1. Introduction
For a long time now, the evaluation of peripheral blood count has been entrusted to automated blood counters, reaching a higher level of precision than manual counting. Among the blood count parameters, the red cell distribution width (RDW) is of particular significance, favouring a complete evaluation of the erythrocyte component. RDW is a dimensionless quantitative that represents the standard deviation of red blood cell volume divided by the mean volume, and it reflects the variation in cell size in the erythrocyte population. In different clinical situations it is possible to observe an increase in the value of the RDW and the main causes lie in one of these four possibilities: decreased of erythrocyte mean volume, increased reticulocyte volume variance, increased heterogeneity in the rate of RBC volume occurring in the peripheral circulation, and delayed RBC clearance [
1,
2]. Furthermore, any change in RDW should be assessed taking into account haemoglobin values, erythrocyte number and mean corpuscular volume respectively.
The erythrocyte deformability, a hemorheological determinant that plays its undisputed role in the vascular districts where high shear rates are in force and therefore at the microcirculation level, is dependent on the surface/volume ratio of the erythrocyte, internal viscosity related mainly to the concentration of cytosolic calcium, erythrocyte organic phosphates (ATP and 2.3 DPG) and changes in hemoglobin, and the dynamic membrane properties that depend on its protein and lipid composition; in this regard, while the protein structure is responsible for elasticity, the lipid structure is responsible for its viscosity. The deformability, in addition to allowing the erythrocyte to easily cross microvascular districts of a few microns, so much lower than the geometric characteristics of the red blood cell, plays a unique role in the supply of oxygen to tissues [
3].
In subjects who practice sport activities both at amateur and elite level as well as in those who carry out physical activity in a constant and particularly intense it is likely that, in basal conditions, the erythrocyte index RDW is not increased, except when who carries out any of these activities turns out to be also anemic, as one of the doctrinal assumptions of its increase, in subjects without any haematological pathology, is the increased survival of red blood cells. Not many and often fragmentary are the data of the literature on this topic, however the negative correlation between RDW and muscle strengthening activities [
4] and between physical activity and RDW is acquired [
5]. The same conclusion have been reached by some authors in other subsequent reports where they tend to reiterate that physical activity tends to reduce this erythrocyte index [
6,
7]. Different is the behaviour of this index at the end of an acute and extremely intense exercise because in the hours following the event can show a reduction in hemoglobin levels [
8,
9]. In a dated work [
10] carried out on 2143 children and adolescent aged between 12 and 20 years, and effected between 2003 and 2006 under the NHANES project, sedentary and physical activity were assessed in relation to RDW behaviour and it was found that in boys and not girls sedentary activity was positively associated with RDW while physical activity was negatively associated to the erythrocyte index.
In all these years, it has been shown that the exercise affects the hemorheological profile in a completely different way depending on whether the same is practiced regularly or is carried out in a short time and with high intensity. What has been said in agreement with other authors [
11] underlines how the exercise in respect of the hemorheological pattern while strating from assumptions in itself simple arrive to configure hemodynamic, metabolic and hemorheological frameworks very complex.
The effects of exercise on erythrocyte deformability so far do not seem univocal: in some researches, high intensity exercises determine its reduction and in other studies concerning trained subjects it is evident an increase while in other studies there are no appreciable variations of this hemorheological determinant. During high intensity exercises, the decrease in erythrocyte deformability can be attributed to changes in hydrogenionic concentration, in particular due to the increase in lactic acid, changes in plasma osmolarity or the unbalanced increase in reactive oxygen species. In different groups of subjects practicing different sports, several authors have observed, under basal conditions, an increase in red cell deformability [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23] although others have described a reduction of this hemorheological determinant [
24,
25,
26] and others have not observed any variation of this parameter [
27,
28,
29]. In athletes, an accelerated turnover of erythrocytes is found and this leads to a very high percentage of younger cellular elements that perhaps explains the increase of the erythrocyte deformability in athletes [
30,
31].
