1. Introduction
In reservoir multiphase flow, the wetting preference is an important parameter due to its pronounced influence on fluid flow properties. Research has shown that the breakthrough time during waterflooding is dictated by the reservoir rock wettability [
1]. He also reported that early water breakthrough can take place in a strongly hydrophobic media while late breakthrough occurs for strongly hydrophilic media. This was attributed to the role of wettability on relative permeability [
2]. Hence, inaccurate wettability estimation can affect field development option and the oil recovery processes [
3]. For a reservoir multiphase system, the wetting preference is the proclivity of one fluid phase to be adsorbed onto the rock if than one non-miscible fluid phases exist [
4]. Several methods of characterizing the wetting preferences notably the Amott test and United State
Bureau of Mines (USBM) method have been developed resulting from the role played by the wetting preferences on the efficiency of the oil recovery. Nonetheless, these techniques are costly and it takes more time to perform the experiment. Thus, a quick and affordable wettability characterization technique is inevitable. Wettability characterization of dominant sandstone rock minerals notably; quartz, kaolinite and calcite via Surface Complexation Modelling (SCM) have been reported in literature [
5]. Not much has been done on estimating wettability of mineral mixtures and rocks SCM.
Research has shown that interfacial charge, chemical composition of the fluids (i.e., crude oil and brine) control the wetting preferences of reservoir rocks [
6,
7]. For example, during rock-fluids (i.e., rock, crude oil and brine) systems, different interfacial charges (i.e., either positive or negative) resulting in diverse chemical interactions. This study seeks to extend the existing our existing model to predict the wettability of rock and mineral mixtures by capturing the properties of the individual mineral in the model using a geochemical solver (PHREEQ-C).
The SCM technique of characterizing the wettability is a quick but affordable technique of characterizing the wetting preferences in the absence of materials for conventional wettability estimation such as reservoir core sample and Stock Tank Oil (STO, stabilized crude oil). SCM technique is a powerful approach of modelling surface reactions and it relies on the thermodynamic properties of the aqueous species [
8,
9,
10]. Constant capacitance, diffuse-layer, triple-layer and two-pK models are the most commonly employed surface complexation models reported in literature[
9,
10]. The rationale behind the SCM technique of characterizing wettability was to assess the COBR interactions during reservoir filling. Site densities, surface area, equilibrium constant for protonation, deprotonation and adsorption reactions are some of the parameters required during surface complexation modelling [
10,
11]. In addition, the type of SCM employed may require one or more additional capacitance values before the surface interactions can be modelled [
9,
10].
To accomplish this, the equilibrium reaction of the surfaces (i.e., oil and minerals) and their reaction constants cannot be ignored. Numerous chemical reactions are bound to take place in the reservoir before and after the migration and accumulation of the crude oil into the reservoir. Since rocks are composed of different minerals, the mineral/brine interactions prior to the crude oil accumulation have also been studied by numerous authors. For instance, the rock and oil reactions and their reaction constants for the different surface-brine systems have been reported in literature [
8,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. Moreover, comprehensive surface complexation studies of numerous minerals have also been reported in literature [
16,
17,
18,
19]. In-depth review on Surface Complexation Modelling of carbonate minerals such as calcite, rhodochrosite, siderite, magnesite and dolomite have been carried out in literature [
15]. In addition, the possible oil-brine interactions and their reaction constants have also been reported in literature [
8,
11,
12]. Numerous developments have been made in recent years by several researchers to exploit these existing SCM data from literature to elucidate the mechanism during the experiment [
20]. For example, zeta potential measurements have successfully been modelled via SCM [
21,
22,
23]. In addition, research has shown that the SCM technique is capable of modelling polymer interactions such as precipitation reactions at high surface coverage [
24]. Surface complexation data of quartz, kaolinite and calcite from literature have succesfully been used to estimate their wetting preferences via SCM [
5]. They accomplished this by evaluating the interfacial charges that exist at the rock-fluid or fluid-fluid interfaces using PHREEQ-C. This presented study seeks to characterize the wetting preference of rocks and mineral mixtures via SCM.
To improve our existing model to predict the wettability of reservoir rocks, the individual properties of the minerals needed to be captured in the model. Minerals have diverse characteristics notably surface area and surface charge. Hence, during reservoir rocks (mineral mixtures) interaction with the fluids (i.e., brine or oil), the wetting preferences will be influenced by the properties of all the surfaces involved. To accomplish this, two techniques were employed namely the flotation test and SCM technique. The flotation experiments were modelled via a geochemical simulator (PHREEQ-C) using similar quantities and qualities of the materials as used in the experiments. This study seeks to evaluate the effect mineralogical constitution of rocks/mineral mixture on wettability. The SCM technique of estimating wettability was compared to their equivalent experimental results before making inferences. The flotation experiment characterizes the wetting preferences by relying on the proclivity the reservoir rock (minerals) to the fluid phases (i.e., either the oil or brine) during COBR interactions [
25]. These COBR interactions were modelled via SCM to better understand their wetting preferences. To evaluate the effect of the intrinsic properties of the individual minerals on the wettability of reservoir rock, the flotation experiment was also carried out for the main minerals in the studied rocks prior to evaluating their contribution to the rock wettability. In addition, the flotation tests were performed for four mineral-mixtures (MM) designed to assess specific properties such as increasing surface area or increasing the hydrophobicity of the mixture.
3. Results
The experimental outcome of the main sandstone reservoir rocks (SR #1 and SR #2) would be presented first to evaluate the role of these minerals on wettability prior to evaluating their effect on the reservoir rock wettability. The results of the predicted flotation test were then presented. Note that, the flotation test results of quartz and calcite have already been presented [
5]. To add to the above, the electrostatic pair interactions at the rock-fluids interfaces were assessed to evaluate the oil adhesion mechanism during the experiment using our developed model. The experimental results with SR and MM were presented prior to presenting their simulated counterparts. To understand the oil adsorption proclivities in the sandstone rocks (SR #1 and SR #2) during the flotation tests, their oil adhesion mechanisms were also assessed via SCM. The role of increasing the equivalent surface areas and the oil-wet mineral fraction were studied by adding illite and calcite respectively. In addition, the oil adhesion mechanisms in the mineral-mixtures were also evaluated to their role the wetting preference. Finally, the correlation between the equivalent surface area of the reservoir rock/mineral(s) and their wetting preferences were also assessed via SCM before meaningful conclusions could be drawn.
3.1. Flotation test results
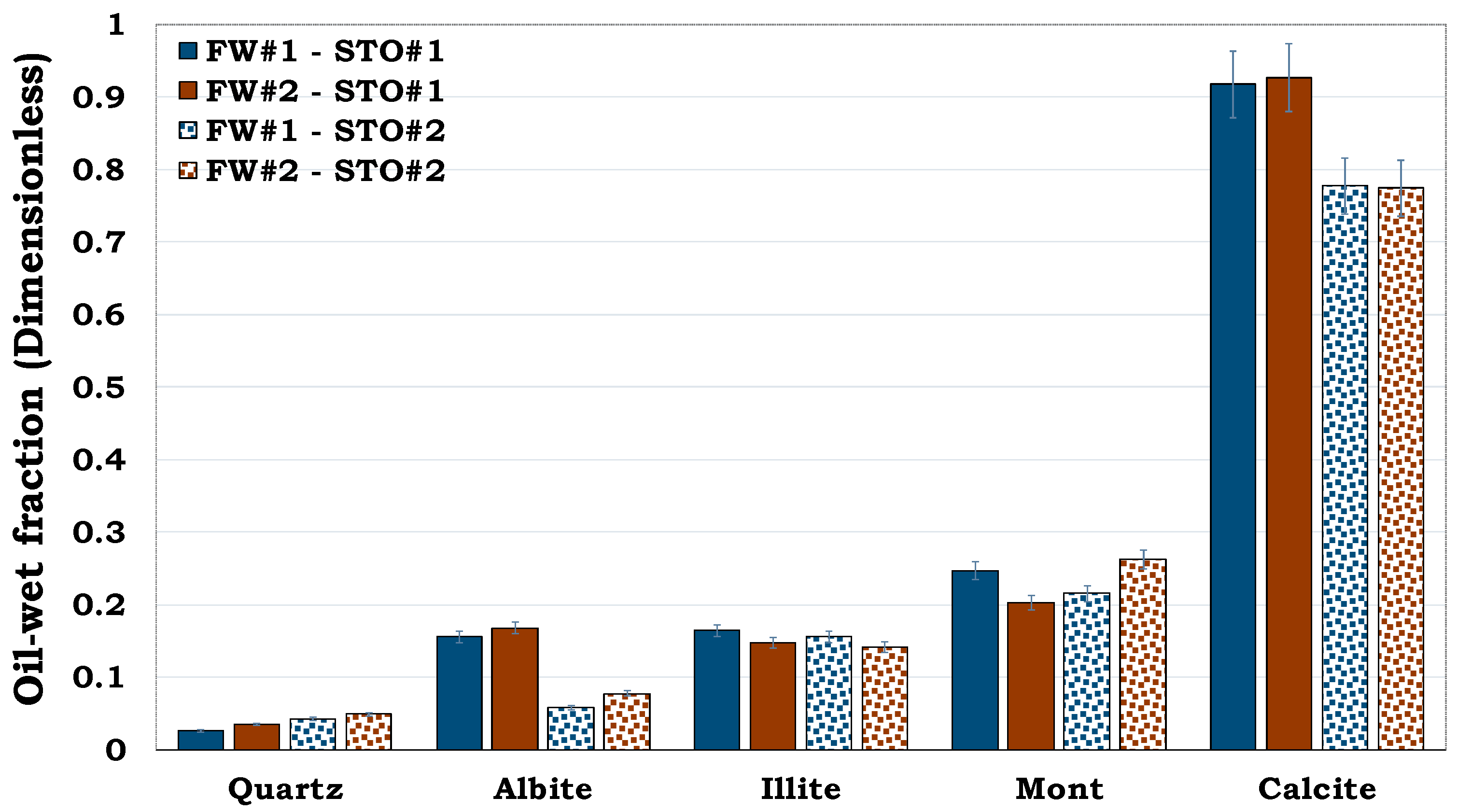
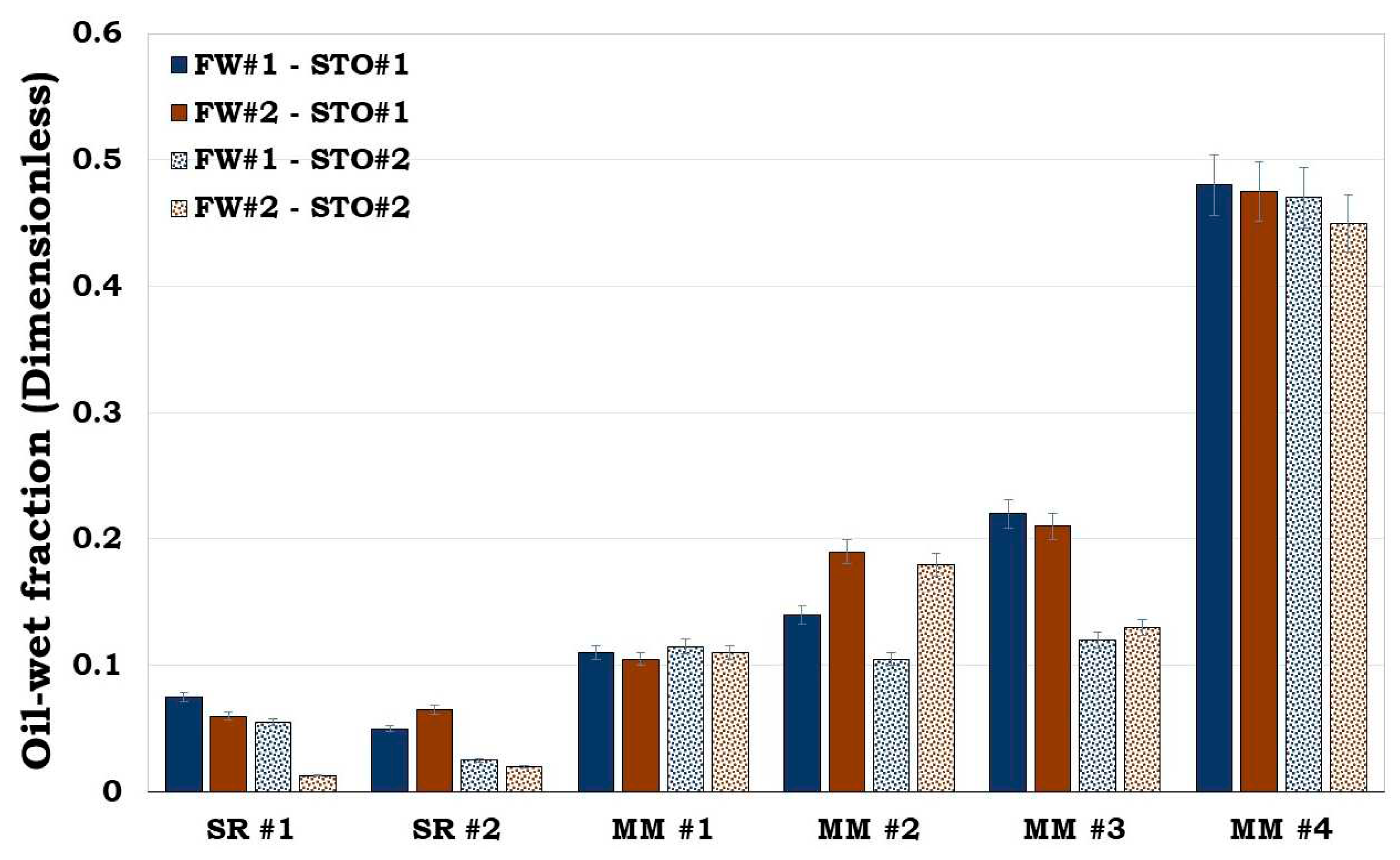
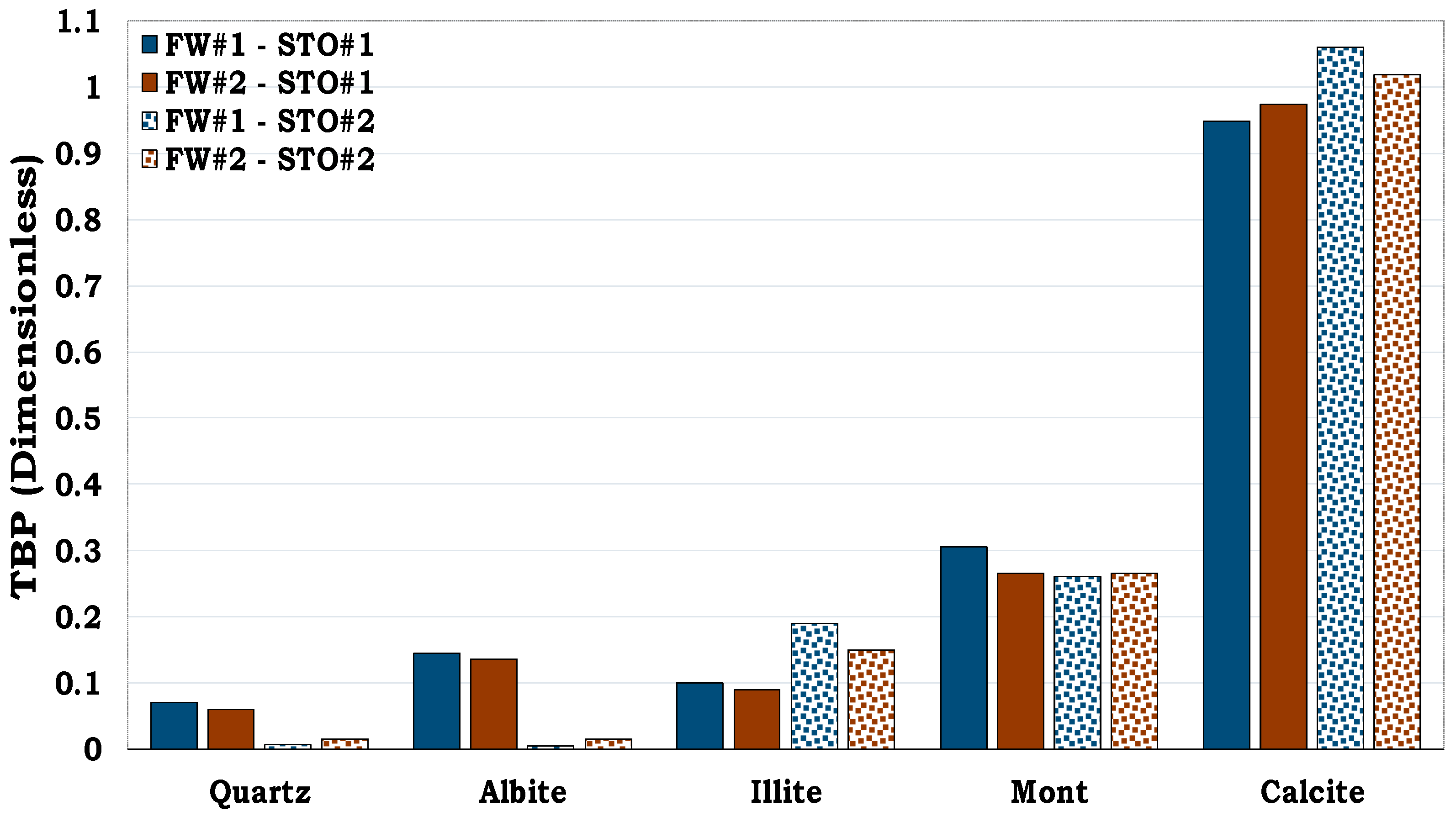
It can be observed from
Figure 3 that, quartz was more hydrophilic (oil-wet fraction < 0.1) whereas calcite was more hydrophobic (oil-wet fraction > 0.7). Conversely, Montmorillonite was observed to be more oil-wet when compared to both illite and albite. Thus, quartz was the least oil-wet, followed by albite, illite, montmorillonite and calcite in that order.
