Submitted:
28 November 2023
Posted:
29 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Casuistry and Local
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Study Design
2.5. Hypotheses
2.6. Development
2.7. Ethical Aspects
2.8. Patient Consent for Publication
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Conflict Interest
Financial Support
Authors contributions
Data availability
References
- Frenkel, L.D.; Gomez, F.; Bellanti, J.A. COVID-19 in children: Pathogenesis and current status. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021 Jan 3;42(1):8-15. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitworth, H.; Sartain, S.E.; Kumar, R.; Armstrong, K.; Ballester, L.; Betensky, M.; et al Rate of thrombosis in children adolescents hospitalized with COVID-19 or, M.I.S.-C. Blood. 2021 Jul 15;138(2):190-198. [CrossRef]
- Ladhani SN, Amin-Chowdhury Z, Davies HG, Aiano F, Hayden I, Lacy J, Sinnathamby M, et al. COVID-19 in children: analysis of the first pandemic peak in England. Arch Dis Child. 2020 Dec;105(12):1180-1185. [CrossRef]
- Di Toro F, Gjoka M, Di Lorenzo G, De Santo D, De Seta F, Maso G, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on maternal and neonatal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Jan;27(1):36-46. [CrossRef]
- Tsankov, B.K.; Allaire, J.M.; Irvine, M.A.; Lopez, A.A.; Sauvé, L.J.; Vallance, B.A.; Jacobson, K. Severe COVID-19 Infection and Pediatric Comorbidities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Feb;103:246-256. [CrossRef]
- Belu A, Trandafir LM, Țarcă E, Cojocaru E, Frăsinariu O, Stârcea M, et al. Variations in Biochemical Values under Stress in Children with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 ;12(5):1213. [CrossRef]
- Sayed IA, Bhalala U, Strom L, Tripathi S, Kim JS, Michaud K, et al. VIRUS Investigators. Gastrointestinal Manifestations in Hospitalized Children With Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Multisystem Inflammatory Condition: An Analysis of the VIRUS COVID-19 Registry. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Luo X, Lv M, Zhang X, Estill J, Yang B, Lei R, Ren M, Liu Y, Wang L, Liu X, Wang Q, Meng M, Chen Y; COVID-19 evidence and recommendations working group. Clinical manifestations of COVID-19: An overview of 102 systematic reviews with evidence mapping. J Evid Based Med. 2022 Sep;15(3):201-215. [CrossRef]
- Souza IV, Scodro RB de Lima, Siqueira VLD, Cardoso RF 2, Ferracioli KRC. Comorbidities And Deaths By Covid-19 In Brazil. Uningá Journal 2021; 58: eUJ4054. 4054. [CrossRef]
- Quast, T.; Andel, R.; Gregory, S.; Storch, E.A. Years of life lost associated with COVID-19 deaths in the USA during the first 2 years of the pandemic. J Public Health (Oxf). 2022 :fdac057. [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Rojas JÁ, Vásquez-Hoyos P, Pérez-Morales R, Monsalve-Quintero AM, Mora-Robles L, Diaz-Diaz A, et al. Association of Cancer Diagnosis and Therapeutic Stage With Mortality in Pediatric Patients With COVID-19, Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study From Latin America. Front Pediatr. 2022 ;10:885633. [CrossRef]
- Pathak, E.B.; Salemi, J.L.; Sobers, N.; Menard, J.; Hambleton, I.R. COVID-19 in Children in the United States: Intensive Care Admissions, Estimated Total Infected, and Projected Numbers of Severe Pediatric Cases in 2020. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2020 Jul/Aug;26(4):325-333. [CrossRef]
- de Siqueira Alves Lopes A, Fontes Vieira SC, Lima Santos Porto R, Santana Santos V, Fontes Leite DC, Eduardo Cuevas L, et al. Coronavirus disease-19 deaths among children and adolescents in an area of Northeast, Brazil: why so many? Trop Med Int Health. 2021 Jan;26(1):115-119. [CrossRef]
- Flaxman S, Whittaker C, Semenova E, Rashid T, Parks RM, Blenkinsop A, et al. Assessment of COVID-19 as the Underlying Cause of Death Among Children and Young People Aged 0 to 19 Years in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jan 3;6(1):e2253590. [CrossRef]
- Efendi F, Haryanto J, Has EMM, Makhfudli M, Indarwati R, Kuswanto H, et al. Predictors of Mortality Among Children with Confirmed and Suspected Cases of COVID-19 in East Java, Indonesia. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023 Feb 7;16:355-362. [CrossRef]
- Castagnoli R, Votto M, Licari A, Brambilla I, Bruno R, Perlini S, et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in children and adolescents: a systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 2020;174:882-9. 1467. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Prado E, Izquierdo-Condoy JS, Fernandez-Naranjo R, Vasconez J, Dávila Rosero MG, Revelo-Bastidas D, et al. The deadly impact of COVID-19 among children from Latin America: The case of Ecuador. Front Pediatr. 2023 Apr 21;11:1060311. [CrossRef]
- Brazil – Ministério da Saúde [homepage on the Internet]. SRAG 2020 - Banco de Dados de Síndrome Respiratória Aguda Grave - incluindo dados da COVID-19 - Conjuntos de dados - Open Data [cited 2021 Oct 19]. Available from: https://opendatasus.saude.gov.br/dataset/bd-srag-2020.