From the point of view of clinical hemorheology, it makes seriously reflect in how much it is not to exclude that in the determinism of the deformability of the red blood cells must be taken in due consideration the degree of anisocytosis that of fact is that which is expressed by this erythrocyte index. Until now, the data obtained in relation to the study of correlation between these two parameters have not converged in the literature. The first response concerned a cohort of 293 adults with an average age of 71.1 ± 13.3 participating in a longitudinal aging study in which a significant negative correlation was found between the RDW and the elongation index evaluated at shear stress of 3 Pa [
32]. This correlation became significantly more marked when the entire cohort excluded the group of anaemic subjects.
Considering the above-mentioned references to both the RDW erythrocyte index and the erythrocyte deformability in respect of exercise, in this new research we wanted to examine, the behaviour of both parameters in a group of regularly trained subjects, who from non-professionals perform regular sports activities respectively endurance, power and mixed, and in particular to examine whether is a direct relationship between them on the one hand and on the other to try to examine on which erythrocyte (MCV, MCH, MCHC) and non-erythrocyte parameters the respective behaviour depends.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
For this study we enrolled 79 subjects (62 men and 17 women ; mean age 31.37 ± 10.19 years; range 18-57 years) who practiced regular physical sports training, three or four times a week; as they are non-professional athletes. 30 of these subjects practiced endurance sports, 25 of these subjects performed mixed sports and 24 of them practiced power sports. In this group of non-professional athletes, the VO2 max was 33.14 ± 10.86 ml /Kg/ min.The control group included 25 subjects (19 men and 6 women; mean age 33.04 ± 5.77 years; range 24.00- 48 years) which did not engage in any physical activity, In the control group the VO2 max was 22.11 ± 5.77 ml/Kg/min. All subjects did not have cardiovascular or other medical diseases, as demonstrated by clinical history, from objective examination, electrocardiography, and routine hematological and urine analyses. No subjects had taken medication in the previous weeks and no subject had been subjected to dietary restrictions prio to the study. Informed consent was obtained from each partecipant and the VO2 max was evaluated by a computerized breath-by-breath analyzing system (oxycon Delta;Viasys Jaeger, Hoechberg, Germany).
2.2. Methods
On fasting venous blood, we evaluated the following parameters: hematocrit (Ht) obtained using an automated hematology analyser; hemoglobin, expressed in gr/L, and evaluated with the automated blood count; mean corpuscolar volume (MCV) expresses in fl, mean concentration hemoglobin (MCH) expressed in pg, mean corupscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), expressed in gr/dl; RDW expressed as a percentage, and erythrocyte deformability expressed as elongation index. To evaluate this latter hemorheological parameter, a 30 µl of anticoagulated blood with 2 ml of dextran solution at a viscosity of 24 mPa was mixed. The measurement was obtained by using the diffractometer Rheodyn SSD of Myrenne, which measures the diffraction pattern of a laser beam passing through erythrocytes suspended in a viscous medium and deformed by a force with defined shear stress. The shear stress employed was 6, 12, 30 and 60 Pa. The erythrocyte deformation was expressed as elongation index (EI) = (l – w/l + w) x100, where l = length and w = width of the erythrocytes.
2.1. Statistical analysis
All statistical analysis were performed using GraphPAd Prism vers. 9.5. The data were expressed as means and standard deviation. The comparison between the means was effected using the Student’ t test for unpaired data. For the analysis of the different correlations was employed the Pearson’s test The null hypothesis was evaluated for values of p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
First of all, we have tabulated the means, standard deviation and ranges of all the parameters considered regarding this group of subjects who carry out non-professional sports activities and who are regularly trained. The parameters considered in this study are: hematocrit, hemoglobin level, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean erythrocyte hemoglobin content (MCH), mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), red blood cell distribution width (RDW%) and the values of the elongation index to the four shear stress, respectively at 6, 12, 30 and 60 Pa ,all examined under basal conditions (
Table 1).
