Submitted:
25 November 2023
Posted:
28 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
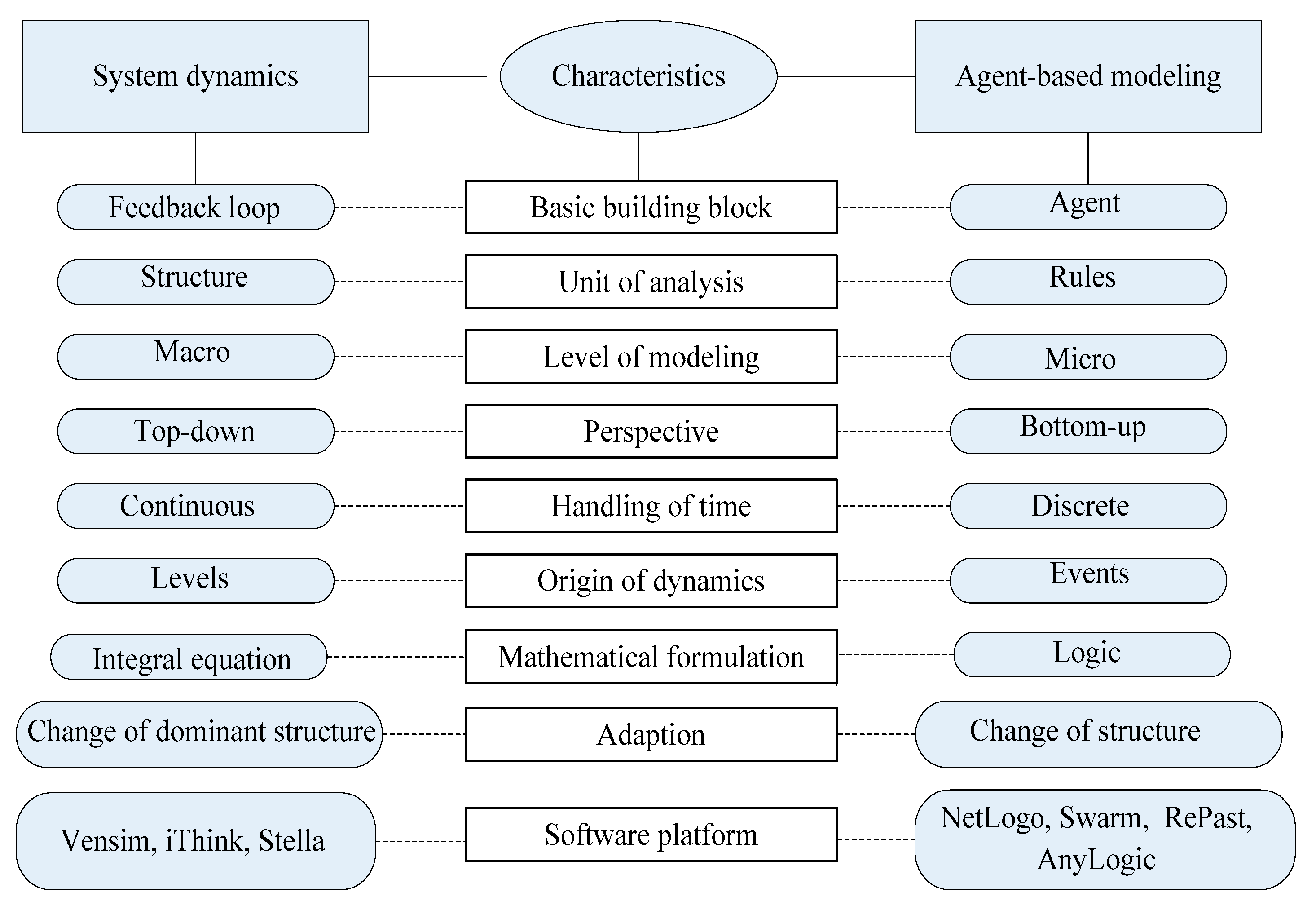
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Farmers’ Features
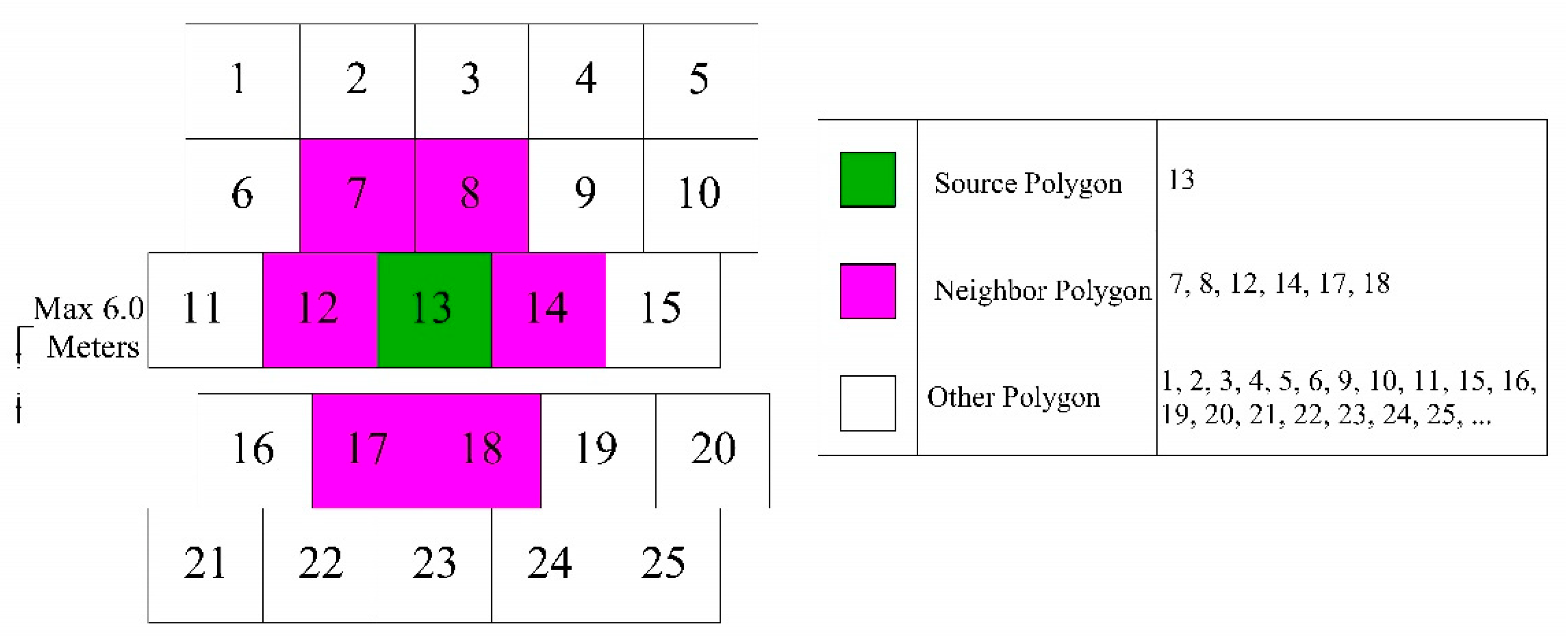
2.2. Neighbourhood
2.3. Farmers’ Decisions
2.4. Formulation
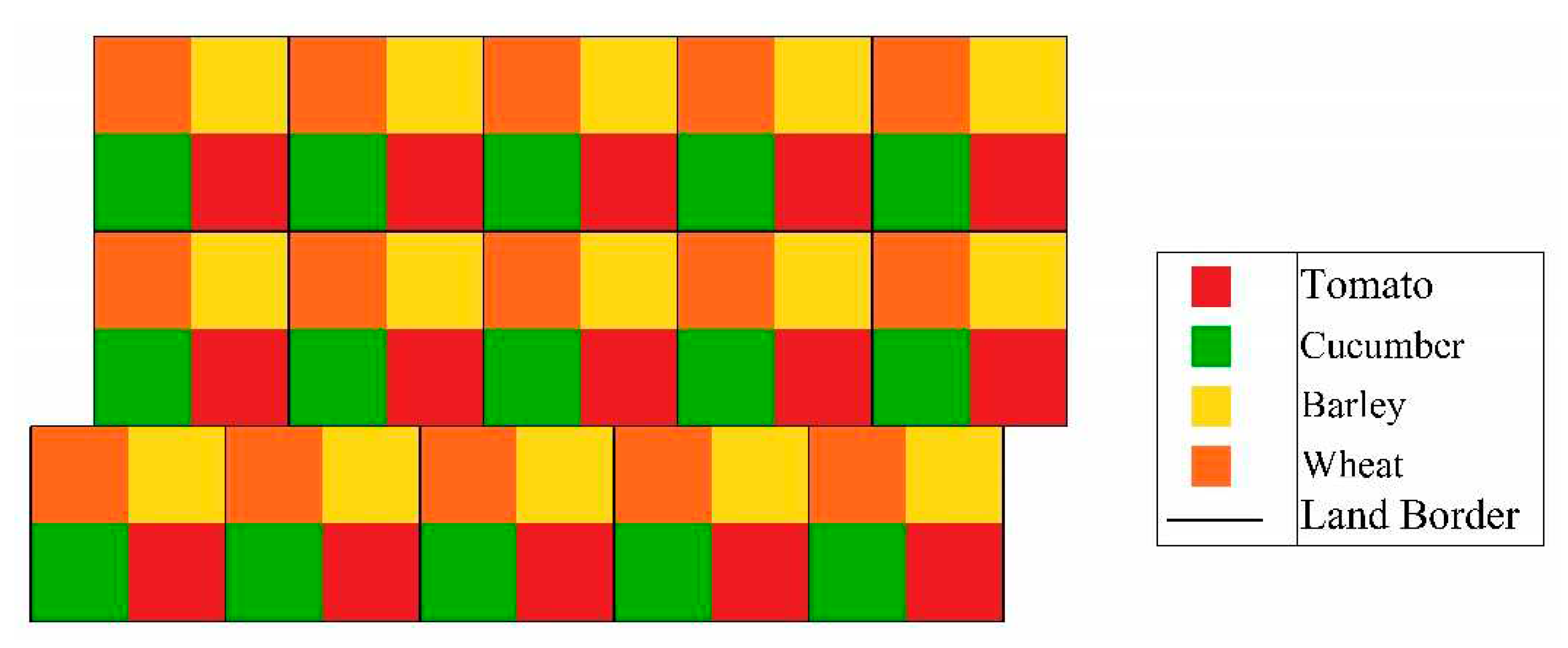
2.4.1. Changing the Cropping Pattern
2.4.2. Installing New Irrigation Technology
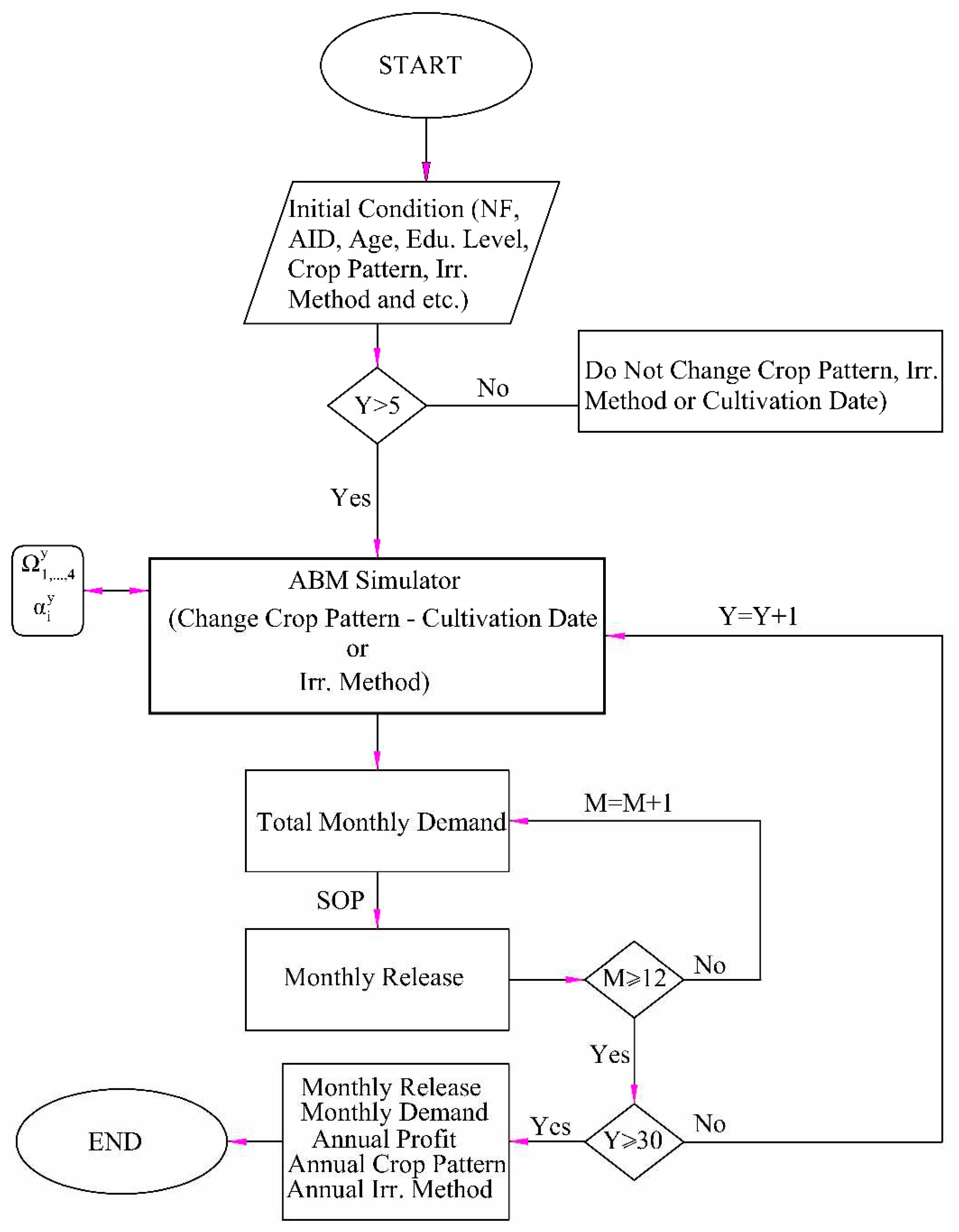
2.5. Model testing
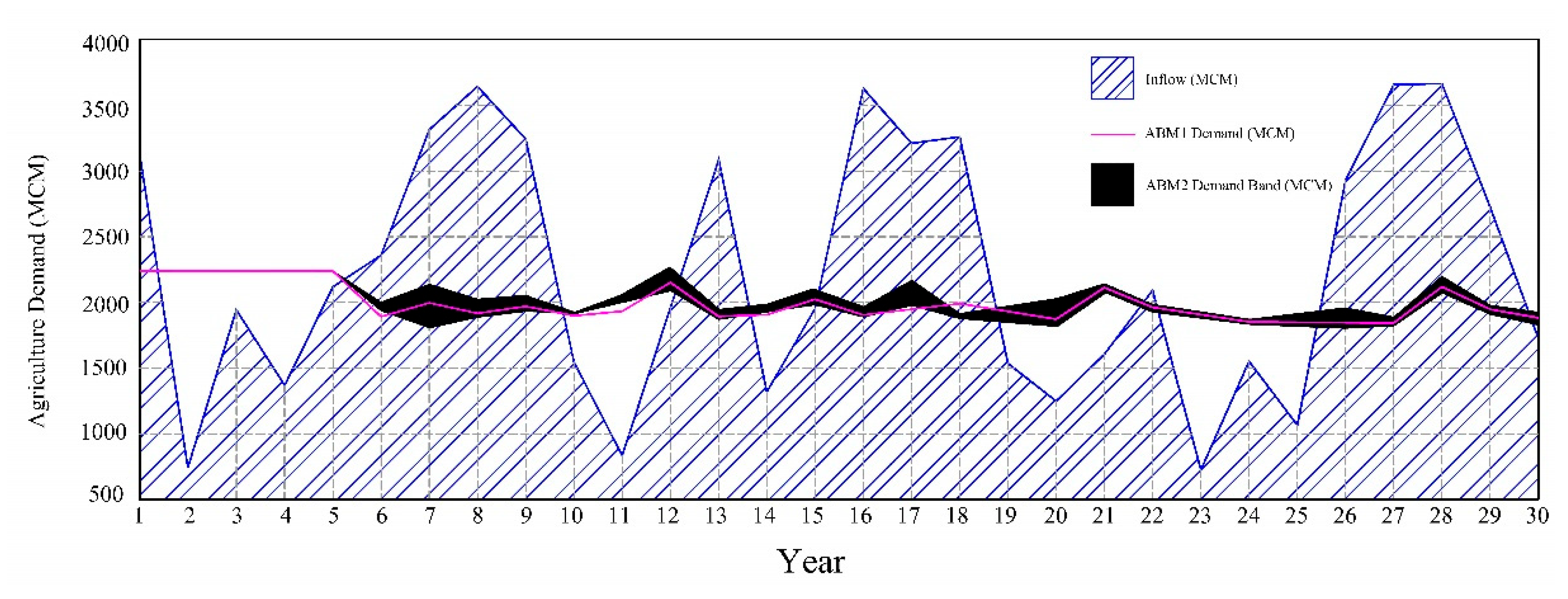
3. Results
3.1. ABM1 Scenario
3.2. ABM2 Scenario
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- Exploration of alternative water resource utilization strategies beyond the SOP, such as the Hedging Rule (HR)
- Expansion of the ABM frameworks to encompass other water demands like domestic and industrial demands, facilitating a comprehensive multi-agent modeling approach
- The inflow model of a dam (with dead volume and maximum storage volume) can be modelled.
- Consideration of additional factors influencing water consumption, such as fertilization timing and types, and the implementation of deficit irrigation strategies, could be integrated into future models.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| i | Index of farmer |
