Submitted:
25 November 2023
Posted:
28 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
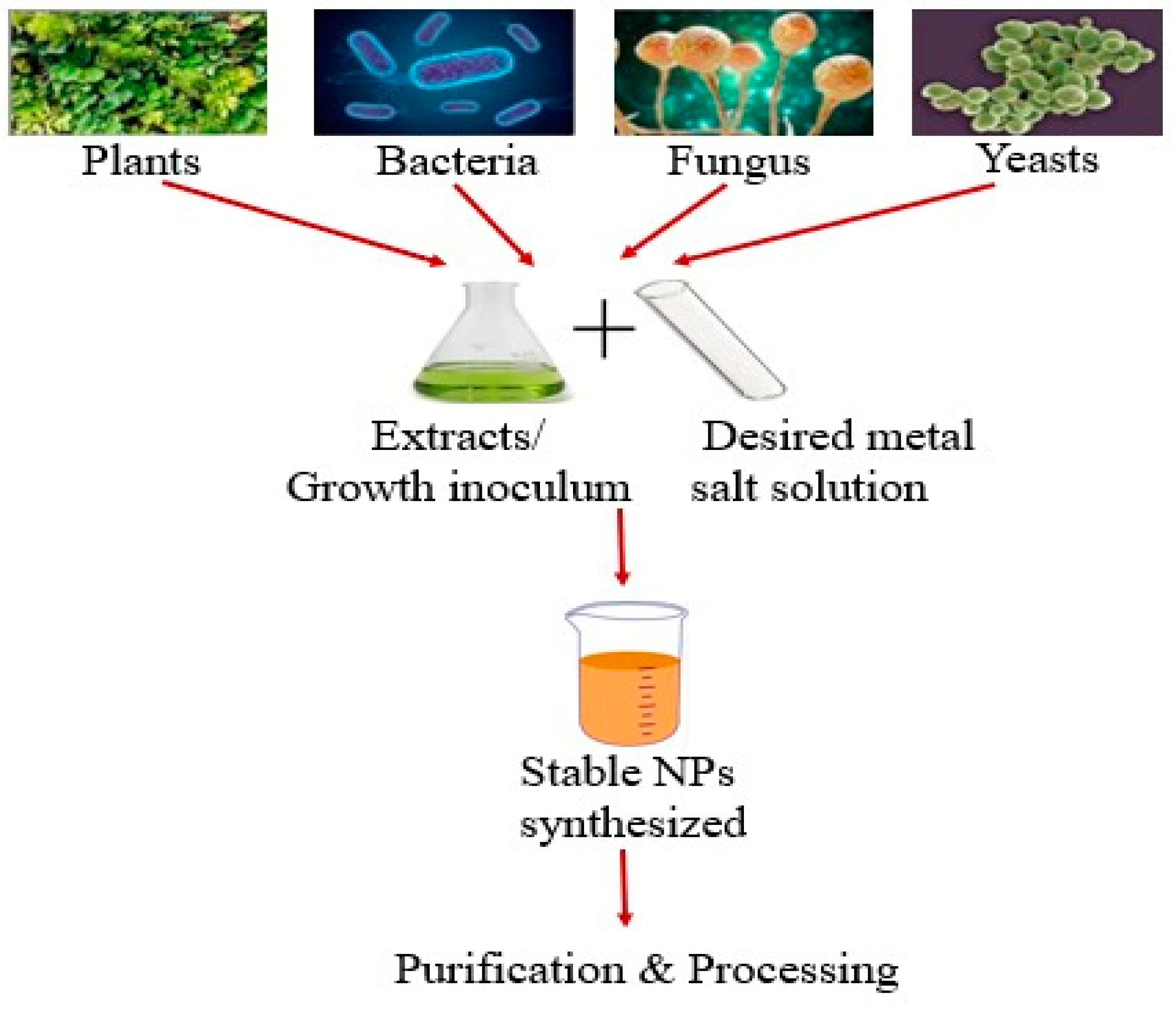
2. Routes of Synthesis of Biogenic Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.1. Plants
2.2. Microorganisms
2.2.1. Bacteria
2.2.2. Fungi
2.2.3. Yeast
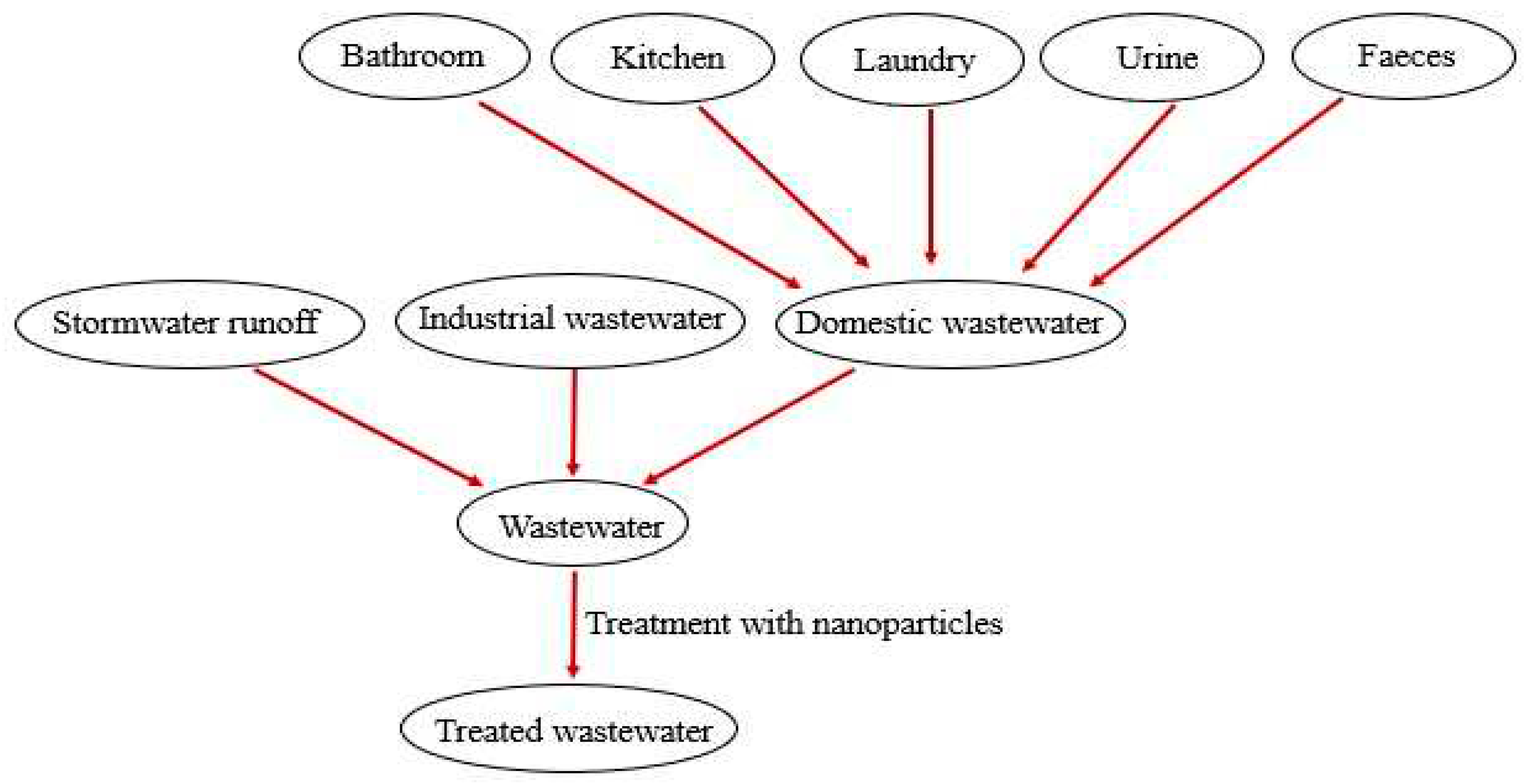
3. Applications of Biogenic Nanoparticles (NPs) for the Treatment of Wastewater
3.1. Removal of Organic Pollutants
3.2. Removal of Pharmaceutical Pollutants
3.3. Removal of Inorganic and Radioactive Pollutants
3.4. Removal of Heavy Metals
4. Conclusions and Future Recommendations
Funding
Author’s Contributions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest/Competing Interest
Availability of Data and Materials
Code Availability
References
- Agnihotri: M. et al. (2009) ‘Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by the tropical marine yeast Yarrowia lipolytica NCIM 3589’, Materials Letters, 63(15), pp. 1231–1234. [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S., Panwar, J. and Yun, Y.S. (2013) ‘Biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by plant extracts’, ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 1(6), pp. 591–602. [CrossRef]
- Al-Ruqeishi, M.S., Mohiuddin, T. and Al-Saadi, L.K. (2019) ‘Green synthesis of iron oxide nanorods from deciduous Omani mango tree leaves for heavy oil viscosity treatment’, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 12(8), pp. 4084–4090. [CrossRef]
- AlNadhari, S. et al. (2021) ‘A review on biogenic synthesis of metal nanoparticles using marine algae and its applications’, Environmental Research, 194, p. 110672. [CrossRef]
- Andjelkovic, I. et al. (2017) ‘Bacterial iron-oxide nanowires from biofilm waste as a new adsorbent for the removal of arsenic from water’, RSC Advances, 7(7), pp. 3941–3948. [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.K., Srivastava, A. and Singh, V.P. (2014) ‘Bacterial degradation of nitrophenols and their derivatives’, Journal of Hazardous Materials, 266, pp. 42–59. [CrossRef]
- Arya, A., Mishra, V. and Chundawat, T.S. (2019) ‘Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from green algae (Botryococcus braunii) and its catalytic behavior for the synthesis of benzimidazoles’, Chemical Data Collections, 20. [CrossRef]
- Baig, N. et al. (2021) ‘Nanomaterials: a review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges’, Materials Advances, 2(6), pp. 1821–1871. [CrossRef]
- Baymiller, M., Huang, F. and Rogelj, S. (2017) ‘Rapid one-step synthesis of gold nanoparticles using the ubiquitous conzyme NADH’, Matters [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, S. et al. (2020) ‘Extracellular synthesis of nanoselenium from fresh water bacteria Bacillus sp., and its validation of antibacterial and cytotoxic potential’, Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 27, p. 101655. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.K. et al. (2019) ‘Bacterial killing efficacy of synthesized rod shaped cuprous oxide nanoparticles using laser ablation technique’, SN Applied Sciences, 1(11), pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L.K. and Jindal, T. (2019) ‘Contamination of Lakes in Broknes Peninsula, East Antarctica through the Pesticides and PAHs’, Asian-Journal of Chemistry, 31(7), pp. 1574–1580. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.K. et al. (2022b) ‘Biogenic and Non-Biogenic Waste for the Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Applications’, in Bioremediation. CRC Press, pp. 207–218. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.K. and Naraian, R. (2021) ‘Cyanobacteria as biochemical energy source for the synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles, mechanism and potential applications: a review’, 3 Biotech, 11(10). [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L. K. et al. (2020) ‘Persistent organic pollutants in lakes of Broknes peninsula at Larsemann Hills area, East Antarctica’, Ecotoxicology, 28(5), pp. 589–596. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L.K., Rath, P. and Choudhury, M. (2022a) ‘A Comprehensive Review on the Classification, Uses, Sources of Nanoparticles (NPs) and Their Toxicity on Health’, Aerosol Science and Engineering, pp. 