Submitted:
27 November 2023
Posted:
28 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
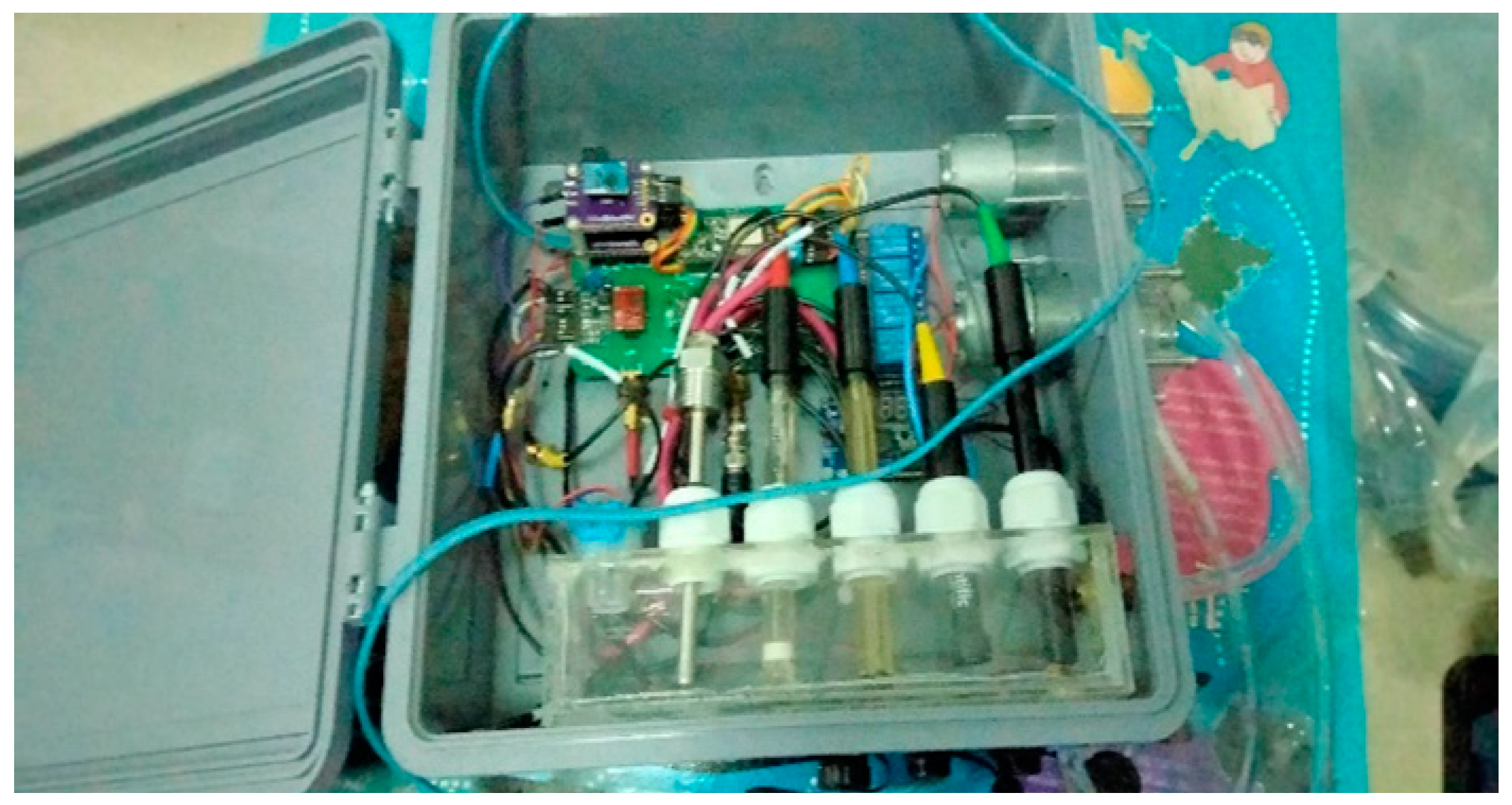
2.1. Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring
2.1.1. pH Sensor Probe
2.1.2. Temperature Sensor Probe
2.1.3. Dissolved Oxygen Sensor Probe
2.1.4. Conductive Sensor Probe