| y | Index of year |
| m | Index of month |
| Level of risk-taking of farmers | |
| Maximum age among farmers in the region (year) | |
| Maximum age among farmers in the region (year) | |
| The age of the ith farmer yth year (year) | |
| AID | The percentage of annual income dependence on agriculture (%) |
| The number of farmers in the neighborhood of ith farmer | |
| Binary parameters of ith farmer in yth year | |
| Pi | Profit of the ith farmer ($) |
| Wa | Actual available water to farmer (m3/ha) |
| Wp | potential water demand by plants (m3/ha) |
| Water share for each farmer (MCM) | |
| The amount of water released from the reservoir (MCM) | |
| sm and em | the first and last months of crop growth |
| η | Irrigation efficiency |
| CD | Monthly water requirement of each crop (m3/ha) |
| Ya | The actual yield (ton/ha) |
| Yp | The potential yield (ton/ha) |
| Ky | Yield response factor |
| The sales price of the cth crop ($/Kg) | |
| The cost of planting, harvesting and preparation of cth crop ($/ha) | |
| ITC | The installation cost of new irrigation technology ($) |
| Summation of Ω values | |
| β | The violation rate |
| The expected water for ith farmer in yth year | |
| δ1,…, δ8 | Thresholds for obtaining knowledge (%) |
References
