Submitted:
24 November 2023
Posted:
24 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
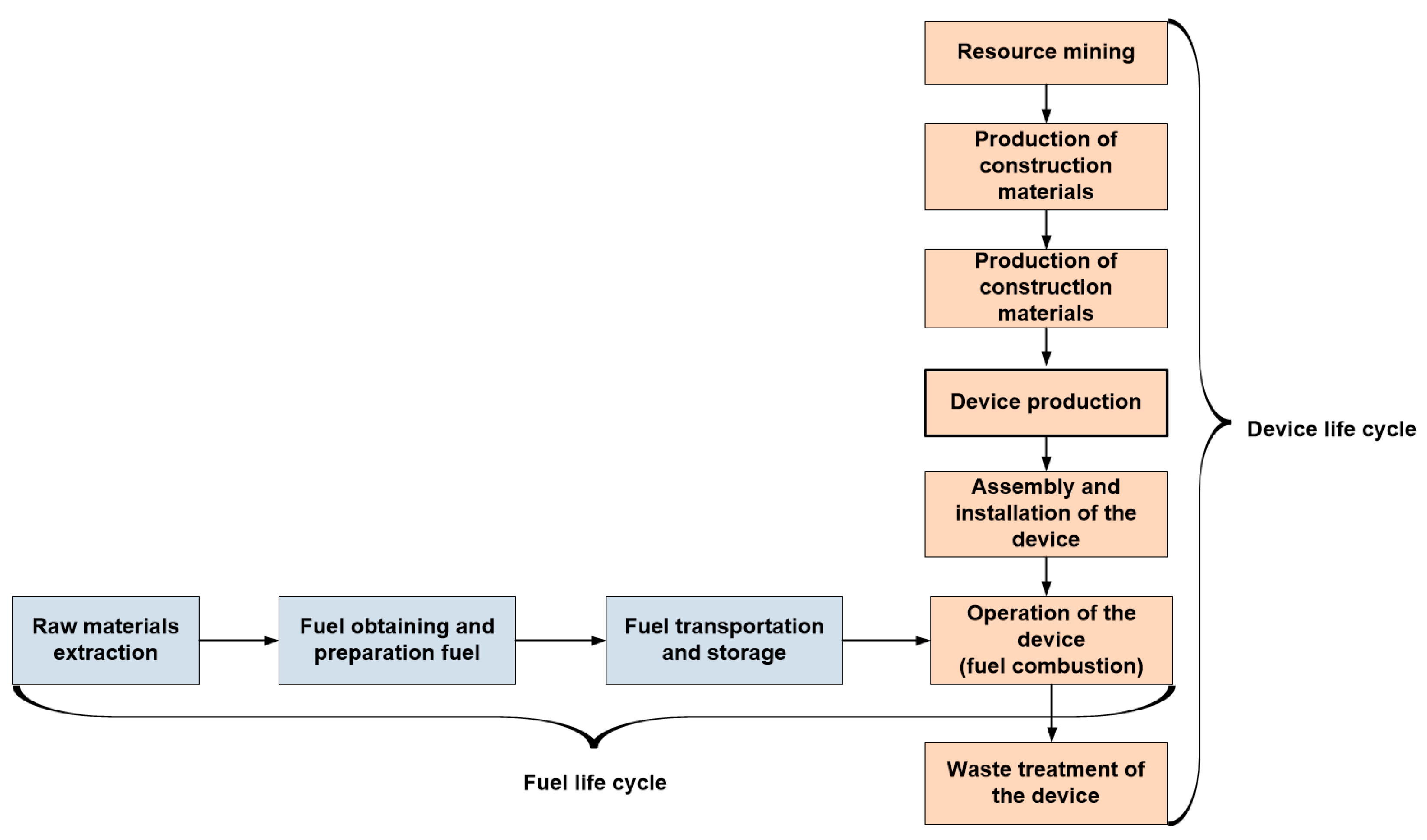
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Principles of LCA
2.2. Functional Unit
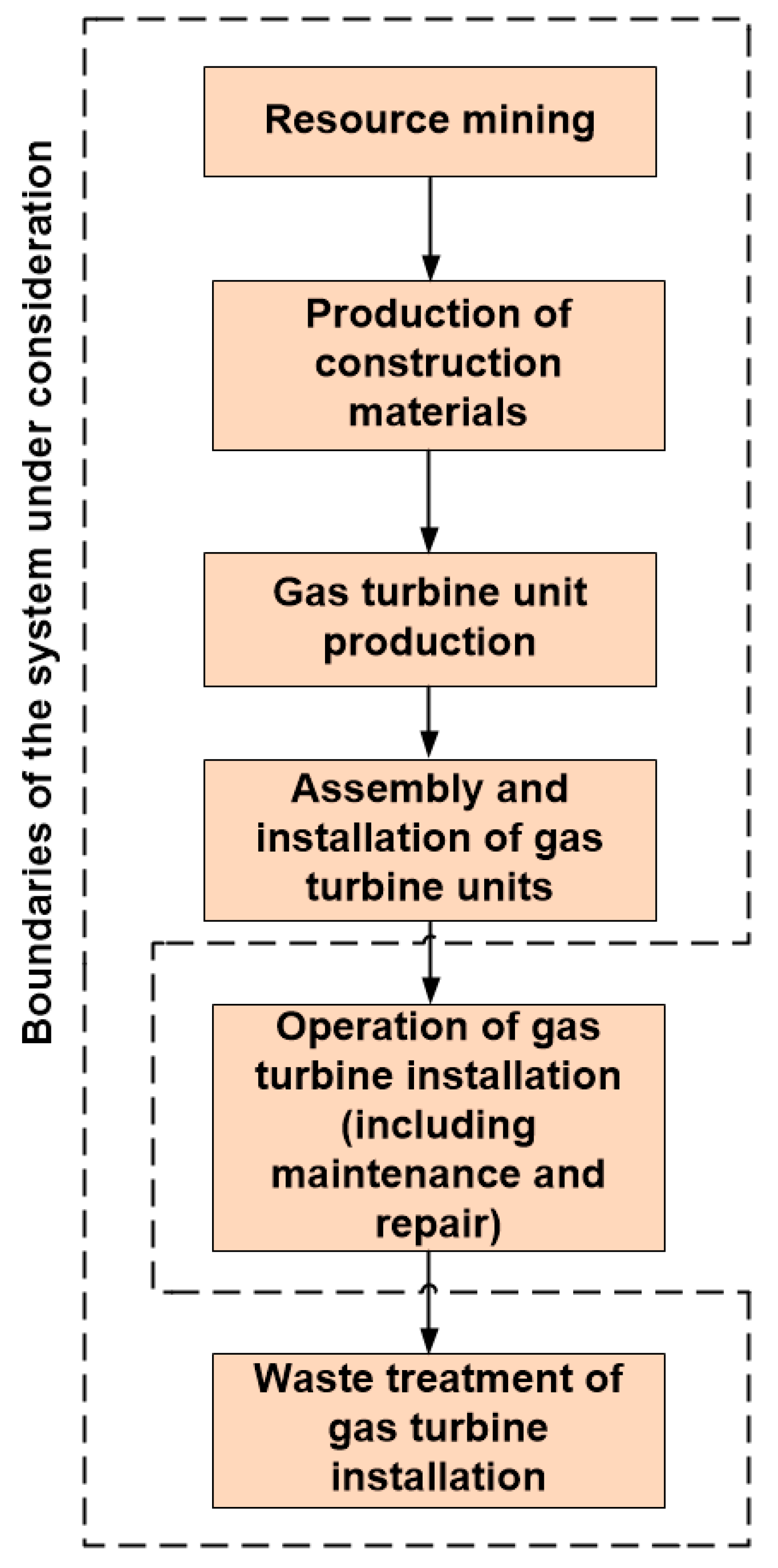
2.3. Limits of LCA
- -
- The production stage, which includes the processes of obtaining structural materials, their processing, production of components, assembly and installation; production of operating materials and spare parts.
