Submitted:
29 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
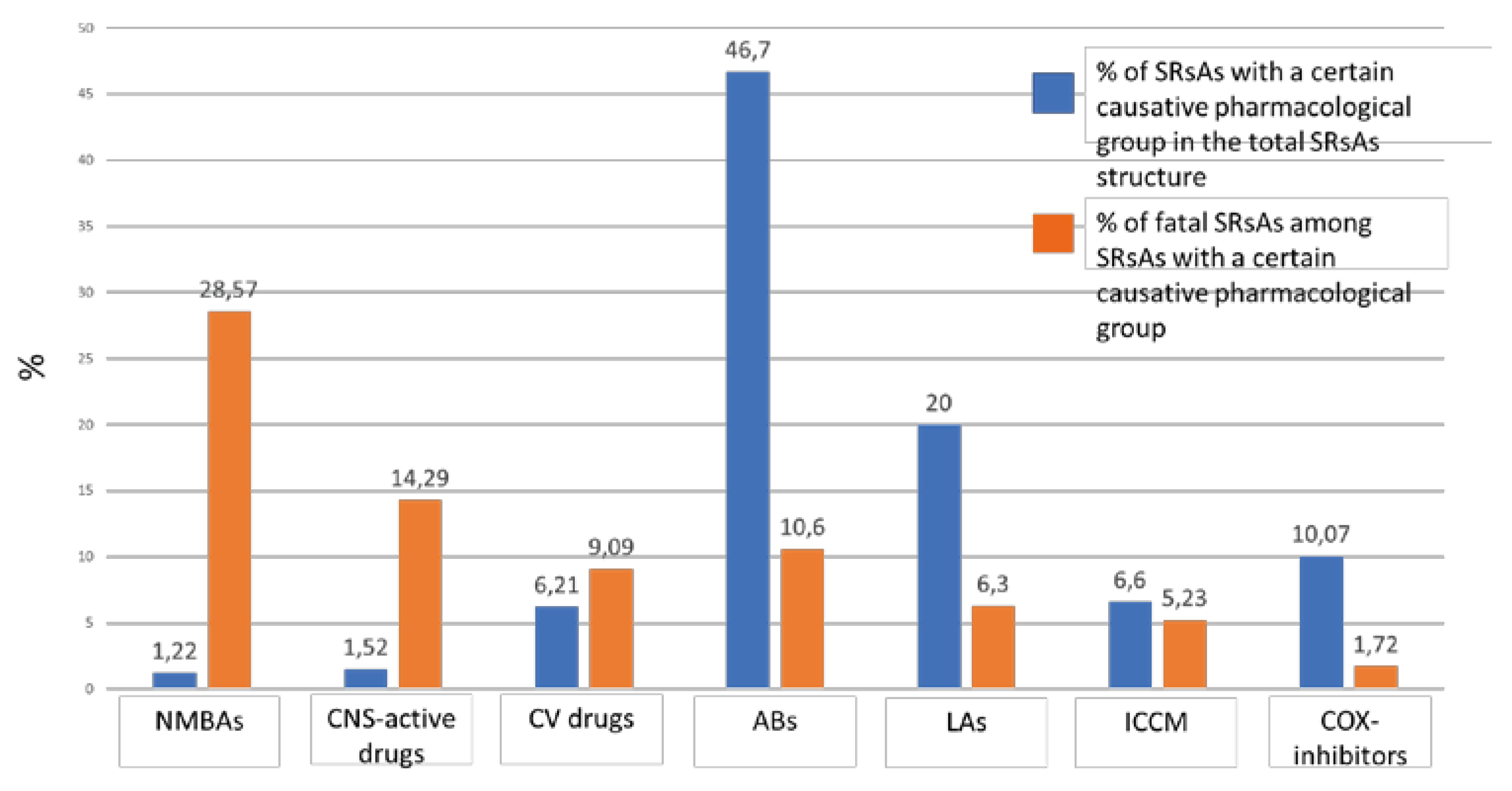
2.1. Analysis of SRsAs
2.1.1. Analysis of ABs Involved in Anaphylaxis
2.1.2. Analysis of LAs Involved in Anaphylaxis
2.1.3. Analysis of COX-Inhibitors Involved in Anaphylaxis.
2.1.4. Analysis of ICCM Involved in Anaphylaxis.
2.1.5. Analysis of CV Drugs Involved in Anaphylaxis
2.1.6. Analysis of CNS-Active Drugs Involved in Anaphylaxis
2.1.7. Analysis of NMBAs Involved in Anaphylaxis
2.2. Analysis of Fatal SRsAs
2.3. Analysis of Pediatric SRsAs
2.4. Analysis of SRsAs in the Elderly
3. Discussion
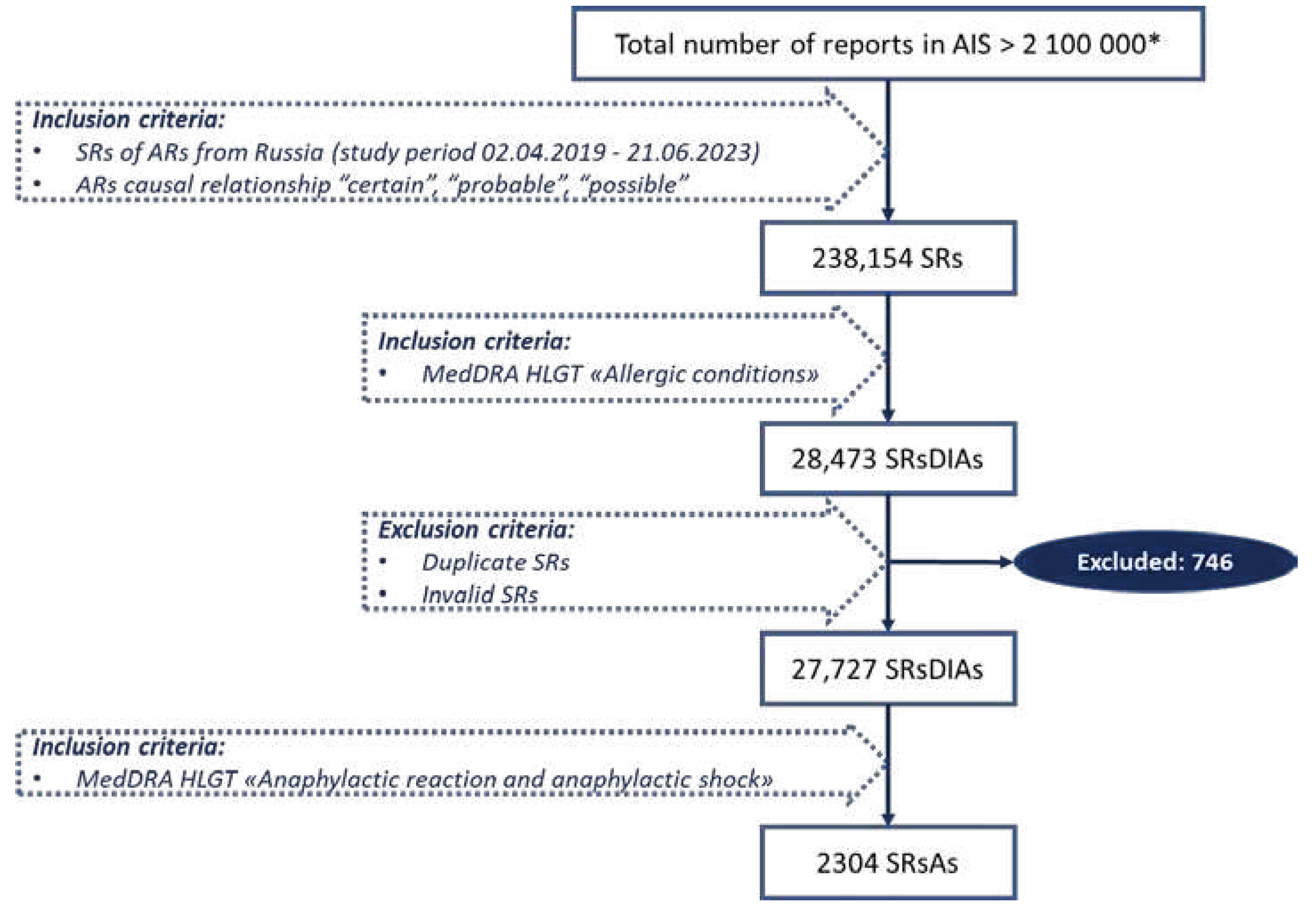
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source
4.2. Definitions
- “Adverse reaction - a response to a medicinal product, which is noxious and unintended. Adverse reaction may arise from use of the product within or outside the terms of the marketing authorization or from occupational exposure. Use outside the marketing authorization includes off-label use, overdose, misuse, abuse and medication errors”.
- “Causality: In accordance with ICH-E2A, the definition of an adverse reaction implies at least a reasonable possibility of a causal relationship between a suspected medicinal product and an adverse event. An adverse reaction, in contrast to an adverse event, is characterized by the fact that a causal relationship between a medicinal product and an occurrence is suspected. For regulatory reporting purposes, as detailed in ICH-E2D, if an event is spontaneously reported, even if the relationship is unknown or unstated, it meets the definition of an adverse reaction. Therefore all spontaneous reports notified by healthcare professionals or consumers are considered suspected adverse reactions, since they convey the suspicions of the primary sources, unless the reporters specifically state that they believe the events to be unrelated or that a causal relationship can be excluded”.
- “A spontaneous report is an unsolicited communication by a healthcare professional, or consumer to a competent authority, marketing authorisation holder or other organisation (e.g. regional pharmacovigilance centre, poison control centre) that describes one or more suspected adverse reactions in a patient who was given one or more medicinal products. It does not derive from a study or any organised data collection systems”.