2.1.5. Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP) Sensor Probe
2.1.6. Turbidity Sensor Probe
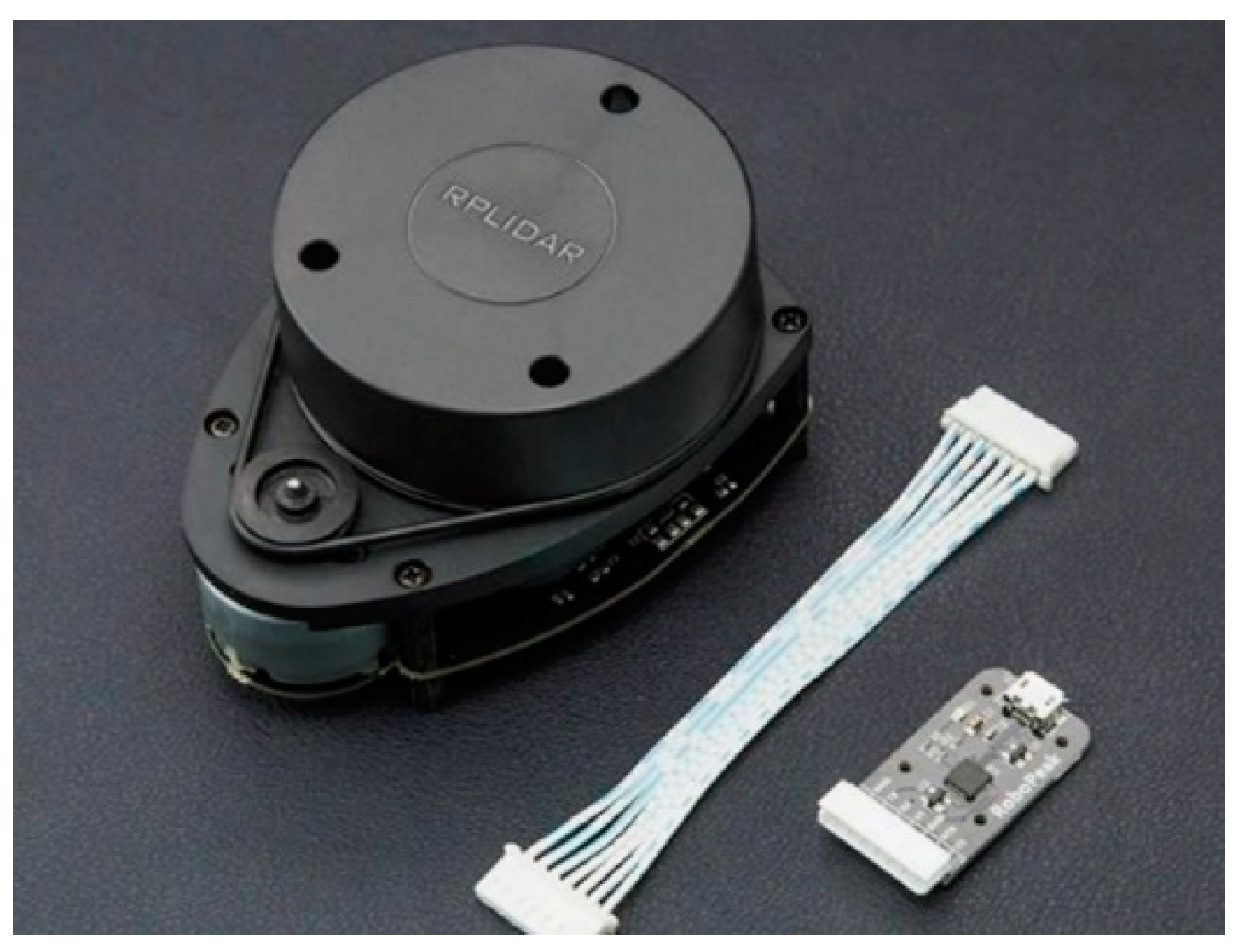
2.2. LiDAR Laser Scanner for Obstacle Detection
2.3. Global Positioning System (GPS) Module for Positioning the Paddle Wheel Aerator
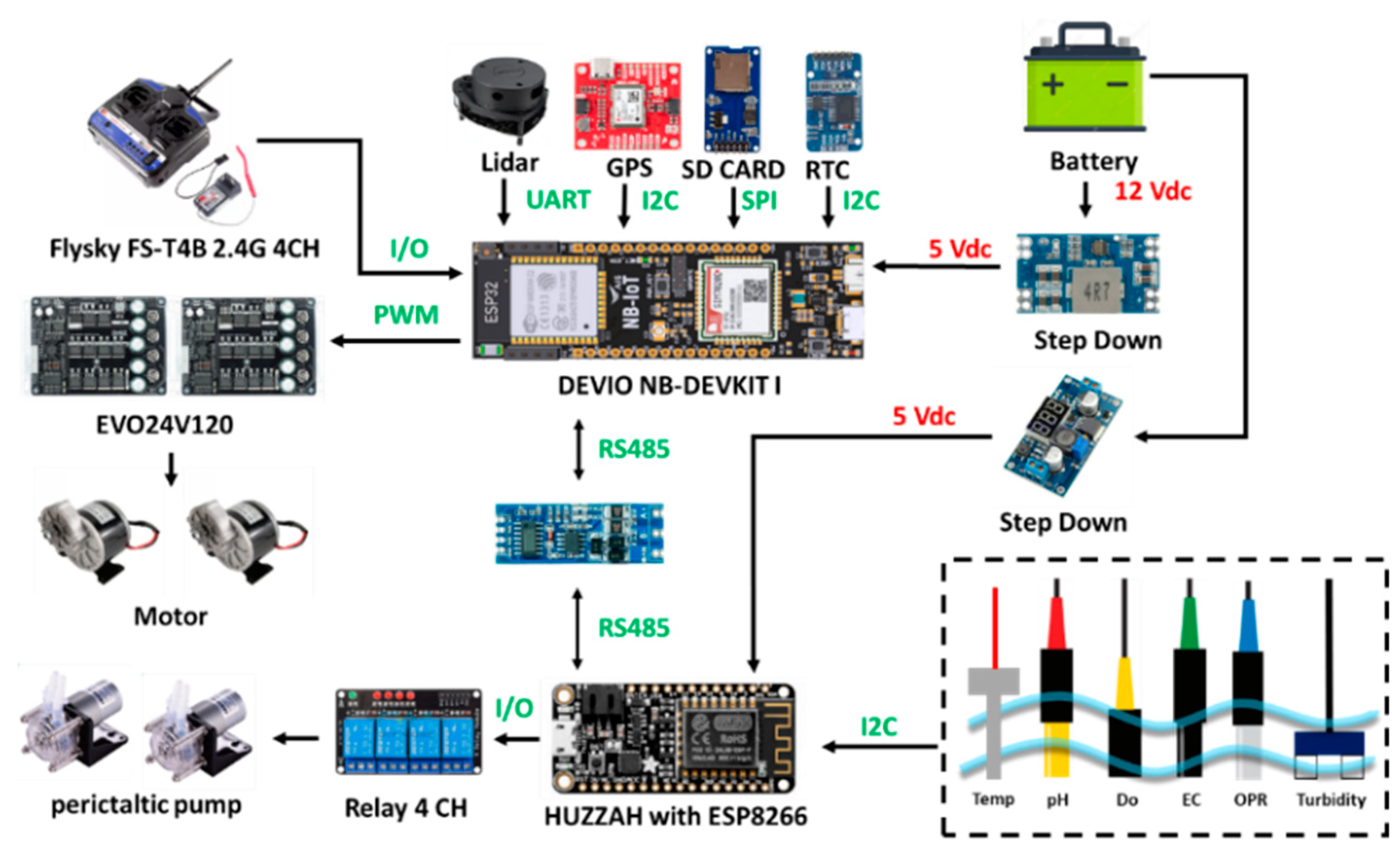