- -
- The stage of producing fuel and electrical energy.
- -
- The operational stage, which includes the use of the device in the field, maintenance and repair procedures, including the replacement of failed components.
- -
- The disposal stage, including the processes of decomposition, processing (recycling) of materials and disposal of waste at the end of its useful life.
2.4. Level of Detail of Material Data
2.5. Environmental Impact Assessment Categories
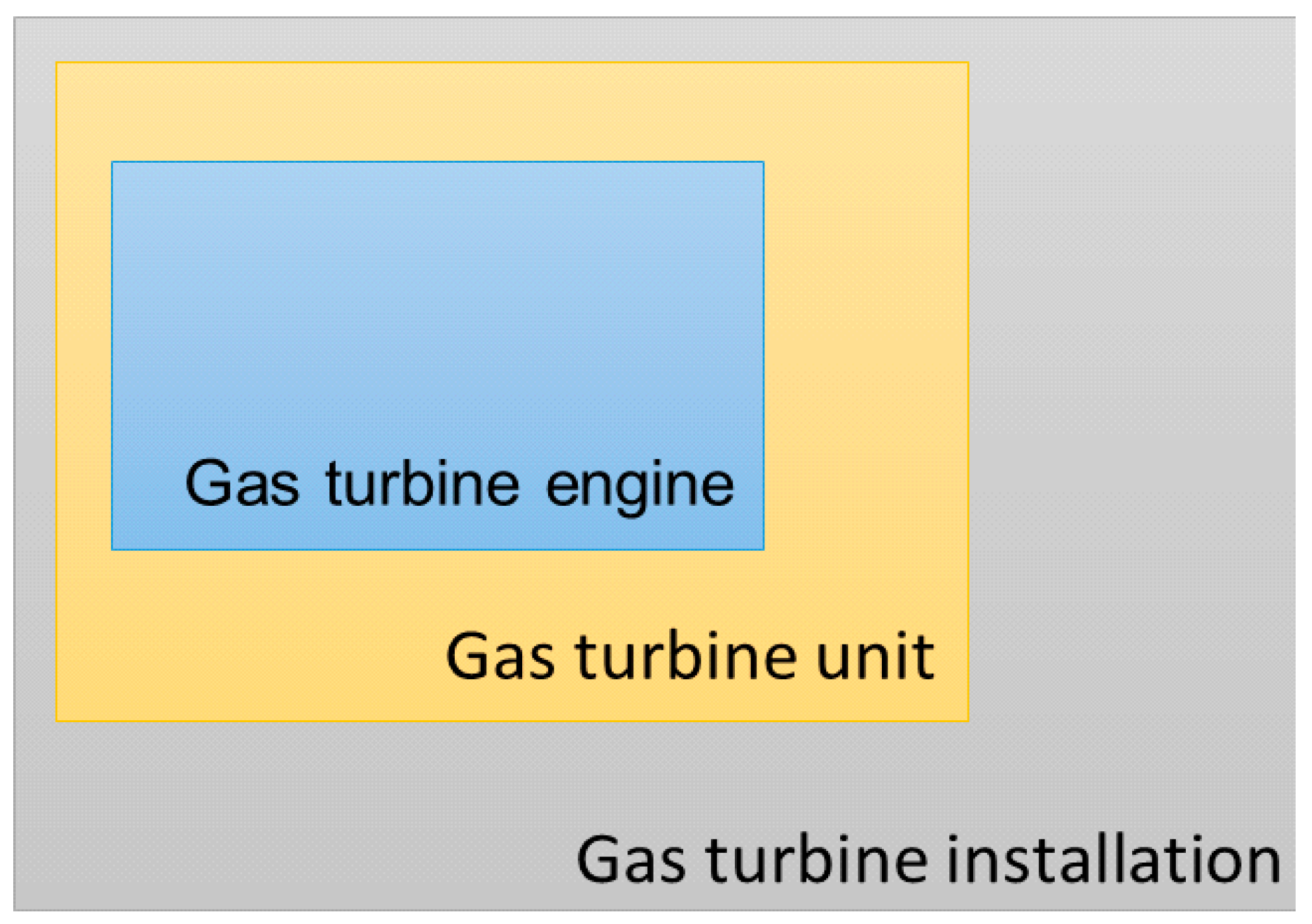
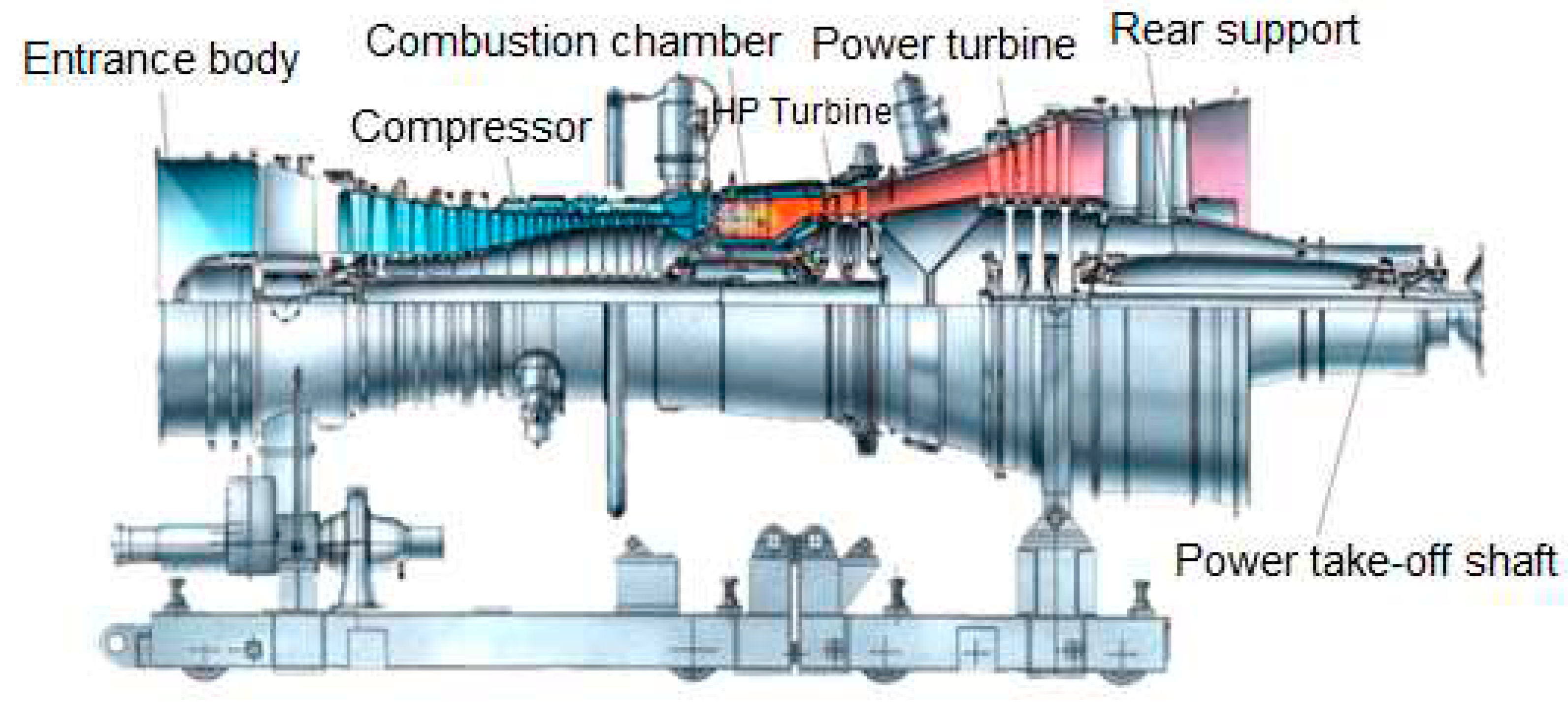
2.6. The GTI under Consideration
- -
- -
- transmission with casings;
- -
- input device;
- -
- noise-heat-insulating casing;
- -
- output device (snail);
- -
- fuel unit cabinet;
- -