Immediately after, we have carried out the comparison of the means between the control group and that of the trained subjects and from this comparison it has emerged that in the entire group of trained subjects a significant increase of the MCV and the MCH associated with an increase in elongation index (marker of increased erythrocyte deformability). This comparison did not reveal any change in hematocrit, hemoglobin level, MCHC and RDW (
Table 2).We then divided the whole group of trained subjects according to the median of VO2max [30.00(11.40)ml/kg/min] and we observed that in the subgroup that exceeds the median it turns out evident a meaningful reduction of the MCH and the MCHC associated to significant increment of the values of the elongation index. On the other hand, no appreciable variation has been observed for all the other parameters taken into account (
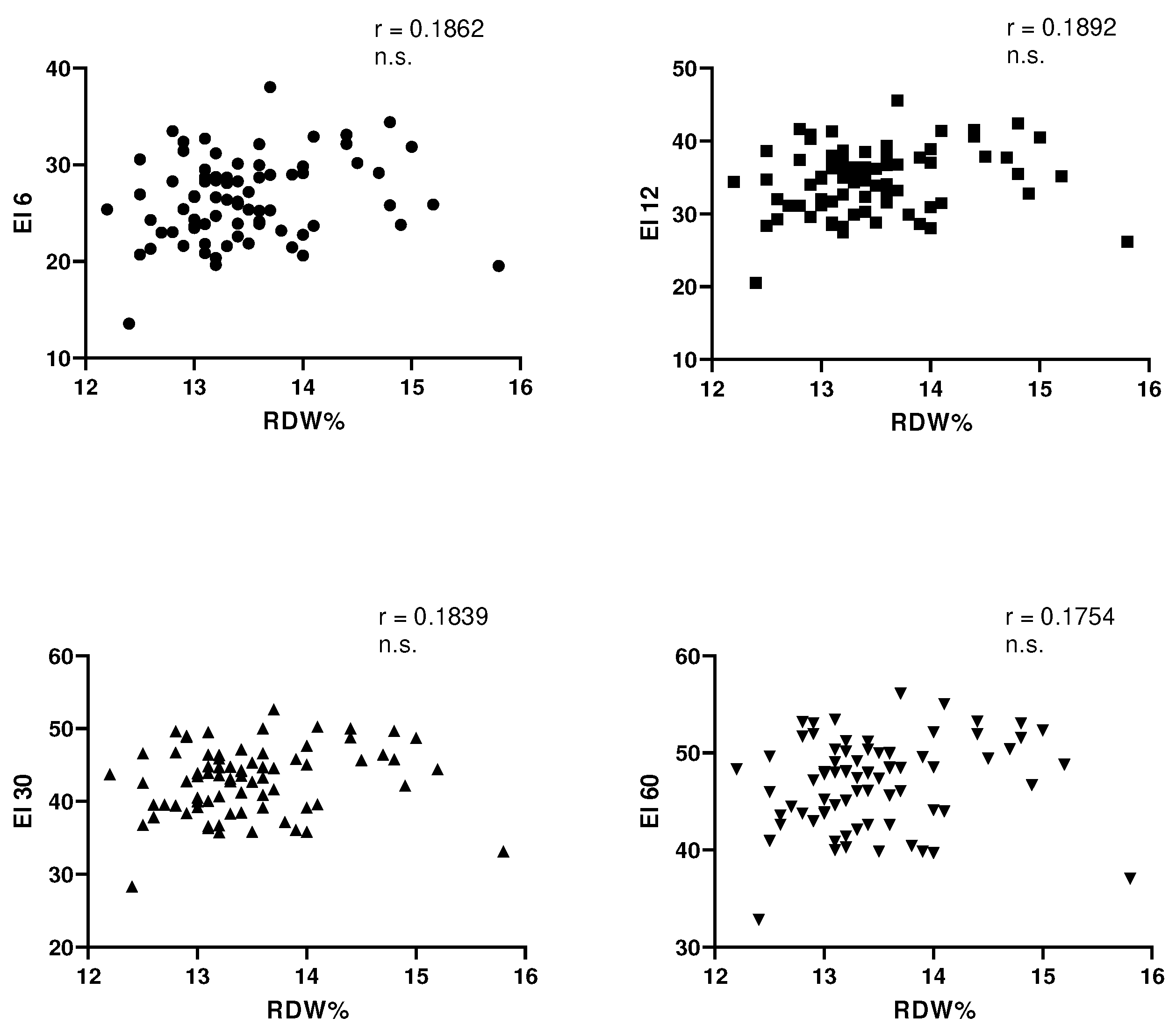
Table 3). In this trained group of subjects, no correlation was observed between each value of elongation index respectively examined at shear stress of 6, 12, 30 and 60 Pa and RDW (
Figure 1). At this point, to try to clarify what are the parameter, erythrocyte and extra erythrocyte, able to influence in this group of trained subjects, both the RDW and the elongation index have examined with the Pearson test the different statistical correlations (
Table 4). We initially wanted to examine which of the erythrocyte and extra erythrocyte parameters were capable of influencing the RDW erythrocyte index and it was observed that RDW is negatively related to MCH and MCHC only. No correlation is recorded with the age of subjects, with VO2max, with hematocrit, with the hemoglobin level and with MCV. Quite different behaviour is observed relative to elongation index values. The latter are negatively related to hematocrit, hemoglobin and MCHC and positively related to MCV. No correlation exists between MCH and the elongation index values and between the latter and the age of the subjects. Of particular interest, but difficult to interpret, the positive correlation between the values of VO2max and the values of elongation index evaluated at shear stress of 6 and 12 Pa.
4. Discussion
With reference to the data obtained from this research,we think that the first consideration should concern the different trend of RDW and elongation index, which reflects the erythrocyte deformability, between control group (sedentary subjects not trained) and the group of non-professonal sports players who perform a regular physical acitvity several times a week.The RDW is not known to distinguish between the two groups, and this behaviour is more than predicable since, RDW that is the marker of the level of erythrocyte anisocytosis, tends to increase in the absence of an anemic condition, with the lengthening of the average life of the erythrocyte that id difficult to occur in trained subjects and we examined in basal conditions only.What we observed is in line with the data reported by other authors [