3.2. Flotation test prediction via our developed model
It can be observed that the SCM could capture the trend of the flotation test results. In other words, the ranking of the minerals in the simulations was similar as observed in the flotation tests.
Figure 4.
This figure illustrates the Prediction of the oil adsorption proclivities of the dominant minerals during the experiment.
Figure 4.
This figure illustrates the Prediction of the oil adsorption proclivities of the dominant minerals during the experiment.
3.3. Mechanisms of oil adhesion during the flotation test using our developed model
To appreciate the wettability of the minerals during the experiment, the attractive electrostatic linkage existing the mineral-fluids interfaces were considered via SCM.
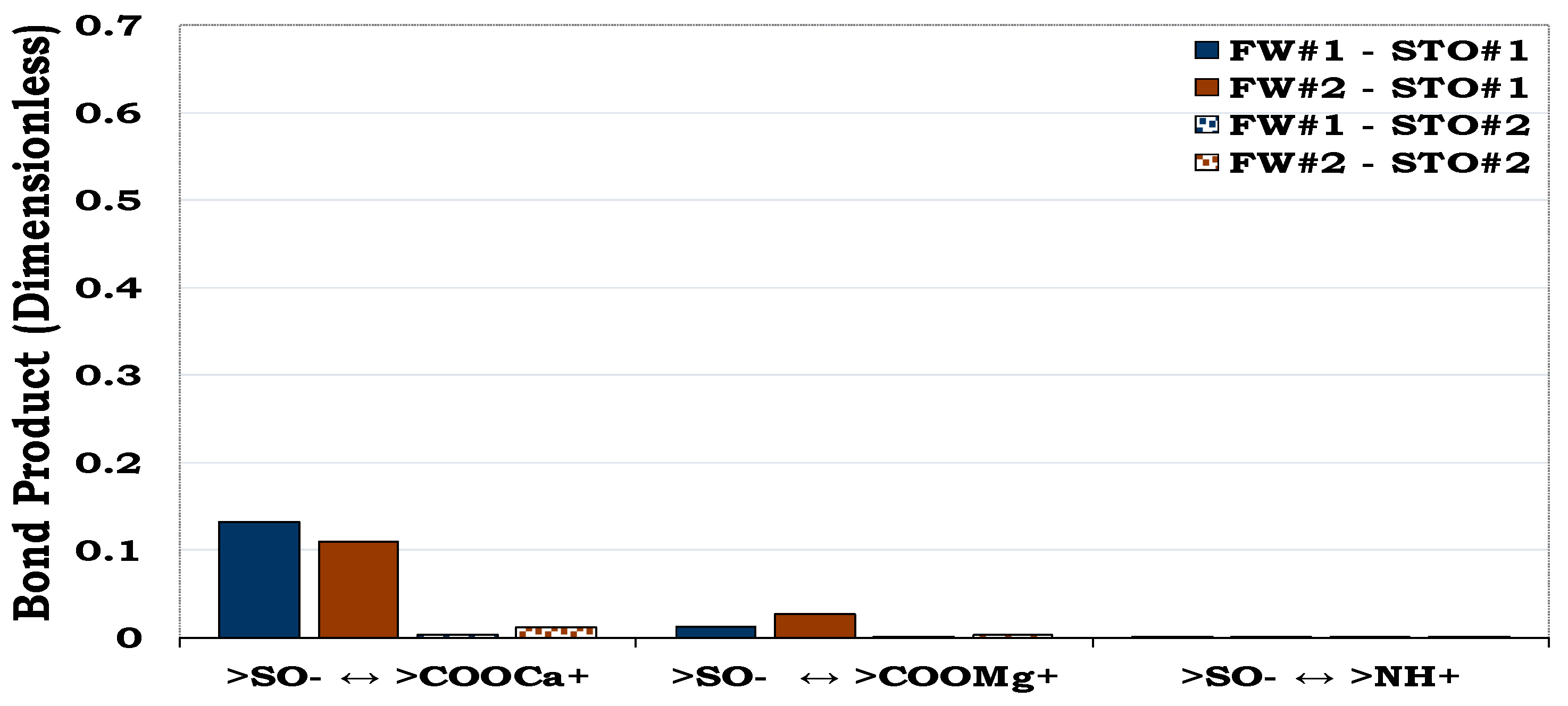
3.3.1. Mechanisms of oil adhesion in quartz
It can be observed that oil adhesion proclivity of the quartz surface was very small as depicted by its low dominant BP (< 0.1). In addition, considering the quartz-FW and STO-FW interactions, it became obvious that bridging of the two anionic interfacial charges by Ca2+ and Mg2+ dominated the adsorption of oil onto the rock/mineral surface. Considering the carboxylate and basic components (NH+) in the STO, it can be observed that the effect of the NH+ is not pronounced as compared to the COO-.
3.3.2. Mechanisms of oil adhesion in albite
Albite was slightly more oil-wet than quartz as depicted by their BP (≈ 0.1 and < 0.1 in
Figure 6 and
Figure 5 respectively). Similar to the quartz, cation bridging mechanisms was the main oil adhesion mechanism for the albite-fluids systems. As observed for quartz, the magnitude of the oil adsorbed onto the surface of the albite from the NH
+ was insignificant as compared to its carboxylic acid counterpart.
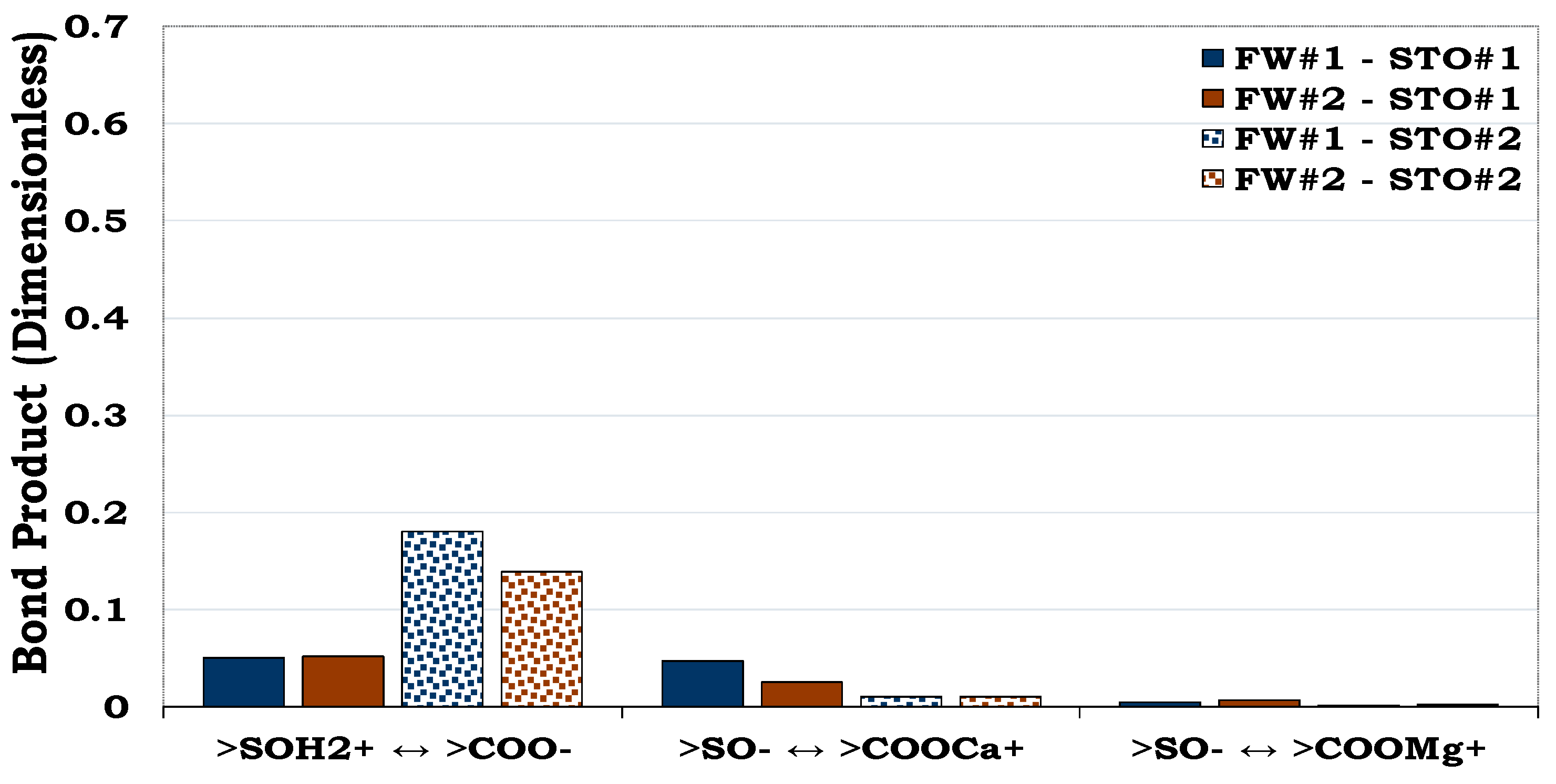
3.3.3. Mechanisms of oil adhesion in illite
Illite was less water-wet (BP ≈ 0.2) when compared to albite and quartz as depicted in
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7. Contrary to the oil adhesion mechanisms in quartz and albite, the illite-fluid systems were dominated by the adsorption of anionic polar oil component (>COO
-) onto the cationic illite site (>SOH
2+). To add to the above, linking of the anionic illite surface (>SO
-) and the negative oil surface (>COO
-) by Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ also occurred. As observed in the earlier results (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6), the contributions from NH
+ was also negligible when compared to >COO
-.
3.3.4. Mechanisms of oil adsorption in montmorillonite
Montmorillonite was more hydrophobic (BP ≈ 0.25) when compared to illite, albite and quartz. Unlike the oil adhesion onto illite which was dominated by the adhesion of >COO
- onto >SOH
2+ (
Figure 7), the oil adhesion in montmorillonite was dominated by cation bridging (
Figure 8). In other words, the dominant oil adhesion mechanism in montmorillonite was as a result of the bridging of the anionic montmorillonite sites (>SO
-) and the carboxylate (>COO
-) by Ca
2+ and Mg
2+. To add to the above, the influence of the >NH
+ was not significant as when compared to the carboxylate (>COO
-) as confirmed by
Figure 5 and
Figure 6.