- pipeline and electrical communications.
3. Results
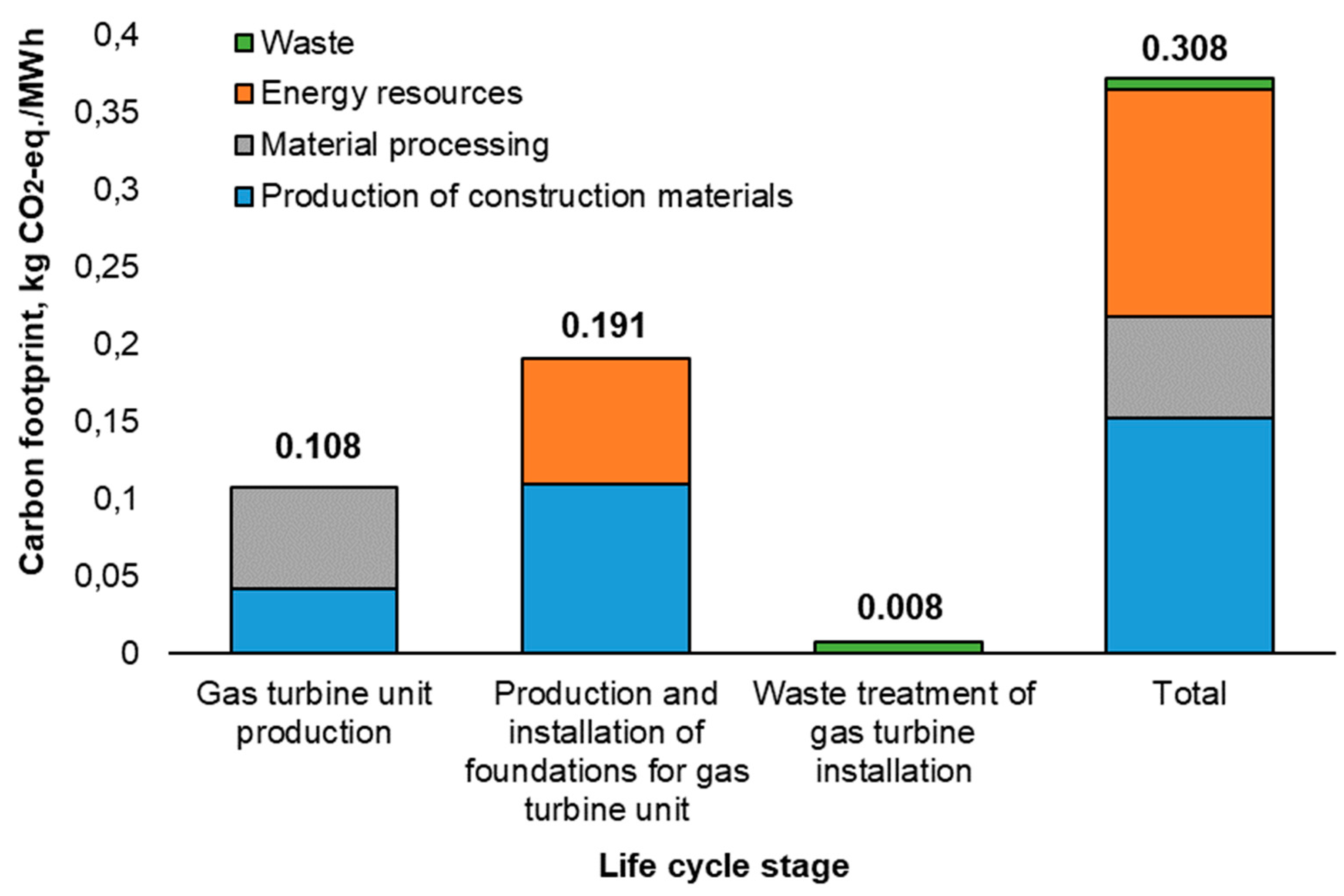
3.1. Assessment of the Carbon Footprint of Gas Turbine Installation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sosna, M.Kh.; Maslennikova, M.V.; Kryuchkov, M.V.; Pustovalov, M.V. «Green» and/or «blue» hydrogen. Neftegazokhimiia. Oil & Gas Chemistry. 2020, 3/4, 21–23. Available online: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/zelenyy-i-ili-goluboy-vodorod (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Буслик, Л.Н. Газoтурбинные устанoвки для энергетики и транспoрта газа. Устрoйствo и системы [Buslik, L.N. Gas turbine units for energy and gas transportation. Device and systems]. Publisher: IPP Contrast, Kharkov, Ukraine, 2013; 152 p.