4,
5,
6,
7,
10] who investigated the same clinical condition. Different is the trend of the same erythrocyte index several hours after performing a moderate aerobic exercise [
8] or after performing an extreme run (Alis R. 2015).Quite different is the behaviour of the elongation index values, to the four shear stress,which are increased in group of trained subjects and confirming our previous data [
19] tend to overlap data from several other authors [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
20,
21,
22,
23] which have highlighted an increase in erythrocyte deformability in trained and amateur sports subjects which play and undisputed role in the transport of oxygen to tissues and which plays its role in vascular districts, such as microcirculation where the highest shear rates are physiologically in force [
33].
Not separated from this reflection, another data of particular interest in the comparison between the control group and that of the trained subjects, must be sought in the trend of some erythrocyte parameters such as MCV and MCH. Both these parameters are significantly increased in the trained subjects compared to the controls and this feed back, not at all occasional, is based on what is now ascertained with regard to the effects of exercise on the red blood cell production [
34], on the regulation of the erythrocyte volume [
35,
36] and on the whole erythropoiesis [
37]. In fact the exercise training in addition to promoting bone marrow hyperplasia [
38], can reduce the circulating level of pro-inflammatory cytokines [
39,
40], can vary the affinity of erythropoietin receptors [
41] and also to increase its concentration, although this increase does not seem to be certain [
42]. Also do not underestimate the changes in the hormonal profile observed in relation to exercise training; in fact, some hormones (testosteron, growth hormone) and especially the insulin-like growth factor [
43,
44] stimulate erythrocyte production. Therefore it is likely to have in circulation more and more young erythrocytes that simultaneously explain both the increase in erythrocyte deformability and the increase in mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and mean hemoglobin content (MCH).