3.3.5. Mechanisms of oil adhesion in calcite
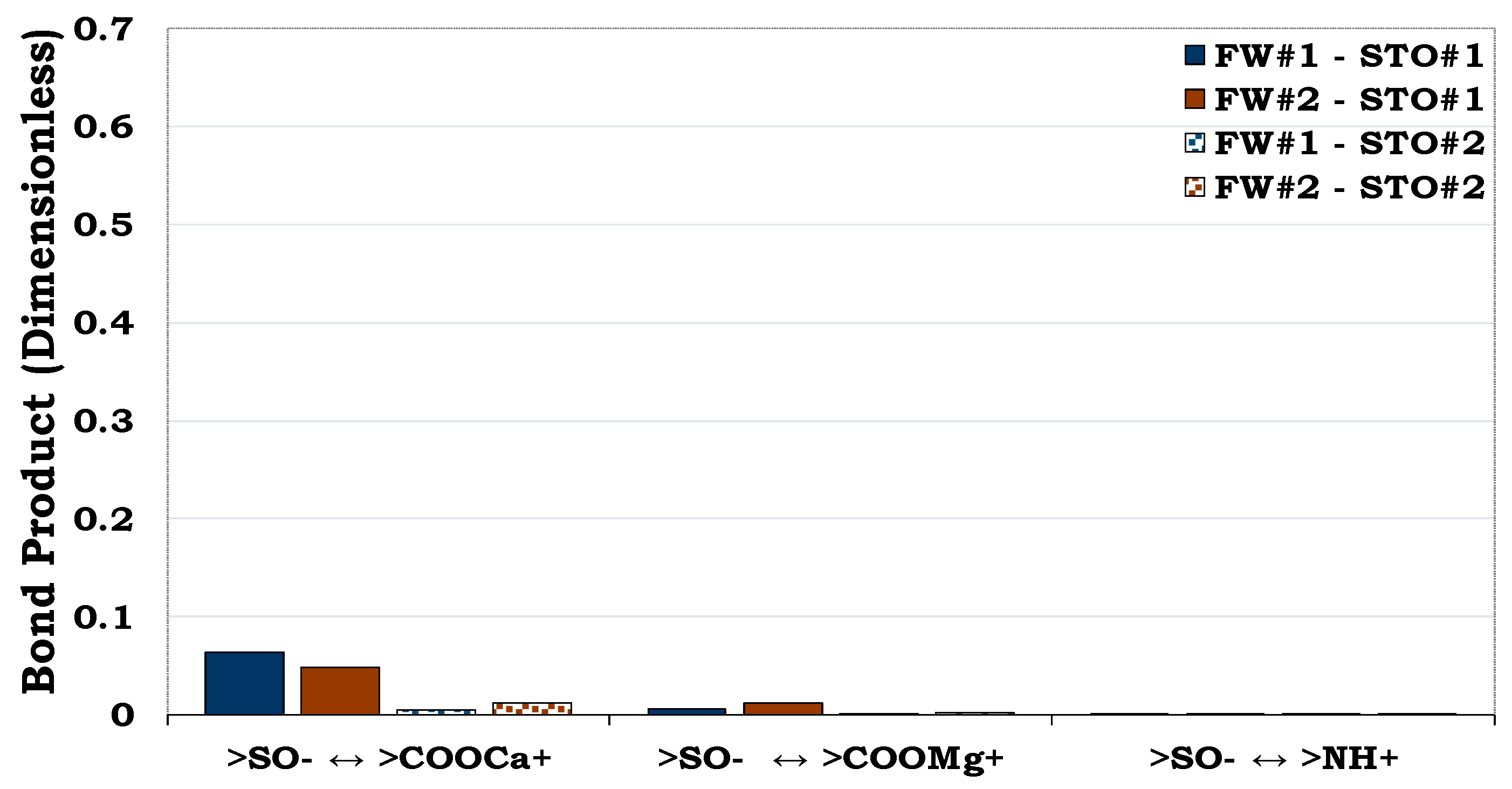
Calcite was more hydrophobic (BP ≈ 0.6) than montmorillonite, illite, albite and quartz. Like the adsorption of >COO
- with anionic surface charge onto illite (>SOH
2+) and montmorillonite (>SOH
2+), adsorption of carboxylic acid onto the positively calcite site (>CaOH
2+) also took place. However, the BP for the calcite (>CaOH
2+ 
>COO
-) was more distinct than that observed in the illite and montmorillonite (>SOH
2+ 
>COO
-) thus confirming the hydrophobic nature of the former. Furthermore, oil adhesion resulting from cation bridging also occurred as observed in the other minerals. As seen in the other mineral/brine/oil interaction, the role played by >NH
+ in the oil adsorption was also negligible when compared to the >COO
-.
3.4. Reservoir rock flotation experiment results
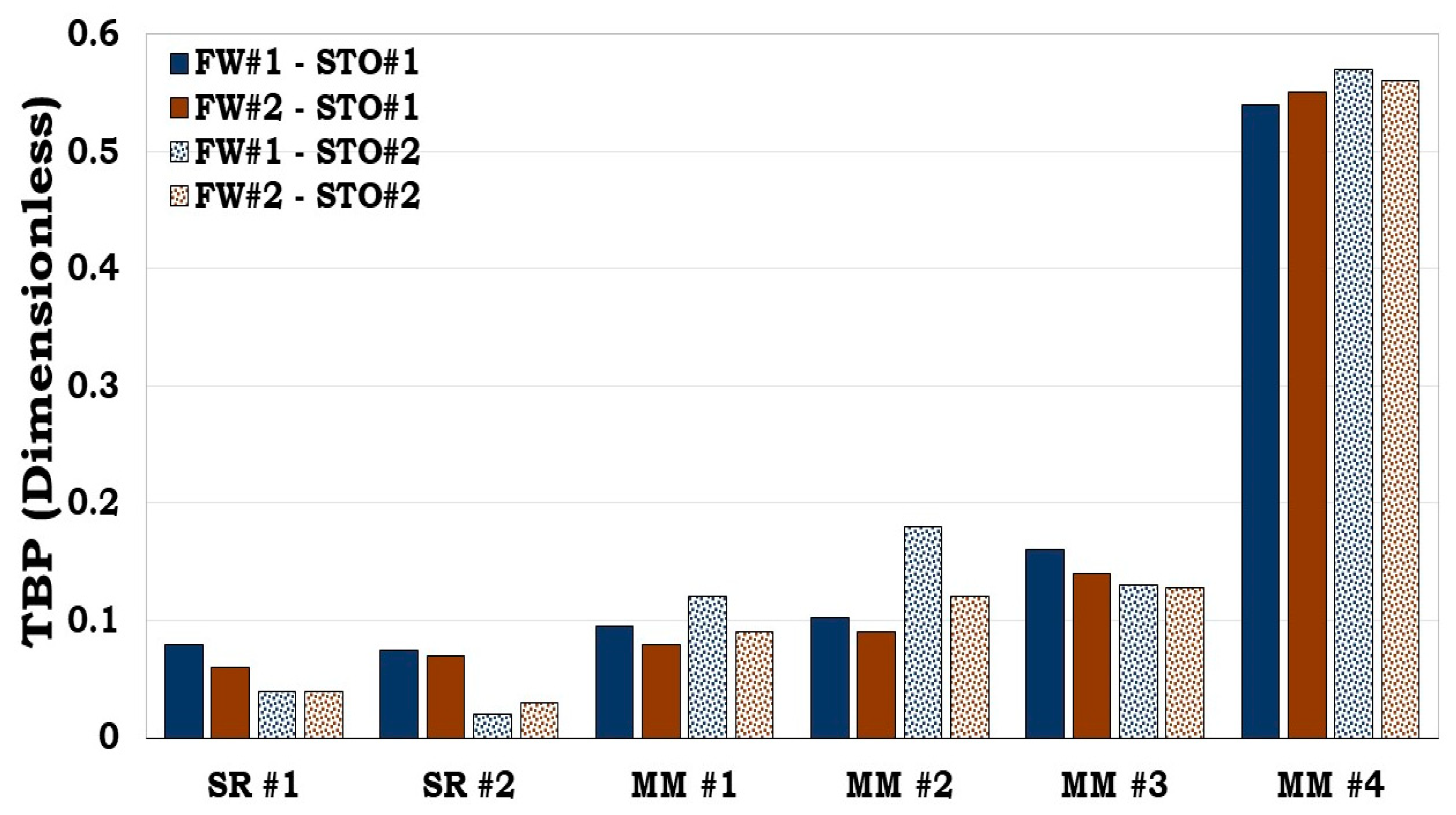
From both SR and the MM flotation test results (
Figure 10), it can be inferred that both the surface area and wetting state of the individual minerals influences the wettability of the SR/MM. For example, the wetting state of MM #1 and MM #2 were dictated by their equivalent surface area The equivalent surface area of MM #1 and MM #2 were 21.98 m
2/g and 36.92 m
2/g correspondingly with the latter being more oil wet than the former. For the MM #3 and MM #4, the equivalent surface area was also dominated by illite (4.40 m
2/g and 2.94 m
2/g correspondingly). However, the dominant mass fraction of the minerals in the MM #3 composition were quartz (62.8%) and calcite (25.2%) while that of the MM #4 were calcite (50.2%) and quartz (41.9%). From
Figure 10, it can be observed that MM #4 was more hydrophobic unlike MM #3. This show that the wetting state of SR/MM is influenced by the calcite content. It was observed that, if the SR/MM is dominated by hydrophilic minerals (e.g., illite) but its mineralogical composition is also dominated by the hydrophobic minerals (e.g., calcite), the latter will dictate the wettability of the SR/MM as confirmed by both the flotation and SCM results (
Figure 10 and
Figure 11).
3.4.1. Prediction of the reservoir rock flotation test results
Like the prediction of the individual minerals during the flotation experiment with the SCM (
Figure 4), it can also be inferred from
Figure 11 that our developed model could predict main trends in the flotation test results for the SR and the MM.
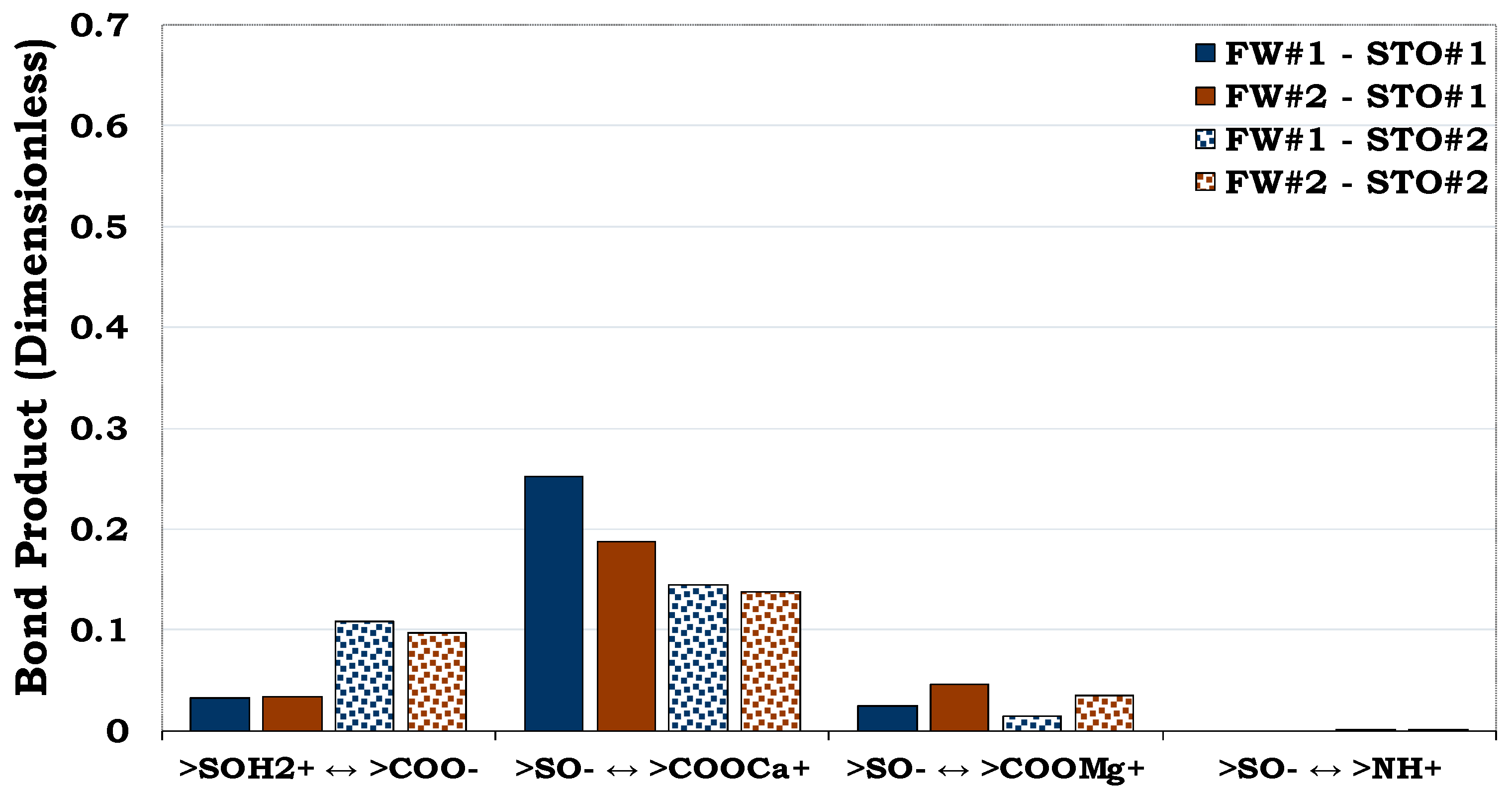
3.4.1. Mechanisms of oil adhesion onto sandstone rock #1 (SR #1)
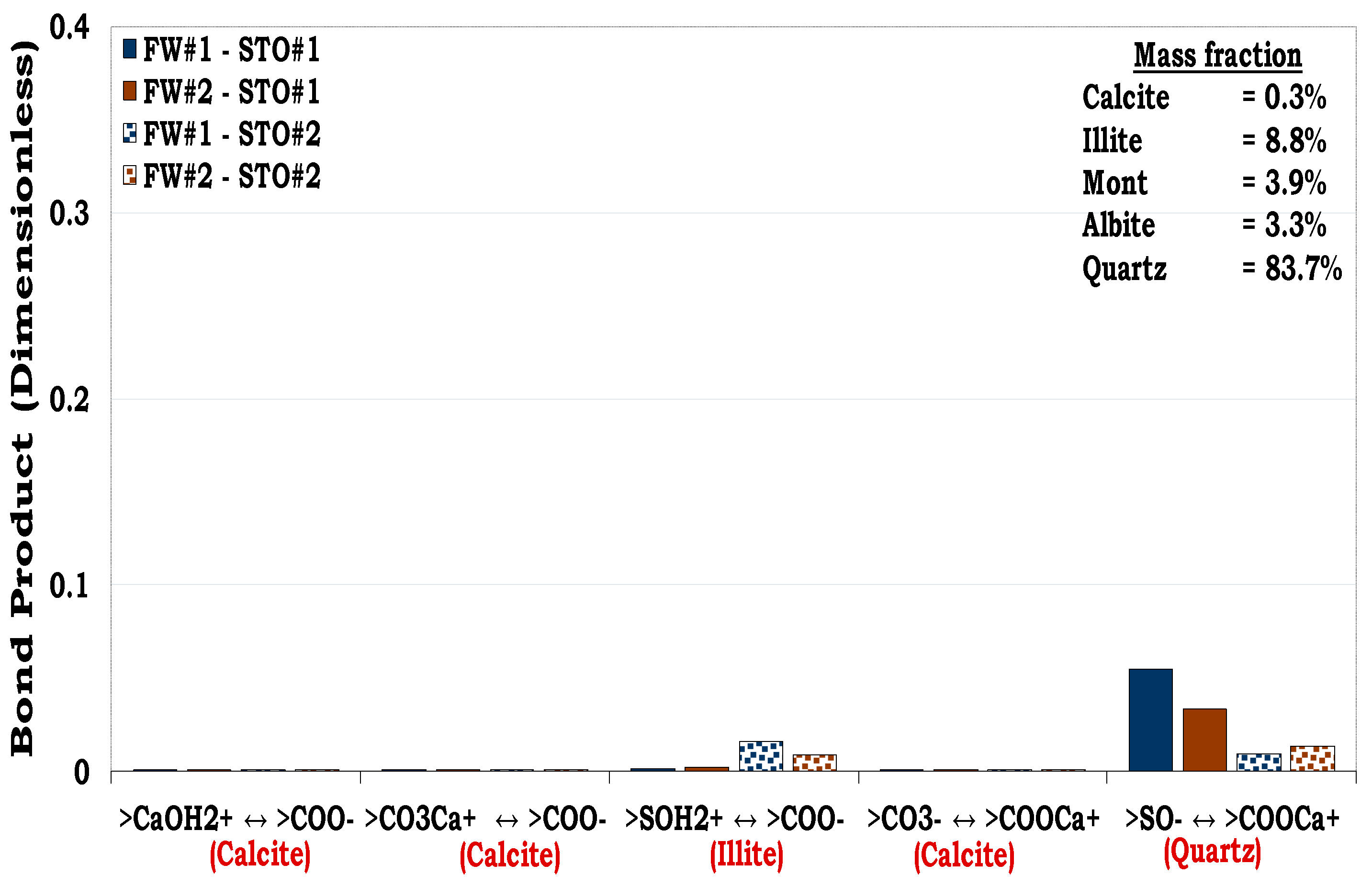
Considering
Figure 12, quartz had the highest mass fraction in the SR#1 (83.7%), but its prominent oil adhesion mechanism was negligible (i.e., BP < 0.1) as confirmed by the pure quartz sample (
Figure 5). In addition, though the content of illite in the SR #1 was small (8.8%), its contribution to the rock wettability was relatively significant compared to the other mineralogical constituents resulting from its dominant surface area. Thus, confirming the role played by the mineralogical constituents on wetting preferences of the rock/mineral mixtures.
