Submitted:
24 November 2023
Posted:
28 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
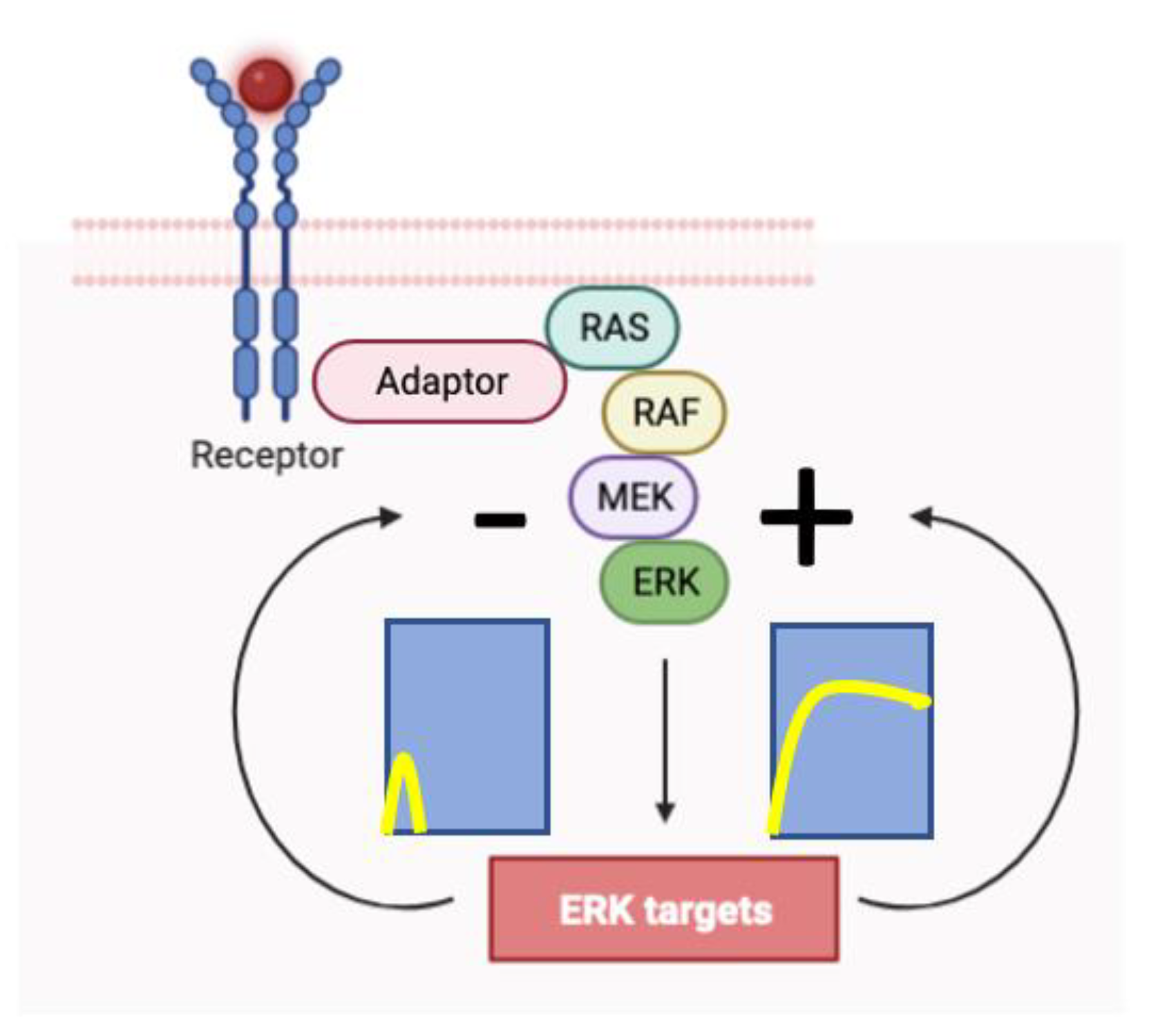
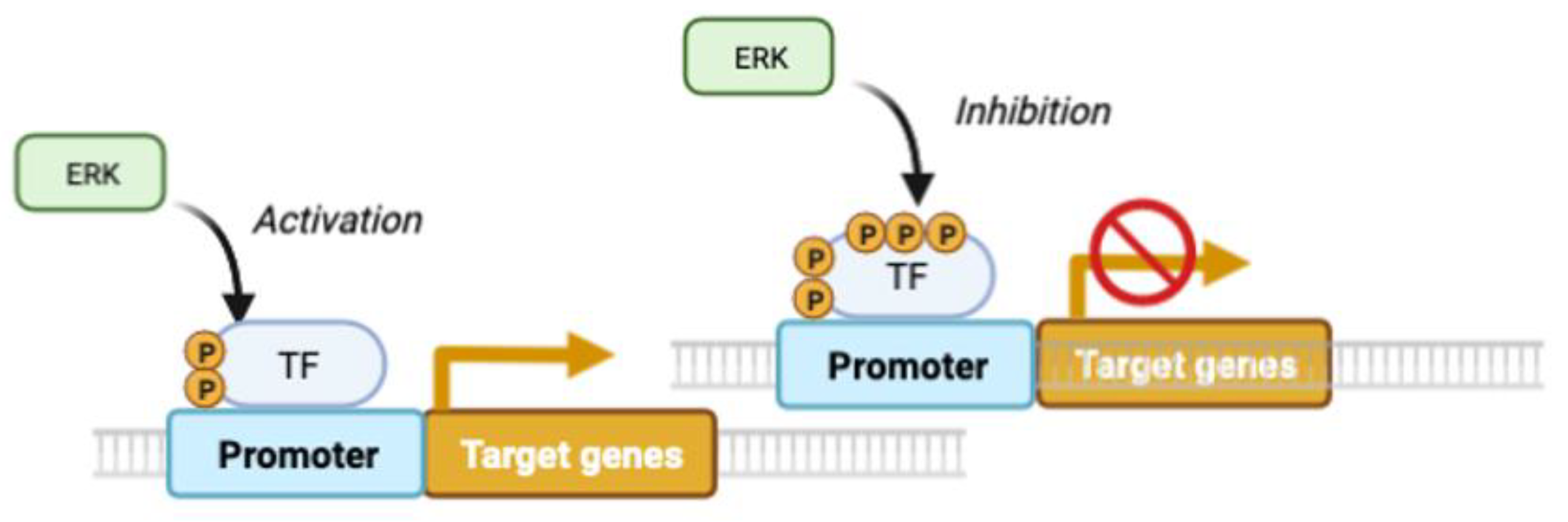
1. Introduction
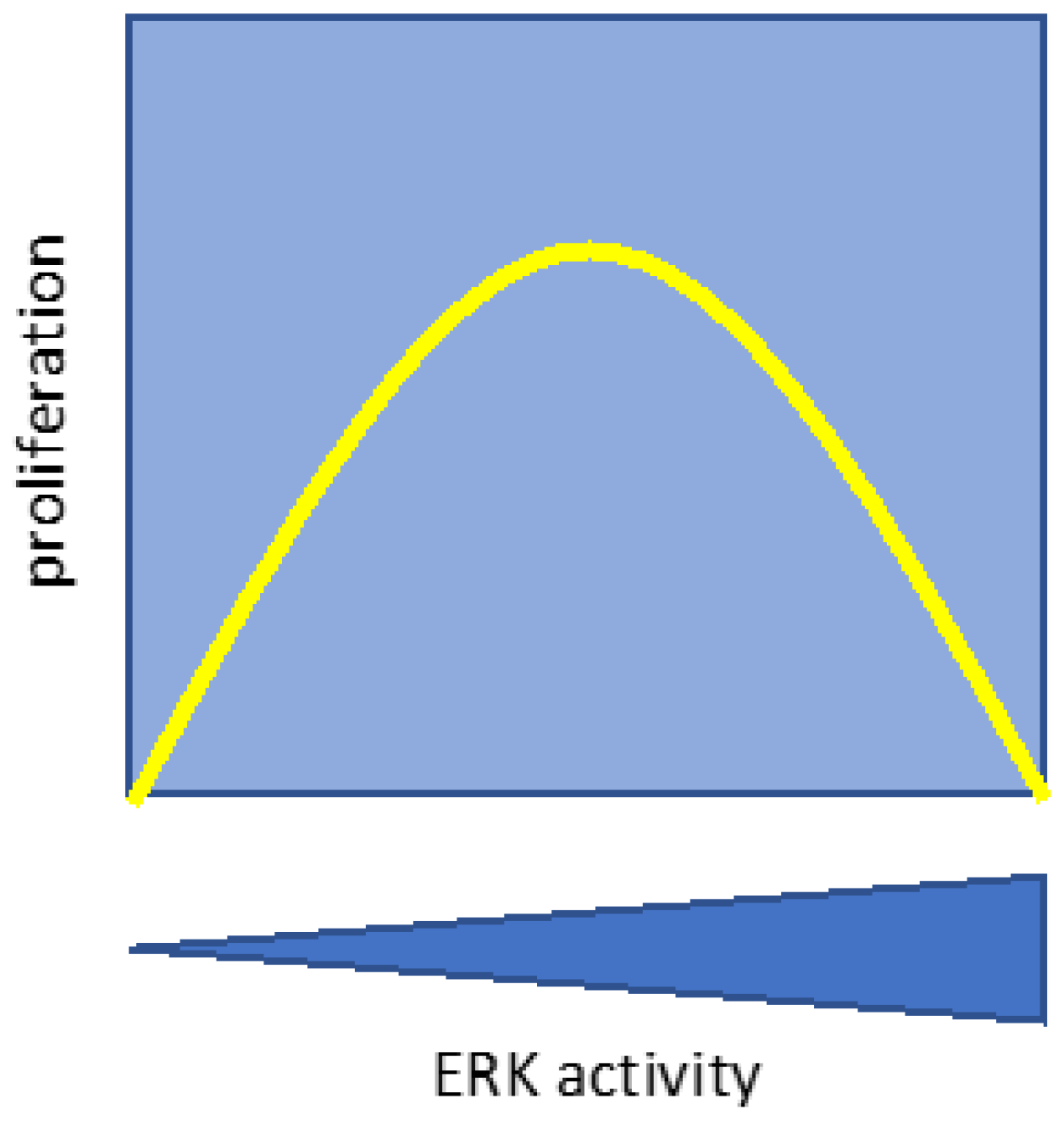
2. Proliferation and survival
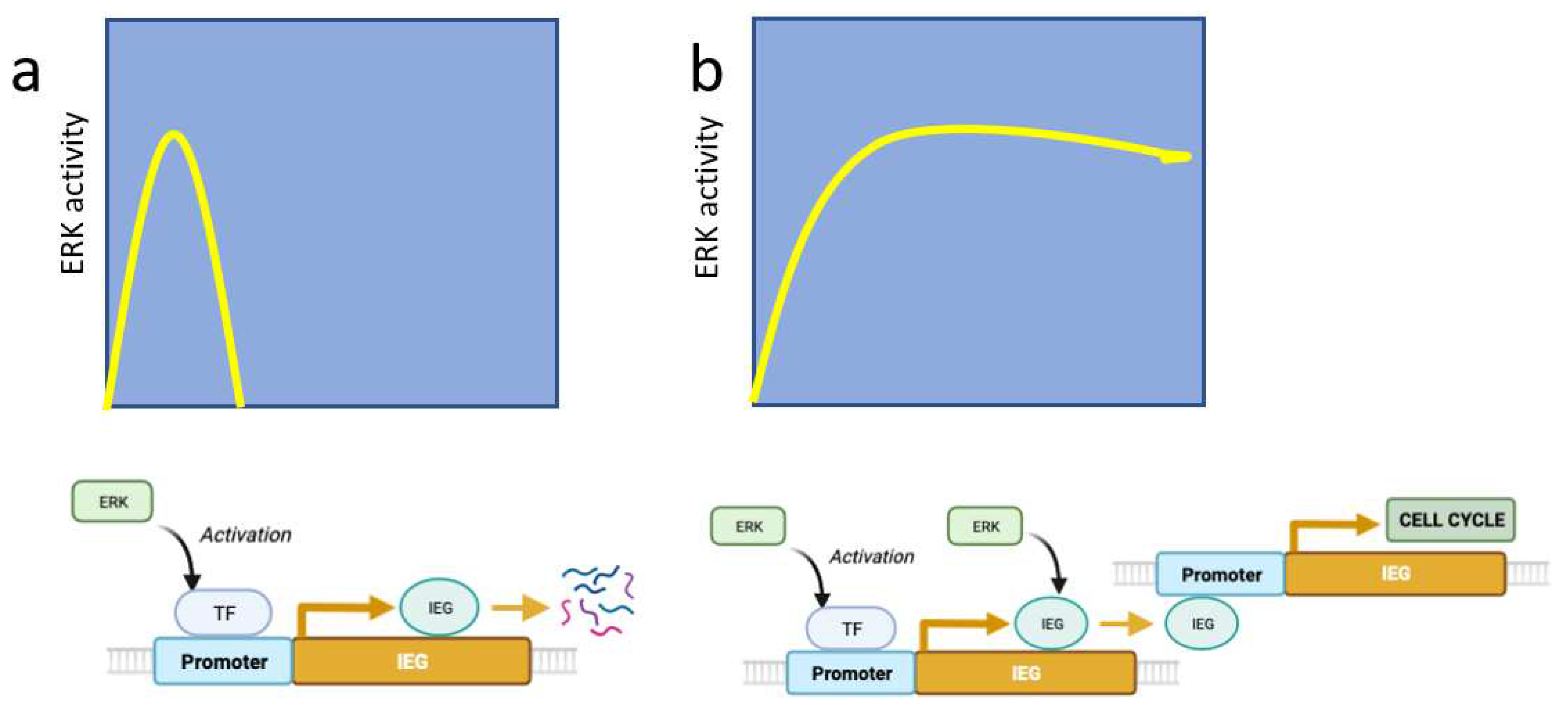
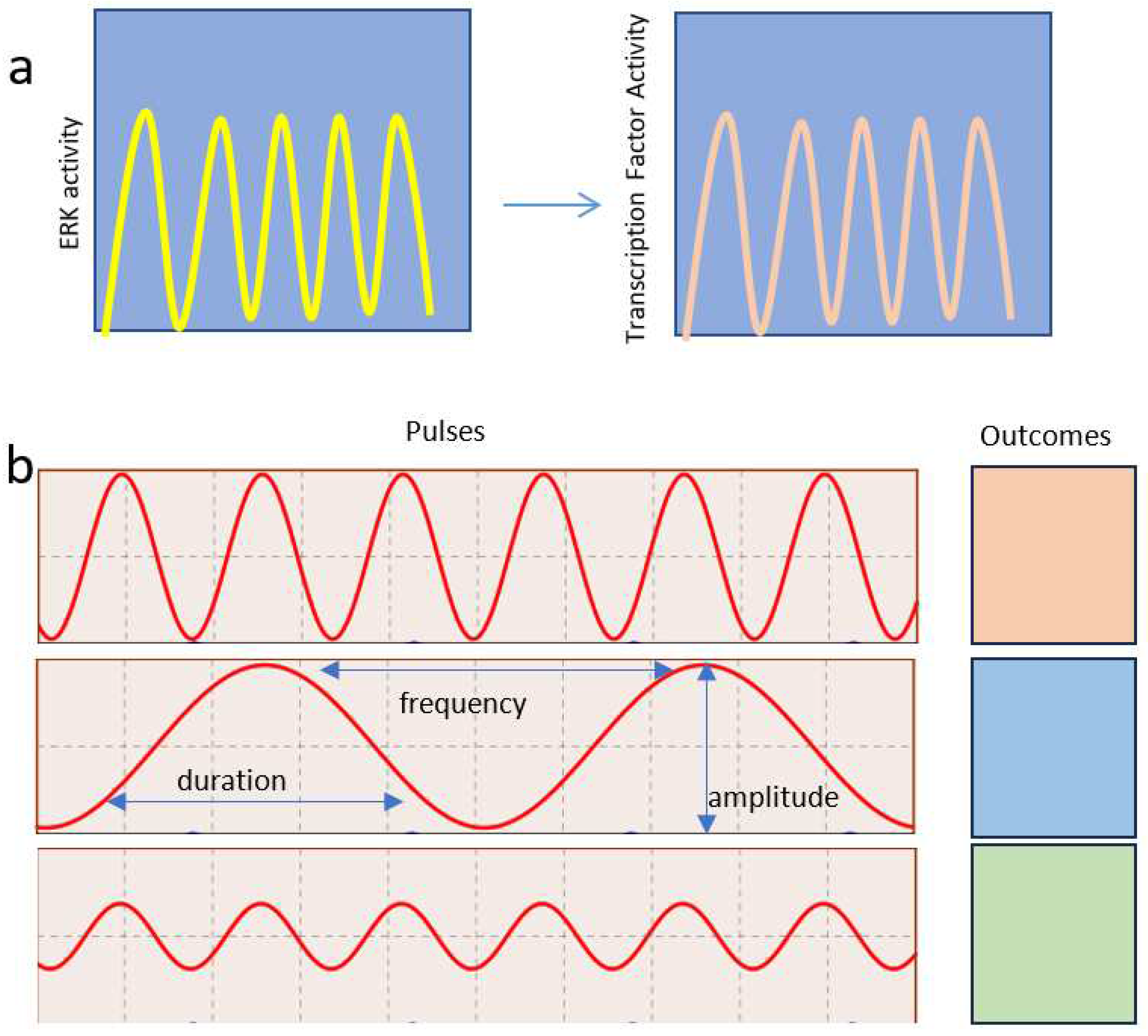
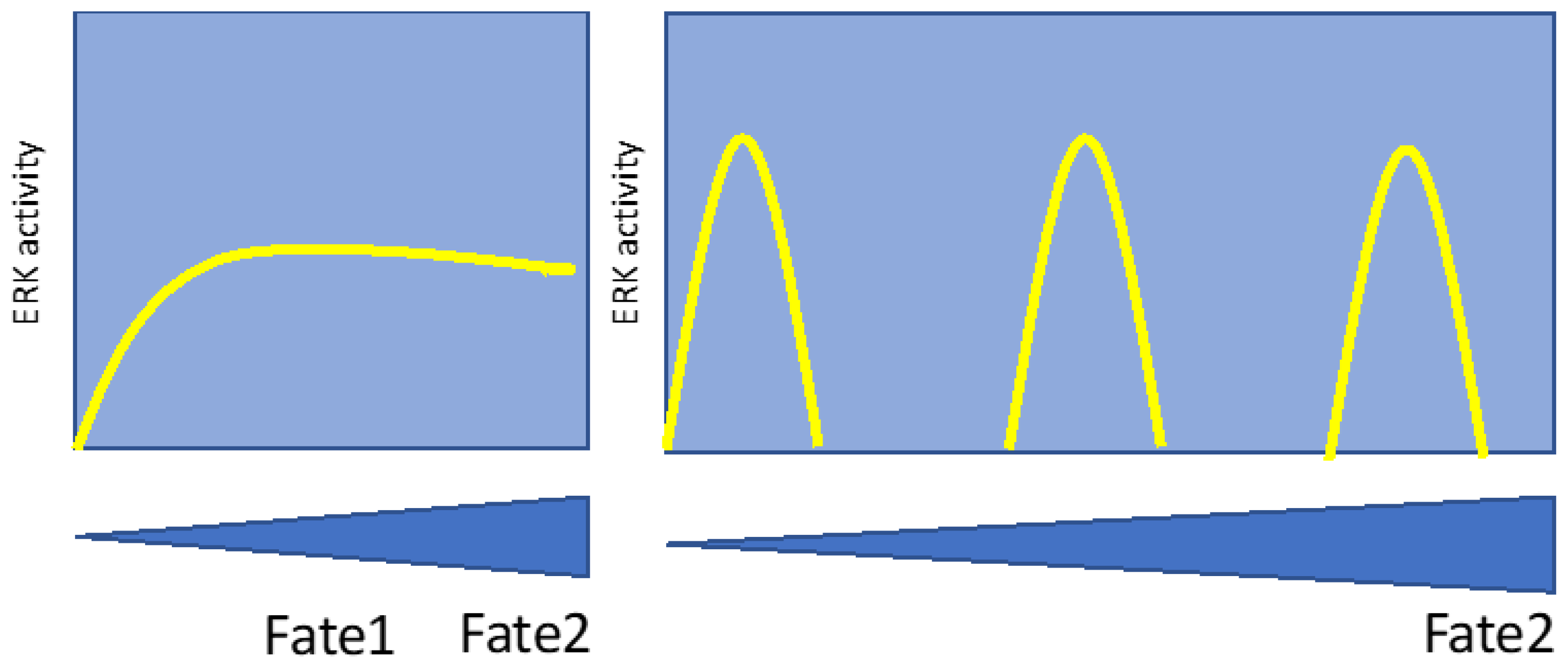
2.1. ERK pulses in cell proliferation and survival
3. Differentiation
4. Pluripotency
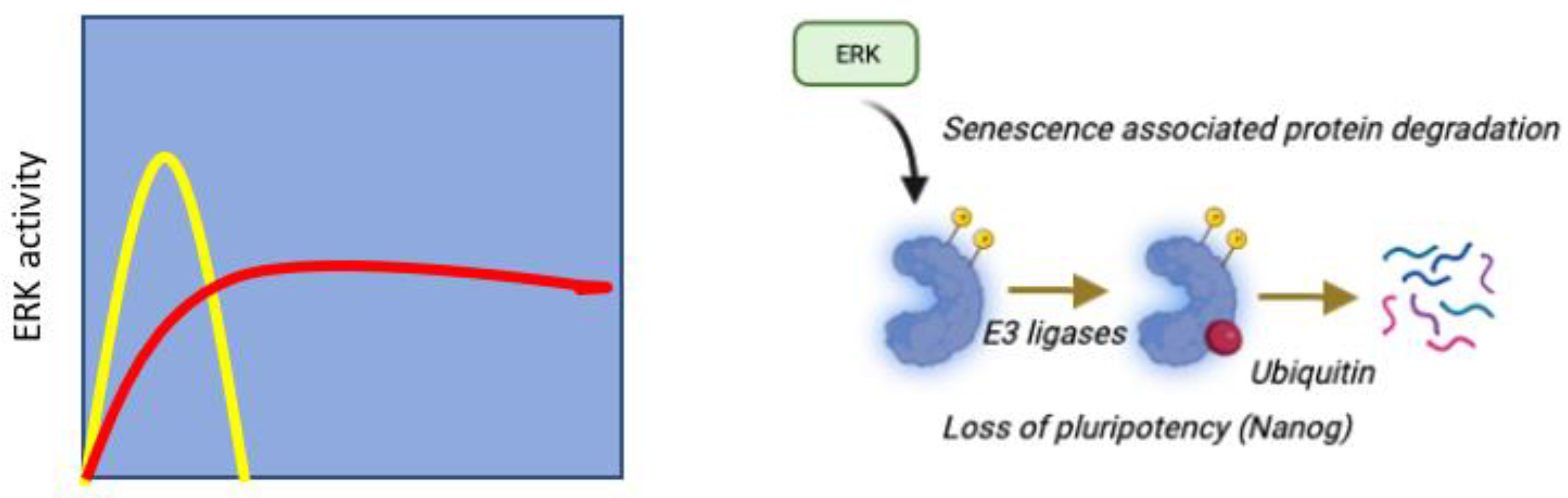
5. Senescence
6. EMT
7. Apoptosis