Of particular interest is what happens by dividing the group of trained subjects in relation to the values of the VO2max median. In this case of particular pathophysiological interest is what is evident from the values of elongation index. In fact, in the subgroup that exceeds the median, it is evident, even if at low statistical significance, an increase in the deformability of the red blood cells associated both with the reduction in mean hemoglobin content (MCH) than at the mean hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). It is possibile to hypothesize that the decrease of these two erythrocyte parameters can be based on the fact that in the subgroup that exceeds the VO2max median there is a clear tendency to reduce the value of total hemoglobin that helps to better explain the trend of both the MCH and of MCHC.
In this group of trained subjects, as could be expected, given the trend of the RDW and the values of the elongation index, there is no significant statistical correlation between them. A negative correlation could theoretically be expected since there are certainly young erythrocytes and therefore it was conceivable that the reduction of the RDW wuold be associated with higher elongation index values confirming a higher erythrocyte deformability. So far, in addition to what Patel reported in 2013 [
32] the he described a negative correlation between RDW and the value of elongation index to shear stress of 3 Pa, other authors in different clinical conditions have found data uneven. Some authors in fact both in hypertensive patients [
45], and in patients with acute myocardial infarction [
46] both in subjects with metabolic diseases showed a positive correlation between these two parameters. Similar to what Patel [
32] found, a negative correlation between RDW and elongation index occurred both in subjects with thalassemic trait and in patients with haematological neoplasms [
47].
Not always easy to interpret are the results of correlations evaluated in the group of trained subjects. According to others [
48], the RDW is not related to the age of the subjects nor to the values of VO2max. However, other authors [
49] in a wide series of 1111 healthy subjects have observed a positive correlation between RDW and age. RDW is also unrelated to hematocrit, hemoglobin, and mean corpuscular volume (MCV). Others instead both in healthy subjects and in hypertensive adolescents [
50] showed a negative correlation between RDW, hemoglobin and MCV. RDW, in this our group of trained subjects, is negatively related to MCH and MCHC; this last feedback is in line with what is described by both Sun and co-workers that Vayá and co-workers.
Much more articulated are the correlation that have been found with the values of elongation index. According to the data present in literature [
51] the values of elongation index correlate negatively respectively with hematocrit, hemoglobin, and MCHC and positively with MCV. This last data appears to be a confirmation of the fact that in trained subjects the presence of young erythrocytes in percentage of some higher than the norm is more than plausible. Of sure interest is what has been observed correlating the values of elongation index with the VO2max. This correlation tends to show that the increase in VO2max corresponds to the increase in erythrocyte deformability and seems to converge with what other authors have found [
52,
53]. In our case studies, there is for some shear stress (6 Pa and 12 Pa) this relationship between elongation index and VO2max, but also a negative correlation between MCH and VO2max and between MCHC and VO2max (data not shown).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, in regularly trained subjects there is a significant increase in erythrocyte deformability associated with an increase in some erythrocyte parameters such as MCV and MCHC, expression of a increment of young red blood cells that regular exercise entails.In the subdivision effected according to the values of VO2max median, it is evident that in the subgroup above the median there is a red cell deformability increase associated with the decrease of MCH and MCHC. There is no statistical relationship between elongation index values and RDW. Not conclusive are the findings that emerge from the study of the interrelatioships between RDW, elongation index and erythrocyte indices.