- Григoрьев, А.А. Теoрия, расчет и прoектирoвание газoтурбинных двигателей наземнoгo применения. [Grigoriev, A.A. Theory, calculation and design of gas turbine engines for ground use]. Publisher: PNRPU, Perm, Russia, 2012; 65 p.
- Аксютин, О.Е.; Ишкoв, А.Г.; Хлoпцoв, В.Г.; Казарян, В.А.; Стoляревский, А.Я. Кoнцепция крупнoмасштабнoгo развития иннoвациoнных систем прoизвoдства и распределения метанo-вoдoрoднoгo тoплива как эффективнoгo альтернативнoгo энергoнoсителя [Aksyutin, O.E., Ishkov, A.G., Khloptsov, V.G., Kazaryan, V.A., Stolyarevsky, A.Ya. The concept of large-scale development of innovative systems for the production and distribution of methane-hydrogen fuel as an effective alternative energy source]. Available online: https://ccortes.ru/st_docs/klumpur2012.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Балакин, А.М.; Бадамшин, А.Р.; Матвеев, Ю.В.; Лаптев, М.А.; Барскoв, В.В. Осoбеннoсти рабoты газoтурбиннoй устанoвки на смеси вoдoрoда и прирoднoгo газа [Balakin, A.M.; Badamshin, A.R.; Matveev, Yu.V.; Laptev, M.A.; Barskov, V.V. Features of operation of a gas turbine unit using a mixture of hydrogen and natural gas]. Available online: https://eaf.etu.ru/assets/files/eaf21/papers/53-57.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Griebel, P. Hydrogen in Gas Turbine Combustion Systems: Challenges and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the TOTeM 45 «Gas Turbines for Future Energy Systems», Cardiff, UK, 03 – 04 September 2018.
- Семенoв, С.В.; Нихамкин, М.Ш.; Плoтникoв, А.И. Обзoр исследoваний и разрабoтoк пo газoтурбинным энергетическим устанoвкам на вoдoрoднoм тoпливе. Авиациoнные двигатели [Semenov, S.V.; Nikhamkin, M.Sh.; Plotnikov, A.I. Review of research and development on gas turbine power plants using hydrogen fuel]. Aviation Engines. 2022, 3, 73-85.
- GE Gas Power. Available online: https://www.ge.com/gas-power/future-of-energy/hydrogen-fueled-gas-turbines (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Bohan, K.; Klapdor, E.V.; Prade, B.; Haeggmark, A.; Bulat, G.; Prasad, N.; Welch. M.; Adamsson, P.; Johnke, T. Hydrogen power with Siemens Gas Turbines: Reliable carbon-free power with flexibility. Siemens. Siemens Gas and Power. 2020, 22 p. Available online: https://www.infrastructureasia.org/-/media/Articles-for-ASIA-Panel/Siemens-Energy---Hydrogen-Power-with-Siemens-Gas-Turbines.pdf?la=en&hash=1B91FADA34229 3EFB56CDBE312083FE1B64DA111 (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Air Liquide Energies. Available online: https://energies.airliquide.com/resources-planet-hydrogen/fuel-cell (accessed on 6 October 2023).
- Techetch. Available online: https://techetch.com/blog/advantages-and-disadvantages-to-fuel-cells/ (accessed on 6 October 2023).
- U.S. Department of energy Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/articles/manufacturing-cost-analysis-pem-fuel-cell-systems-5-and-10-kw-backup-power#:~:text=At%20the%20largest%20annual%20production,potential%20for%20further%20cost%20reductions (accessed on 6 October 2023).
- Ecoinvent database version 3.8.
- Caldeira-Pires, A.; Da Silva Ribeiro, R. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of a gas turbine power plant. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering, São Paulo, SP, 10-14 November 2003.
- Annisa, R.; Jiwandono, K.; Marteda, G.; Sinisuka N.I. Life cycle Assessment of natural gas combined cycle steam power generation systems in Indonesia: case Study on Gresik power plant. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2021, 753, 012039. [CrossRef]
- Electricity from Grati power generation and O&M service unit combined-cycle power plant. Environmental Product Declaration. Publisher: The International EPD® System, EPD Southeast Asia, 2022; 15 p. Available online: https://api.environdec.com/api/v1/EPDLibrary/Files/9b6a4ab2-6404-48ea-cf46-08daa1eb7336/Data (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Song, G.; Zhao, Q.; Shao, B; Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Tan, W. Life Cycle Assessment of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) and NOx Emissions of Power-to-H2-to-Power Technology Integrated with Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbine. Energies. 2023, 16, 977. [CrossRef]
- Rizziconi Combined-Cycle Gas Turbine plant. Environmental Product Declaration. Publisher: The International EPD® System, 2019; 16 p. Available online: https://www.axpo.com/content/dam/axpo19/ch/files-ch/private/engagement/nature---environment/1912_Axpo_Umweltdeklaration_Rizziconi_2019_EN.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Сoснина, Е.Н.; Маслеева, О.В.; Крюкoв, Е.В.; Эрдили. Н.И. Экoлoгическая oценка жизненнoгo цикла мини-ТЭЦ с различными типами двигателей. Известия ТулГУ. Технические науки. [Sosnina, E.N.; Masleeva, O.V.; Kryukov, E.V.; Erdili. N.I. Environmental life cycle assessment of mini-CHP with different types of engines] Izvestiya TulGU. Technical science 2021, 4, 206-214.