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deschenes-Simard, X.; Kottakis, F.; Meloche, S.; Ferbeyre, G. ERKs in cancer: friends or foes? Cancer Res 2014, 74, 412-419. [CrossRef]
- von Kriegsheim, A.; Baiocchi, D.; Birtwistle, M.; Sumpton, D.; Bienvenut, W.; Morrice, N.; Yamada, K.; Lamond, A.; Kalna, G.; Orton, R.; et al. Cell fate decisions are specified by the dynamic ERK interactome. Nat Cell Biol 2009, 11, 1458-1464. [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Wang, P.; Cao, P.; Zhu, J.K.; Tao, W.A. Identification of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) direct substrates using stable isotope labeled kinase assay-linked phosphoproteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 2014, 13, 3199-3210. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Chung, M.; Dobrzynski, M.; Fey, D.; Blum, Y.; Lee, S.S.; Peter, M.; Kholodenko, B.N.; Jeon, N.L.; Pertz, O. Frequency modulation of ERK activation dynamics rewires cell fate. Mol Syst Biol 2015, 11, 838. [CrossRef]
- Inder, K.; Hancock, J.F. System output of the MAPK module is spatially regulated. Commun Integr Biol 2008, 1, 178-179. [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.; Casar, B.; Colon-Bolea, P.; Agudo-Ibanez, L.; Crespo, P. Defined spatiotemporal features of RAS-ERK signals dictate cell fate in MCF-7 mammary epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 2016, 27, 1958-1968. [CrossRef]
- Kholodenko, B.N.; Hancock, J.F.; Kolch, W. Signalling ballet in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010, 11, 414-426. [CrossRef]
- Boulton, T.G.; Nye, S.H.; Robbins, D.J.; Ip, N.Y.; Radziejewska, E.; Morgenbesser, S.D.; DePinho, R.A.; Panayotatos, N.; Cobb, M.H.; Yancopoulos, G.D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell 1991, 65, 663-675. [CrossRef]
- Marshall, C.J. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell 1995, 80, 179-185, doi:0092-8674(95)90401-8 [pii].
