 |
| 01/2021-02/2021 | 1.44 | 2.31 | 3.01 | 11.22 | 10.52 | 8.80 | 8.72 | 5.76 | 7.35 | 6.00 | 5.08 | 5.07 | |
| 03/2021-04/2021 | 1.41 | 2.14 | 3.10 | 9.70 | 9.06 | 7.03 | 6.71 | 5.68 | 6.12 | 5.89 | 5.19 | 4.33 | |
| 05/2021-06/2021 | 0.97 | 1.56 | 2.24 | 6.85 | 6.34 | 5.62 | 6.08 | 3.73 | 5.02 | 4.65 | 3.40 | 3.23 | |
| 07/2021-08/2021 | 1.41 | 1.69 | 2.61 | 7.56 | 6.74 | 5.80 | 5.47 | 4.60 | 5.54 | 4.62 | 4.23 | 3.57 | |
| 09/2021-10/2021 | 1.24 | 1.90 | 2.72 | 9.05 | 7.98 | 6.9 | 6.27 | 5.52 | 5.83 | 5.42 | 4.74 | 3.98 | |
| Heavy metal | Soil layer (cm) | |||||
| 0-5 | 5-10 | 10-20 | ||||
| KMO | Bartlett | KMO | Bartlett | KMO | Bartlett | |
| 0.805 | 0.000 | 0.700 | 0.000 | 0.741 | 0.000 | |
| Components | ||||||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| Cu | 0.863 | 0.060 | 0.854 | -0.556 | 0.832 | -0.190 |
| Zn | 0.907 | -0.079 | 0.831 | 0.025 | 0.875 | 0.084 |
| As | 0.869 | -0.105 | 0.818 | -0.178 | 0.834 | -0.373 |
| Pb | 0.823 | -0.271 | 0.521 | 0.612 | 0.530 | 0.558 |
| Cr | 0.963 | 0.120 | 0.738 | 0.463 | 0.802 | -0.448 |
| Cd | 0.856 | 0.255 | 0.440 | 0.687 | 0.348 | 0.759 |
| Eigenvalue | 3.746 | 1.086 | 3.224 | 1.025 | 3.512 | 1.026 |
| Contribution rate % | 62.441 | 18.105 | 53.727 | 19.083 | 52.529 | 20.102 |
| Cumulative contribution rate % | 62.441 | 80.546 | 53.727 | 72.810 | 52.529 | 72.631 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