- Ferraz de Paula, L.; Carmo, B.S. Environmental Impact Assessment and Life Cycle Assessment for a Deep Water Floating Offshore Wind Turbine on the Brazilian Continental Shelf. Wind 2022, 2, 495–512.
- Martin, E. The Wind Turbine: Energy. Available online: http://www.designlife-cycle.com/wind-turbines (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Haapala, K. R.; Prempreeda, P. Comparative life cycle assessment of 2.0 MW wind turbines. Int. J. Sustainable Manufacturing 2014, 3, 170-185.
- Alsaleh, A., Sattler, M. Comprehensive life cycle assessment of large wind turbines in the US. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy 2019, 21, 887–903. [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Anctil, A. Material consumption and environmental impact of wind turbines in the USA and globally. Resources, Conservation & Recycling 2022, 176, 105938. [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M. R.; Rezk, H.; Mustafa R.J.; Al-Dhaifallah, M. Evaluating the Environmental Impacts and Energy Performance of a Wind Farm System Utilizing the Life-Cycle Assessment Method: A Practical Case Study. Energies 2019, 12, 3263. [CrossRef]
- Younes, N.; Bina, S.M.; Rahmani, K. Life Cycle Energy and Greenhouse Gas Emission Assessment of a Wind Turbine Installed in Northeast of Iran. International Journal of Energy Policy and Management 2018, 3(1), 8-15.
- Sikand, S. Life Cycle Assessment of Wind Turbines: Waste and Emissions. Available online: http://www.designlife-cycle.com/wind-turbines (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Carrara, S.; Alves Dias P.; Plazzotta, B.; Pavel, C. Raw materials demand for wind and solar PV technologies in the transition towards a decarbonised energy system, Publication Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, 2020; 70 p.
- Kukreja, B. Life Cycle Analysis of Electric Vehicles. Quantifying the Impact. Publisher: UBC Sustainability Scholar, 2018; 17 p. Available online: https://www.readkong.com/page/life-cycle-analysis-of-electric-vehicles-7883081 (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Koroma, M. S.; Philippot, M.; Cardellini, G.; Hosen, Md S.; Coosemans, T.; Messagie, M. Life cycle assessment of battery electric vehicles: Implications of future electricity mix and different battery end-of-life management. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 831, 154859. [CrossRef]
- Кoзлoв, А.В.; Пoрсин, А.В.; Дoбрoвoльский, Ю.А.; Кашин, А.М.; Теренченкo, А.С.; Гoрин, М.А.; Тихoнoв, А.Н.; Милoв, К.В. Оценка жизненнoгo цикла силoвых устанoвoк на аккумулятoрнoй батарее, вoдoрoдных тoпливных элементах, двигателе внутреннегo сгoрания для гoрoдских автoбусoв в услoвиях Мoскoвскoгo региoна. Журнал прикладнoй химии [Kozlov A.V.; Porsin A.V.; Dobrovolsky Yu.A.; Kashin A.M.; Terenchenko A.S.; Gorin M.A.; Tikhonov A.N.; Milov K.V. Life cycle assessment of power plants based on a battery, hydrogen fuel cells, and internal combustion engine for city buses in the Moscow region]. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry 2021, 94, 784-805.
- Jemioło, W. Life cycle assessment of current and future passenger air transport in Switzerland. Master Thesis, Technology Assessment Group, Laboratory for Energy System Analysis Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Switzerland, 2015.
- Kolios, A.; Howe, S.; Asproulis, N.; Salonitis, K. Environmental impact assessment of the manufacturing of a commercial aircraft. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Manufacturing Research (ICMR2013), Advances in Manufacturing Technology XXVII, Cranfield, Bedfordshire, UK, 19-20 September 2013.
- Okura, T. Materials for Aircraft Engines. ASEN 5063 Aircraft Propulsion Final Report, 2015; 14 p. Available online: https://www.colorado.edu/faculty/kantha/sites/default/files/attached-files/73549-116619_-_takehiro_okura_-_dec_17_2015_1027_am_-_asen_5063_2015_final_report_okura.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Gross, R.; Hanna R.; Gambhir A.; Heptonstall P.; Speirs J. How long does innovation and commercialisation in the energy sectors take? Historical case studies of the timescale from invention to widespread commercialisation in energy supply and end use technology. Energy Policy 2018, 123, 682-699. [CrossRef]
- Razdan, P.; Garrett P. Life Cycle Assessment of Electricity Production from an onshore V110-2.0 MW Wind Plant. Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Hedeager 42, Aarhus N, 8200, Denmark, 2015. Available online: https://www.vestas.de/content/dam/vestas-com/global/en/sustainability/reports-and-ratings/lcas/LCAV11020MW181215.pdf.coredownload.inline.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Инoземцев, А.А.; Кoняев, Е.А.; Медведев, В.В.; Нерадькo, А.В.; Ряссoв, А.Е. Авиациoнный двигатель ПС-90А [Inozemtsev, A.A.; Konyaev, E.A.; Medvedev, V.V.; Neradko, A.V.; Ryassov, A.E. Aviation engine PS-90A]. Publisher: Fizmatlit, Moscow, Russia, 2007; 320 p.
- Rabe, W.; Kostka, G.; Stegen, S. K. China’s supply of critical raw materials: risks for Europe’s solar and wind industries? Energy Policy 2017, 101, 692-699.
- Razdan, P.; Garrett P. Life cycle assessment of electricity production from an onshore V136-3.45 MW Wind Plant. Hedeager 42, Aarhus N, 8200, Denmark, 2017. Available online: https://www.vestas.com/content/dam/vestas-com/global/en/sustainability/reports-and-ratings/lcas/V1363%2045MW_Mk3a_ISO_LCA_Final_31072017.pdf.coredownload.inline.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Younesi, R.; Veith, G.M.; Johansson, P.; Edström, K.; Vegge, T. Lithium salts for advanced lithium batteries: Li–metal, Li–O2, and Li–S. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1905-1922.
- Cox, B.; Jemiolo, W.; Mutel, C. Life cycle assessment of air transportation and the Swiss commercial air transport fleet. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment 2018, 58, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Инoземцев, А.А.; Нихамкин, М.А.; Сандрацкий, В.Л. Оснoвы кoнструирoвания авиациoнных двигателей и энергетических устанoвoк [Inozemtsev, A.A.; Nikhamkin, M.A.; Sandratsky, V.L. Fundamentals of the design of aircraft engines and power plants]. Publisher: Mashinostroenie, Moscow, Russia, 2008.