- Ashofteh, P.-S.; Haddad, O.B.; Akbari-Alashti, H.; Marino, M.A. Determination of irrigation allocation policy under climate change by genetic programming. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering 2015, 141, 04014059. [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Hosseini, S.; Asadi, R.; Akbari Nodehi, D. Measurement of water consumption of Promising Rice Cultivars Using Mini-Cylindrical Lysimeters in Amol City. Journal of Water and Soil Resources Conservation 2023.
- Feola, G.; Lerner, A.M.; Jain, M.; Montefrio, M.J.F.; Nicholas, K.A. Researching farmer behaviour in climate change adaptation and sustainable agriculture: Lessons learned from five case studies. Journal of Rural Studies 2015, 39, 74-84. [CrossRef]
- Buelow, F.; Cradock-Henry, N. What you sow is what you reap?(Dis-) incentives for adaptation intentions in farming. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1133. [CrossRef]
- Sušnik, J.; Vamvakeridou-Lyroudia, L.S.; Savić, D.A.; Kapelan, Z. Integrated modelling of a coupled water-agricultural system using system dynamics. Journal of water and climate change 2013, 4, 209-231. [CrossRef]
- Egerer, S.; Cotera, R.V.; Celliers, L.; Costa, M.M. A leverage points analysis of a qualitative system dynamics model for climate change adaptation in agriculture. Agricultural Systems 2021, 189, 103052. [CrossRef]
- Moglewer, S. A game theory model for agricultural crop selection. Econometric: Journal of the Econometric Society 1962, 253-266. [CrossRef]
- Yoosefdoost, I.; Abrão, T.; Santos, M.J. Water Resource Management Aided by Game Theory. In Essential Tools for Water Resources Analysis, Planning, and Management; Springer: 2021; pp. 217-262. [CrossRef]
- Goli, A.; Khademi-Zare, H.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Sadeghieh, A.; Sasanian, M.; Malekalipour Kordestanizadeh, R. An integrated approach based on artificial intelligence and novel meta-heuristic algorithms to predict demand for dairy products: a case study. Network: computation in neural systems 2021, 32, 1-35. [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Guan, W.; Yang, M.; Cao, J.; Zou, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Dong, N. The Optimization of Water Storage Timing in Upper Yangtze Reservoirs Affected by Water Transfer Projects. Water 2023, 15, 3393. [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.; Garg, C. Optimal Operation policies for Reservoir Operation using Differential Evolution and Particle Swarm Optimization. Journal of Water Resources and Pollution Studies (e-ISSN: 2581-5326) 2023, 1-10.