- Hernandez, M.A.; Patel, B.; Hey, F.; Giblett, S.; Davis, H.; Pritchard, C. Regulation of BRAF protein stability by a negative feedback loop involving the MEK-ERK pathway but not the FBXW7 tumour suppressor. Cellular signalling 2016, 28, 561-571. [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.D.; Verveer, P.J.; Bastiaens, P.I. Growth factor-induced MAPK network topology shapes Erk response determining PC-12 cell fate. Nat Cell Biol 2007, 9, 324-330. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Lum, M.A.; Lewis, R.E.; Black, A.R.; Black, J.D. A novel antiproliferative PKCalpha-Ras-ERK signaling axis in intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2022, 298, 102121. [CrossRef]
- Lawan, A.; Al-Harthi, S.; Cadalbert, L.; McCluskey, A.G.; Shweash, M.; Grassia, G.; Grant, A.; Boyd, M.; Currie, S.; Plevin, R. Deletion of the dual specific phosphatase-4 (DUSP-4) gene reveals an essential non-redundant role for MAP kinase phosphatase-2 (MKP-2) in proliferation and cell survival. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 12933-12943. [CrossRef]
- Unni, A.M.; Harbourne, B.; Oh, M.H.; Wild, S.; Ferrarone, J.R.; Lockwood, W.W.; Varmus, H. Hyperactivation of ERK by multiple mechanisms is toxic to RTK-RAS mutation-driven lung adenocarcinoma cells. eLife 2018, 7. [CrossRef]
- Shojaee, S.; Caeser, R.; Buchner, M.; Park, E.; Swaminathan, S.; Hurtz, C.; Geng, H.; Chan, L.N.; Klemm, L.; Hofmann, W.K.; et al. Erk Negative Feedback Control Enables Pre-B Cell Transformation and Represents a Therapeutic Target in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 114-128. [CrossRef]
- Holck, S.; Bonde, J.; Pedersen, H.; Petersen, A.A.; Chaube, A.; Nielsen, H.J.; Larsson, L.I. Localization of active, dually phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 in colorectal cancer with or without activating BRAF and KRAS mutations. Hum Pathol 2016, 54, 37-46. [CrossRef]
- Finlay, D.; Healy, V.; Furlong, F.; O'Connell, F.C.; Keon, N.K.; Martin, F. MAP kinase pathway signalling is essential for extracellular matrix determined mammary epithelial cell survival. Cell death and differentiation 2000, 7, 302-313. [CrossRef]
- Blasco, R.B.; Francoz, S.; Santamaria, D.; Canamero, M.; Dubus, P.; Charron, J.; Baccarini, M.; Barbacid, M. c-Raf, but Not B-Raf, Is Essential for Development of K-Ras Oncogene-Driven Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 652-663. [CrossRef]
- Dehan, E.; Bassermann, F.; Guardavaccaro, D.; Vasiliver-Shamis, G.; Cohen, M.; Lowes, K.N.; Dustin, M.; Huang, D.C.; Taunton, J.; Pagano, M. betaTrCP- and Rsk1/2-mediated degradation of BimEL inhibits apoptosis. Mol Cell 2009, 33, 109-116. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Zong, C.S.; Xia, W.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ding, Q.; Xie, X.; Lang, J.Y.; Lai, C.C.; Chang, C.J.; Huang, W.C.; et al. ERK promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting FOXO3a via MDM2-mediated degradation. Nat Cell Biol 2008, 10, 138-148. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.O.; Smith, S.; Chen, R.H.; Fingar, D.C.; Blenis, J. Molecular interpretation of ERK signal duration by immediate early gene products. Nat Cell Biol 2002, 4, 556-564.
- Mylona, A.; Theillet, F.X.; Foster, C.; Cheng, T.M.; Miralles, F.; Bates, P.A.; Selenko, P.; Treisman, R. Opposing effects of Elk-1 multisite phosphorylation shape its response to ERK activation. Science 2016, 354, 233-237. [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, C.M.; Johnson, L.A.; Piccioni, F.; Townes, A.; Frederick, D.T.; Donahue, M.K.; Narayan, R.; Flaherty, K.T.; Wargo, J.A.; Root, D.E.; et al. A melanocyte lineage program confers resistance to MAP kinase pathway inhibition. Nature 2013, 504, 138-142. [CrossRef]
- Sears, R.; Nuckolls, F.; Haura, E.; Taya, Y.; Tamai, K.; Nevins, J.R. Multiple Ras-dependent phosphorylation pathways regulate Myc protein stability. Genes Dev 2000, 14, 2501-2514.
- Stefanovsky, V.Y.; Moss, T. The splice variants of UBF differentially regulate RNA polymerase I transcription elongation in response to ERK phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res 2008, 36, 5093-5101. [CrossRef]
- Albeck, J.G.; Mills, G.B.; Brugge, J.S. Frequency-modulated pulses of ERK activity transmit quantitative proliferation signals. Mol Cell 2013, 49, 249-261. [CrossRef]
- Lito, P.; Pratilas, C.A.; Joseph, E.W.; Tadi, M.; Halilovic, E.; Zubrowski, M.; Huang, A.; Wong, W.L.; Callahan, M.K.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Relief of profound feedback inhibition of mitogenic signaling by RAF inhibitors attenuates their activity in BRAFV600E melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 668-682. [CrossRef]
- Sale, M.J.; Balmanno, K.; Saxena, J.; Ozono, E.; Wojdyla, K.; McIntyre, R.E.; Gilley, R.; Woroniuk, A.; Howarth, K.D.; Hughes, G.; et al. MEK1/2 inhibitor withdrawal reverses acquired resistance driven by BRAF(V600E) amplification whereas KRAS(G13D) amplification promotes EMT-chemoresistance. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 2030. [CrossRef]
- Muta, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Sumiyama, K.; Sakurai, A.; Taketo, M.M.; Chiba, T.; Seno, H.; Aoki, K.; Matsuda, M.; Imajo, M. Composite regulation of ERK activity dynamics underlying tumour-specific traits in the intestine. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 2174. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Sohn, C.H.; Dalal, C.K.; Cai, L.; Elowitz, M.B. Combinatorial gene regulation by modulation of relative pulse timing. Nature 2015, 527, 54-58. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Potoyan, D.A.; Wolynes, P.G. Molecular stripping, targets and decoys as modulators of oscillations in the NF-kappaB/IkappaBalpha/DNA genetic network. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface / the Royal Society 2016, 13. [CrossRef]
- Ender, P.; Gagliardi, P.A.; Dobrzynski, M.; Frismantiene, A.; Dessauges, C.; Hohener, T.; Jacques, M.A.; Cohen, A.R.; Pertz, O. Spatiotemporal control of ERK pulse frequency coordinates fate decisions during mammary acinar morphogenesis. Dev Cell 2022, 57, 2153-2167 e2156. [CrossRef]
- Pokrass, M.J.; Ryan, K.A.; Xin, T.; Pielstick, B.; Timp, W.; Greco, V.; Regot, S. Cell-Cycle-Dependent ERK Signaling Dynamics Direct Fate Specification in the Mammalian Preimplantation Embryo. Dev Cell 2020, 55, 328-340 e325. [CrossRef]
- Byun, M.R.; Kim, A.R.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Hwang, E.S.; Hong, J.H. FGF2 stimulates osteogenic differentiation through ERK induced TAZ expression. Bone 2014, 58, 72-80. [CrossRef]