4.3. Study Design and Data Selection
4.4. Drug Identification and Analyzed Categories
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardona V, Ansotegui IJ, Ebisawa M, et al. World allergy organization anaphylaxis guidance 2020. World Allergy Organ J. 2020;13(10):100472. Published 2020 Oct 30. [CrossRef]
- Regateiro FS, Marques ML, Gomes ER. Drug-Induced Anaphylaxis: An Update on Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2020;181(7):481-487. [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-González RV, Canel-Paredes A, Arias-Cruz A, et al. Alergia a medicamentos: aspectos fundamentales en el diagnóstico y tratamiento. Reporte de grupo del Colegio Mexicano de Inmunología Clínica y Alergia [Drug allergy: Fundamental aspects in diagnosis and treatment.]. Rev Alerg Mex. 2023;69(4):195-213. Published 2023 Apr 19. [CrossRef]
- Bruhns P, Chollet-Martin S. Mechanisms of human drug-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147(4):1133-1142. [CrossRef]
- Kiechle ES, McKenna CM, Carter H, et al. Medication Allergy and Adverse Drug Reaction Documentation Discrepancies in an Urban, Academic Emergency Department. J Med Toxicol. 2018;14(4):272-277. [CrossRef]
- Yu TC, Cunneen J. Prevalence of Antibiotic Allergy at a Spinal Cord Injury Center. Fed Pract. 2023;40(5):142-145. [CrossRef]
- Alkanhal R, Alhoshan I, Aldakhil S, et al. Prevalence triggers and clinical severity associated with anaphylaxis at a tertiary care facility in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(31):e11582. [CrossRef]
- Alen Coutinho I, Ferreira D, Regateiro FS, et al. Anaphylaxis in an emergency department: a retrospective 10-year study in a tertiary hospital. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;52(1):23-34. [CrossRef]
- Wong A, Seger DL, Lai KH, Goss FR, Blumenthal KG, Zhou L. Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions Documented in Electronic Health Records within a Large Health System. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(4):1253-1260.e3. [CrossRef]
- Lerch M, Mainetti C, Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B, Harr T. Current Perspectives on Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;54(1):147-176. [CrossRef]
- Dhopeshwarkar N, Sheikh A, Doan R, et al. Drug-Induced Anaphylaxis Documented in Electronic Health Records. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(1):103-111. [CrossRef]
- Wang C, Li Z, Yu Y, Feng M, Liu A. Active surveillance and clinical analysis of anaphylaxis based on the China Hospital Pharmacovigilance System. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1180685. Published 2023 Jul 11. [CrossRef]
- Yang SC, Hu S, Zhang SZ, et al. The Epidemiology of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in China [published correction appears in J Immunol Res. 2018 Jun 28;2018:4154507]. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:4320195. Published 2018 Feb 11. [CrossRef]
- Lee EY, Knox C, Phillips EJ. Worldwide Prevalence of Antibiotic-Associated Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159(4):384–392. [CrossRef]
- Esh CJ, Chrismas BCR, Mauger AR, Taylor L. Pharmacological hypotheses: Is acetaminophen selective in its cyclooxygenase inhibition?. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021;9(4):e00835. [CrossRef]
- van Diepen ATN, Simons P, Bos JM, Kramers C. Pijnbestrijding met metamizol in de Nederlandse praktijk [Metamizol: current status in Dutch practice]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2022;166:D6182. Published 2022 Jan 19.
- Pagani S, Lombardi N, Crescioli G, et al. Drug-Related Hypersensitivity Reactions Leading to Emergency Department: Original Data and Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 2022;11(10):2811. Published 2022 May 16. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Y, Sun S, Li X, et al. Drug-induced anaphylaxis in China: a 10 year retrospective analysis of the Beijing Pharmacovigilance Database. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40(5):1349-1358. [CrossRef]
- Poziomkowska-Gęsicka I, Kurek M. Clinical Manifestations and Causes of Anaphylaxis. Analysis of 382 Cases from the Anaphylaxis Registry in West Pomerania Province in Poland. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(8):2787. Published 2020 Apr 17. [CrossRef]