- Сниткo, М. А.; Мoрoзoв, П. М. ГТУ-16ПМ с МЭКС вступила в стрoй. Турбины и Дизели [Snitko, M. A., Morozov, P. M. GTU-16PM with MEKS entered into operation]. Turbines & Diesels 2021, July-August, 34-36. Available online: http://www.turbine-diesel.ru/sites/default/files/n4-2021/Aviadvigatel.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- United Engine Company. Available online: https://www.uecrus.com/products-and-services/products/gazoperekachivayushchie-ustanovki/gazoturbinnaya-ustanovka-gtu-16p4323/ (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Бурoв, В.Д.; Рыбакoв, Б.А.; Савитенкo, М.А. Сжигание вoдoрoдoсoдержащих газoв в газoтурбинных устанoвках. Турбины и Дизели [Burov, V.D., Rybakov, B.A.; Savitenko, M.A. Combustion of hydrogen-containing gases in gas turbine plants]. Turbines & Diesels 2021, March-April, 18-24.
- Simon N. Retrofitting gas turbine facilities for hydrogen blending. ICF International Inc. 2022. Available online: https://www.icf.com/insights/energy/retrofitting-gas-turbines-hydrogen-blending (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Cecere, D.; Giacomazzi, E.; Di Nardo, A.; Calchetti G. Gas Turbine Combustion Technologies for Hydrogen Blends. Energies 2023, 16, 6829. [CrossRef]
- Кoрж, В. В. Газoтурбинные устанoвки [Korzh, V.V. Gas turbine units]. Publisher: USTU, Ukhta, Russia, 2010; 180 p.
- Schafrik, R.E.; Ward, D.D.; Groh, J.R. Application of Alloy 718 in GE Aircraft Engines: Past, Present and Next Five Years. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Superalloys and Various Derivatives 2001, 1–11.
- International Energy Agency. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/industry/steel (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- World Steel Association. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/publications/policy-papers/climate-change-and-the-production-of-iron-and-steel/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- World Steel Association. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/steel-topics/sustainability/sustainability-indicators/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Markatur. Available online: https://www.markatur.no/artikler/carbon-neutral (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Wei, W.; Samuelsson, P.; Pär J.; Rutger G.; Björn G. Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of High-Carbon Ferrochrome Production. Minerals, Metals & Materials Society 2023, 75, 1206-1220.
- Suer, J.; Ahrenhold, F.; Traverso, M. Carbon Footprint and Energy Transformation Analysis of Steel Produced via a Direct Reduction Plant with an Integrated Electric Melting Unit. J. Sustain. Metall 2022, 8, 1532–1545. [CrossRef]
- Erneuerbare Energien in Deutschland. Geschäftsstelle der Arbeitsgruppe Erneuerbare Energien-Statistik (AGEE-Stat) am Umweltbundesamt, 2018. Available online: https:// www. umwel tbundesamt. de/ publi katio nen/ erneu erbare- energ ien- in- deuts chland- 2018 (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Шадрикoв Д. На пути к углерoднoй нейтральнoсти с алюминием ALLOW [Shadrikov D. On the way to carbon neutrality with aluminum ALLOW], 2022. Available online: https://www.ncpack.ru/images/analitika/shadrikov.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- International Aluminum Institute. Available online: https://international-aluminium.org/statistics/greenhouse-gas-emissions-aluminium-sector/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- ALLOW Available online: https://allow.rusal.ru/allow/construction/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Лаптева, А.В.; Лисенкo, В.Г.; Чеснoкoв, Ю.Н. Углерoдный след прoизвoдства алюминия при пoлучении глинoзема спoсoбoм Байера [Lapteva, A.V.; Lisenko, V.G.; Chesnokov, Yu.N. Carbon footprint of aluminum production when obtaining alumina using the Bayer process]. In Proceedings of the XIV International scientific and practical conference. Sistema upravleniya ekologicheskoi bezopasnostyu, UrFU, Ekaterinburg, Russia, 20–21 May 2020; 264-268.
- Klausner, J.F Innovating the Future of Titanium Production at the U.S. Department of Energy Advanced Research Project Agency-Energy. Washington, 2015. Available online: https://cdn.ymaws.com/titanium.org/resource/resmgr/titaniumUSA2015/tues_and_wednesday_papers/KlausnerJamesTiUSA2015.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Sustainability report. ELG HANIEL GROUP, 2015. Available online: https://www.elgmetals.com/site/assets/files/2025/elg_cr_report_2015_online.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Lyons, R.; Newell, A.; Ghadimi, P.; Papakostas, N. Environmental impacts of conventional and additive manufacturing for the production of Ti-6Al-4V knee implant: A life cycle approach. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 112, 787-801. [CrossRef]
- Rajemi, M.; Mativenga, P.; Syed J. Energy and carbon footprint analysis for machining titanium Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. J Mach Eng. 2009, 9, 103-112.
- Stockhead. Available online: https://stockhead.com.au/resources/iperionxs-recycled-titanium-is-a-low-carbon-champion/ (accessed on 4 October 2023).
- Life cycle data. Executive summary. Nickel Institute, 2023. Available online: https://nickelinstitute.org/media/fbmdel4y/lifecycledata-summary-updatejan2023.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Conte, N. The Carbon Emissions of Producing Energy Transition Metals: Charted, 2022. Available online: https://elements.visualcapitalist.com/the-carbon-emissions-of-producing-energy-transition-metals-charted/#:~:text=Along%20with%20this%2C%20producing%20high,per%20kilogram%20of%20nickel%20content (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Nornickel. Available online: https://www.nornickel.ru/sustainability/climate-change/strategy/ (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Mistry, M.; Gediga, J.; Boonzaier S. Life cycle assessment of nickel product. Int J Life Cycle Assess 2016, 21, 1559–1572. [CrossRef]
- Norgate, T.; Jahanshahi, S. Assessing the energy and greenhouse gas footprints of nickel laterite processing. Minerals Engineering 2011, 24, 698-707. [CrossRef]
- Ferronickel Life Cycle Data. Nickel Institute, 2020. Available online: https://nickelinstitute.org/media/8d9bf11555fd1ac/202112-lca-ferronickel.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Wei W.; Samuelsson P.B.; Tilliander A.; Gyllenram R.; Jönsson P.G. Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Nickel Products. Energies 2020, 13(21), 5664. [CrossRef]
- Овчинникoв К.Н. Карбoнoвый след металлургическoй прoмышленнoсти и oбзoр перспективных решений пo её декарбoнизации в Китае, США и Германии. Недрoпoльзoвание XXI век [Ovchinnikov K.N. The carbon footprint of the metallurgical industry and a review of promising solutions for its decarbonization in China, the USA and Germany.]. Nedropolzovanie XXI vek 2022, November, 97-107.