- Sousa, B.L.A.; Silva, C.A.; Ferraro, A.A. An update on the epidemiology of pediatric COVID-19 in Brazil Editorial Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2022; 40. [CrossRef]
- Mucalo L, Brandow AM, Dasgupta M, Mason SF, Simpson PM, Singh A, et al. Comorbidities are risk factors for hospitalization and serious COVID-19 illness in children and adults with sickle cell disease. Blood Adv. 2021 Jul 13;5(13):2717-2724. [CrossRef]
- Trapani S, Rubino C, Lasagni D, Pegoraro F, Resti M, Simonini G,et al. Thromboembolic complications in children with COVID-19 and MIS-C: A narrative review. Front Pediatr. 2022 Aug 11;10:944743. [CrossRef]
- Conway EM, Mackman N, Warren RQ, Wolberg AS, Mosnier LO, Campbell RA, et al. Understanding COVID-19-associated coagulopathy. Nat Rev Immunol 2022; 22: 639–649. [CrossRef]
- Renzaho, A.M.N. The Need for the Right Socio-Economic and Cultural Fit in the COVID-19 Response in Sub-Saharan Africa: Examining Demographic, Economic Political, Health, and Socio-Cultural Differentials in COVID-19 Morbidity and Mortality. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 ;17(10):3445. [CrossRef]