- Ben Mansour, A. , Daghfous H., Ben Saad S., Slim A., Bellali H., Tritar F. Drug related severe anaphylaxis investigation: A Tunisian retrospective study. Revue Française d'Allergologie. 2023;63(2):103309. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen KD, Nguyen HA, Vu DH, et al. Drug-Induced Anaphylaxis in a Vietnamese Pharmacovigilance Database: Trends and Specific Signals from a Disproportionality Analysis. Drug Saf. 2019;42(5):671-682. [CrossRef]
- Ahn KM, Kim BK, Yang MS. Risk factors of anaphylaxis in Korea: Identifying drug-induced anaphylaxis culprits using big data. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(35):e30224. [CrossRef]
- Yu RJ, Krantz MS, Phillips EJ, Stone CA Jr. Emerging Causes of Drug-Induced Anaphylaxis: A Review of Anaphylaxis-Associated Reports in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(2):819-829.e2. [CrossRef]
- Sari Dogan F, Ozaydin V. Drug-induced anaphylaxis in the emergency department: A prospective observational study. North Clin Istanb. 2021;8(6):595-600. Published 2021 Dec 31. [CrossRef]
- Demir S, Erdenen F, Gelincik A, et al. Evaluation of the Potential Risk Factors for Drug-Induced Anaphylaxis in Adult Patients. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2019;178(2):167-176. [CrossRef]
- Khan DA, Banerji A, Bernstein JA, et al. Cephalosporin Allergy: Current Understanding and Future Challenges. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(7):2105-2114. [CrossRef]
- D'Errico S, Frati P, Zanon M, et al. Cephalosporins' Cross-Reactivity and the High Degree of Required Knowledge. Case Report and Review of the Literature. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020;9(5):209. Published 2020 Apr 25. [CrossRef]
- Romano A, Valluzzi RL, Caruso C, Zaffiro A, Quaratino D, Gaeta F. Evaluating Immediate Reactions to Cephalosporins: Time Is of the Essence. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(4):1648-1657.e1. [CrossRef]
- Mori F, Liccioli G, Piccorossi A, et al. The Diagnosis of Ceftriaxone Hypersensitivity in a Paediatric Population. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2019;178(3):272-276. [CrossRef]
- Jung IY, Kim JJ, Lee SJ, et al. Antibiotic-Related Adverse Drug Reactions at a Tertiary Care Hospital in South Korea. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4304973. [CrossRef]
- Rhyou HI, Nam YH, Kim SC, et al. Cefaclor-induced hypersensitivity: Differences in the incidence of anaphylaxis relative to other 2nd and 3rd generation cephalosporins. PLoS One. 2021;16(7):e0254898. Published 2021 Jul 22. [CrossRef]
- Jevon P, Shamsi S. Management of anaphylaxis in the dental practice: an update. Br Dent J. 2020;229(11):721-728. [CrossRef]
- Zuo J, Gong R, Liu X, Zhao J. Risk of True Allergy to Local Anesthetics: 10-Year Experience from an Anesthesia Allergy Clinic in China. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:1297-1303. Published 2020 Dec 29. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., Gong, R., Xin, X. et al. Clinical characteristics and allergen detection of perioperative anaphylaxis: a 12-year retrospective analysis from an anesthesia clinic in China. Perioper Med 11, 5 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Park KK, Sharon VR. A Review of Local Anesthetics: Minimizing Risk and Side Effects in Cutaneous Surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43(2):173-187. [CrossRef]
- Bhole MV, Manson AL, Seneviratne SL, Misbah SA. IgE-mediated allergy to local anaesthetics: separating fact from perception: a UK perspective [published correction appears in Br J Anaesth. 2012 Oct;109(4):669]. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108(6):903-911. [CrossRef]
- Cherobin ACFP, Tavares GT. Safety of local anesthetics. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95(1):82-90. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M., Hotta, K., Inoue, S. et al. Mepivacaine-induced anaphylactic shock in a pregnant woman undergoing combined spinal and epidural anesthesia for cesarean delivery: a case report. JA Clin Rep 5, 84 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Simionescu AA, Danciu BM, Stanescu AMA. Severe Anaphylaxis in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review of Clinical Presentation to Determine Outcomes. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1060. [CrossRef]