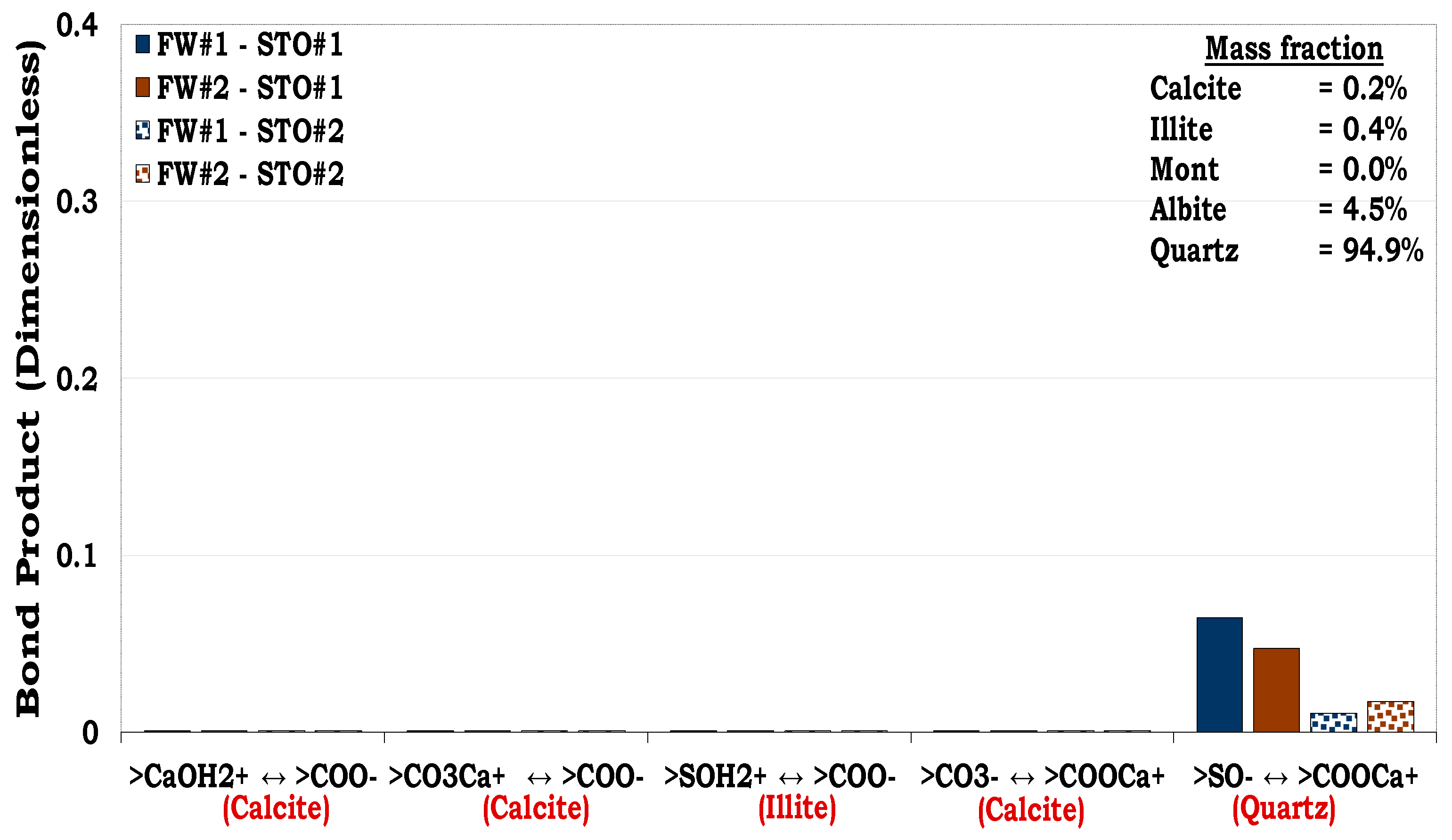
3.4.2. Mechanisms of oil adhesion onto sandstone rock #2 (SR #2)
Similar to the composition of SR #1 in which the dominant mineralogical constituent was quartz (83.7%), SR #2 was had quartz as the mineral with the highest mass fraction (94.9%) as depicted in
Table 1. Hence, SR #2-fluids system also resulted in approximately the same magnitude of oil adhesion (i.e., BP < 0.1) as observed in the SR #1. It can also be observed that unlike SR#1 mineralogical composition with high illite content (8.8%), the SR #2 mineralogical composition on the other hand has relatively low content of illite (0.4%). Hence, direct adsorption of carboxylic oil component onto the cationic illite sites (>SOH
2+) was not distinct in the latter as compared to the former. This was due to the smaller equivalent illite surface area available to be bonded by the oil in the SR #2 resulting from the lower illite content (0.4%) than in the SR #1 (8.8%). The main mechanism for oil adhesion onto the SR#2 was cation bridging (Ca
2+) of the two anionic interfacial polarities namely, quartz site (>SO
-) and carboxylic oil site (>COO
-). In addition, attractive electrostatic pair linkage existed between>COO
- and the cationic SR #2 sites such as calcite (>CaOH
2+) and illite (>SOH
2+) took place but was its magnitude was negligible. This was linked to their negligible equivalent surface area available for the surface-active oil components to be bonded onto it due to their low mass fractions in the rock.
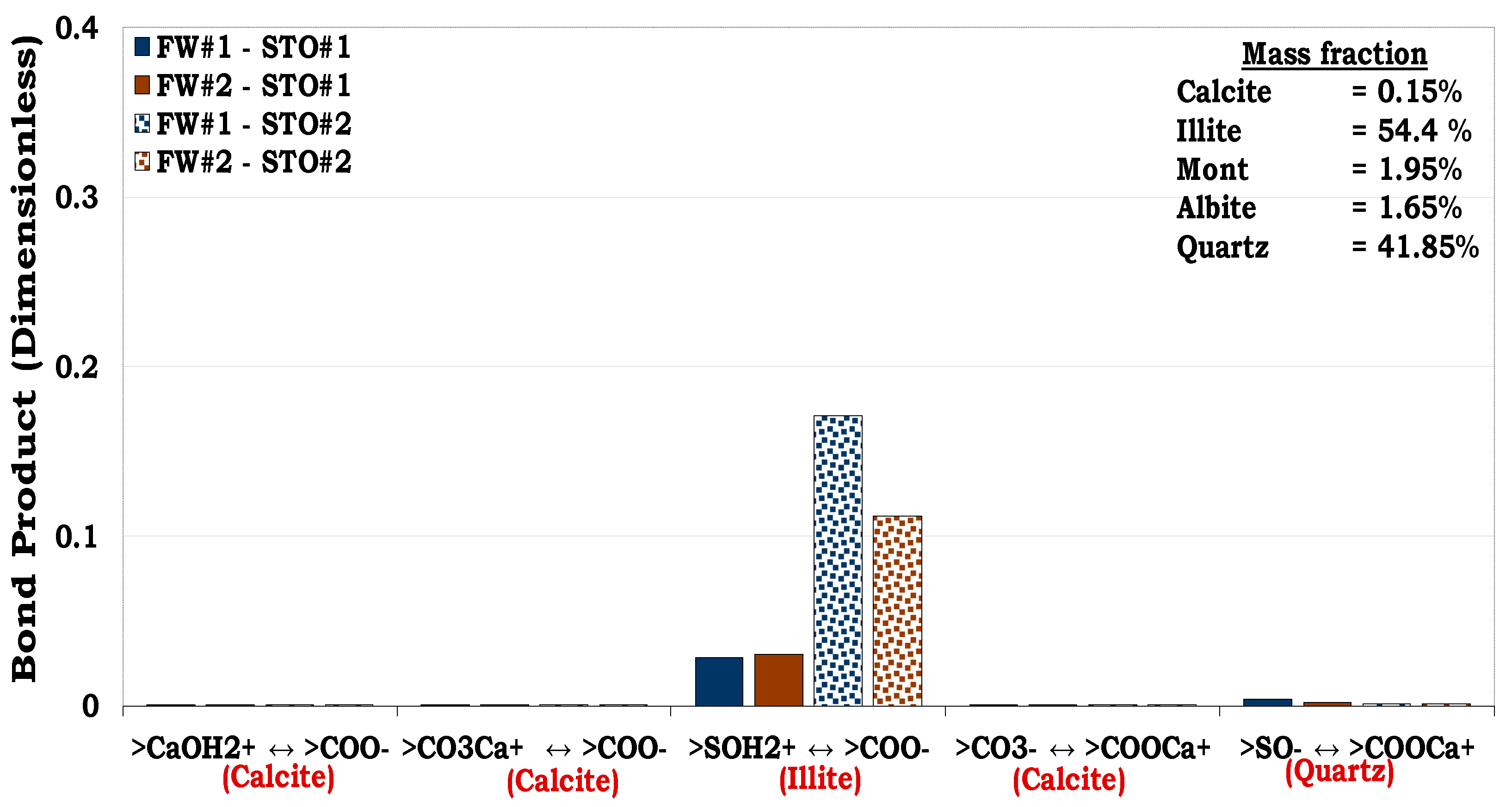
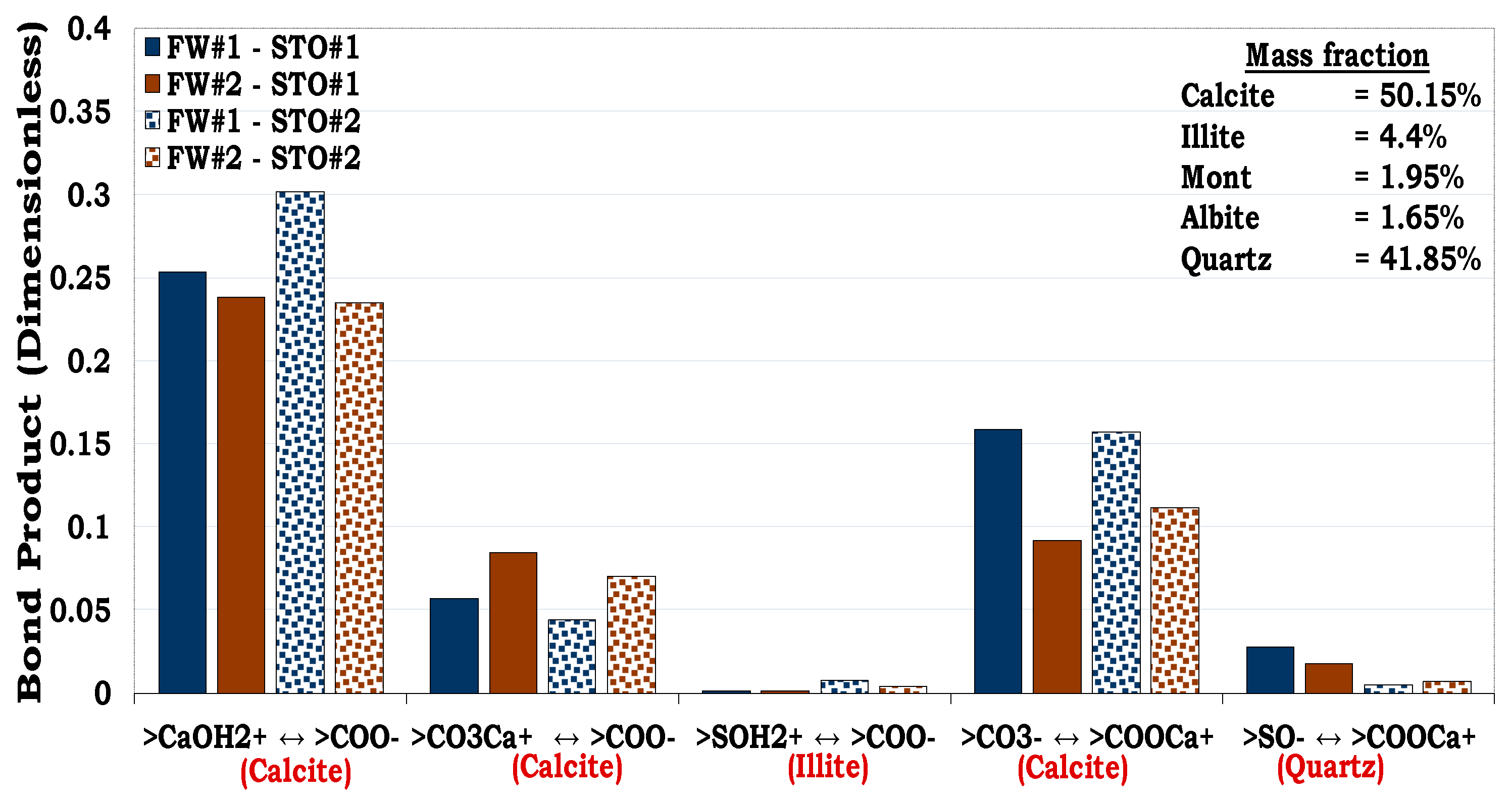
3.4.3. Mechanisms of oil adhesion onto Mineral Mixture #1 and #2 (MM #1 and MM #2)
Unlike SR#1 and SR#2 with quartz dominating their mineralogical constituents (83.7% and 94.9% correspondingly) that of MM #1 and MM #2 were formulated to evaluate the consequence of increase in surface area of MM by adding illite. For the MM #1 with approximately 32% illite, attractive electrostatic pair linkage existed between >COO
- and illite sites (>SOH
2+) as depicted in
Figure 14. In addition, bridging by divalent cation (e.g., Ca
2+) also took place between the negatively oil site (>COO
-) and that of quartz (>SO
-).