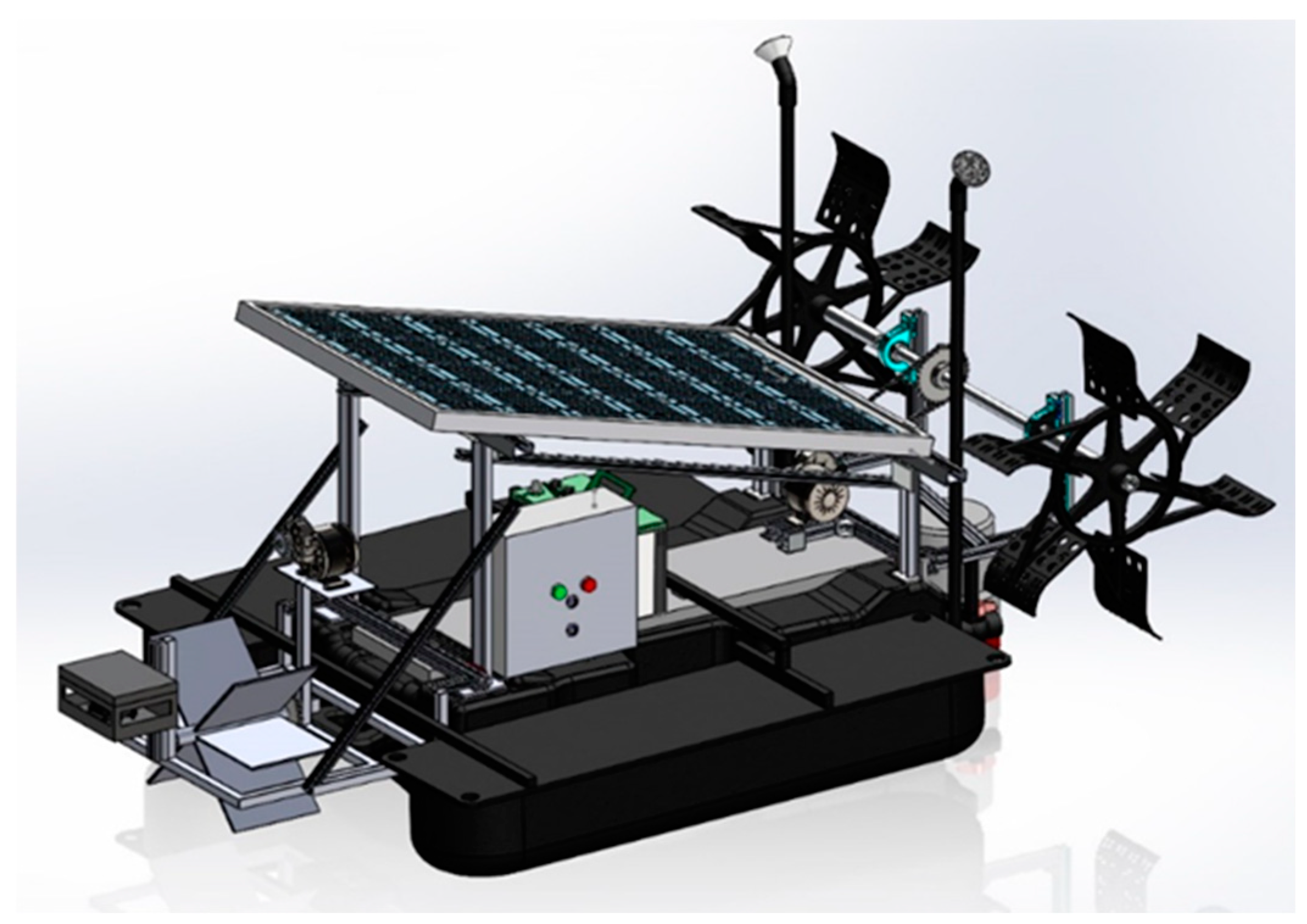
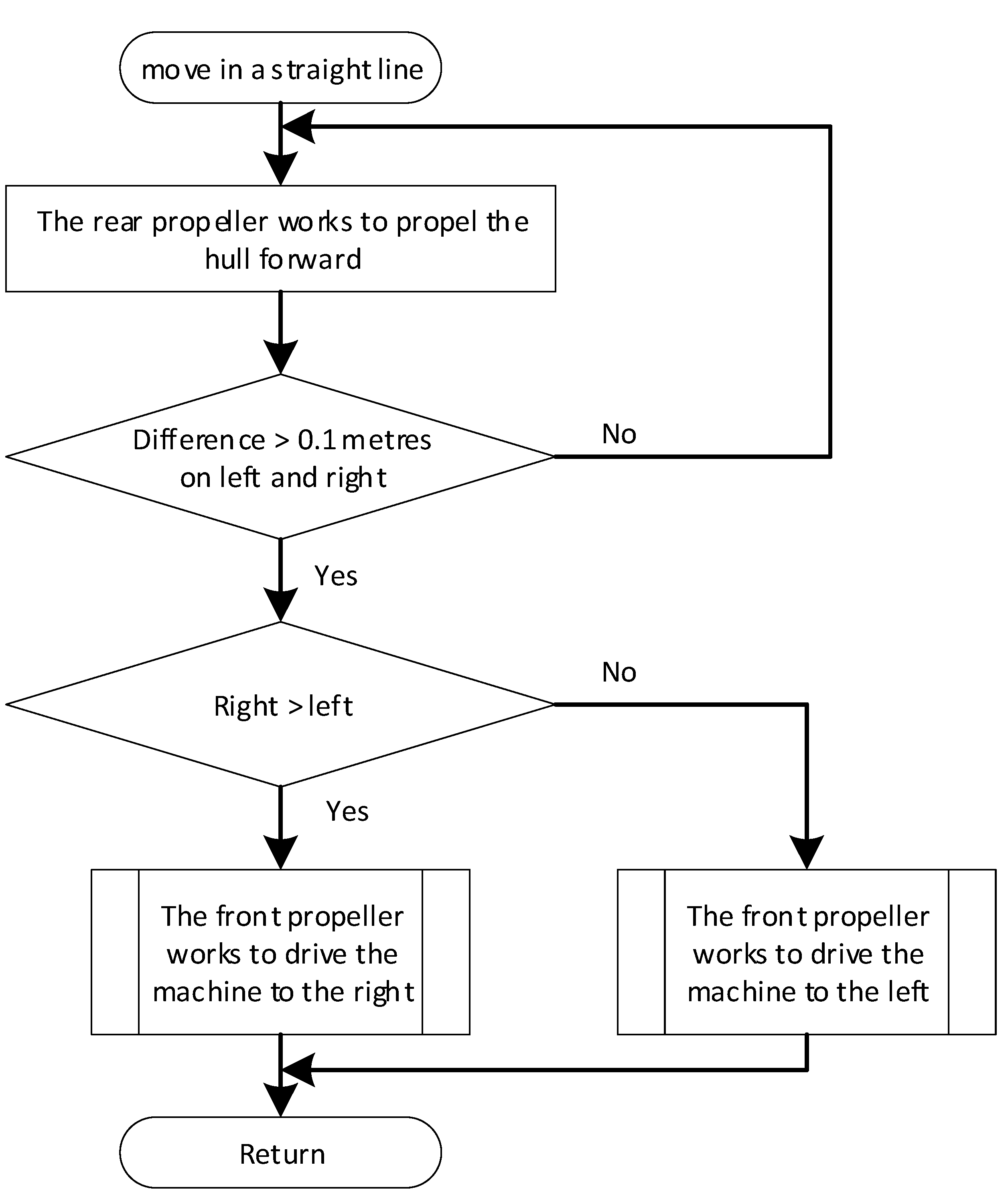
2.4. Hardware Implementation
2.5. Energy Computation for the Paddle Wheel Aerator
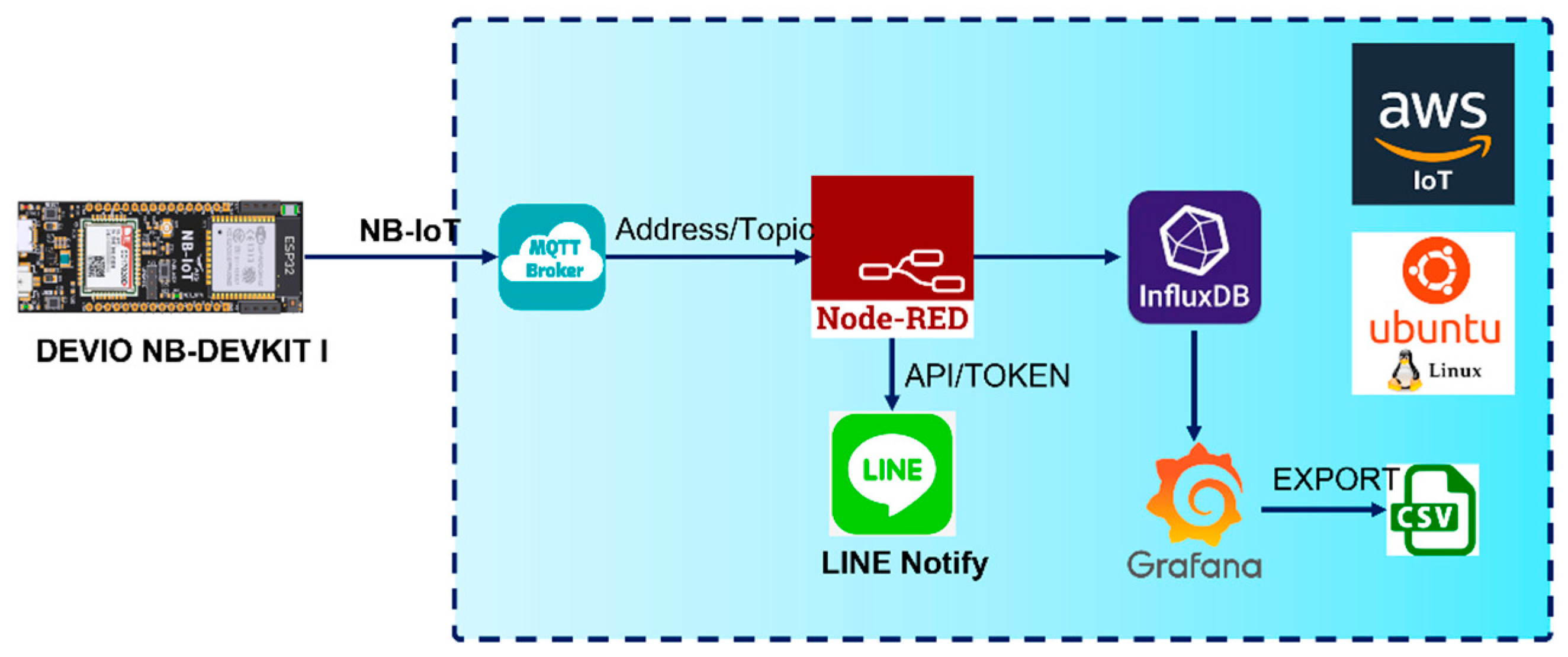
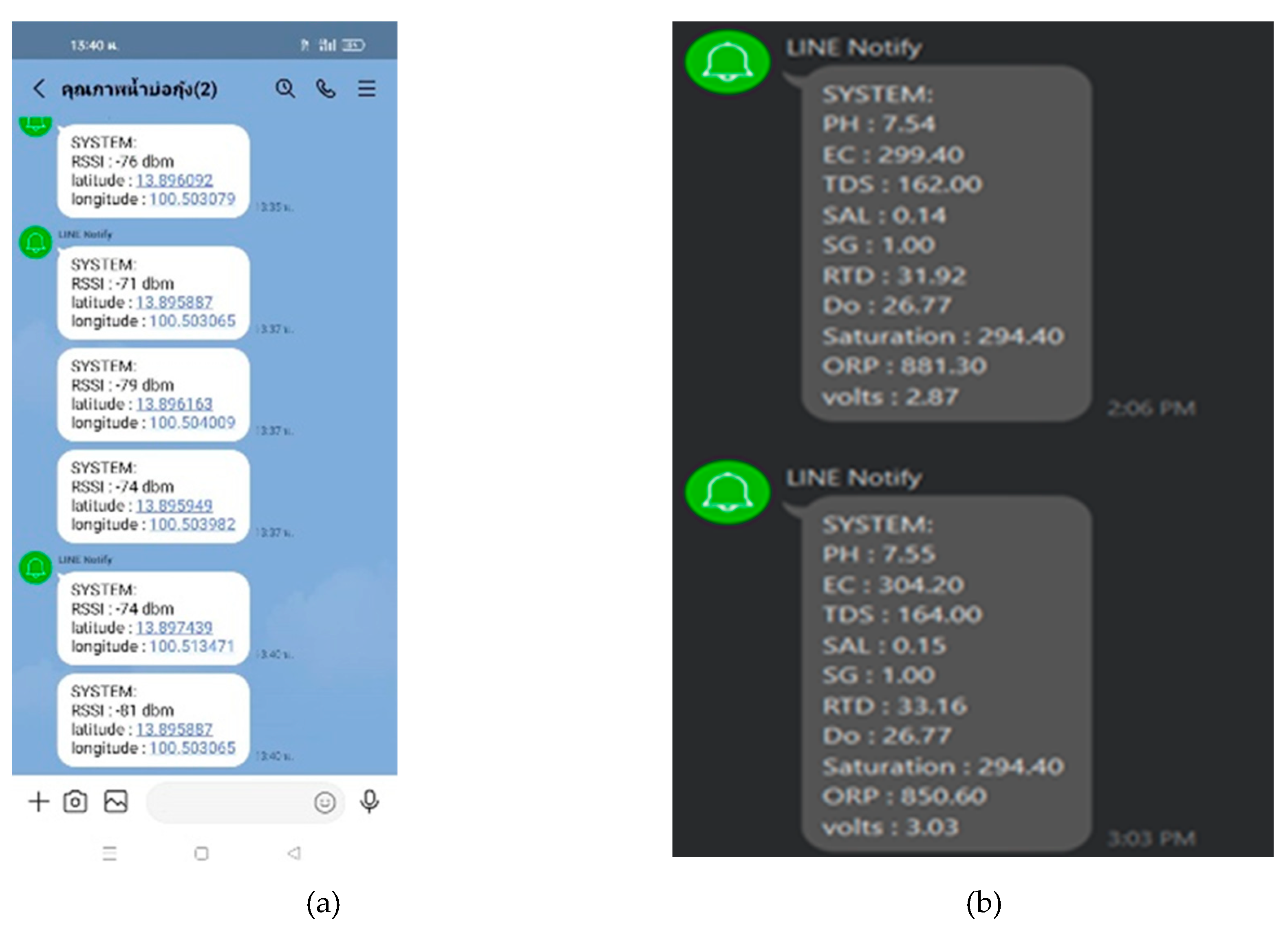
2.6. IoT Implementation
2.7. Algorithms