- Hascoët E, Mahé J, Meillard H, Théophile H, Cloitre A, Lesclous P. Anaphylactic reac-tions to local anesthetics in dental practice: a nationwide French retrospective study. Clin Oral Investig. 2022;26(2):1667-1676. [CrossRef]
- Matveev AV, Krasheninnikov AE, Yagudina RI, Egorova EA, Konyaeva EI. Nezhelatel'nye reaktsii na mestnye anestetiki pri ikh primenenii v stomatologii [Adverse drug reactions of local anesthetics used in dentistry]. Stomatologiia (Mosk). 2020;99(6):82-88. [CrossRef]
- Blanca-Lopez N, Soriano V, Garcia-Martin E, Canto G, Blanca M. NSAID-induced reactions: classification, prevalence, impact, and management strategies. J Asthma Allergy. 2019;12:217-233. Published 2019 Aug 8. [CrossRef]
- Cimen SS, Suleyman A, Yucel E, Guler N, Tamay Z. Evaluation of the triggers and the treatment models of anaphylaxis in pediatric patients. North Clin Istanb. 2023;10(5):609-617. Published 2023 Aug 25. [CrossRef]
- Popiołek I, Piotrowicz-Wójcik K, Porebski G. Hypersensitivity Reactions in Serious Adverse Events Reported for Paracetamol in the EudraVigilance Database, 2007⁻2018. Pharmacy (Basel). 2019;7(1):12. Published 2019 Jan 17. [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli S, Langlois A, Ben-Shoshan M. Prevalence of Hypersensitivity Reactions in Children Associated with Acetaminophen: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018;176(2):106-114. [CrossRef]
- Sachs B, Dubrall D, Fischer-Barth W, Schmid M, Stingl J. Drug-induced anaphylactic reactions in children: A retrospective analysis of 159 validated spontaneous reports. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2019;28(3):377-388. [CrossRef]
- Qiu L, Cui Q, Gong X, Zhou H. Anaphylaxis Following Contrast-Enhanced CT with Iodixanol: A Case Report and Literature Review [published correction appears in J Asthma Allergy. 2023 Mar 02;16:239-240]. J Asthma Allergy. 2023;16:195-200. Published 2023 Jan 25. [CrossRef]
- Fukushima Y, Taketomi-Takahashi A, Suto T, Hirasawa H, Tsushima Y. Clinical features and risk factors of iodinated contrast media (ICM)-induced anaphylaxis. Eur J Radiol. 2023;164:110880. [CrossRef]
- Sugizaki C, Sato S, Yanagida N, Ebisawa M. Analysis of drug-induced anaphylaxis cases using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database - secondary publication. Allergol Int. 2023;72(4):580-587. [CrossRef]
- Kim MH, Lee SY, Lee SE, et al. Anaphylaxis to iodinated contrast media: clinical characteristics related with development of anaphylactic shock. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100154. Published 2014 Jun 16. [CrossRef]
- Coop CA, Schapira RS, Freeman TM. Are ACE Inhibitors and Beta-blockers Dangerous in Patients at Risk for Anaphylaxis?. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5(5):1207-1211. [CrossRef]
- Tejedor-Alonso MA, Farias-Aquino E, Pérez-Fernández E, Grifol-Clar E, Moro-Moro M, Rosado-Ingelmo A. Relationship Between Anaphylaxis and Use of Beta-Blockers and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(3):879-897.e5. [CrossRef]
- Yeğit OO, Aslan AF, Coşkun R, et al. Comparison of recent anaphylaxis diagnostic criteria in real life: Can more patients be diagnosed as having anaphylaxis?. World Allergy Organ J. 2023;16(8):100810. Published 2023 Aug 26. [CrossRef]
- Teshigawara A, Nishibe S, Horie S, et al. Fentanyl-associated anaphylaxis in an infant with tetralogy of Fallot: a case report. JA Clin Rep. 2019;5(1):34. Published 2019 May 21. [CrossRef]
- Laguna JJ, Archilla J, Doña I, et al. Practical Guidelines for Perioperative Hypersensitivity Reactions. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2018;28(4):216-232. [CrossRef]
- Teshigawara A, Nishibe S, Horie S, et al. Fentanyl-associated anaphylaxis in an infant with tetralogy of Fallot: a case report. JA Clin Rep. 2019;5(1):34. Published 2019 May 21. [CrossRef]
- Tomar GS, Tiwari AK, Chawla S, Mukherjee A, Ganguly S. Anaphylaxis related to fentanyl citrate. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2012;5(3):257-261. [CrossRef]
- Joo J, Bae H, Lee J. Intraoperative allergic reaction to fentanyl: A case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2009;57(6):776-779. [CrossRef]
- Belso N, Kui R, Szegesdi I, et al. Propofol and fentanyl induced perioperative anaphylaxis. Br J Anaesth. 2011;106(2):283-284. [CrossRef]
- Haybarger E, Young AS, Giovannitti JA Jr. Benzodiazepine Allergy With Anesthesia Administration: A Review of Current Literature. Anesth Prog. 2016;63(3):160-167. [CrossRef]