- Yoosefdoost, I.; Basirifard, M.; Álvarez-García, J. Reservoir operation management with new multi-objective (MOEPO) and metaheuristic (EPO) algorithms. Water 2022, 14, 2329.
- Zhou, S.-d.; Mueller, F.; Burkhard, B.; CAO, X.-j.; Ying, H. Assessing agricultural sustainable development based on the DPSIR approach: case study in Jiangsu, China. Journal of integrative Agriculture 2013, 12, 1292-1299.
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Wu, P.; Geng, Q.; Xu, L. Sustainability assessment of regional water resources under the DPSIR framework. Journal of Hydrology 2016, 532, 140-148.
- Epstein, J.M.; Axtell, R. Growing artificial societies: social science from the bottom up; Brookings Institution Press: 1996.
- De Marchi, S.; Page, S.E. Agent-based models. Annual Review of political science 2014, 17, 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q. Data acquisition and simulation of natural phenomena. Science China Information Sciences 2011, 54, 683-716.
- POLJAK, D.; JAKIĆ, M. A note on the character of physical models representing natural phenomena. International Journal of Design & Nature and Ecodynamics 2017, 12, 254-263.
- Bonabeau, E. Agent-based modeling: Methods and techniques for simulating human systems. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences 2002, 99, 7280-7287.
- Nejat, A.; Damnjanovic, I. Agent-based modeling of behavioral housing recovery following disasters. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering 2012, 27, 748-763. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Butner, J.D.; Kerketta, R.; Cristini, V.; Deisboeck, T.S. Simulating cancer growth with multiscale agent-based modeling. In Proceedings of the Seminars in cancer biology, 2015; pp. 70-78.
- Nikolic, I. Co-evolutionary method for modelling large scale socio-technical systems evolution. 2009.
- Wu, D.D.; Kefan, X.; Hua, L.; Shi, Z.; Olson, D.L. Modeling technological innovation risks of an entrepreneurial team using system dynamics: an agent-based perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2010, 77, 857-869.
- Barbati, M.; Bruno, G.; Genovese, A. Applications of agent-based models for optimization problems: A literature review. Expert Systems with Applications 2012, 39, 6020-6028.
- Osman, H. Agent-based simulation of urban infrastructure asset management activities. Automation in Construction 2012, 28, 45-57.
- Lättilä, L.; Hilletofth, P.; Lin, B. Hybrid simulation models–when, why, how? Expert systems with applications 2010, 37, 7969-7975.
- Ding, Z.; Gong, W.; Li, S.; Wu, Z. System dynamics versus agent-based modeling: A review of complexity simulation in construction waste management. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2484.
- Bousquet, F.; Cambier, C.; Mullon, C.; Morand, P.; Quensière, J.; Pavé, A. Simulating the interaction between a society and a renewable resource. Journal of biological systems 1993, 1, 199-214.
- Balmann, A. Farm-based modelling of regional structural change: A cellular automata approach. European review of agricultural economics 1997, 24, 85-108.
- Becu, N.; Perez, P.; Walker, A.; Barreteau, O.; Le Page, C. Agent based simulation of a small catchment water management in northern Thailand: description of the CATCHSCAPE model. Ecological modelling 2003, 170, 319-331. [CrossRef]
- Linkola, L.; Andrews, C.J.; Schuetze, T. An agent based model of household water use. Water 2013, 5, 1082-1100.
- Ng, T.L.; Eheart, J.W.; Cai, X.; Braden, J.B. An agent-based model of farmer decision-making and water quality impacts at the watershed scale under markets for carbon allowances and a second-generation biofuel crop. Water Resources Research 2011, 47.
- Cancian, F. Stratification and risk-taking: A theory tested on agricultural innovation. American Sociological Review 1967, 912-927.
- Jianakoplos, N.A.; Bernasek, A. Financial risk taking by age and birth cohort. Southern Economic Journal 2006, 72, 981-1001.
- Knight, J.; Weir, S.; Woldehanna, T. The role of education in facilitating risk-taking and innovation in agriculture. The journal of Development studies 2003, 39, 1-22.
- Spicka, J. Socio-demographic drivers of the risk-taking propensity of micro farmers: Evidence from the Czech Republic. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies 2020, 12, 569-590. [CrossRef]
- Balbi, S.; Bhandari, S.; Gain, A.K.; Giupponi, C. Multi-agent agro-economic simulation of irrigation water demand with climate services for climate change adaptation. Italian Journal of Agronomy 2013, 8, 175-185.