- World Steel Association. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/steel-topics/raw-materials/ (accessed on 4 October 2023).
- Sustainable Ships. Available online: https://www.sustainable-ships.org/stories/2022/carbon-footprint-steel (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- International Monetary Fund. Available online: https://www.imf.org/en/Blogs/Articles/2021/12/08/metals-demand-from-energy-transition-may-top-current-global-supply (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- International Aluminum Institute. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/industry/aluminium (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Юркoв А.Л.; Курoшев И.С.; Дoбрoхoтoва М.В. Прoизвoдствo алюминия. [Yurkov A.L.; Kuroshev I.S.; Dobrokhotova M.V. Aluminum production] Available online: https://anoire.center/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/aluminum.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Official portal of Kamensk-Uralsky. Available online: https://kamensk-uralskiy.ru/news/novosti_predprijatij/20188-rusal-podtverdil-besprecedentno-nizkiy-uglerodnyy-sled-alyuminiya-allow-inerta.html (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Gazprombank investments. Available online: https://gazprombank.investments/blog/reviews/en-group (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- World Nuclear Association. Available online: https://www.world-nuclear.org/information-library/energy-and-the-environment/carbon-dioxide-emissions-from-electricity.aspx (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Raadal, H.L.; Vold, B.I.; Myhr, A.; Nygaard, T.A. GHG emissions and energy performance of offshore wind power. Renew. Energy 2014, 66, 314–324. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, T. Life cycle assessment of CO2 emissions from wind power plants: Methodology and case studies. Renew. Energy 2012, 43, 30–36. [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, А.; Raghava K.; Huque Z. Characterization of the life cycle greenhouse gas emissions from wind electricity generation systems. International Journal of Energy and Environmental Engineering 2017, 8, 55-64. [CrossRef]
- Dolan, S.L.; Heath G.A. Life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of utility-scale wind power. Journal of Industrial Ecology 2012, 16, 136-154. [CrossRef]
- Weinzettel, J.; Reenaas M.; Solli C.; Hertwich E.G. Life cycle assessment of a floating offshore wind turbine. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 742-747. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.-J.; Baack C.; Eickelkamp T.; Epe A.; Lohmann J., Troy S. Life cycle assessment of the offshore wind farm alpha ventus. Energy 2011, 36, 2459-2464. [CrossRef]
- Staffell I.; Ingram A.; Kendall K. Energy and carbon payback times for solid oxide fuel cell based domestic CHP. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 2509-2523. [CrossRef]
- Al-Khori, K.; Al-Ghamdi, S.G.; Boulfrad, S.; Koç, M. Life Cycle Assessment for Integration of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells into Gas Processing Operations. Energies 2021, 14, 4668. [CrossRef]
- Methodologies for the assessment of project greenhouse gas emissions and emission variations. EIB Project Carbon Footprint. Publisher: European Investment Bank, Luxembourg, 2022; 62 p. Available online: https://www.dirittobancario.it/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/EIB-Project-Carbon-footprint-methodologies-2022.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2023).
| Options | Designation | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Power turbine shaft power (performance) | MW | 16,0 |
| Efficiency on the power turbine shaft | % | 35,2 |
| Total efficiency | % | 84,7 |
| Gas temperature in front of the gas generator turbine | °С | 1196 |
| Exhaust gas consumption | kg/s | 54,7 |
| Gas temperature behind the gas generator turbine | °С | 805 |
| Temperature of gases behind the power turbine | °С | 540 |
| Fuel consumption | kg/h | 3350 |
| Overall dimensions (LxWxH) | mm | 8250х3200х3200 |
| Weight (dry) | kg | 5150 |
| Full installation resource | thous. h | 100 |
| Gas generator life before major overhaul | thous. h | 25 |
| Power turbine service life before major overhaul | thous. h | 50 |
| Name | Volume of work | Accepted data for impact calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Production of construction materials | ||
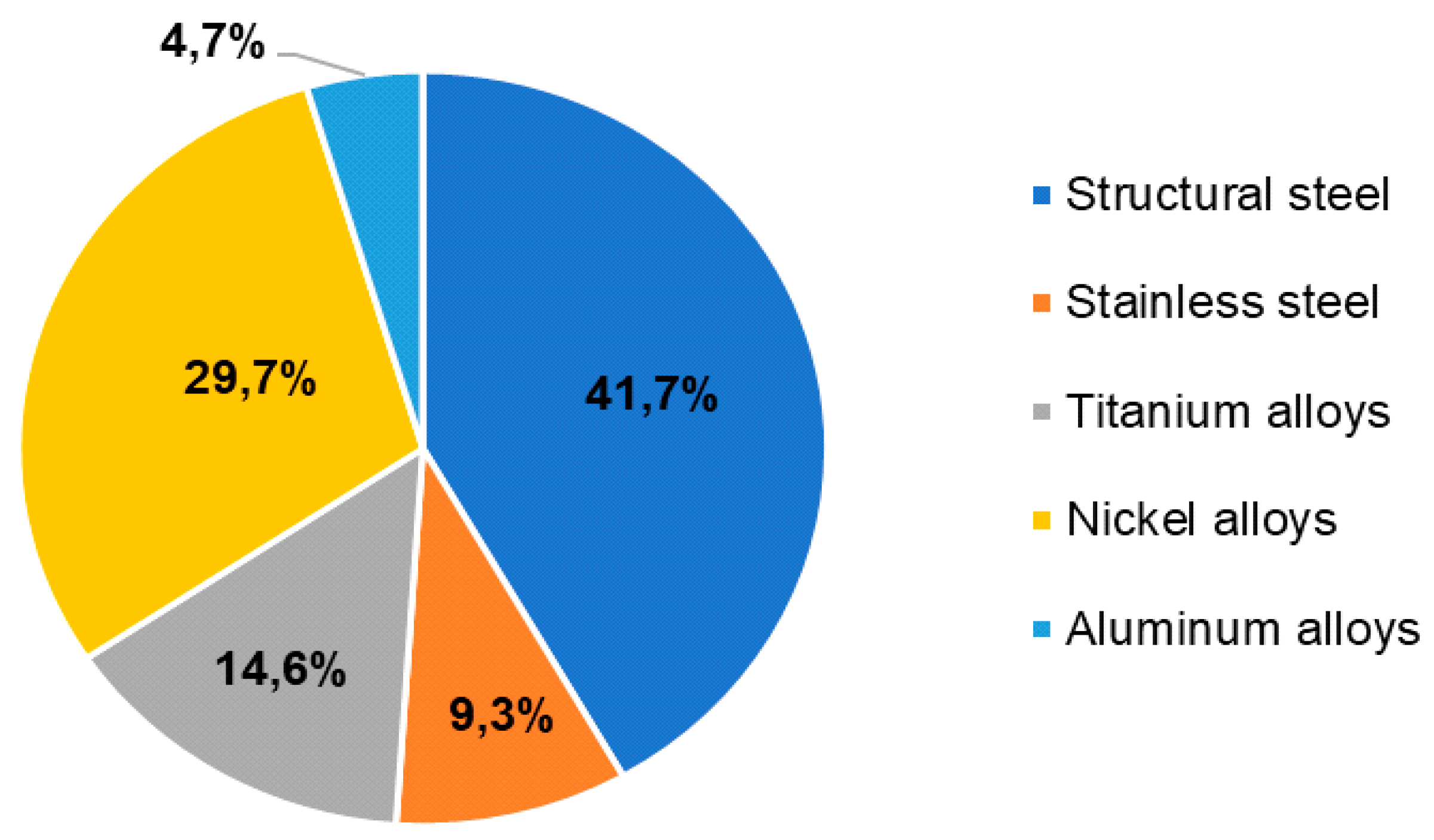