- Mali S. Anaphylaxis during the perioperative period. Anesth Essays Res. 2012;6(2):124-133. [CrossRef]
- Mori F, Barni S, Manfredi M, et al. Anaphylaxis to Intravenous Tramadol in a Child. Pharmacology. 2015;96(5-6):256-258. [CrossRef]
- Hallberg P., Brenning G. Angioedema induced by tramadol—a potentially life-threatening condition. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 2005;60: 901-903. [CrossRef]
- Arslan K. Tramadol-Induced Anaphylaxis: A Rare Case. Türkiye Klinikleri Journal of Case Reports. 2022;30(4): 238 – 241. [CrossRef]
- Dejoux A, de Chaisemartin L, Bruhns P, Longrois D, Gouel-Chéron A. Neuromuscular blocking agent induced hypersensitivity reaction exploration: an update. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2023;40(2):95-104. [CrossRef]
- Di Leo E, Delle Donne P, Calogiuri GF, Macchia L, Nettis E. Focus on the agents most frequently responsible for perioperative anaphylaxis. Clin Mol Allergy. 2018;16:16. Published 2018 Jul 9. [CrossRef]
- Misbah SA, Krishna MT. Peri-Operative Anaphylaxis-An Investigational Challenge. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1117. Published 2019 May 29. [CrossRef]
- Zou Y, Shao LJ, Xue FS. Perioperative anaphylaxis: a potential hazard to the safety of surgical patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(5):609-612. [CrossRef]
- Petitpain N, Argoullon L, Masmoudi K, et al. Neuromuscular blocking agents induced anaphylaxis: Results and trends of a French pharmacovigilance survey from 2000 to 2012. Allergy. 2018;73(11):2224-2233. [CrossRef]
- Turner PJ, Jerschow E, Umasunthar T, Lin R, Campbell DE, Boyle RJ. Fatal Anaphylaxis: Mortality Rate and Risk Factors. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5(5):1169-1178. [CrossRef]
- Xing Y, Zhang H, Sun S, et al. Clinical features and treatment of pediatric patients with drug-induced anaphylaxis: a study based on pharmacovigilance data. Eur J Pediatr. 2018;177(1):145-154. [CrossRef]
- Cavkaytar O, Karaatmaca B, Cetinkaya PG, et al. Characteristics of drug-induced anaphylaxis in children and adolescents. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2017;38(5):56-63. [CrossRef]
- Bilò MB, Corsi A, Martini M, Penza E, Grippo F, Bignardi D. Fatal anaphylaxis in Italy: Analysis of cause-of-death national data, 2004-2016. Allergy. 2020;75(10):2644-2652. [CrossRef]
- Perez-Codesido S, Rosado-Ingelmo A, Privitera-Torres M, et al. Incidence of Fatal Anaphylaxis: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2022;32(4):245-260. [CrossRef]
- Jerschow E, Lin RY, Scaperotti MM, McGinn AP. Fatal anaphylaxis in the United States, 1999-2010: temporal patterns and demographic associations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134(6):1318-1328.e7. [CrossRef]
- Tanno LK, Molinari N, Annesi-Maesano I, Demoly P, Bierrenbach AL. Anaphylaxis in Brazil between 2011 and 2019. Clin Exp Allergy. 2022;52(9):1071-1078. [CrossRef]
- Tejedor-Alonso MA, Martínez-Fernandez P, Vallejo-de-Torres G, Navarro-Escayola E, Moro-Moro M, Alberti-Masgrau N. Clinical and demographic characteristics of fatal anaphylaxis in Spain (1998-2011): A comparison between a series from the hospital system and a national forensic series. Clin Exp Allergy. 2019;49(1):82-91. [CrossRef]
- Jares EJ, Cardona V, Gómez RM, et al. Latin American anaphylaxis registry. World Allergy Organ J. 2023;16(2):100748. Published 2023 Feb 5. [CrossRef]
- Pauwels I, Versporten A, Drapier N, Vlieghe E, Goossens H; Global-PPS network. Hospital antibiotic prescribing patterns in adult patients according to the WHO Access, Watch and Reserve classification (AWaRe): results from a worldwide point prevalence survey in 69 countries. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021;76(6):1614-1624. [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH E2B (R3) Electronic transmission of individual case safety reports (ICSRs) – data elements and message specification – implementation guide – Scientific guideline. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-e2b-r3-electronic-transmission-individual-case-safety-reports-icsrs-data-elements-message (Accessed 18 November 2023).