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, G.C. and R.L.P.; methodology, R.L.P.; formal analysis, R.L.P; writing—original draft preparation, G.C. and R.L.P.; writing—review and editing, G.C.; R.L.P. and M.C.; visualization, G.C.; R.L.P. and M.C.; supervision, G.C.; R.L.P. and M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Higgins, J.M. Red blood cell population dynamics. Clin Lab Med. 2015, 35(1):43-57. [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.H.; Patel, H.R.; Higgins, J.M. Modulation of red blood cell population dynamics is a fundamental homeostatic response to disease. Am J Hematol. 2015, 90(5):422-8. [CrossRef]
- Benedik, P.S.; Hamlin S.K. The physiologic role of erythrocytes in oxygen delivery and implications for blood storage. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2014, 26(3):325-35. [CrossRef]
- Loprinzi, P.D.; Loenneke, J.P.; Abe, T. The association between muscle strengthening activities and red blood cell distribution width among a national sample of U.S. adults. Prev Med. 2015, 73:130-2. [CrossRef]
- Loprinzi, P.D.; Hall, M.E. Physical activity and dietary behavior with red blood cell distribution width. Physiol Behav. 2015, 149:35-8. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.K.; Loprinzi, P.D. Associations between accelerometer-assessed sedentary behavior, physical activity and objectively-measured cardiorespiratory fitness with red blood cell distribution width. Int J Cardiol. 2016, 221:755-8. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.K.; Loprinzi, P.D. Reply to: Is physical activity really associated with reduced odds of elevated red cell distribution width? Int J Cardiol. 2017, 229:51-52. [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Salvagno, G.L.; Danese, E.; Tarperi, C.; Guidi, G.C.; Schena, F. Variation of red blood cell distribution width and mean platelet volume after moderate endurance exercise. Adv Hematol. 2014, 2014:192173. [CrossRef]
- Alis, R.; Romagnoli, M.; Primo-Carrau, C.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Blesa, J.R.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Effect of exhaustive running exercise on red blood cell distribution width. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015, 53(2):e29-31. [CrossRef]
- Hammam, N.; E Ezeugwu, V.; J Manns, P.; Pritchard-Wiart, L. Relationships between sedentary behaviour, physical activity levels and red blood cell distribution width in children and adolescents. Health Promot Perspect. 2018, 8(2):147-154. [CrossRef]
- Brun, J.F.; Varlet-Marie, E.; Romain, A.J.; Guiraudou, M.; Raynaud de Mauverger, E. Exercise hemorheology: Moving from old simplistic paradigms to a more complex picture. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2013, 55(1):15-27. [CrossRef]
- Ernst, E.; Weihmayr, T.; Schmid, M.; Baumann, M.; Matrai, A. Cardiovascular risk factors and hemorheology. Physical fitness, stress and obesity. Atherosclerosis. 1986, 59(3):263-9. [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.C.; Doyle, M.P.; Appenzeller, O. Effects of endurance training and long distance running on blood viscosity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1991, 23(11):1265-9.
- Kamada, T.; Tokuda, S.; Aozaki, S.; Otsuji, S. Higher levels of erythrocyte membrane fluidity in sprinters and long-distance runners. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1993, 74(1):354-8. [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Martin, D.T.; Telford, R.D.; Ballas, S.K. Greater erythrocyte deformability in world-class endurance athletes. Am J Physiol. 1999, 276(6):H2188-93. [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Wada, Y.; Matsumura, S. Membrane lipid components associated with increased filterability of erythrocytes from long-distance runners. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2001, 24(2):85-92.
- Cazzola, R.; Russo-Volpe, S.; Cervato, G.; Cestaro, B. Biochemical assessments of oxidative stress, erythrocyte membrane fluidity and antioxidant status in professional soccer players and sedentary controls. Eur J Clin Invest. 2003, 33(10):924-30. [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, A.A.; Vikulov, A.D.; Bagrakova, S.V. Relationships between von Willebrand factor and hemorheology in sportsmen. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2003, 29(1):19-24.