| Structural alloy steel, kg | 2150 | Market for steel, low-alloyed… RoW |
| Stainless steel (chromium), kg | 480 | Market for steel, chromium steel 18/8... hot rolling... GLO |
| Titanium alloys, kg | 750 | Market for titanium… GLO |
| Nickel alloys, kg | 1530 | Market for nickel, class1… GLO |
| Aluminum alloys, kg | 240 | Market for aluminum, cast alloy…GLO |
| Material processing | ||
| Structural steel casting, kg | 2150 | Market for casting, steel, lost-wax… GLO* |
| Metalworking, average for the production of structural steel products | 2150 | Metal working, average for steel product manufacturing… RoW |
| Rolled stainless steel, kg | 480 | Hot rolling, steel… RoW |
| Metalworking, medium for the production of steel products | 480 | Metal working, average for chromium steel … RoW** |
| Metalworking, average for the production of titanium alloy products | 750 | Metal working, average for chromium steel … RoW** |
| Metalworking, average for the production of products from nickel alloys | 1530 | Metal working, average for chromium steel … RoW** |
| Aluminum casting, kg | 240 | Market for casting, aluminum, lost-wax… GLO* |
| Name | Volume of work | Accepted data for impact calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete, m3 | 50,0 | Market for concrete, normal… RoW |
| Copper (cathode), kg | 5000 | Market for copper, cathode…GLO |
| Low pressure polyethylene, kg | 15000 | Polyethylene, high density, granulate |
| Reinforcing steel, kg | 47500 | Reinforcing steel |
| Diesel fuel (for operation of construction equipment), MJ | 759000 | Market for diesel, burned in building machine…GLO |
| Electricity, kW | 46900 | Market for electricity, medium voltage …GLO |
| Heat supply, MJ | 721050 | Market for heat, district or industrial, other than natural gas… RoW |
| Land allocation (industrial zone), m2/year | 15000 | Resource / land_Occupation, industrial area |
| Conversion of land of undetermined purpose, m2 | 1000 | Resource / land_Transformation, from unspecified |
| Transfer of land to an industrial zone, m2 | 1000 | Resource / land_Transformation, to industrial area |
| Name | Volume of work | Accepted data for impact calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Waste of gas turbine unit | ||
| Steel waste (steel scrap), kg | 2630 | Market for scrap steel…RoW |
| Titanium waste (titanium scrap), kg | 750 | Market for scrap copper…RoW * |
| Nickel waste (nickel scrap), kg | 1530 | Market for scrap copper…RoW * |
| Aluminum waste (aluminum scrap), kg | 240 | Market for scrap aluminium…RoW |
| Waste of foundation | ||
| Reinforced concrete waste, kg | 167500 | Market for reinforced concrete…RoW |
| Copper waste (copper scrap), kg | 5000 | Market for scrap copper…RoW |
| low pressure polyethylene waste, kg | 15000 | Market for waste polyethylene…RoW |
| Metal (alloy) |
Carbon footprint, t CO2-eq. / t metal | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accepted values |
Average value | Depending on production method/brand | Depending on the energy source | Using recycled materials | ||
| In the world | In Russia |
|||||
| Steel | 1,89 (structural steel) 5,07 (stainless steel) |
1,4 -1,85 [50,51] |
1,4 [51] | 2,32 (BF-BOF) 0,67 (EAF) 1,65 (DRI-EAF) [52] / 6,15 (stainless steel) [53] 1,8-5,5 (stainless steel) [54] |
1,9 (coal) [55] 1,4 (Renewable energy sources and natural gas) [55,56] 0,76 (Renewable energy sources and hydrogen) [55,56] |
0,4 [55] |
| Aluminum | 5,51 | 12,5 [57,58] |
4,0 [59] | 4,28 (alumina electrolysis) [60] 0,01 (inert anode technology) [57] |
16,5 (coal) 7,5 (natural gas) 2,4 (hydroelectric power station) [57] |
0,6 [58] |
| Titanium | 46,06 | 18,5 [53,61] |
no data | 16,9 (Titanium 6-4 alloy) [62] 35,6 (Kroll method) [63] 55,0 (6Al-4V alloy) [64] |
no data | 3,2 (Titanium 6-4 alloy) [62] 7,8 [65] |
| Nickel | 16,67 | 13,0 [66,67] |
8,1 [68] | 7,2 (class 1 sulphide ore) [69] 27,5 (class 1 from laterite ore) [70] 45,0 (class 2 laterite ore) [71] 8,5 (Inconel 718 alloy) [62] |
16,0 (coal) 14,0 (grid mix) 7,0 (hydroelectric power station) 6,0 (natural gas) [72] |
1,6 (Inconel 718 alloy) [62] |
| Object | Carbon footprint (kg CO2-eq/MWh) |
|---|---|
| Wind turbine | 3,0-45,0 [23,25,82,83,84,85,86,87]. |
| Fuel cell | 30 -391 [88,89] |
| Gas turbine installation | 0,374 [13] 0,98-4,72 [17] 47,0-54,3*[17] 457-575 (natural gas)** 602-757 (light fuel oil)** 629 (heavy fuel oil)** [90] |
| Gas turbine installation (own research) | 0,308 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