- MedDRA. Available online: https://www.meddra.org/how-to-use/support-documentation/english (Accessed 18 November 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on good pharmacovigilance practices (GVP) Module VI – Collection, management and submission of reports of suspected adverse reactions to medicinal products (Rev 2). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/regulatory-procedural-guideline/guideline-good-pharmacovigilance-practices-gvp-module-vi-collection-management-submission-reports_en.pdf (Accessed 18 November 2023).
- Eurasian Economic Union “Good pharmacovigilance practice” guideline (edition No. 2 dated 05/19/2022). Available online: https://docs.eaeunion.org/docs/ru-ru/01433831/err_09062022_81 (Accessed 18 Nov 2023).
- Bassir F, Varghese S, Wang L, Chin YP, Zhou L. The Use of Electronic Health Records to Study Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions from 2000 to 2021: A Systematic Re-view. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2022;42(2):453-497. [CrossRef]
| ABs | N (Total - 1028) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Beta-lactams | 902 | 87.7 |
| Ceftriaxone | 687 | 66.8 |
| Cefotaxime | 87 | 8.5 |
| Cefazolin | 39 | 3.8 |
| Ampicillin sulbactam | 17 | 1.7 |
| Cefepime | 15 | 1.5 |
| Cefuroxime | 10 | 1.0 |
| Meropenem | 10 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin clavulanate | 8 | 0.8 |
| Cefoperazone sulbactam | 7 | 0.7 |
| Ertapenem | 5 | 0.5 |
| Cefoperazone | 4 | 0.4 |
| Ampicillin | 4 | 0.4 |
| Cefepime sulbactam | 3 | 0.3 |
| Amoxicillin sulbactam | 2 | 0.2 |
| Piperacillin tazobactam | 2 | 0.2 |
| Cephalexin | 1 | 0.1 |
| Cefixime | 1 | 0.1 |
| Other | 126 | 12.3 |
| Vancomycin | 28 | 2.7 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 22 | 2.1 |
| Levofloxacin | 18 | 1.8 |
| Metronidazole | 14 | 1.4 |
| Linezolid | 7 | 0.7 |
| Amikacin | 7 | 0.7 |
| Nitrofurantoin | 7 | 0.7 |
| Fosfomycin | 5 | 0.5 |
| Sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim | 3 | 0.3 |
| Tigecycline | 3 | 0.3 |
| Polymyxin B | 2 | 0.2 |
| Kanamycin | 2 | 0.2 |
| Amphotericin B | 2 | 0.2 |
| Gentamicin | 1 | 0.1 |
| Ofloxacin | 1 | 0.1 |
| Erythromycin | 1 | 0.1 |
| Clindamycin | 1 | 0.1 |
| Rifampicin | 1 | 0.1 |
| Isoniazid | 1 | 0.1 |
| LAs | N (Total - 460) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Lidocaine | 293 | 63.7 |
| Procaine | 68 | 14.8 |
| Articaine | 61 | 13.3 |
| Ropivacaine | 16 | 3.5 |
| Bupivacaine | 14 | 3.0 |
| Mepivacaine | 8 | 1.7 |
| COX-inhibitors | N (Total - 232) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | 49 | 21.1 |
| Metamizole | 48 | 20.7 |
| Ibuprofen | 35 | 15.1 |
| Diclofenac | 29 | 12.5 |
| Ketorolac | 26 | 11.2 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 25 | 10.8 |
| Ketoprofen | 6 | 3.0 |
| Celecoxib | 5 | 2.2 |
| Aceclofenac | 3 | 1.3 |
| Meloxicam | 3 | 1.3 |
| Lornoxicam | 2 | 0.9 |
| Nimesulide | 1 | 0.4 |
| ICCM | N (Total - 153) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Iopromide | 97 | 63.4 |
| Iohexol | 39 | 25.5 |
| Iomeprol | 13 | 8.5 |
| Iodixanol | 2 | 1.3 |
| Ioversol | 1 | 0.7 |
| Iopamidol | 1 | 0.7 |
| CV drug | N (Total – 143) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| ACEIs | 29 | 20.3 |
| Enalapril | 17 | 11.9 |
| Captopril | 11 | 7.8 |
| Perindopril | 1 | 0.7 |
| Beta-blockers | 22 | 15.4 |
| Bisoprolol | 13 | 9.1 |
| Metoprolol | 5 | 3.5 |
| Atenolol | 3 | 2.1 |
| Propranolol | 1 | 0.7 |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | 21 | 14.7 |
| Nifedipine | 9 | 6.3 |
| Amlodipine | 8 | 5.6 |
| Verapamil | 4 | 2.8 |
| Potassium-magnesium-asparaginate | 19 | 13.3 |
| Antiarrhythmics | 12 | 8.4 |
| Amiodarone | 10 | 7.0 |
| Digoxin | 1 | 0.7 |
| Propafenone | 1 | 0.7 |
| Diuretics | 11 | 7.7 |
| Furosemide | 7 | 4.9 |
| Spironolactone | 3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | 1 | 0.7 |
| Sartans (Losartan) | 8 | 5.6 |
| Statins | 6 | 4.2 |
| Rosuvastatin | 4 | 2.8 |
| Atorvastatin | 2 | 1.4 |
| Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist (Clonidine) | 4 | 2.8 |
| Indirect oral anticoagulant (Warfarin) | 4 | 2.8 |
| Direct oral anticoagulants | 2 | 1.4 |
| Rivaroxaban | 1 | 0.7 |
| Apixaban | 1 | 0.7 |
| Unfractionated heparin | 2 | 1.4 |
| Antiplatelet drugs | 2 | 1.4 |
| Clopidogrel | 1 | 0.7 |
| Ticagrelor | 1 | 0.7 |
| Thrombolytic agent (Alteplase) | 1 | 0.7 |
| CNS-active drugs | N (Total - 35) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Fentanyl | 20 | 57.1 |
| Diazepam | 4 | 11.4 |
| Tramadol | 4 | 11.4 |