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L.K. and Sharma, A. (2021) ‘Estimation of Physico-Chemical, Trace Metals, Microbiological and Phthalate in PET Bottled Water’, Chemistry Africa, 4(4), pp. 981–991. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L.K. (2022) ‘Evaluation of Bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in the PET Bottled Mineral Water of Different Brands and Impact of Heat by GC-MS/MS’, Chemistry Africa, 5(4), pp. 929–942. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L.K., Sharma, S. and Jindal, T. (2021) ‘Occurrence of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Lake Water at Grovnes Peninsula Over East Antarctica’, Chemistry Africa, 4(4), pp. 965–980. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L.K., Kumar, D. and Kumar, A. (2023a) ‘Phytoremediation Potential of Ocimum Sanctum: A Sustainable Approach for Remediation of Heavy Metals’. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L.K., Sharma, S. and Jindal, T. (2023b) ‘Estimation of Physico-Chemical and Heavy Metals in the Lakes of Grovnes & Broknes Peninsula, Larsemann Hill, East Antarctica’, Chemistry Africa, pp. 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A. et al. (2016) ‘Utilizing metal tolerance potential of soil fungus for efficient synthesis of gold nanoparticles with superior catalytic activity for degradation of rhodamine B’, Journal of environmental management, 183, pp. 22–32. [CrossRef]
- Buzea, C., Pacheco, I.I. and Robbie, K. (2007) ‘Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: Sources and toxicity’, Biointerphases, 2(4), p. MR17. [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A., Alonso, A. and Salamanca, A. (2005) ‘Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: a review with new data for freshwater invertebrates’, Chemosphere, 58(9), pp. 1255–1267. [CrossRef]
- Camp, J.E. et al. (2014) ‘Glucose-derived palladium(0) nanoparticles as in situ-formed catalysts for suzuki-miyaura cross-coupling reactions in isopropanol’, ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 2(3), pp. 500–505. [CrossRef]
- Cao, D. et al. (2016) ‘Removal of phosphate using iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by eucalyptus leaf extract in the presence of CTAB surfactant’, Chemosphere, 159, pp. 23–31. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S. et al. (2020) ‘Biofabrication of iron oxide nanoparticles using manglicolous fungus Aspergillus niger BSC-1 and removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution’, Chemical Engineering Journal, 385, p. 123790. [CrossRef]
- Chipasa, K.B. (2003) ‘Accumulation and fate of selected heavy metals in a biological wastewater treatment system’, Waste management (New York, N.Y.), 23(2), pp. 135–143. [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.H. et al. (2017) ‘Efficient bioremediation of radioactive iodine using biogenic gold nanomaterial-containing radiation-resistant bacterium, Deinococcus radiodurans R1’, Chemical Communications, 53(28), pp. 3937–3940. [CrossRef]
- Colin, J.A. et al. (2018) ‘Gold nanoparticles synthesis assisted by marine algae extract: Biomolecules shells from a green chemistry approach’, Chemical Physics Letters, 708, pp. 210–215. [CrossRef]
- Costa Silva, L.P. et al. (2017) ‘Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the cell-free filtrate of nematophagous fungus Duddingtonia flagrans’, International Journal of Nanomedicine, 12, p. 6373. [CrossRef]
- De Corte, S. et al. (2012) ‘Biosupported bimetallic Pd-Au nanocatalysts for dechlorination of environmental contaminants’, Environmental science & technology, 45(19), pp. 8506–8513. [CrossRef]
- De Gusseme, B. et al. (2011) ‘Biogenic palladium enhances diatrizoate removal from hospital wastewater in a microbial electrolysis cell’, Environmental Science and Technology, 45(13), pp. 5737–5745. [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, P. et al. (2020) ‘Ureolytic bacteria mediated synthesis of hairy ZnO nanostructure as photocatalyst for decolorization of dyes’, Materials Chemistry and Physics, 243, p. 122619. [CrossRef]
- Ehrampoush, M.H. et al. (2015) ‘Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by green synthesis iron oxide nanoparticles with tangerine peel extract’, Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 13(1), pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Fewtrell, L. (2004) ‘Drinking-Water Nitrate, Methemoglobinemia, and Global Burden of Disease: A Discussion’, Environmental Health Perspectives, 112(14), p. 1371. [CrossRef]