- Heo, M.H.; Kwon, Y.D.; Cheon, J.; Kim, K.B.; Noh, J.W. Association between the Human Development Index and Confirmed COVID-19 Cases by Country. Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jul 29;10(8):1417. [CrossRef]
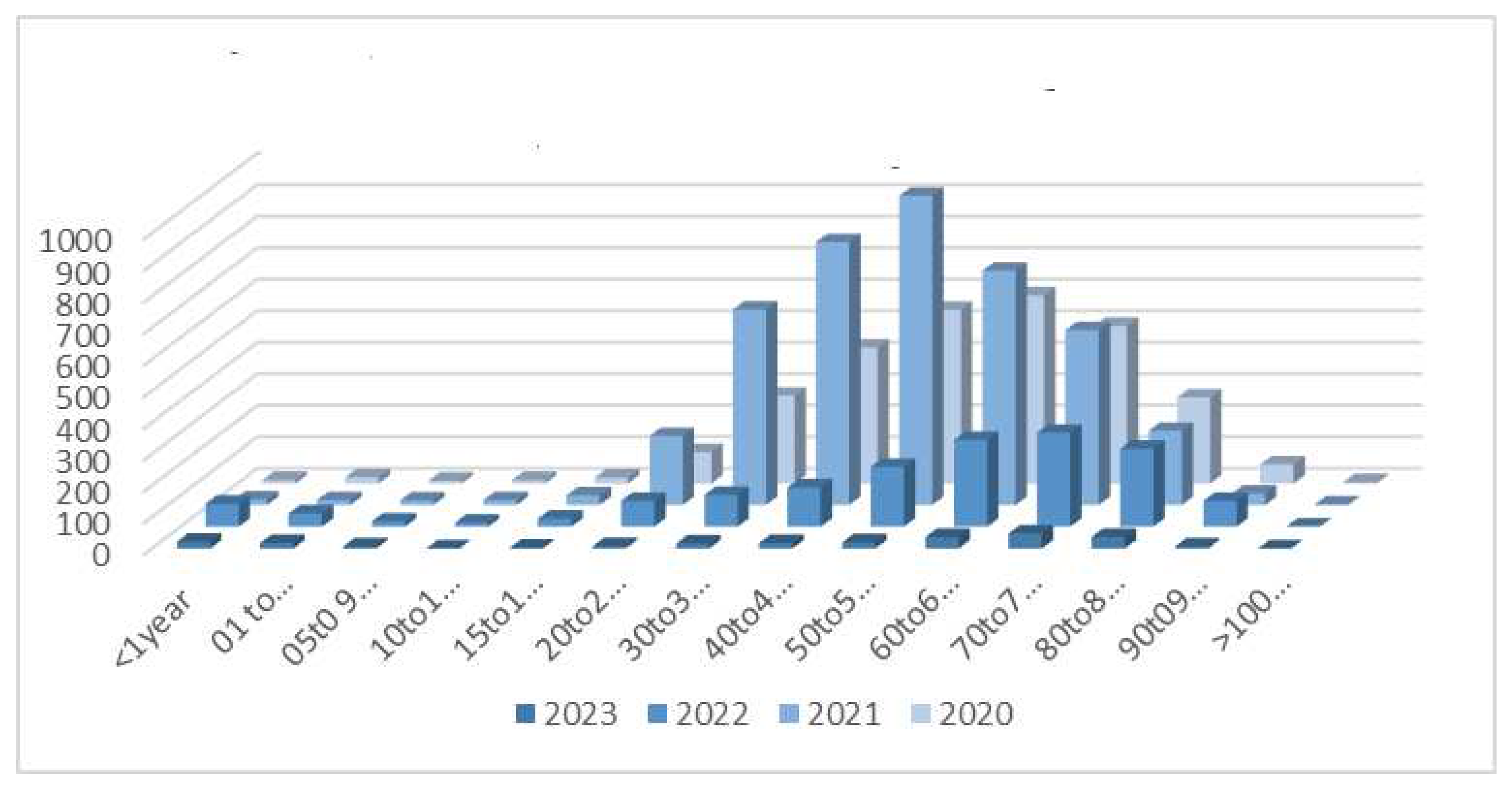
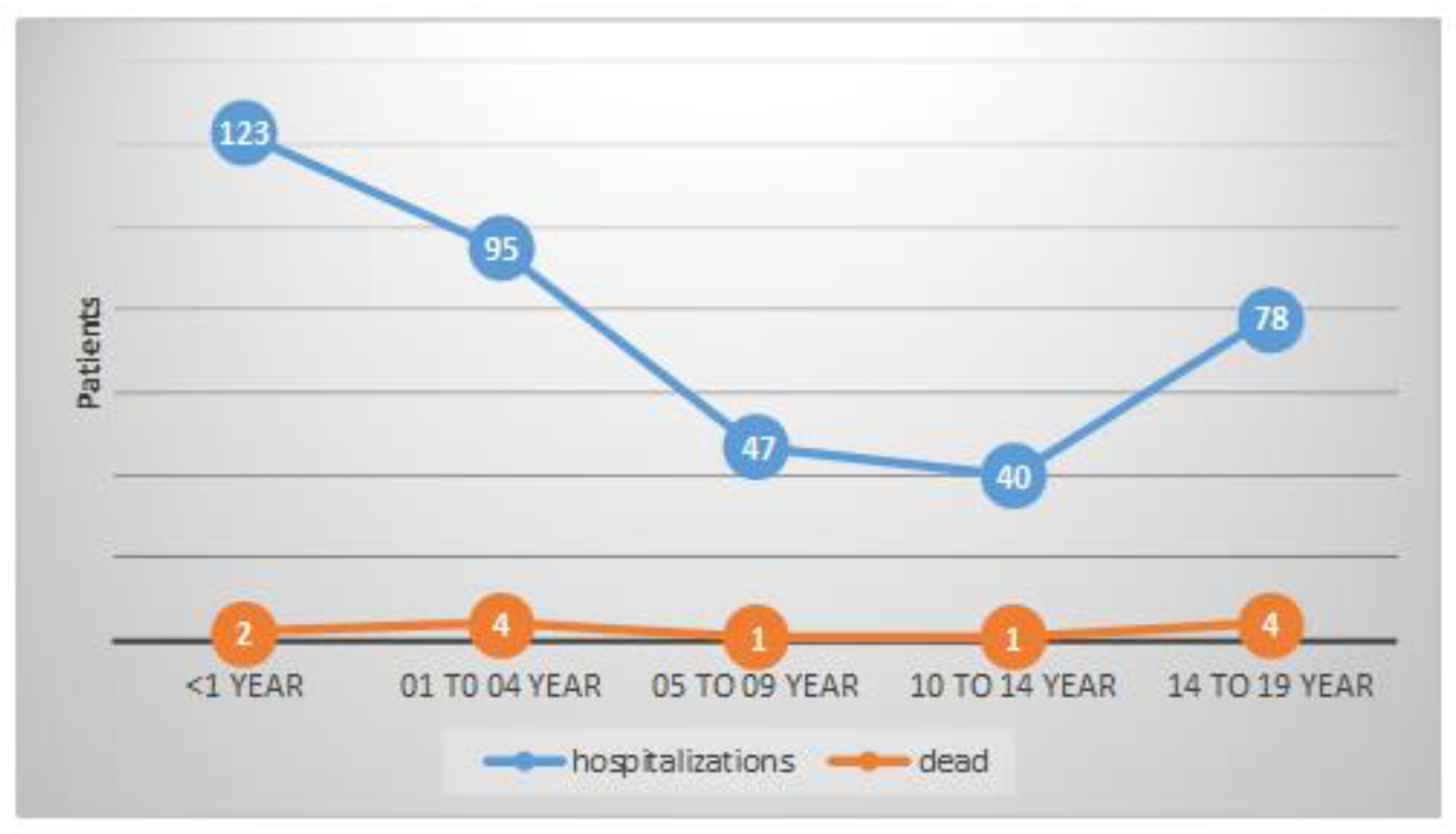
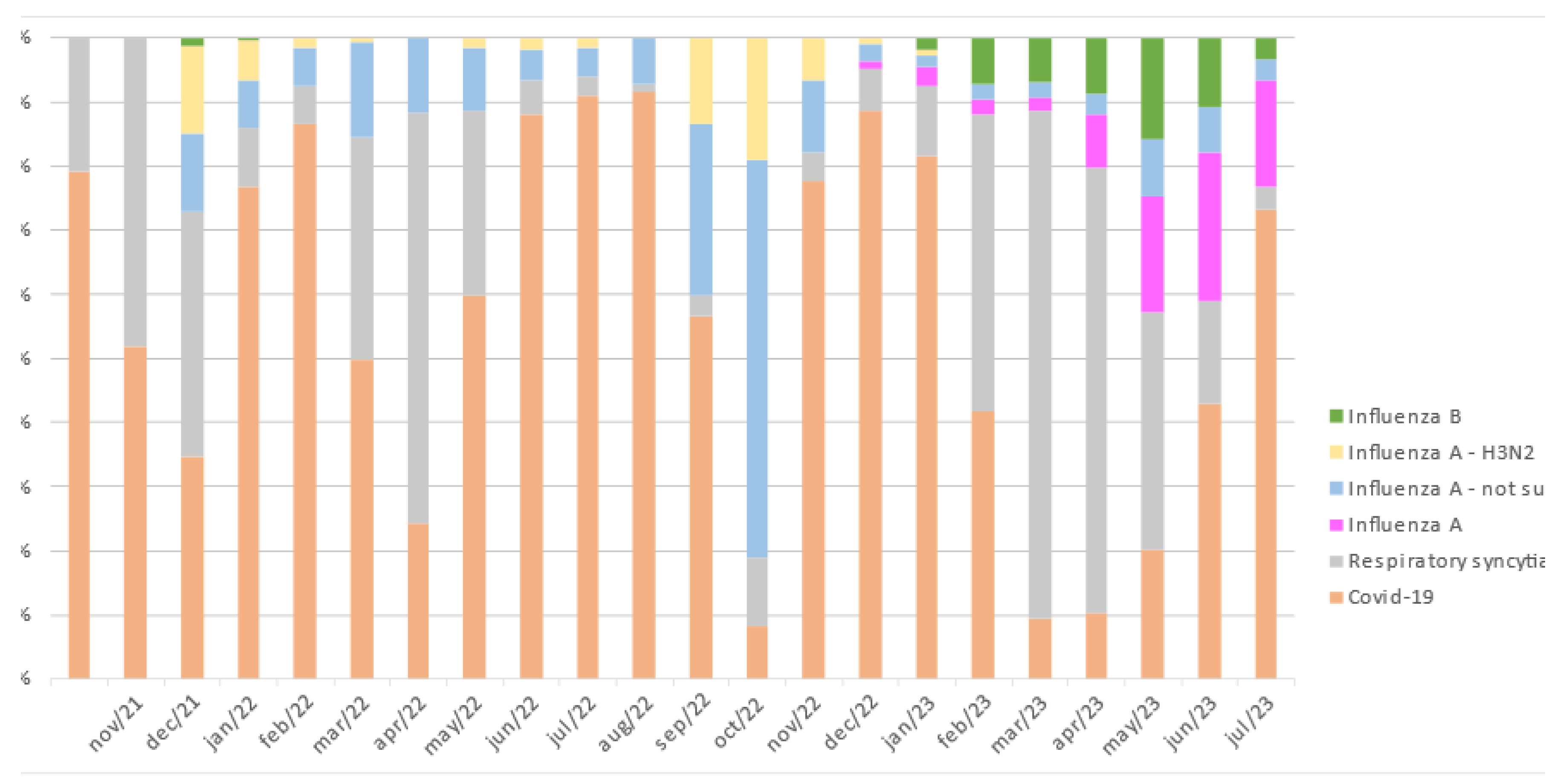
| Age | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| years | Hospital | Deaths | Hospital | Deaths | Hospital | Deaths | Hospital | Deaths | Hospital | Deaths | |
| < 1 | 11 | 0 | 18 | 1 | 73 | 1 | 21 | 0 | 123 | 2 | |
| 1-4 | 20 | 1 | 16 | 1 | 42 | 2 | 17 | 0 | 95 | 4 | |
| 5-9 | 9 | 0 | 15 | 1 | 17 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 47 | 1 | |
| 10-14 | 11 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 1 | |
| 15-19 | 19 | 2 | 31 | 0 | 26 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 78 | 4 | |