| Midazolam | 3 | 8.6 |
| Venlafaxine | 1 | 2.9 |
| Droperidol | 1 | 2.9 |
| Carbamazepine | 1 | 2.9 |
| Levetiracetam | 1 | 2.9 |
| NMBAs | N (Total - 28) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Rocuronium | 10 | 35.7 |
| Atracurium | 8 | 28.6 |
| Suxamethonium | 5 | 17.9 |
| Cisatracurium | 5 | 17.9 |
| Drug | N (Total - 218) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| ABs | 109 | 50.00 |
| Ceftriaxone | 68 | 31.2 |
| Cefotaxime | 13 | 6.0 |
| Fosfomycin | 5 | 2.3 |
| Amoxicillin clavulanate | 3 | 1.4 |
| Levofloxacin | 3 | 1.4 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 3 | 1.4 |
| Cefazolin | 3 | 1.4 |
| Ampicillin sulbactam | 2 | 0.9 |
| Ertapenem | 2 | 0.9 |
| Amphotericin B | 1 | 0.5 |
| Meropenem | 1 | 0.5 |
| Tigecycline | 1 | 0.5 |
| Sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim | 1 | 0.5 |
| Vancomycin | 1 | 0.5 |
| Metronidazole | 1 | 0.5 |
| LAs | 29 | 13.3 |
| Lidocaine | 19 | 8.7 |
| Bupivacaine | 7 | 3.2 |
| Articaine | 1 | 0.5 |
| Procaine | 1 | 0.5 |
| Ropivacaine | 1 | 0.5 |
| CV drugs | 13 | 6.0 |
| Beta blockers | 3 | 1.4 |
| Bisoprolol | 2 | 0.9 |
| Metoprolol | 1 | 0.5 |
| ACEi (Enalapril) | 3 | 1.4 |
| Sartans (Losartan) | 1 | 0.5 |
| Calcium Channel Blockers (Amlodipine) | 2 | 0.9 |
| Antiarrhythmics (Amiodorone) | 1 | 0.5 |
| Statins (Rosuvastatin) | 1 | 0.5 |
| Antiplatelet drugs (Ticagrelor) | 1 | 0.5 |
| Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist (Clonidine) | 1 | 0.5 |
| NMBAs | 8 | 3.7 |
| Rocuronium | 4 | 1.8 |
| Suxamethonium | 2 | 0.9 |
| Atracurium | 1 | 0.5 |
| Cisatracurium | 1 | 0.5 |
| ICCM | 8 | 3.7 |
| Iopromide | 4 | 1.8 |
| Iohexol | 3 | 1.4 |
| Iomeprol | 1 | 0.5 |
| CNS-active drugs | 5 | 2.3 |
| Fentanyl | 2 | 0.9 |
| Diazepam | 1 | 0.5 |
| Levetiracetam | 1 | 0.5 |
| Midazolam | 1 | 0.5 |
| COX-inhibitors | 4 | 1.8 |
| Diclofenac | 2 | 0.9 |
| Ibuprofen | 1 | 0.5 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 1 | 0.5 |
| Other drugs | 42 | 19.3 |
| Causative Group of Drugs | Age | Females | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Min; Max | % (N) | |
| ABs | 48.2 (16.1) | 15 months; 85 years | 53.8 (50) |
| LAs | 39.4 (14.4) | 5 months; 68 years | 55.1 (16) |
| CV drugs | 62.6 (10.6) | 48 years; 86 years | 30.8 (4) |
| ICCM | 74.0 (8.2) | 65 years; 86 years | 62.5 (5) |
| NMBAs | 37.0 (12.7) | 22 years; 61 years | 75.0 (6) |
| COX-inhibitors | 50.7 (0.4) | 50 years; 51 years | 75.0 (3) |
| CNS-active drugs | 45.6 (7.7) | 32 years; 55 years | 60.0 (3) |
| Other drugs | 51.4 (15.2) | 1 month; 80 years | 57.8 (41) |
| ABs | N (Total - 57) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Beta-lactams | 50 | 87.7 |
| Ceftriaxone | 29 | 50.9 |
| Cefotaxime | 7 | 12.3 |
| Cefazolin | 5 | 8.8 |
| Ampicillin sulbactam | 4 | 7.0 |
| Cefepime | 2 | 3.5 |
| Cefoperazone sulbactam | 1 | 1.8 |
| Meropenem | 1 | 1.8 |
| Amoxicillin clavulanate | 1 | 1.8 |
| Other | 7 | 12.3 |
| Vancomycin | 4 | 7.0 |
| Metronidazole | 2 | 3.5 |
| Linezolid | 1 | 1.8 |
| LAs | N (Total - 17) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Lidocaine | 9 | 52.9 |
| Articaine | 6 | 35.3 |
| Mepivacaine | 2 | 11.8 |
| Drug | N (Total - 65) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| ABs | 26 | 40.0 |
| Ceftriaxone | 23 | 35.4 |
| Amoxicillin clavulanate | 2 | 3.1 |
| Cefixime | 1 | 1.5 |
| CV-drugs | 13 | 20.0 |
| Antiarrhythmic (Amiodarone) | 3 | 4.6 |
| Unfractionated heparin | 2 | 3.1 |
| Beta-blockers (Bisoprolol) | 2 | 3.1 |
| Calcium Channels Blockers | 3 | 4.6 |
| Amlodipine | 2 | 3.1 |
| Nifedipine | 1 | 1.5 |
| Diuretics | 2 | 3.1 |
| Furosemide | 1 | 1.5 |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | 1 | 1.5 |
| Thrombolytic agent (Alteplase) | 1 | 1.5 |
| ICCM | 8 | 12.3 |
| Iopromide | 4 | 6.2 |
| Iohexol | 3 | 4.6 |
| Iomeprol | 1 | 1.5 |
| COX-inhibitors | 5 | 7.7 |
| Diclofenac | 3 | 4.6 |
| Lornoxicam | 1 | 1.5 |
| Metamozole | 1 | 1.5 |
| NMBAs | 4 | 6.2 |
| Rocuronium | 2 | 3.1 |
| Atracurium | 1 | 1.5 |
| Cisatracurium | 1 | 1.5 |
| LAs | 2 | 3.1 |
| Bupivacaine | 1 | 1.5 |
| Procaine | 1 | 1.5 |
| Other drugs | 7 | 10.8 |
| Prednisolone | 1 | 1.5 |
| Iron formulations | 2 | 3.1 |
| Ethyl-methyl-hydroxypyridine succinate | 1 | 1.5 |
| Venlafaxine | 1 | 1.5 |
| Oxaliplatin | 1 | 1.5 |
| Pentoxifylline | 1 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