- Forrez, I. et al. (2011) ‘Biogenic metals for the oxidative and reductive removal of pharmaceuticals, biocides and iodinated contrast media in a polishing membrane bioreactor’, Water research, 45(4), pp. 1763–1773. [CrossRef]
- Furgal, K.M., Meyer, R.L. and Bester, K. (2015) ‘Removing selected steroid hormones, biocides and pharmaceuticals from water by means of biogenic manganese oxide nanoparticles in situ at ppb levels’, Chemosphere, 136, pp. 321–326. [CrossRef]
- Gan, L. et al. (2018) ‘Effects of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide on the morphology of green synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles used to remove phosphate’, Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications, 82, pp. 41–45. [CrossRef]
- Gangappa, R., Farrier, A. and Macaskie, L.E. (2017) ‘Eu3+ Sequestration by Biogenic Nano-Hydroxyapatite Synthesized at Neutral and Alkaline pH’, Geomicrobiology Journal, 34(9), pp. 753–759. [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.K. et al. (2019) ‘Synthesis and applications of biogenic nanomaterials in drinking and wastewater treatment’, Journal of Environmental Management, 231, pp. 734–748. [CrossRef]
- Gawande, K. and Jenkins-Smith, H. (2001) ‘Nuclear Waste Transport and Residential Property Values: Estimating the Effects of Perceived Risks’, Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 42(2), pp. 207–233. [CrossRef]
- González-Ballesteros, N. et al. (2017) ‘Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using brown algae Cystoseira baccata: Its activity in colon cancer cells’, Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 153, pp. 190–198. [CrossRef]
- Gudikandula, K., Vadapally, P. and Charya, M.A.S. (2017) ‘Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles from white rot fungi: Their characterization and antibacterial studies’, OpenNano, 2, pp. 64–78. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P., Sharma, A. and Bhardwaj, L.K. (2023) ‘Solid Waste Management (SWM) and Its Effect on Environment & Human Health’. [CrossRef]
- Handley-Sidhu, S. et al. (2011a) ‘Nano-crystalline hydroxyapatite bio-mineral for the treatment of strontium from aqueous solutions’, Biotechnology letters, 33(1), pp. 79–87. [CrossRef]
- Handley-Sidhu, S. et al. (2011b) ‘Uptake of Sr 2+ and Co 2+ into biogenic hydroxyapatite: Implications for biomineral ion exchange synthesis’, Environmental Science and Technology, 45(16), pp. 6985–6990. [CrossRef]
- Handley-Sidhu, S. et al. (2014) ‘Bacterially produced calcium phosphate nanobiominerals: Sorption capacity, site preferences, and stability of captured radionuclides’, Environmental Science and Technology, 48(12), pp. 6891–6898. [CrossRef]
- Hannah, W. and Thompson, P.B. (2008) ‘Nanotechnology, risk and the environment: a review’, Journal of environmental monitoring : JEM, 10(3), pp. 291–300. [CrossRef]
- Hulikere, M.M. and Joshi, C.G. (2019) ‘Characterization, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using marine endophytic fungus-Cladosporium cladosporioides’, Process biochemistry, 82, pp. 199–204. [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. and Varma, R.S. (2020) ‘Greener synthesis of lignin nanoparticles and their applications’, Green Chemistry, 22(3), pp. 612–636. [CrossRef]
- Jain, R. et al. (2015) ‘Adsorption of zinc by biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles’, Chemical Engineering Journal, 260, pp. 855–863. [CrossRef]
- Jannathul Firdhouse, M. and Lalitha, P. (2022) ‘Biogenic green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their applications – A review of promising properties’, Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 143, p. 109800. [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K., Prasad, K. and Kulkarni, A.R. (2009) ‘Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using microorganisms’, Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 71(2), pp. 226–229. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z., Shi, M. and Shi, L. (2020) ‘Degradation of organic contaminants and steel corrosion by the dissimilatory metal-reducing microorganisms Shewanella and Geobacter spp.’, International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 147, p. 104842. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, C.G. et al. (2017) ‘Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles by marine endophytic fungus-Cladosporium cladosporioides isolated from seaweed and evaluation of their antioxidant and antimicrobial properties’, Process Biochemistry, 63, pp. 137–144. [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, R. (2017) ‘A novel single step synthesis and surface functionalization of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles and thereof for the copper removal from pigment industry effluent’, Separation and Purification Technology, 188, pp. 458–467. [CrossRef]
- Katata-Seru, L. et al. (2017) ‘Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera extracts and their applications: Removal of nitrate from water and antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli’, Journal of Molecular Liquids, 256, pp. 296–304. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.T. and Jamil Khan, M. (2017) ‘Biogenic Nanoparticles: An Introduction to What They Are and How They Are Produced’, International Journal of Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 3(3), pp. 66–70. [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.H. et al. (2016) ‘Enhanced photocatalytic and electrocatalytic applications of green synthesized silver nanoparticles’, Journal of Molecular Liquids, 220, pp. 248–257. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.D. et al. (2007) ‘Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in South Korean surface, drinking, and waste waters’, Water research, 41(5), pp. 1013–1021. [CrossRef]
- Klaus-Joerger, T. et al. (2001) ‘Bacteria as workers in the living factory: Metal-accumulating bacteria and their potential for materials science’, Trends in Biotechnology, 19(1), pp. 15–20. [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y. et al. (2013) ‘Heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation of monochlorobenzene using green synthesis of iron nanoparticles’, Journal of colloid and interface science, 410, pp. 67–73. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V. et al. (2019) ‘Preparation of yeast mediated semiconductor nanoparticles by candida albicans and its bactericidal potential against Salmonella typhi and Staphylococcus aureus’, Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci., 10(2), pp. 861–864. [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J. et al. (2012) ‘Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: A review of sources, fate and occurrence’, Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987), 163, pp. 287–303. [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T. et al. (2011) ‘Novel silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties and applications’, International Journal of Nanotechnology, 8(3–5), pp. 278–290. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H. and Jun, B.H. (2019) ‘Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Application for Nanomedicine’, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(4), p. 865. [CrossRef]
- Lian, S. et al. (2019) ‘Characterization of biogenic selenium nanoparticles derived from cell-free extracts of a novel yeast Magnusiomyces ingens’, 3 Biotech, 9(6), pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Lingamdinne, L.P. et al. (2017) ‘Biogenic reductive preparation of magnetic inverse spinel iron oxide nanoparticles for the adsorption removal of heavy metals’, Chemical Engineering Journal, 307, pp. 74–84. [CrossRef]
- Lunge, S., Singh, S. and Sinha, A. (2014) ‘Magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles from tea waste for arsenic removal’, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 356, pp. 21–31. [CrossRef]
- Madhavi, V. et al. (2013) ‘Application of phytogenic zerovalent iron nanoparticles in the adsorption of hexavalent chromium’, Spectrochimica acta. Part A, Molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy, 116, pp. 17–25. [CrossRef]
- Majhi, K.C. and Yadav, M. (2021) ‘Synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using carbohydrates’, Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science: Green Inorganic Synthesis, pp. 109–135. [CrossRef]