In a similar vein, direct adsorption of carboxylic oil component (>COO
-) onto the positively charged illite sites (>SOH
2+) also dominated the oil adhesion mechanisms in the MM #2. From
Figure 14, it became obvious that though illite had the second highest mass fraction (
~ 31.6%) in the MM#1, its interaction was stronger than that of quartz (
~ 62.8%). It can also be observed from
Figure 15 that though, quartz was also the second mineralogical constituent in the MM #2 (41.85%), the quartz-brine and oil-brine interaction was not distinct. This was attributed to the fact that, the illite overshadowed the contributions of the quartz as a result of its high surface area.
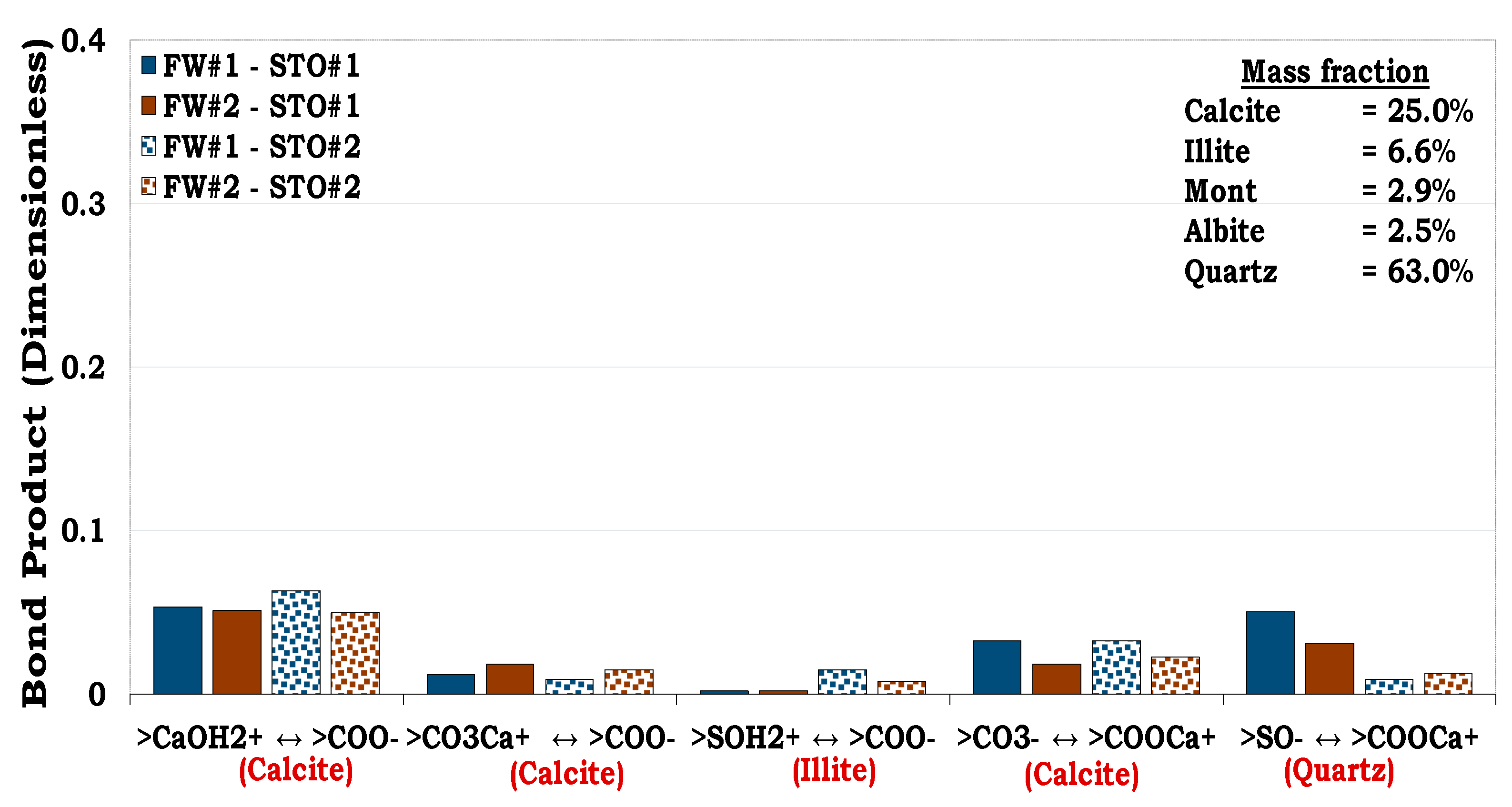
3.4.4. Mechanisms of oil adhesion in Mineral Mixtures #3 and #4 (MM #3 and MM #4)
Unlike MM #1 and MM #2 with illite dominated contents, MM #3 and MM #4 on the other hand were formulated to have high hydrophobic mineral content e.g., calcite. This was to evaluate the role of increasing the mass fraction of hydrophobic mineral constituents on wettability. The dominant oil adhesion mechanism for the MM#3-fluids system was less than 0.1 (i.e., BP < 0.1) as depicted in
Figure 16.
From
Figure 17 it can be inferred that, the main oil adhesion mechanism in MM #4 was approximately 0.3 (i.e., BP ≈ 0.3). Thus, confirming that increasing the calcite mass fraction of the sandstone rock increases its hydrophobicity as observed in MM #4 (
Figure 17). It can be observed that even with the same content of quartz (41.85%) in both the MM #2 and MM #4 (
Figure 15 and
Figure 17 respectively), the adhesion of oil onto the latter was more distinct than the former. This was confirmed by the indistinct cation bridging (Ca
2+) existing between quartz-FW (>SO
-) and the STO-FW (>COO
-) interfaces in the MM #2 as compared to MM #4. This was due to the fact that the contributions from the quartz in MM #2 was overshadowed by the mineralogical constituent with high surface area.
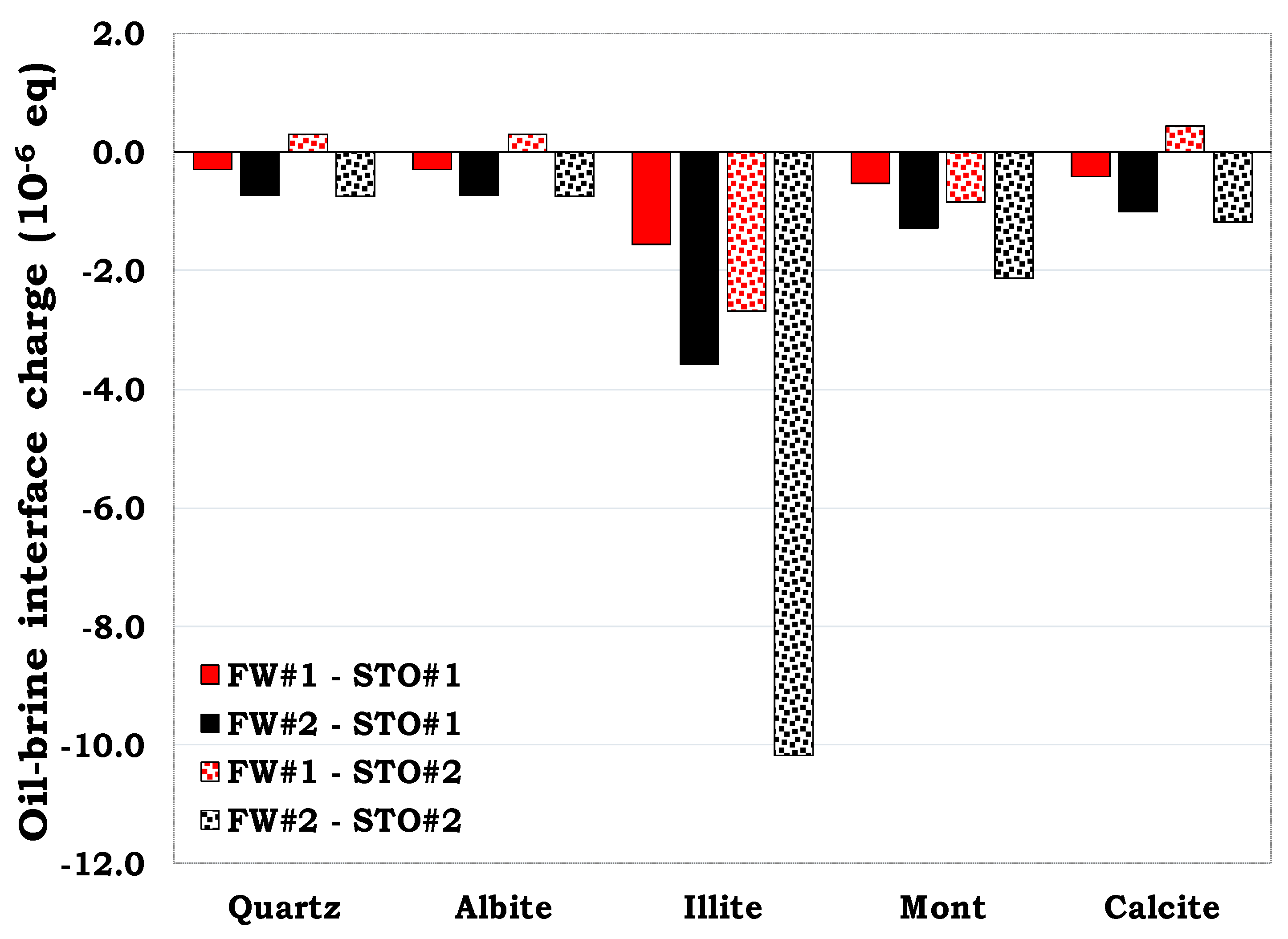
3.5. Interfacial Charge Prediction via SCM
To better understand the flotation test results for SR and MM, the mineral-brine and the oil-brine interface charges were also predicted via SCM for the individual minerals to assess the role of the surface charge on wetting state of the rock (SR and MM).
3.5.1. Mineral-brine interface charge estimation
From
Figure 18, the surface charge of the illite-FW and the calcite-FW interface were positively charged. This was attributed to the dominant positive sites in both illite (>SOH
2+) and calcite (>CaOH
2+). Hence, increasing the content of these minerals in the MM increases their tendencies to adsorb the carboxylate components in the oil (>COO
-), thus the observed outcome. Conversely, the negative mineral-FW interface charge was attributed to the dominance of >SO
- sites in quartz, albite and montmorillonite.
3.5.2. Prediction of the Oil-brine interfacial charge
The oil-FW interfaces were mostly negatively charged with the exception of the STO#2-FW#1 interfaces which was predominantly cationic. This was attributed to the positive oil-complex formed by Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ in brine with carboxylate (>COO
-). Since the concentration of Ca
2+ in the FW#1 was higher than that of FW#2 (
Table 3), it can be concluded that more divalent cations are available to be bonded to the carboxylate (>COO
-) to form the positive oil complexes (>COOCa
+ and >COOMg
+).