- Ghazali, M.; Honar, T.; Nikoo, M.R. A hybrid TOPSIS-agent-based framework for reducing the water demand requested by stakeholders with considering the agents’ characteristics and optimization of cropping pattern. Agricultural Water Management 2018, 199, 71-85.
- Schreinemachers, P.; Berger, T. An agent-based simulation model of human–environment interactions in agricultural systems. Environmental Modelling & Software 2011, 26, 845-859. [CrossRef]
- Kahan, D. Managing risk in farming; Food and agriculture organization of the united nations Rome: 2008.
- Edwards, M.; Ferrand, N.; Goreaud, F.; Huet, S. The relevance of aggregating a water consumption model cannot be disconnected from the choice of information available on the resource. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory 2005, 13, 287-307.
- Noël, P.H.; Cai, X. On the role of individuals in models of coupled human and natural systems: Lessons from a case study in the Republican River Basin. Environmental Modelling & Software 2017, 92, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Kappelman, L.A. Measuring user involvement: A diffusion of innovation perspective. ACM SIGMIS Database: the DATABASE for Advances in Information Systems 1995, 26, 65-86.
- Yoosefdoost, I.; Basirifard, M.; Álvarez-García, J.; del Río-Rama, M.d.l.C. Increasing agricultural resilience through combined supply and demand management (Case study: Karaj Reservoir Dam, Iran). Agronomy 2022, 12, 1997.
- Hazbavi, Z.; Baartman, J.E.; Nunes, J.P.; Keesstra, S.D.; Sadeghi, S.H. Changeability of reliability, resilience and vulnerability indicators with respect to drought patterns. Ecological Indicators 2018, 87, 196-208. [CrossRef]
- Hoque, Y.M.; Hantush, M.M.; Govindaraju, R.S. On the scaling behavior of reliability–resilience–vulnerability indices in agricultural watersheds. Ecological Indicators 2014, 40, 136-146. [CrossRef]