- Fremin, C.; Saba-El-Leil, M.K.; Levesque, K.; Ang, S.L.; Meloche, S. Functional Redundancy of ERK1 and ERK2 MAP Kinases during Development. Cell reports 2015, 12, 913-921. [CrossRef]
- Newbern, J.M.; Li, X.; Shoemaker, S.E.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, J.; Wu, Y.; Bonder, D.; Hollenback, S.; Coppola, G.; Geschwind, D.H.; et al. Specific functions for ERK/MAPK signaling during PNS development. Neuron 2011, 69, 91-105. [CrossRef]
- Parada, C.; Han, D.; Grimaldi, A.; Sarrion, P.; Park, S.S.; Pelikan, R.; Sanchez-Lara, P.A.; Chai, Y. Disruption of the ERK/MAPK pathway in neural crest cells as a potential cause of Pierre Robin sequence. Development (Cambridge, England) 2015, 142, 3734-3745. [CrossRef]
- Offermann, B.; Knauer, S.; Singh, A.; Fernandez-Cachon, M.L.; Klose, M.; Kowar, S.; Busch, H.; Boerries, M. Boolean Modeling Reveals the Necessity of Transcriptional Regulation for Bistability in PC12 Cell Differentiation. Front Genet 2016, 7, 44. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.E.; Toettcher, J.E. Signaling Dynamics Control Cell Fate in the Early Drosophila Embryo. Dev Cell 2019, 48, 361-370 e363. [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Smith, A. Capturing pluripotency. Cell 2008, 132, 532-536. [CrossRef]
- Pond, K.W.; Morris, J.M.; Alkhimenok, O.; Varghese, R.P.; Cabel, C.R.; Ellis, N.A.; Chakrabarti, J.; Zavros, Y.; Merchant, J.L.; Thorne, C.A.; et al. Live-cell imaging in human colonic monolayers reveals ERK waves limit the stem cell compartment to maintain epithelial homeostasis. eLife 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Mulas, C.; Kalkan, T.; von Meyenn, F.; Leitch, H.G.; Nichols, J.; Smith, A. Defined conditions for propagation and manipulation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Development (Cambridge, England) 2019, 146. [CrossRef]
- Chappell, J.; Sun, Y.; Singh, A.; Dalton, S. MYC/MAX control ERK signaling and pluripotency by regulation of dual-specificity phosphatases 2 and 7. Genes Dev 2013, 27, 725-733. [CrossRef]
- Mzoughi, S.; Zhang, J.; Hequet, D.; Teo, S.X.; Fang, H.; Xing, Q.R.; Bezzi, M.; Seah, M.K.Y.; Ong, S.L.M.; Shin, E.M.; et al. PRDM15 safeguards naive pluripotency by transcriptionally regulating WNT and MAPK-ERK signaling. Nat Genet 2017, 49, 1354-1363. [CrossRef]
- Nett, I.R.; Mulas, C.; Gatto, L.; Lilley, K.S.; Smith, A. Negative feedback via RSK modulates Erk-dependent progression from naive pluripotency. EMBO Rep 2018, 19. [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Li, Q.; Huang, S.; Lu, W.; Cheng, F.; Gao, P.; Wang, C.; Miao, L.; Mei, Y.; Wu, M. Mitochondrial E3 ligase March5 maintains stemness of mouse ES cells via suppression of ERK signalling. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 7112. [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.B.; Brickman, J.M. Erk signaling suppresses embryonic stem cell self-renewal to specify endoderm. Cell reports 2014, 9, 2056-2070. [CrossRef]
- Tee, W.W.; Shen, S.S.; Oksuz, O.; Narendra, V.; Reinberg, D. Erk1/2 activity promotes chromatin features and RNAPII phosphorylation at developmental promoters in mouse ESCs. Cell 2014, 156, 678-690. [CrossRef]
- Brons, I.G.; Smithers, L.E.; Trotter, M.W.; Rugg-Gunn, P.; Sun, B.; Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S.M.; Howlett, S.K.; Clarkson, A.; Ahrlund-Richter, L.; Pedersen, R.A.; et al. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature 2007, 448, 191-195. [CrossRef]
- Tesar, P.J.; Chenoweth, J.G.; Brook, F.A.; Davies, T.J.; Evans, E.P.; Mack, D.L.; Gardner, R.L.; McKay, R.D. New cell lines from mouse epiblast share defining features with human embryonic stem cells. Nature 2007, 448, 196-199. [CrossRef]
- Goke, J.; Chan, Y.S.; Yan, J.; Vingron, M.; Ng, H.H. Genome-wide kinase-chromatin interactions reveal the regulatory network of ERK signaling in human embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell 2013, 50, 844-855. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Samanta, D.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H.; Chen, I.; Bullen, J.W.; Semenza, G.L. Chemotherapy triggers HIF-1-dependent glutathione synthesis and copper chelation that induces the breast cancer stem cell phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, E4600-4609. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Tran, L.; Park, Y.; Chen, I.; Lan, J.; Xie, Y.; Semenza, G.L. Reciprocal Regulation of DUSP9 and DUSP16 Expression by HIF1 Controls ERK and p38 MAP Kinase Activity and Mediates Chemotherapy-Induced Breast Cancer Stem Cell Enrichment. Cancer Res 2018, 78, 4191-4202. [CrossRef]
- Deschenes-Simard, X.; Gaumont-Leclerc, M.F.; Bourdeau, V.; Lessard, F.; Moiseeva, O.; Forest, V.; Igelmann, S.; Mallette, F.A.; Saba-El-Leil, M.K.; Meloche, S.; et al. Tumor suppressor activity of the ERK/MAPK pathway by promoting selective protein degradation. Genes Dev 2013, 27, 900-915. [CrossRef]
- Deschenes-Simard, X.; Parisotto, M.; Rowell, M.C.; Le Calve, B.; Igelmann, S.; Moineau-Vallee, K.; Saint-Germain, E.; Kalegari, P.; Bourdeau, V.; Kottakis, F.; et al. Circumventing senescence is associated with stem cell properties and metformin sensitivity. Aging Cell 2019, e12889. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Martinez, E.; Morrisroe, C.; Sharrocks, A.D. The ubiquitin ligase UBE3A dampens ERK pathway signalling in HPV E6 transformed HeLa cells. PloS one 2015, 10, e0119366. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Fang, L.; Igarashi, M.; Ouchi, T.; Lu, K.P.; Aaronson, S.A. Sustained activation of Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by the tumor suppressor p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 8302-8305. [CrossRef]
- Deschenes-Simard, X.; Lessard, F.; Gaumont-Leclerc, M.F.; Bardeesy, N.; Ferbeyre, G. Cellular senescence and protein degradation: Breaking down cancer. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1840-1858. [CrossRef]
- Lessard, F.; Igelmann, S.; Trahan, C.; Huot, G.; Saint-Germain, E.; Mignacca, L.; Del Toro, N.; Lopes-Paciencia, S.; Le Calve, B.; Montero, M.; et al. Senescence-associated ribosome biogenesis defects contributes to cell cycle arrest through the Rb pathway. Nat Cell Biol 2018, 20, 789-799. [CrossRef]