| Algorithm 1: Reading water quality value algorithm on DEVIO NB-DEVKIT 1. |
| If the 485 port is available for ESP8266 communication |
| if I2C port is available for sensors |
| for data reading in each sensor, do |
| pH data reading |
| EC data reading |
| Temperature data reading |
| DO data reading |
| ORP data reading |
| end |
| end |
| Turbidity data reading from analogue input |
| Convert all data to float |
| Send all data sensors from ESP8266 to DEVIO NB-DEVKIT 1 |
| end |
| Publish the topics that contain the package to the MQTT broker |
2.8. Cost Analysis
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
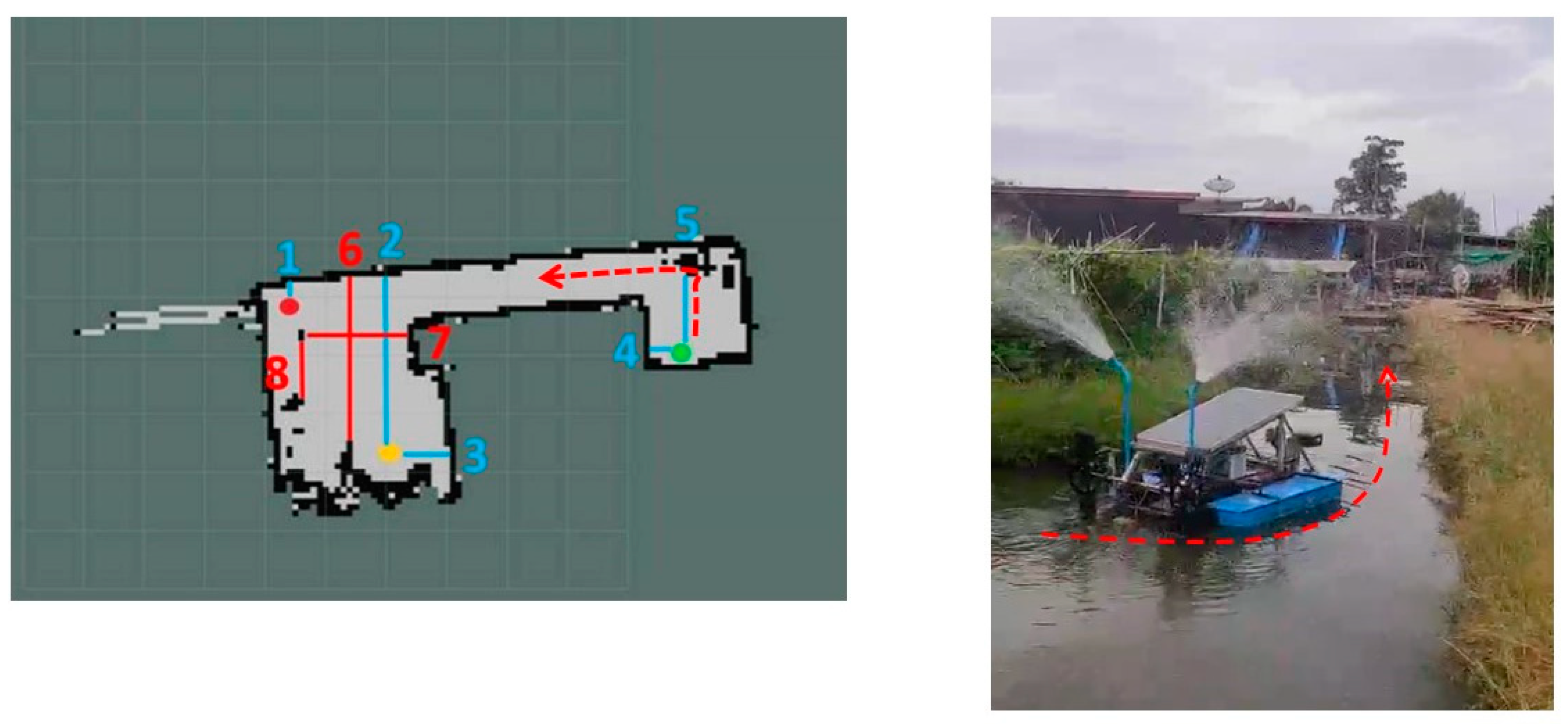
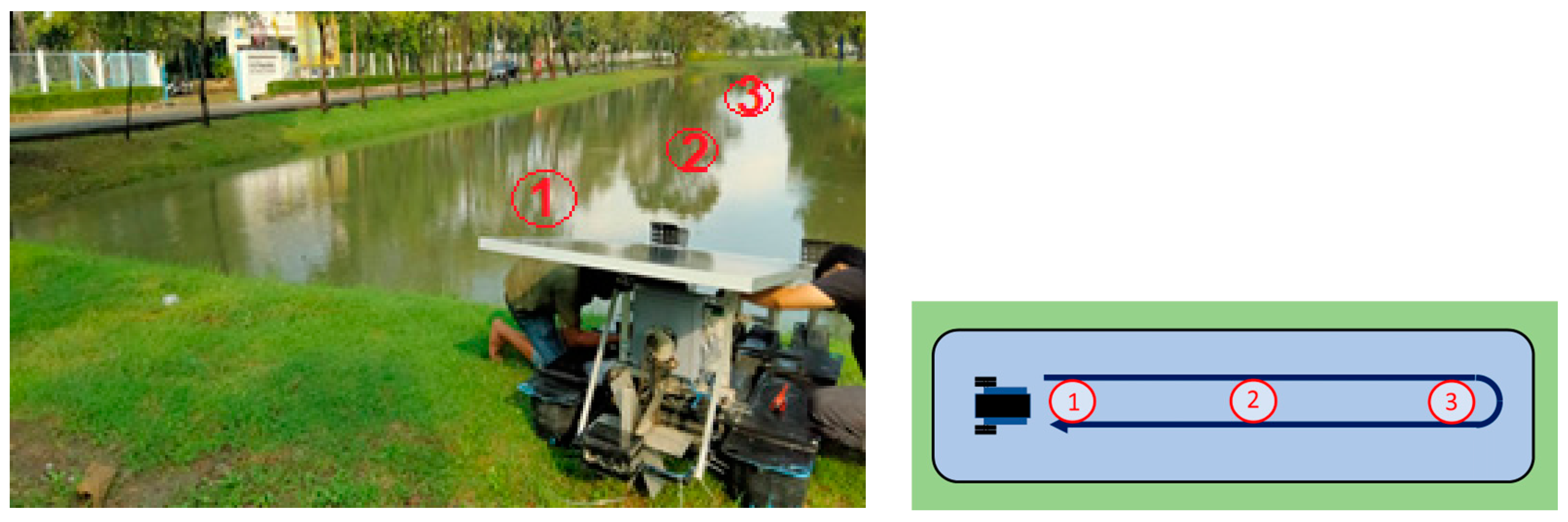
3.1. Verification of Paddle Wheel Aerator Movement and Position
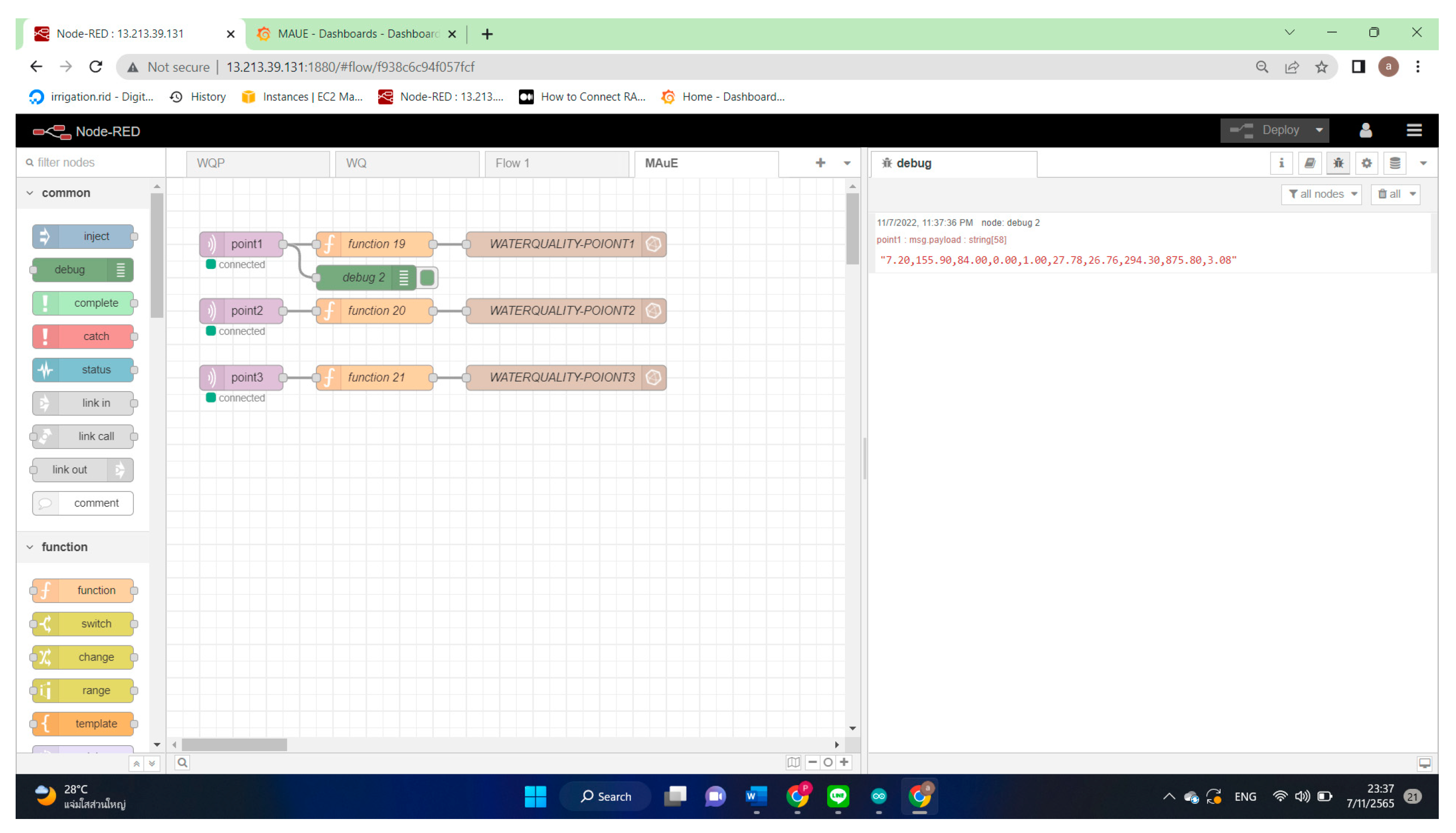
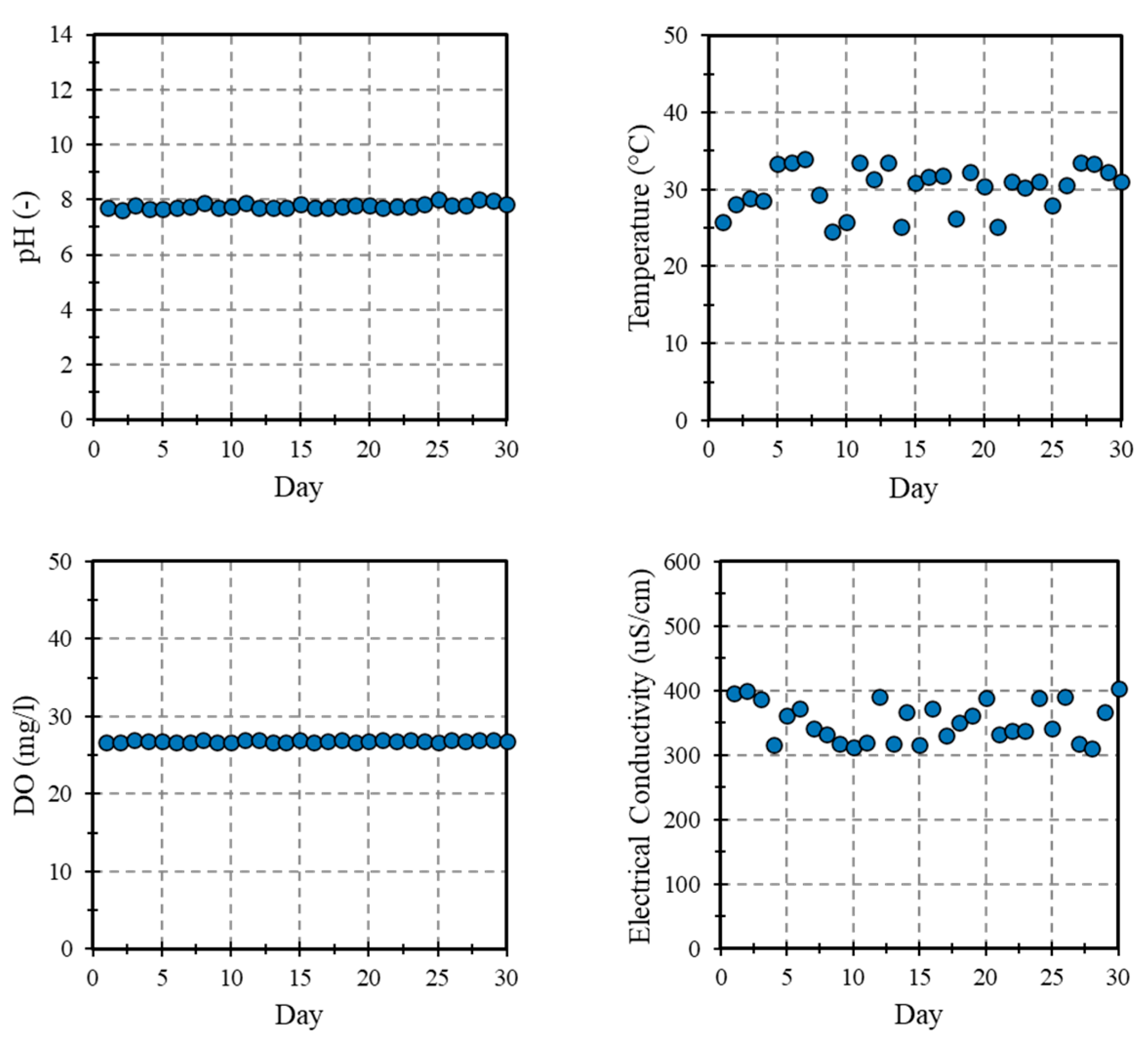
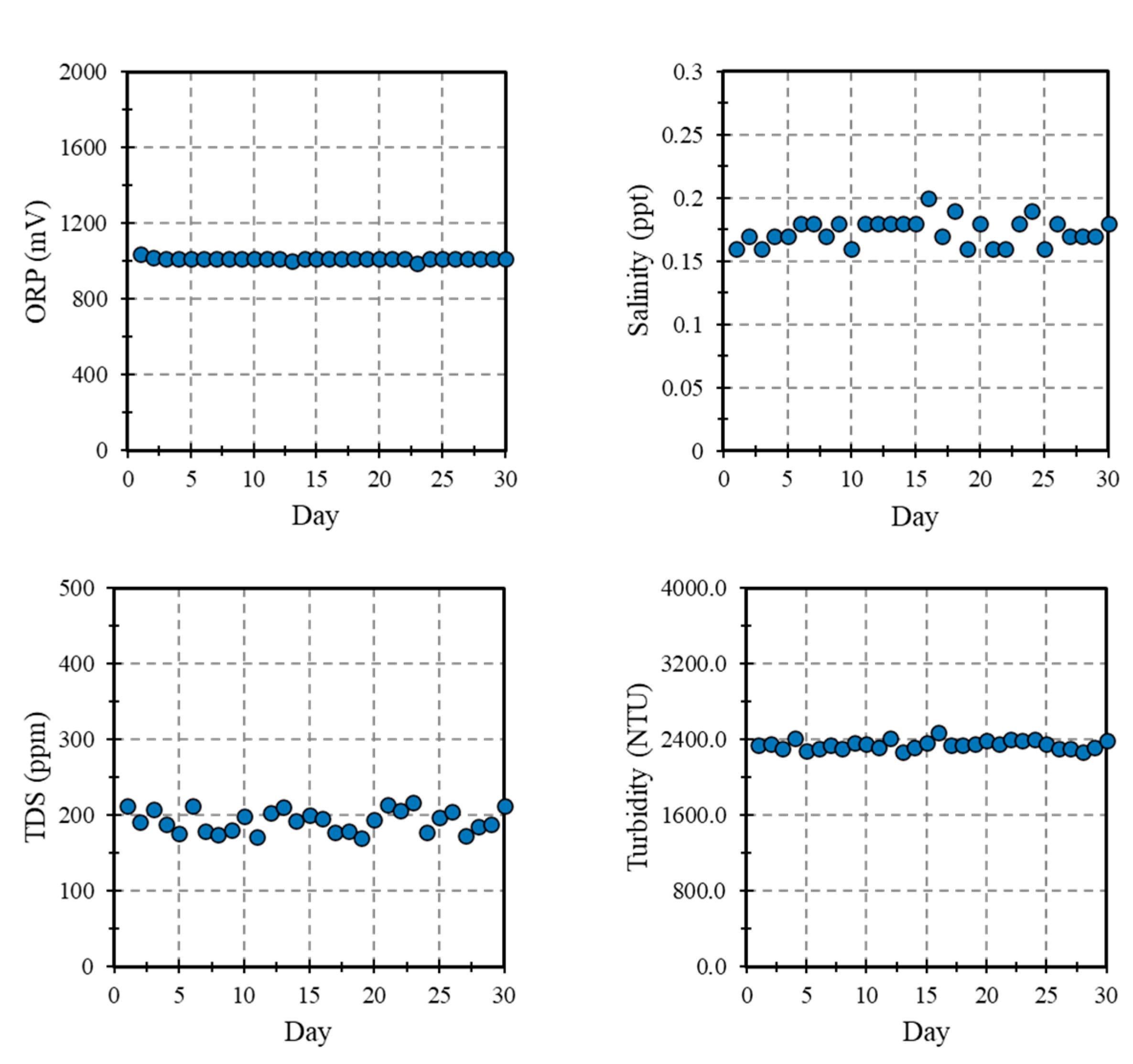
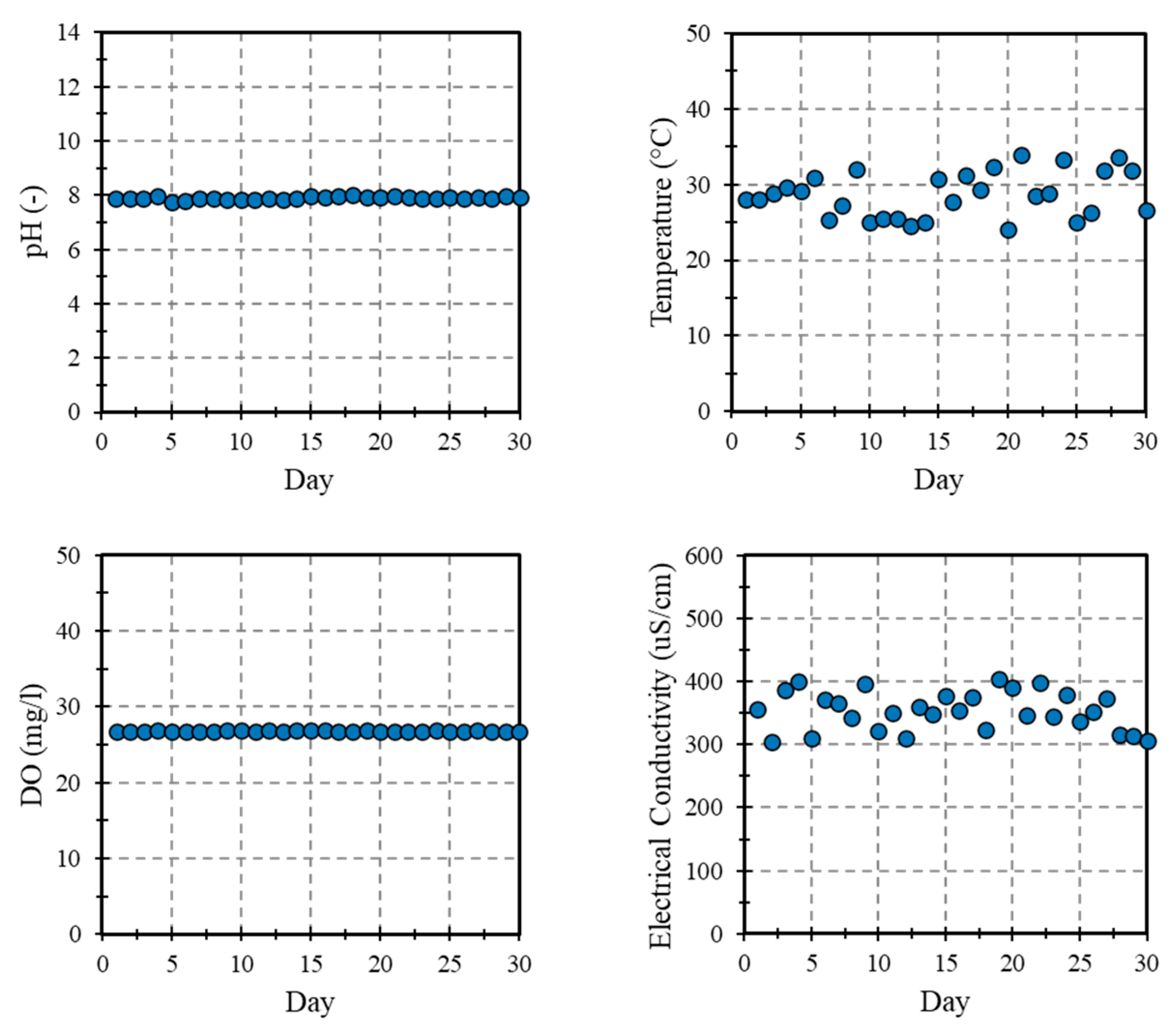
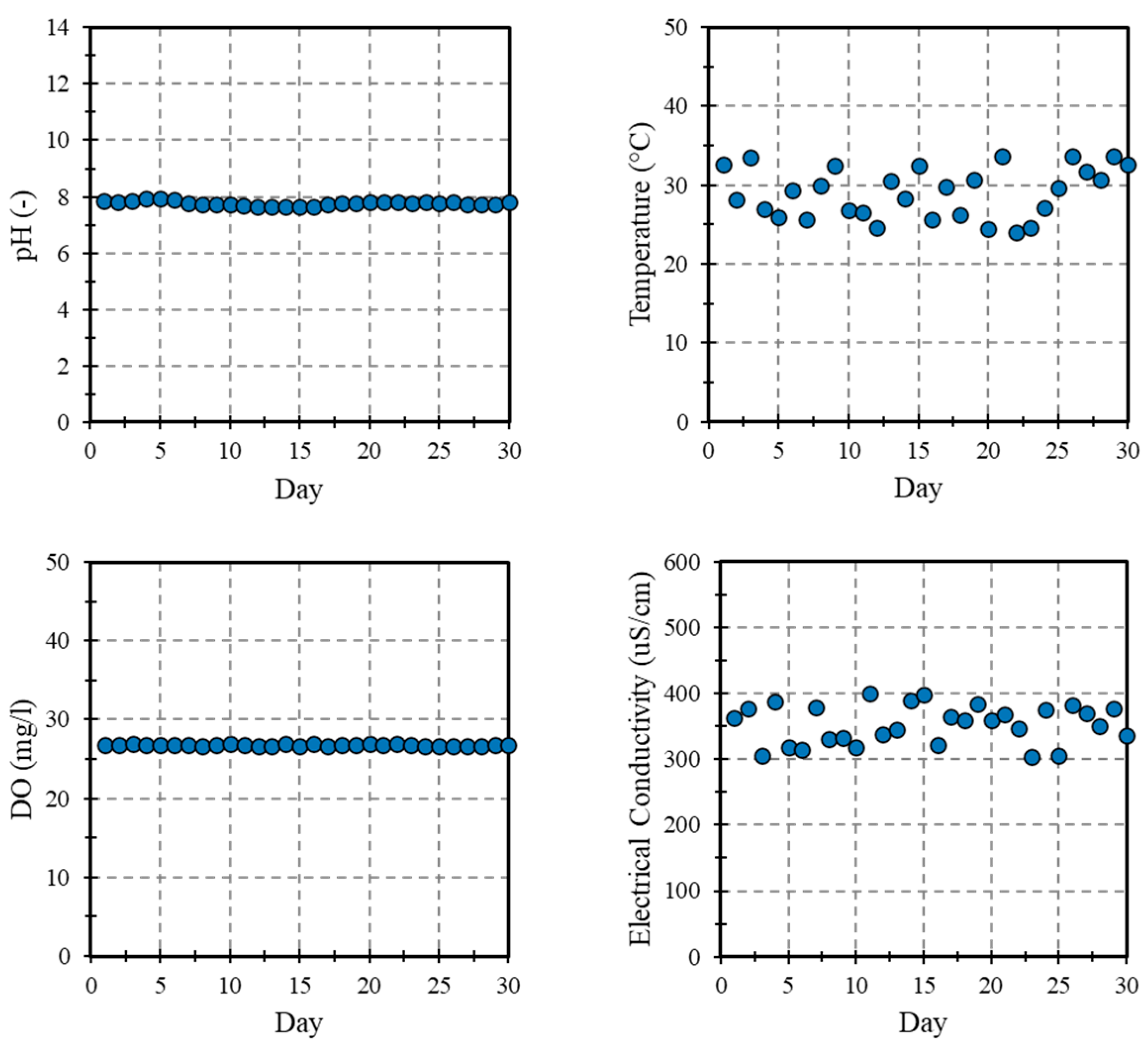