- Malik, B. et al. (2017) ‘Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Application in Pharmaceutical Industry’, Nanotechnology: Food and Environmental Paradigm, pp. 235–252. [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D. et al. (2006) ‘The use of microorganisms for the formation of metal nanoparticles and their application’, Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 69(5), pp. 485–492. [CrossRef]
- Manikandakrishnan, M. et al. (2019) ‘Facile green route synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Caulerpa racemosa for biomedical applications’, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 54, p. 101345. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cabanas, M. et al. (2016) ‘Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. Development of magnetic hybrid materials for efficient As(V) removal’, Chemical Engineering Journal, 301, pp. 83–91. [CrossRef]
- Martins, M. et al. (2017) ‘Biogenic platinum and palladium nanoparticles as new catalysts for the removal of pharmaceutical compounds’, Water research, 108, pp. 160–168. [CrossRef]
- Markus, J. et al. (2016) ‘Intracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles with antioxidant activity by probiotic Lactobacillus kimchicus DCY51T isolated from Korean kimchi’, Enzyme and microbial technology, 95, pp. 85–93. [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, K. et al. (2019) ‘Biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria: Synthesis, calcination and characterization’, Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 22, p. 101373. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A. et al. (2014) ‘Biocatalytic and antimicrobial activities of gold nanoparticles synthesized by Trichoderma sp’, Bioresource technology, 166, pp. 235–242. [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, A.B. et al. (2015) ‘Nanoparticles Biosynthesized by Fungi and Yeast: A Review of Their Preparation, Properties, and Medical Applications’, Molecules, 20(9), p. 16540. [CrossRef]
- Molnár, Z. et al. (2018) ‘Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles by thermophilic filamentous fungi’, Scientific Reports, 8(1), pp. 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S., Pallares, R.M. and Thanh, N.T.K. (2018) ‘Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties’, Nanoscale, 10(27), pp. 12871–12934. [CrossRef]
- Mughal, B. et al. (2021) ‘Biogenic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterisation and Applications’, Applied Sciences, 11(6), p. 2598. [CrossRef]
- Mubarakali, D. et al. (2012) ‘Synthesis and characterization of CdS nanoparticles using C-phycoerythrin from the marine cyanobacteria’, Materials Letters, 74, pp. 8–11. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D. et al. (2016) ‘Green synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for arsenic(V) remediation with a novel aspect for sludge management’, Journal of environmental chemical engineering, 4(1), pp. 639–650. [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, H. et al. (2017) ‘Biogenic synthesis of nano-biomaterial for toxic naphthalene photocatalytic degradation optimization and kinetics studies’, International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 119, pp. 587–594. [CrossRef]
- Mystrioti, C. et al. (2016) ‘Comparative evaluation of five plant extracts and juices for nanoiron synthesis and application for hexavalent chromium reduction’, The Science of the total environment, 539, pp. 105–113. [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, S., Cheirmadurai, K. and Thanikaivelan, P. (2021) ‘Visible-light active collagen-TiO2 nanobio-sponge for water remediation: A sustainable approach’, Cleaner Materials, 1, p. 100011. [CrossRef]