3.6. Effect of Rock and fluid properties on wettability; Flotation test versus equivalent surface area
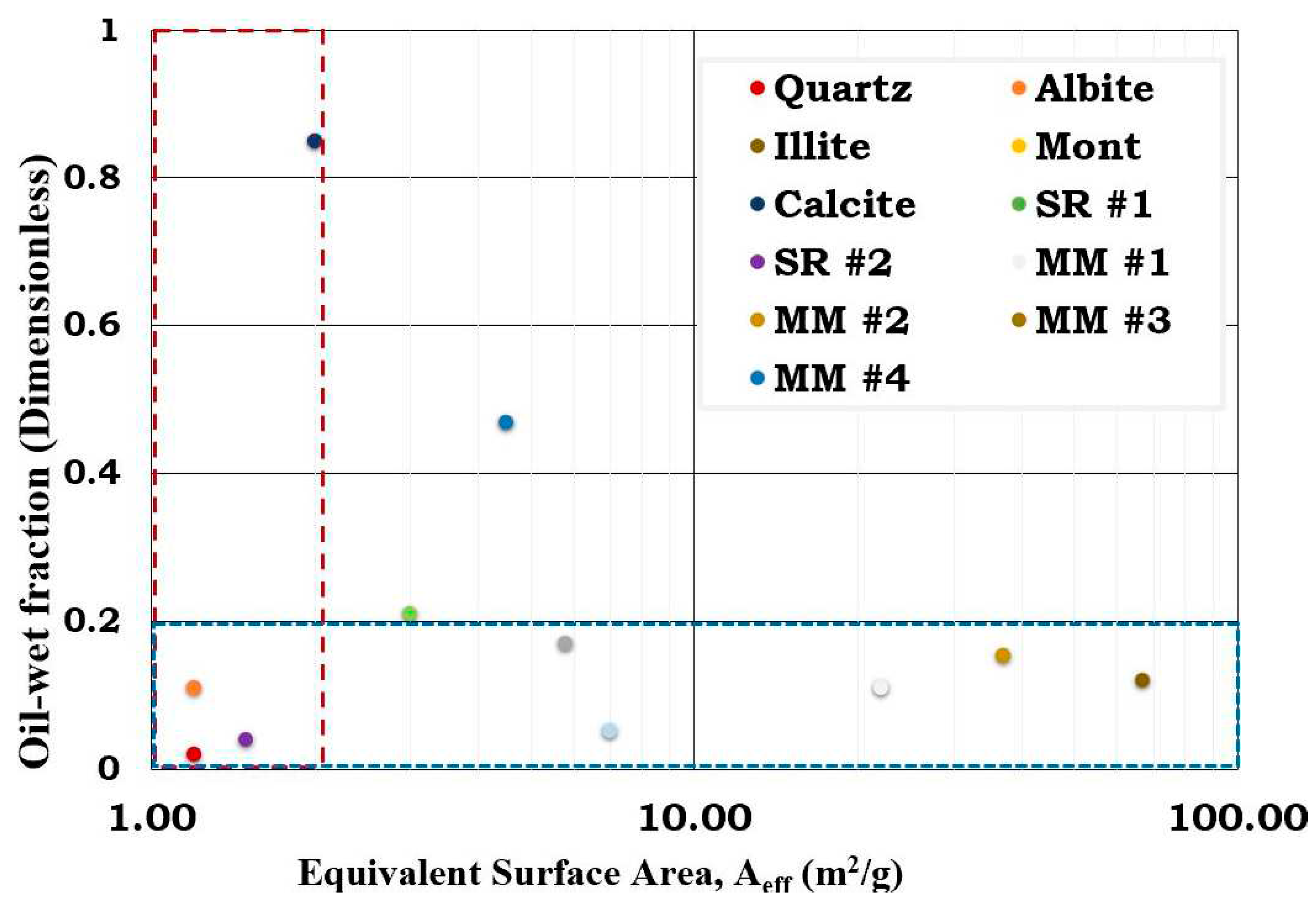
This presented study seeks to investigate the role of increasing illite and calcite contents in the sandstone reservoir rock (SR #1). It can be inferred from
Figure 20 that the wetting state of the reservoir rocks were dictated by either the surface area or calcite content. In other words, MM #1 and MM #2 were illite dominated while the MM #3 and MM #4 were calcite dominated. Based on mass fraction, the dominant minerals in the studied SR and MM were quartz, illite and calcite with surface area 1.2 m
2/g, 66.8 m
2/g and 2 m
2/g correspondingly. For SR #1, its equivalent surface area (7.0 m
2/g) was illite dominated (5.88 m
2/g) and the second dominant mineral being quartz (1.00 m
2/g). Though the mass fraction of illite in the SR #1 was relatively small (8.8%) when likened to quartz (83.7%), the inherent surface area of illite (66.8 m
2/g) was higher than quartz (1.2 m
2/g) and hence, the observed results. Since the wettability of the two dominant minerals in SR #1 notably quartz (~0.05) and illite (~0.15) were both hydrophilic (
Figure 3), it was not surprising that SR #1 was also observed to be hydrophilic (
Figure 20). Unlike the illite dominated SR #1 with relatively high equivalent surface area (7.0 m
2/g), the SR #2 on the other hand was quartz dominated and hence relatively small equivalent surface area (1.5 m
2/g). The equivalent surface area of the two dominant minerals in the SR #2 were 1.14 m
2/g (quartz) and 0.27 m
2/g (illite). Though the mass fraction of illite in SR #2 was negligible (0.4%) as compared to quartz (94.9%), the former also contributed meaningfully to the equivalent surface area of SR #2 due to its relatively large surface area (66.8 m
2/g) when likened to quartz (1.2 m
2/g). It was not surprising that the SR #2 was hydrophilic since the dominant minerals in its composition such as quartz (~0.05) and illite (~0.15) were also observed to be strongly hydrophilic as depicted by the flotation tests results (
Figure 3). Hence, it can be concluded that the wetting preferences of the reservoir rocks (SR #1 and SR #2) were dictated by their equivalent surface area.
Considering the MM with high illite contents (MM #1 and MM #2), it can be concluded that the wetting state of the reservoir rock was influenced by the surface area of illite. In other words, the wetting state MM #1 and MM #2 were observed to be in the same order as the mineral with predominant surface area. Though the mass fraction of the illite in the MM #1 was relatively small (31.6%) as compared to that of quartz (62.8%), its contribution to the equivalent surface area of the MM #1 (22.0 m
2/g) was 21.11m
2/g as compared to quartz (0.75 m
2/g). As discussed earlier since both the experimental results and its simulated counterpart revealed that illite and quartz were hydrophilic at the studied conditions, the wetting preference of the MM #1 was as expected. Like the MM #1, the equivalent surface area of the MM #2 (36.9 m
2/g) was dominated by illite (36.34 m
2/g) while the contribution from quartz was negligible (0.5 m
2/g). This was attributed to the mass fraction of the constituent minerals (
Table 1) and their surface areas (
Table 5). Unlike the MM #1 and MM #2 which were mainly controlled by water-wet minerals MM #3 and MM #4 were dictated by both water-wet minerals and hydrophobic (calcite) minerals. Nonetheless, the flotation test and the SCM results reveal that the hydrophobic minerals have distinct impact on wetting preferences of the SR and MM than the hydrophilic counterparts and hence, the observed results.
3.7. Understanding IOR mechanisms via the SCM technique
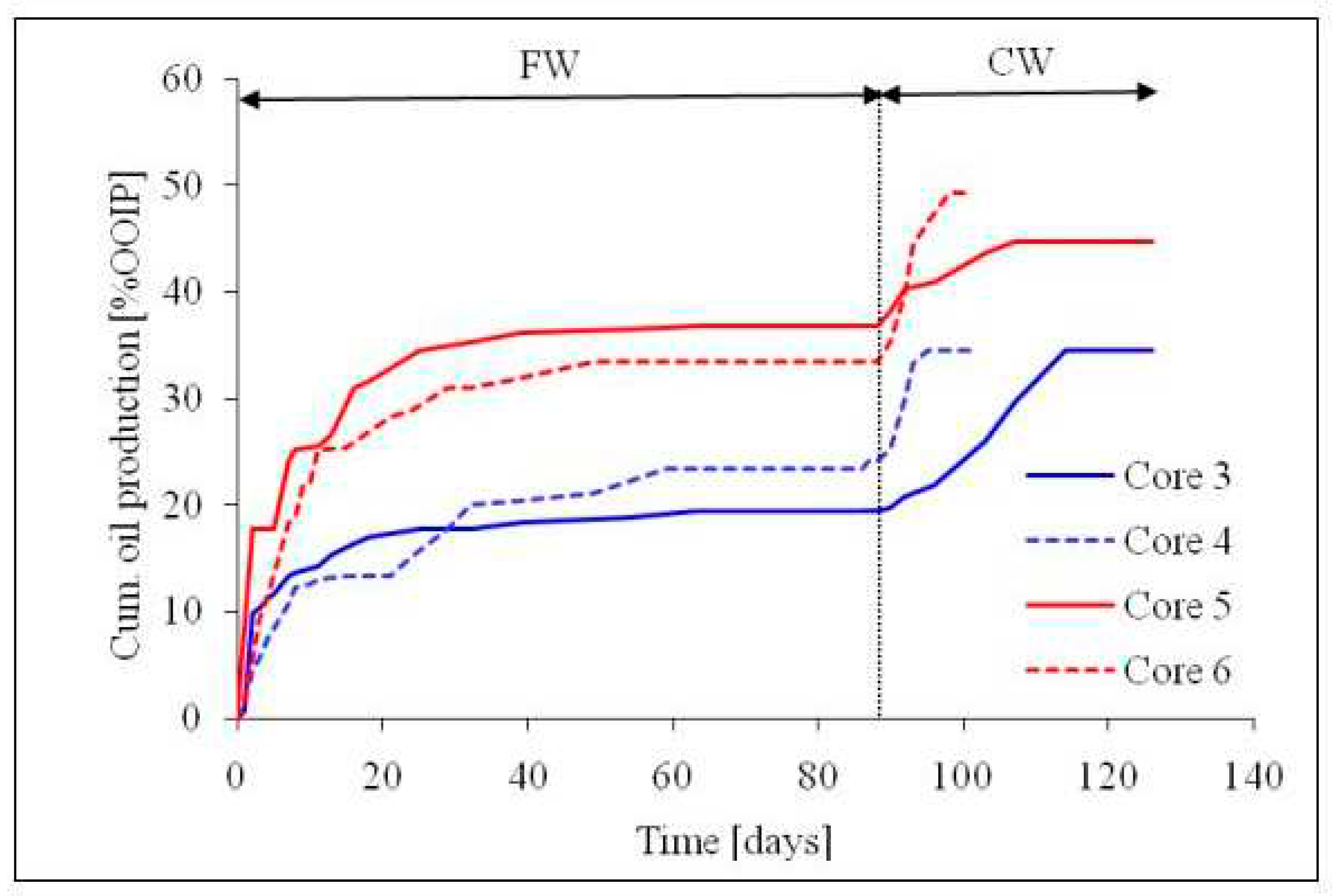
The impact of both carbonated water (CW) and formation water (FW) on the oil recovery efficiency have been assessed in literature [
26]. They reported that the CW was observed to optimize the oil recovery during spontaneous imbibition of an outcrop calcite core at realistic reservoir conditions.
3.7.1. Prediction of COBR interactions during carbonated water (CW) imbibition in chalk
To understand the mechanisms during the FW and CW imbibition, the chalk-fluids system during the experiment [
26] were investigated via SCM. This was achieved by modelling the chalk-brine and oil-brine interactions during the spontaneous imbibition experiment via SCM. To accomplish this, the oil and chalk characteristics used in the spontaneous imbibition experiment were also used as input into the SCM. The SCM input parameters is as reported earlier.
Table 7 gives the chemistry of the brine employed during the literature experiment. Dominant oil adhesion mechanism in the chalk exists between the positive chalk site (>CaOH
2+) and the carboxylate (>COO
-) as depicted in
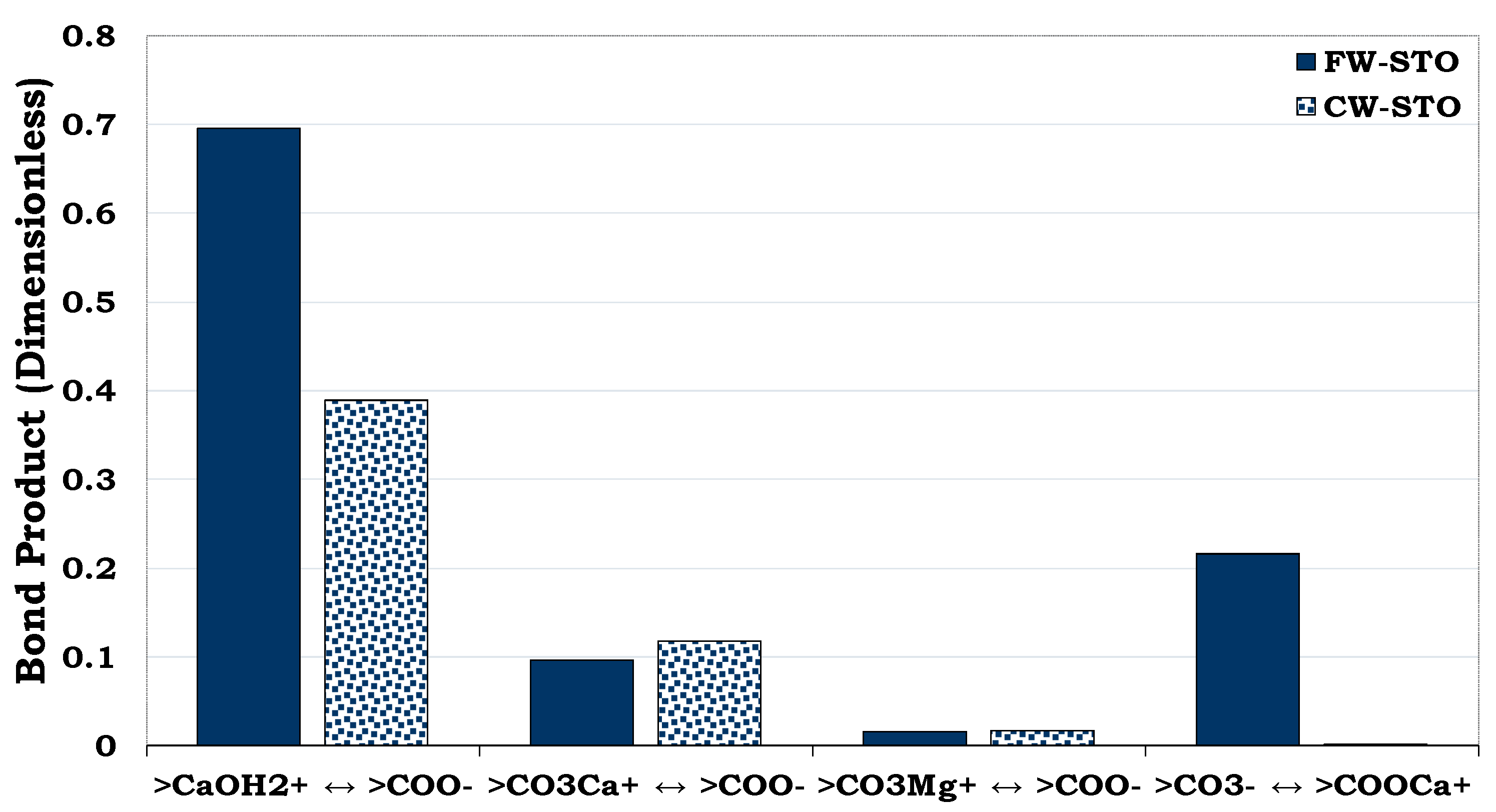
Figure 22. The SCM results revealed that the CW has the potential to change the wetting preference of the chalk from more hydrophobic to less hydrophobic state (
Figure 22). In other words, the oil adhesion proclivity onto the chalk sites as depicted by the Bond Product was observed to be higher for the FW (BP ≈ 0.7) than CW (BP ≈ 0.4). Thus, CW has the potential to desorb some of the adsorbed oil from the rock so that it can be mobilized to be produced with the injected brine.