| 20-29 | 100 | 8 | 219 | 20 | 82 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 408 | 33 | |
| 30-39 | 279 | 13 | 620 | 76 | 101 | 8 | 14 | 2 | 1014 | 99 | |
| 40-49 | 431 | 27 | 834 | 125 | 125 | 11 | 17 | 3 | 1407 | 166 | |
| 50-59 | 551 | 85 | 981 | 241 | 190 | 23 | 19 | 3 | 1741 | 352 | |
| 60-69 | 597 | 147 | 744 | 287 | 275 | 71 | 34 | 11 | 1650 | 516 | |
| 70-79 | 500 | 187 | 555 | 257 | 298 | 90 | 47 | 11 | 1400 | 545 | |
| 80-89 | 273 | 141 | 236 | 136 | 247 | 94 | 34 | 6 | 790 | 377 | |
| 90-99 | 61 | 43 | 37 | 22 | 82 | 28 | 6 | 0 | 186 | 93 | |
| >100 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 4 | |
| TOTAL | 2866 | 658 | 4324 | 1168 | 1572 | 334 | 224 | 37 | 8986 | 2197 | |
| Age | Sex | Comorbidity | Infect | ATB | Image | VAD | MV | ICU | DS | HS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Years | ||||||||||
| 19 | F | Hodgkin’s lymphoma | Y | Y | TC 25% compromised (frost glass) | Y | Y | Y | Y | 45 |
| 14 | F | Down Syndrome | Y | Y | TC - 70% | Y | Y | Y | Y | 12 |
| 2 | M | Down Syndrome, heart disease | Y | Y | Rx | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| 19 | F | Down Syndrome, schizophrenia, | Y | Y | TC - 50% compromised | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| asthma, corrected heart disease | ||||||||||
| 0 | M | None | Y | Y | Rx - infiltrated | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| 2 | M | encephalopathy | Y | Y | Rx | Y | Y | Y | Y | 24 |
| 5 | M | Renal transplant | Y | Y | TC > 50% infiltrated (frosted glass) | Y | Y | Y | N | 20 |
| 3 | M | Congenital heart disease | Y | Y | Rx | Y | Y | Y | N | 3 |
| 16 | F | Tumor CNS | Y | Y | TC > 50% infiltrated (frosted glass) | Y | Y | Y | Y | 10 |
| 17 | F | Lupus | Y | Y | TC < 25% | Y | Y | Y | N | 55 |
| 3 | F | Hydranencephaly | Y | Y | Rx | N | Y | Y | Y | 1 |
| 1 | F | Congenital heart disease | N | N | Rx | Y | Y | N | N | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