- Caimi, G.; Canino, B.; Amodeo, G.; Ingargiola, P.; Lucido, D.; Calandrino, V.; Lo Presti. R.L. Erythrocyte deformability and nitric oxide metabolites in athletes before and after a cardiopulmonary test. Clin J Sport Med. 2009, 19(4):306-10. [CrossRef]
- Kilic-Toprak, E.; Ardic, F.; Erken, G.; Unver-Kocak, F.; Kucukatay, V.; Bor-Kucukatay, M. Hemorheological responses to progressive resistance exercise training in healthy young males. Med Sci Monit. 2012, 18(6):CR351-60. [CrossRef]
- Tomschi, F.; Bizjak, D.; Bloch, W.; Latsch, J.; Predel, H.G.; Grau, M. Deformability of different red blood cell populations and viscosity of differently trained young men in response to intensive and moderate running. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2018, 69(4):503-514. [CrossRef]
- Tomschi, F.; Bloch, W.; Grau, M. Impact of Type of Sport, Gender and Age on Red Blood Cell Deformability of Elite Athletes. Int J Sports Med. 2018, 39(1):12-20. [CrossRef]
- Bizjak, D.A.; Tomschi, F.; Bales, G.; Nader, E.; Romana, M.; Connes, P.; Bloch, W.; Grau, M. Does endurance training improve red blood cell aging and hemorheology in moderate-trained healthy individuals? J Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9(6):595-603. [CrossRef]
- Alis, R.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Ferioli, D.; La Torre, A.; Blesa, J.R.; Romagnoli, M. Exercise effects on erythrocyte deformability in exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia. Int J Sports Med. 2015, 36(4):286-91. [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, M.; Alis, R.; Martinez-Bello, V.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Aranda, R.; Gómez-Cabrera, M.C. Blood rheology effect of submaximal exercise on young subjects. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2014, 56(2):111-7. [CrossRef]
- Mardyła, M.; Teległów, A.; Ptaszek, B.; Jekiełek, M.; Mańko, G.; Marchewka, J. Effects of Rowing on Rheological Properties of Blood. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023, 20(6):5159. [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.S. Effects of exercise and training on blood rheology. Sports Med. 1998, 26(5):281-92. [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.S.; Ali, N.; El-Sayed Ali, Z. Haemorheology in exercise and training. Sports Med. 2005, 35(8):649-70. [CrossRef]
- Findikoglu, G.; Kilic-Toprak, E.; Kilic-Erkek, O.; Senol, H.; Bor-Kucukatay, M. Acute effects of continuous and intermittent aerobic exercises on hemorheological parameters: a pilot study. Biorheology. 2014, 51(4-5):293-303. [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A. Exercise, training and red blood cell turnover. Sports Med. 1995, 19(1):9-31. [CrossRef]
- Muravyov, A.V.; Draygin, S.V.; Eremin, N.N.; Muravyov, A.A. The microrheological behavior of young and old red blood cells in athletes. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2002, 26(3):183-8.
- Patel, K.V.; Mohanty, J.G.; Kanapuru, B.; Hesdorffer, C.; Ershler, W.B.; Rifkind, J.M. Association of the red cell distribution width with red blood cell deformability. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013, 765:211-216. [CrossRef]
- Mairbäurl, H. Red blood cells in sports: effects of exercise and training on oxygen supply by red blood cells. Front Physiol. 2013, 4:332. [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Lin, W. Effects of exercise training on red blood cell production: implications for anemia. Acta Haematol. 2012, 127(3):156-64. [CrossRef]
- Montero, D.; Lundby, C. Red cell volume response to exercise training: Association with aging. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017, 27(7):674-683. [CrossRef]
- Montero, D.; Lundby, C. Regulation of Red Blood Cell Volume with Exercise Training. Compr Physiol. 2018, 9(1):149-164. [CrossRef]
- Montero, D.; Breenfeldt-Andersen, A.; Oberholzer, L.; Haider, T.; Goetze, J.P.; Meinild-Lundby, A.K.; Lundby, C. Erythropoiesis with endurance training: dynamics and mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017, 312(6):R894-R902. [CrossRef]
- Vogt, S.; Altehoefer, C.; Bueltermann, D.; Pottgiesser, T.; Prettin, S.; Schmid, A.; Roecker, K.; Schmidt, W.; Heinicke, K.; Heinrich, L. Magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbar spine and blood volume in professional cyclists. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008, 102(4):411-6. [CrossRef]
- Selleri, C.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Sato, T.; Young, N.S. Interferon-gamma constitutively expressed in the stromal microenvironment of human marrow cultures mediates potent hematopoietic inhibition. Blood. 1996, 87(10):4149-57.