4. Discussion
SCM technique of estimating wettability is a fast and affordable technique of estimating the wetting preferences of minerals and reservoir rock via SCM. One striking benefit of the SCM approach over the existing wetting preferences estimation approach is that, the SCM technique can simulate the wetting tendencies of the minerals (rock). In addition, our developed model could estimate the oil adsorption mechanisms onto the rock surface. Hence, the SCM has the potential to be used in the design of wettability alteration processes for improving the oil recovery. The characteristics of the oil and rock surfaces together with their corresponding quantities involved are used the SCM input and hence less time consuming unlike the existing experimental approach. Though, the SCM accounts for the effect of the mineralogical compositions in the model; nonetheless, the role of the distribution of the minerals are yet to be captured as compared to the Amott and the USBM techniques. The mineral surfaces available for the mineral-fluids interactions are determined by the mineral distribution.
To add to the above, the Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D) technique have been reported to characterizes the wetting preference by measuring the amount of oil adsorption onto mineral surfaces [
30]. Unlike the Amott and the USBM techniques, the QCM-D wettability characterization method was based on mineral-fluids reaction. The SCM technique of characterizing wettability is also based on the oil and mineral interactions at the contact surface area. The tendency of the rock (minerals) to adsorb oil during COBR interactions were incorporated into the SCM using their equivalent surface area.
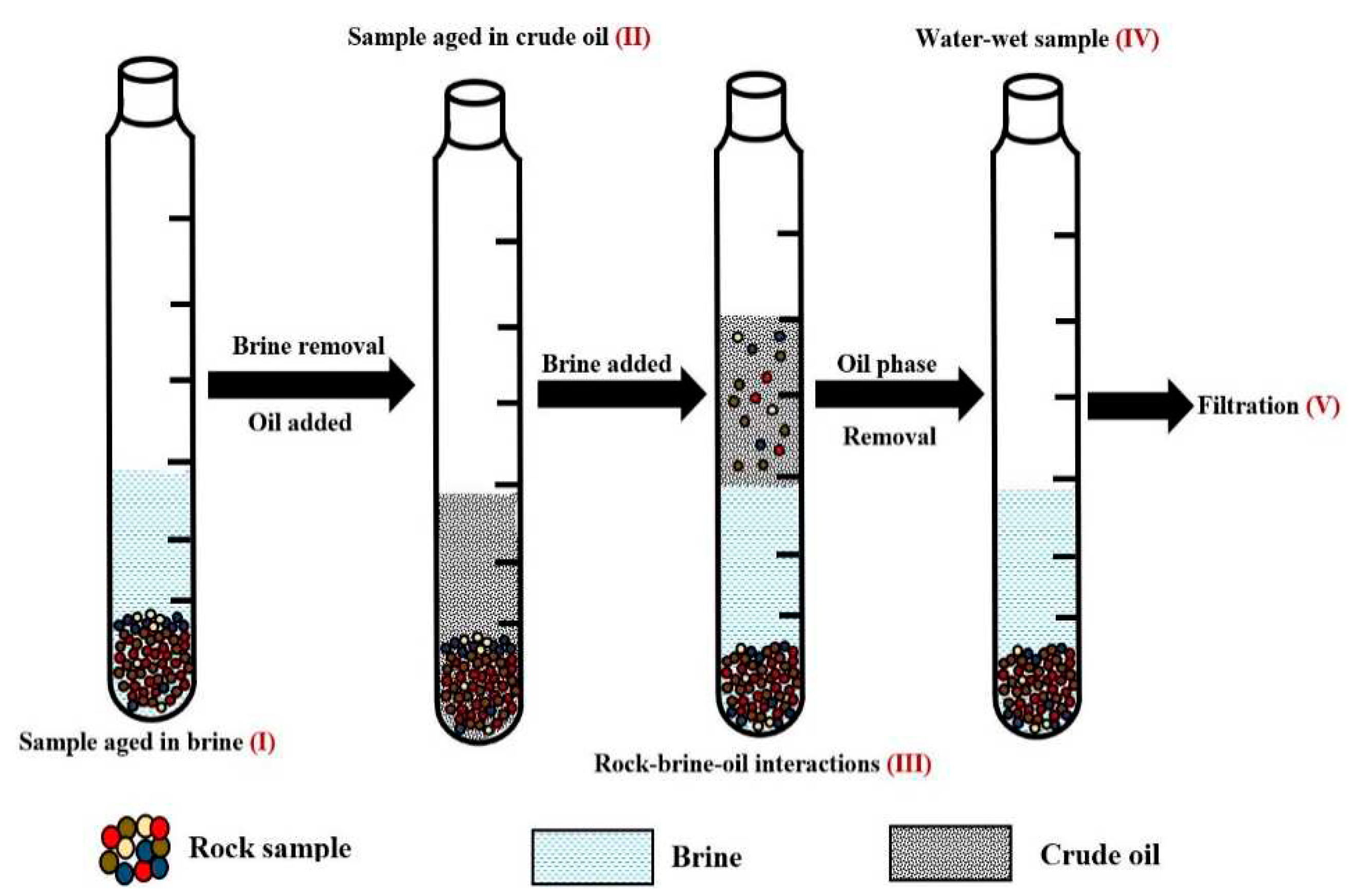
Figure 1.
This figure illustrate the flotation test procedure.
Figure 1.
This figure illustrate the flotation test procedure.
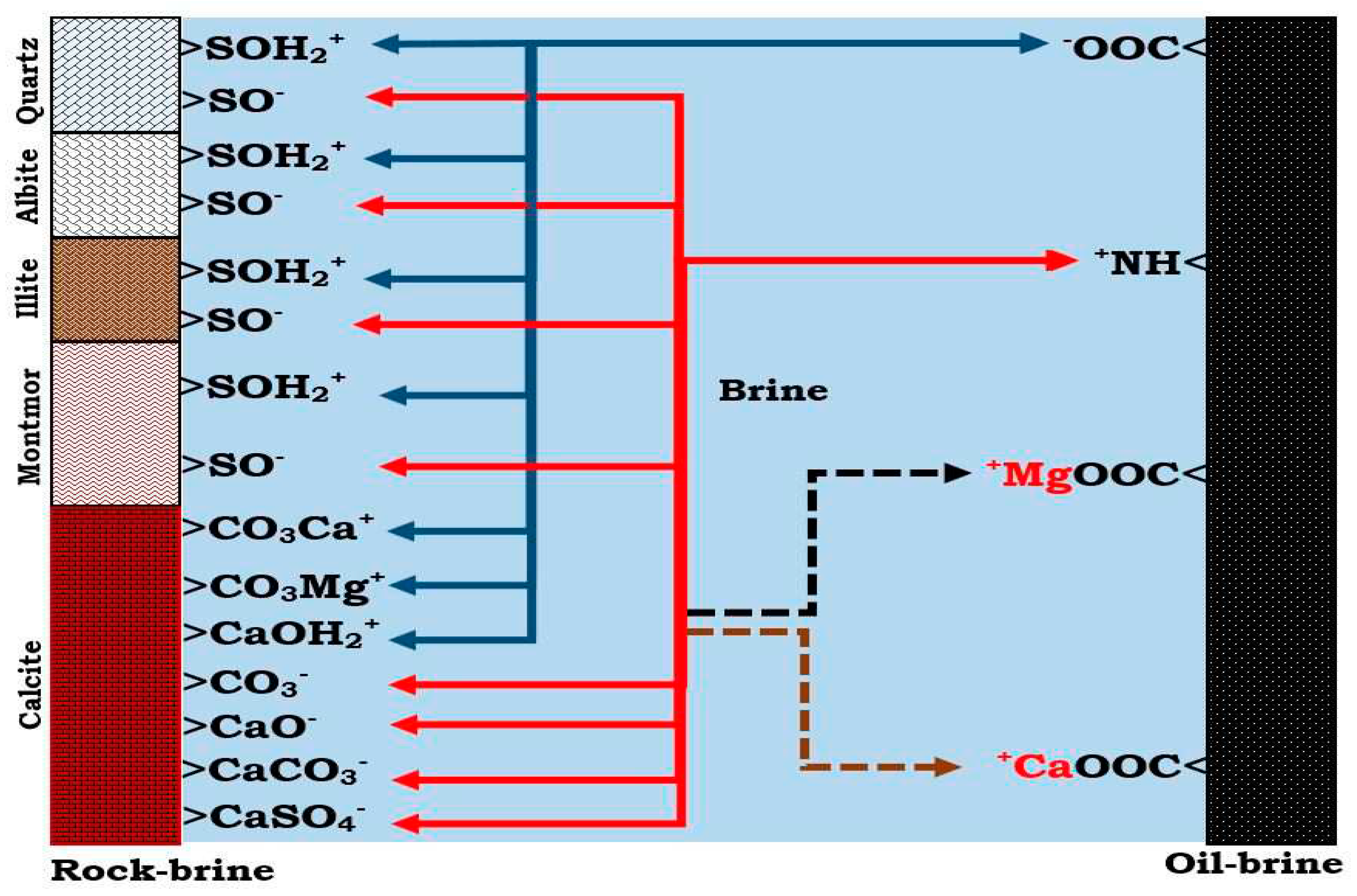
Figure 2.
This figure illustrate the oil adhesion mechanism at the rock-brine and the oil-brine interfaces.
Figure 2.
This figure illustrate the oil adhesion mechanism at the rock-brine and the oil-brine interfaces.
Figure 3.
This figure illustrates wettability characterization of the reservoir rock mineral using the flotation tests. It can be observed that quartz is strongly hydrophilic while calcite is strongly hydrophobic.
Figure 3.
This figure illustrates wettability characterization of the reservoir rock mineral using the flotation tests. It can be observed that quartz is strongly hydrophilic while calcite is strongly hydrophobic.
Figure 5.
This figure illustrates the attractive electrostatic forces at the quartz-FW and the oil-brine interface with dissimilar polarities.
Figure 5.
This figure illustrates the attractive electrostatic forces at the quartz-FW and the oil-brine interface with dissimilar polarities.
Figure 6.
This figure illustrates the oil adsorption mechanism for the albite-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarity. Albite is relatively less hydrophilic (i.e., BP ≈ 0.1) than quartz (< 0.1, see
Figure 5).
Figure 6.
This figure illustrates the oil adsorption mechanism for the albite-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarity. Albite is relatively less hydrophilic (i.e., BP ≈ 0.1) than quartz (< 0.1, see
Figure 5).
Figure 7.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism during the illite-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. Illite is more hydrophobic (BP ≈ 0.2) as compared to quartz (BP < 0.1,
Figure 5) and albite (BP ≈ 0.1,
Figure 6).
Figure 7.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism during the illite-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. Illite is more hydrophobic (BP ≈ 0.2) as compared to quartz (BP < 0.1,
Figure 5) and albite (BP ≈ 0.1,
Figure 6).
Figure 8.
This figure illustrates oil adhesion mechanism for the montmorillonite-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. Montmorillonite is more hydrophobic (BP ≈ 0.3) than quartz (BP < 0.1,
Figure 5), albite (BP ≈ 0.1,
Figure 6) and illite (BP ≈ 0.2,
Figure 7).
Figure 8.
This figure illustrates oil adhesion mechanism for the montmorillonite-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. Montmorillonite is more hydrophobic (BP ≈ 0.3) than quartz (BP < 0.1,
Figure 5), albite (BP ≈ 0.1,
Figure 6) and illite (BP ≈ 0.2,
Figure 7).
Figure 9.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism during calcite-fluids system with dissimilar inter facial charge. Calcite is strongly hydrophobic as a result its high BP (≈ 0.6) as compared to quartz (BP < 0.1,
Figure 5), albite (BP ≈ 0.1,
Figure 6), illite (BP ≈ 0.2,
Figure 7) and montmorillonite (BP ≈ 0.3,
Figure 8).
Figure 9.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism during calcite-fluids system with dissimilar inter facial charge. Calcite is strongly hydrophobic as a result its high BP (≈ 0.6) as compared to quartz (BP < 0.1,
Figure 5), albite (BP ≈ 0.1,
Figure 6), illite (BP ≈ 0.2,
Figure 7) and montmorillonite (BP ≈ 0.3,
Figure 8).
Figure 10.
This figure illustrates flotation tests results of the Sandstone Rock (SR #1 & SR #2) and the Mineral Mixture (MM #1, MM #2, MM #3 & MM #4). It can be observed that SR #1 & SR #2 were strongly hydrophilic while MM #4 was observed to be hydrophobic.
Figure 10.
This figure illustrates flotation tests results of the Sandstone Rock (SR #1 & SR #2) and the Mineral Mixture (MM #1, MM #2, MM #3 & MM #4). It can be observed that SR #1 & SR #2 were strongly hydrophilic while MM #4 was observed to be hydrophobic.
Figure 11.
This figure illustrates oil adhesion tendencies of SR and MM via TBP. It became obvious our developed model predicted the experimental results.
Figure 11.
This figure illustrates oil adhesion tendencies of SR and MM via TBP. It became obvious our developed model predicted the experimental results.
Figure 12.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanisms for SR #1-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. It can be concluded that the SR #1 is strongly hydrophilic due to its low oil adhesion tendencies.
Figure 12.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanisms for SR #1-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. It can be concluded that the SR #1 is strongly hydrophilic due to its low oil adhesion tendencies.
Figure 13.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanisms during SR #2-fluids systems with dissimilar interfacial polarities. Similar to the SR #1, the SR #2 was also strongly hydrophilic as confirmed by the experimental and its simulated counterpart.
Figure 13.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanisms during SR #2-fluids systems with dissimilar interfacial polarities. Similar to the SR #1, the SR #2 was also strongly hydrophilic as confirmed by the experimental and its simulated counterpart.
Figure 14.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism for MM #1-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities.
Figure 14.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism for MM #1-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities.
Figure 15.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism during MM #2-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. It can be observed that the surface area of the minerals has an overriding effect on the wetting preferences of the reservoir rock.
Figure 15.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism during MM #2-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. It can be observed that the surface area of the minerals has an overriding effect on the wetting preferences of the reservoir rock.