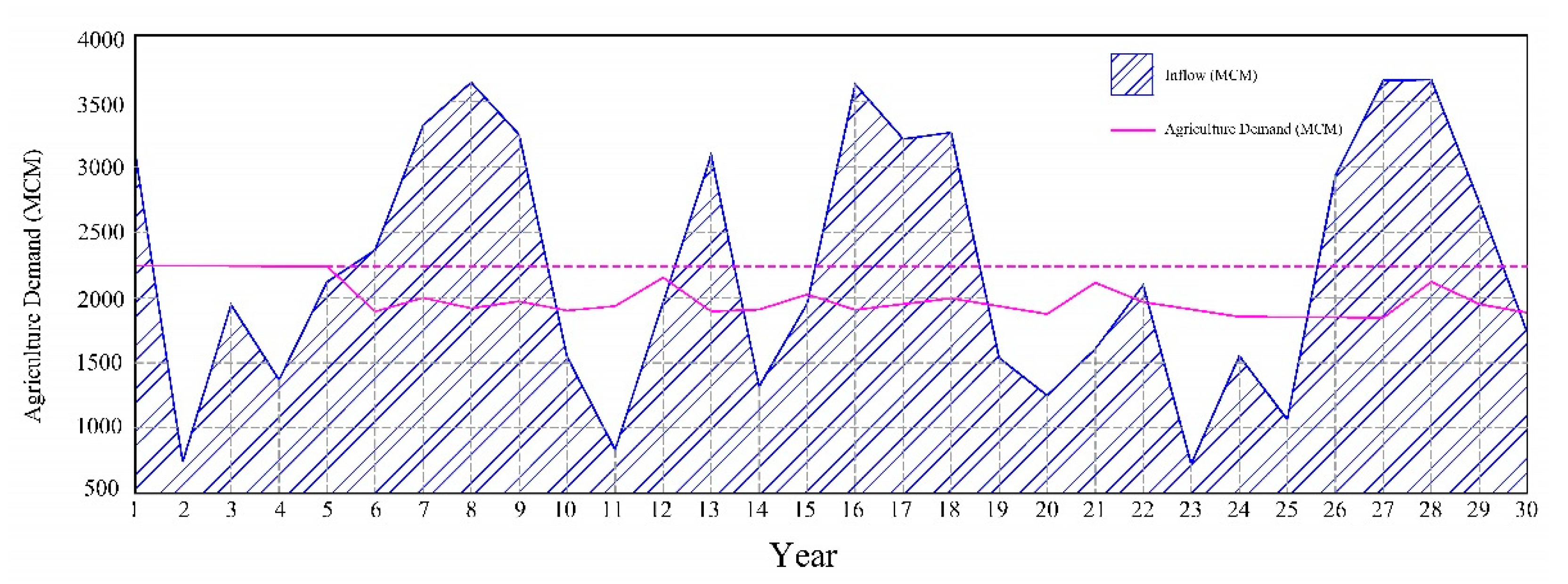
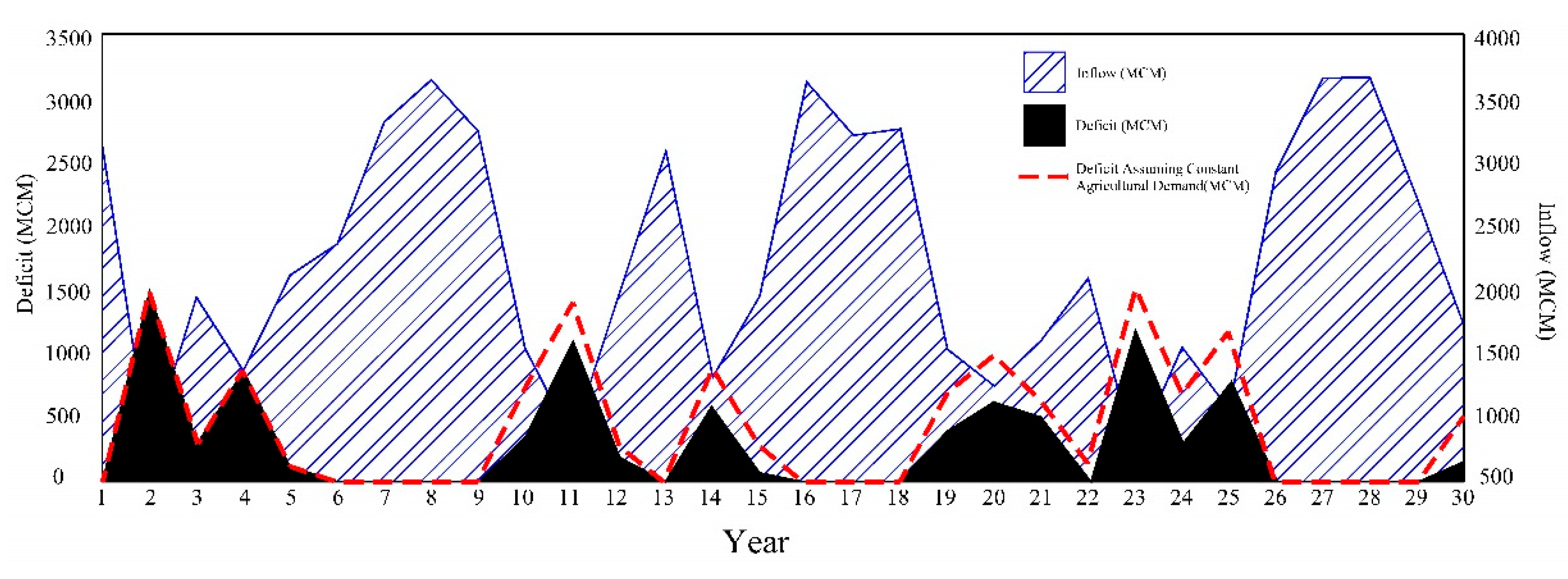
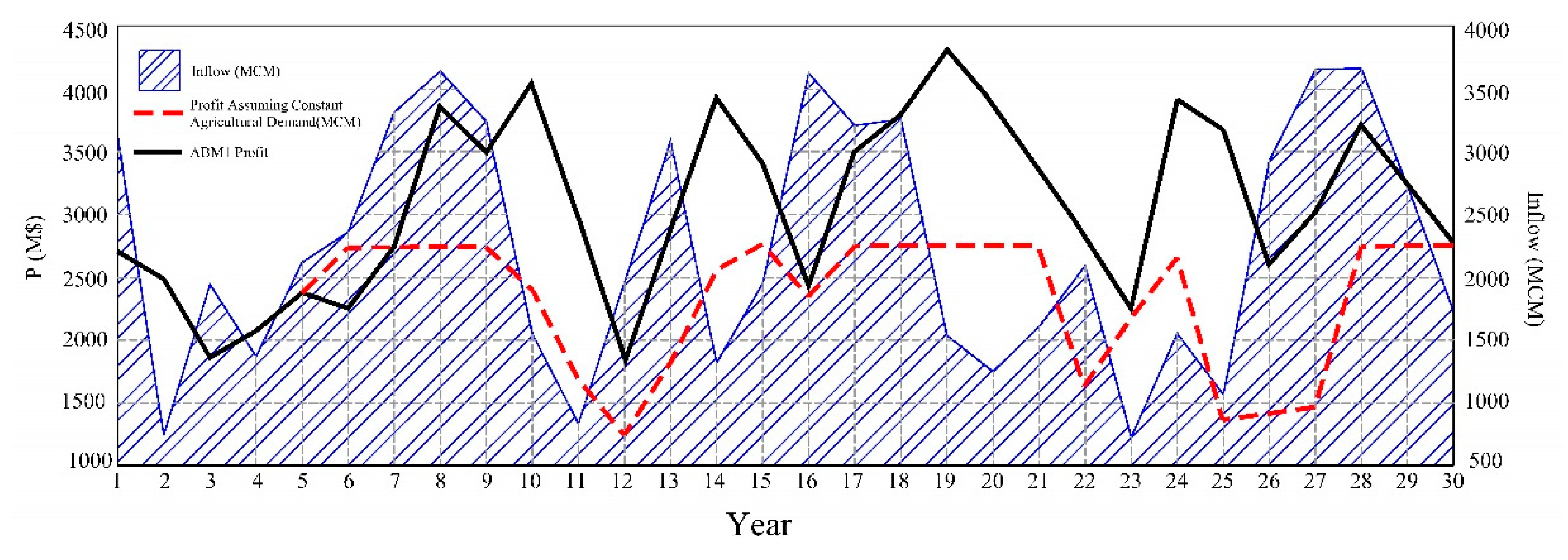
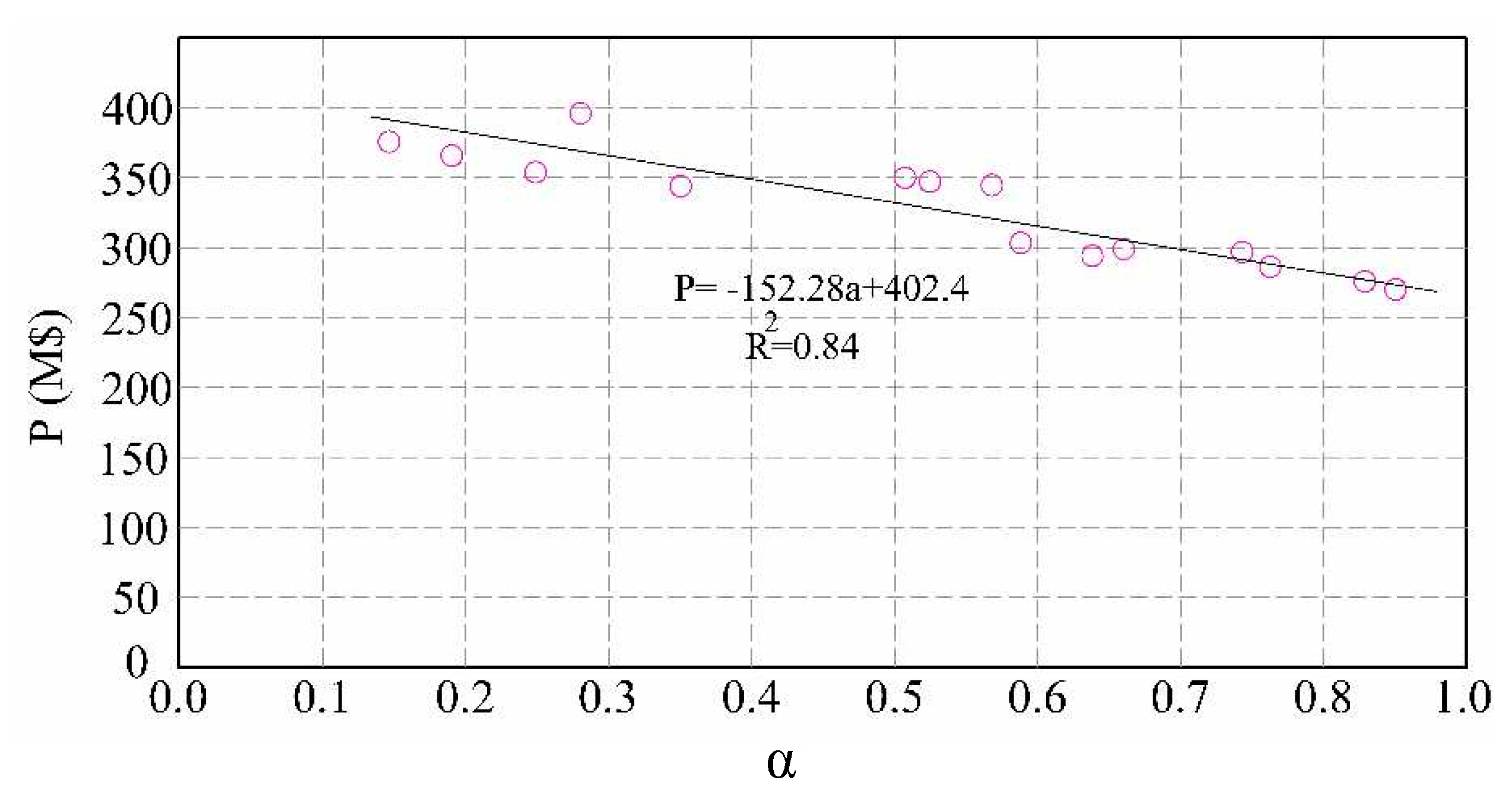

| High Educated Farmer | δ1 | δ2 | δ3 | δ4 |
| Low Educated Farmer | δ5 | δ6 | δ7 | δ8 |
| High Educated Farmer | - | 0 | + | + |
| Low Educated Farmer | - | - | 0 | + |
| Farmer ID | Age | AID (%) | Edu. Level | α |
| 1 | 24 | 15 | H | 0.85 |
| 2 | 36 | 35 | H | 0.64 |
| 3 | 55 | 85 | L | 0.15 |
| 4 | 60 | 45 | L | 0.51 |
| 5 | 18 | 55 | L | 0.57 |
| 6 | 45 | 45 | H | 0.53 |
| 7 | 30 | 35 | L | 0.66 |
| 8 | 20 | 30 | H | 0.74 |
| 9 | 19 | 20 | L | 0.83 |
| 10 | 42 | 80 | L | 0.25 |
| 11 | 38 | 40 | H | 0.59 |
| 12 | 25 | 25 | L | 0.76 |
| 13 | 55 | 70 | L | 0.28 |
| 14 | 45 | 65 | H | 0.35 |
| 15 | 55 | 80 | L | 0.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