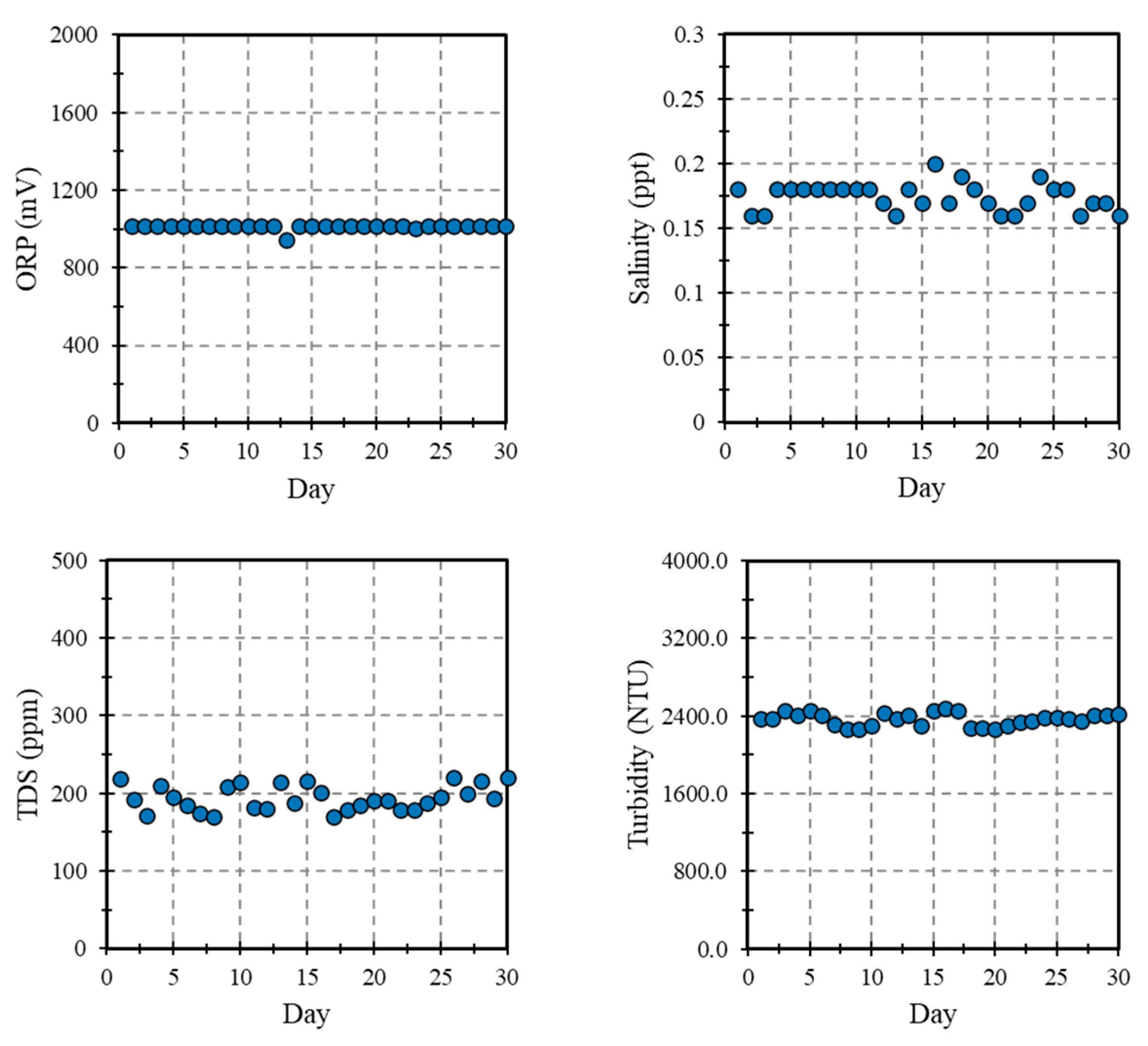
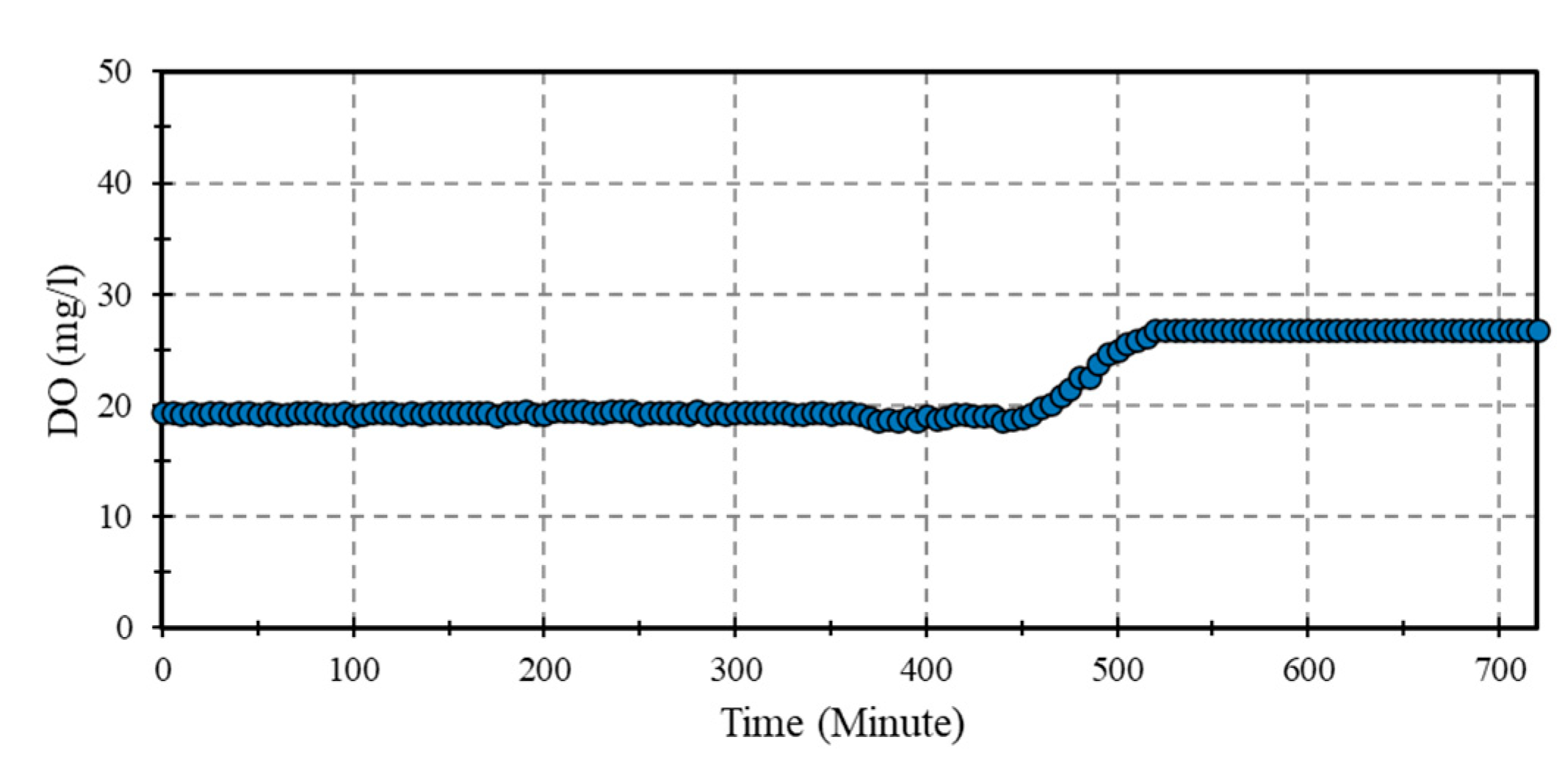
3.2. Water Quality Monitoring
3.3. Water Quality Monitoring
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2015. Available online: https://www.fisheries.go.th/strategy/fisheconomic/pages/fish%20shrimp.html.