Figure 15.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism for MM #3-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. It can be inferred that increasing the contents of the hydrophobic mineral increases the hydrophobicity of the rock resulting from increase in its equivalent surface area.
Figure 15.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism for MM #3-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. It can be inferred that increasing the contents of the hydrophobic mineral increases the hydrophobicity of the rock resulting from increase in its equivalent surface area.
Figure 17.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism for MM #4-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. It can be inferred that increasing the contents of the hydrophobic mineral increases the hydrophobicity of the rock resulting from increase in its equivalent surface area.
Figure 17.
This figure illustrates the oil adhesion mechanism for MM #4-fluids system with dissimilar interfacial polarities. It can be inferred that increasing the contents of the hydrophobic mineral increases the hydrophobicity of the rock resulting from increase in its equivalent surface area.
Figure 18.
This figure illustrates mineral-FW interfacial polarity prediction.
Figure 18.
This figure illustrates mineral-FW interfacial polarity prediction.
Figure 19.
This figure illustrates prediction of the oil-FW interfacial polarity.
Figure 19.
This figure illustrates prediction of the oil-FW interfacial polarity.
Figure 20.
This figure illustrates the effect of equivalent surface area on wetting preferences.
Figure 20.
This figure illustrates the effect of equivalent surface area on wetting preferences.
Figure 21.
This figure illustrates the result of the spontaneous imbibition experiment in chalk from literature [
26].
Figure 21.
This figure illustrates the result of the spontaneous imbibition experiment in chalk from literature [
26].
Figure 22.
This figure illustrates the SCM predictions of the chalk/CW/oil interactions during the literature experiment.
Figure 22.
This figure illustrates the SCM predictions of the chalk/CW/oil interactions during the literature experiment.
Table 1.
This table illustrates the mass fraction (%) of the SR and MM used in this study.
Table 1.
This table illustrates the mass fraction (%) of the SR and MM used in this study.
| Mineral |
SR#1 |
SR#1 |
MM#1 |
MM#2 |
MM#3 |
MM#4 |
| Quartz |
83.7 |
94.9 |
62.8 |
41.9 |
62.8 |
41.9 |
| Albite |
3.3 |
4.0 |
2.5 |
1.6 |
2.5 |
1.6 |
| Montmorillonite |
3.9 |
0.0 |
2.9 |
1.9 |
2.9 |
1.9 |
| Illite |
8.8 |
0.4 |
31.6 |
54.4 |
6.6 |
4.4 |
| Siderite |
0.0 |
0.5 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
| Calcite |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
25.2 |
50.2 |
Table 2.
This table gives the ionic composition of the brines employed in this study at 20oC.
Table 2.
This table gives the ionic composition of the brines employed in this study at 20oC.
| Ions |
FW#1
(10-3 mol/L) |
FW#2
(10-3 mol/L) |
| Na+
|
1326.16 |
701.88 |
| K+
|
5.62 |
7.11 |
| Mg2+
|
17.46 |
23.90 |
| Ca2+
|
147.94 |
72.85 |
| Sr2+
|
8.44 |
1.65 |
| Ba2+
|
0.00 |
0.04 |
| Cl-
|
1677.67 |
898.69 |
| SO42-
|
0.89 |
3.59 |
| Density (gcm-3) |
1.07 |
1.04 |
Table 3.
This table provides the crude oil composition employed in this study.
Table 3.
This table provides the crude oil composition employed in this study.
| Oil |
Density
(gcm-3) at 25oC |
TAN
(mg KOH/g oil) |
TBN
(mg KOH/g oil) |
| STO#1 |
0.86 |
0.10 |
1.90 |
| STO#1 |
0.90 |
0.38 |
2.30 |
Table 4.
This table gives the oil input parameters used in the SCM.
Table 4.
This table gives the oil input parameters used in the SCM.
| Mineral/Rock |
Equivalent Oil Surface |
STO#1 Site Densities
(Site/nm2) |
STO#2 Site Densities
(Site/nm2) |
Equivalent Surface Area
(m2/g) |
| Quartz |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.89
16.99 |
3.40
20.56 |
1.20
1.20 |
| Albite |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.89
16.99 |
3.40
20.56 |
1.20
1.20 |
| Illite |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.02
0.31 |
0.06
0.37 |
66.8
66.8 |
| Montmorillonite |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.36
6.79 |
1.36
8.23 |
3.0
3.0 |
| Calcite |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.54
10.20 |
2.04
12.34 |
2.0
2.0 |
| SR#1 |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.15
2.89 |
0.58
3.50 |
7.0
7.0 |
| SR#2 |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.73
13.85 |
2.77
16.76 |
1.5
1.5 |
| MM#1 |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.05
0.93 |
0.19
1.12 |
22.0
22.0 |
| MM#2 |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.03
0.55 |
0.11
0.67 |
36.9
36.9 |
| MM#3 |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.19
3.52 |
0.70
4.27 |
5.8
5.8 |
| MM#4 |
>COOH
>NH+
|
0.24
4.51 |
0.90
5.46 |
4.5
4.5 |
Table 5.
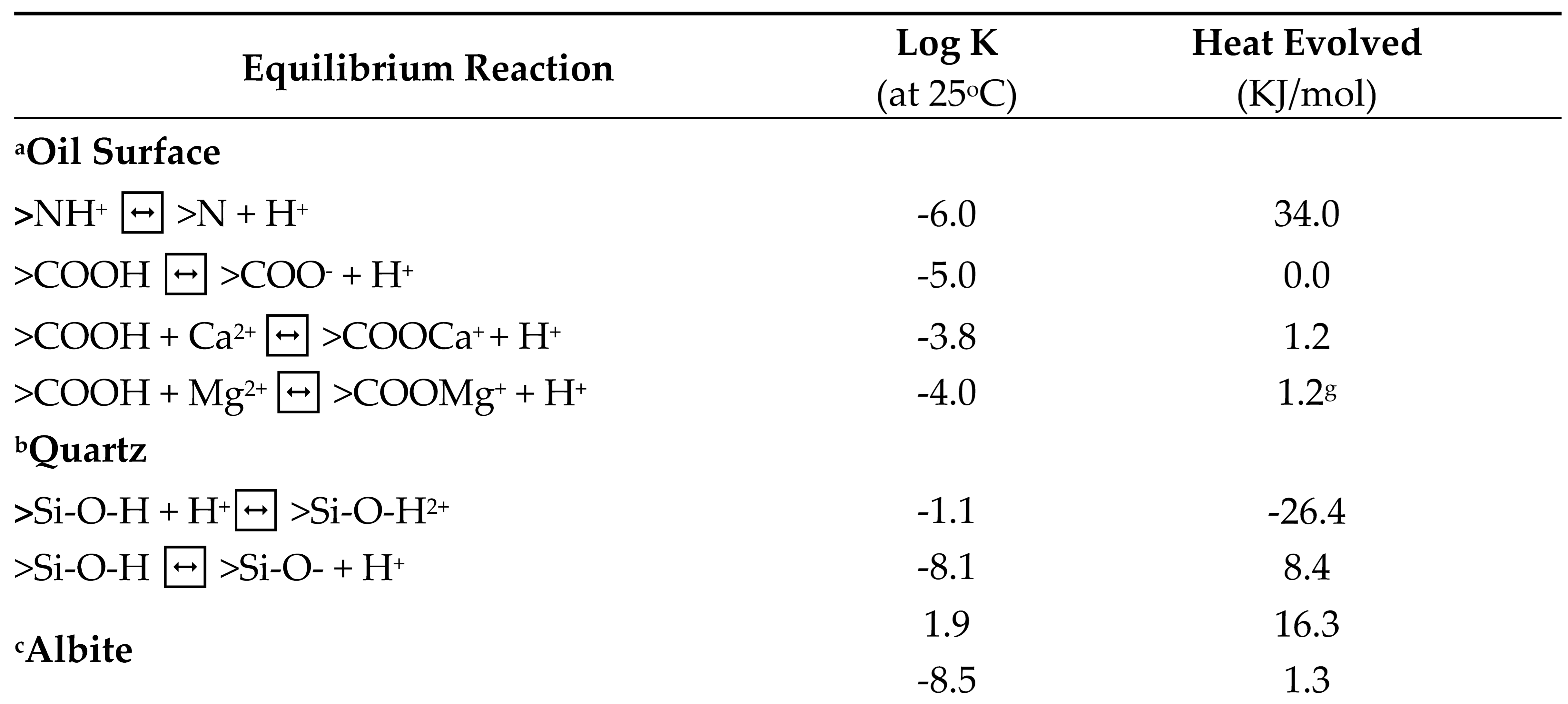
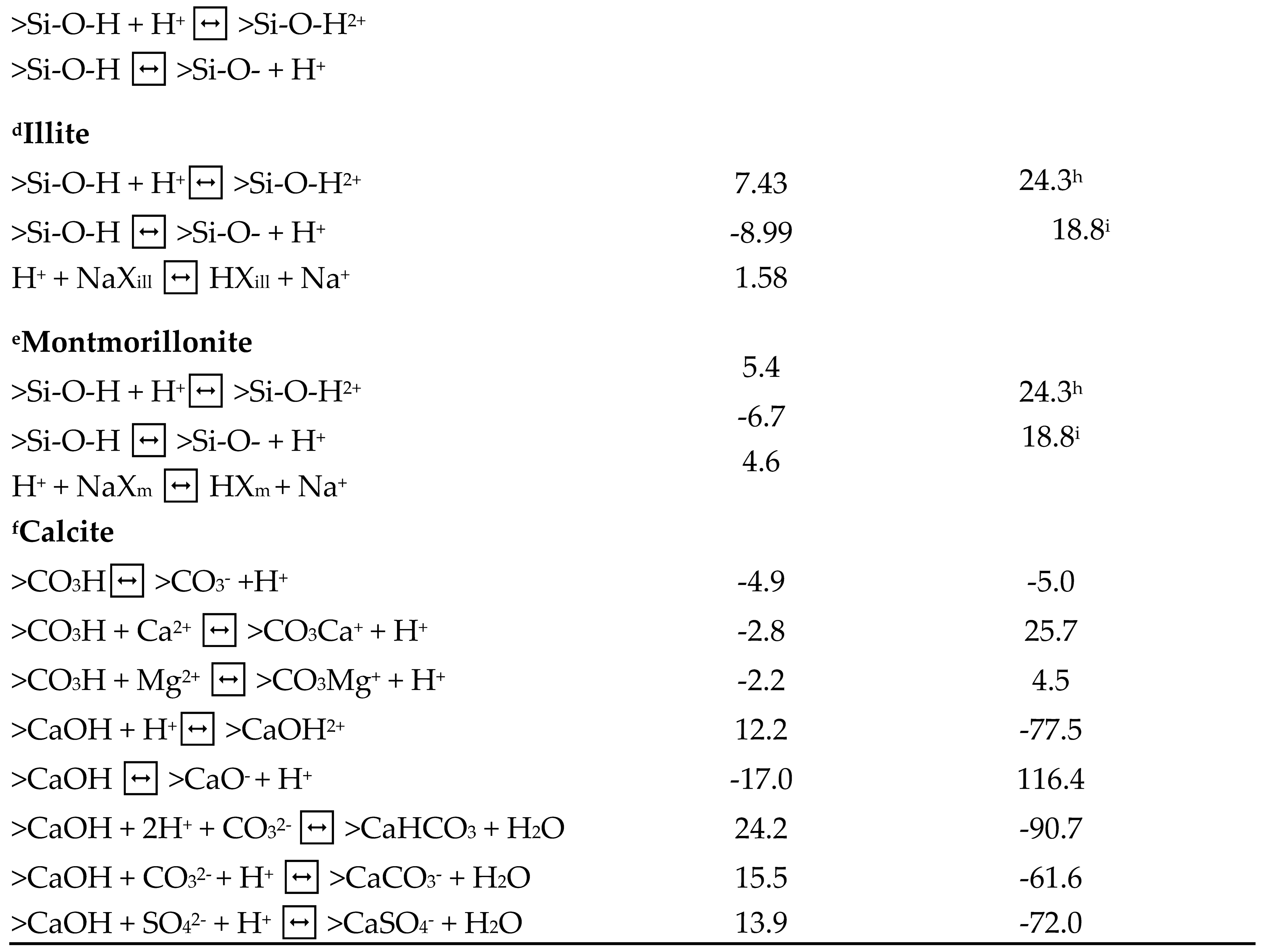
This table gives the surface (i.e., oil and minerals) reactions and reaction constants.
Table 5.
This table gives the surface (i.e., oil and minerals) reactions and reaction constants.
Table 6.
This table gives the mineral/reservoir rock input parameters considered in this study.
Table 6.
This table gives the mineral/reservoir rock input parameters considered in this study.
| Mineral/Rock |
Site Density
(site/nm2) |
Equivalent Surface Area
(m2/g) |
| Quartz |
10.00 |
1.20 |
| Albite |
1.155 |
1.20 |
| Illite |
1.37 |
66.8 |
| Montmorillonite |
5.7 |
3.0 |
| Calcite |
4.90 |
2.0 |
| SR#1 |
|
7.0 |
| SR#2 |
|
1.5 |
| MM#1 |
|
22.0 |
| MM#2 |
|
36.9 |
| MM#3 |
|
5.8 |
| MM#4 |
|
4.5 |
Table 7.
This table provides the chemical composition of the brine employed in the literature experiment of chalk [
26].
Table 7.
This table provides the chemical composition of the brine employed in the literature experiment of chalk [
26].
| Ion |
FW
(10-3 mol/L) |
| Na+
|
629.85 |
| K+
|
4.16 |
| Mg2+
|
22.03 |
| Ca2+
|
226.16 |
| Cl-
|
1130.40 |
 >COO-) was more distinct than that observed in the illite and montmorillonite (>SOH2+
>COO-) was more distinct than that observed in the illite and montmorillonite (>SOH2+  >COO-) thus confirming the hydrophobic nature of the former. Furthermore, oil adhesion resulting from cation bridging also occurred as observed in the other minerals. As seen in the other mineral/brine/oil interaction, the role played by >NH+ in the oil adsorption was also negligible when compared to the >COO-.
>COO-) thus confirming the hydrophobic nature of the former. Furthermore, oil adhesion resulting from cation bridging also occurred as observed in the other minerals. As seen in the other mineral/brine/oil interaction, the role played by >NH+ in the oil adsorption was also negligible when compared to the >COO-.