- Naraian, R. and Abhishek, A.K.B. (2020) ‘Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver NPs Using Oyster Mushroom Extract For Antibacterial Efficacy’, Journal of Chemistry, Environmental Sciences and its Applications, 7(1), pp. 13–18–13–18. [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B. and Sakthivel, N. (2010) ‘Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles by microbes’, Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 156(1–2), pp. 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.F. (2004) ‘Cadmium and health in the 21st century--historical remarks and trends for the future’, Biometals : an international journal on the role of metal ions in biology, biochemistry, and medicine, 17(5), pp. 485–489. [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.A. and Shin, H.S. (2015) ‘Simple and sensitive determination of hydrazine in drinking water by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry after derivatization with naphthalene-2,3-dialdehyde’, Journal of Chromatography A, 1395, pp. 73–78. [CrossRef]
- Paixão, R.M. et al. (2017) ‘Activated carbon of Babassu coconut impregnated with copper nanoparticles by green synthesis for the removal of nitrate in aqueous solution’, Environmental technology, 39(15), pp. 1994–2003. [CrossRef]
- Pantidos, N. and Horsfall, L.E. (2014) ‘Biological Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles by Bacteria, Fungi and Plants’, Journal of Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology, 5(5), p. 1000233. [CrossRef]
- Patel, A. et al. (2021) ‘Integrating biometallurgical recovery of metals with biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles’, Chemosphere, 263, p. 128306. [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.P. et al. (2019) ‘Extracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using the marine bacterium Paracoccus haeundaensis BC74171T and evaluation of their antioxidant activity and antiproliferative effect on normal and cancer cell lines’, Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 183. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.S., Gandhi, P. and Selvaraj, K. (2014) ‘Synthesis of green nano iron particles (GnIP) and their application in adsorptive removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solution’, Applied Surface Science, 317, pp. 1052–1059. [CrossRef]
- Priyabrata Mukherjee et al. (2001) ‘Fungus-Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Immobilization in the Mycelial Matrix: A Novel Biological Approach to Nanoparticle Synthesis’, Nano Letters, 1(10), pp. 515–519. [CrossRef]
- Probin Phanjom et al. (2012) ‘Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles using Leaf Extract of Myrica esculenta ’, International Journal of NanoScience and Nanotechnology, 3(2), pp. 73–79https://p.urbanpro.com/tv-prod/documents%2Fnull-Paper+publication.pdf (Accessed: 21 March 2023).
- Qu, Y. et al. (2017) ‘Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Aspergillum sp. WL-Au for degradation of aromatic pollutants’, Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 88, pp. 133–141. [CrossRef]
- Raj, R. et al. (2016) ‘Extracellular polymeric substances of a marine bacterium mediated synthesis of CdS nanoparticles for removal of cadmium from aqueous solution’, Journal of colloid and interface science, 462, pp. 166–175. [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R. et al. (2013) ‘Aqueous phase synthesis of copper nanoparticles: A link between heavy metal resistance and nanoparticle synthesis ability in bacterial systems’, Nanoscale. [Preprint]https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23223802/ (Accessed: 21 February 2023).
- Rao, A. et al. (2013) ‘Removal of hexavalent chromium ions by Yarrowia lipolytica cells modified with phyto-inspired Fe0/Fe3O4 nanoparticles’, Journal of contaminant hydrology, 146, pp. 63–73. [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.A. et al. (2017) ‘Biomimetically synthesized ZnO nanoparticles attain potent antibacterial activity against less susceptible S. aureus skin infection in experimental animals’, RSC Advances, 7(58), pp. 36361–36373. [CrossRef]
- Rauwel, P. et al. (2015) ‘Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications’, Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Revathy, R. et al. (2022) ‘Synthesis and catalytic applications of silver nanoparticles: a sustainable chemical approach using indigenous reducing and capping agents from Hyptis capitata’, Environmental Science: Advances, 1(4), pp. 491–505. [CrossRef]
- Sadre Alam et al. (2023) ‘Estimation of Heavy Metals and Fluoride Ion in Vegetables Grown Nearby the Stretch of River Yamuna, Delhi (NCR), India’, Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 43(1), pp. 64–73https://www.e-ijep.co.in/43-1-64-73/ (Accessed: 21 March 2023).