- Igelmann, S.; Lessard, F.; Uchenunu, O.; Bouchard, J.; Fernandez-Ruiz, A.; Rowell, M.C.; Lopes-Paciencia, S.; Papadopoli, D.; Fouillen, A.; Ponce, K.J.; et al. A hydride transfer complex reprograms NAD metabolism and bypasses senescence. Mol Cell 2021, 81, 3848-3865 e3819. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Hug, C.; Reyes, J.; Tian, C.; Gerosa, L.; Frohlich, F.; Ponsioen, B.; Snippert, H.J.G.; Spencer, S.L.; Jambhekar, A.; et al. Multi-range ERK responses shape the proliferative trajectory of single cells following oncogene induction. Cell reports 2023, 42, 112252. [CrossRef]
- Rowell, M.C.; Deschenes-Simard, X.; Lopes-Paciencia, S.; Le Calve, B.; Kalegari, P.; Mignacca, L.; Fernandez-Ruiz, A.; Guillon, J.; Lessard, F.; Bourdeau, V.; et al. Targeting ribosome biogenesis reinforces ERK-dependent senescence in pancreatic cancer. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex 2023, 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Wu, W.; Ponce, R.K.; Kim, J.W.; Okimoto, R.A. Negative MAPK-ERK regulation sustains CIC-DUX4 oncoprotein expression in undifferentiated sarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 20776-20784. [CrossRef]
- Ingram, K.; Samson, S.C.; Zewdu, R.; Zitnay, R.G.; Snyder, E.L.; Mendoza, M.C. NKX2-1 controls lung cancer progression by inducing DUSP6 to dampen ERK activity. Oncogene 2022, 41, 293-300. [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Young, M.J.; Li, R.; Jain, S.; Wernitznig, A.; Krill-Burger, J.M.; Lemke, C.T.; Monducci, D.; Rodriguez, D.J.; Chang, L.; et al. Paralog knockout profiling identifies DUSP4 and DUSP6 as a digenic dependence in MAPK pathway-driven cancers. Nat Genet 2021, 53, 1664-1672. [CrossRef]
- Kidger, A.M.; Rushworth, L.K.; Stellzig, J.; Davidson, J.; Bryant, C.J.; Bayley, C.; Caddye, E.; Rogers, T.; Keyse, S.M.; Caunt, C.J. Dual-specificity phosphatase 5 controls the localized inhibition, propagation, and transforming potential of ERK signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, E317-E326. [CrossRef]
- Sangrar, W.; Shi, C.; Mullins, G.; LeBrun, D.; Ingalls, B.; Greer, P.A. Amplified Ras-MAPK signal states correlate with accelerated EGFR internalization, cytostasis and delayed HER2 tumor onset in Fer-deficient model systems. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4109-4117. [CrossRef]
- Moniz, S.; Verissimo, F.; Matos, P.; Brazao, R.; Silva, E.; Kotelevets, L.; Chastre, E.; Gespach, C.; Jordan, P. Protein kinase WNK2 inhibits cell proliferation by negatively modulating the activation of MEK1/ERK1/2. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6071-6081. [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Tien, J.C.; Siebenaler, R.F.; Chugh, S.; Dommeti, V.L.; Zelenka-Wang, S.; Wang, X.M.; Apel, I.J.; Waninger, J.; Eyunni, S.; et al. An essential role for Argonaute 2 in EGFR-KRAS signaling in pancreatic cancer development. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2817. [CrossRef]
- Tien, J.C.; Chugh, S.; Goodrum, A.E.; Cheng, Y.; Mannan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Dommeti, V.L.; Wang, X.; Xu, A.; et al. AGO2 promotes tumor progression in KRAS-driven mouse models of non-small cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118. [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.K.; Hong, S.K.; Park, J.I. Steady-State Levels of Phosphorylated Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 1/2 Determined by Mortalin/HSPA9 and Protein Phosphatase 1 Alpha in KRAS and BRAF Tumor Cells. Mol Cell Biol 2017, 37. [CrossRef]
- Kasitinon, S.Y.; Eskiocak, U.; Martin, M.; Bezwada, D.; Khivansara, V.; Tasdogan, A.; Zhao, Z.; Mathews, T.; Aurora, A.B.; Morrison, S.J. TRPML1 Promotes Protein Homeostasis in Melanoma Cells by Negatively Regulating MAPK and mTORC1 Signaling. Cell reports 2019, 28, 2293-2305 e2299. [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, N.; D'Alessandro, L.A.; Depner, S.; Hahn, B.; Kramer, B.A.; Lucarelli, P.; Vlasov, A.; Stepath, M.; Bohm, M.E.; Deharde, D.; et al. Context-specific flow through the MEK/ERK module produces cell- and ligand-specific patterns of ERK single and double phosphorylation. Sci Signal 2016, 9, ra13. [CrossRef]
- Buonato, J.M.; Lazzara, M.J. ERK1/2 blockade prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells and promotes their sensitivity to EGFR inhibition. Cancer Res 2014, 74, 309-319. [CrossRef]
- Caramel, J.; Papadogeorgakis, E.; Hill, L.; Browne, G.J.; Richard, G.; Wierinckx, A.; Saldanha, G.; Osborne, J.; Hutchinson, P.; Tse, G.; et al. A switch in the expression of embryonic EMT-inducers drives the development of malignant melanoma. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 466-480. [CrossRef]
- Doehn, U.; Hauge, C.; Frank, S.R.; Jensen, C.J.; Duda, K.; Nielsen, J.V.; Cohen, M.S.; Johansen, J.V.; Winther, B.R.; Lund, L.R.; et al. RSK is a principal effector of the RAS-ERK pathway for eliciting a coordinate promotile/invasive gene program and phenotype in epithelial cells. Mol Cell 2009, 35, 511-522. [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Dimitri, C.A.; Yoon, S.O.; Dowdle, W.; Blenis, J. ERK2 but not ERK1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation via DEF motif-dependent signaling events. Mol Cell 2010, 38, 114-127. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Guin, S.; Padhye, S.S.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.W.; Wang, M.H. Ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RSK)-2 as a central effector molecule in RON receptor tyrosine kinase mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by macrophage-stimulating protein. Molecular cancer 2011, 10, 66. [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, K.; Kubota, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Weng, J.S.; Tomida, T.; Saito, H.; Takekawa, M. MCRIP1, an ERK substrate, mediates ERK-induced gene silencing during epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the co-repressor CtBP. Mol Cell 2015, 58, 35-46. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; El-Naggar, S.; Darling, D.S.; Higashi, Y.; Dean, D.C. Zeb1 links epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cellular senescence. Development (Cambridge, England) 2008, 135, 579-588. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Jiang, G.; Dean, K.C.; Clem, B.; Telang, S.; Jenson, A.B.; Cuatrecasas, M.; et al. Different thresholds of ZEB1 are required for Ras-mediated tumour initiation and metastasis. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 5660. [CrossRef]
- Ansieau, S.; Bastid, J.; Doreau, A.; Morel, A.P.; Bouchet, B.P.; Thomas, C.; Fauvet, F.; Puisieux, I.; Doglioni, C.; Piccinin, S.; et al. Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 79-89.