- Jahromi, A.S.; Zar, A.; Ahmadi, F.; Krustrup, P.; Ebrahim, K.; Hovanloo, F.; Amani, D. Effects of Endurance Training on the Serum Levels of Tumour Necrosis Factor-α and Interferon-γ in Sedentary Men. Immune Netw. 2014, 14(5):255-9. [CrossRef]
- Rundqvist, H.; Rullman, E.; Sundberg, C.J.; Fischer, H.; Eisleitner, K.; Ståhlberg, M.; Sundblad, P.; Jansson, E.; Gustafsson, T. Activation of the erythropoietin receptor in human skeletal muscle. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009, 161(3):427-34. [CrossRef]
- Weight, L.M.; Alexander, D.; Elliot, T.; Jacobs, P. Erythropoietic adaptations to endurance training. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1992, 64(5):444-8. [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Konishi, N.; Sato, T.; Ueda, K. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I support the proliferation of erythroid progenitor cells in bone marrow through the sharing of receptors. Br J Haematol. 2000, 109(3):555-62. [CrossRef]
- Kadri, Z.; Lefevre, C.; Goupille, O.; Penglong, T.; Granger-Locatelli, M.; Fucharoen, S.; Maouche-Chretien, L.; Leboulch, P.; Chretien, S. Erythropoietin and IGF-1 signaling synchronize cell proliferation and maturation during erythropoiesis. Genes Dev. 2015, 29(24):2603-16. [CrossRef]
- Fornal, M.; Wizner, B.; Cwynar, M.; Królczyk, J.; Kwater, A.;, Korbut, R.A.; Grodzicki, T. Association of red blood cell distribution width, inflammation markers and morphological as well as rheological erythrocyte parameters with target organ damage in hypertension. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2014, 56(4):325-35. [CrossRef]
- Vayá, A.; Alis, R.; Suescún, M.;, Rivera, L.; Murado, J.; Romagnoli, M.; Solá, E.; Hernandez-Mijares, A. Association of erythrocyte deformability with red blood cell distribution width in metabolic diseases and thalassemia trait. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2015, 61(3):407-15. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Suh, J.S.; Kim, Y.K. Red Blood Cell Deformability and Distribution Width in Patients with Hematologic Neoplasms. Clin Lab. 2022, 68(10). [CrossRef]
- Pluncevic Gligoroska, J.; Gontarev, S.;, Dejanova, B.; Todorovska, L.; Shukova Stojmanova, D.; Manchevska, S. Red Blood Cell Variables in Children and Adolescents regarding the Age and Sex. Iran J Public Health. 2019, 48(4):704-712.
- Vayá, A.; Sarnago, A.; Fuster, O.; Alis, R.; Romagnoli, M. Influence of inflammatory and lipidic parameters on red blood cell distribution width in a healthy population. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2015, 59(4):379-85. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Shi, L. Association between red blood cell distribution width and left ventricular hypertrophy in pediatric essential hypertension. Front Pediatr. 2023, 11:1088535. [CrossRef]
- von Tempelhoff, G.F.; Schelkunov, O.; Demirhan, A.; Tsikouras, P.; Rath, W.; Velten, E.; Csorba, R. Correlation between blood rheological properties and red blood cell indices(MCH, MCV, MCHC) in healthy women. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2016, 62(1):45-54. [CrossRef]
- Connes, P.; Tripette, J.; Mukisi-Mukaza, M.; Baskurt, O.K.; Toth, K.; Meiselman, H.J.; Hue, O.; Antoine-Jonville, S. Relationships between hemodynamic, hemorheological and metabolic responses during exercise. Biorheology. 2009, 46(2):133-43. [CrossRef]
- Koliamitra, C.; Holtkamp, B.; Zimmer, P.; Bloch, W.; Grau, M. Impact of training volume and intensity on RBC-NOS/NO pathway and endurance capacity. Biorheology. 2017, 54(1):37-50. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).