- Salem, S.S. (2022) ‘Baker’s Yeast-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles: Characterisation and Antimicrobial Biogenic Tool for Suppressing Pathogenic Microbes’, BioNanoScience, 12(4), pp. 1220–1229. [CrossRef]
- Salem, D.M.S.A., Ismail, M.M. and Aly-Eldeen, M.A. (2019) ‘Biogenic synthesis and antimicrobial potency of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using algae harvested from the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt’, The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 45(3), pp. 197–204. [CrossRef]
- Sandana Mala, J.G. and Rose, C. (2014) ‘Facile production of ZnS quantum dot nanoparticles by Saccharomyces cerevisiae MTCC 2918’, Journal of Biotechnology, 170(1), pp. 73–78. [CrossRef]
- Santhoshkumar, T. et al. (2011) ‘Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Nelumbo nucifera leaf extract and its larvicidal activity against malaria and filariasis vectors’, Parasitology research, 108(3), pp. 693–702. [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, S., Saranya, K. and Kowshik, M. (2011) ‘Green synthesis of lead sulfide nanoparticles by the lead resistant marine yeast, Rhodosporidium diobovatum’, Biotechnology Progress, 27(5), pp. 1464–1469. [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.P. et al. (2020) ‘Bottom-Up and Top-Down Approaches for MgO’, Sonochemical Reactions [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P. et al. (2021) ‘Biogenic and Non-Biogenic Waste Utilization in the Synthesis of 2D Materials (Graphene, h-BN, g-C2N) and Their Applications’, Frontiers in Nanotechnology, 3, p. 685427. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. and Nalwa, H.S. (2011) ‘Medical applications of nanoparticles in biological imaging, cell labeling, antimicrobial agents, and anticancer nanodrugs’, Journal of biomedical nanotechnology, 7(4), pp. 489–503. [CrossRef]
- Smuleac, V. et al. (2011) ‘Green synthesis of Fe and Fe/Pd bimetallic nanoparticles in membranes for reductive degradation of chlorinated organics’, Journal of Membrane Science, 379(1–2), pp. 131–137. [CrossRef]
- Srinath, B.S. and Rai, V.R. (2015) ‘Rapid biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Staphylococcus epidermidis: its characterisation and catalytic activity’, Materials Letters, 146, pp. 23–25. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N. and Mukhopadhyay, M. (2014) ‘Biosynthesis of SnO2 Nanoparticles Using Bacterium Erwinia herbicola and Their Photocatalytic Activity for Degradation of Dyes’, Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 53(36), pp. 13971–13979. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K. et al. (2013) ‘Biogenic synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles by Escherichia coli K12 and its heterogeneous catalysis in degradation of 4-nitrophenol’, Nanoscale Research Letters, 8(1), p. 70. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K. and Constanti, M. (2012) ‘Room temperature biogenic synthesis of multiple nanoparticles (Ag, Pd, Fe, Rh, Ni, Ru, Pt, Co, and Li) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa SM1’, Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 14(4), pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V., Sharma, Y.C. and Sillanpää, M. (2015) ‘Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoflower and its application for the removal of divalent metallic species from synthetic wastewater’, Ceramics International, 5 Part B(41), pp. 6702–6709. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S. et al. (2019) ‘Production, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles produced by Fusarium oxysporum and monitoring of protein-ligand interaction through in-silico approaches’, Microbial pathogenesis, 129, pp. 136–145. [CrossRef]
- Tu, J., Yang, Z. and Hu, C. (2015) ‘Efficient catalytic aerobic oxidation of chlorinated phenols with mixed-valent manganese oxide nanoparticles’, Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 90(1), pp. 80–86. [CrossRef]
- Tu, W. et al. (2022) ‘The CO3O4 nanosheet hybridized with silver nanoparticles affords long-acting synergetic antimicrobial and catalytic degradation activity’, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 914, p. 165284. [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S. et al. (2018) ‘Strategies for Nitrate removal from aqueous environment using Nanotechnology: A Review’, Journal of Water Process Engineering, 21, pp. 84–95. [CrossRef]
- Vaseghi, Z., Nematollahzadeh, A. and Tavakoli, O. (2018) ‘Green methods for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles using biogenic reducing agents: A review’, Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 34(4), pp. 529–559. [CrossRef]
- Verma, N. and Kumar, N. (2019) ‘Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: An Expanding Horizon’, ACS Biomaterials Science and Engineering, 5(3), pp. 1170–1188. [CrossRef]