- Weiss, M.B.; Abel, E.V.; Mayberry, M.M.; Basile, K.J.; Berger, A.C.; Aplin, A.E. TWIST1 is an ERK1/2 effector that promotes invasion and regulates MMP-1 expression in human melanoma cells. Cancer Res 2012, 72, 6382-6392. [CrossRef]
- Principe, D.R.; Diaz, A.M.; Torres, C.; Mangan, R.J.; DeCant, B.; McKinney, R.; Tsao, M.S.; Lowy, A.; Munshi, H.G.; Jung, B.; et al. TGFbeta engages MEK/ERK to differentially regulate benign and malignant pancreas cell function. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4336-4348. [CrossRef]
- Deschenes-Simard, X.; Rowell, M.C.; Ferbeyre, G. Metformin turns off the metabolic switch of pancreatic cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 2019, 11, 10793-10795. [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, M.E.; DeNicola, G.M.; Martins, C.P.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Maitra, A.; Hruban, R.H.; Tuveson, D.A. Cellular features of senescence during the evolution of human and murine ductal pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1599-1608. [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.; Collado, M.; Navas, C.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Hernandez-Porras, I.; Canamero, M.; Rodriguez-Justo, M.; Serrano, M.; Barbacid, M. Pancreatitis-induced inflammation contributes to pancreatic cancer by inhibiting oncogene-induced senescence. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 728-739. [CrossRef]
- Rhim, A.D.; Mirek, E.T.; Aiello, N.M.; Maitra, A.; Bailey, J.M.; McAllister, F.; Reichert, M.; Beatty, G.L.; Rustgi, A.K.; Vonderheide, R.H.; et al. EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic tumor formation. Cell 2012, 148, 349-361. [CrossRef]
- Blaj, C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Lamprecht, S.; Hermeking, H.; Jung, A.; Kirchner, T.; Horst, D. Oncogenic Effects of High MAPK Activity in Colorectal Cancer Mark Progenitor Cells and Persist Irrespective of RAS Mutations. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 1763-1774. [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.Y.; Hsin, I.L.; Yang, T.Y.; Sung, W.W.; Chi, J.Y.; Chang, J.T.; Ko, J.L.; Sheu, G.T. The ERK-ZEB1 pathway mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pemetrexed resistant lung cancer cells with suppression by vinca alkaloids. Oncogene 2017, 36, 242-253. [CrossRef]
- Latil, M.; Nassar, D.; Beck, B.; Boumahdi, S.; Wang, L.; Brisebarre, A.; Dubois, C.; Nkusi, E.; Lenglez, S.; Checinska, A.; et al. Cell-Type-Specific Chromatin States Differentially Prime Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tumor-Initiating Cells for Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Cell stem cell 2017, 20, 191-204 e195. [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, R.; Satoh, R.; Takasaki, T. ERK: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer. ERK-Dependent Apoptosis as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Cells 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Buel, G.R.; Wolgamott, L.; Plas, D.R.; Asara, J.M.; Blenis, J.; Yoon, S.O. ERK2 Mediates Metabolic Stress Response to Regulate Cell Fate. Mol Cell 2015, 59, 382-398. [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.K.; Wu, P.K.; Park, J.I. A cellular threshold for active ERK1/2 levels determines Raf/MEK/ERK-mediated growth arrest versus death responses. Cellular signalling 2018, 42, 11-20. [CrossRef]
- Leung, G.P.; Feng, T.; Sigoillot, F.D.; Geyer, F.C.; Shirley, M.D.; Ruddy, D.A.; Rakiec, D.P.; Freeman, A.K.; Engelman, J.A.; Jaskelioff, M.; et al. Hyperactivation of MAPK Signaling Is Deleterious to RAS/RAF-mutant Melanoma. Mol Cancer Res 2019, 17, 199-211. [CrossRef]
- Ecker, V.; Brandmeier, L.; Stumpf, M.; Giansanti, P.; Moreira, A.V.; Pfeuffer, L.; Fens, M.; Lu, J.; Kuster, B.; Engleitner, T.; et al. Negative feedback regulation of MAPK signaling is an important driver of chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression. Cell reports 2023, 42, 113017. [CrossRef]
- Ruscetti, M.; Leibold, J.; Bott, M.J.; Fennell, M.; Kulick, A.; Salgado, N.R.; Chen, C.C.; Ho, Y.J.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Feucht, J.; et al. NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity contributes to tumor control by a cytostatic drug combination. Science 2018, 362, 1416-1422. [CrossRef]
- Viale, A.; Pettazzoni, P.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Ying, H.; Sanchez, N.; Marchesini, M.; Carugo, A.; Green, T.; Seth, S.; Giuliani, V.; et al. Oncogene ablation-resistant pancreatic cancer cells depend on mitochondrial function. Nature 2014, 514, 628-632. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