- Shahriar, A.; Dhrubo, B.; Md Sazzad, H. Environmental Impacts of Commercial Shrimp Farming in Coastal Zone of Bangladesh and Approaches for Sustainable Management. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2019, 20, 556038. [Google Scholar]
- Iber, B.T.; Kasan, N.A. Recent advances in Shrimp aquaculture wastewater management. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, D.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Ma, D.; Li, F. A platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 71, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Istiaq, M.F.; Rasadin, M.; Talukder, M.R. Freshwater shrimp farm monitoring system for Bangladesh based on internet of things. Eng. Rep. 2020, 2, e12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandap, J.P.; Sze, D.; Reyes, G.N.; Matthew, D.; Reyes, R.; Danny Chung, W.Y. Aquaponics pH Level, Temperature, and Dissolved Oxygen Monitoring and Control System Using Raspberry Pi as Network Backbone. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2018 - 2018 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Jeju, Republic of Korea; 2018; pp. 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, D. Intelligent fish farm—the future of aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 2681–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustijai, J.; Andika, F. Control - Monitoring System Of Oxygen Level, Ph,Temperature And Feeding in Pond Based on IOT. J. Pengabdi. Kpd. Masy. 2021, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneha, P.S.; Rakesh, V.S. Automatic monitoring and control of shrimp aquaculture and paddy field based on embedded system and IoT. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Inventive Computing and Informatics (ICICI), Coimbatore, India; 2017; pp. 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, R.A.B.; Cordova, L.R.M.; Nunez, J.C.G.; Galaviz, J.G.; Gamez, J.C.L. Hernandez R C. Implementation and Evaluation of Open-Source Hardware to Monitor Water Quality in Precision Aquaculture. Sensors 2020, 20, 6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco-Lugo, A.G.; McLernon, D.C.; Lara, M.; Zaidi, S.A.R.; González, B.J.; Illescas, O.; Pérez-Macías, C.I.; Nájera-Bello, V.; Balderas, J.A.; Pizano-Escalante, J.L.; et al. Monitoring of water quality in a shrimp farm using a FANET. Internet Things 2022, 18, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, T.; Inagaki, T.; Nakamura, C.; Hashimoto, R.; Negoro, N.; Hyodo, J.; Honda, S. Water circulation induced by mechanical aerators in a rectangular vessel for shrimp aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2019, 85, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENV-40-pH, pH Probe, Datasheet Manual, AtlasScientific Environmental Robotics, 2019.
- Bekmezci, I.; Sahingoz, O.K.; Temel, S. Flying ad-hoc networks (FANETs): a survey, Ad Hoc. Networks 2013, 11, 1254–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENV-40-DC, Dissolved Oxygen Probe, Datasheet Manual, AtlasScientific Environmental Robotics, 2019.
- Technical information, condumax CLS16 and CLS16D, Endress+Hauser, 2010.
- 2023. Available online: https://www.neonics.co.th/water-quality-testing/what-is-orp-oxidation-reduction-potential.html.
- 2016. Available online: https://legatool.com/wp/78/.
- Thong-un, N.; Hirata, S.; Orino, Y.; Kurosawa, M.K. A linearization-based method of simultaneous position and velocity measurement using ultrasonic waves. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2023. Available online: https://www.arduitronics.com/product/4324/sparkfun-gps-dead-reckoning-breakout-neo-m8u-qwiic-sparkfun-usa.
- Thong-un, N.; Wongsaroj, W. Productivity enhancement using low-cost smart wireless programmable logic controllers: A case study of an oyster mushroom farm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 195, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsuwan, T.; Thong-Un, N.; Pudchuen, N.; Runglin, K.; Wongsaroj, W. The Failure Protection of Wireless-Based IIoT Technology for Fluid Level Control Systems. Trends Sci. 2022, 19, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarsh, J.K.; Sreedevi, V.T.; Thangavelusamy, D. Product Review System with BERT for Sentiment Analysis and Implementation of Administrative Privileges on Node-RED. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 65968–65976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickels, W.G.; McHugh, J.; McHugh, S. Understanding Business, 9th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: Pennsylvania, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chitra, L.P.; Satapathy, R. Performance comparison and evaluation of Node.js and traditional web server (IIS). In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Algorithms, Methodology, Models and Applications in Emerging Technologies (ICAMMAET), Chennai, India; 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajal-Hernández, J.J.; Sánchez-Fernández, L.P.; Carrasco-Ochoa, J.A.; Martínez-Trinidad, J.F. Immediate water quality assessment in shrimp culture using fuzzy inference systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 10571–10582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sensor Type | Communication | Voltage | Range | Temperature | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | I2C & UART | 3.3– 5 V | -50–200 °C | -50–200 °C | +/-0.1 °C |
| pH | I2C & UART | 3.3–5 V | 0.001–14.000 pH | -5–99 °C | +/-0.002 pH |
| Dissolved oxygen | I2C & UART | 3.3–5 V | 0–100 mg/L | 1–60 °C | +/-0.05 mg/L |
| ORP | I2C | 3.3–5 V | -1100mV–1100mV | 1–60 °C | +/-1.1 mV |
| EC | I2C & UART | 3.3–5 V | 5–200,000 uS/cm | 1–110 °C | +/-2 % |
| Turbidity | Analogue | 5 V | 0–100 % | -30–80 °C | +/-1 % |
| Power Supply Device | Range |
|---|---|
| Solar Panel | 12 V 130 W |
| Solar Charger | 360 W |
| Battery | 12 V 85 A-hr |
| Components | Cost in USD |
|---|---|
| Solar Panel 350 W | 100.43 |
| Solar Charger 360 W | 22.38 |
| Battery 12 V 85 Ahr | 70.30 |
| Paddles | 9.75 |
| Buoy | 16.93 |
| DC Motors 12V 250W | 25.82 |
| LiDAR | 103.03 |
| Motor Driver | 57.36 |
| Controlling + IoT Unit | 60.24 |
| pH Sensor | 149.99 |
| Temperature Sensor | 29.99 |
| Turbidity Sensor | 7.09 |
| Dissolved Oxygen Sensor | 230.99 |
| ORP Sensor | 69.50 |
| EC + Salinity Sensors | 199.99 |
| Point | Actual Distance (m) | Measured Distance (m) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.3 | 1.31 | 0.77 |
| 2 | 1.7 | 1.66 | 2.35 |
| 3 | 0.47 | 0.51 | 8.51 |
| 4 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 5.88 |
| 5 | 0.34 | 0.38 | 11.76 |
| 6 | 1.55 | 1.60 | 3.22 |
| 7 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 8.43 |
| 8 | 3.03 | 3.09 | 1.98 |
| Point | RSSI (dbm) | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -76 | 13.896092 | 100.503079 |
| 2 | -71 | 13.895887 | 100.503065 |
| 3 | -79 | 13.896163 | 100.504009 |
| 4 | -74 | 13.895949 | 100.503982 |
| 5 | -74 | 13.897439 | 100.513471 |
| 6 | -80 | 13.895887 | 100.503065 |
| 7 | -81 | 13.896112 | 100.503056 |
| 8 | -81 | 13.896078 | 100.503089 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