- Vijayanandan, A.S. and Balakrishnan, R.M. (2018) ‘Biosynthesis of cobalt oxide nanoparticles using endophytic fungus Aspergillus nidulans’, Journal of environmental management, 218, pp. 442–450. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. et al. (2017) ‘Biogenic manganese oxides generated by green algae Desmodesmus sp. WR1 to improve bisphenol A removal’, Journal of hazardous materials, 339, pp. 310–319. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. et al. (2014) ‘Green synthesized iron nanoparticles by green tea and eucalyptus leaves extracts used for removal of nitrate in aqueous solution’, Journal of Cleaner Production, 83, pp. 413–419. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. et al. (2018) ‘Interactions between biogenic selenium nanoparticles and goethite colloids and consequence for remediation of elemental mercury contaminated groundwater’, The Science of the total environment, 613–614, pp. 672–678. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z. et al. (2016) ‘Plant-mediated synthesis of highly active iron nanoparticles for Cr (VI) removal: Investigation of the leading biomolecules’, Chemosphere, 150, pp. 357–364. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. et al. (2018) ‘Effect of anodes decoration with metal and metal oxides nanoparticles on pharmaceutically active compounds removal and power generation in microbial fuel cells’, Chemical Engineering Journal, 335, pp. 539–547. [CrossRef]
- Yong, P. et al. (2004) ‘Synthesis of nanophase hydroxyapatite by a Serratia sp. from waste-water containing inorganic phosphate’, Biotechnology Letters, 26(22), pp. 1723–1730. [CrossRef]
- Zambonino, M.C. et al. (2023) ‘Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles in Biomedical Sciences: Properties, Current Trends, Novel Opportunities and Emerging Challenges in Theranostic Nanomedicine’, Nanomaterials, 13(3), p. 424. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. et al. (2021) ‘High Stability Au NPs: From Design to Application in Nanomedicine’, International Journal of Nanomedicine, 16, p. 6067. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L. et al. (2020) ‘The controlled synthesis of Fe3C/Co/N-doped hierarchically structured carbon nanotubes for enhanced electrocatalysis’, Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 261, p. 118224. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. et al. (2019) ‘Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles mediated by fungus Mariannaea sp. HJ and their characterization’, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 571, pp. 9–16. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.Q. et al. (2018) ‘Continuous degradation of ciprofloxacin in a manganese redox cycling system driven by Pseudomonas putida MnB-1’, Chemosphere, 211, pp. 345–351. [CrossRef]
| S. No. | Biogenic Sources (Bacteria/Fungi/Algae) | Nanoparticles (NPs) | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | ||||
| 1 | Lactobacillus kimchicus | Gold | Drug delivery, cancer diagnostic | Mathivanan et al., 2019 |
| 2 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | Catalysts | Pantidos and Horsfall, 2014 | |
| 3 | Paracoccus haeundaensis | Antioxidants | Srinath and Rai, 2015 | |
| 4 | Cupriavidus sp. | Silver | Antibacterial | Markus et al. 2016 |
| 5 | Bacillus subtilis | Patil et al., 2019 | ||
| 6 | Staphylococcus aureus | Zinc oxide | Rauf et al., 2017 | |
| 7 | Bacillus subtillis | Synthetic dyes | Dhandapani et al., 2020 | |
| 8 | Bacillus sp. | Nanoselenium | Biomedical | Bharathi et al., 2020 |
| 9 | Desulfovibrio vulgaris | Platinum and palladium | Catalysts | Martins et al., 2017 |
| Fungi | ||||
| 10 | Aspergillus niger | Iron oxide | Wastewater treatment | Mughal et al., 2021 |
| 11 | Aspergillus terreus | Silver | Antibacterial, anticancer | Hulikere and Joshi, 2019 |
| 12 | Cladosporium cladosporioides | Antioxidant, antimicrobial | Zhang et al., 2020 | |
| 13 | Aspergillus niger | Copper | Antidiabetic and Antibacterial | Zhang et al., 2019 |
| 14 | Mariannaea sp. HJ | Selenium | Medicinal and electronics | Vijayanandan and Balakrishnan, 2018 |
| 15 | Aspergillus nidulans | Cobalt oxide | Energy storage | Joshi et al., 2017 |
| 16 | Cladosporium cladosporioides | Gold | Antioxidant, antimicrobial | Bhargava et al., 2016 |
| 17 | Cladosporium oxysporum | Catalysis | Srivastava et al., 2019 | |
| 18 | Fusarium oxysporum | Platinum | Nano medicine | Chatterjee et al., 2020 |
| Algae | ||||
| 19 | Botryococcus braunii | Silver | Catalysis | Manikandakrishnan et al., 2019 |
| 20 | Portieria hornemannii | Antibacterial | Arya et al., 2019 | |
| 21 | Colpomenia sinuosa and Pterocladia capillacea | Iron oxide | Colin et al., 2018 | |
| 22 | Caulerpa racemosa | Gold | Biomedical | Salem et al., 2019 |
| 23 | Egregia sp. | Gonzalez-Ballesteros et al., 2017 | ||
| 24 | Cystoseira baccata | Cancer | Mourdikoudis et al., 2018 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





